physics wave
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
mechanical wave
mechanical wave is a vibration in matter that transfers energy through a materia
transverse wave
Medium is displaced perpendicular to the direction of the wave

longitudinal wave
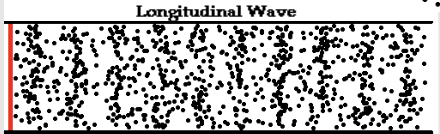
electromagnetic wave
a form of radiation that travel though the universe.
frequency
the number of waves that pass a given point in one secon
interference
the net effect of the combination of two or more wave trains moving on intersecting or coincident paths.
What do waves transfer?
energy from one place to another without transferring matter
What determines the speed of a wave?
wavelength, medium, and temperature
Characteristics of sound waves
longitudinal wave
sound waves travel on a medium
fastest through solid
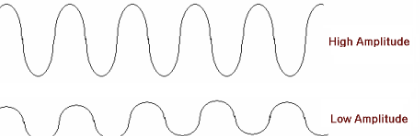
What does amplitude tell us?
Displacement from the line of equilibrium to the height of a crest or trough
Law of Reflection
The angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection
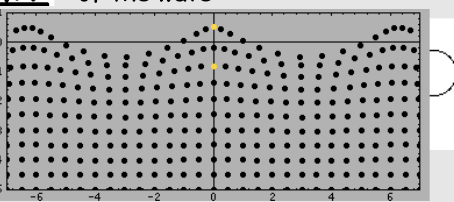
Standing waves
Standing wave patterns are also characterized by antinodal positions - positions along the medium that undergo maximum displacement from a high upward displacement to a high downward displacement.
Waves standing wave pattern is a pattern which results from the interference of two or more waves along the same medium. All standing wave patterns are characterized by positions along the medium which are standing stil
Node and antinode
describes the position of a point on a standing wave
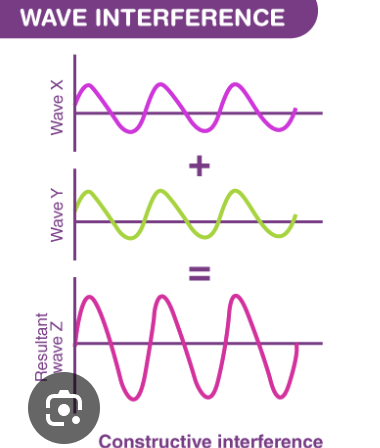
Constructive Interference
happens when two waves overlap in such a way that they combine to create a larger wave
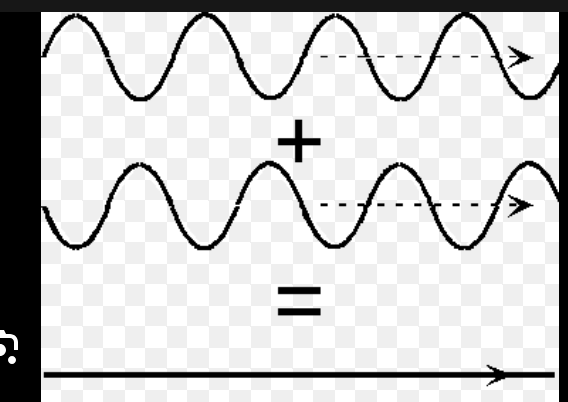
Total/complete destructive
When the amplitude of the crest and trough are equal in magnitude (size) when the waves interact they will cancel each other out completely.
incomplete destructive
When the crest or trough is greater in magnitude (size) when the waves interact they will only partially cancel each other out and a smaller wave will remain until the wave pass one another.
surface waves
Medium is displaced both perpendicular and parallel to the direction of the wave
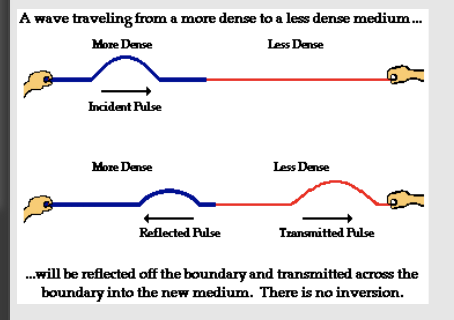
If a wave travels from a more dense medium to a less dense medium
the reflected wave will be erect (upright). The transmitted pulse is also erect.
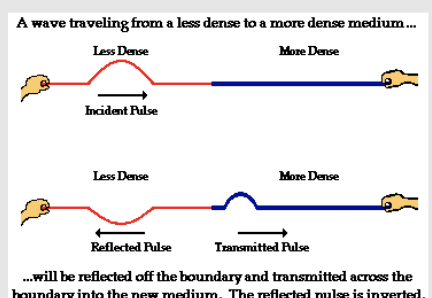
If a wave travels from a less dense medium to a more dense medium,
the reflected wave will be inverted. The transmitted pulse stays erect.
wave speed is always greatest
in the least dense medium
he wavelength is always greatest in
the least dense medium
The frequency of a wave is not altered
by crossing a boundary.
The reflected pulse becomes inverted when
a wave in a less dense medium is heading towards a boundary with a more dense medium.
The amplitude of the incident pulse is always greatest
than the amplitude of the reflected pulse.
reflection
Waves may “bounce off” barriers

Wave length and wave velocity may ____ frequency _____ (refrecation)
change
remains constant
Diffraction
Diffraction is the bending of waves around a barrier
Principle of superposition
The displacement of a medium caused by two or more waves is the algebraic sum of the displacements caused by the individual waves.
The result of superposition is interference
Period T
is the time to move a distance of one wavelength.
Frequency
s -1 or hertz (Hz)
Loudness
depends on the amplitude of sound wave
amplitude indicates
energy of wave
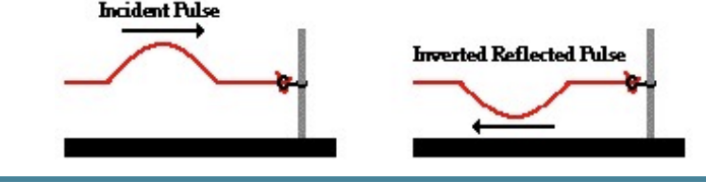
fixed end reflection
it comes back upside down.
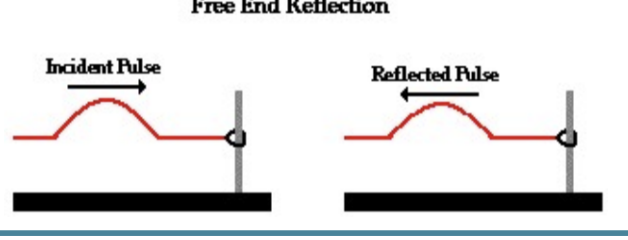
free end reflection
the wave moving toward the boundary will be reflected in the same orientation as the incoming wave and with the same amplitude as the incoming wave
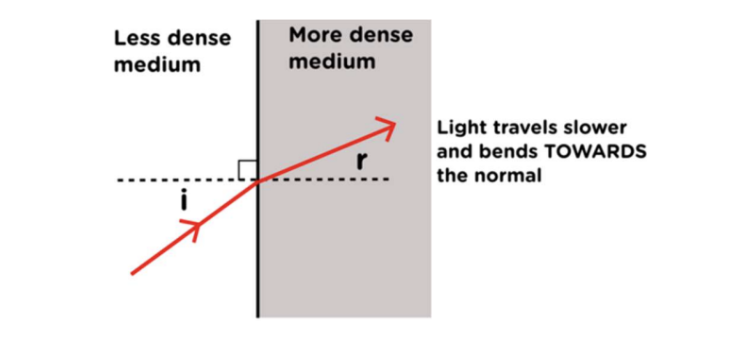
refraction in less to more dense medium
light travels slower and bend towards the normal
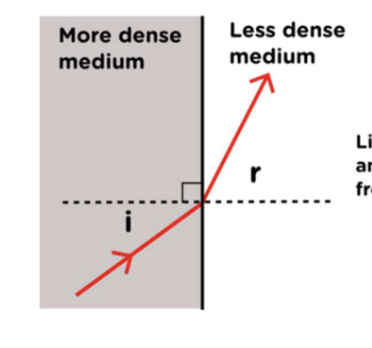
refraction in more to less dense medium
light travels faster and bends away from the normal
wave pulse
a sudden disturbance in which only one wave or a few waves are generated
period
The time it takes for two successive crests (one wavelength) to pass a specified point
diffraction
the spreading of waves as they pass through or around an obstacle.
reflecion (angle/normal)
The angle of incidence is the same as the angle of reflection. A normal is an imaginary line that is 90∘ to the surface.
loudness
amplitude
pitch
frequency
medium = ?
wavespeed
waves transfer energy by ___ and ___ on neighboring particles
pushing, pulling
a mechanial wave is produced by objects that are
vibrating
Hertz is measure of frequency ___
Hz