Form 4 Chapter 3 Biology - Movement of Substances Across The Plasma Membrane
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
what is the plasma membrane?
semi-permeable lipid bilayer found in all cells
what does plama membrane do?
controls water and certain substances in and out of the cell
function of plasma membrane?
protects the cell.
separate the intracellular components from the extracellular environment.
controls what enters and exits the cell
necessities for the movement of substances across the plasma membrane?
to transport nutrients into the cell.
for gases exchange
to excrete metabolic waste
substances leaving the cell through membrane
secretion, oxygen, carbon dioxide, excess water and nitrogenous waste
substances entering the cell through membrane? |
nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, water and ionic salts |
structure of the plasma membrane? |
fluid mosaic model |
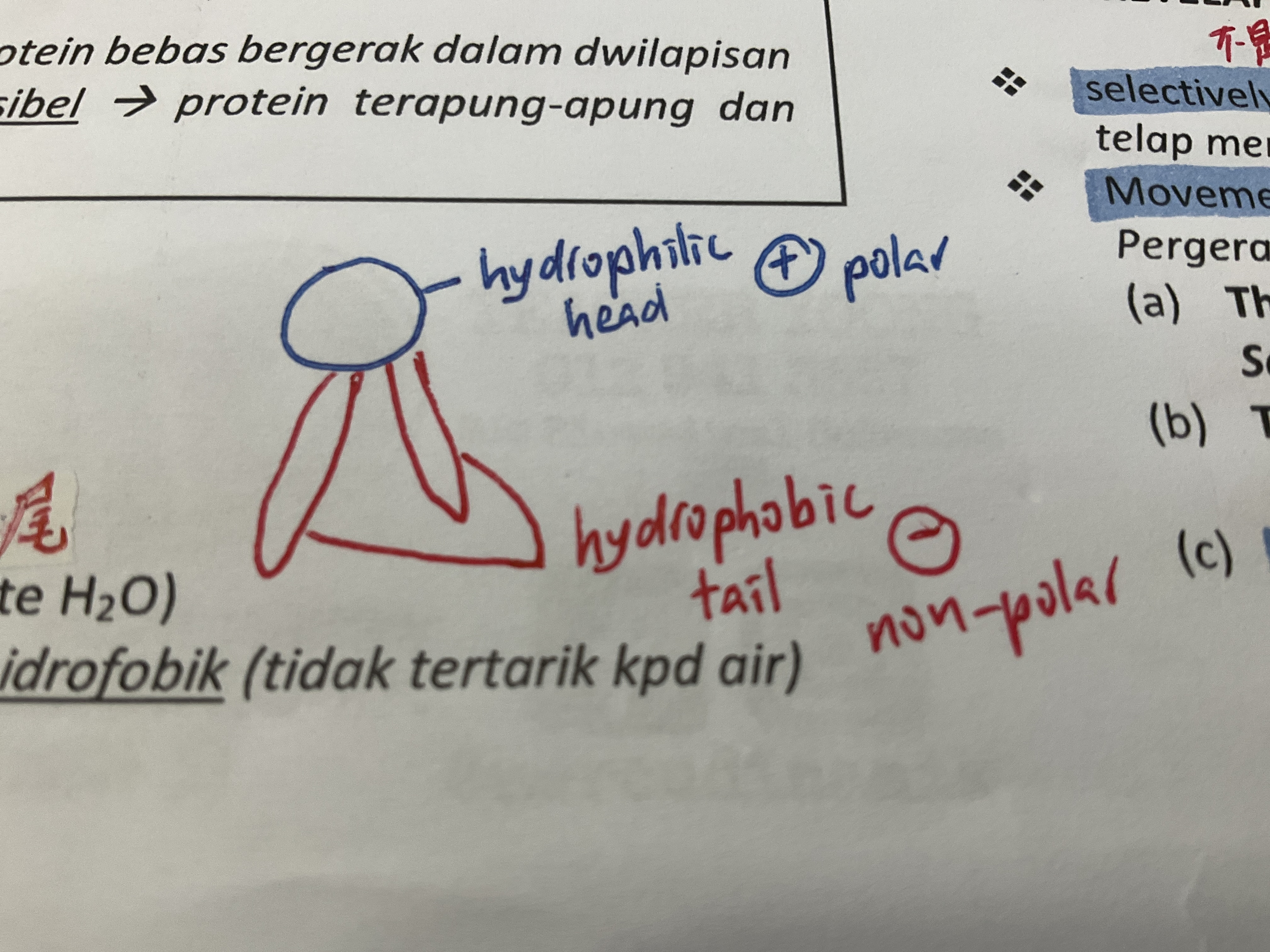
phospholipid
bilayer ( double layer )
polar head (hydrophilic) [ love
H2O
non-polar tail ( hydrophobic ) [hate H20]
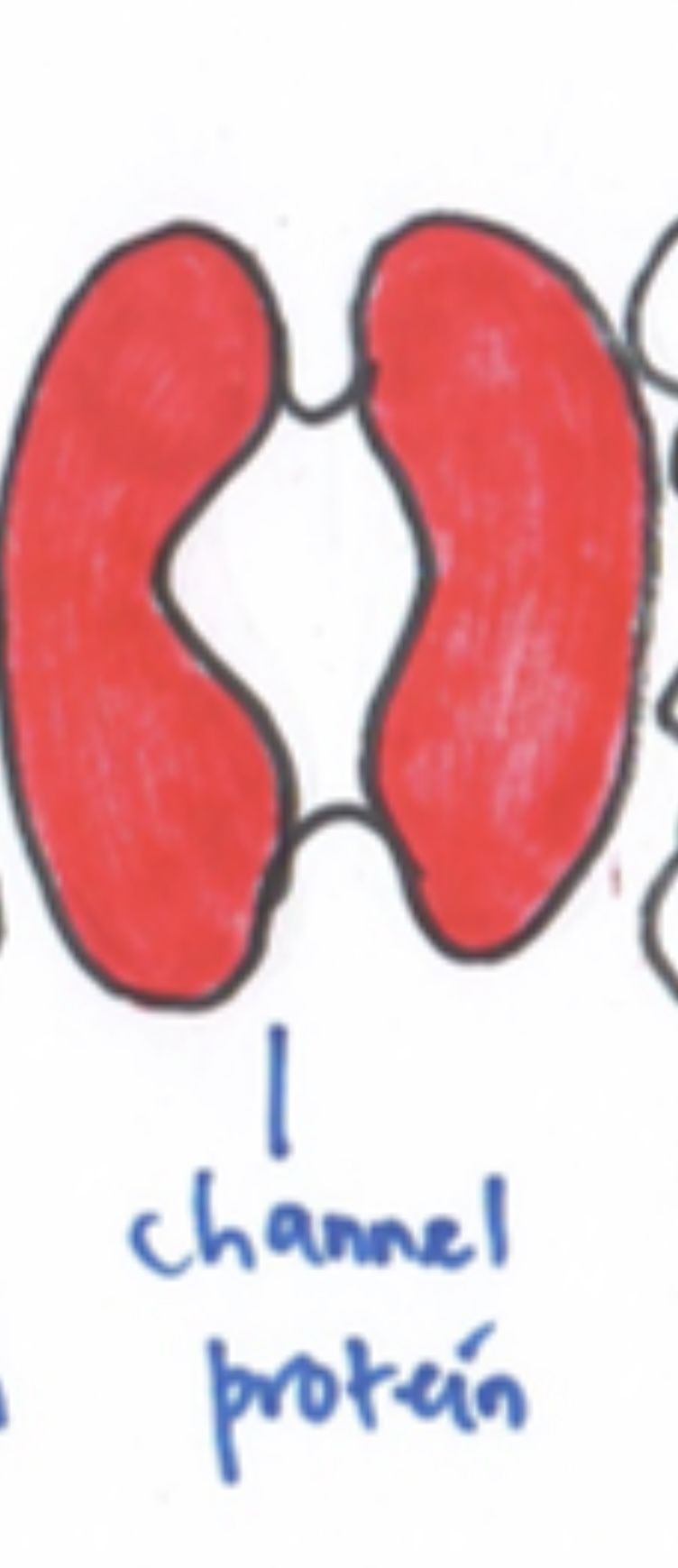
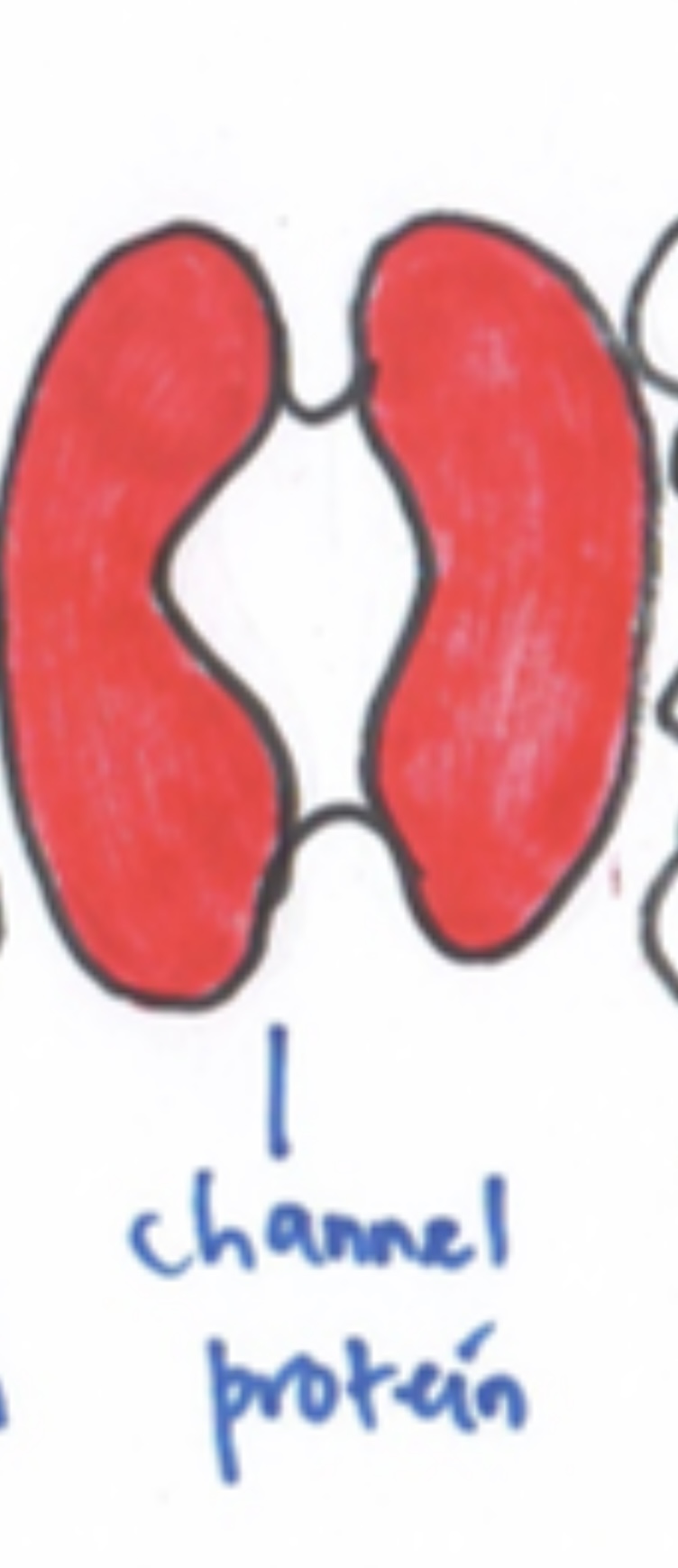
Protein
-Pore protein : protein with pore 有洞的protein -Carrier protein : protein carry substance in&out -Glycoprotein: protein attached with carbohydrates [ receptors to hormones ]exp:insulin, stabilise membrane by forming hydrogen bonds with water & act as antigens for cell identification |
![<table style="min-width: 25px"><colgroup><col style="min-width: 25px"></colgroup><tbody><tr><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p><span>-Pore protein : protein with pore</span></p><p><span>有洞的protein</span></p><p><span>-Carrier protein : protein carry substance in&out</span></p><p><span>-Glycoprotein: protein attached with carbohydrates [ receptors to hormones ]exp:insulin, stabilise membrane by forming hydrogen bonds with water & act as antigens for cell identification</span></p></td></tr></tbody></table><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/c6bf65a2-6552-46d8-b25b-798c35a7c0bf.jpg)
Function of pore protein & carrier protein
1.Pore protein
-allow movement [ small water - soluble substances & ions ] 可以让小水进
2.Carrier protein 太大进不到?
carrier protein 会带你 -sites to bind specific molecule ( exp : glucose)
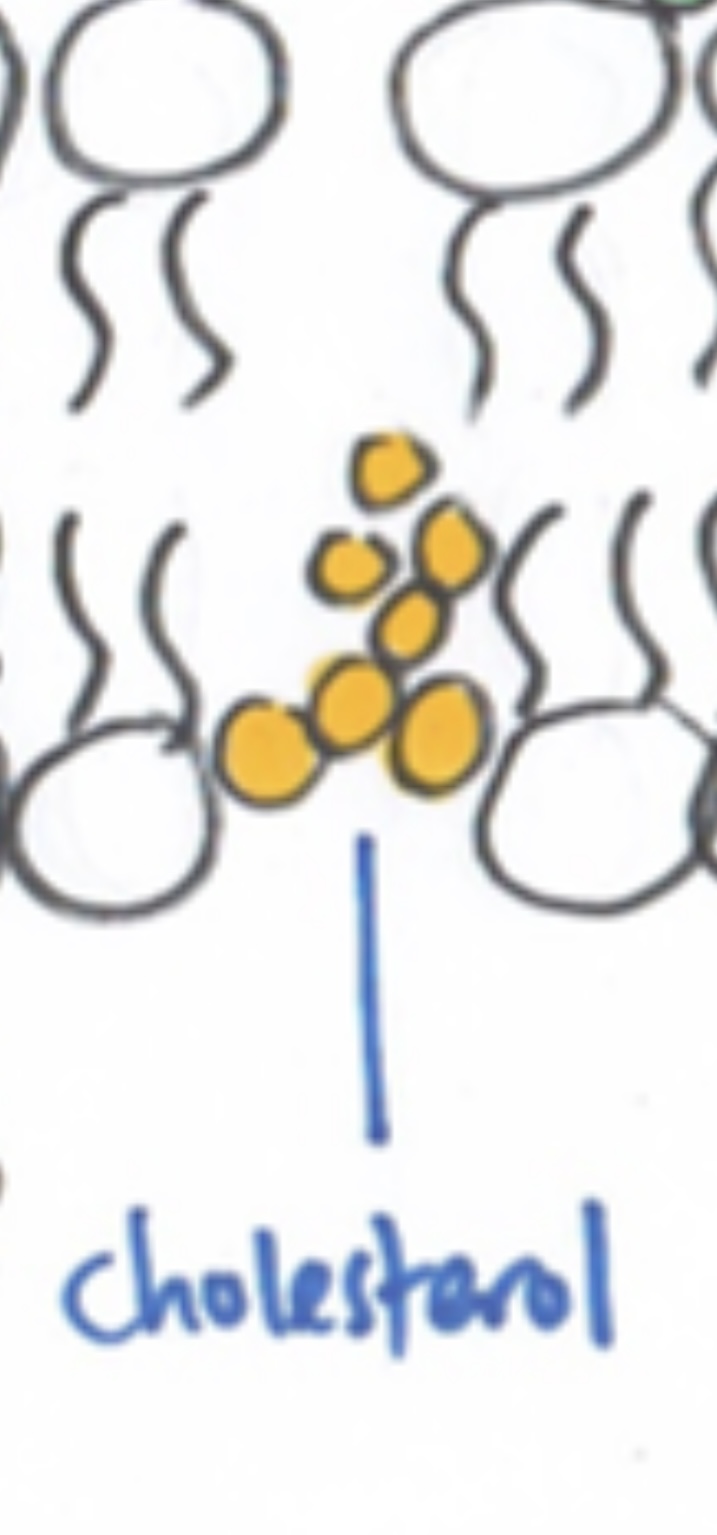
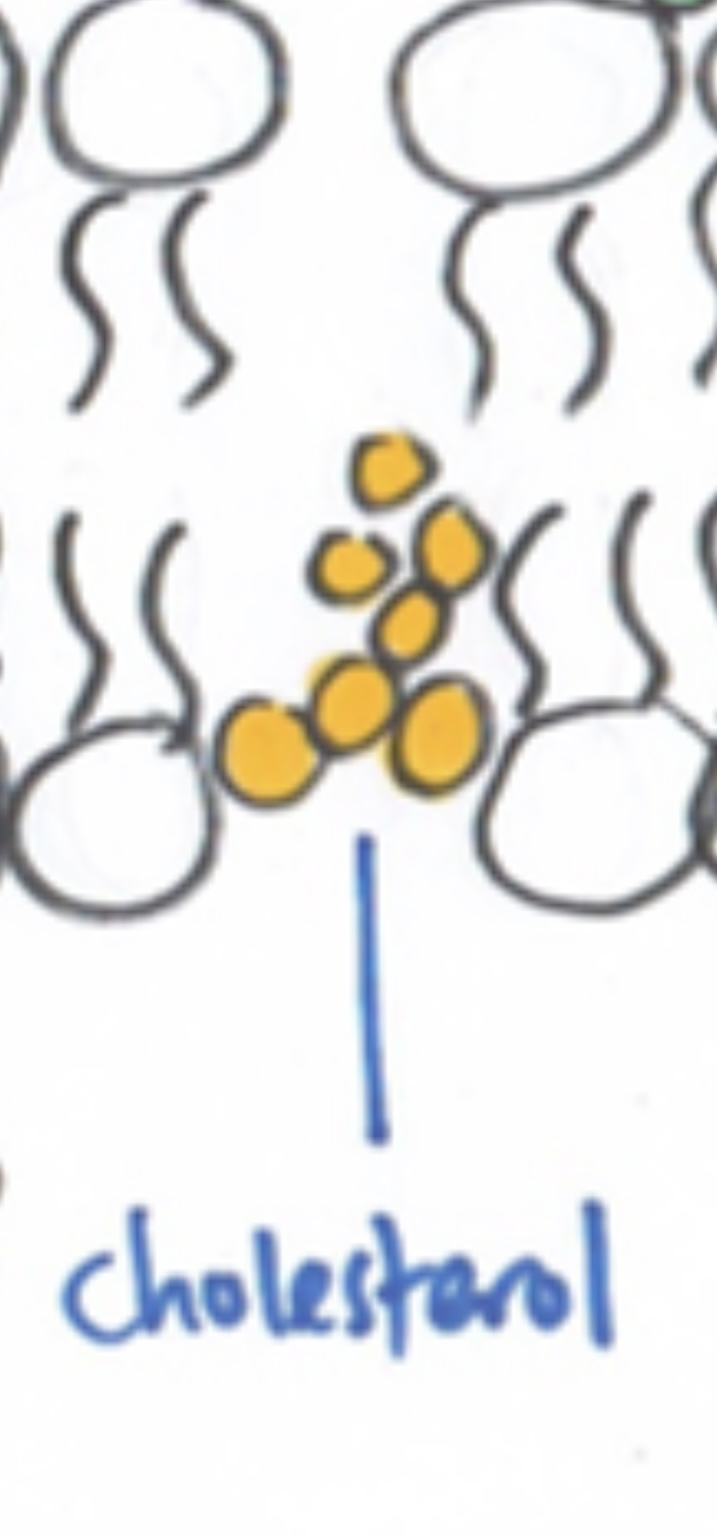
Cholesterol
make phospholipid bilayer
stronger
more flexible
less permeable to water-soluble substances
whats the 3 characteristics to determine
the permeability of the phospholipid
bilayer?(3个特征 plasma membrane)
the molecular size
the ionic charge
the polarity of the substances pass through it
CHARACTERIS
TICS OF MOVEMENT OF SUBSTANCES
ACROSS A PLASMA MEMBRANE她的允许进出条规
-lipid soluble molecules permeable
-non-polar molecule (02 & CO2 )permeable
-hydrophobic tail prevent polar substances 尾巴避免+-的
BUT H2O is so small, can slide through pores between the phospholipid layer
what is passive transport?
movement of substances across the cell membrane without / does
not involve the use of energy
# simple diffusion
# osmosis
# facilitated diffusion
what happens during passive transport?
substances move down their concentration gradient
what are the 3 different channels passive
transports can happen through?
lipid bilayer
pore protein
carrier protein
Simple diffusion meaning
- the [movement of substance] from an area of (high concentration) to an area of (low concentration) until an equilibrium is achieved
what is the particles that move through the plasma membrane
through diffusion?
-substances soluble in fat (vitamins
A,D,E, K)
- neutral particles (water, oxygen,carbon dioxide)
example of diffusion?
between alveoli and blood capillaries in the lung during gases exchange
what is Osmosis ?
[ movement of water molecules ] from an area of (high water potential) to an area of (low water potential) through a semi-permeable membrane until equilibrium achieved
what is the
direction of movement for osmosis?
high to low concentration
Facilitated diffusion
-dos not require energy (down a concent gradient)
Process of : Lipid-insoluble molecules (ions) [ channel protein ] , large molecule (amino acids & glucose ) [ carrier protein ] unable to pass through the phospholipid bilayer. [ across by transport protein ]
The process of the movement of glucose molecules
across a plasma membrane
occurs through a facilitated
diffusion
1) molecule move toward the binding sites of carrier proteins 往前去黏
2)molecule binds to a specific sit
on carrier protein 黏住他
3) the carrier protein changes its shape, allow molecule to pass
through 改自己形状,让他进
4) carrier protein return its original shape
what is active transport?
- movement of molecules across the plasma membrane (against the concentration gradient)
what is the
energy required used in active
transport?
energy (ATP) adenosine triphosphate
what is the simillarity between passive transport and active transport? |
1. Moving a substance across a membrane 2. Occurs through a selectively permeable membrane |
what is the direction of movement for passive transport & active transport |
following concentration gradient lI against the concentration gradient |
type of
molecules involve in
passive transport & active
water Il glucose & mineral salt
what is the
energy requirement for
passive transport &active
transport?
absent, not required II required
Movement
Movement of substance in everyday life
1) Hypotonic solution 里面cell的水
少,外面的水多,所以要进去cell
-solution with a [lower solute concentration ] than solute concentration within the cell
2) Hypertonic solution 里面cell的
水多过外面的水所以里面cell的水
会出来
-solution with [higher solute concentration] than solute concentration within the cell
3) Isotonic solution
-solution with [equal solute concentration with the cytoplasmic fluid ]
Effect of hypotonic, hypertonic and isotonic solutions on
ANIMAL CELLS
1) direction 2) cell shape
3)process name
Hypotonic solution
Water diffuse [into] cell by osmosis
Cell become [turgid & burst] 水
太多所以爆开,cuz plasma
membrane too thin to contain water
Hypertonic solution
Water diffuse [out] cell by osmosis
Cell become [ shrink / shrivel] 没水扁
3. Crenation
Isotonic solution
Water diffuse [in & out] at the same rate
Maintain normal shape
Effect of hypotonic, hypertonic and isotonic solutions on
PLANT CELLS
1) direction 2)
cell shape
3)process name
Hypotonic solution
Water diffuse [into] cell by osmosis
Cell become [turgid ]
Cell [does not burst ]cuz [cell wall is rigid & strong ]
[Cell turgidity ] cause guard cell swell to allow stomata open for [photosynthesis]
Hypertonic solution
Water diffuse [out] cell by osmosis
Cell become [shrink &flaccid ]ix
7K cuz plasma membrane pulled away from the cell wall - called [Plasmolysis ]
3. Deplasmolysis 让水进回去变回
size
Isotonic solution
Water diffuse [in & out] at the same rate
Cell become [ flaccid ]
Effect on STEM
OF NON-WOODY PLANT
Put DISTILLED WATER (hypotonic solution)里solute 少,外多
- Strip become longer, turgid, curved outwards
17%SUCROSE SOLUTION (isotonic solution)
-the length, shape of strip remain the same
30%SUCROSE SOLUTION (hypertonic solution ) 里solute 多, 外少
-strip become shorter , softer , curved inwards (flaccid )
Effect & application of
osmosis
1. WILITING IN PLANTS 枯了
-excessive fertilisers, dissolve soil water, hypertonic to cell sap of root, water diffuse out, flaccid【肥料太多,里solute多,外少,导致
root give water, root flaccid, 缺水,枯了(wilt)】
2. FOOD PERSERVATION
-salt/sugar solution hypertonic to cell, cell lose water, prevent microorganisms growth [solute&
水少,cell will give water,没水,干了,细菌不会生长】
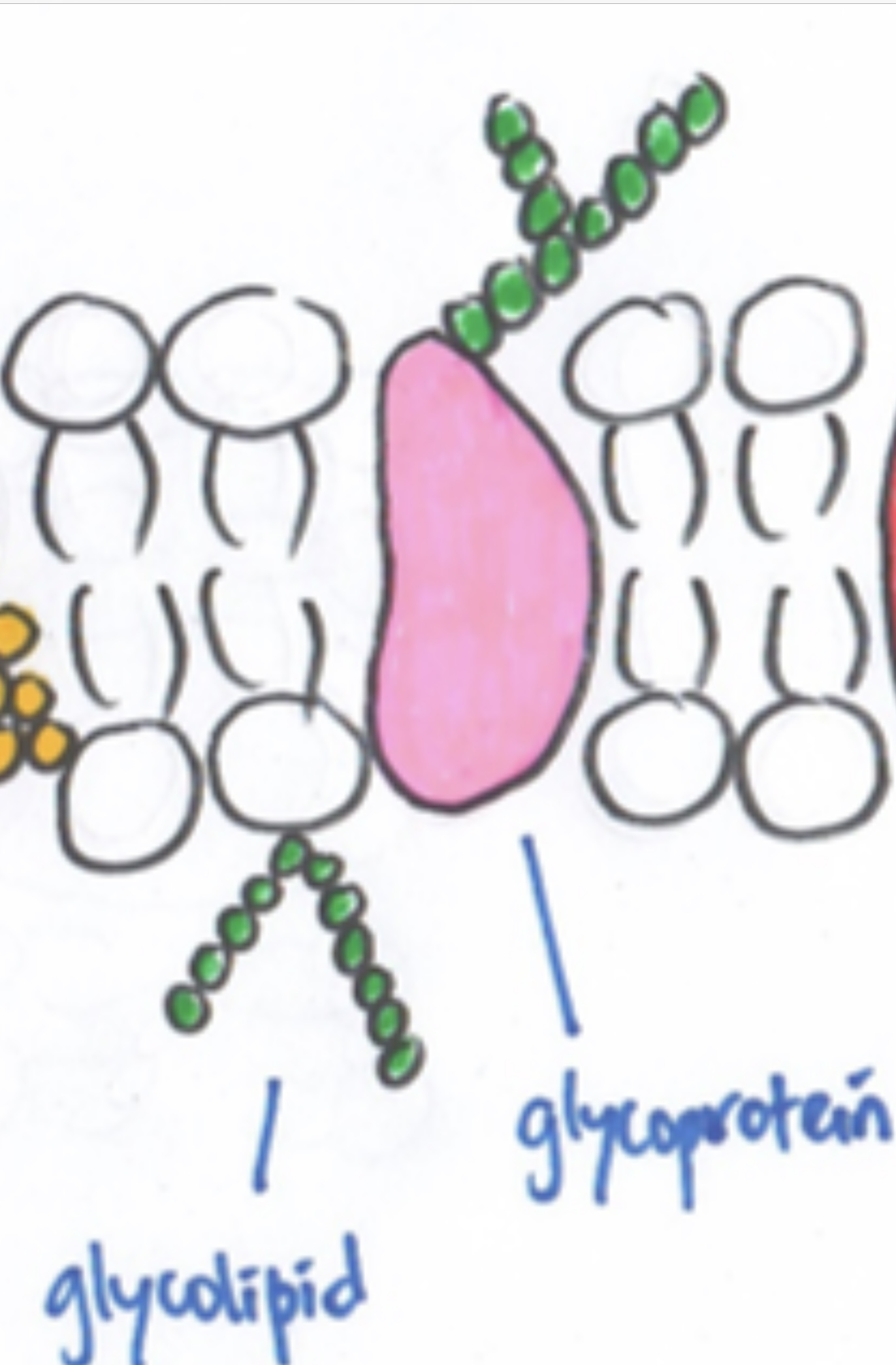
glycolipid , glycoprotein
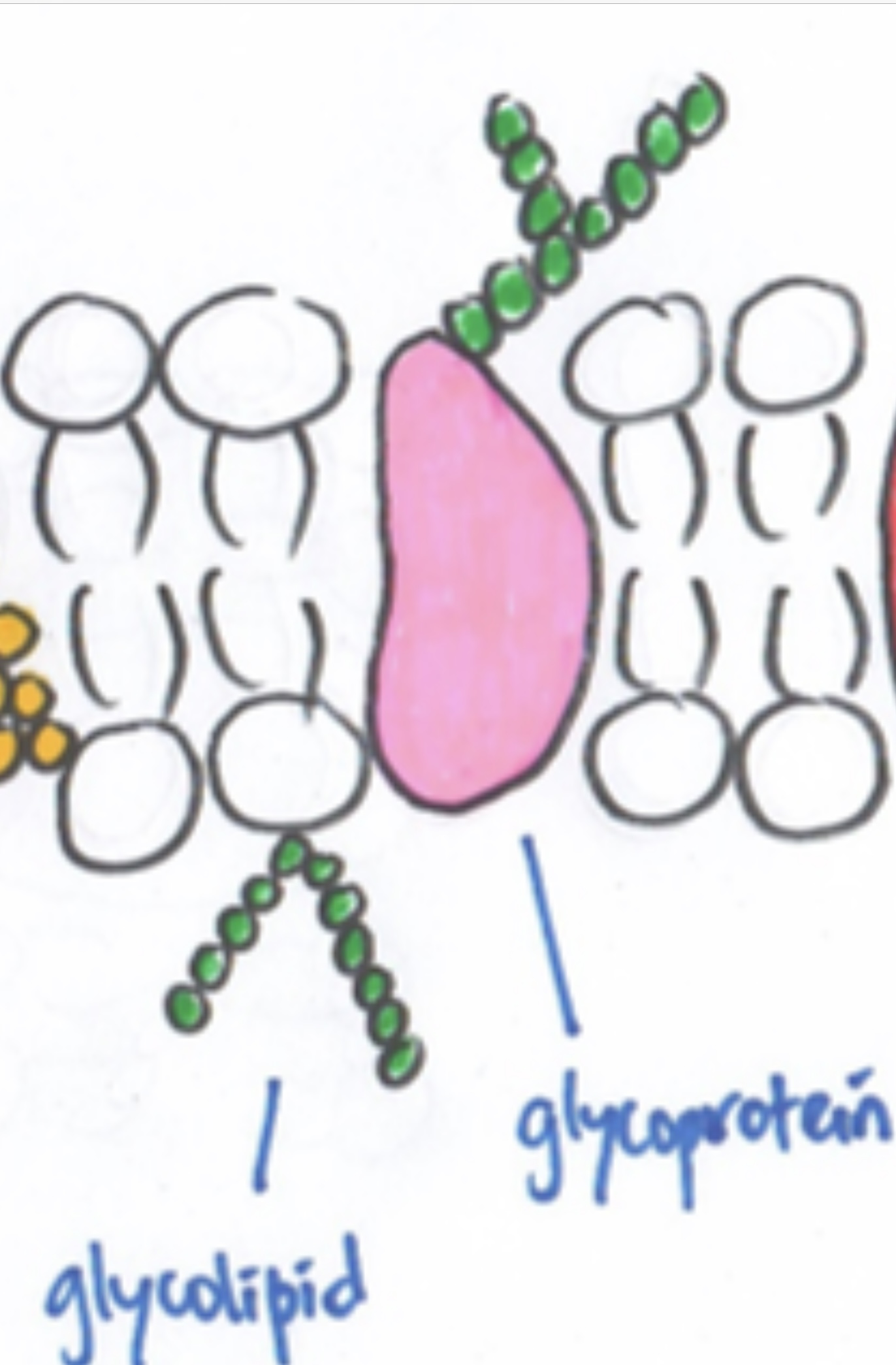
Channel protein
Cholesterol