Med-Surg Final (NURS 301-Liberty University)
1/455
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
456 Terms
General Adaptation Syndrome consists of what three stages?
Alarm
Resistance
Exhaustion (or recovery)
Hardiness
Individual has an internal center of locus
They have a sense of meaningfulness and personal goals and values
Sense of coherence
How the person sees the world and their place in it; more powerful than hardiness
Comprehensibility
Manageability
Meaningfulness
What does stress do to NKC's, inflammatory mediators, and immunity?
Suppresses all of the above
Name 4 ways to manage stress (List of 9)
Biofeedback
Relaxation
Imagery
Hypnosis
Therapeutic touch
4x4 breathing
Music
Prayer and encouragement
What are the three main functions of blood?
1. Transport O2, nutrients, hormones, and waste
2. Regulate fluid electrolyte balance, acid base balance, and temperature
3. Protect through clotting and immune function
What kind of tissue is blood?
Connective tissue
Where in the body is bone marrow abundant?
Sternum, scapulae, clavicle, pelvis, flat cranial bones, end of long bones
What are the two types of bone marrow?
Red (produces blood cells)
Yellow (adipose)
What is the stimulator for blood cell production?
Erythropoietin
What cells become blood cells?
Hematopoietic stem cells
Why is bone marrow aspiration performed?
To evaluate hematopoiesis or obtain a specimen for cytopathology/chromosomal abnormality testing
What are the three best places for bone marrow aspiration from ideal to less ideal?
1. Posterior iliac crest
2. Anterior iliac crest
3. Sternum
RBC lab value
4-6 million
Hgb lab value
12-18
Hct lab value
38-50
MCV lab value
80-95
MCH value
27-31
MCHC lab value
32-36
WBC lab value
5,000-10,000
Neutrophil lab value
2,500-8,000
Platelet lab value
150,000-400,000
How do blood counts change with age?
Stem cells drop after 30 and again at 65
Hgb drops after middle age
WBCs don't increase as much with infection
Shift to the right
Fewer and older WBCs
Chronic disease
Shift to the left
High numbers of immature WBCs
Acute disease
MAP equation
(SBP + 2DBP)/3
MAP equation
(SBP + 2DBP)/3
What is a good MAP?
>70
What is an MAP that needs to be watched?
<70
1 oz is how many mL?
30 mL
cc's are the same as what?
mL's
How many pounds are in a kilogram?
2.2 pounds
A undiagnosed chest pain patient comes in with a BNP level of 74. What do you do?
Assess other things for the cause because this is an okay BNP
An undiagnosed chest pain patient comes in with a BNP level of 126. What do you do?
Notify the doctor of possible heart failure diagnosis and assess the patient
What level of BNP is indicative for HF?
100+
What is the gold standard for the diagnosis of heart failure?
BNP
What is a reticulocyte?
An immature RBC
What does a high reticulocyte mean?
RBC's are being created and destroyed rapidly
What is a normal RBC level?
4-5 for women
4-6 for men
What system does the stress response activate?
Sympathetic nervous system
What is the goal of the resistance stage?
Adaptation
Stress leaves a patient at a higher risk for what?
Infection
What is the biggest question about cardiac?
ARE THEY PERFUSING??????
Blood flow through the heart from vena cava to the body
Vena cava
Right atrium
Tricuspid
Right ventricle
Pulmonic
Lungs
Left artium
Mitral (Bicuspid)
Left ventricle
Aortic
Body
Do all arteries carry oxygenated blood?
No, the pulmonary artery is the exception
Endocardium
Thin inner lining of the heart
Myocardium
Muscular layer of the heart
Epicardium
Outer fibrous membrane of heart
Pericardium
2 layered sac surrounding the heart that protects it from friction
Visceral definition
Inner
Parietal definition
Outer
AV valves
Tricuspid and mitral (bicuspid)
Semilunar valves
Pulmonic and aortic
What direction is blood flow supposed to be?
Unidirectional
What is it called when blood flow is not unidirectional?
Turbulent
What is the risk of turbulent blood flow?
Platelet aggregation causing a clot/ thrombus/ embolus
How does the heart stay oxygenated?
The sinuses of Valsalva, located above the aortic valve cusps, open to the right and left coronary arteries and perfuse the heart
When does the heart perfuse itself?
During diastole
What happens to the heart if the diastolic blood pressure is too low?
It is not perfused
Prolonged tachycardia can lead to what heart condition?
Myocardial ischemia
What is myocardial ischemia?
Tissue hypoxia
How long can myocardial ischemia last before it becomes infarction?
20 minutes
What causes ST depression?
Myocardial ischemia
What causes ST elevation?
Myocardial infarction
List the phases of conduction from beginning to contraction
SA node
AV node
Bundle of His
Bundle branches
Purkinje fibers
Contraction
What does the P wave represent?
Atrial depolarization
What does the QRS complex represent?
Ventricular depolarization
What does the ST segment represent?
Ventricular repolarization
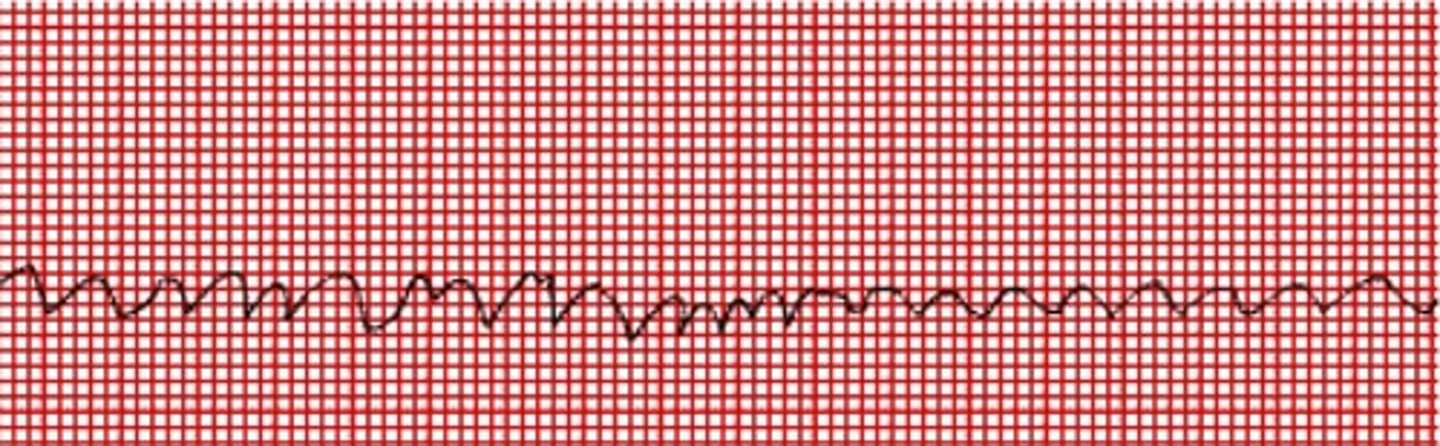
What does atrial fibrillation look like?
-Irregularly, irregular
-Heart rate varies from slow to rapid
-No discernible P wave
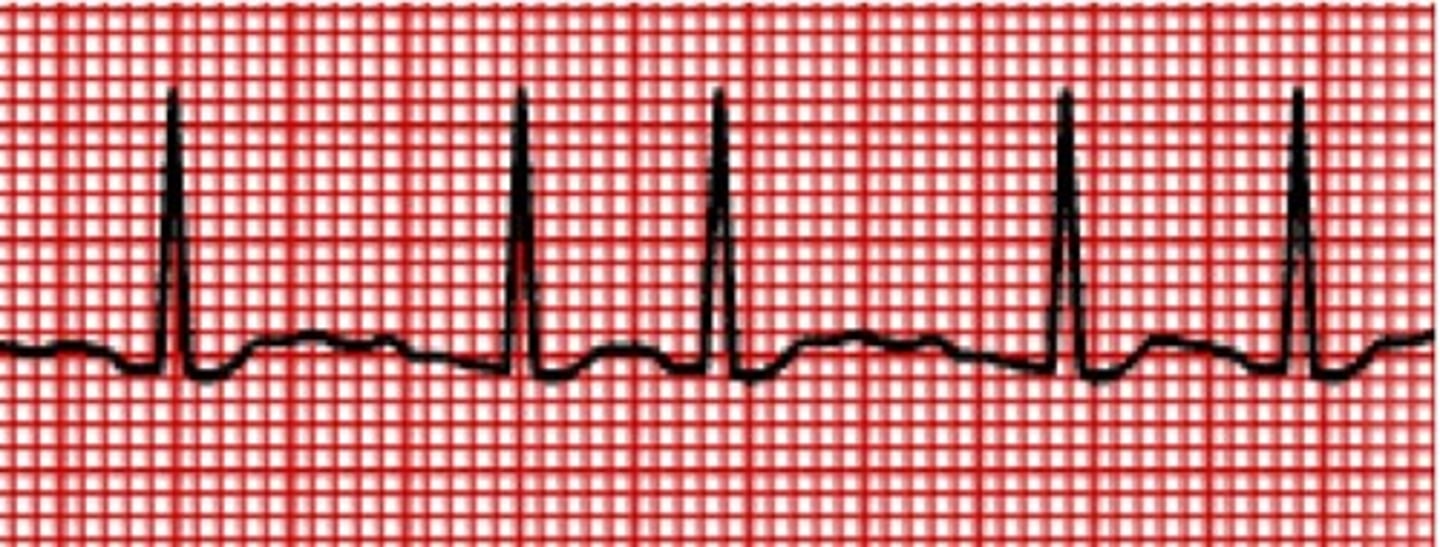
What does atrial flutter look like?
"Sawtooth"
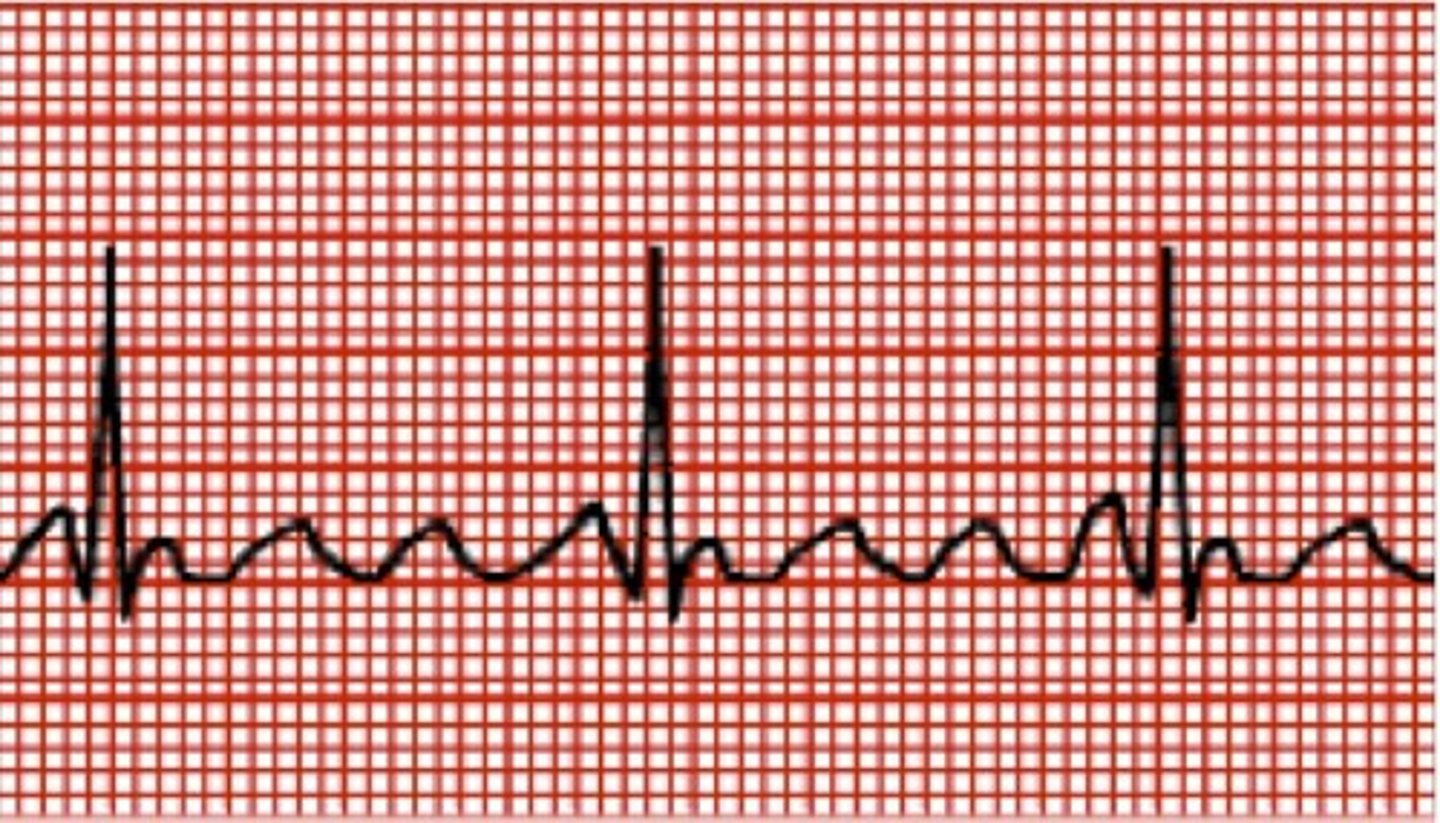
What does ventricular tachycardia look like?
Wide QRS with no P-wave
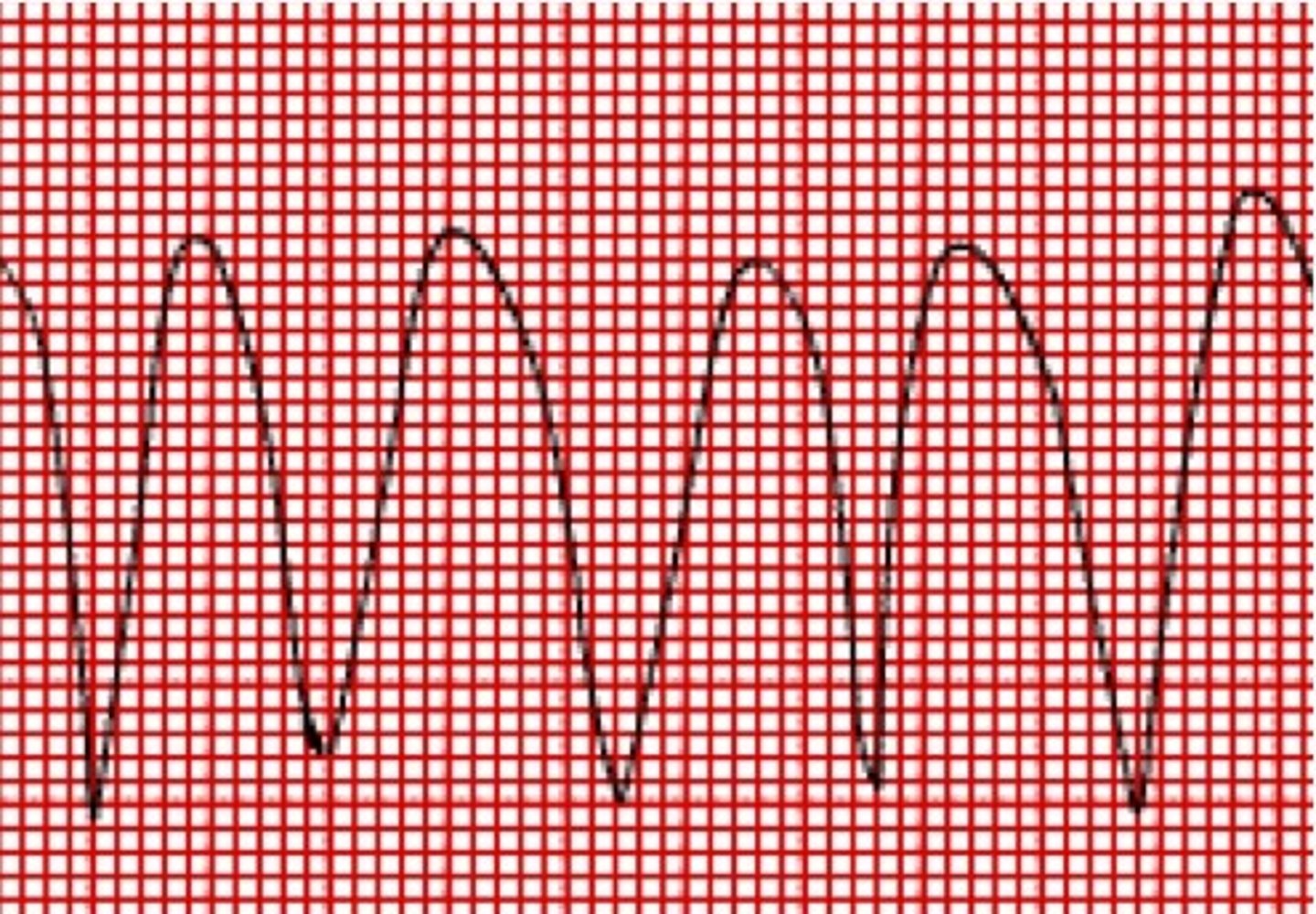
What does ventricular fibrillation look like?
TWITCHING VENTRICLES DON'T MOVE BLOOD. undefinable waves irregular in size, shape, frequency
Cardiac output equation
CO = HR x SV
What is a normal stroke volume?
60-70
What is a normal heart rate?
60-100
What is a normal cardiac output?
4-8
Little boxes on the EKG are equal to how much time?
0.04 seconds
Big boxes on the EKG are equal to how much time?
0.2 seconds
How long should the P wave be?
0.06-0.12 seconds
How long should the P-R interval be?
0.12-0.2 seconds
How long should the QRS complex be?
0.04-0.12 seconds
Preload is...
Volume
Afterload is...
Resistance
People with chronically increased preload have what condition?
CHF
List a few reasons why there would be an increased preload
Hypervolemia (Fluid overload
Aggressive fluid resuscitation
Cardiac valve regurgitation
Pump failure (CHF)
List a few reasons why there would be a decreased preload
Hypovolemia
Bleeding
Shock
Diabetes insipidus
What main medication decreases preload?
Lasix
What affects afterload?
Size of ventricle
Vascular wall tension
Arterial BP
What main medication decrease afterload?
Nitroglycerin
Starling's law
Fibers have a greater force of contraction the more they are stretched
Think of a rubber band being stretched
What three meds increase contractility?
Epi
NorEpi
Digoxin
What three things increase the workload of the heart?
Preload
Afterload
Contractility
When the workload of the heart increases what else increases?
O2 demand
Inotrope
Force of contraction
Chronotrope
Rate of contraction
Digoxin does what related to inotrope and chronotropes?
Positive inotrope and negative chronotrope
Pumps harder and slower so check HR and BP before giving
What is the most common anemia in the US?
Iron deficiency anemia
How do you treat iron deficiency anemia?
Iron pills
What is the most common anemia for alcoholics?
Folic acid deficiency anemia
How to treat folic acid deficiency anemia?
Replace folic acid
Possible blood transfusion if Hgb is really low