bio318L exam 2: lab#8
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 6:00 PM on 5/3/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
1
New cards
What is *Staphylococcus*?
* gram positive cocci (in clumps like grapes)
* all members are highly resistant to **drying, extremes in pH,** and **high temperatures**
* increase in **community acquired** cases, with infections associated with schools, prisons, and shared athletic equipment
* all members are highly resistant to **drying, extremes in pH,** and **high temperatures**
* increase in **community acquired** cases, with infections associated with schools, prisons, and shared athletic equipment
2
New cards
*S. epidermis*
common cause of hospital-acquired infections in immunocompromised patients
3
New cards
*S. saprophyticus*
an occasional cause of UTIs
4
New cards
*S. aureus*
common cause of hospital-acquired skin infections
* normal flora of humans: nasal membranes & skin
* opportunistic infections
* normal flora of humans: nasal membranes & skin
* opportunistic infections
5
New cards
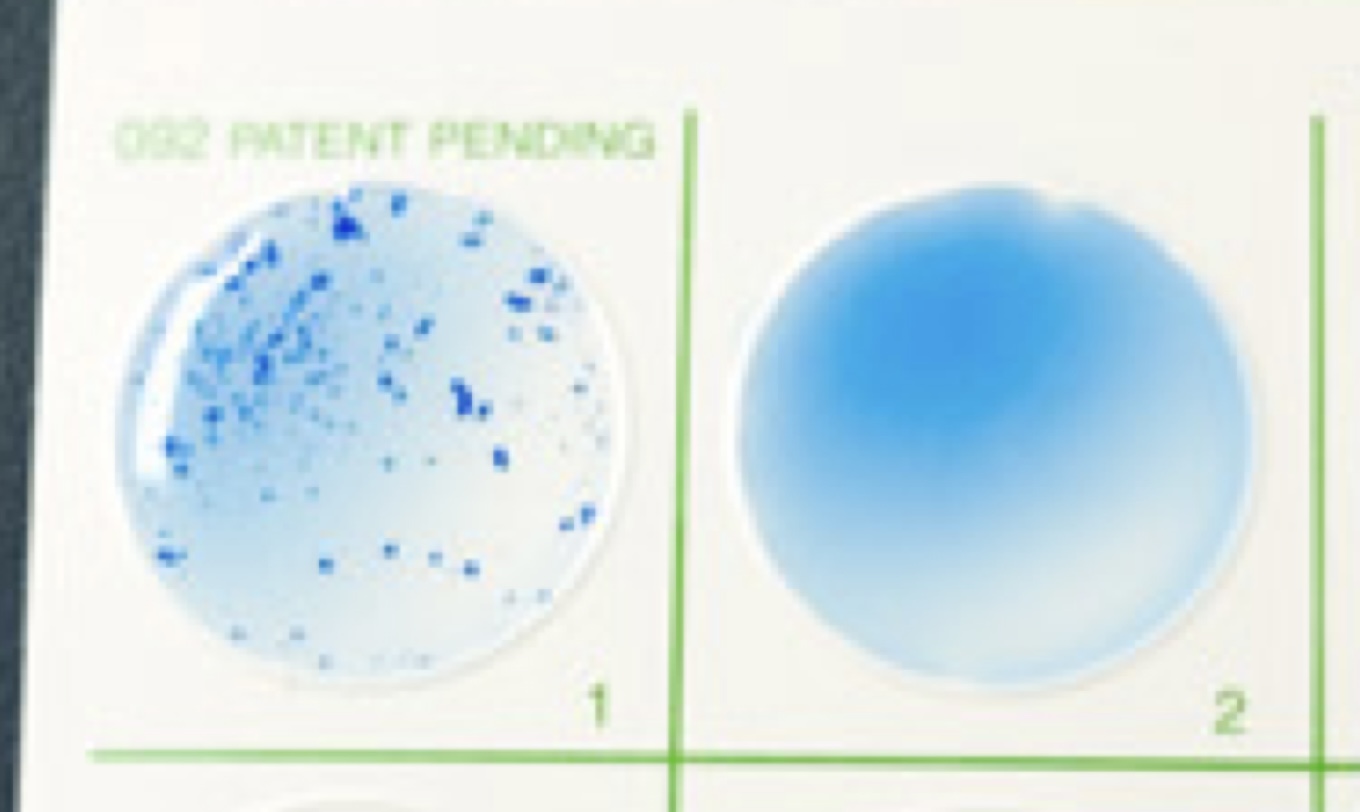
Latex Agglutination Test
rapid identification for *S. aureus*
* **Protein A** is a virulence factor found on the cell wall of only *S. aureus*
* antibodies in the test solution bind antigens on Protein A, resulting in a positive result of **clumping**
* **Protein A** is a virulence factor found on the cell wall of only *S. aureus*
* antibodies in the test solution bind antigens on Protein A, resulting in a positive result of **clumping**
6
New cards
Latex Agglutination Test Results
positive = *S. aureus*
* clumping occurs because the antibodies in the test solution bind with the antigens found on Protein A which is located on the cell wall of only *S. aureus*
negative = not *S. aureus*
* no clumping occurs due to the absence of Protein A
* clumping occurs because the antibodies in the test solution bind with the antigens found on Protein A which is located on the cell wall of only *S. aureus*
negative = not *S. aureus*
* no clumping occurs due to the absence of Protein A
7
New cards
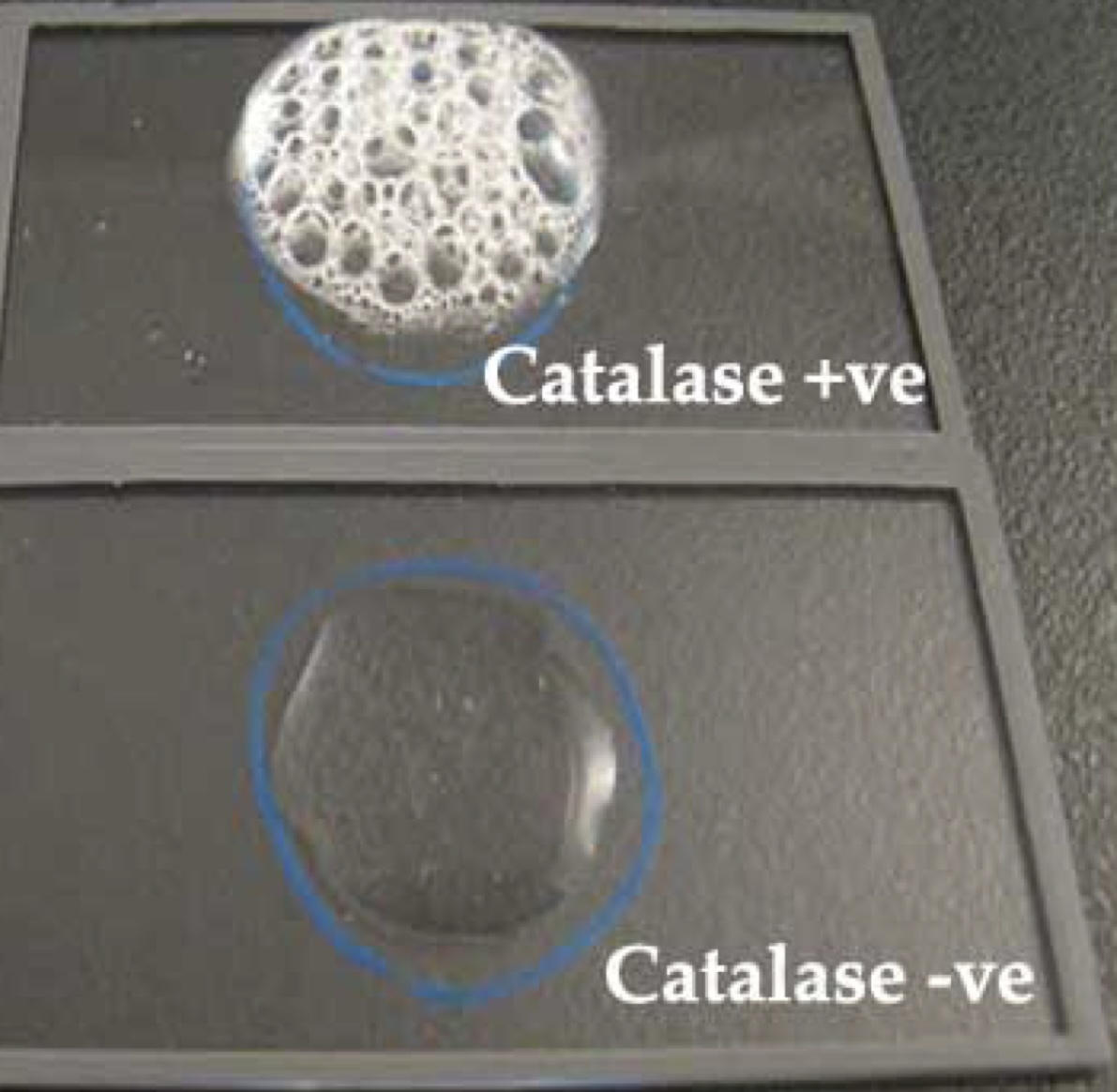
Catalase Test
key test in differentiating Gram (+) cocci
* substrate is **hydrogen peroxide**
* distinguishes Staph from Strep
* substrate is **hydrogen peroxide**
* distinguishes Staph from Strep
8
New cards
Catalase Test Results
positive = Staph
* bubbling will occur due to the presence of catalase
* the catalase reacts with the hydrogen peroxide, resulting in oxygen to be released as seen by the bubbling
negative = Strep
* no bubbling occurs due to the absence of catalase and thus no release of oxygen
* bubbling will occur due to the presence of catalase
* the catalase reacts with the hydrogen peroxide, resulting in oxygen to be released as seen by the bubbling
negative = Strep
* no bubbling occurs due to the absence of catalase and thus no release of oxygen
9
New cards
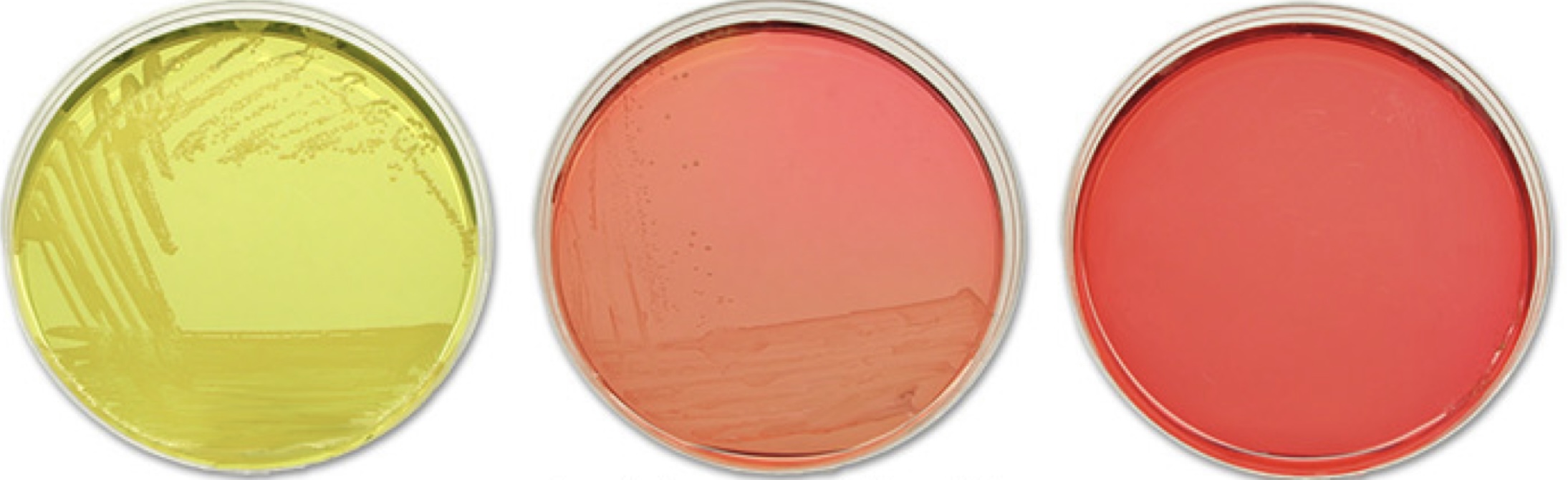
Mannitol Salt Agar
Selective & differential media for *Staphylococcus*
* contains **7.5% salt** to inhibit the growth of most bacteria
* contains **phenol-red dye** to detect **mannitol fermentation**
* highly selective for *S. aureus* and some strains of *S. saprophyticus*
* contains **7.5% salt** to inhibit the growth of most bacteria
* contains **phenol-red dye** to detect **mannitol fermentation**
* highly selective for *S. aureus* and some strains of *S. saprophyticus*

10
New cards
Mannitol Salt Agar Test Results
positive = *S. aureus* or *S. saprophyticus*
* a color change from red to **yellow** indicates the fermentation of mannitol, which *S. aureus* and some strains of *S. saprophyticus* are able to do
negative = *S. epidermis*
* no color change indicates the inability to ferment mannitol
* a color change from red to **yellow** indicates the fermentation of mannitol, which *S. aureus* and some strains of *S. saprophyticus* are able to do
negative = *S. epidermis*
* no color change indicates the inability to ferment mannitol
11
New cards
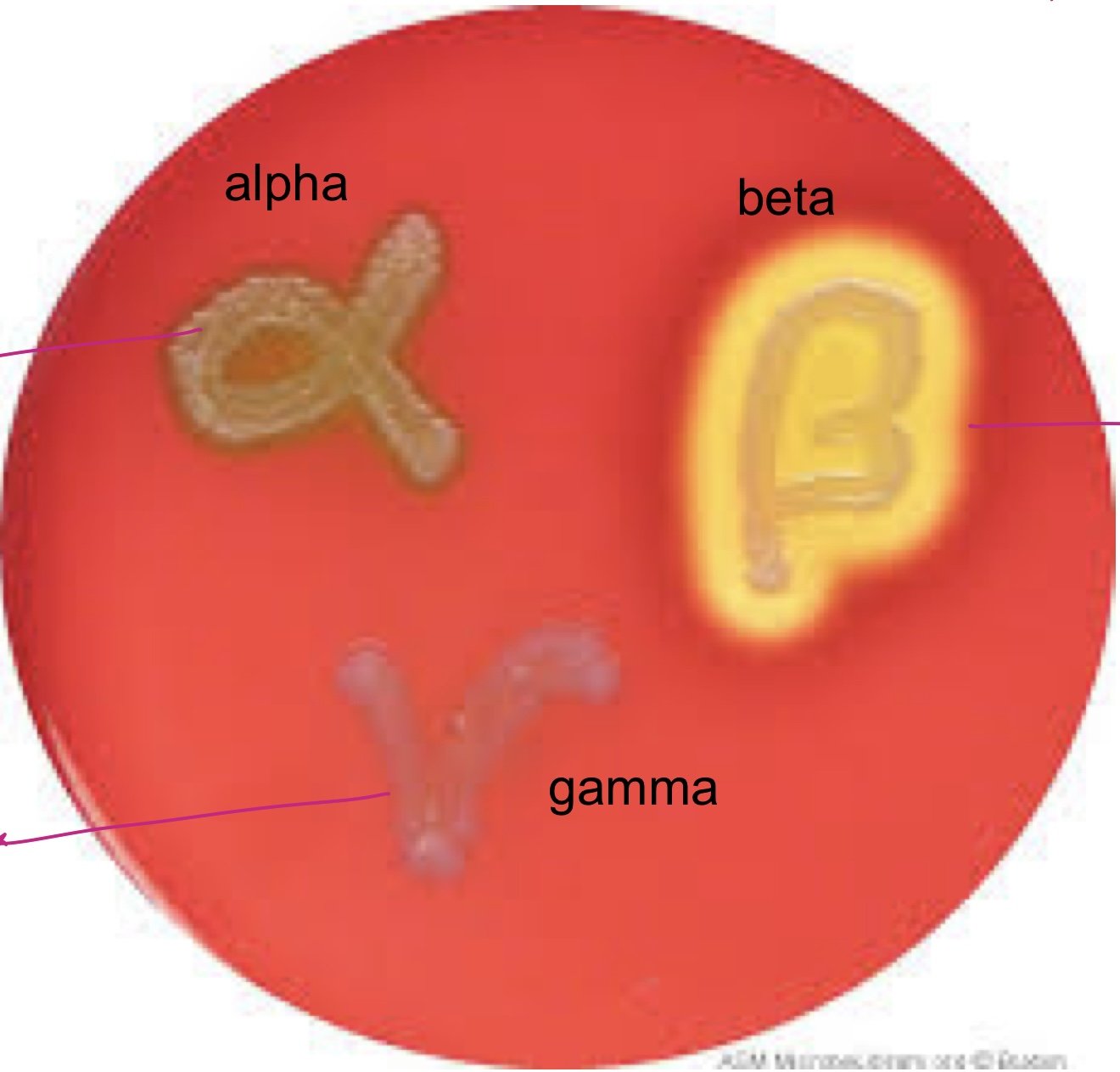
Blood Agar Plates
Tests for hemolysis ability
* contains Tripticase Soy Agar (TSA) and **5% sheeps blood**
* beta, alpha, and gamma
* contains Tripticase Soy Agar (TSA) and **5% sheeps blood**
* beta, alpha, and gamma
12
New cards
Blood Agar Plates Results
**beta** = *S. aureus*
* indicates **complete** breakdown of red blood cells
* if the plate is held up to a light, you **will** be able to see through it
**partial** = none
* indicates **partial** breakdown of red blood cells
* seen by a green tint around the growth
**gamma** = *S. saprophyticus* & *S. epidermis*
* indicates **no breakdown** of red blood cells
* if the plate is held up to a light, you will **not** be able to see through it
* indicates **complete** breakdown of red blood cells
* if the plate is held up to a light, you **will** be able to see through it
**partial** = none
* indicates **partial** breakdown of red blood cells
* seen by a green tint around the growth
**gamma** = *S. saprophyticus* & *S. epidermis*
* indicates **no breakdown** of red blood cells
* if the plate is held up to a light, you will **not** be able to see through it
13
New cards
Novobiocin Susceptibility
Distinguishes coagulase-negative Staph species
* does not apply to *S. aureus*
* does not apply to *S. aureus*
14
New cards
Novobiocin Susceptibility Test Results
positive for coag-negative = *S. epidermis*
* seen by a zone of inhibition
negative for coag-negative = *S. saprophyticus*
* seen by no zone of inhibition
* seen by a zone of inhibition
negative for coag-negative = *S. saprophyticus*
* seen by no zone of inhibition
15
New cards
What is *Streptococcus*?
* gram positive cocci (in a chain-like pattern)
* highly environmentally sensitive
* normal human **commensal**
* mouth, skin, intestine, and upper respiratory tract
* highly environmentally sensitive
* normal human **commensal**
* mouth, skin, intestine, and upper respiratory tract
16
New cards
*Strep. mutans*
most common cause of dental plaque
17
New cards
*Strep. pneumoniae*
most common cause of bacterial pneumonia
18
New cards
*Strep. pyogenes*
common cause of throat infections; “Strep throat”
* responsible for **pharyngitis** and systemic infection like scarlet fever
* able to completely lyse RBC
* responsible for **pharyngitis** and systemic infection like scarlet fever
* able to completely lyse RBC
19
New cards
4 *Streptococcus* strains identified in lab
* *S. pyogenes*
* *S. agalactiae*
* *S. equi*
* *E. faecalis*
* *S. agalactiae*
* *S. equi*
* *E. faecalis*
20
New cards
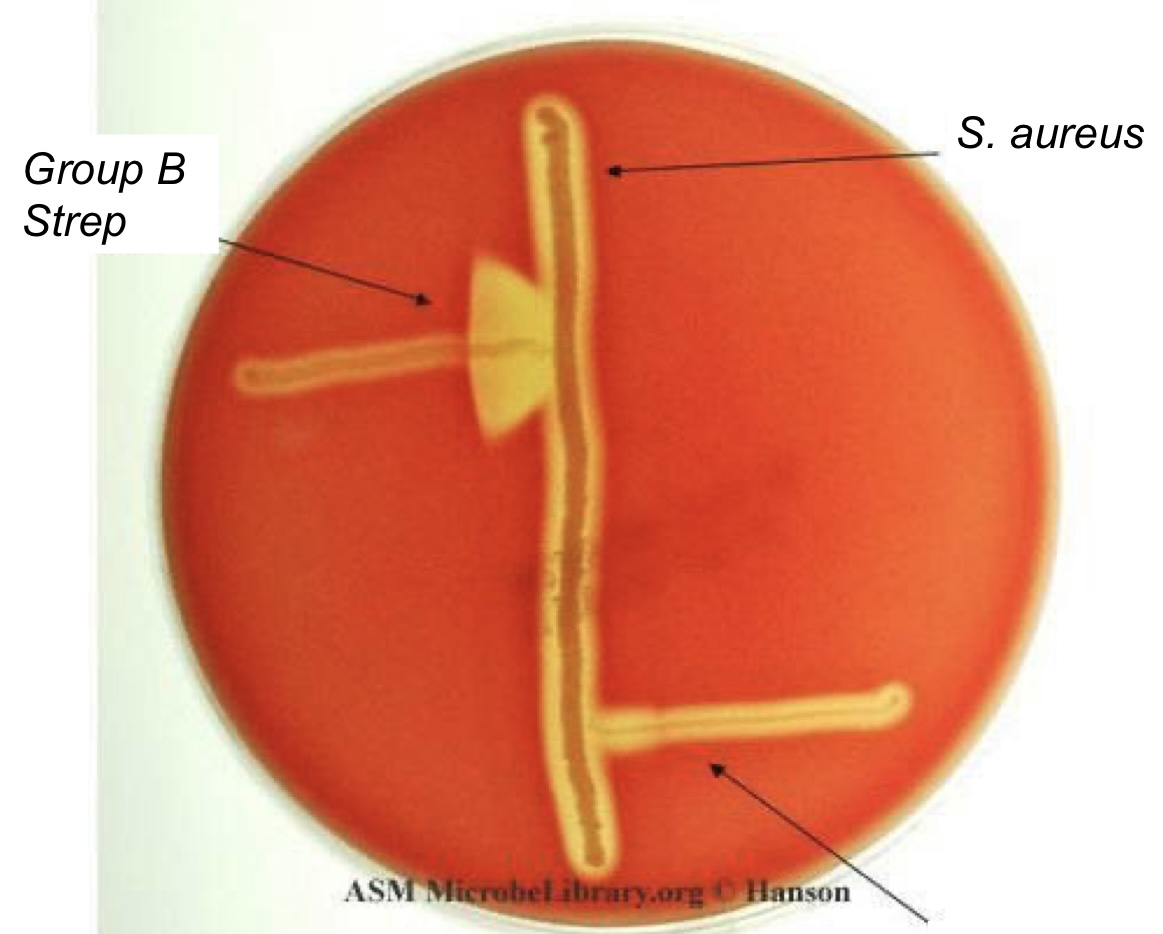
CAMP Test
Identification for **Group B** or ***S. agalactiae***
21
New cards
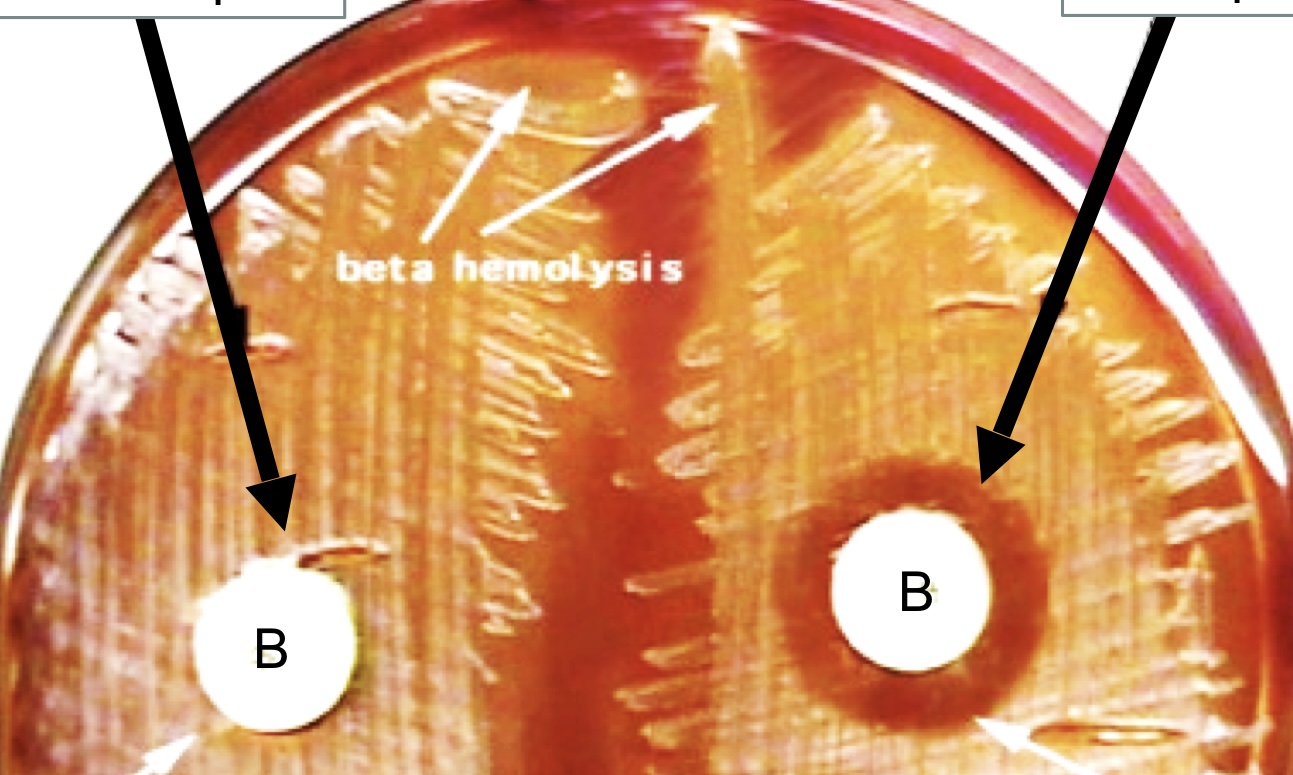
Bacitracin Susceptibility Test
Identification for **Group A** or ***S. pyogenes***
22
New cards
Bacitracin Susceptibility Test Results
positive = *S. pyogenes* or Group A
* seen by a zone of inhibition around the disk
negative = not *S. pyogenes* or Group A
* seen by no zone of inhibition around the disk
* seen by a zone of inhibition around the disk
negative = not *S. pyogenes* or Group A
* seen by no zone of inhibition around the disk
23
New cards
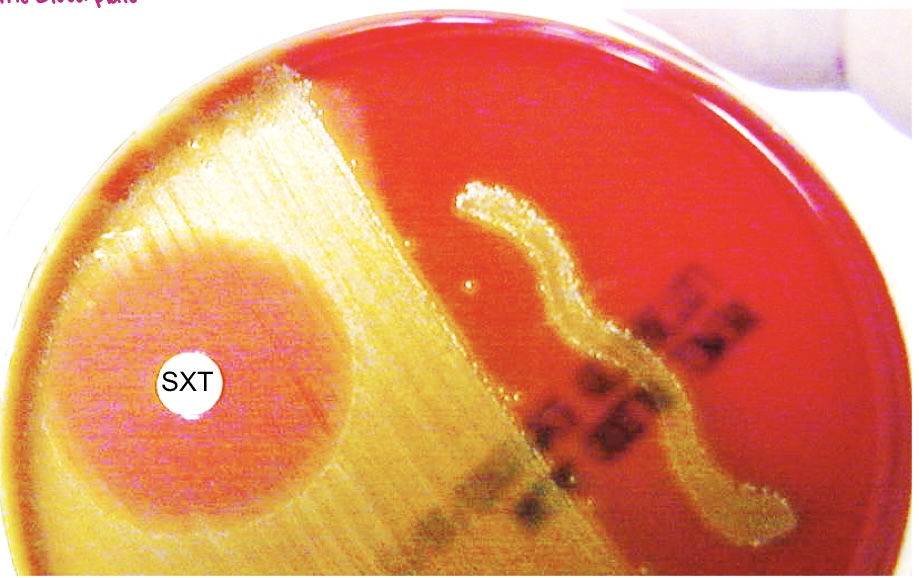
SXT Sensitivity Test
Identification for **Group C** or **S. equi**
* enzyme inhibitor (blocks folic acid synthesis)
* enzyme inhibitor (blocks folic acid synthesis)
24
New cards
SXT Sensitivity Test Result
positive = *S. equi* or Group C
* seen by a zone of inhibition around the disk
negative = not *S. equi* or Group C
* seen by no zone of inhibition around the disk
* seen by a zone of inhibition around the disk
negative = not *S. equi* or Group C
* seen by no zone of inhibition around the disk
25
New cards
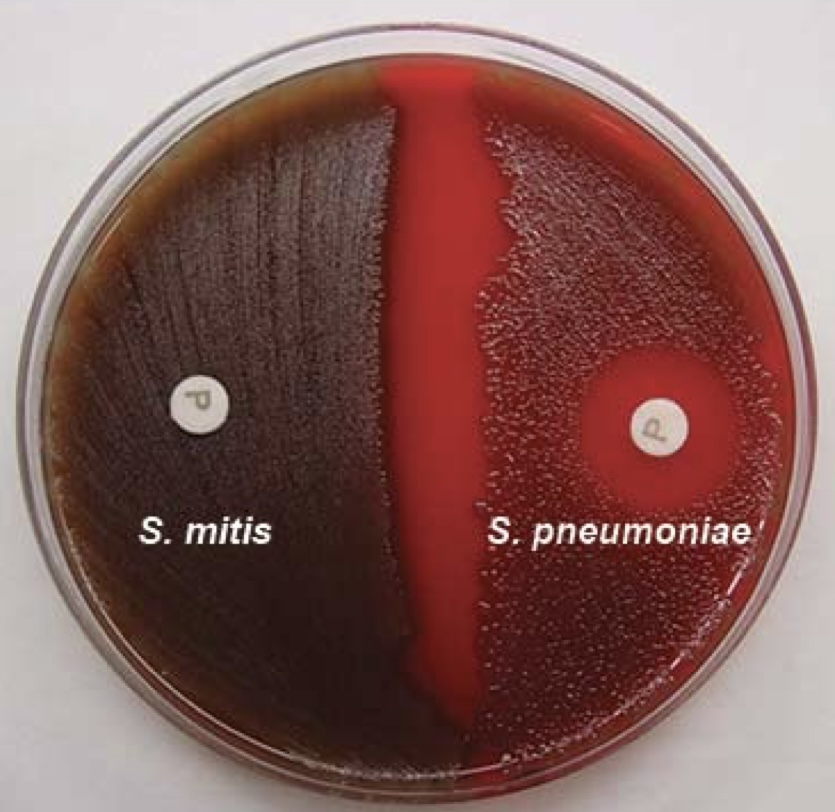
Optochin Sensitivity Test
Identification for *S. pneumoniae*
* was not performed in lab
* a zone of inhibition indicates a positive result for *S. pneumoniae*
* was not performed in lab
* a zone of inhibition indicates a positive result for *S. pneumoniae*
26
New cards
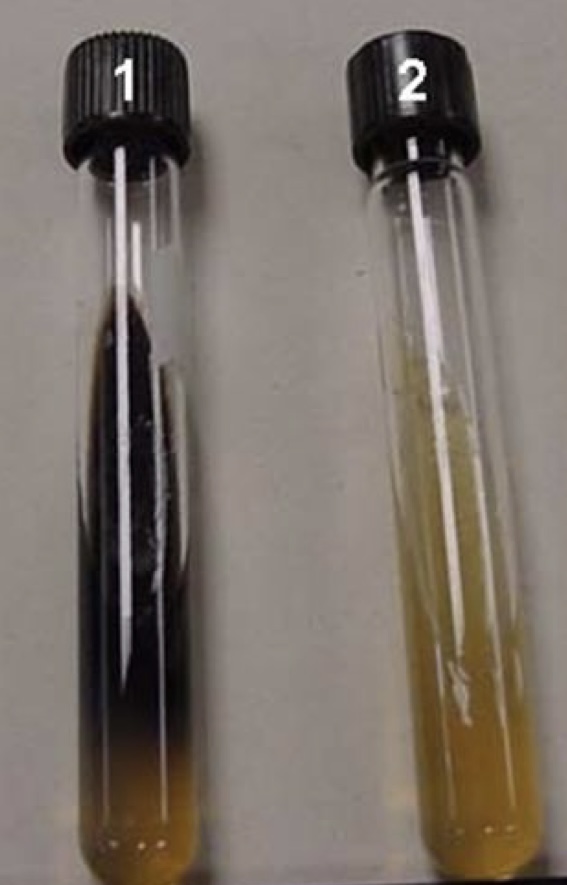
Bile Esculin Media
Identification for **Group D** or ***E. faecalis***
* bile salts inhibit non-Group D species
* esculin hydrolysis forms black precipitate
* bile salts inhibit non-Group D species
* esculin hydrolysis forms black precipitate

27
New cards
Bile Esculin Media Results
positive = *E. faecalis* or Group D
* seen by the formation of black precipitate
* bacteria is able to hydrolyze esculin
negative = not *E. faecalis* or Group D
* seen by no change in the test tube
* bacteria is unable to hydrolyze esculin
* seen by the formation of black precipitate
* bacteria is able to hydrolyze esculin
negative = not *E. faecalis* or Group D
* seen by no change in the test tube
* bacteria is unable to hydrolyze esculin