Embryonic and Fetal Development: Stages, Structures, and Processes
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Embryonic Development
The process by which the embryo forms and develops.
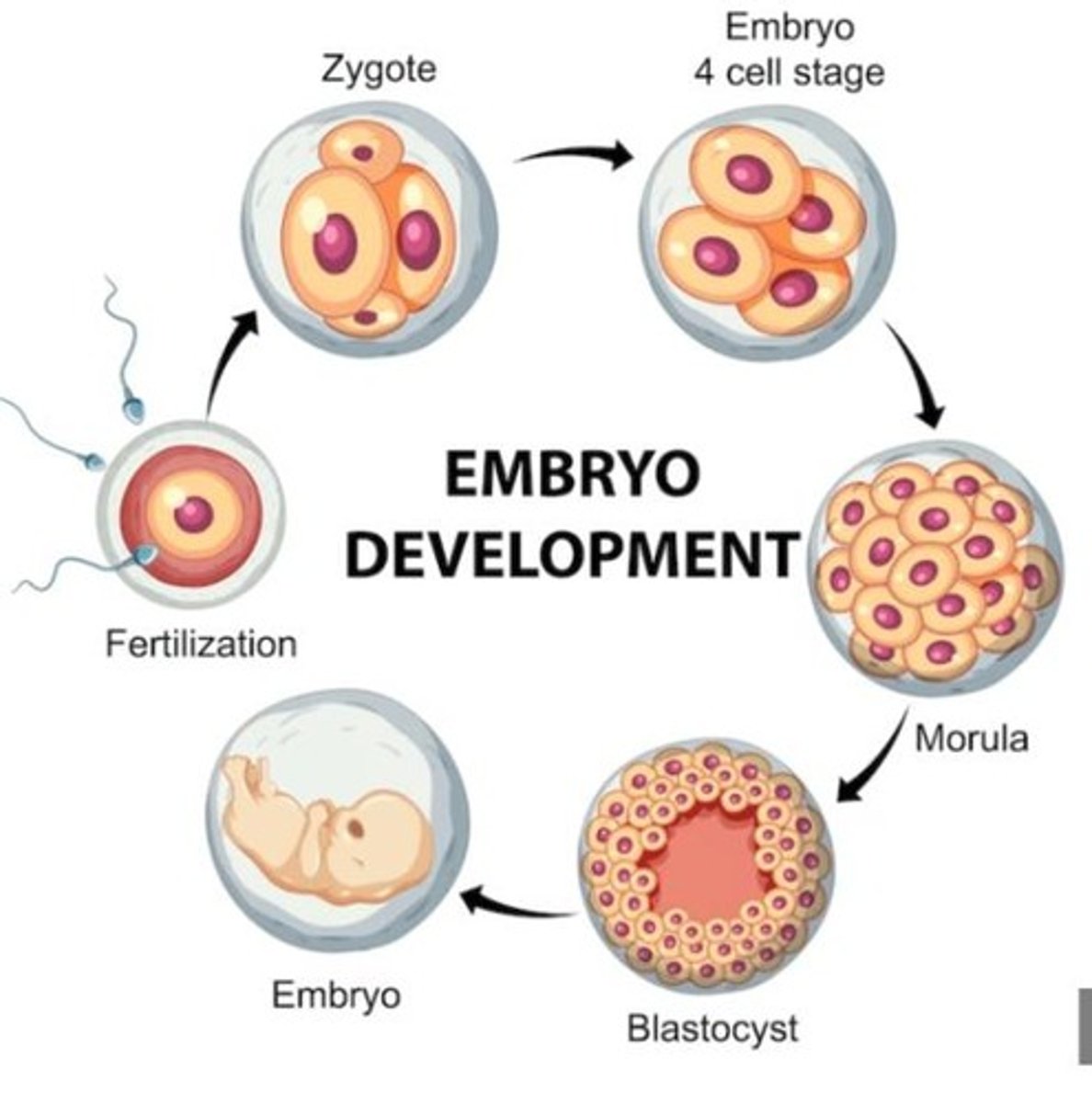
Zygote
1 cell
Embryo
multicell
Fetus
week 9 after fertilization
Cleavage
a period of cell division during day 1 - day 3 or 4 of embryonic development that includes rapid cell division of embryo with NO cell growth
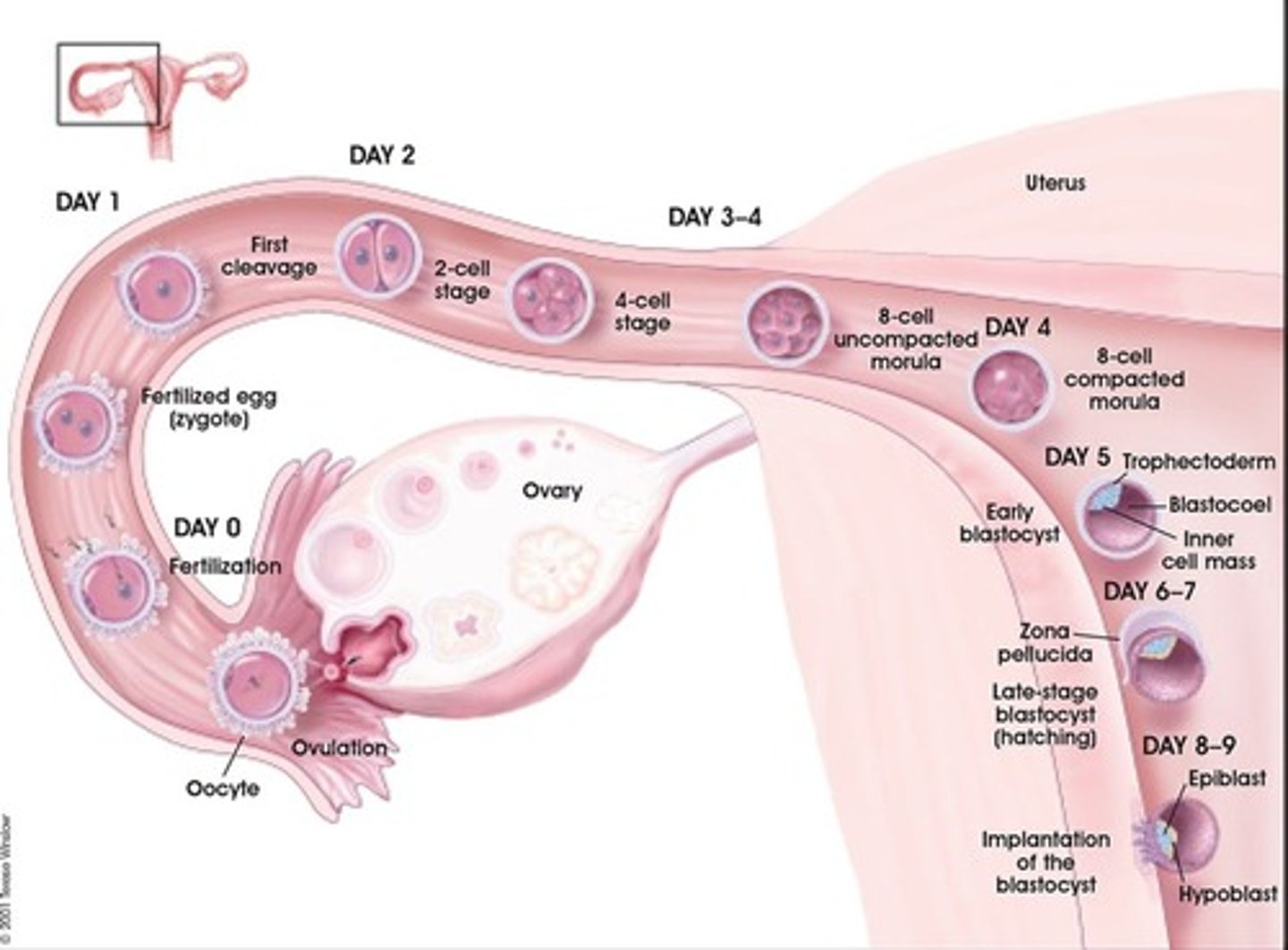
Day 1
First cleavage begins post fertilization
Day 2
2-cell embryo formed
Day 3 & 4
rapid cell division occurs; 4 cell embryo formed; 8 cell embryo formed; Morula formed (16+ cells)
Blastulation
The process of a blastocyst (100+ cells) being formed from a morula (16+ cells); morula becomes hollowed out and develops a fluid filled cavity
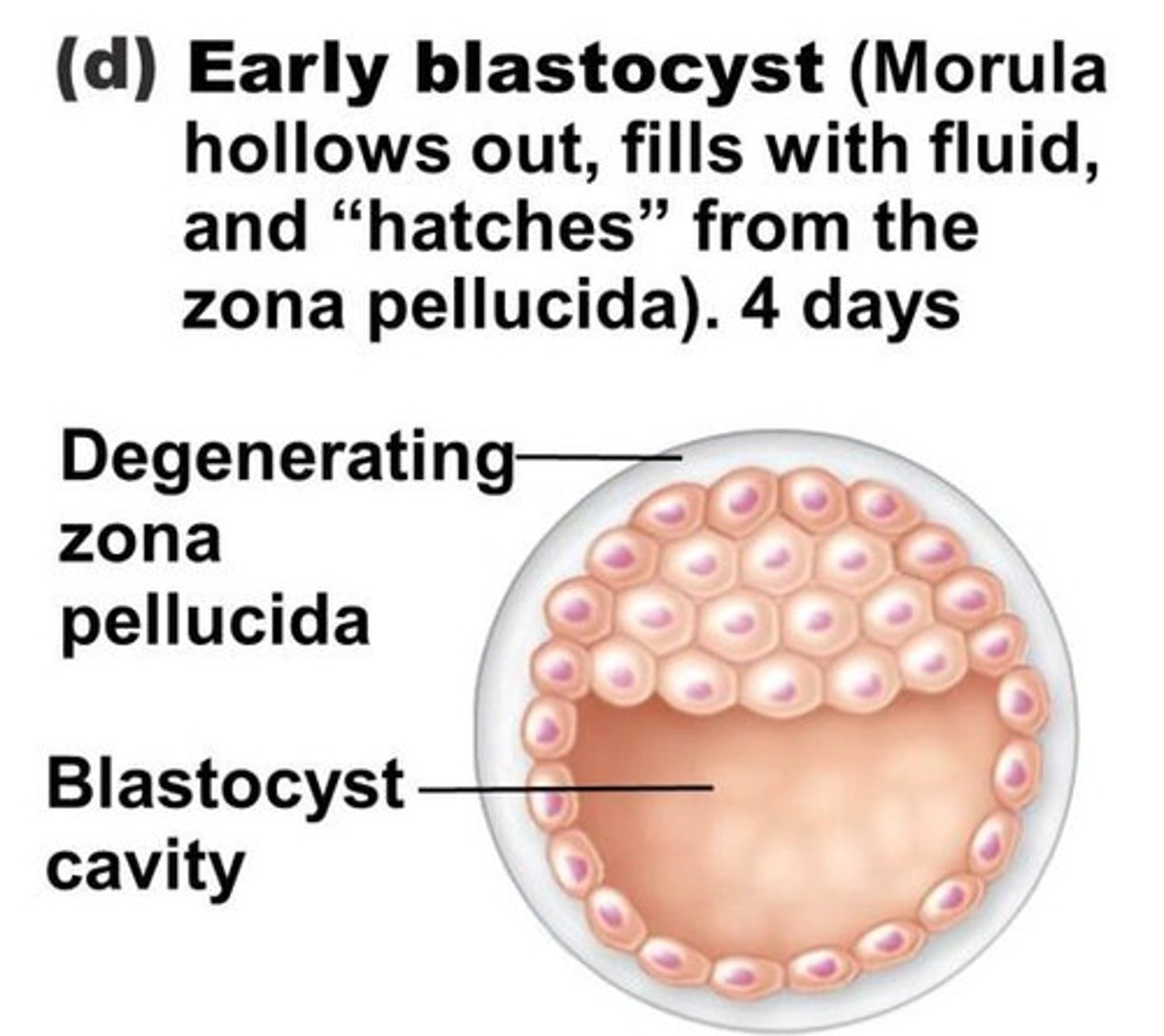
Hollowed out morula
blastocyst
Fluid filled cavity
blastocyst cavity
Inner Cell Mass (ICM)
inner cell group of 20-30 cells; precursor to a bilayered embryonic disc
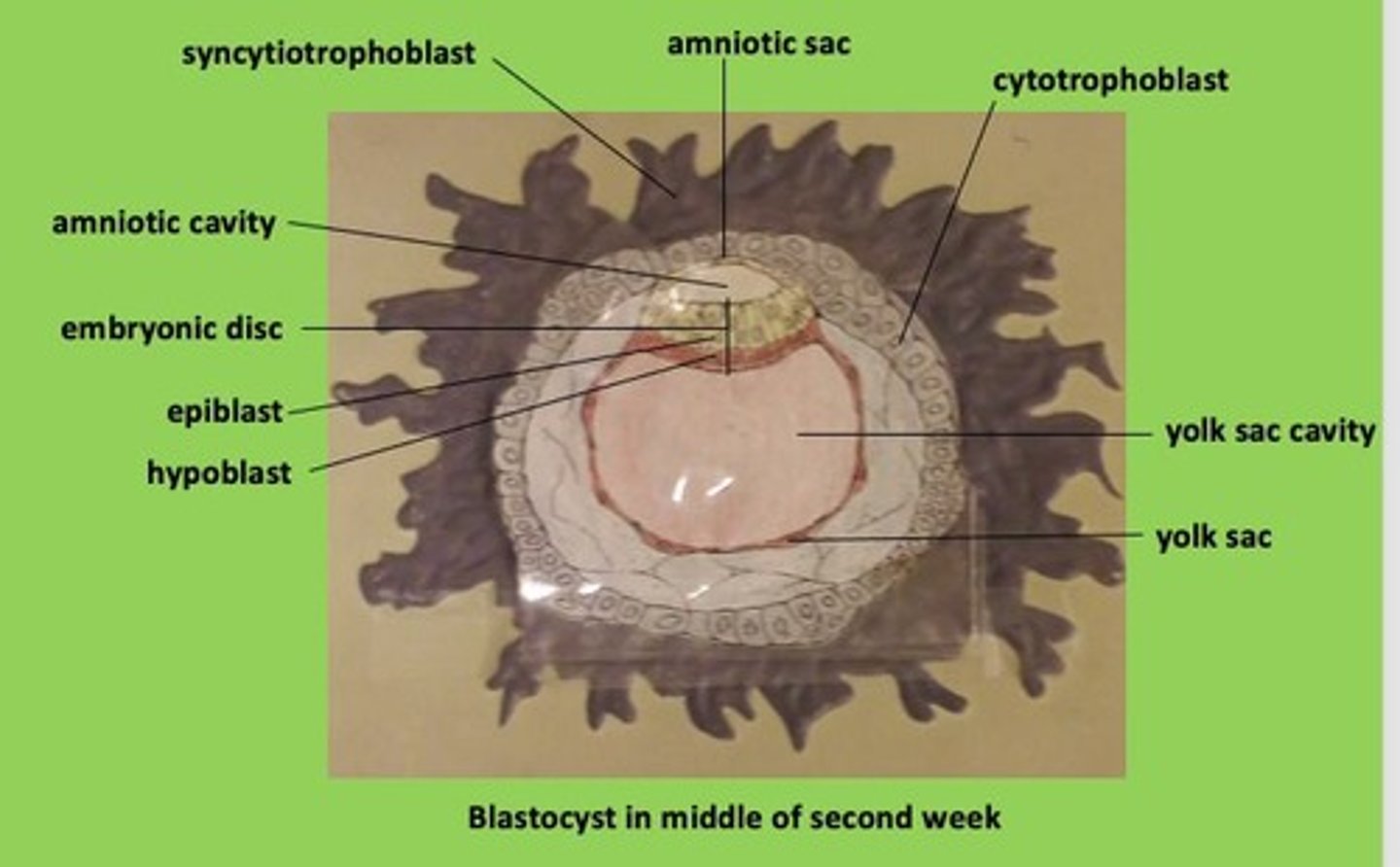
Epiblast
upper cells, gives rise to embryo proper & amnion
Hypoblast
lower cells, gives rise to yolk sac
Trophoblast
outer single layer of cells; precursor to chorion, which forms fetal placenta; responsible for obtaining oxygen & nutrients from mother's blood supply once implanted in uterus
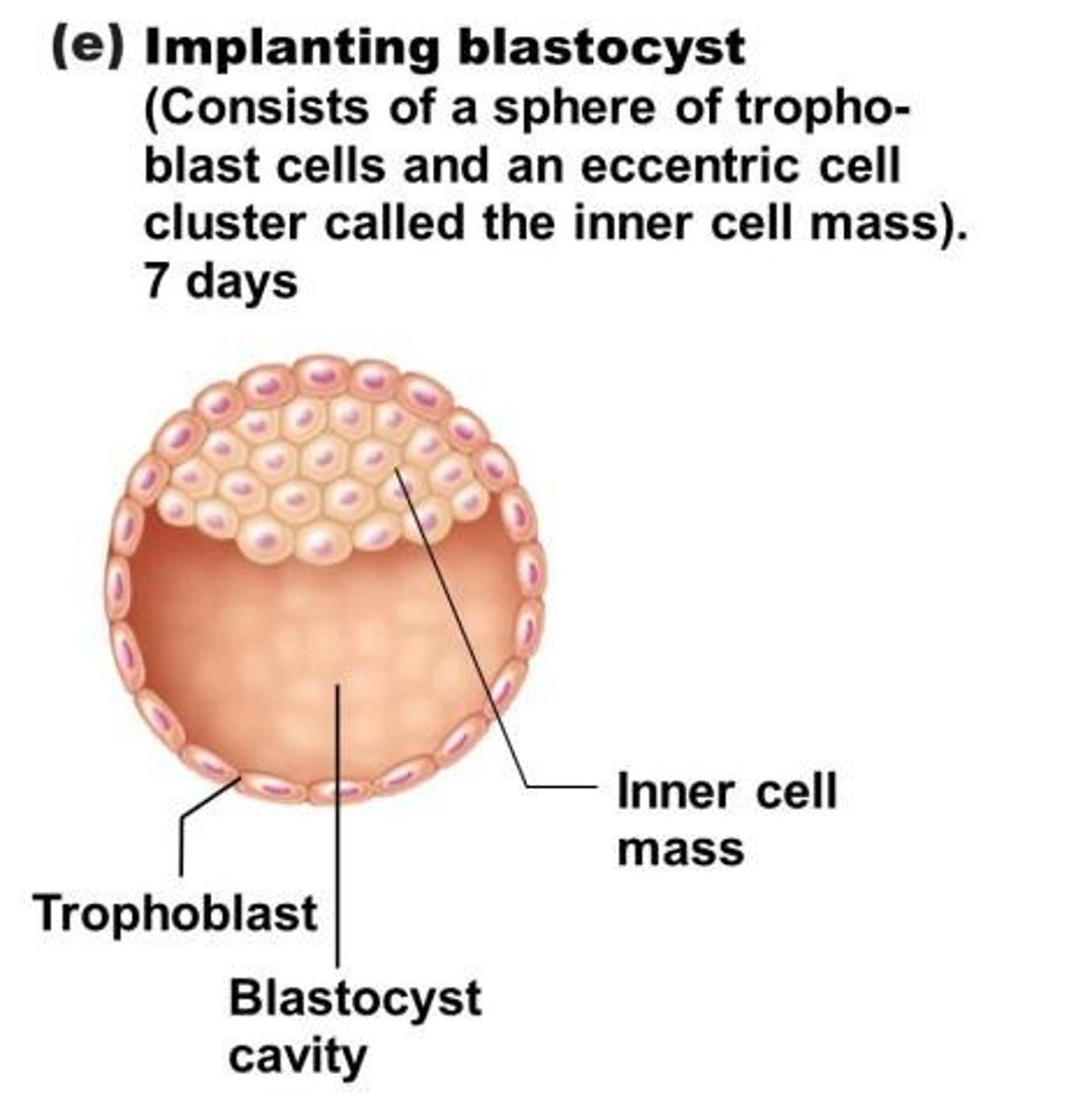
Implantation
occurs around day 7-9 in the endometrium; trophoblast cells adhere to inner surface of endometrium and secrete digestive enzymes to destroy endometrial cells
Amniotic cavity
begins to form in epiblast
Extraembryonic membranes
4 membranes that serve the developing embryo: Amnion, Chorion, Placenta, Yolk sac, Allantois
Amnion
sac around embryo filled with amniotic fluid in amniotic cavity; protects embryo
Chorion
helps to form fetal part of placenta
Placenta
temporary organ composed of both maternal and fetal tissues; provides nutrients and oxygen to embryo/fetus while removing its wastes
Yolk sac
lost original function in humans (placenta has taken over), but is still source of earliest blood cells
Allantois
base for umbilical cord that links embryo to placenta
Gastrula
developed from epiblast, has three germ layers, which are precursors to various organ systems
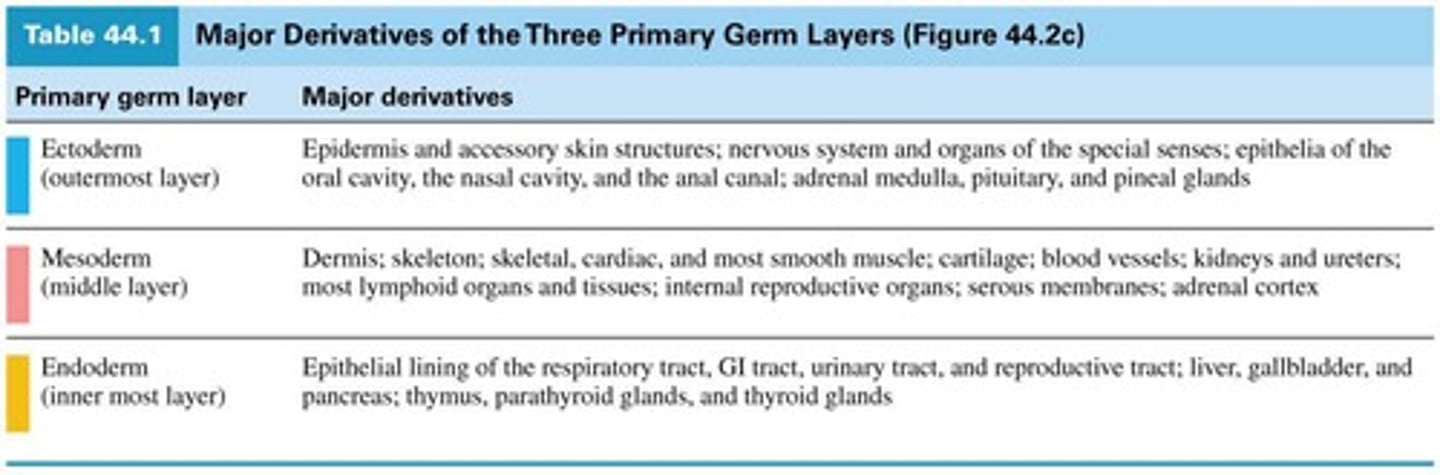
Ectoderm
outermost layer; gives rise to epidermis, CNS, various endocrine glands
Mesoderm
middle layer; gives rise to dermis, bones, smooth muscle, blood vessels, kidneys, ureters, reproductive organs
Endoderm
innermost layer; gives rise to lining of various tracts, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, various accessory glands
Facial expression
Some features of facial bones, facial n. 3rd arch: glossopharyngeal nerve
Heart
Find left atrium and left ventricle; heart is simple and functioning at this point
Liver
Just below and dorsal to heart
Somites
Series arranged along dorsal margin of the embryo; give rise to vertebrae and associated muscles
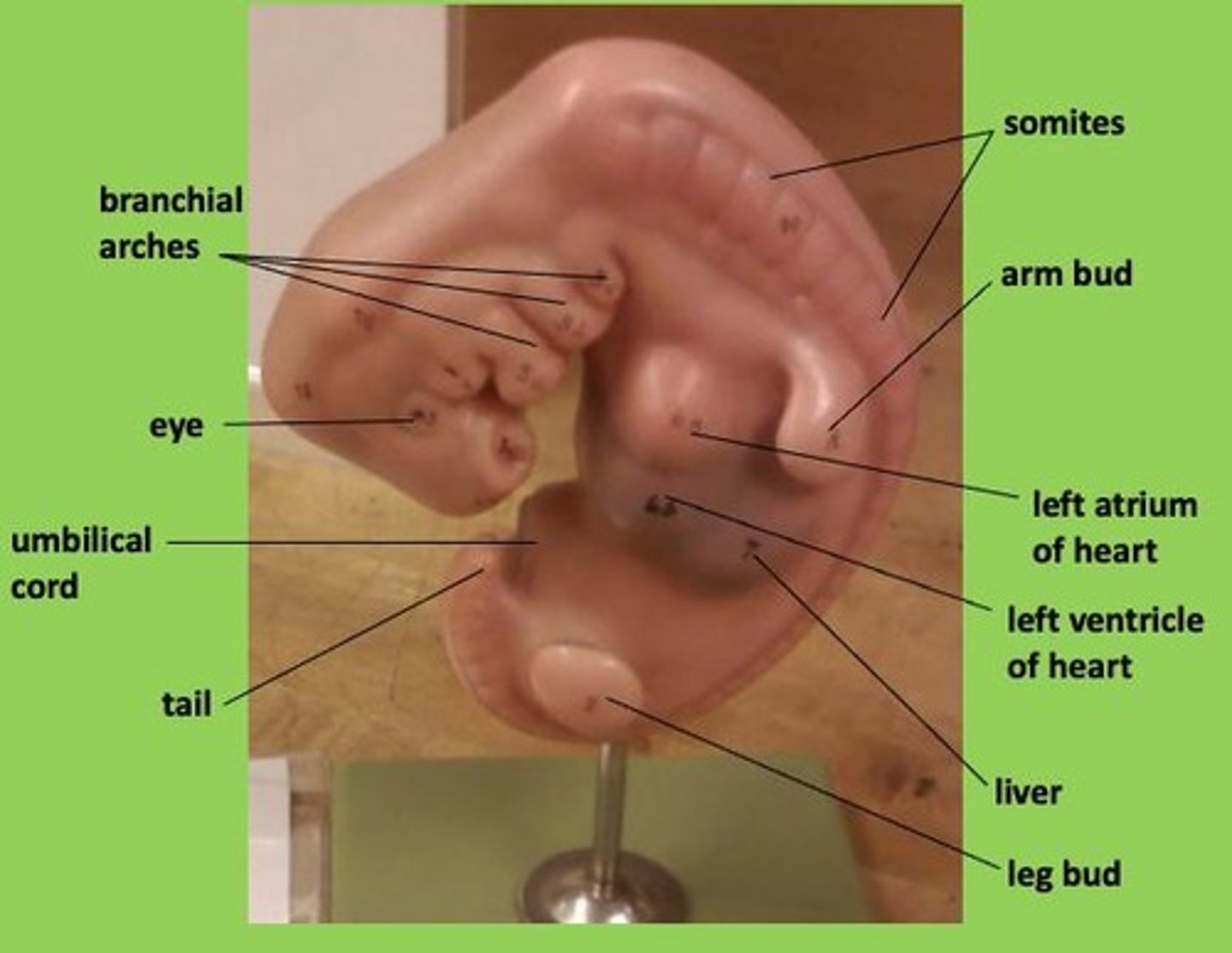
Arm bud
Seen just above liver; will develop into arm and hand
Leg bud
Found near tail; will develop into leg and foot
Tail
All mammalian embryos have a tail at this stage, whether or not the adult has a tail
2 month embryo
Look for: Ear shape, Eye shape, Presence of limbs (arms/legs)
Fetal Development
3 months/12 weeks; during 3rd month, fetus grows rapidly and its organs enlarge and mature; kidneys begin producing urine, reproductive organs are developed enough to structurally determine sex of fetus
3-month fetus model
Look for: Eyes, ears, nose and mouth, Well developed arms/fingers, legs/toes, Amniotic sac (transparent bubble) filled with amniotic fluid that surrounds fetus, Umbilical cord between fetus and placenta
Fetal Development: Full Term
9 or 10 months / 40 weeks; further fetal development involves growth, refinement, and maturation of body organs
Sensory systems
Mature and fetus becomes aware of its surroundings (hear sounds, faintly see light, taste amniotic fluid)
Fetus movement
Fetus moves around more and more strenuously
Fetus fat reserves
Fetus accumulates fat reserves and looks much chubbier than 3-month fetus
Fetus position
Fetus assumes head-down position for childbirth
Lab Activity 1
Case Studies (2 extra credit pts); you will receive a clinician/patient scenario where you are the clinician
Lab Activity 1 details
Pt background, symptoms, clinician notes, physical exam results, other relevant information; case studies are based on organ systems we covered in this class; answer all questions to the best of your ability
Lab Activity 2
Structure Identification of Models
Models in Lab Activity 2
Full term fetus, 1 month embryo, 2.5 week embryo