Parasitology final
1/367
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
368 Terms
What is the common name for Habronema spp.
Stomach Worm
What species is being described?
Horse
Stomach
Indirect through the fly
DX through embryonated eggs or L1 larvae
prepatent- 2 months
TX- anthelmintics and fly control
Summer sores, gastric issues, colic, diarrhea
Habronema spp. (Stomach Worm)
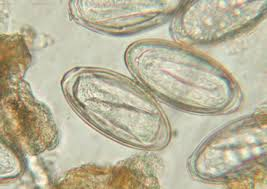
What egg is this?
Habronema spp.
What is the common name for Parascaris equorum
Roundworm of the horse (Equine Roundworm)
What species is being described?
Horse, common is foals
small intestine
Largest equine parasite
DX through eggs in feces
prepatent- 10-12 weeks
TX- anthelmintics
Anorexia, colic, nasal discharge, coughing, unthriftiness
Parascaris equorum (Equine Roundworm)
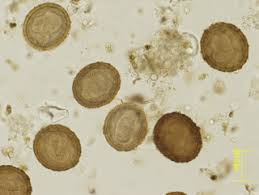
What egg is this?
Parascaris equorum (Equine Roundworm)
What is the common name for Strongylus spp.
Strongyles
What species is being described?
Horse
Large intestine/cecum
looks like hookworm
DX through eggs in feces
prepatent- 6 months
TX- anthelmintics
Anemia, colic, anorexia, fever
larvae can migrate
Strongylus spp. (Strongyles)
What egg is this?
Strongylus spp. (Strongyles)
What is the common name for Strongyloides westeri
Equine threadworm
What species is being described?
females don’t need a male to reproduce
Horse, more common in foals
small intestine
Transmammary, orally, cutaneously
needs warm, moist soil
DX through Baermann’s
prepatent- 5-7 days
TX- oxibendazole, ivermectin
diarrhea, anorexia, anemia, loss of appetite
Strongyloides wester (equine threadworm)
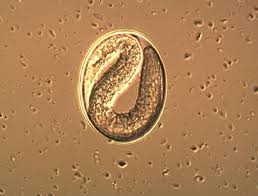
What egg is this?
Strongyloides westeri (equine threadworm)
What is the common name for Oxyuris equi
pinworm of horses
What species is being described?
Horse
Cecum/rectum/colon
Eggs on outside of anus
DX through scotch tape method
prepatent- 4-5 months
TX- anthelmintics, wash anus
raw tail head, itchy
Oxyuris equi (pinworm of horses)
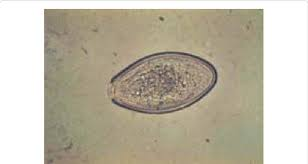
What egg is this?
Oxyuris equi (pinworm of horses)
What is the common name for Onchocerca cervicalis
Equine neck threadworms
What species is being described?
Horse
Indirect through biting midges or gnats
Intermediate hosts injects microfilariae
DX through skin biopsy
prepatent- 3-4 weeks
TX- through anthelmintics and insect control
Scaly, itchy pieces of alopecia a long the neck/cervical line, opthalmic issues, looks like sweet itch
Onchocerca cervicalis (Equine neck threadworms)
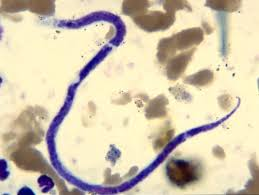
What species does this microfilariae belong to?
Onchocerca cervicalis (equine neck threadworms)
What is the common name for Anoplocephala perfoliata
equine tapeworm
What species is being described?
Horse
small and large intestine/cecum
indirect through grain mites
DX through eggs or segments in feces
prepatent- 28-42 days
TX- prazi/epsiquantel
asymptomatic, maybe a blockage or colic
cysticercoid
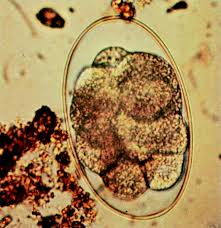
Anoplocephala perfoliata (equine tapeworm)
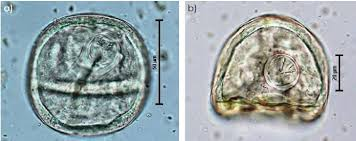
What egg is this?
Anoplocephala perfoliata (equine tapeworm)
What are 2 other scientific names for equine tapeworm?
Anoplocephala magna
Paranoplocephala mamillana
What species is being described?
equine tapeworm
small intestine/stomach
indirect through grain mites
DX through eggs or segments in feces
prepatent- 28-42 days
TX- prazi/epsiquantel
asymptomatic, maybe a blockage or colic
cysticercoid
Anoplocephala magna
Paranoplocephala mamillana
What is the main difference between Anoplocephala perfoliata and Anoplocephala magna/Paranoplocephala mamillana
Location!
Anaplocephala perfoliata (small & large intestine, cecum)
Anoplocephala magna/Paranoplocephala mamillana (small intestine & stomach)
What is the common name for Eimeria leuckarti
equine coccidia
What species is being described?
Horse
immune to parasite after getting over it
small intestine
DX through oocytes in feces
prepatent- 30 days
TX- sulfa drugs
asymptomatic, inflammation of intestinal cells
sporulated oocytes
Eimeria leuckarti (equine coccidia)
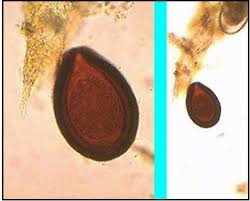
What egg is this?
Eimeria leuckarti (equine coccidia)
What is the common name for Babesia caballi
equine piroplasmosis
What is another scientific name for Babesia caballi
Theileria equi
What species is being described?
Horse
Reportable to government
Indirect through tick
Mares can pass in utero
DX through blood smear
blue balls
prepatent- 10-30 days
TX- imidocarb dipropionate
fever, depression, icteric, anorexia
Babesia caballi (equine piroplasms)
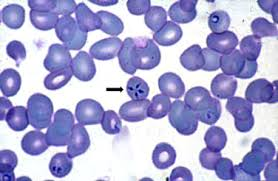
What species is this?
Babesia caballi (equine piroplasms)
What can Sarcocystis neurona also be called?
Sarcocystis
What species is being described?
main host is a possum (horse is aberrant)
DX through a blood test
TX- ponzeril or diclazuril
EPM, ataxia, weakness, muscle loss
sporulated oocytes
Sarcocystis neurona
what is EPM
equine protozoal myelitis

What species is this?
Sarcocystis neurona
What is the common name for Gasterophilus spp.
Horse/stomach bots
What species is being described?
Horse
stomach
DX through larvae in feces, eggs on hair of legs
TX- ivermectin, moxidectin
gastric ulcers, irritated gastric mucosa
larval in horse, adult in fly
Gasterophilus spp. (horse/stomach bots)

What species is this?
Gasterophilus spp. (horse/stomach bots)
What parasite of horses is often mistaken for foal heat diarrhea?
Strongyloides westeri (equine threadworm)
What method of parasite detection would usually never be used for horses?
Sedimentation
What is the best way to manage parasites in horses?
rotate pastures
perform fecal egg counts
deworm accordingly
Where are adults of Onchocerca cervicalis found?
ligamentum nuchae
German scientist _________ ________ ___________discovered X-Rays in the year_______.
Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen; 1895
describe X-Rays
invisible
electrically neutral
travel in straight lines
fluorescent in certain substances
can produce scatter radiation
what is scatter radiation also known as
secondary radiationwhat
what are the 3 parts of an atom
protons (+)
neutrons
electrons (-)
where are protons and neutrons located in the atom
in the nucelus
where are electrons located in the atom
in the rings on the outer edges
as the number of protons increase, the number of corresponding electrons _________
increase
as the number of rings increase, does electrical charge increase or decrease
decrease
what metal has the highest melting point of other metals
tungsten
what is frequency
the number of waves passing a given point per unit of time
higher frequency = _______ penetration
more
what does mA stand for
milliamperage
what does kVp stand for
killavolt peak
what is the current
mA is used to measure the electric current that activates the x-ray tube
what is the voltage
speed in which electrons transfer energy along the circuit
what is the time
timer controls the length of time that x-rays are produced
what does rectification ensure
that the current travels in the same direction as a direct current
what kind of animals is a single-phase circuit used for
small animals, birds, lizards
what kind of animals is a three-phase circuit used for
large animals, horses, elephants
what is the filament made of in a x-ray machine
tungsten
what is the first step in the process of taking a radiograph
mA heats the filament to take the electrons from it to produce an electron cloud
cathode
negative side
anode
positive side
2 varieties of anodes
rotating
stationary
what is the second step in the process of taking a radiograph
electrons released from the cathode hit the target to break the electrons, producing radiation
what controls how hard the electrons hit the target
kVp
describe the anode heel effect
radiation is more intense on the cathode side
what is Step-Up
volts to kVp, slamming electrons into the target
what is Step-Down
volts to mA, heating the filament (tungsten)
what does pressing the pedal halfway down do
rev the anode, heat the filament
what does pressing the pedal all the way down do
sends cloud to target, takes the radiograph
___% radiation to ___% heat
1% to 99%
changing the kVp level affects what
contrast, quality of the image; inside of the image
how much should you change kVp by at a time
10%-15%
changing the mA level affects what
density, quantity of electrons; degree of blackness
how much should you change mA by at a time
30%-50%
what is Sante’s Rule
2 times thickness + SID (source image distance) + GF (grid factor) = kVp
what is the common source image distance in stationary machines
40 in
what does high contrast show on radiographs
blacks and whites (extremities/bones)
what does low contrast show on a radiograph
many grays (thorax/abdomen)
what kinds of subjects does the contrast level depend on
thickness
body part
bone/muscle/fat ratio
contrast media
what is collimation
moves around the field of view (etch-a-sketch)
why should we collimate
allows for less scatter radiation
what does ALARA stand for
as low as reasonably achievable
stochasitc effects
occur in your lifetime
deterministic effects
genetic effects
may not show up for 2-3 generations
what thickness of led protects us from scatter radiation
0.5 mm
radiation can affect the cell in 4 ways
pass through with no damage
repairable damage
irreparable damage
kills the cells
what is a dosimeter
measures exposure levels
what is the absorbed dose
RAD or Gy amount of radiation absorbed per unit of mass matter
what is the dose equivalent
REM or Sv unit measured by dosimeter
1 Sv = ___ REM
1 mSv = ___ REM
100; 100
T or F; shielding protects you from the direct beam
False
what are the 3 Cardinal Rules
reduce time of exposure
increase distance between source of radiation and the subject
shield or barrier between operator and source of radiation
what is the number 1 issue when taking radiographs
motion of the patient
radiolucent means
cannot see on a film
radiopaque means
can see on a film