OB: Newborn Assessment & Nursing Care
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
What Respiratory transition does the newborn infant go through?
Go from a fluid filled environment to air filled
What is Surfactant?
a surface-active phospholipid critical for alveolar stability
What are some Reflex Breathing Triggers in the newborn?
Low blood oxygen levels
Increase blood carbon dioxide
Low blood pH
Temperature Changes
Drying
What is the normal respiratory rate of a newborn?
30-60/min
While apnea can be common in the newborn, how long is considered abnormal?
More than 20 seconds
What is the normal heart rate of the newborn?
110-160
What is the typical BP of a newborn?
50-75 mmHg systolic & 30-45 mmHg diastolic
What is the newborns typical temp range?
97.7-99.5
What is Thermogenesis?
physiological process of heat production in the body, crucial for maintaining body temperature and contributing to energy balance
How does the newborn produce heat?
Shivering
Non-shivering
brown fat
What is Brown fat?
a process in which brown adipose tissue (BAT) burns calories to generate heat
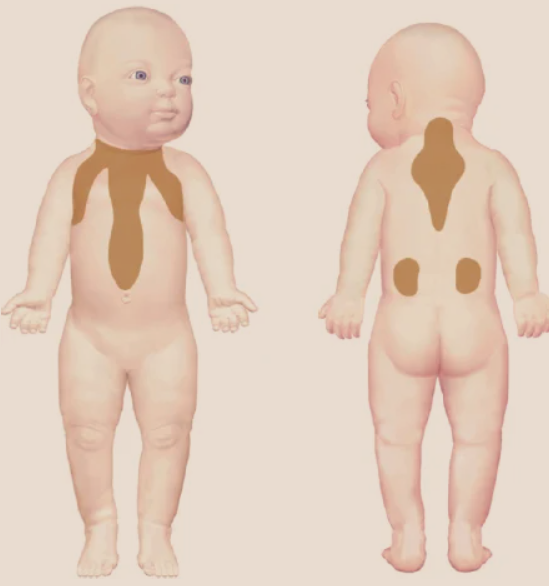
What are the sites of brown fat?
Midscapular area
Around Neck
Axilla
Around Trachea
Esophagus
Abdominal Aorta
Kidneys
Adrenal Gland
What is Convection heat loss in newborns?
Exposure to cool air currents
What is Radiation heat loss in the newborn infant?
Exposure to cool objects near infant
What is Evaporation Heat Loss in the newborn infant?
Wet body surface
What is Conduction heat loss in the newborn infant?
Cool surface exposure on infant (cold clothes, towels, stethoscope)
What is Cold Stress?
Excessive heat loss resulting in compensatory mechanisms (increased respirations and nonshivering thermogenesis) to maintain core body temperature.
What are the stools like for breastfed babies?
6-10 small, semi liquid yellow stools per day by 3rd or 4th day after milk production is established
What are the stools like for Formula-fed babies?
1-2 stools per day, more formed, yellow or yellow brown
How often should a healthy newborn urinate?
6-8 wet diapers per day
Should have first urination in first 24 hours of life
What is Unconjugated (indirect) bilirubin?
breakdown of hemoglobin from RBCs
Not an excretable form and a potential toxin
What is Conjugated (direct) bilirubin?
conversion of yellow pigmented fluid into a water-soluble pigment
How do you calculate the total bilirubin?
Take the sum of both Conjugated and Unconjugated bilirubin
Normal range: < 3 mg/dl
What is the risk of Jaundice buildup?
Bilirubin deposits in tissues & brain if unable to get rid of buildup can cause irreversible brain damage
What is Physiologic Jaundice?
Most common
acceleration of destruction of RBCs impaired conjugation of bilirubin; not pathological normal variation of newborn
“imbalance between the production and elimination of bilirubin”
60% of FT and 80% pre-term babies on 2-3 day
What is Pathologic Jaundice?
More concerning
occurs within first 24 hours
Needs hydration, warmth, monitor for adequate stools, early feedings, phototherapy
What is Breastfeeding Jaundice?
rise after the first 24 hours. Need to increase number of feedings.
What does Phototherapy do to treat Jaundice?
Changes bilirubin into a form that can be excreted
What Integumentary coloring of the skin will you likely see in the newborn?
Pallor
Pink
Jaundice
Cyanosis
Acrocyanosis
What is Lanugo in the newborn?
The fine, soft, downy hair that covers the body of a fetus during pregnancy. It typically appears around the 16th week of gestation and covers the entire body except for the palms, soles, lips, and genitals
Is Temporary
What is Milia in the newborn?
tiny, white bumps that commonly appear on newborns' skin. They are caused by trapped keratin, a protein found in skin cells
Temporary
What is Telangiectatic Nevi in the newborn?
flat, pink spots on their skin often referred to as “stork bites”
Fade by age 2
What is Erythema Toxicum in the newborn?
a common, benign skin rash that typically appears in newborns within the first few days of life
What are Mongolian spots on newborns?
also known as congenital dermal melanocytosis or slate gray nevi, are harmless, flat, bluish-gray birthmarks that commonly appear on the lower back or buttocks of newborns, especially those of Asian, African, or Native American descent
What is Vernix Caseosa?
a greasy deposit covering the skin of a baby at birth.
Protects baby’s skin while in womb & has Antimicrobial properties
What is the Tonic Neck reflex?
causes the baby to assume a fencing-like posture when their head is turned to one side
What is the Palmar Grasp reflex?
a newborn reflex where touching a baby's palm causes them to grasp tightly, and typically disappears around 5-6 months of age
What is the Plantar Grasp Reflex?
an involuntary reflex present in infants that causes them to curl their toes when the sole of their foot is stimulated
What is the Moro Reflex?
a normal, involuntary response in newborns where they throw their arms and legs outward and cry when startled or feel like they are falling, usually disappearing by 3-4 months
What is the root reflex?
newborn reflex triggered by touching a baby's cheek or mouth, causing them to instinctively turn their head and open their mouth, helping them find and latch onto a nipple for feeding
What is the Step Reflex?
a newborn reflex where a baby appears to take steps or dance when held upright with their feet touching a solid surface
What is the Babinski Reflex?
neurological reflex where stroking the sole of the foot causes the big toe to extend upwards (dorsiflexion), and the other toes to fan out.
What does the APGAR test look for?
A: appearance (color)
P: pulse (heart rate)
G: grimace (reflex irritability)
A: activity (muscle tone)
R: respiratory (respiratory effort)
What is being looked for with appearance for the APGAR test?
Cyanotic or pale (0)
Appropriate body color, blue extremities (1)
Complete Appropriate color (2)
What is being looked for with HR for the APGAR test?
Absent (0)
Slow <100 (1)
>100 (2)
What is being looked for with reflex irritibility for the APGAR test?
None (no response) (0)
Grimace or frown when irritated (1)
Sneeze, cough, or Vigorous cry (2)
What is being looked for with Muscle tone for the APGAR test?
Limp, Flaccid (0)
Some flexion of extremities (1)
Active motion. Tight flexion (2)
What is being looked for with Respiratory effort for the APGAR test?
Apneic (0)
Slow-irregular, shallow (1)
Regular Respirations (30-60 min), Strong good cry (2)
What is the average weight for the newborn?
Average 3405g (7lb 8oz)
Range 2500-4000g (5lb 8oz – 8lb 14oz)
What is the typical length of a newborn?
50 cm (20 in)
What is the average head circumference of a newborn?
33-35 cm (13-14 in)
What is the average chest circumference of a newborn?
Average 32 cm (12.5 in)
What is molding of the neck/head in newborns?
pressure of the birth canal causes the baby's skull bones to shift and overlap, temporarily making the head appear elongated or pointed, but usually resolves within a few days
What is Cephalhematoma in the newborn?
a collection of blood that accumulates between the scalp and the skull of a newborn baby. It is a common birth injury that occurs when pressure is applied to the baby's head during delivery
Resolves on own
What is Caput Succedaneum in the newborn?
a common, benign condition in newborns characterized by swelling or edema of the scalp, caused by pressure on the baby's head during labor and delivery
What Assessment are you looking for with the eyes of a newborn?
Symmetry
Eye color established approx. 3 months
Eyelids edematous during first few days of life
What Assessment are you looking for with the nose of a newborn?
small and narrow
What Assessment are you looking for with the mouth of a newborn?
lips should be pink
Saliva normally scant
Epstein’s Pearls
Thrush
What Assessment are you looking for with the Ears of a newborn?
top of ears (pinna) should be parallel to the outer and inner canthus of the eye
What Assessment is needed for the Abdomen of a newborn?
Should be cylindrical, protrude slightly, and move with respiration
Auscultate bowel sounds before palpate
What should you look for with the Umbilical Cord on the newborn?
White and gelatinous
Cord bleeding is abnormal
Assess for infection
Umbilical Hernia
Cord begins drying 1-2 hours after birth (shrivels and blackens by 2nd or 3rd day)
When should you first bathe baby in water?
After the umbilical cord falls off, typically in 1-2 weeks
What should you assess for with male genitalia in the newborn?
Hypospadias (urethral opening located posterior or distal to proper opening)
Cryptorchidism (balls don’t decend)
Increase risk of infertility
Hydrocele (fluid-filled sac surrounding testicles)
What should you assess for with female genitalia in the newborn?
Pseudomenstruation
Smegma
What is Hyperspadias in the male newborn?
opening of the urethra is located on the upper part of the penis, instead of on the tip
What is Cryptochordism in the male newborn?
a condition where one or both testes fail to descend into the scrotum before birth
What is Hydrocele in the newborn?
a collection of fluid in the scrotum, the sac that contains the testicles
What is Pseudomenstruation in the female newborn?
A temporary, false menstration. It is caused by the withdrawal of maternal hormones, such as estrogen, from the baby's body after birth
What does the Physical Maturity Assessment do?
determines a newborn’s gestational age between 20 and 44 weeks
What are Plantar creases in the newborn?
creases on the soles of the feet, which range from absent to covering the entire foot, depending on maturity (the greater the number of creases, the greater the newborn’s maturity).
What does a Neuromuscular Maturity Assessment test?
Posture
Square window
Arm recoil
Popliteal angle
Scarf sign
Heel to ear
Scoring of 0 (Preterm) to 4 (term)
What does it mean by SGA?
Small for gestation age, weight less than the 10th percentile (usually <5.5lb)
What does it mean by AGA?
Appropriate for gestational age, between 10th and 90th percentile
What does it mean by LGA
Large for gestational age, more than the 90th percentile (usually >9lbs or anything greater than 4000g
What immediate care is needed for newborn?
Maintain clear airway
Thermoregulation
Medications
Vitamin K (AquaMephyton) IM
Erythromcyin
Antibiotic ophthalmic ointment
Hepatitis B Vaccine
Initiation of first feeding
Parent-newborn attachment
Where is the IM injection site on a newborn? (Vastus lateralis)
Divide outer thigh into thirds b/w hip and knee.
Shot goes in junction of middle and upper third
What are the signs of Neonatal Distress?
Retractions
Nasal Flaring
Grunting
Facial Grimacing
Cyanosis
Abdominal Distention
Vomiting
Jitteriness (Glucose less than 40)
What is some ongoing Newborn care the nurse needs to insure?
Thermoregulation
Nutrition
Suctioning
Safety
Circumcision
Bonding
Care of Baby
Newborn Screening and Immunizations
Sleep
When can a newborn get a metabolic screen?
Has to be at least 24 hours old
What safety measures does the nurse need to educate the parents about the baby?
General safety
Hospital safety
Car seat
SIDS (Sudden Infant Death Syndrome)