BIO220 (Genomes to Ecosystems) - Lecture 6, Week 4
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
Difference between the genetic mechanisms of continuous phenotypes relative to Mendelian phenotypes.
Multiple genes inform the resulting phenotypic expression, and are influenced by the environment.
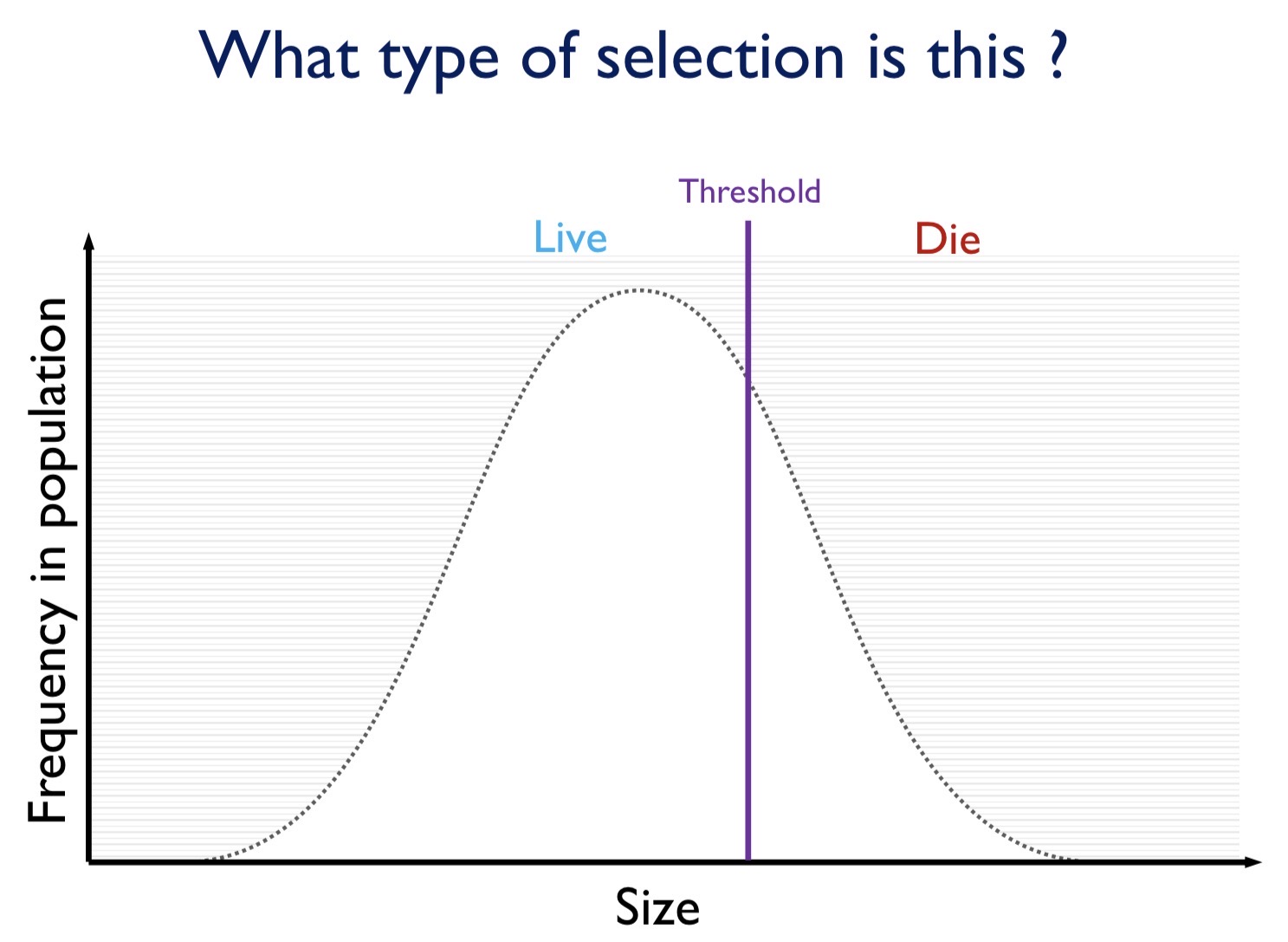
What selection is being imposed in this figure?
Truncation selection
Definition of truncation selection
Form of directional selection where members of a population whose expression of a particular phenotype is outside a assigned threshold are selected for (i.e., survive)
What is the equation to measure the intensity of truncation selection?
S (Intensity of Truncation Selection) = Z* (Mean of the Population Post-Selection) - (Mean of the Population Pre-Selection)
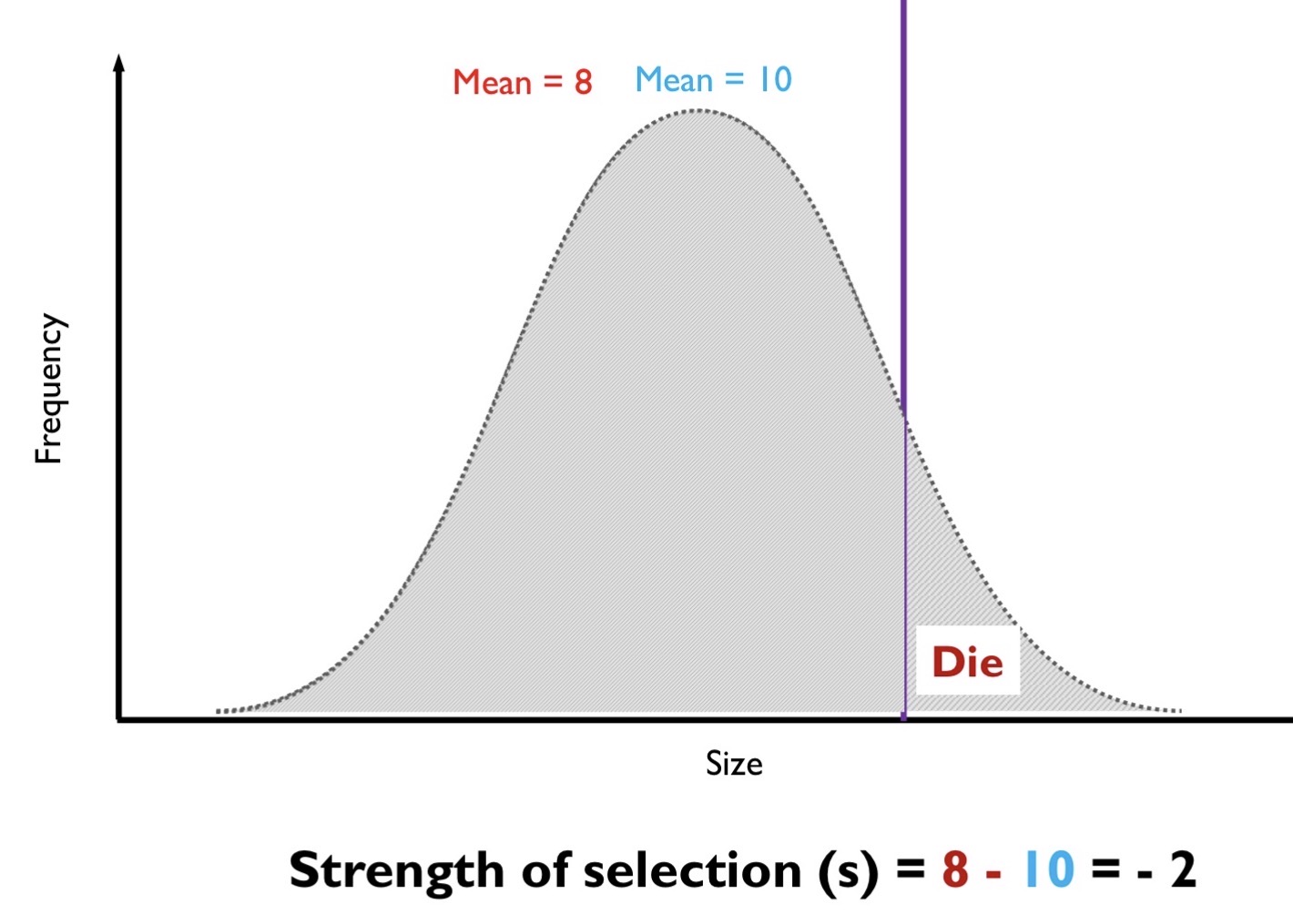

What information does the value of S in the S = Z* - Z communicate?
The sign indicates the direction of selection, while the number indicates the magnitude of selection.
What does R² communicate?
The amount of variation that is accounted for in a graphical model (i.e., R² = 0.60, graphical model accommodates for 60% of variation)
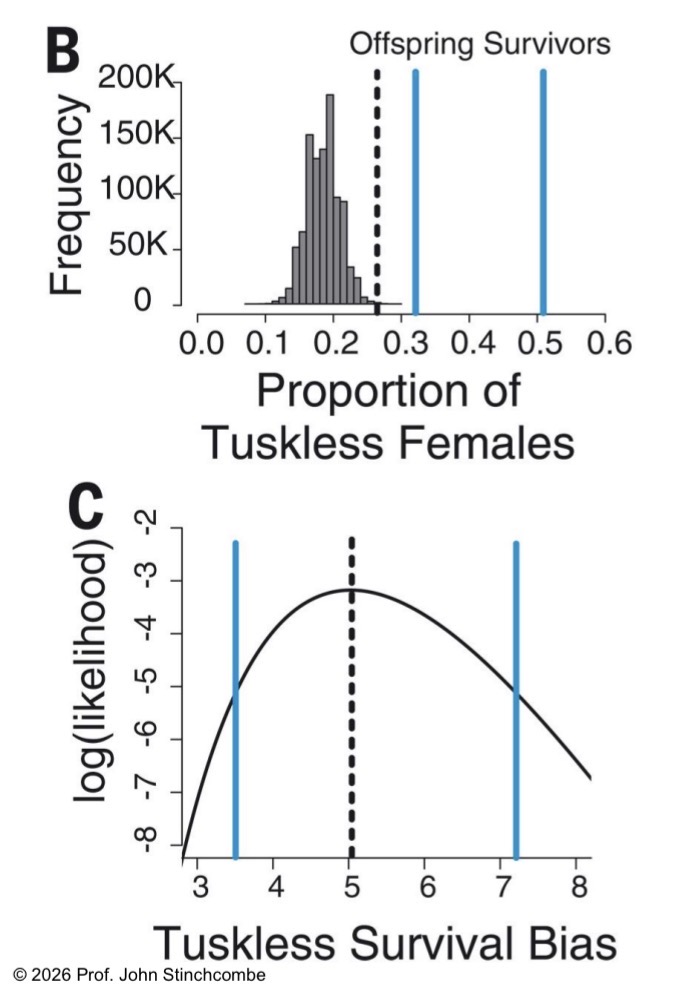
What are the two the characteristics of the locus responsible for producing tusklessness in elephants?
Dominant, x-linked locus that is lethal in male progeny.
Assuming X denotes the wild type, tusked phenotype, and x denotes the mutant, tuskless phenotype, why are xx female progeny never observed in the population?
xY male are non-viable; therefore, are unable to produce xx female progeny with an xX female