Current-Voltage Characteristics
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
What does Ohm's law state?
For a conductor at constant temperature, the current through it is proportional to the potential difference across it.
What equation represents Ohm's law?
V=IR Voltage= current*resistance
What does the current-voltage graph of a resistor look like?
I is proportional to V, obeys Ohm's law.
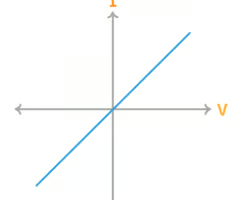
What is the gradient of a current-voltage graph of a resistor equal to?
1/R (resistance)
On a current-voltage graph for a resistor what does a steeper gradient mean?
A lower resistance.
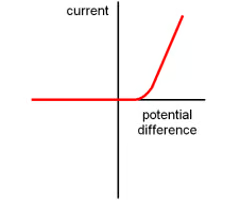
What is the current-voltage graph for a semiconductor diode?
A diode only allows current to flow in one direction. The sharp increase in potential difference is forward bias, the flat line on the left side is called reverse bias. The threshold voltage is where the potential difference first increases from zero.
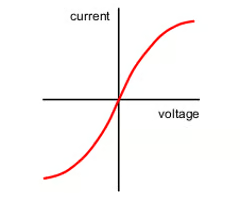
What is the current-voltage graph for a filament lamp?
For very low currents, ohm's law is obeyed. As the current increases the temperatue of the filament lamp increases. The higher temperature causes an increase in resistance causing the current to increase at a slower rate.
Why does resistance increase with temperature?
Higher temperatures cause the atoms within the conductor to vibrate more vigorously, which increases the number of collisions between free electrons and the atoms, thus hindering the flow of electricity.
In current-voltage graphs when does an electrical component obey ohm's law?
When it is a straight line through origin.