Biolgoy IB, cry myself to sleep
1/136
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
137 Terms
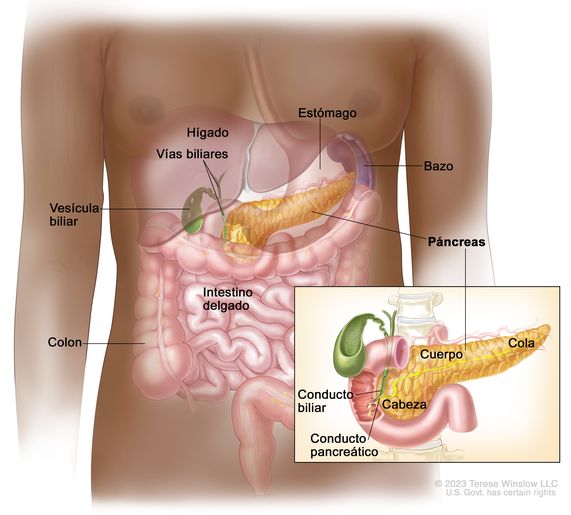
Mouth
Mechanical digestion using the teeth and tongue. Starting Chemical digestion using amylase from the salivary glands.
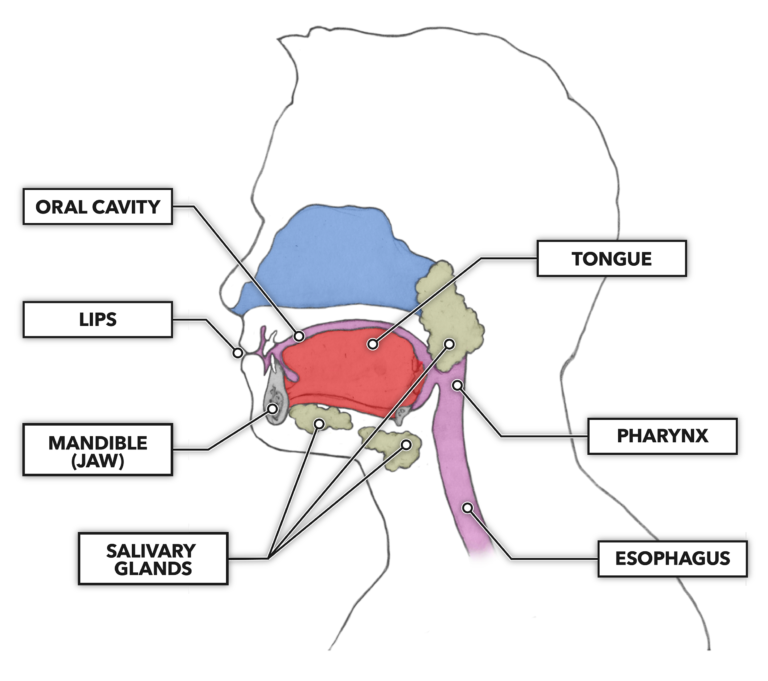
Esophagus
Moves food from mouth to stomach via peristalsis
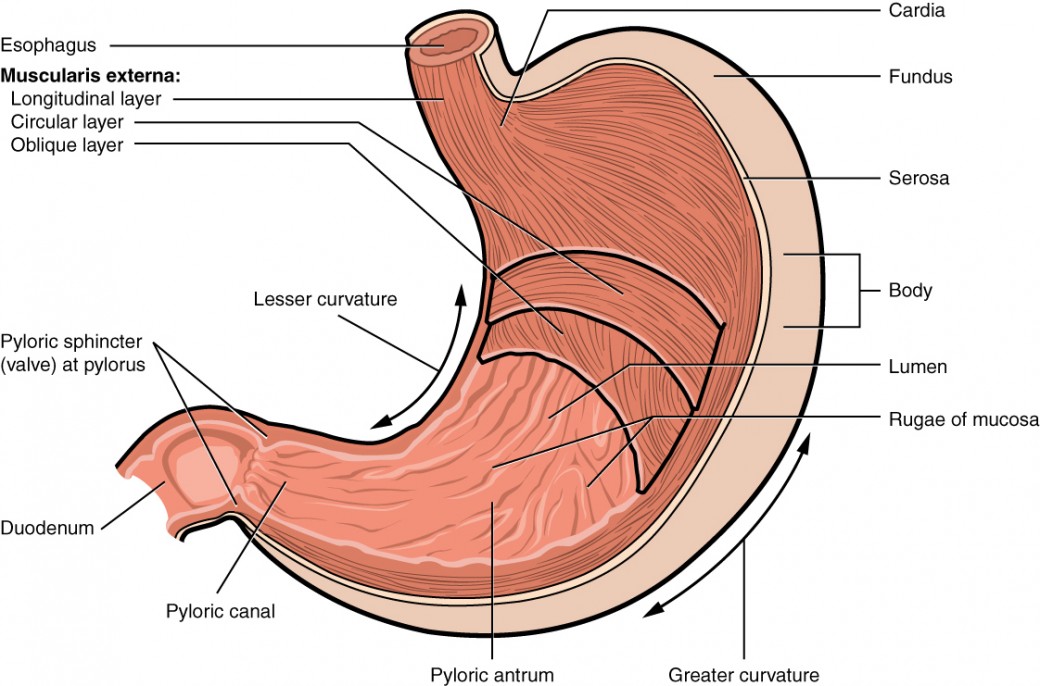
Stomach
Mechanical digestion by churning and mixing. Starts chemical digestion of proteins using proteases (pepsin)
HCl and enzymes
Small Intestine
Mostly chemical digestion of lipids, carbohydrates and proteins via enzymes secreted by accessory glands.
Majority of nutrient absorption takes place here.
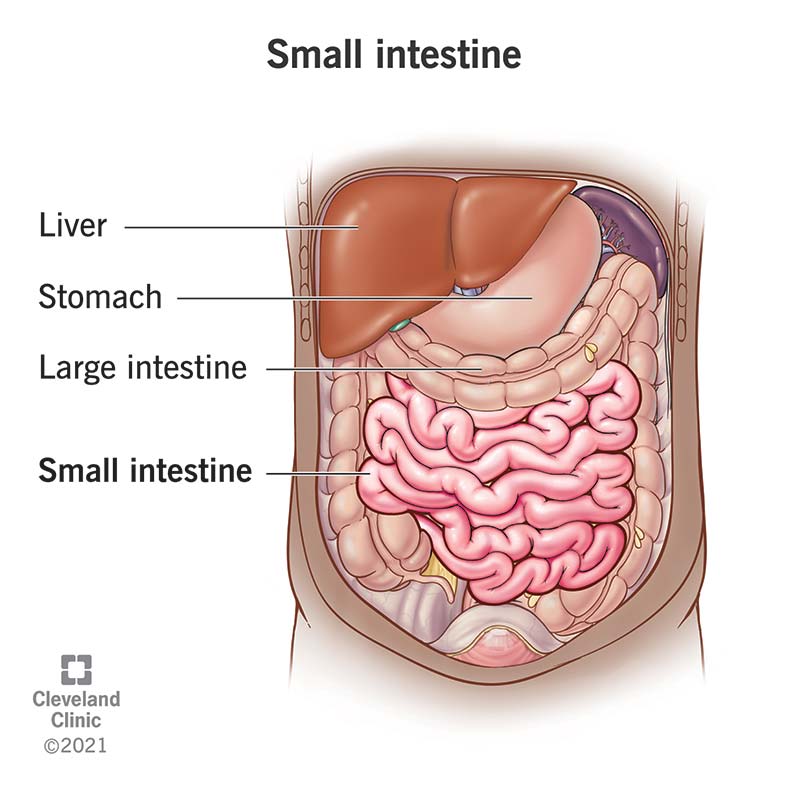
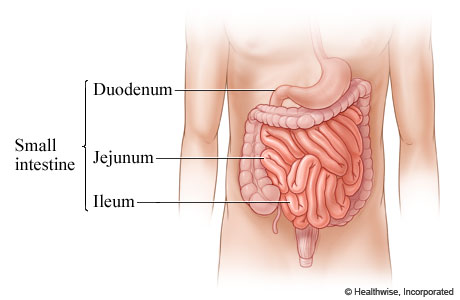
Small Intestine parts
Duodenum
Jejunum
Ileum
Large intestine
Also called colon
Water is reabsorbed back into the bloodstream, some final digestion of carbohydrates.
Feces are formed and stored here.
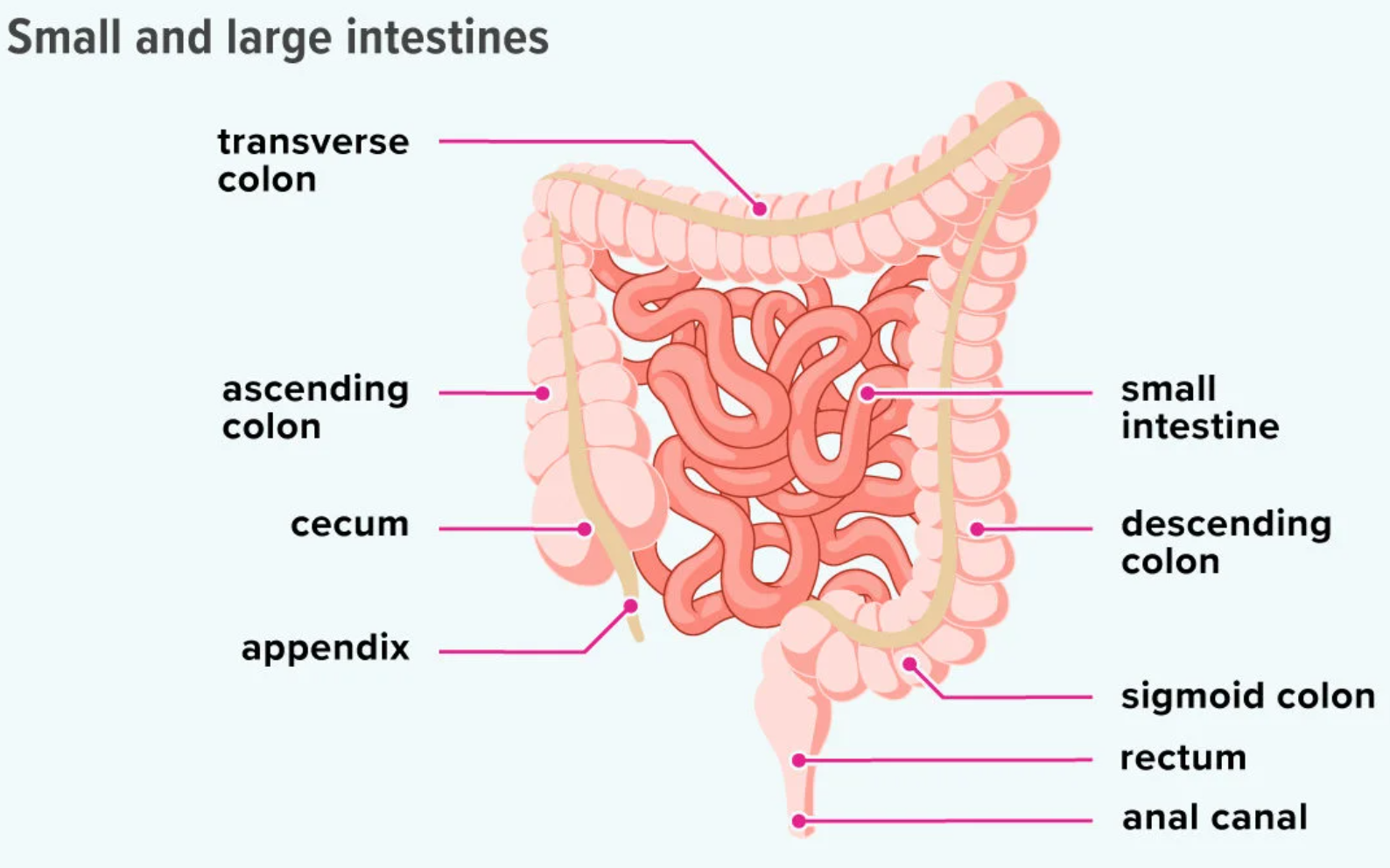
Liver
Produces bile, which is a fat emulsifier to help break lipids down into small droplets. These are easier to absorb.
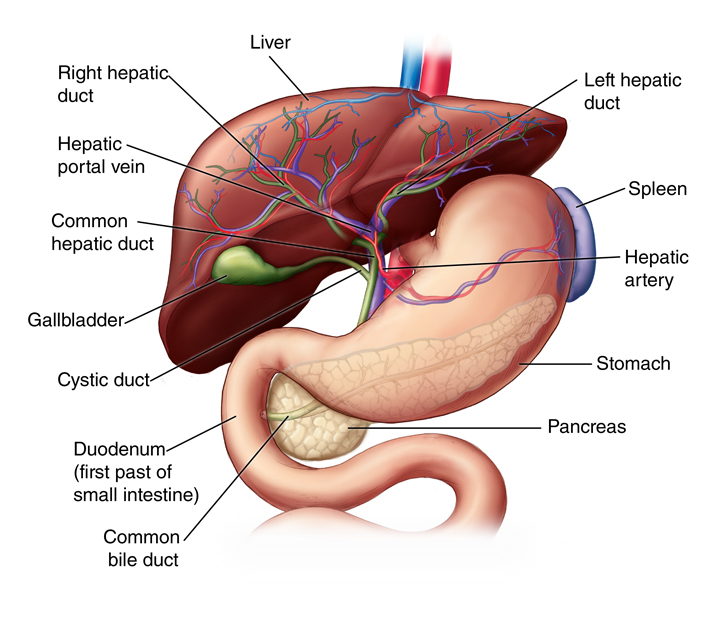
Gall bladder
For storage and regulation of bile
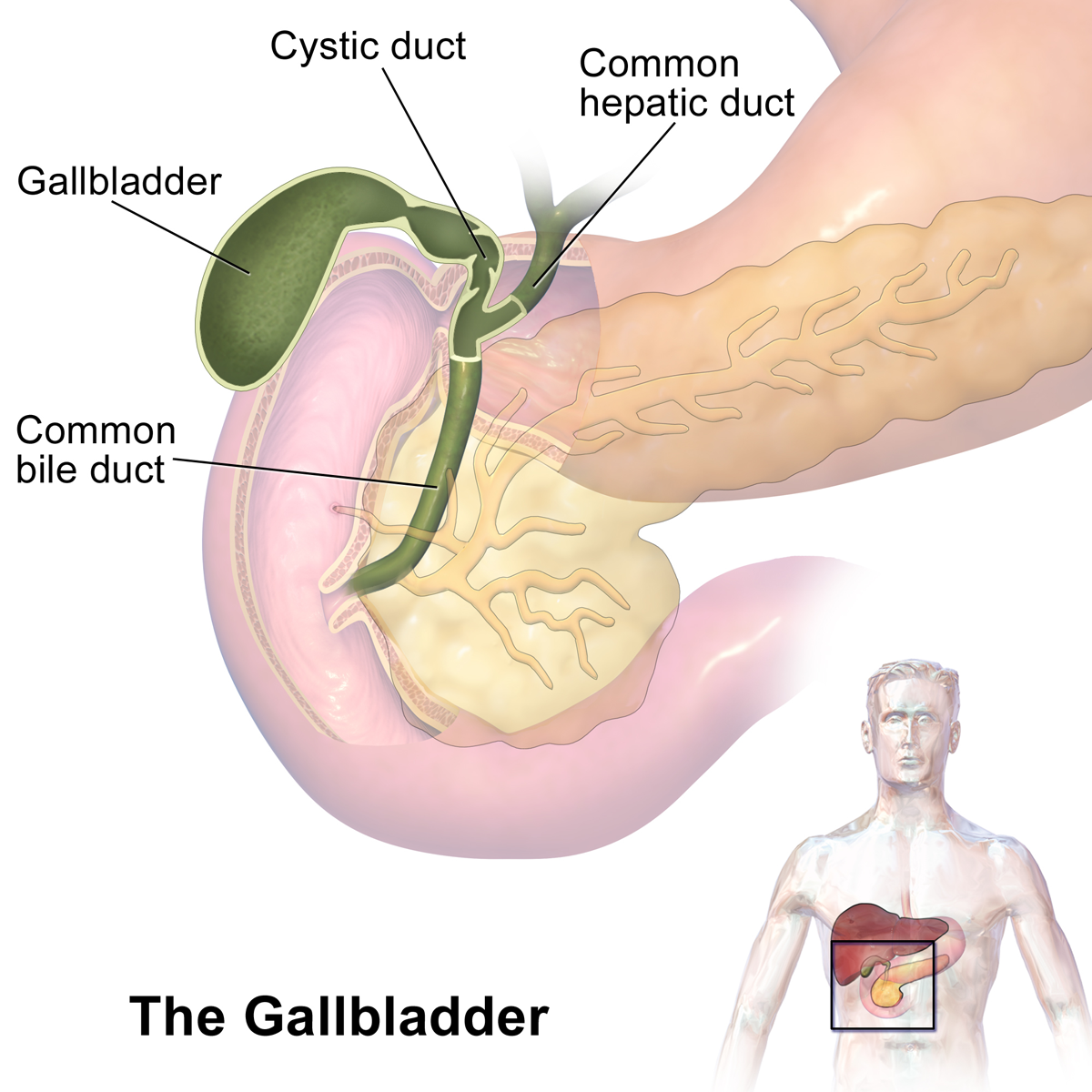
Pancreas
Secretes lipase, amylase and protease into the lumen of the small intestine for digestion
What muscles compose the digestive system?
Smooth and longitudinal muscles
Smooth muscles
Made of short fibers
These muscles produce a moderate force, along with short, vigorous contractions to move food along the tube
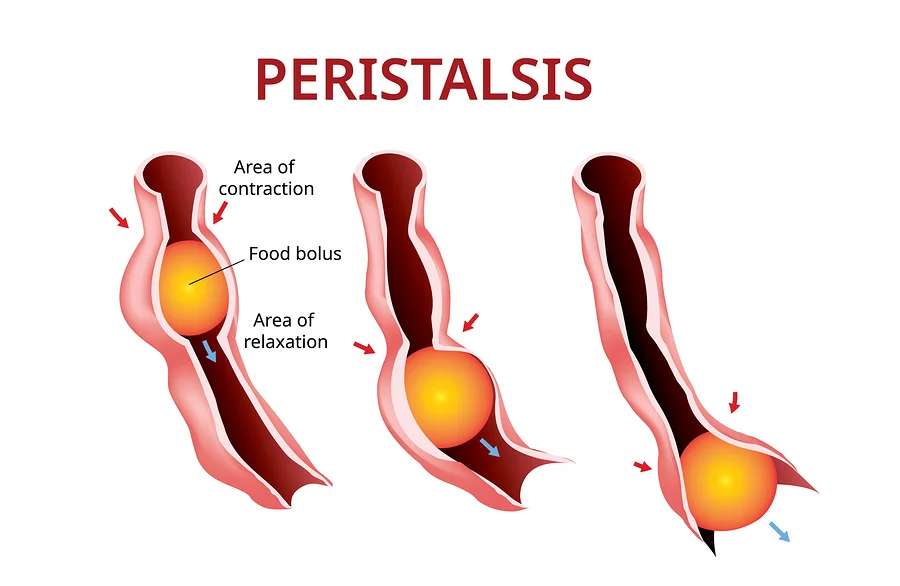
Peristalsis
Food (bolus) is moved from the mouth to the stomach with muscles working together in a wave-like motion
This action extends throughout both small and large intestines, continuing the mixing action
Mechanical digestion
Mixing, via the muscles contracting
Chemical digestion
Continued digestion from the stomach acid/enzymes
and new secretions from the pancreas
Reasons for digestion (4)
To make sure the nutrients are small enough to enter a cell.
Provide fuel for ATP Production.
Provide raw materials for building.
Acquire micronutrients like vitamins and minerals that the body needs to prevent disease.
What are enzymes used for?
To break down the larger, macromolecules into monomers (catabolism)
These smaller pieces can then be absorbed in the small intestine
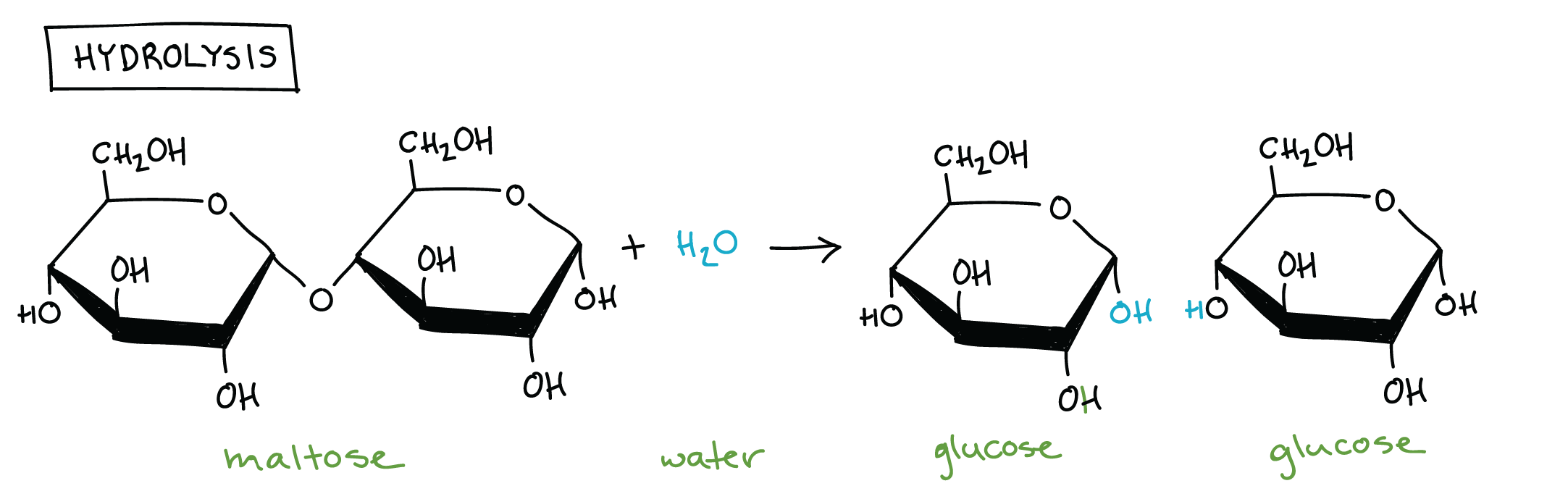
Catabolism via hydrolysis reactions
Use H2O to breakdown polymers (hydrolysis)
Reverse of dehydration synthesis
Cleave off one monomer at a time
H2O is split into H+ and OH–
H+ & OH– attach to ends of newly split compounds
Requires enzymes
Pancreas components
A gland that is made of 2 tissue types:
Hormonal tissue (endocrine)
Digestive tissue (exocrine)
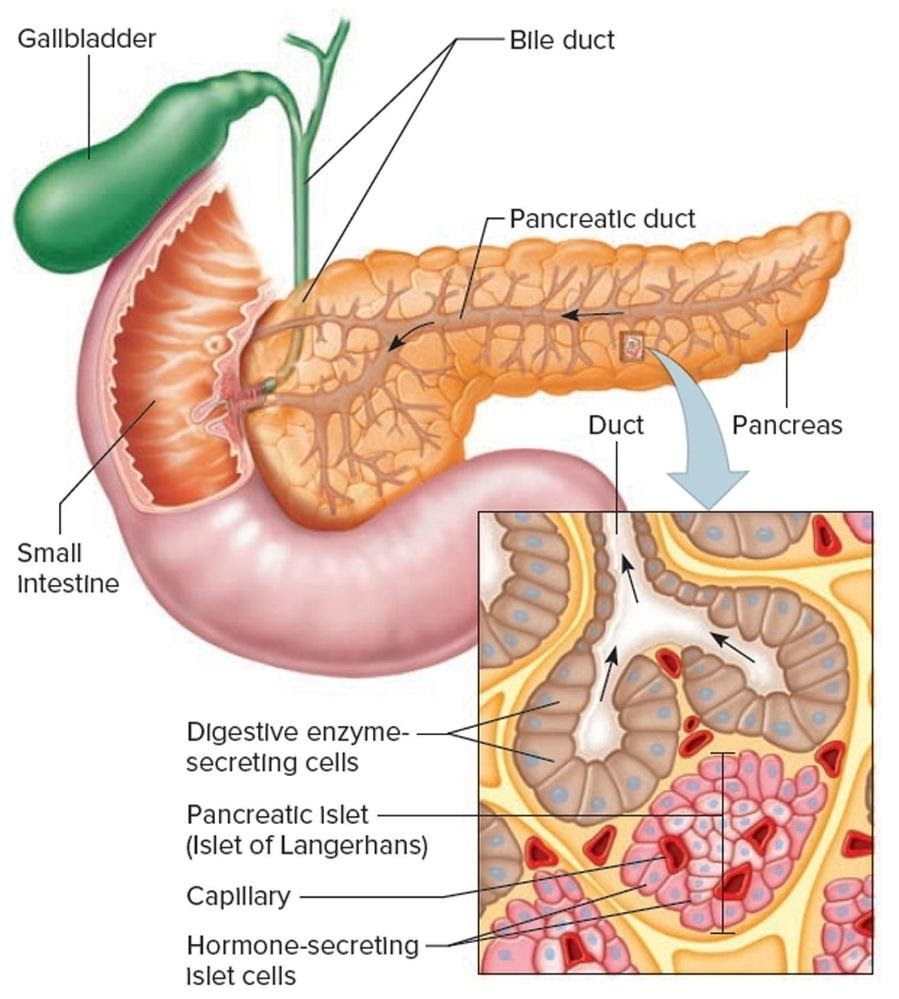
Pancreas Hormonal tissue (Endocrine)
Produces insulin and glucagon critical in regulation of blood sugar level.
Pancreas Digestive tissues(Exocrine)
Makes enzymes, 3 types.
All enzymes are secreted int o the duodenum through the pancreatic duct
Pancreas enzymes
Amylase
Protease
Lipase
Pancreatic amylase
Breaks down starches
Most of the starch digestion happens here.
Lipase
Breaks down triglycerides and phospholipids into glycerol and fatty acids
Proteases
Breaks down proteins and peptides (trypsin)
The digestions of these starts in the stomach but continues in the small intestine
Amylase:
Source
Substrate
Products
Optimum pH
Source: Salivary glands, pancreas
Substrate: Starches
Products: Maltose
Optimum pH: 4.5-7
Trypsin:
Source
Substrate
Products
Optimum pH
Source: Pancreas
Substrate: Proteins
Products: Amino acids
Optimum pH: 7.8
Pepsin
Source
Substrate
Products
Optimum pH
Source: Stomach walls’ gastric glands (pits)
Substrate: Proteins
Products: Amino acids
Optimum pH: 1.5-2
Lipase
Source
Substrate
Products
Optimum pH
Source: Pancreas
Substrate: triglycerides
Products: fatty acids and monoglycerides
Optimum pH: 4.5 to 7.5
Carbohydrate
Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a ratio of roughly one carbon atom to one water molecule
Protein
Chains of amino acids, which then fold into unique three-dimensional shapes
Amine group + R group (R group gives the protein specific characteristics)
Triglyceride / fatty acids
Glycerol bound to three fatty acid molecules
Calories for macromolecules
Protein and Carb = 4 calories per gram
Lipids = 9 calories per gram
Chemical digestine continues…
… the small intestine
Nucleases
Digest DNA and RNA into nucleotides
Maltase
Digests maltose into 2 glucoses
Lactase
Digests lactose into glucose and galactose
Sucrase
Digests sucrose into glucose and fructose
The gall bladder releases (1) into the (2), which (3)…
Bile
Small intestine
…coats fat globules, preventing small droplets from becoming large globules, increasing exposure to lipase
The structure of the small intestine wall allows it to… (3)
Move
Digest
and Absorb food
Structural component of the small intestine that aids in the absorption of more nutrients?
Folds and projections to increase surface area
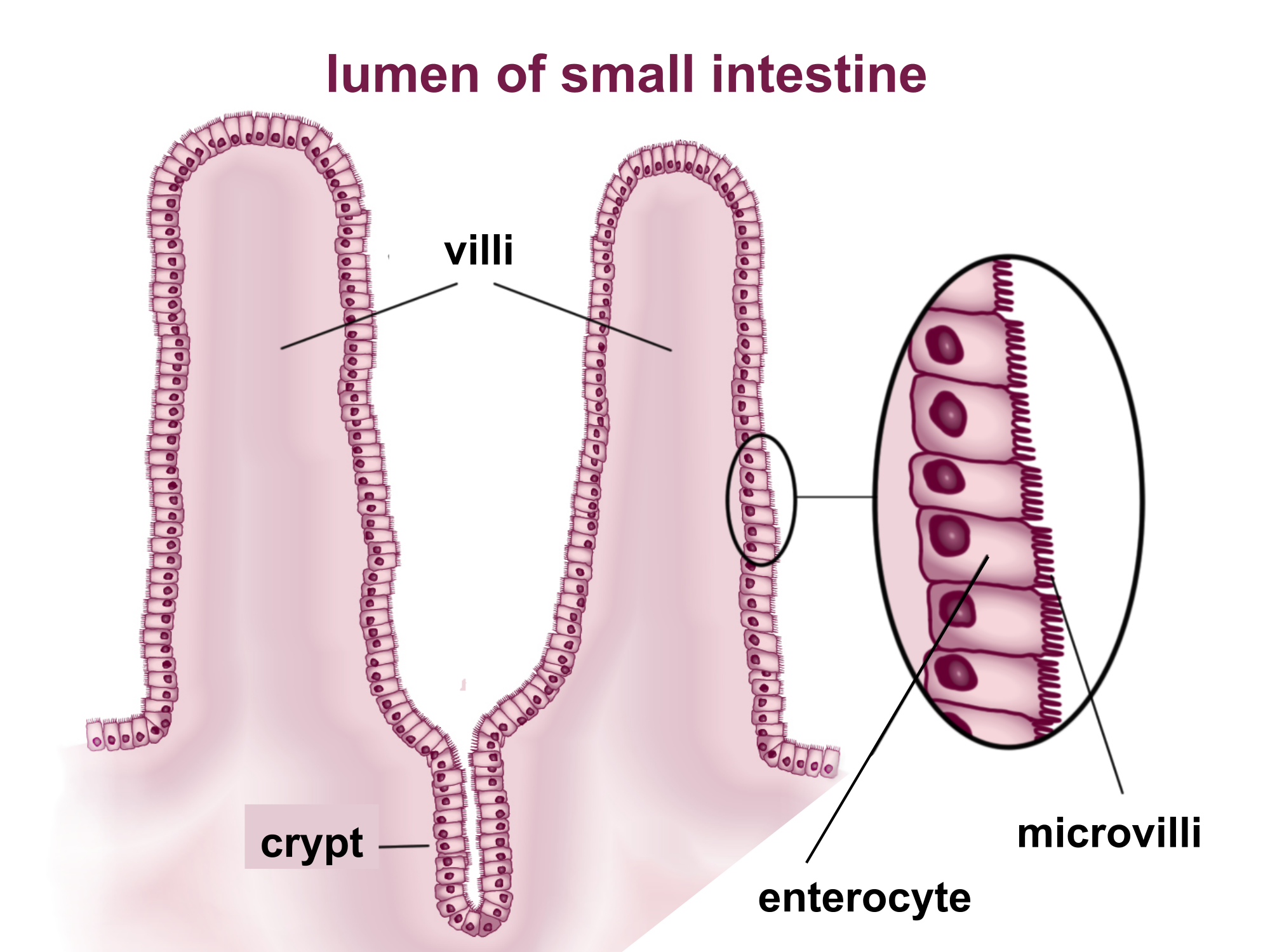
Increased surface area means…
… more absorption!!!
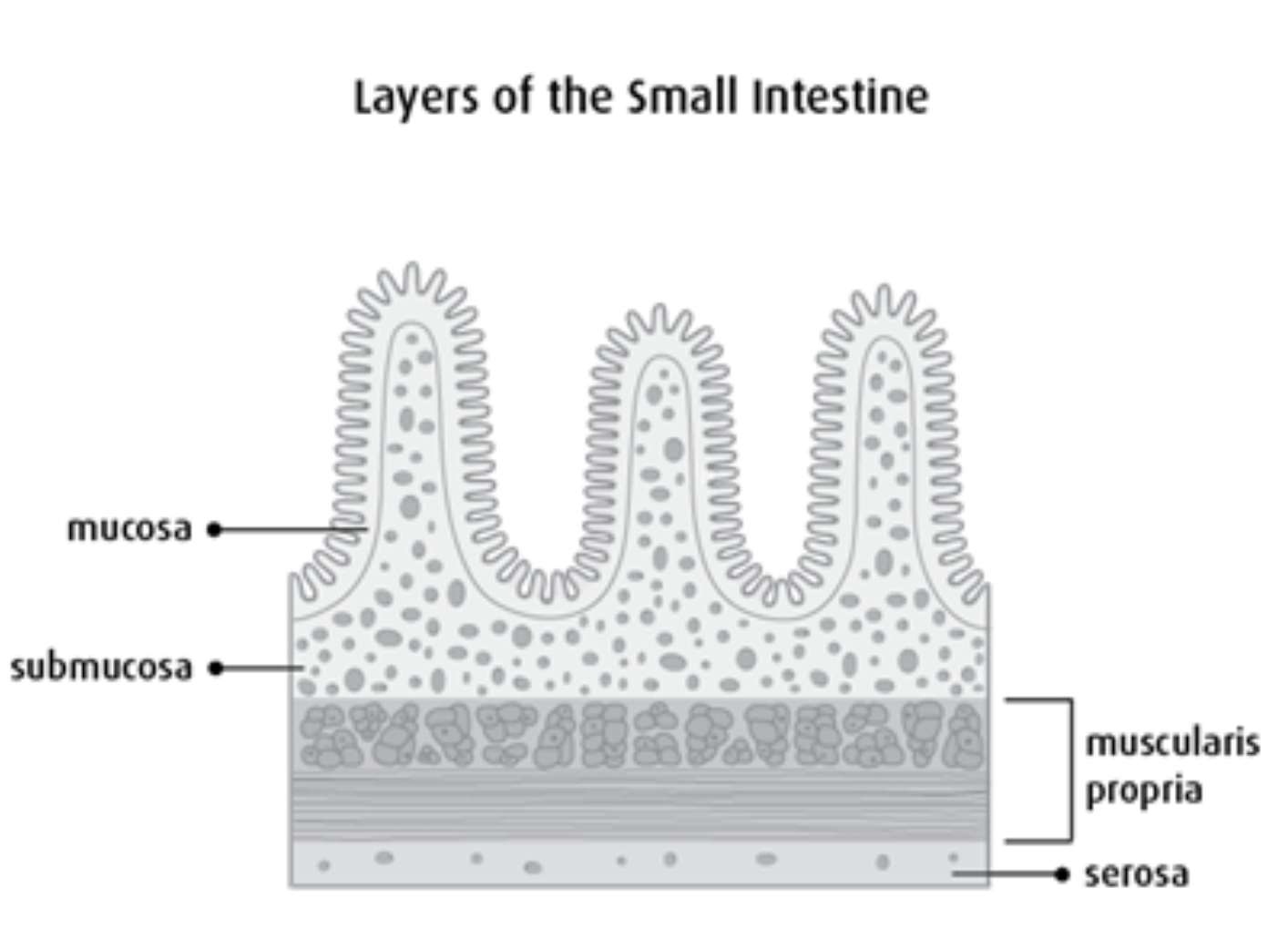
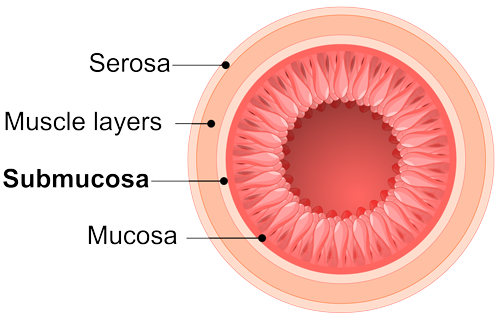
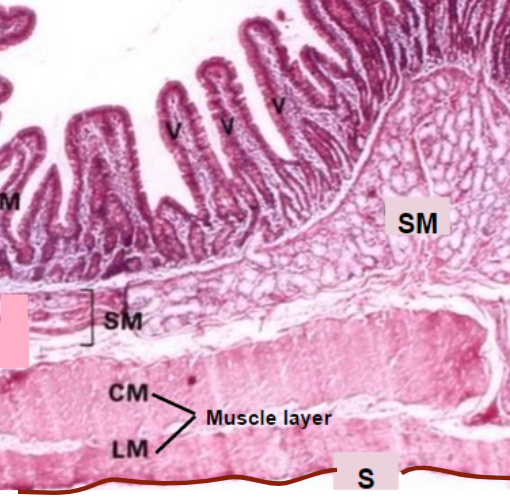
Small intestine Structure
Parts to know:
V - Villus* (has its own, in-depth structures)
M - Muscosa
SM - Sub muscosa
CM/LM - Circular muscle (PINCH) and Longitudinal muscle (PUSH)
Both types of smooth muscle
Serosa
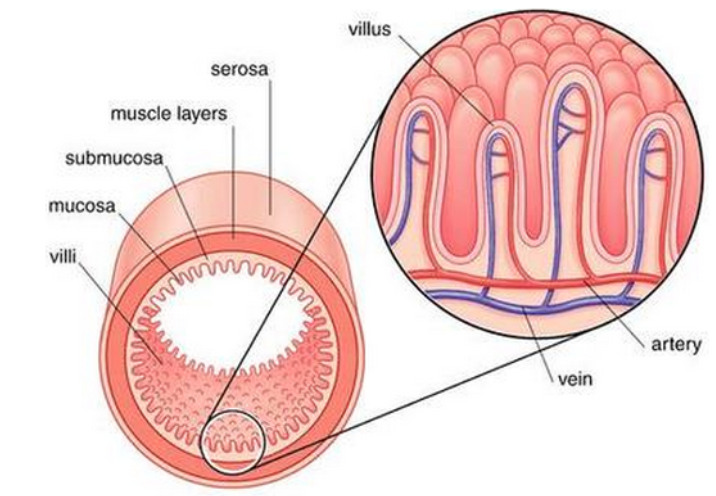
Muscosa
Epithelial layer, responsible for nutrient absorption
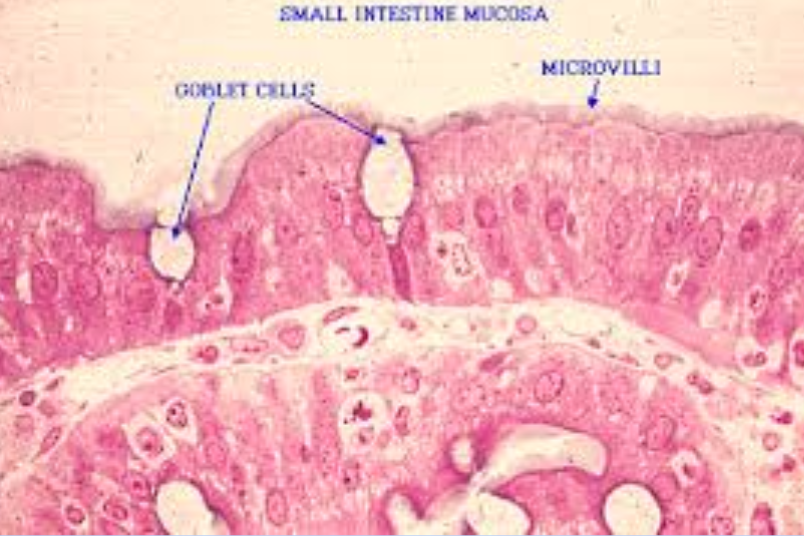
Goblet cells of the Muscosa
Help to create mucus to move the chyme along the intestinal tract.
Submucosa
Layer containing blood and lymph vessels
Circular and Longitudinal muscles
Circular - pinch
Longitudinal - push
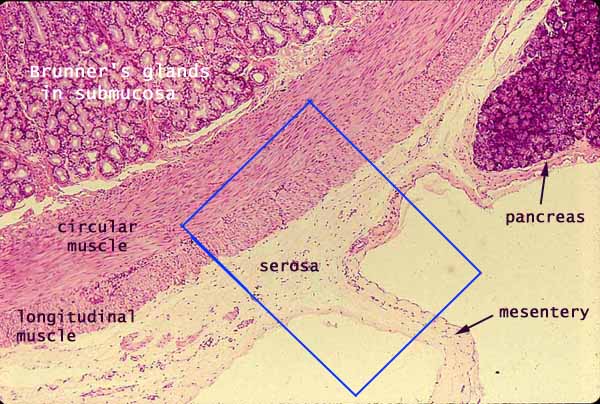
Serosa
Outer covering of intestine.
Epithelial means…
… most external
The structure of the wall of the small intestine allows it to a), b), and c)
a) move (peristalsis),
b) digest,
c) an absorb food
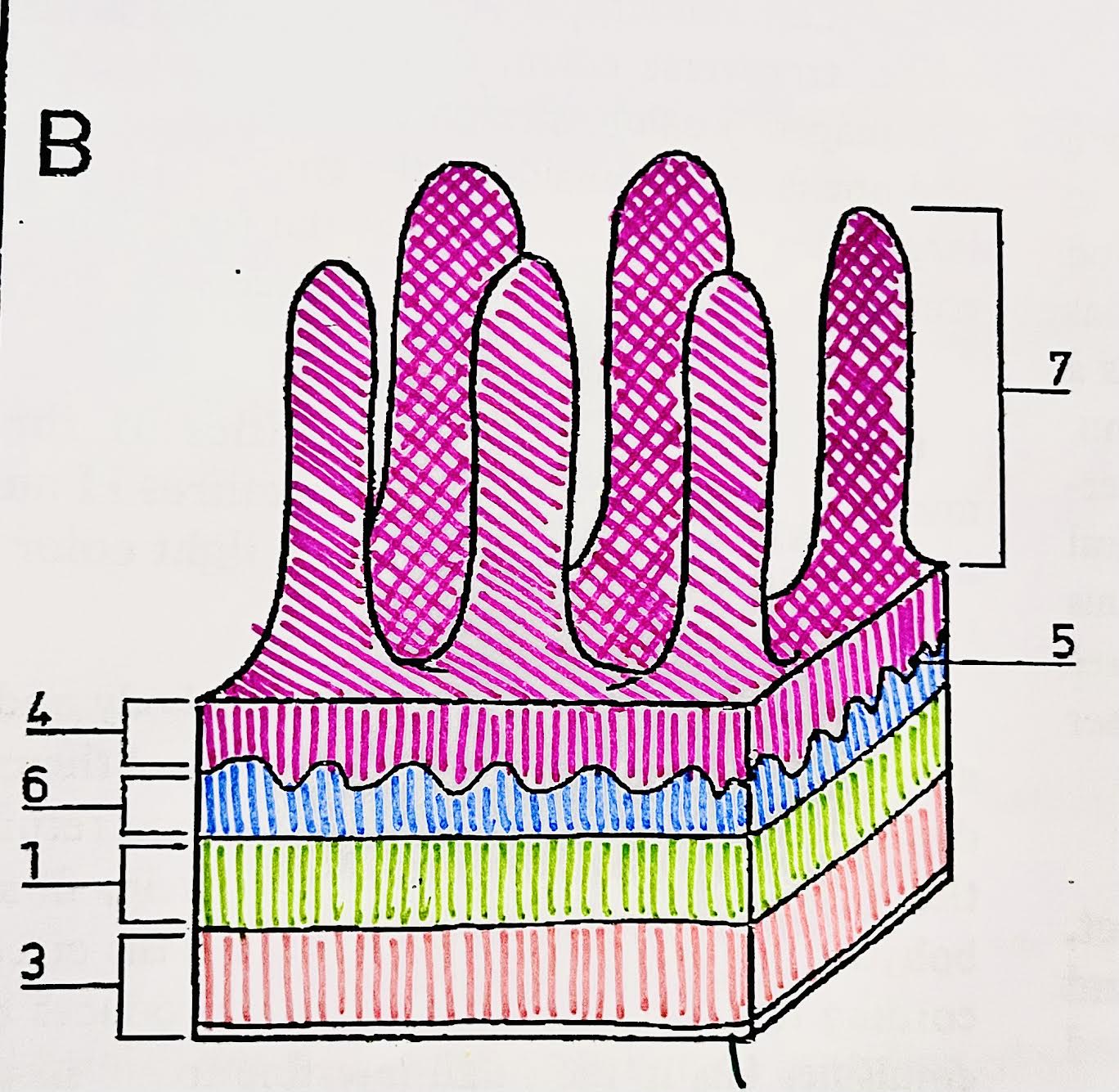
Identify each piece (small intestine)
(Bottom to top)
Serosa = bottom
(3) Longitudinal muscle
(1) Circular muscle
(6) Submucosa
(5) Thin muscle layer (not relevant)
(4) Mucosa
(7) Villus
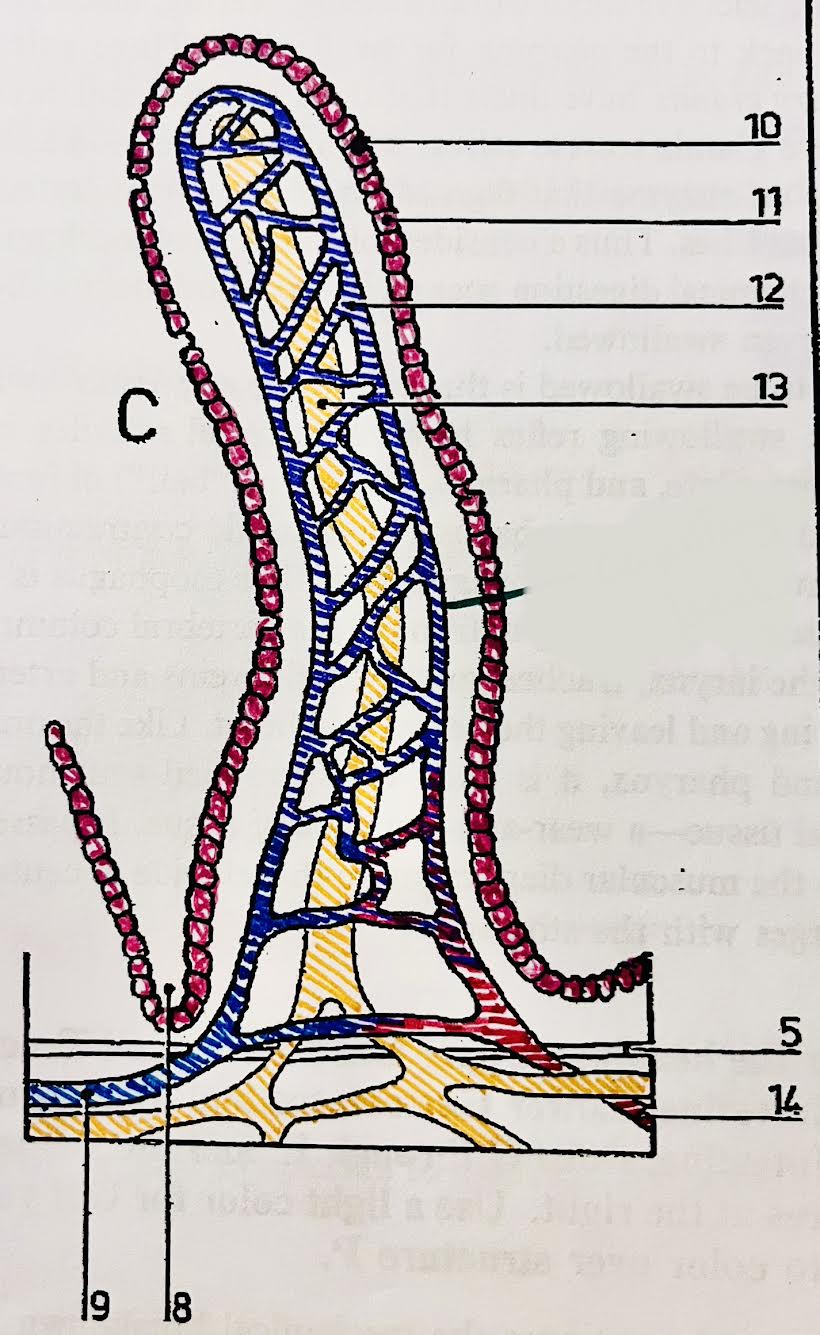
Identify each piece (villus of a small intestine)
(8) Crypt of Lieberkühn
(9) Ateriole
(10) Goblet cell = Mucus-secreting cell
(11) Epithelium
Microvilli on top of these
(12) Network of blood capillaries
(13) Lacteal = carrying fatty acids and glycerol
(14) Venule = carrying amino acids and monosaccharides
Villi
Small intestines are full of these tiny folds and projections
Microvilli
Cells that cover each villus, increasing the surface area and potential for absorption
ruffling of epithelial membrane further increases SA
Lacteal
Fats move through it
Absorbs lipids from the intestine into the lymphatic system
“Virtually all nutrients enter the body through this… covering the villus”
Epithelial layer
Nutrients (that enter through epithelial layer) include
Amino acids
Sugars
Vitamins
Mineral ions
Simple diffusion
Nutrients pass between the phospholipids of the membrane with the concentration gradient (High to Low)
How do fatty acids and glycerol enter the epithelial cells of the villus?
Simple diffusion
Why can fatty acids and glycerol go through simple diffusion?
Fatty acids and glycerol created by lipase digestion are small and nonpolar therefore they can move directly through the cell membrane.
After fatty acids and glycerol are inside the epithelium cells, what are created?
Triglycerides
After triglycerides are created, how will they move out?
Exocytosis
Endo/Exocytosis
Nutrients (droplets of liquid) pass across the membrane by forming vesicles to bring inside.
- Energy is required
Transport of fat summary
After being broken down into their monomer forms (glycerol + fatty acids), they enter across the membrane of the epithelial cells via simple diffusion (small and nonpolar)
They recombine into triglycerides
They leave the epithelial cells by in a vesicle through exocytosis
They move into the lacteal (lymph / blood system)
Active Co-Transport
Nutrients pump across the membrane, via pump proteins, against the concentration gradient (Low to High)
Energy is required
How does glucose cross the membrane of the villus’ epithelial cells?
Active co-transport
Why can’t glucose perform simple diffusion?
Polar
In active co-transport, what does glucose move with?
Na+
Transport of glucose summary
Na+ is pumped outside of the epithelial cells against the gradient, which requires ATP.
Na+ and glucose enter the epithelial cell via facilitated diffusion
Glucose enters bloodstream through facilitated diffusion
Facilitated diffusion (fructose)
Nutrients pass across the membrane, via channel proteins, with the concentration gradient (High to Low)
Amylase breaks down what starches?
Amylose (spiral)
Amylopectin (branching)
What bonds does amylase break?
1-4 bonds
What bonds does amylopectin have?
1-4 and 1-6 bonds
In addition to amylase, what is needed to break down amylopectin?
Enzymes called dextrin
One nutrients are absorbed, where do they go?
Assimilated (assembling materials) into cellular structures —> make us
Storage as fat or in certain storage locations (carbs in the liver)
Energy use
Why can’t all monomers and digested nutrients be absorbed?
Lack the correct enzymes
What is indigestible?
Cellulose, found in plant cell walls
Function of cellulose (fiber) in digestion
Helps to keep the system moving and clean as it scrapes along the intestines.
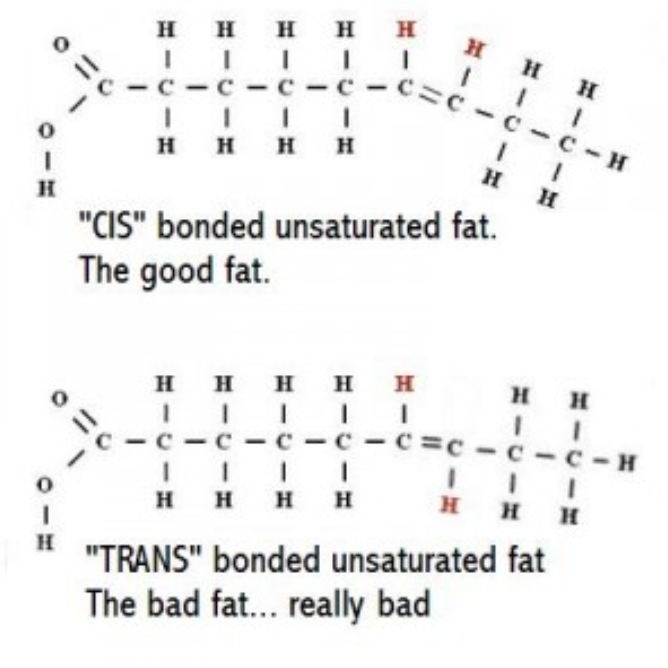
Unsaturated fat types
CIS
Trans
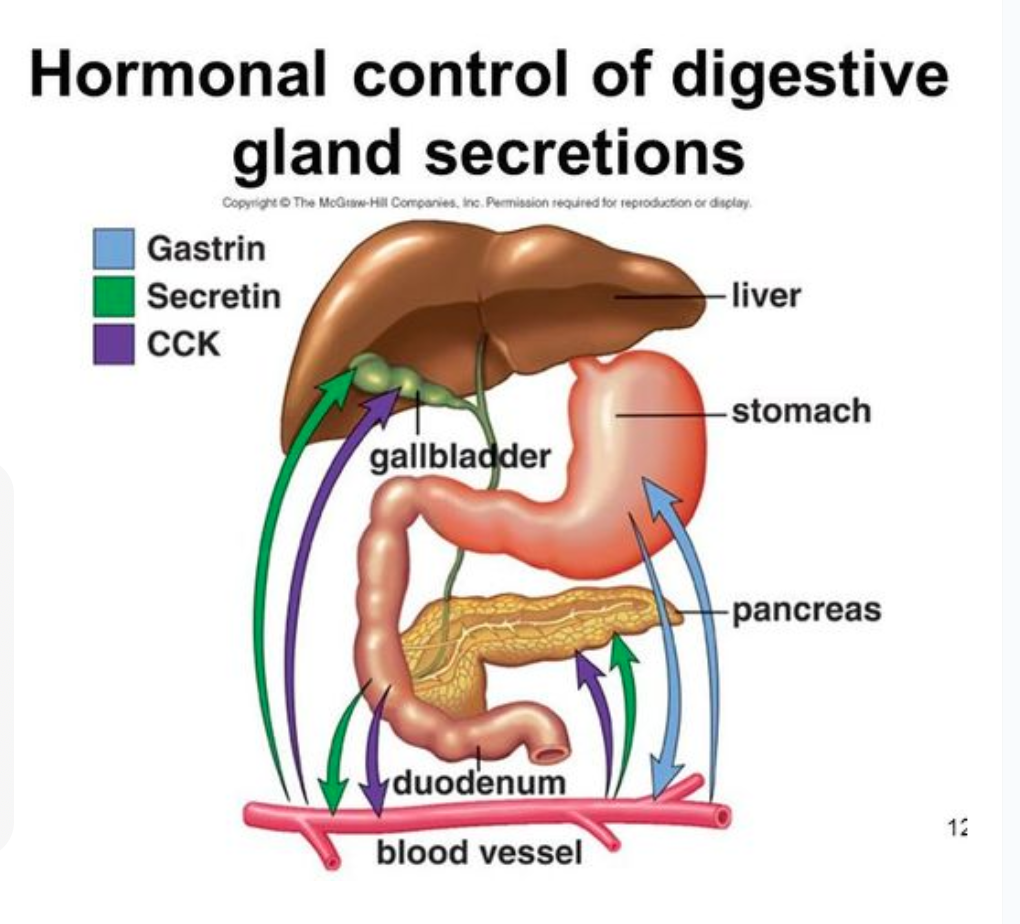
How is the digestion system regulated?
The nervous system and hormones regulate how often digestive secretions are made when needed so that energy can be conserved.
When will the brain make gastric secretions?
When you see or smell food, the nervous system may send an signal to make digestive juices.
If your brain detects the presence (pressure) of food in your stomach, it will make secretions
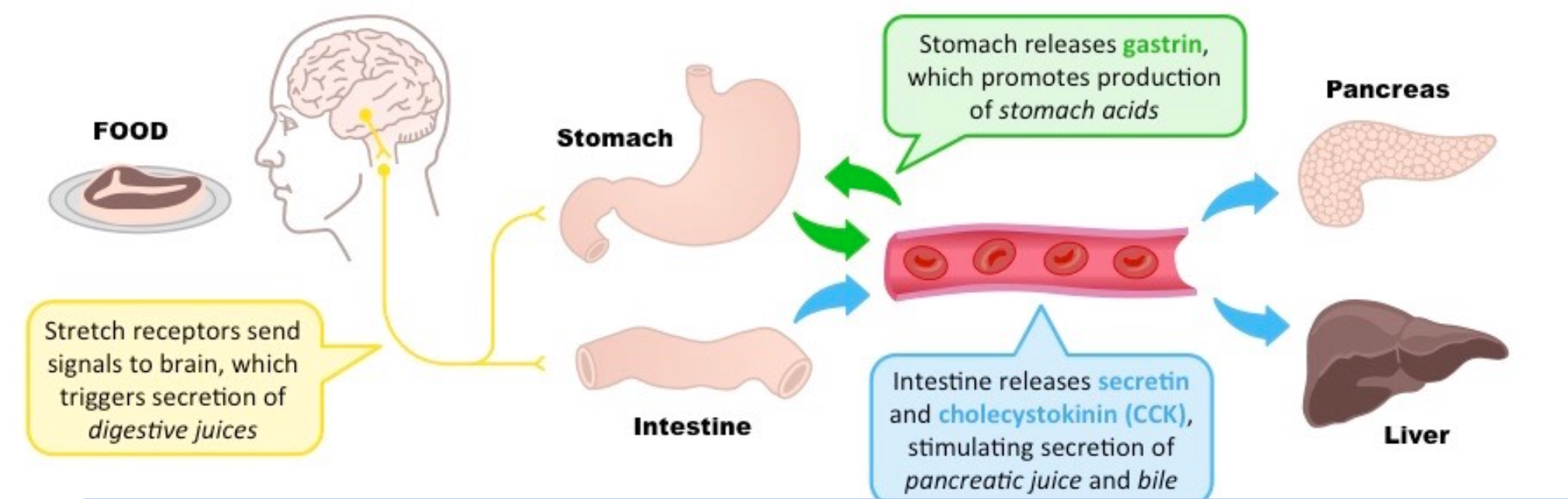
What hormone is released from the stomach to help make stomach acid?
Gastrin
The HCl is then released form parietal cells.
What hormones stimulate the production of pancreatic juice and bile from the liver?
Secretin
Cholecystokinin (CCK)
What glands secrete directly into the digestive tract?
Exocrine glands
Exocrine glands release secretions via a…
…tube called a duct
Salivary glands
Exocrine Glands that Secrete Saliva
Saliva is compose of what?
Water
Electrolytes
Mucus
Amylase
What funnels saliva into the mouth?
A duct
What do gastric glands (pits) in the stomach wall secrete?
Water
Mucus
Pepsin
Microvilli
Ruffling of epithelial membrane further increases surface area
Rich blood supply
Dense capillary network rapidly transports absorbed products
Single layer epithelium
Minimizes diffusion distance between lumen and blood
Lacteals
Absorbs lipids from the intestine into the lymphatic system
Intestinal glands
Exocrine pits (crypts of Lieberkuhn) release digestive juices
Membranes proteins
Facilitates transport of digested materials into epithelial cells
Villi with celiac disease
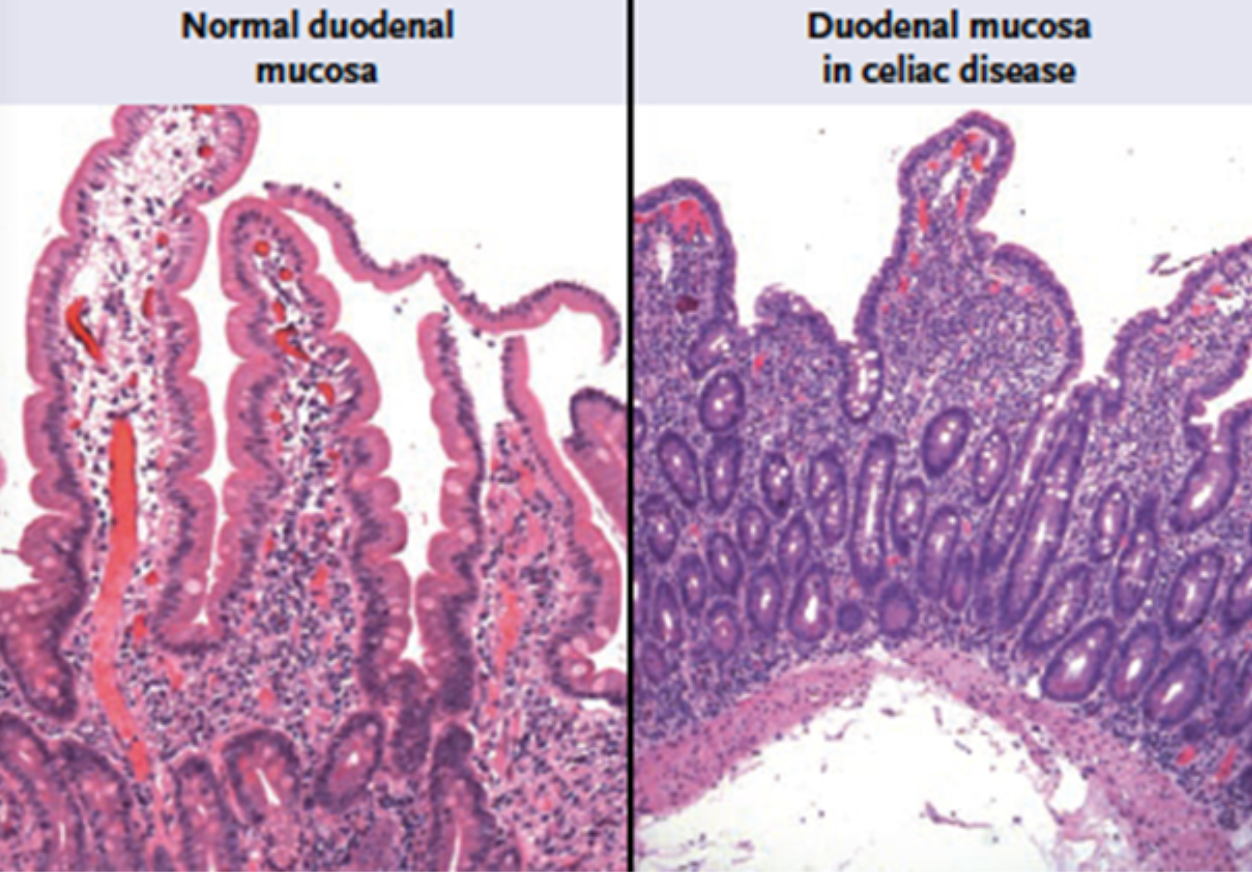
Acid helps quicken hydrolysis reactions by:
Disrupting the ECM (extra cellular matrix) holding cells together
Denaturing proteins