APES unit 1-3
1/137
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
138 Terms
Individual
One organism
Population
Group of individuals of same species
Community
All living organisms in an area
Ecosystem
All living & nonliving things in an area (plants, animals, rocks, soil, water, air)
Biome
Large area with similar climate conditions that determine plant & animal species there
Symbiosis
A close long term interaction between 2 species in an ecosystem
Mutualism
A relationship in which both species are mutually benefitted
long term and both species have evolved traits over many generations that aid the relationship.
Commensalism
a relationship in which one organism benefits but the other’s neither helped nor harmed
long term and the species involved have evolved these relationships many generations
Parasitism
when one species benefits and the other is harmed by the interaction
they harm their host but rarely cause their death
Competition
Organisms fighting over a resource like food or shelter
limits pop size
resource partitioning
Division of limited resources by species to help avoid competition in ecological niche
allows for more species to thrive
Temporal Partitioning
Using resources at different times
ex: wolves and coyotes hunting at diff times of the day
Lichen
composite organism of fungi living with algae; algae provides sugars (energy) & fungi provides nutrients
Spatial Partitioning
Using different areas of shared habitat
Morphological Partitioning
Using different resources based of different evolved body features
Terrestrial biome
Distribution based of precipitation, average temp, geography, latitude, altitude, nutrient availability, biodiversity and soil.
Taiga
poor soil nutrients
Some birds, lots of migration
Has permafrost
Coniferous forests (evergreens)
Clearcutting is a threat
Canada Russia
Temperate Rainforests
Mid latitude forest
Some pines & broad leafed trees
Some of the tallest trees
Deep hummus layer, more nutrient rich
Cool climate, deforestation, climate change
Temperate seasonal Forests
Mid latitude forest
Receive cold & warm air masses
More nutrient filled soils
Trees lose leaves in fall and winter fro dormancy
Clearcutting and acid rain are threats
Forest species are common
Shrubland
middle latitude
Gets more rain than desserts, not as much as forests
Shrubs, grasses and aromatic herbs grow
Somewhat acidic soils
Threatened by climate change
Mediterranean
Savanna
Wet & dry climate, species shape the area like grasslands
Tall perennial grasses with some trees
Soils are low fertility due to bedrock type
Largest diversity of hoofed animals
Climate change, agriculture, overgrazing and irrigation practices.
Tropical Rainforest
Conditions are optimal abundant precipitation warm/light
Many layers of vegetation: canopy< subcanopy, shrub layer, ground layer
Poor soil nutrients- massive plant growth
climate change, farming/agriculture hydroelectric projects are some threats
Amazon, congo
Temperate grassland
Middle latitude area
mix of gasses and forbs
most fertile soil
perennial grass, sunflower pea plants
overgrazing by cattle agriculture and urban development
american “cornbelt”
Deserts
Cover 1/5 of the surface
to conserve water, plants adapt spines to protect from animals
soils are made of sand, gravel, stone
animals have adapted to heat and lack of water through aestivation, large ears for cooling
deserts spread due to poor agricultural practices
Tundra
Near Arctic high latitudes
Lichens, mosses, shrubs are common vegetation
no true soil, permafrost below rocks serve as ground
small mammals with thick fur
climate change is a threat due to melting ice and permafrost
canada and russia
Latitude and altitude
As these factors increase biomes and vegetation change
Freshwater biomes
streams
rivers
ponds
lakes
Marine Biomes
oceans
coral reef
marshlands
estuaries
Algae
Supply a large portion of the Earth's oxygen and also take in carbon dioxide from the atmosphere
Aquatic Biome Factors
salinity
depth
turbidity
nutrients
temperature
fresh water
drinking source
only 1% of it can be used and that is found in glaciers
Marshes & Swamps
Most productive freshwater biome
Estuaries
Areas where rivers empty into the ocean (mix of fresh and saltwater)
high productivity (plant growth)
bacterial decomposition consumes oxygen
Littoral zone
Edge of a pond/lake
more plant life
more nutrients
bets place for plants
Bnethic Zone
a lot of nutrients that have settled down into the bottom
Photic zone
the deper you go down the less sunlight and plant life there is
Profundal zone
no light
no photosynthesis
Coral reefs & estuaries
Most productive and biodiverse marine biomes
Upwelling
Bring nutrients to the surface by circling them back around
also bring nutrients from the depths of the ocean to the surface for phytoplankton
open ocean
Low productivity area as only algae and phytoplankton can survive in most of the ocean
Carbon Source
the origin or place where something is derived from
fossil fuel combustions
animal ag (cow burps & farts) ch4
deforestation
Carbon Sink
a reservoir or process that absorbs more of a substance than it releases.
Ocean (algae & sediments), plants, soil
photosynthesis
Process of converting carbon dioxide and water into sugar and oxygen
Plants and algae are primarily photosynthesisers
algae is responsible for 40 to 60% of photosynthesis globally
Respiration
Process of burning a sugar molecule with oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water
producers and consumers tend to undergo this process
this release can be used back in photosynthesis
sedimentation
When Marine organisms die, their bodies sink to the ocean floor where they're broken down into sediments that contain carbon
Burial
Over long periods of time, pressure of water compresses carbon containing sediments on ocean floor and sedimentary stone
long time reservoir
Nitrogen cycle
Movement of atoms and molecules containing the element of nitrogen between sources and sinks
Biogeochemical cycles
A self-regulating, naturally occurring, movement of chemical molecules through various sources and sinks
these cycles stabilize and regulate the flow of matter through ecosystems
nitrogen and phosphorus
limiting factor
Nitrification
N2 fixed by lightning (abiotic) or microbes in the soil / root nodules (biotic)
Ammonification
NH3 converted to NH4 by soil bacteria; NH3 can also be added by decay of organic matter
Nitrification
NH4 converted to NO2 then NO3
Assimilation
NO3 uptaken by plants through roots
Denitrification
NO3 can be converted back to N2 by soil bactreia
Phosphorus cycle
slow cycle
no atmospheric process
mainly driven by geological processes
limiting factor
Needed element for growth of plants and animals to make DNA, bones, ATP
sources of nitrogen
Weathered rocks
sinks of nitrogen
Oceans, lakes,land/water, food web
soil, ocean/rock sediments
geological uplift
Tectonic plate collision forcing up rock layers that form mountains
transpiration
The process plants use to draw groundwater from roots up to their leaves
evapotranspiration
Amount of water that enters atmosphere from transpiration and evaporation combined
Primary productivity
The rate at which solar energy is converted into organic compounds via photosynthesis over a unit of time
Gross primary productivity (GPP)
The rate of energy produced through photosynthesis
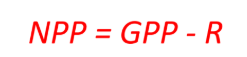
Net primary productivity (NPP)
The rate of energy available after respiration typically calculated in a given area
eutrophic zone
A lake or other habitat that is rich in nutrients and has abundant plant life
ecologicxal efficiency
99% Of the solar energy is reflected or it passes through producers without being observed
1% of solar energy shrinking producers is captured by photosynthesis
60% of GPP is lost to respiration
40% of GPP supports the growth in reproduction of producers
Trophic
different levels ina food chian or food web where organisms obtain energy
omnivore
Organisms that eat a variety of materials including plants animals algae, fungi
carnivore
Organisms that primarily eat meat and usually at the top of the food chain
herbivore
Organisms that primarily eat plants algae and other producers
autotrophs
An organism that can produce its own food
heterotrophs
An organism that must obtain its energy by consuming other organsisms
10% rule
In trophic pyramids only about 10% of the energy from 1 level makes to the next tlevel ; the other 90% is of used by the organsims and lost its heat
food chain
shows the flow of energy from primary producer of several trophic levelsfood
food web
Consists of several food chains and interlocking pattern meant to show energy and nutrient movement
positive feedback loop
Reaction causes more of the original reaction to occur
negative feedback loop
Reaction causes a return to normal
gentic diversity
How different the genes are of individuals within a population
more diversity allows for a better response to environment
Species diversity
The number of different species in an ecosystem and the balance of eveness of the population size
of all species in the
habitat diversity
The number of different habitats available in a given area
generalists
Species that can handle a wide variety of habitats and situations
specialist
Species that can only handle a limited range of habitats and situations
richness
Total number of different species found in an ecosystem
Evenness
A measure of how all of the individual organs in an ecostom are balanced between the different species
Richness
A measure of how all of the individual organisms in an ecosystem are balanced between the different species
high genetic diversity
low variation in environmental conditions
evolution
minor disturbances
high habitat diversity
low genetic diversity
continuous environmental stress
extinction
extreme disturbances
geographic isolation
invasive species
bottleneck
an environmental disturbance that drastically reduces population size & kills organisms regardless of their genome
ecosystem resilience
the ability of an organism to return to its original condition after a major disturbance
provisioning services
any type of benefit to people that can be extracted from nature.
food
drinking water
timber
wood
Regulating Services
Benefit provided by ecosystem process that moderate natural phenomena
tress providing shade
regulating pollutants through plants
storing carbon
soaking up water
Cultural Services
Non-Material benefit that contributes to the development and cultural advancement of people, including how ecosystems play a role in local, national and global cultures
Supporting Services
ecosystems couldn’t be sustained without the consistency of underlying natural processes. process allows earth to sustain basic life forms
incorporates all 2 services
island biogeography
The study of ecological relationships and distributions of populations on islands
Large Islands
Greater ecosystem diversity- more food & habitat resources
More niches or roles organisms can play in the ecosystem
Greater the island, the greater the ecosystem diversity
Islands close to mainland
easier for colonizing organisms to get to island from mainland
More colonizing organisms-more genetic diversity in new populations
Frequent migration brings more genetic diversity and larger pop size
Generalists in islands
leads to drop in specialists
Outcompete specialists
Specialists have limited defenses
Ecological Tolerance
the range of conditions such as temperature, salinity, flow rate, sunlight that an organism can endure before injury or death
x axis abiotic pH, Temp, salinity
Y axis population
range of optimum
Area of greatest abundance
Zone of physiological stress
Low population
Not adapted
Change in temp, pH, pressure etc
Zone of intolerance
species absent
No animals can survive