Genetics Chapter 1 Pt. 1
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
nuclear DNA
linear chromosomes inside thenucleus
nuclear envelope
the distinguishingfeature of eukaryotes
organelle DNA
circular chromosomes in themitochondria and, in plants and algae, the chloroplasts
G-1 phase
cell growth
G-2 phase
cell growth
S-phase
DNA replication (synthesis)
M-phase
mitosis and cytokinesis; eukaryotic cell division
what does interphase consist of
G1, S, G2
G0
the cell may exit the division cycle during G1 to become a non-dividing cell (quiescience)
checkpoints
steps at which the progression through thecell division cycle is monitored and regulated
At the end of mitosis and during G1 or G0,
a chromosome consists of a single DNA molecule
After S-phase and during G2 each chromosome
consists of two DNA molecules (two identical sister chromatids)
telomeres
stable ends of linear chromosomes
centromere
region of the chromosome at which sister chromatids are joined. Also present before DNA replication
before DNA replication ____ DNA molecule
one
after DNA replication ____ DNA molecule
two
chromatin
condenses into visible chromosomes before cell division due to the tightening of interactions between DNA and chromatin proteins
histones
protein molecules around which DNA is tightly coiled in chromatin
sequence that encodes a trait
gene
p arm
short arm of chromosome
q arm
long arm of chromosome
chromatin
fibers of decondensed DNA chromosomes; occurs during the non-divisional phases of the cell cycle
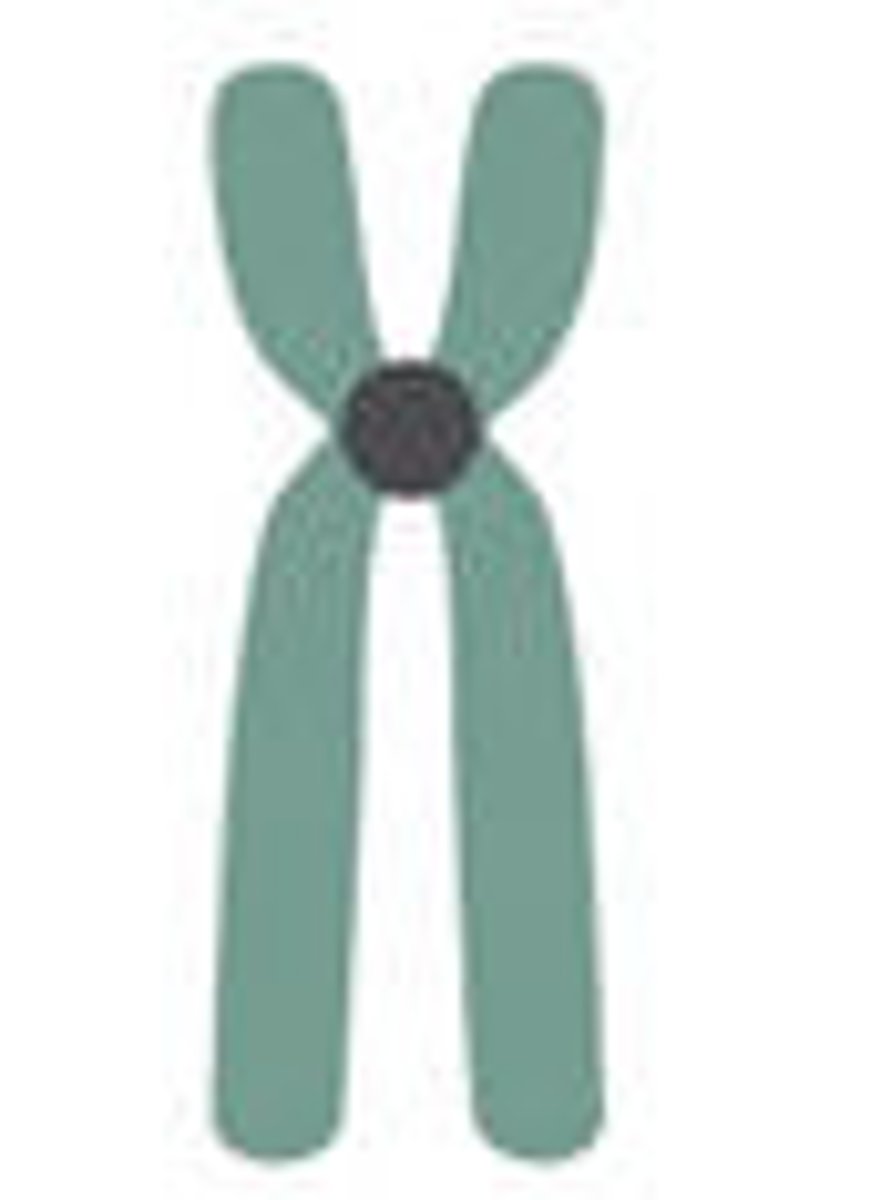
submetacentric
near the center

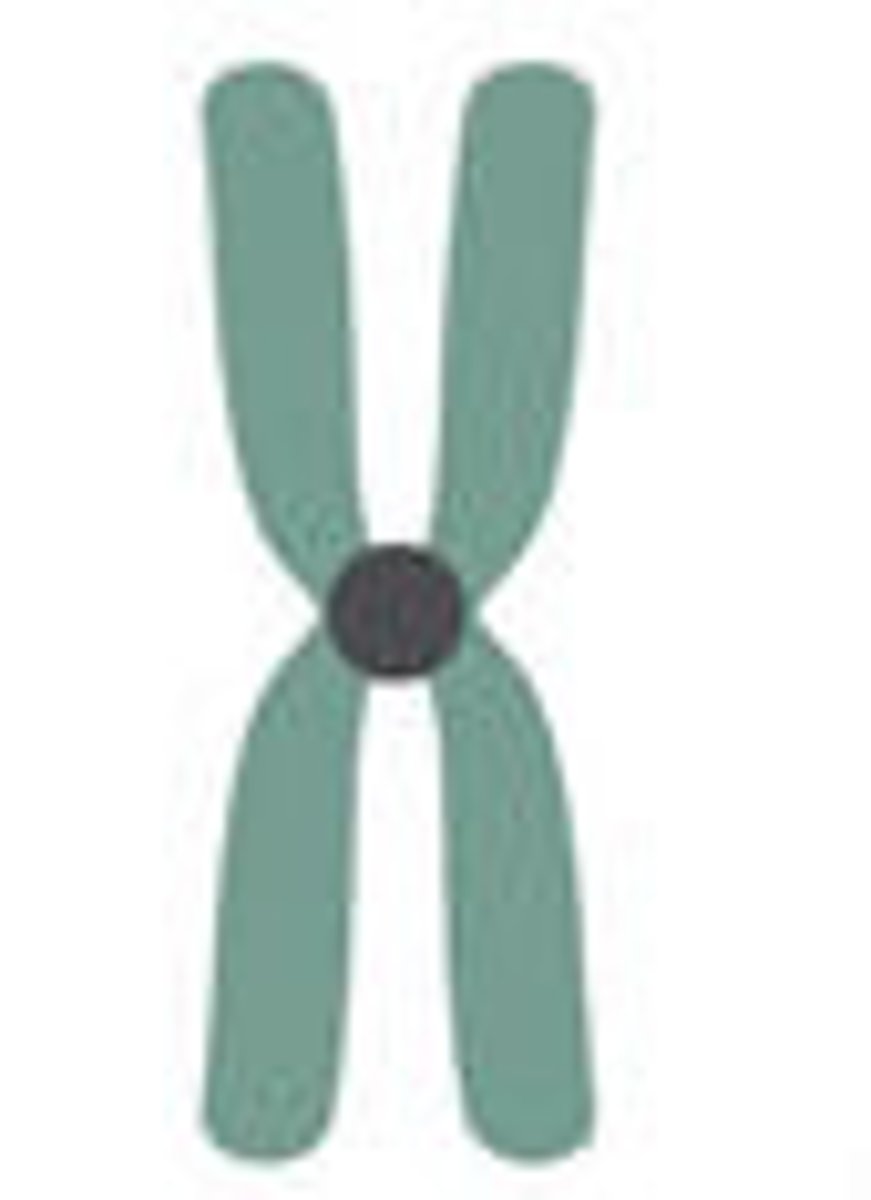
metacentric
at the center

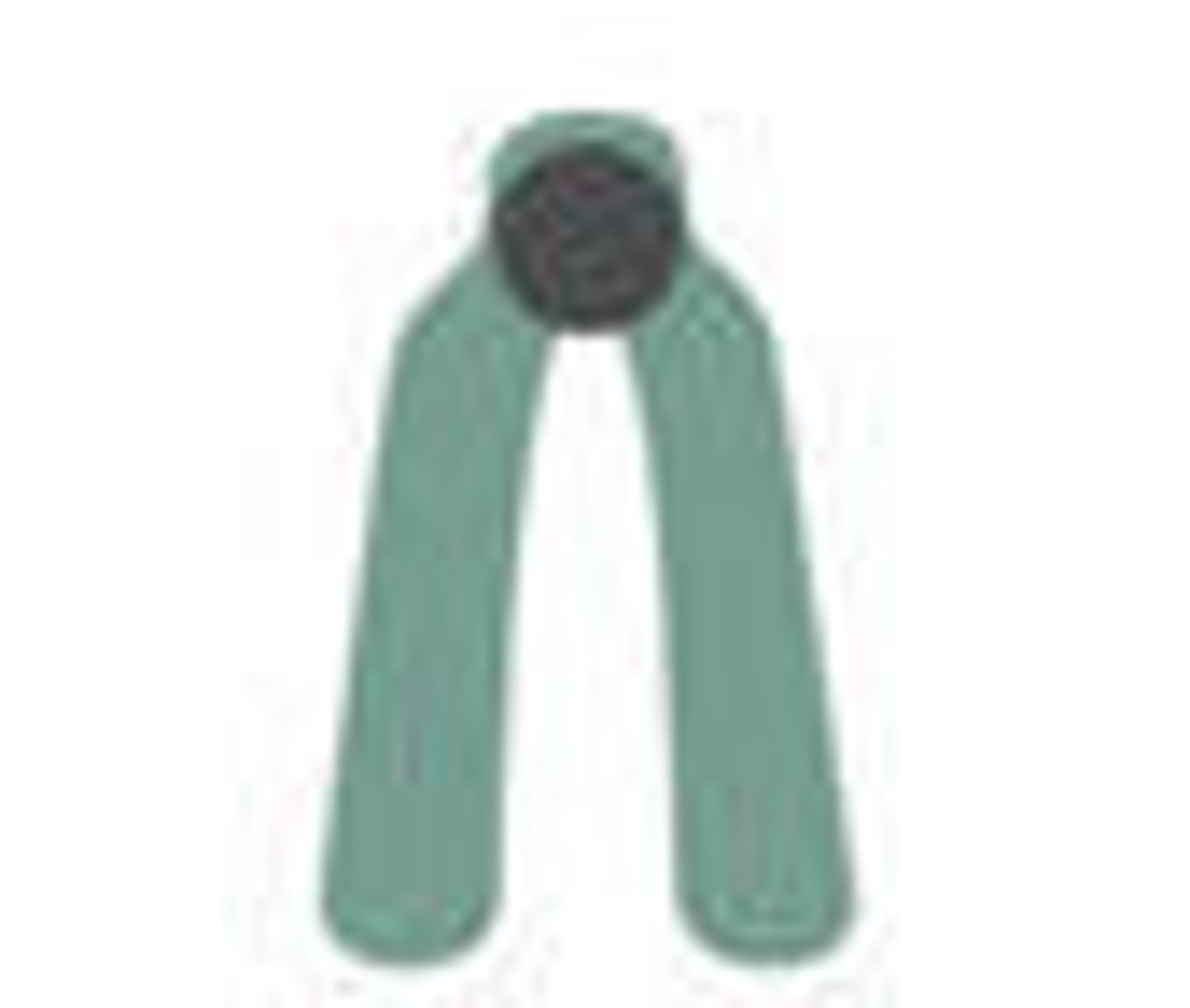
telocentric
at the telomere

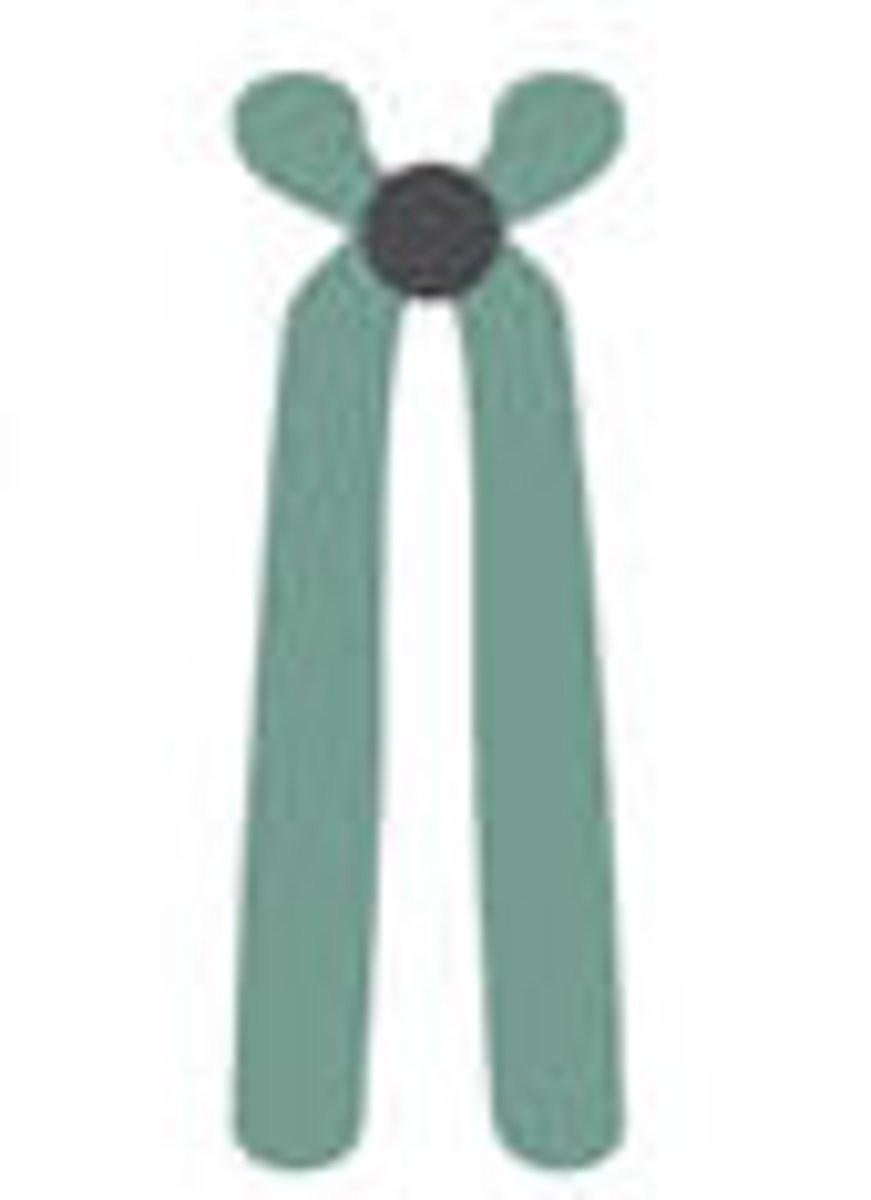
acrocentric
near telomere

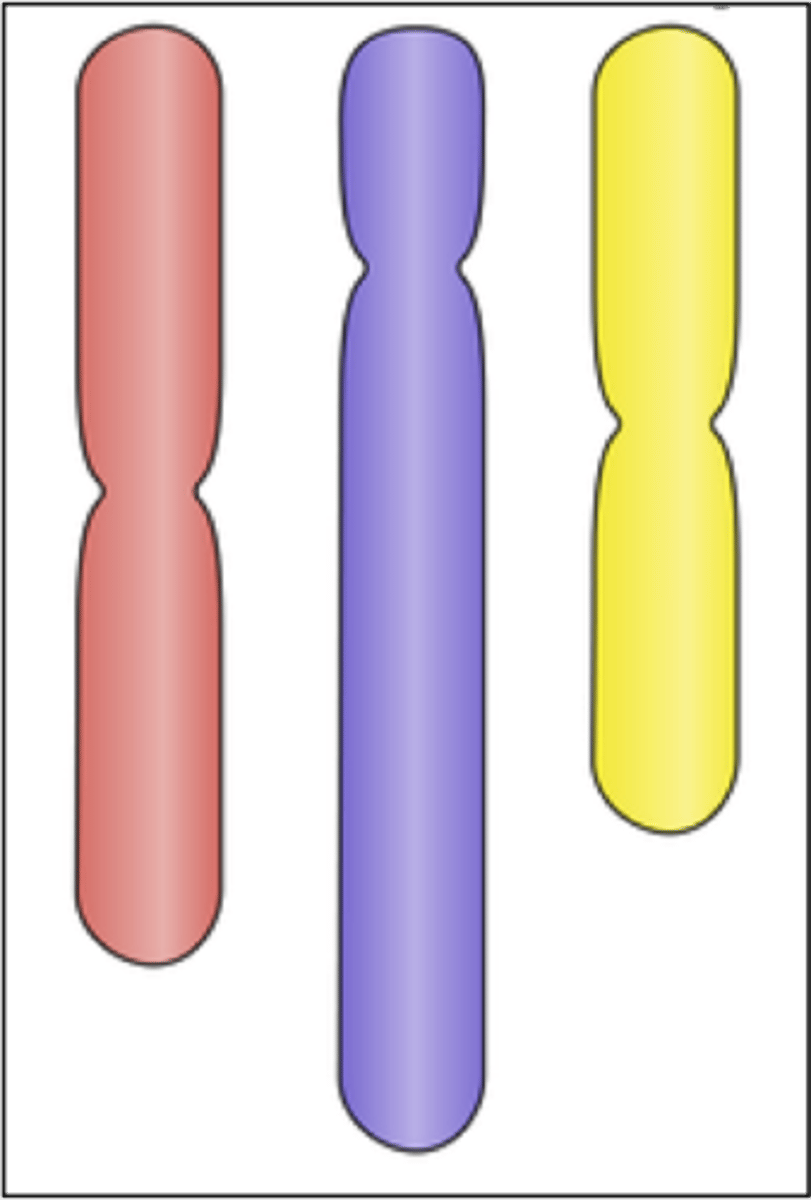
haploid (n)
one copy of genetic material subdivided into chromosomes
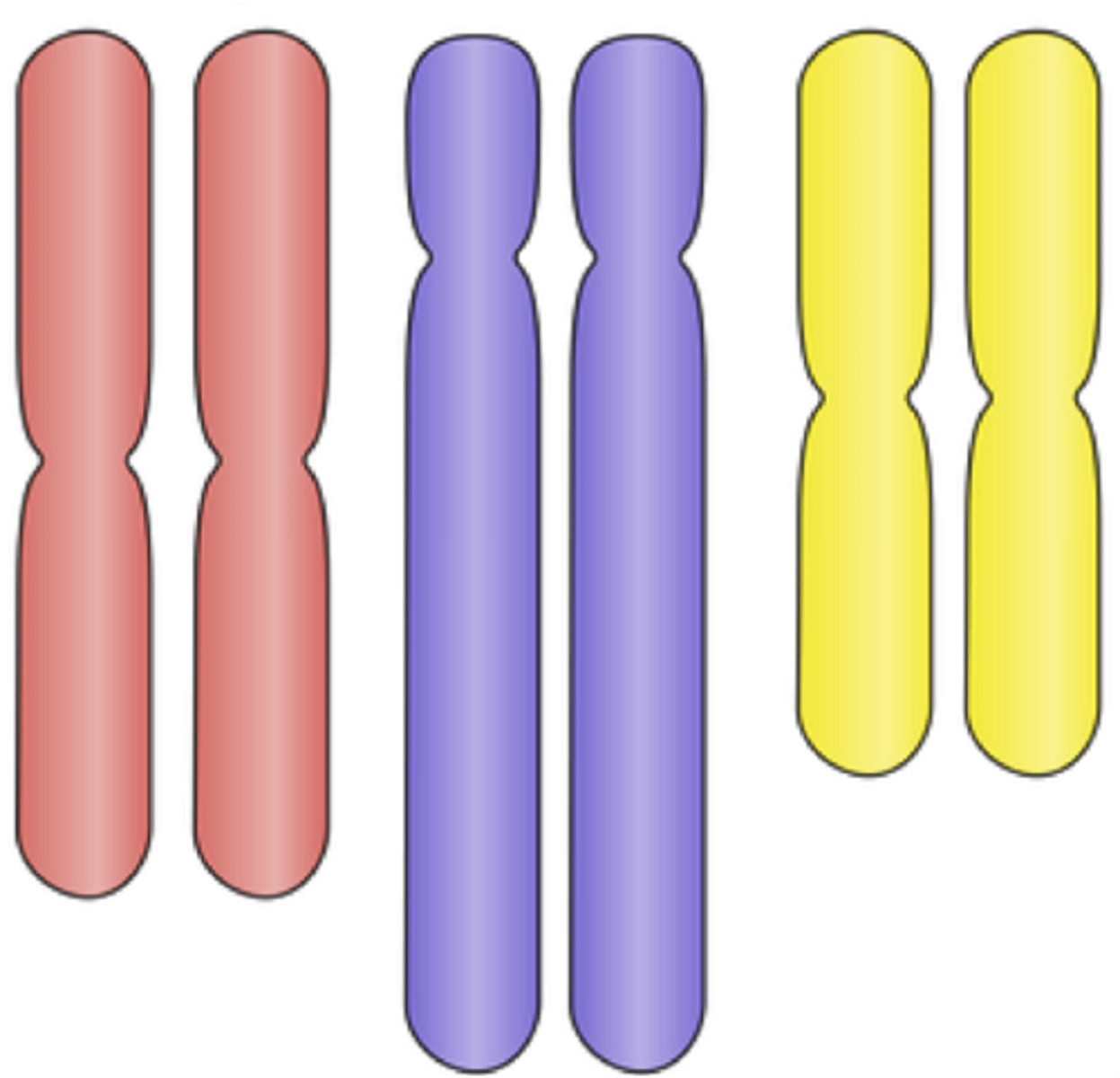
diploid (2n)
two copies of genetic material subdivided into chromosomes
alleles
alternative forms of a gene found at the sameposition (locus) of homologous chromosomes
locus
Location of a gene on a chromosome
homologous chromosome
chromosomes with the same length and centromere location; contain the same linear sequence of loci, but not necessarily identical DNA; NOT sister chromatids
gene (transmission genetics)
a unit of heredity that is transferred from a parent to offspring and is held to determine some characteristic of the offspring
gene (molecular genetics)
a region of a chromosome that codes for a functional product
all genes are loci but
not all loci contain genes
karyotype
visual representation of the complete set of chromosomes of an individual organism
autosomal
all the other genes in the body that are not sex-linked
normal human karyotype
22 pairs of autosomal chromosomes and 1 pair of sex chromosomes
polyploid
3n, 4n, 5n, etc.
aneuploid
Abnormal number of chromosomes (in humans, a number of
chromosomes that is not 46)
mitosis
division of the nucleus.
cytokinesis
the division of the cytoplasm and the cellmembrane
Chromosome (DNA) replication
the duplication of theDNA molecules in the nucleus; results in sisterchromatids
kinetochore
protein structure that is assembled on the centromer, spindle microtubules attach to it and mediate disjunction of sister chromatids
spindle microtubules
attach to the kinetochores of chromosomes and move the chromosomes to the metaphase plate
centrosome
a pair of centrioles. It is the microtubule-organizing center (MTOC) of animal cells
centrioles
Cell organelle that aids in cell division in animal cells only
prophase
the chromatin condenses into visible chromosomes. The centrosome is duplicated. The two centrosomes will become the poles (ends) of the mitotic spindle, made of microtubules.

prometaphase/metaphase
he nuclear envelope breaks down (except in fungi), the mitotic spindles attach to the centromeres of the chromatids, and the chromosomes lineup at the metaphase plate
anaphase
the chromatids are pulled apart by the mitoticspindles
telophase
the chromatids are segregated and their DNAdecondenses. The chromatids become the chromosomesof the daughter cells. The nuclear envelopes reassemble
when does the nuclear envelope disintegrate in mitosis?
prometaphase
are sister chromatids pulled to the metaphase plate in mitosis
no, they go there themselves and are not connected
what is the outcome of mitosis
2 identical diploid daughter cells
when does cytokinesis occur
simultaneously with or following telophase
each chromosome consists of how many DNA molecules
a single DNA molecule
during anaphase of mitosis, the chromosmes...
are disjoined and are segregated to daughter cells
do chromosomes pair in mitosis
homolgous chromosomes do not pair at any time