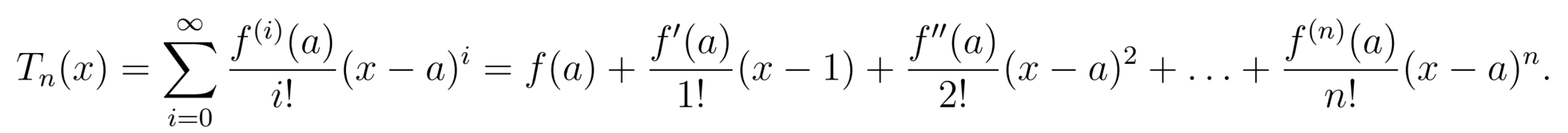Power Series, Taylor Series, Maclaurin Series
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
Power Series
A power series centered at a is a series of the form
a is some number
when a is zero the form just looks like cn xn
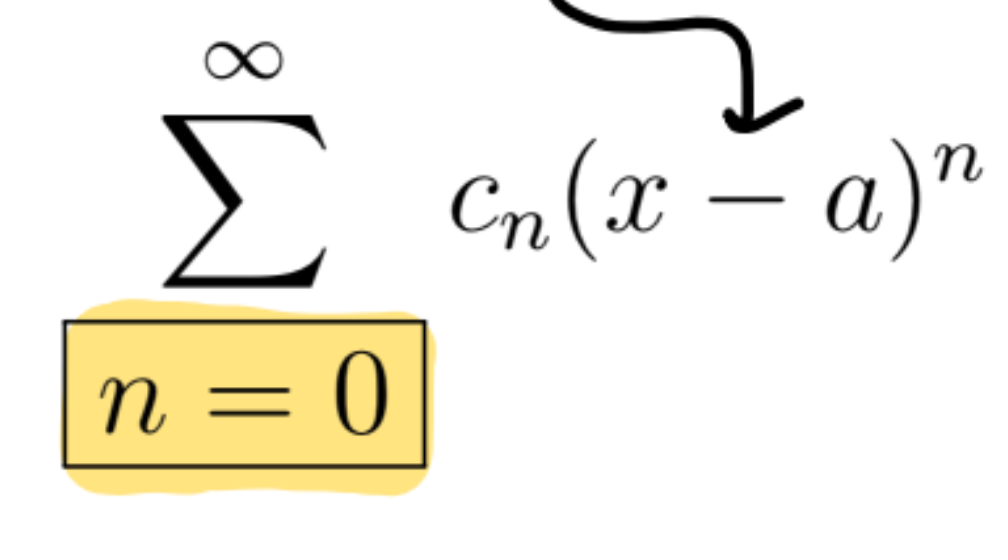
Power Series
A power series may…
converge for all x
converge for | x - a | < R, diverge for | x - a | > R
converge only for x = a, diverge for all other values of x.
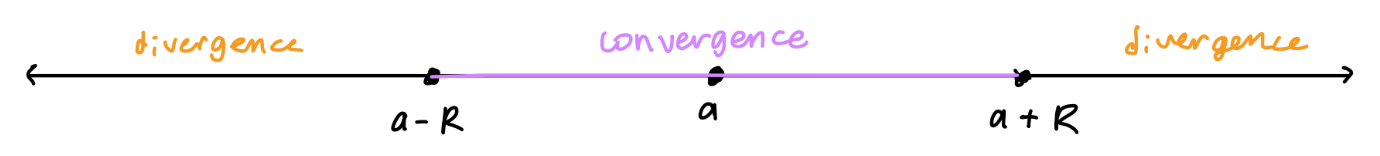
R = radius of convergence
Power Series
The interval of convergence may be…
I = (-∞, ∞)
I = [a - R, a + R] or [a - R, a + R) or (a - R, a + R] or (a -R, a + R)
Just a point I = {a}, radius of convergence R = 0
Power Series
To determine convergence…
STEP 1: Determine the radius of convergence (by the ratio test).
STEP 2: Determine what happens at the endpoints (by tests other than the ratio test). Plug in endpoints (x-values) into the original series.
Taylor Series Expansion
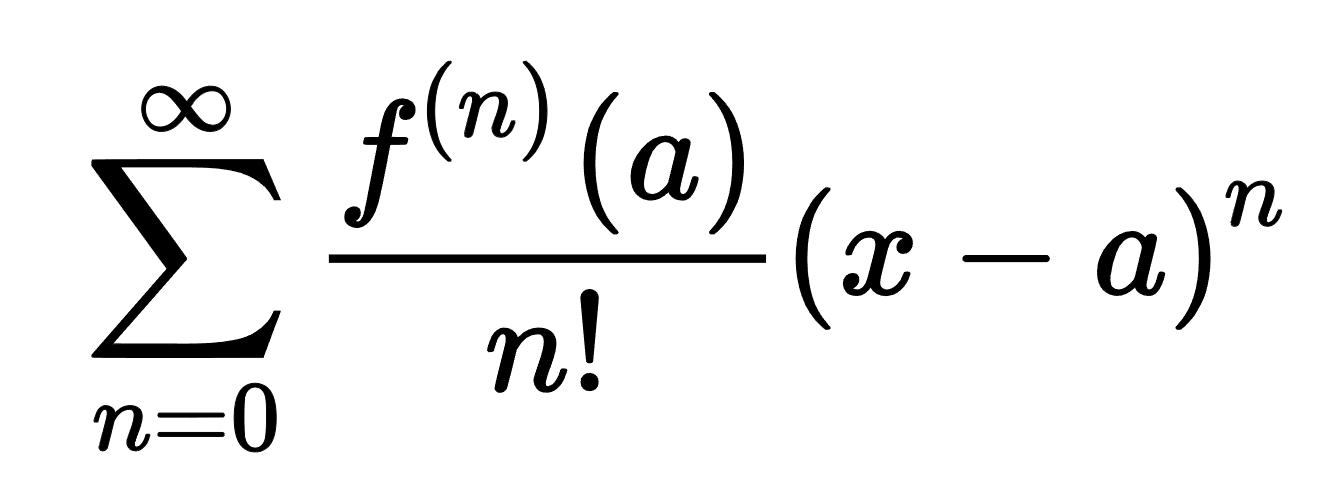
Maclaurin Series Expansion
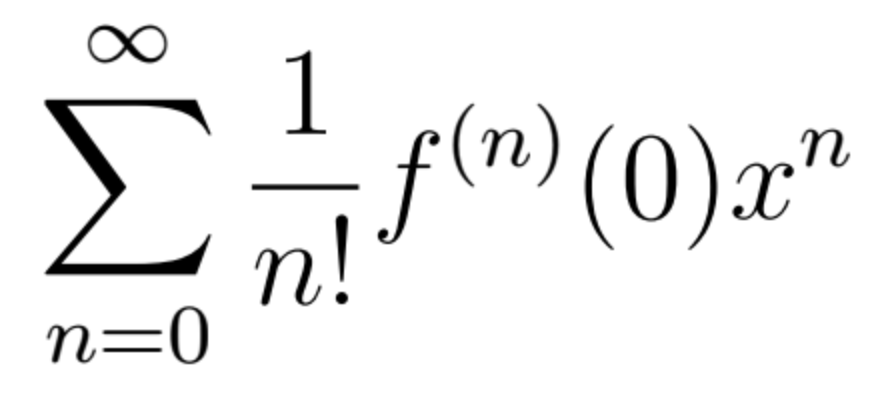
Method for expanding series from funcitons
Determine if you are making a Taylor Series or Maclaurin Series
Write out f(x) = series expansion of Taylor or Maclaurin around a
Find derivatives of function usually up to 5th derivative (n=5). Then plug in a to the derivatives.
Write out the sum of the series with found derivatives
Find pattern to determine series for the function
Taylor Polynomial
Taylor Approximation
Partial sum = Taylor polynomial
Find Tn(x) by computing derivatives and writing out partial sum up to the nth degree