W12- using qualitative research in evidence-based/informed practice
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
evidence infromed practie
•Is the conscientious and judicious use of current best evidence in conjunction with clinical expertise and patient values to guide health care decision
evidence infromed practice process stepsinformed
•Selection of a topic
•Problem-focused triggers
•Knowledge-focused triggers
•Form a team
•Formulate EIP question
•Qualitative evidence retrieval
•Evidence rating and critique
•Synthesis of findings
translational science
•The investigation of methods, interventions, and variables that influence adoption of evidence informed practices by individuals and organizations to improve clinical practice
•Includes testing effect of interventions in promoting and sustaining adoption of evidence informed practices
knowledge translation
•A process where knowledge moves from where it was first created and refined to where it has to get in order to make an impact on clinical practice and patient care.” (p. 294)
•Kitson, A.L., & Harvey, H. (2016). Journal of Nursing Scholarship, 48(3), 294-302.
•Terminology used:
•Knowledge transfer
•Knowledge translation
•Implementation science
•Knowledge to action
•
what is dissemination and how
•Communication of research findings
•Modes of dissemination
ØPublications
ØConferences
ØConsultations
ØTraining programs
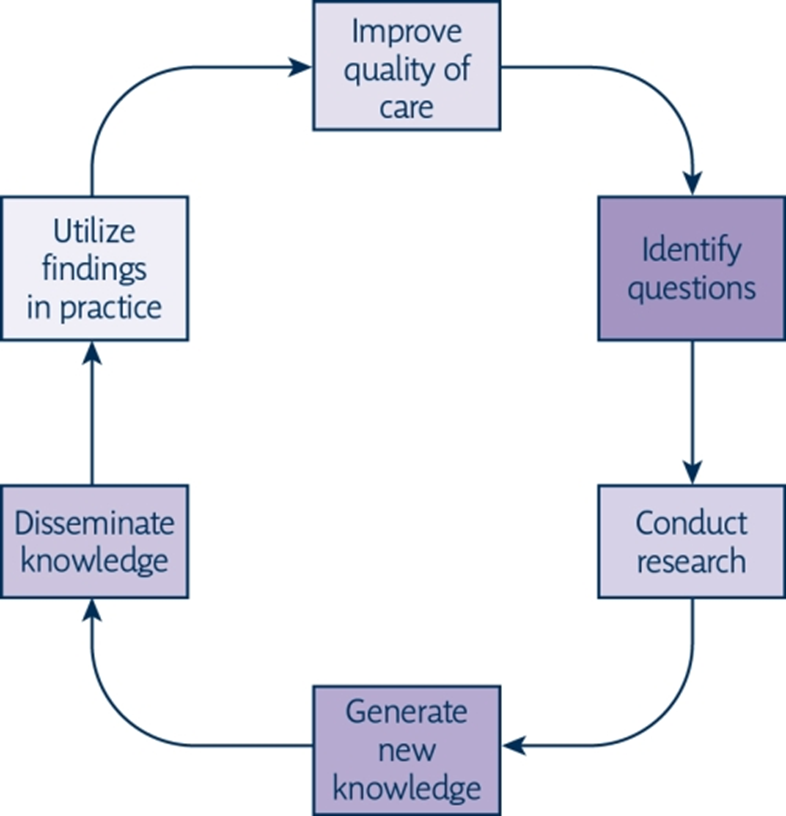
model fo the relationship among conduct dissemination and use of research
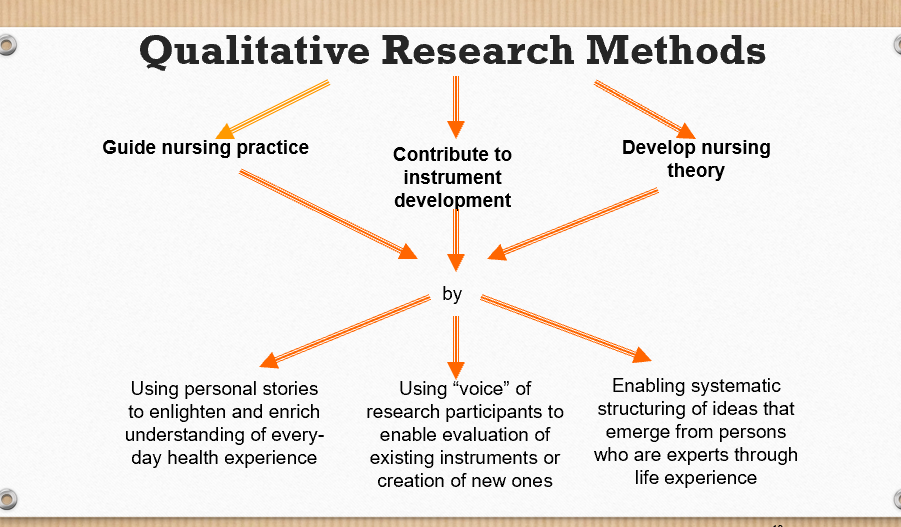
qualitative research methods diagram
metasynthesis
•Systematic review of qualitative research studies
•Uses comparative analysis and interpretative synthesis of qualitative findings
•Retains essence and unique contribution of each qualitative study included in the review
•Builds critical mass of qualitative research evidence that can inform clinical practice
use/purpose of meta synthesis
• To inform policy, practice, and education
•Making decisions
•Generate powerful understandings (meaning)
•Broader, more encompassing theories (explanations)
•Belief that it will yield more complete picture
•To inform change or intervention (testing)
•Creating testable hypotheses to inform/challenge practice
•Contributes to instrument development
•Greater transferability of qualitative findings
•Reduce waste of research investment and high reading burden
key considerations
•Understand qualitative methodologies and nuances of the various qualitative methods
•Read and critically appraise research
•Clear understanding of methods of of evaluating qualitative research e.g CASP
•Constitution of research team e.g, having different qualitative expertise
forms of meta synthesis
meta entho
theamtic synthesis - evolvin not too many used
over view slide of the generic apporach to meta synthesis
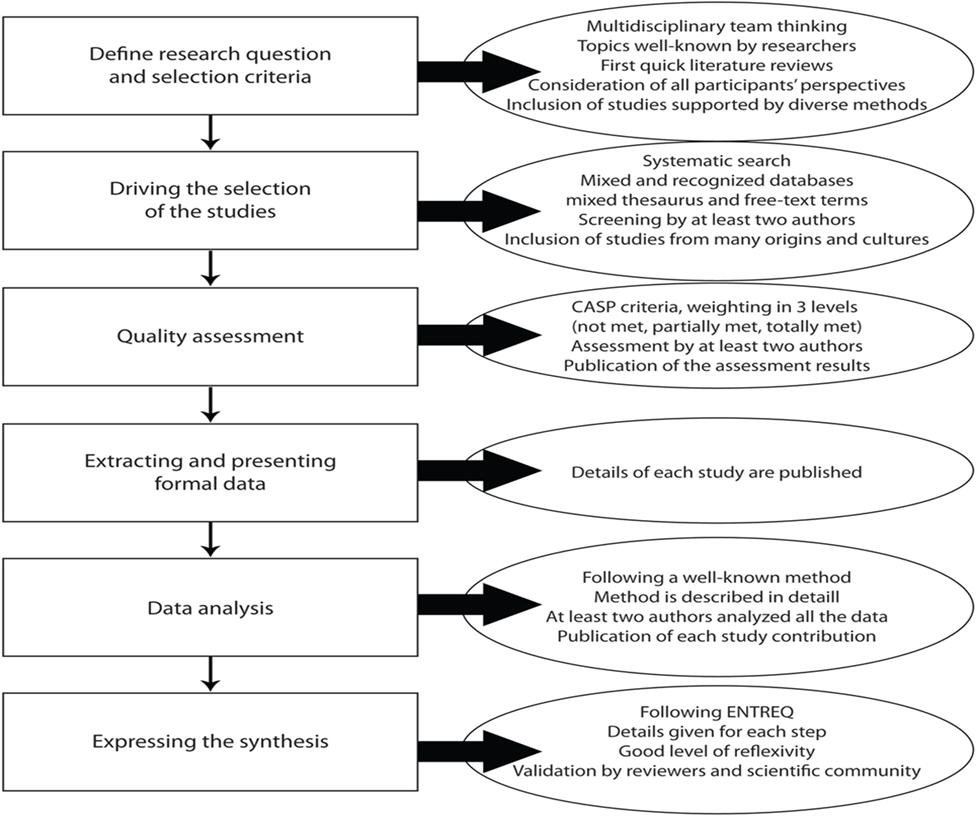
assessing quality of quali reserach
•Using CASP criteria or other criteria to assess the quality of the selected studies
•Determine quality and assign 3 level criteria
•(met, partially, and not met)
•Two authors or more authors required to approve quality of the selected studie
extracting data from selected studeis
non traditional methods to disseminating qualitative research findings
Arts-based knowledge translation methods
Examples: photography, theatre, poetry, dance, video