Gene expression topic Y12 - nucleotides to redundant code
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
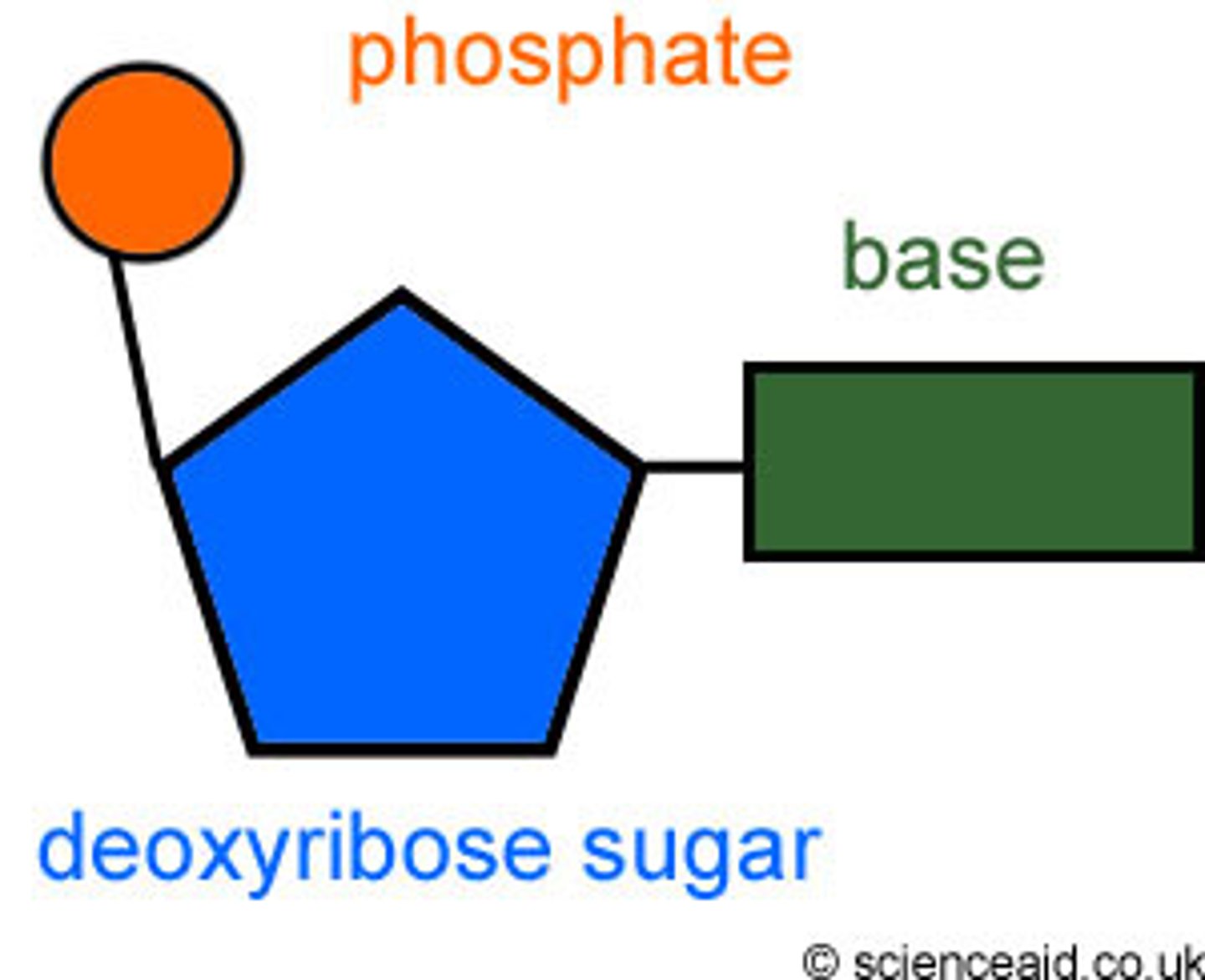
Nucleotide
monomer of nucleic acids made up of a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base
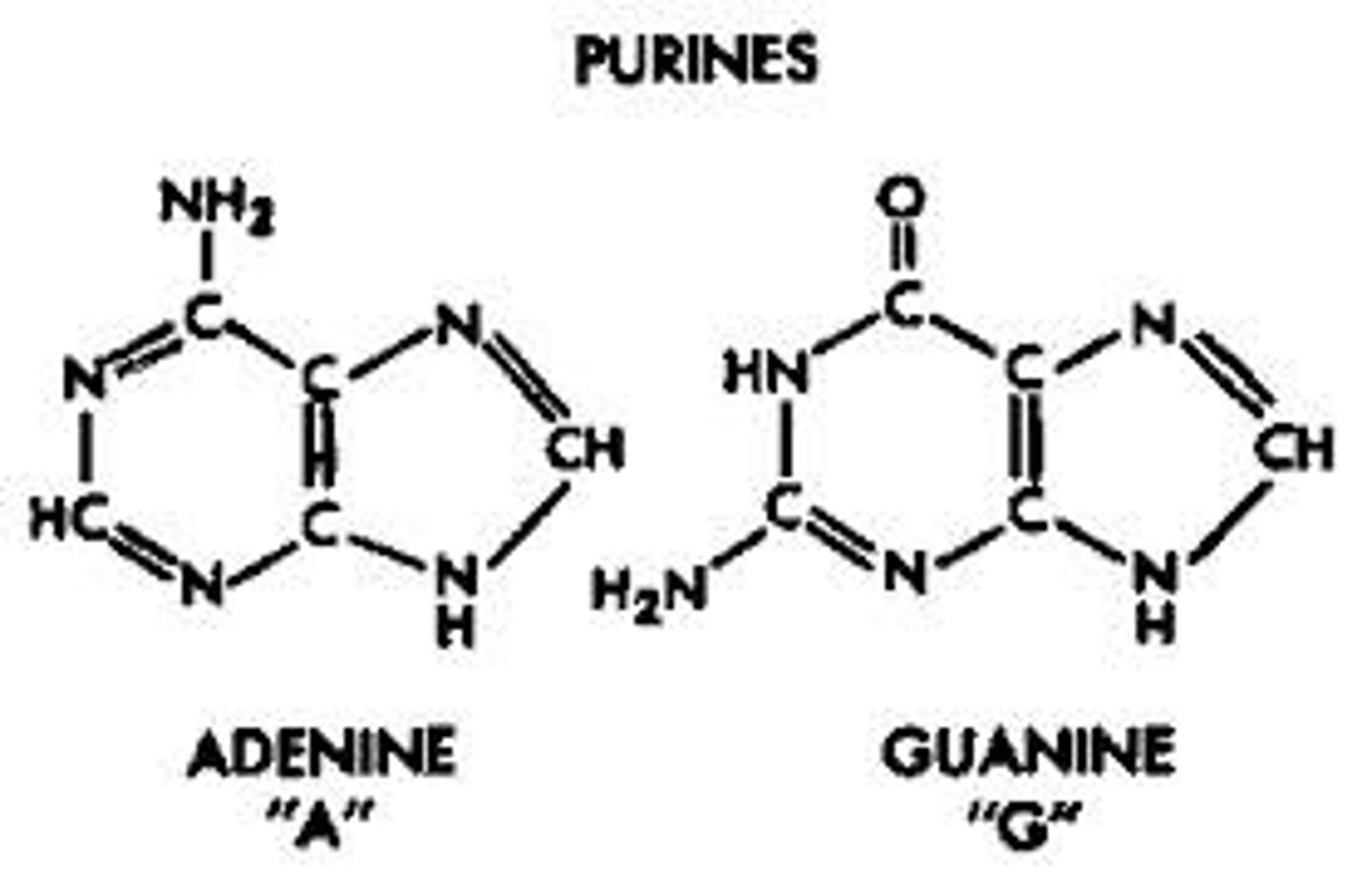
Purine
Classification of bases such as adenine and guanine(A + G). Has a double ring structure.
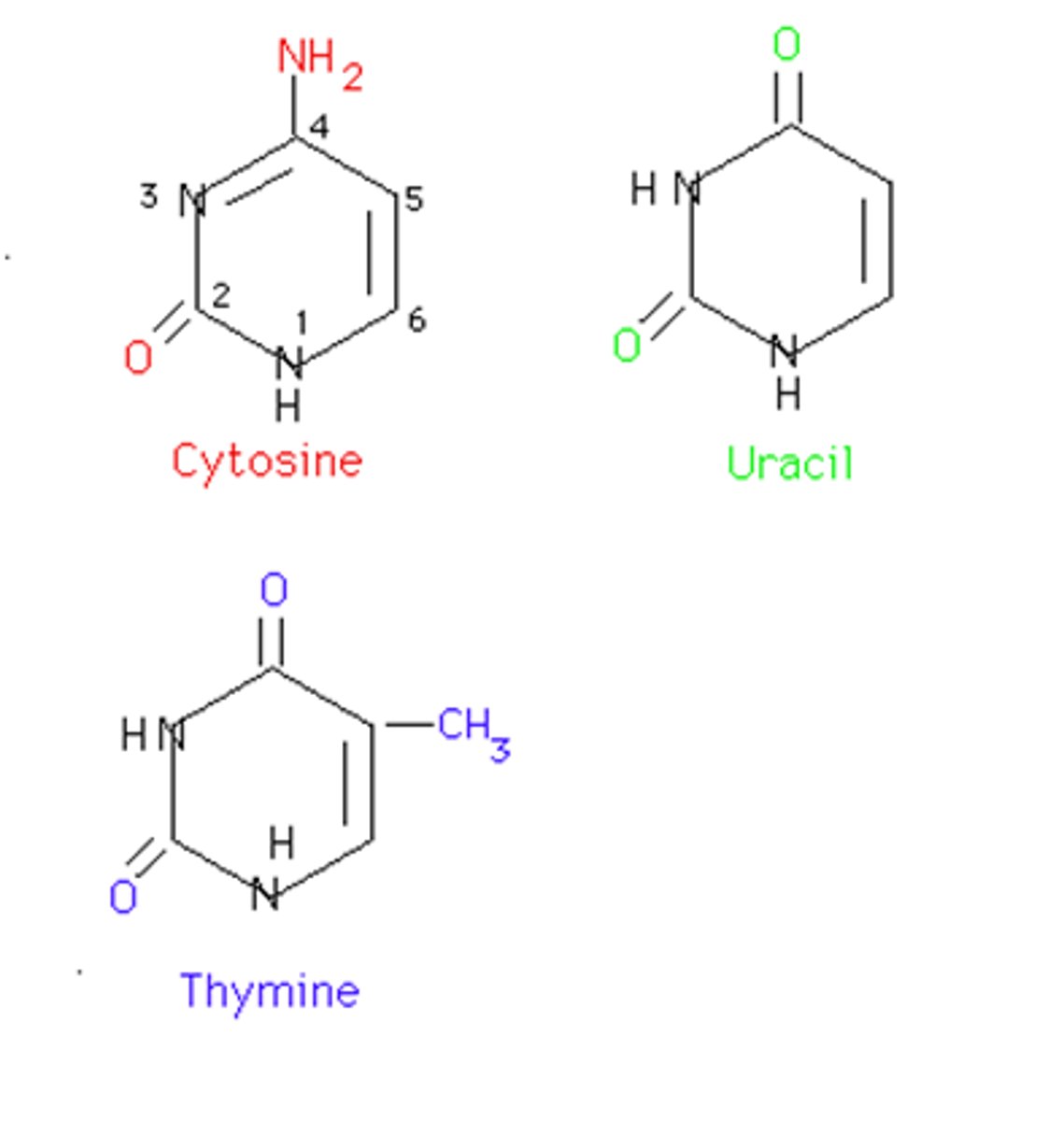
Pyrimidine
Bases such as thymine and cytosine (T + C).Has a single ring structure.
RNA
Ribonucleic acid. A single strand nucleic acid important in protein synthesis.
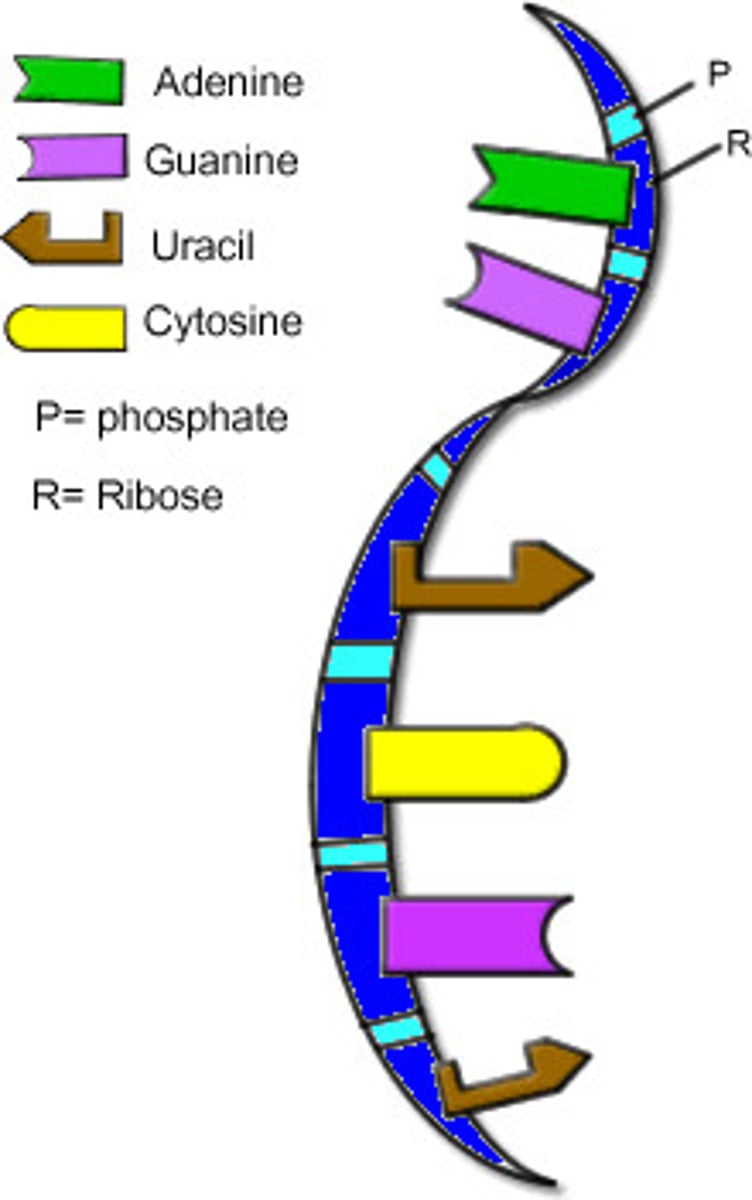
Uracil
Base found in RNA only. Present instead of THYMINE.
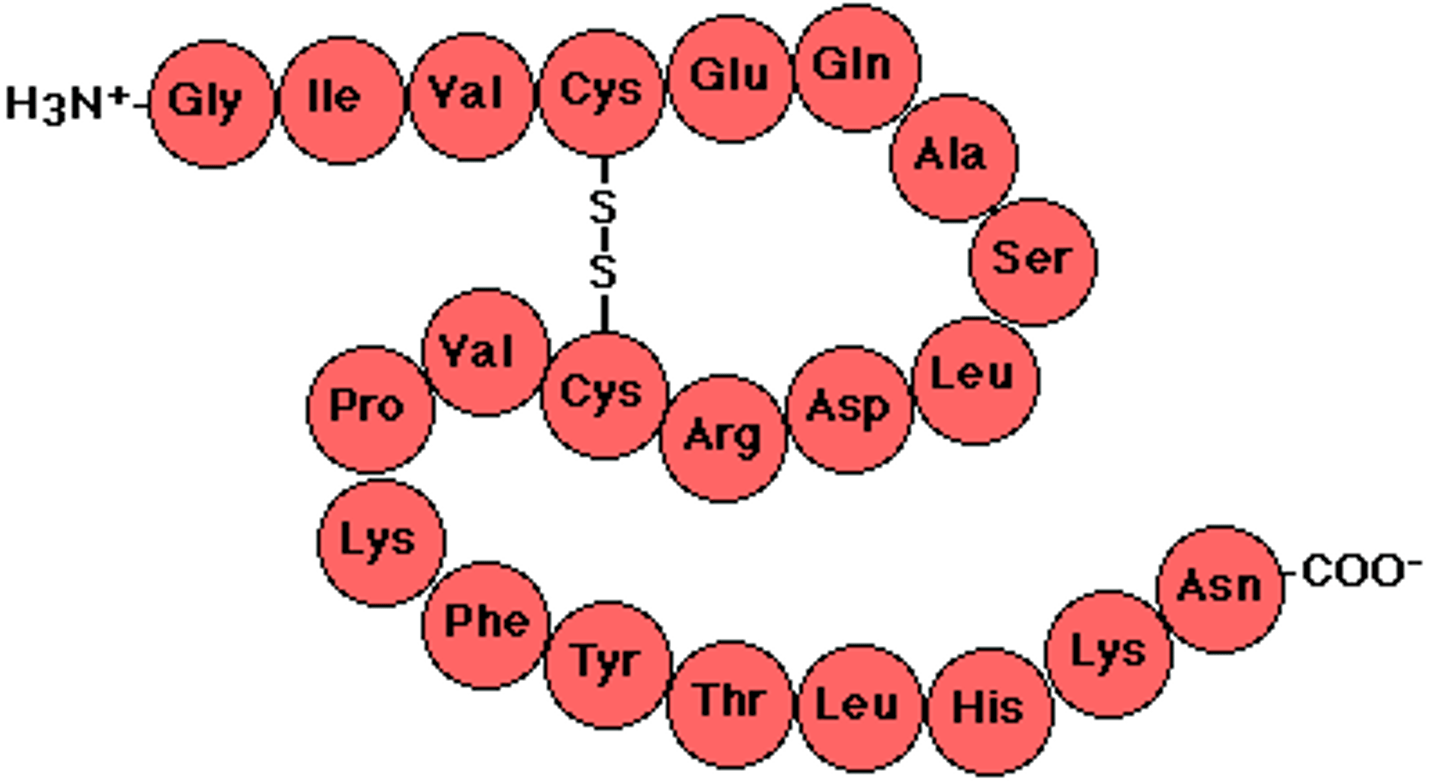
Polypeptide
Long chain of amino acids joined together by peptide bonds.
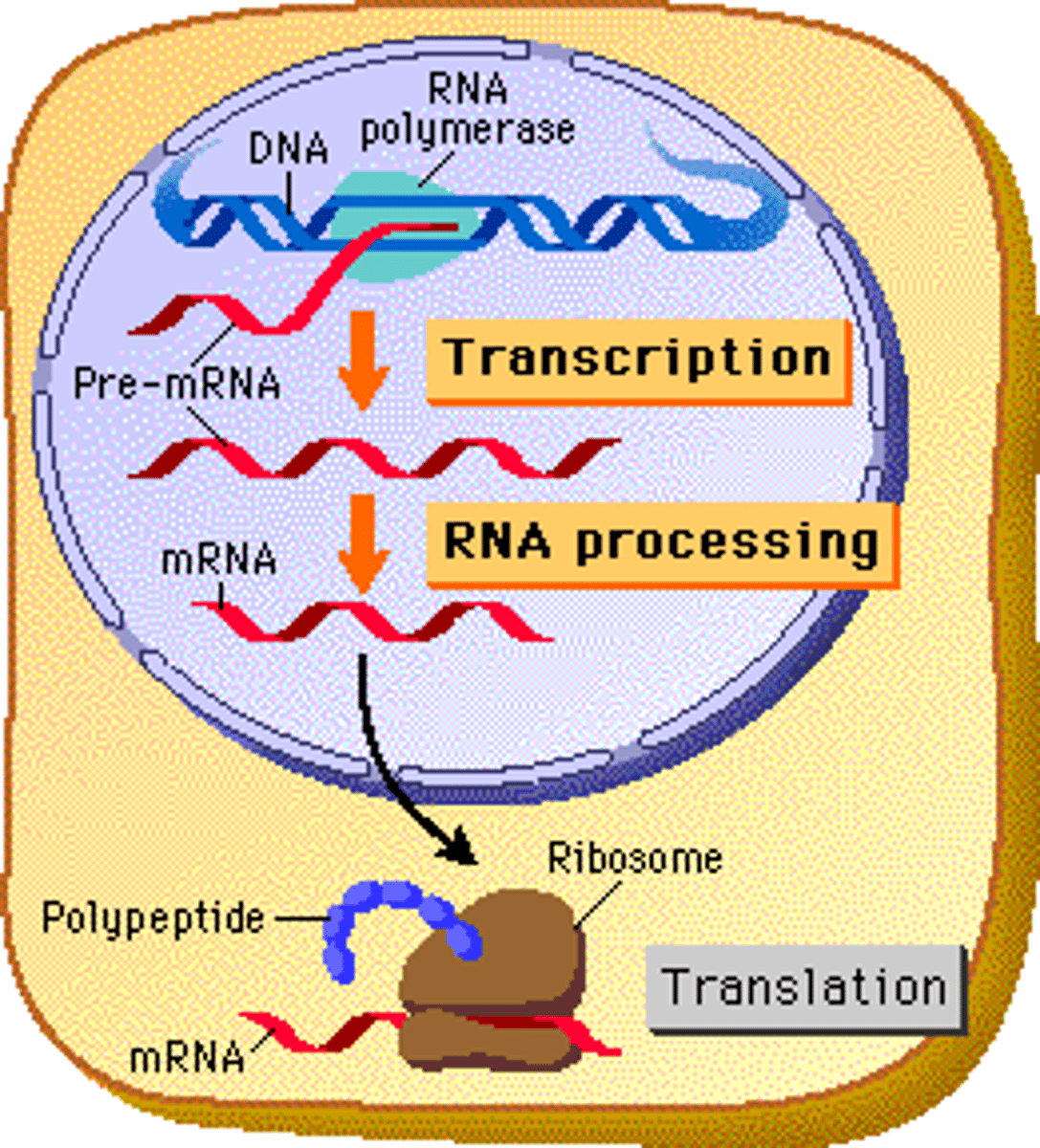
Transcription
Making of mRNA using free nucleotide base pairing against DNA template strand. DNA sequence in a gene is copied.
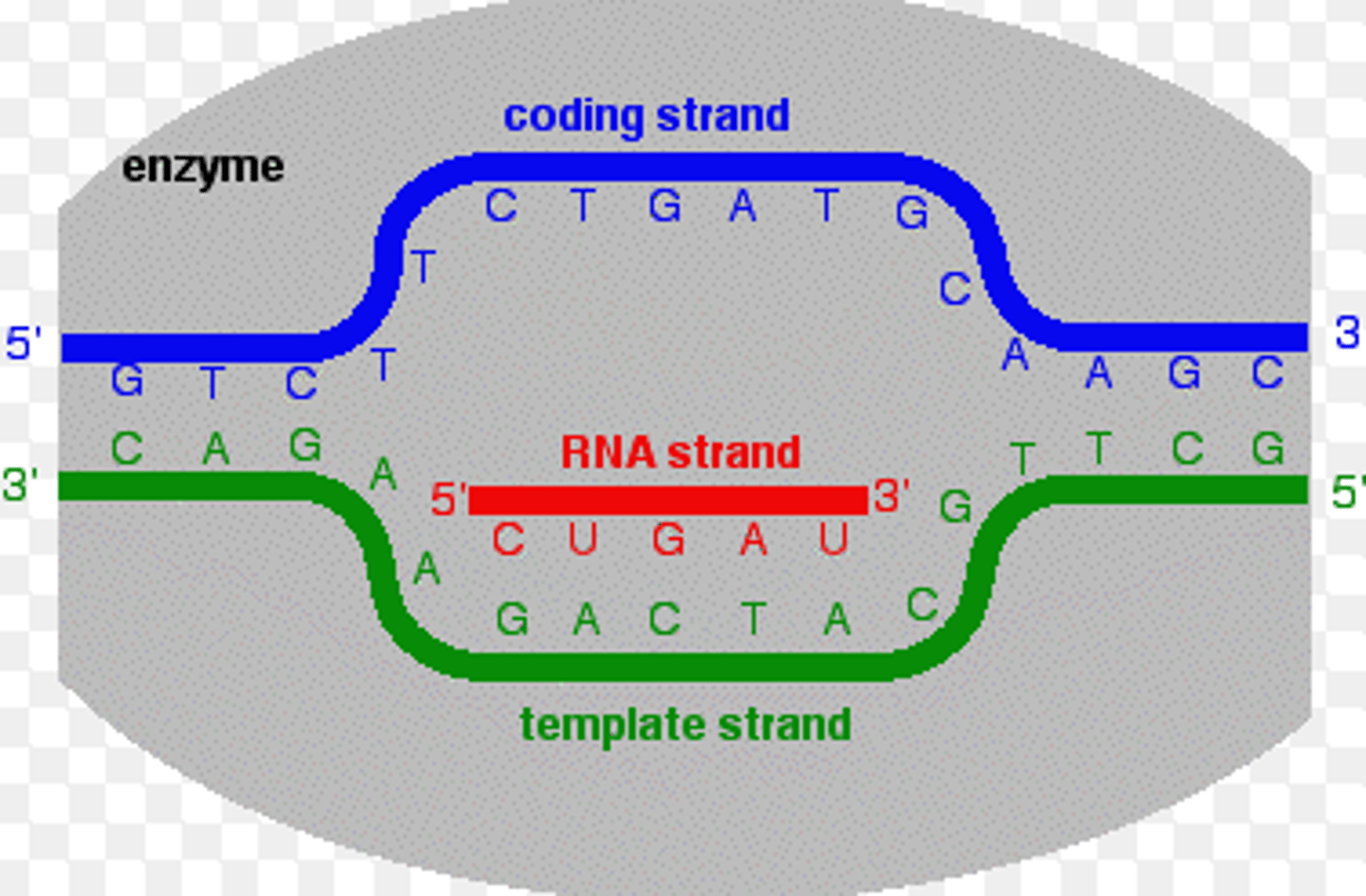
Coding strand
Strand of DNA where mRNA is an exact copy of this DNA strand ( U instead of T). Not used for transcription.
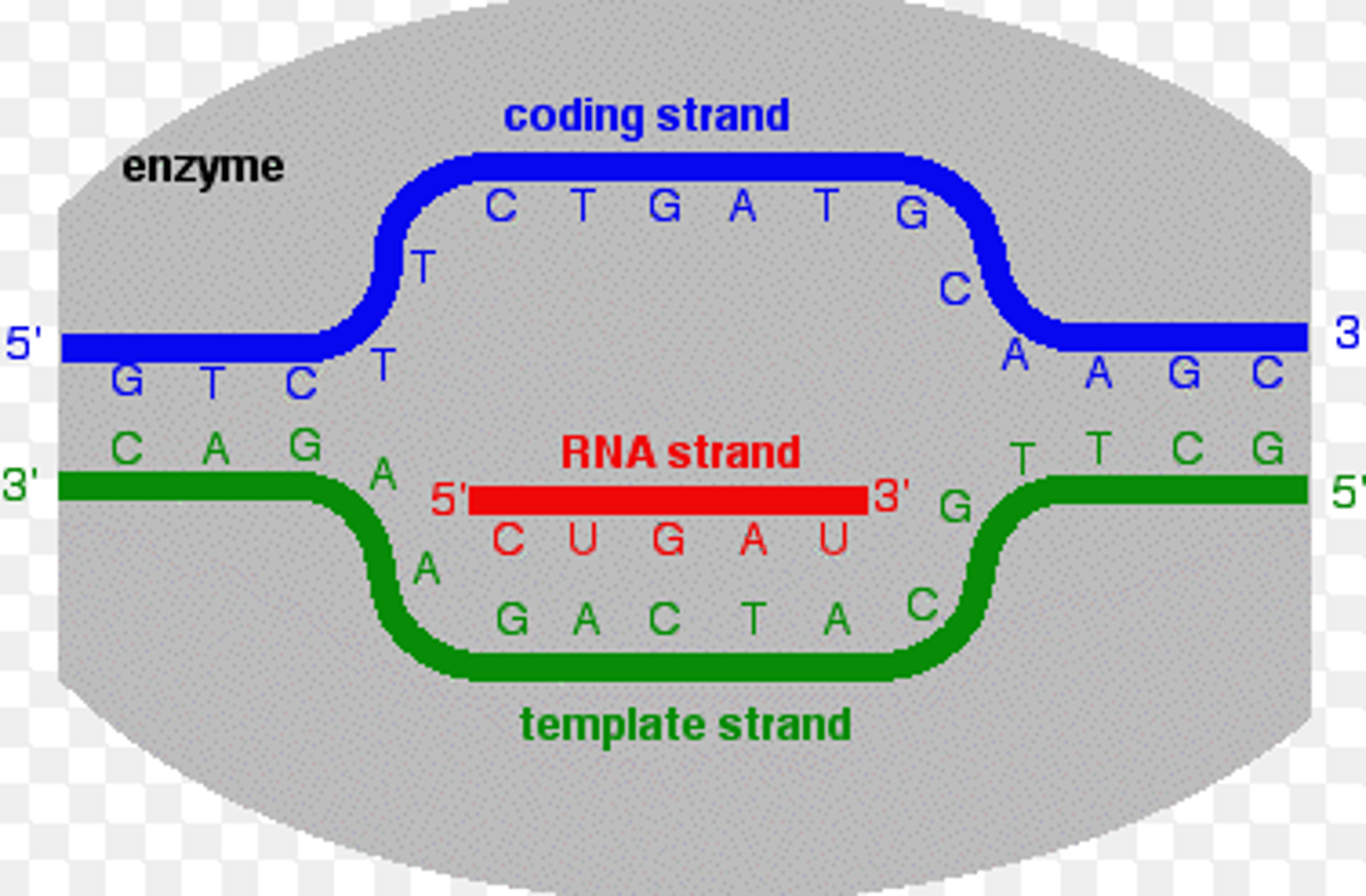
Template strand
Free nucleotide base pair match this DNA strand during transcription.
Start codon
AUG - 3 nucleotides where transcription starts
Stop codon
UAA, UAG, UGA - 3 nucleotides where transcription stops
Promoter
3 nucleotides on DNA where RNA polymerase attaches and unwinds it.
Terminator
Base sequence where transcription stops
RNA polymerase
Enzyme causes DNA helix to unwind ahead of transcription.
mRNA
Single stranded polynucleotide which copies section DNA sequence to carry out of nucleus for proteins to be made. (messenger RNA)

Translation
Information carried by mRNA is converted into specific sequence of amino acids to form a polypeptide/protein.
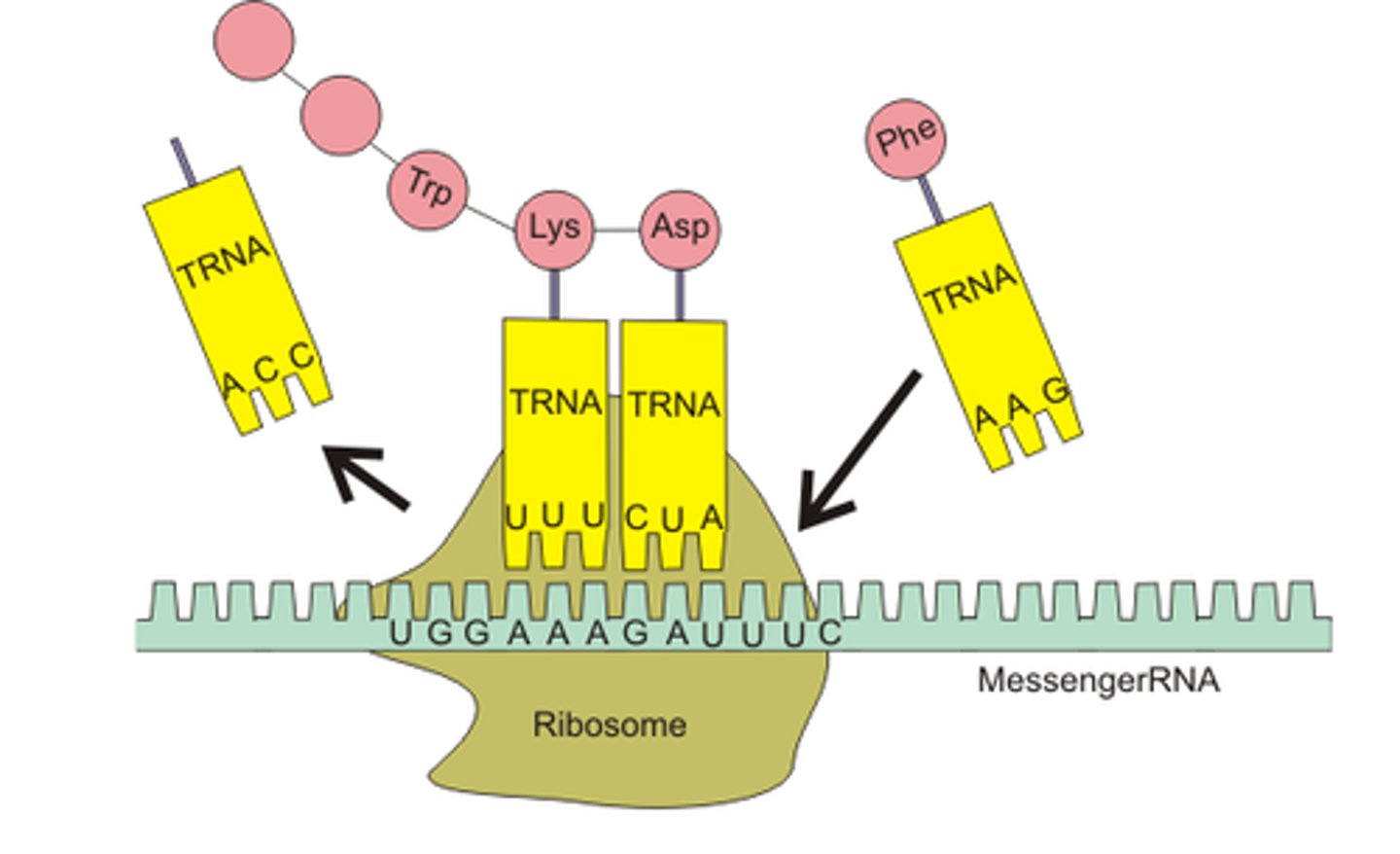
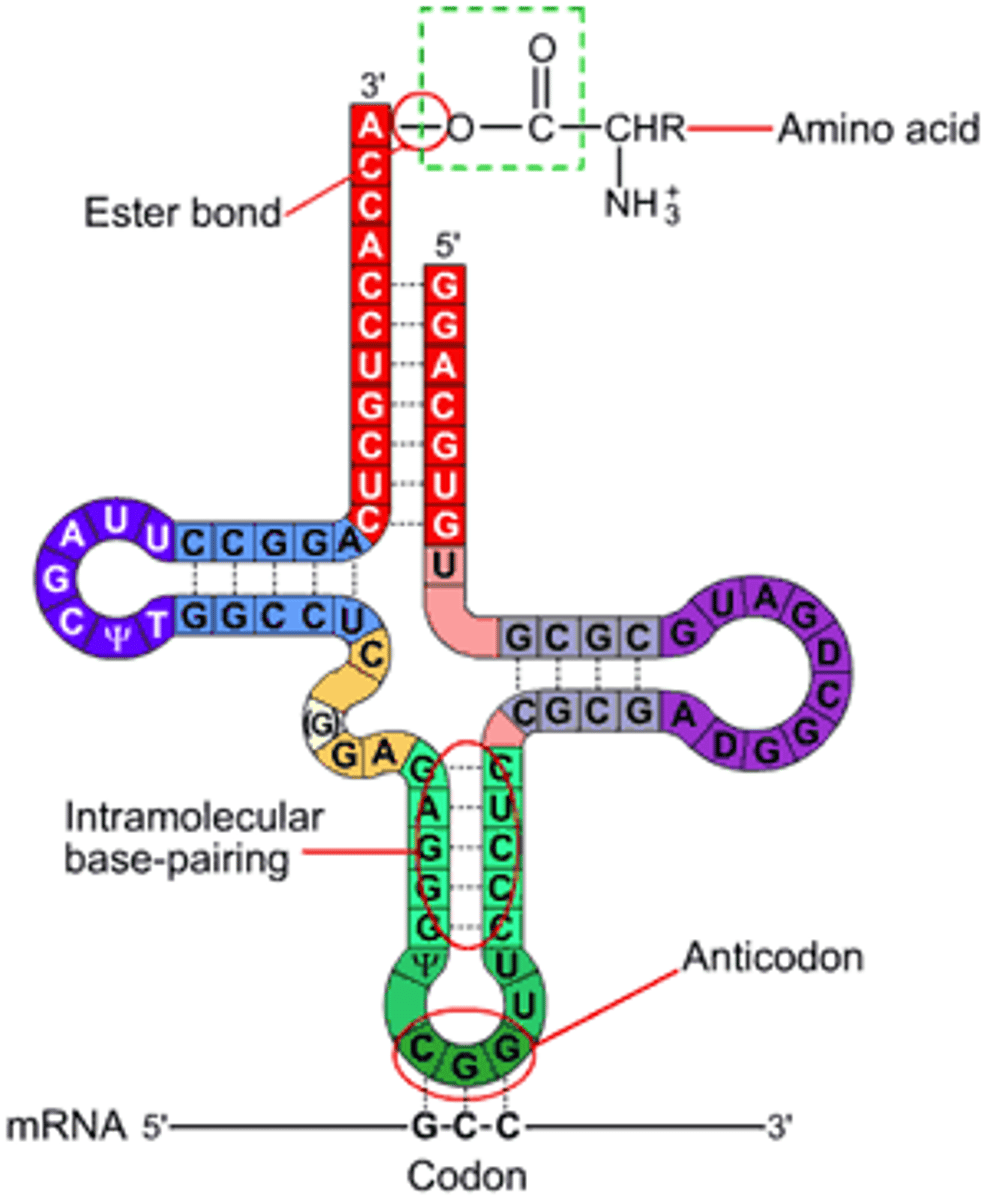
tRNA
Transfer RNA. Attaches to amino acids found in cytoplasm based on 3 bases on end of tRNA (anti-codon)
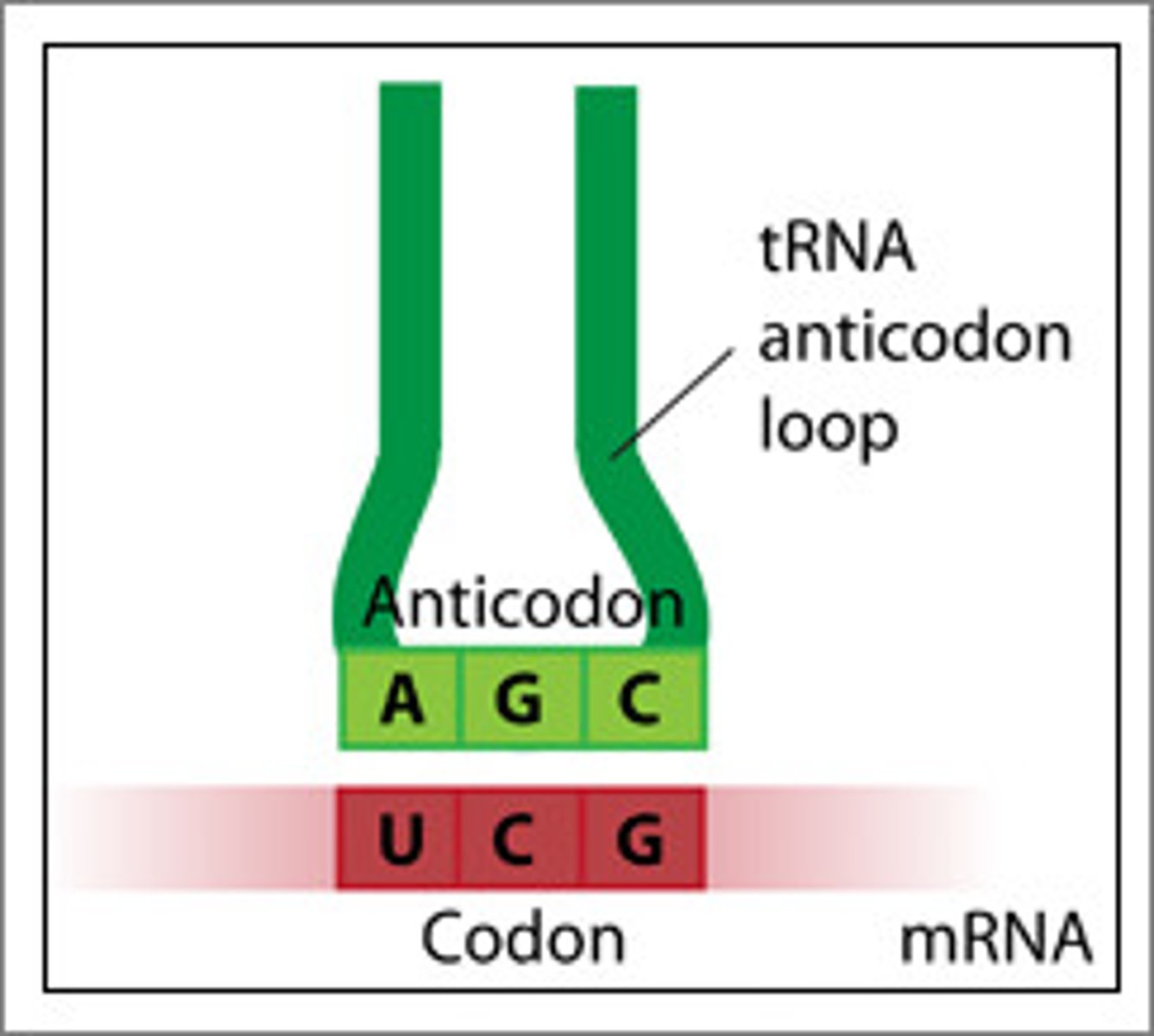
Codon
3 bases on mRNA read by anti-codons on tRNA to make proteins.
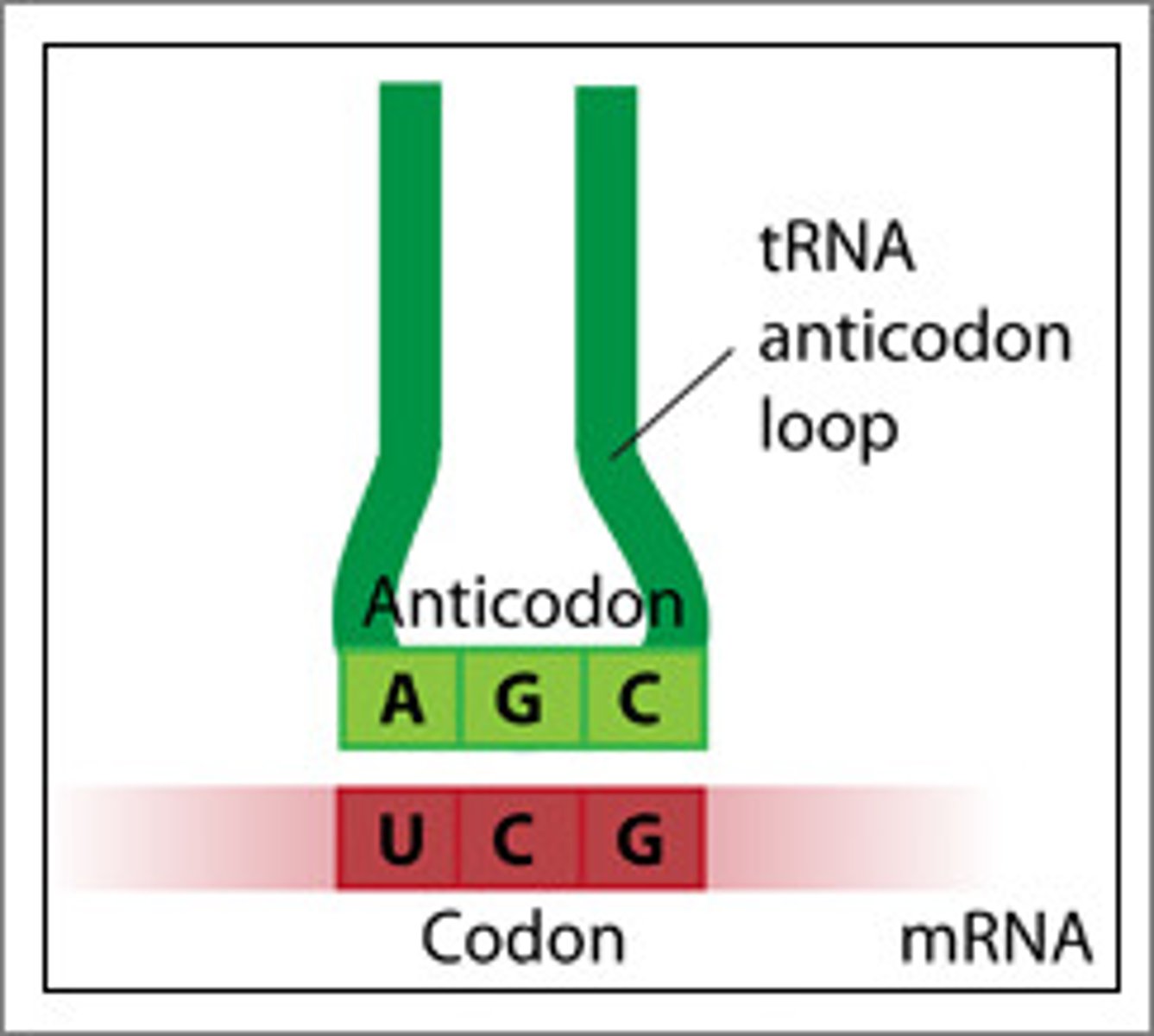
Anti-codon
group of three bases on a tRNA molecule that are complementary to an mRNA codon
Redundant code (redundancy):
Genetic code is referred to this as some codons (UUU, UUC..) code for same amino acid.
Only different in last base.