CH 12 Social Psychology
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
117 Terms
humans depend
on each other
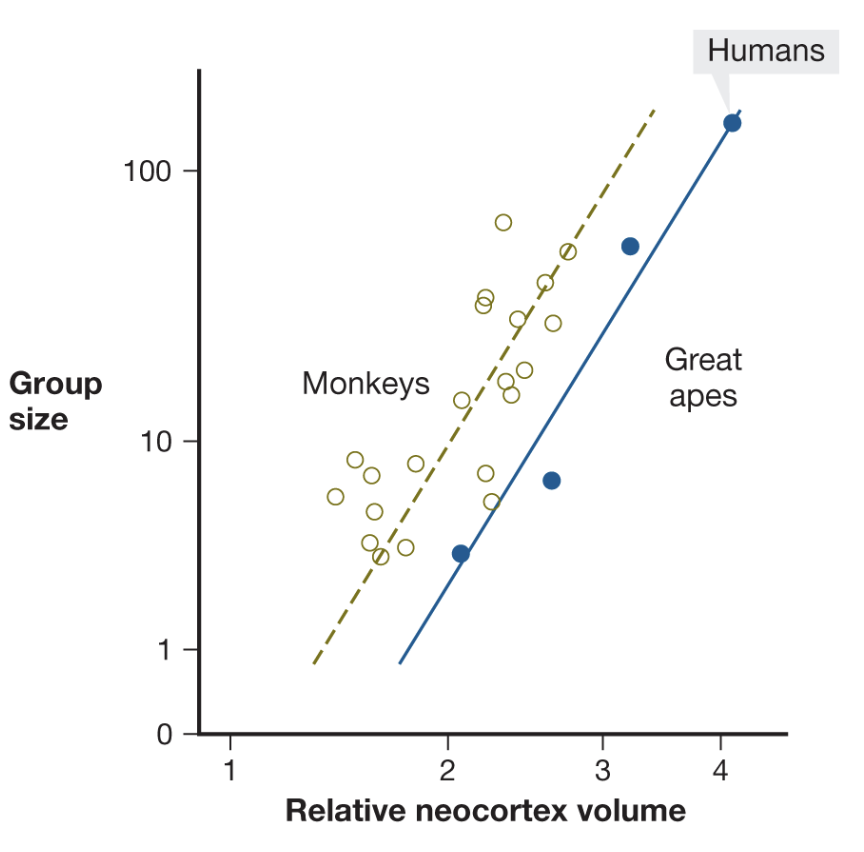
social brain hypothesis
primates have large brains because they live in complex social groups that change over time
being a good group member requires the capacity to understand complex/subtle social rules, recognize what actions might offend others, control desires that could violate group norms
ingroups
groups particular people belong to
outgroups
groups these people do not belong to
groups form when
they have reciprocity and transitivity
ig reciprocal treatment and similar opinions of other people
outgroup homogeneity effect
the tendency to view outgroup members as less varied than ingroup members
positivity bias for ingroup members
“they all look alike” effect with racial groups
social identity theory
the idea that ingroups consist of individuals who perceive themselves to be of the same social category and experience pride through their group membership
ingroup favoritism
the tendency for people to evaluate favorably and privilege members of the ingroup more than the outgroup
part of brain for thinking of other people
medial prefrontal cortex
less active when thinking of members of outgroups
dehumanization
effect of seeing people in outgroup as less human
groups influence
individual behavior
risky shift effect
groups often make riskier decisions than individuals do
group polarization
the process by which initial attitudes from groups become more extreme over time
groupthink
the tendency of a group to make a bad decision in attempt to preserve the group and maintain its cohesiveness; especially likely when the group is under pressure, is facing external threats, or is biased in one direction
prevent groupthink
leaders should avoid expressing strong opinions at beginning of discussions, try to have alternative ideas first
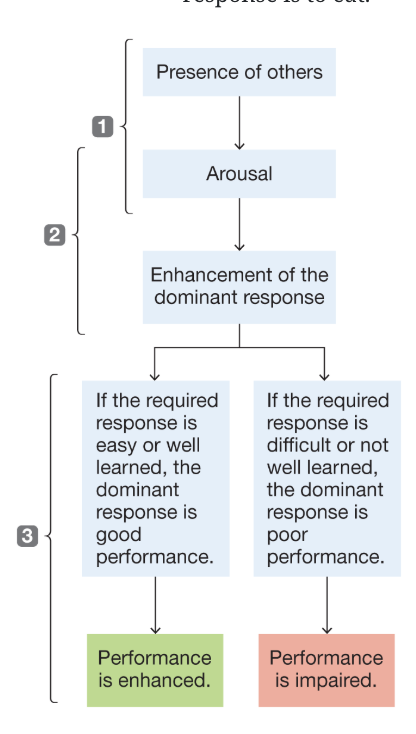
social facilitation
the idea that the presence of others generally enhances performance
social loafing
the tendency for people to work less hard in a group than they would alone
Deinviduation
a state of reduced individuality, reduced self-awareness, and reduced attention to personal standards; may occur when people are part of a group
individuated
to have a sense of self as an individual controlling their own actions
we are more individuated than disinviduated
disindividuation can accelerate
aggression
conformity
the altering of one’s behaviors and opinions to match those of other people or to match people’s expectations
normative influence
the tendency for people to conform to fit into a group
informational influence
the tendency for people to conform when they believe the behavior of others is the correct way to respond
basically looking for social cues on how to respond - what is everyone else doing right now
social norms
expected forms of conduct that influence behavior
autokinetic effect
a perceptual phenomenon in which a stationary point of light appears to move when viewed in a totally dark environment
happens when people have no frame of reference and can’t correct for small eyemovements
people were able to come up with group estimates, and when placed in new groups agreed with the previous group norm
conformity
levels off - about the same effect as a group of 7 and a group of 16
social norms marketing and binge drinking on campus
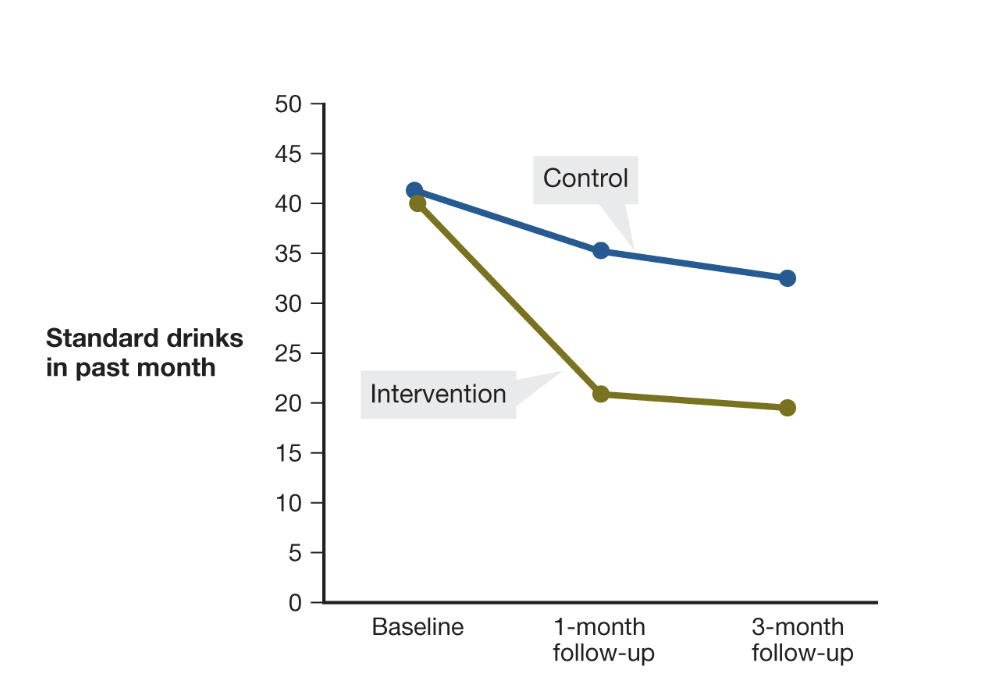
social norms marketing backfired with
nondrinkers and light drinkers
people who drank one drink occasionally were more likely to drink 2-3 if that was considered the norm
obedience
following the orders of a person of authority
Milgram’s experiments
proved that people could be coerced into obedience
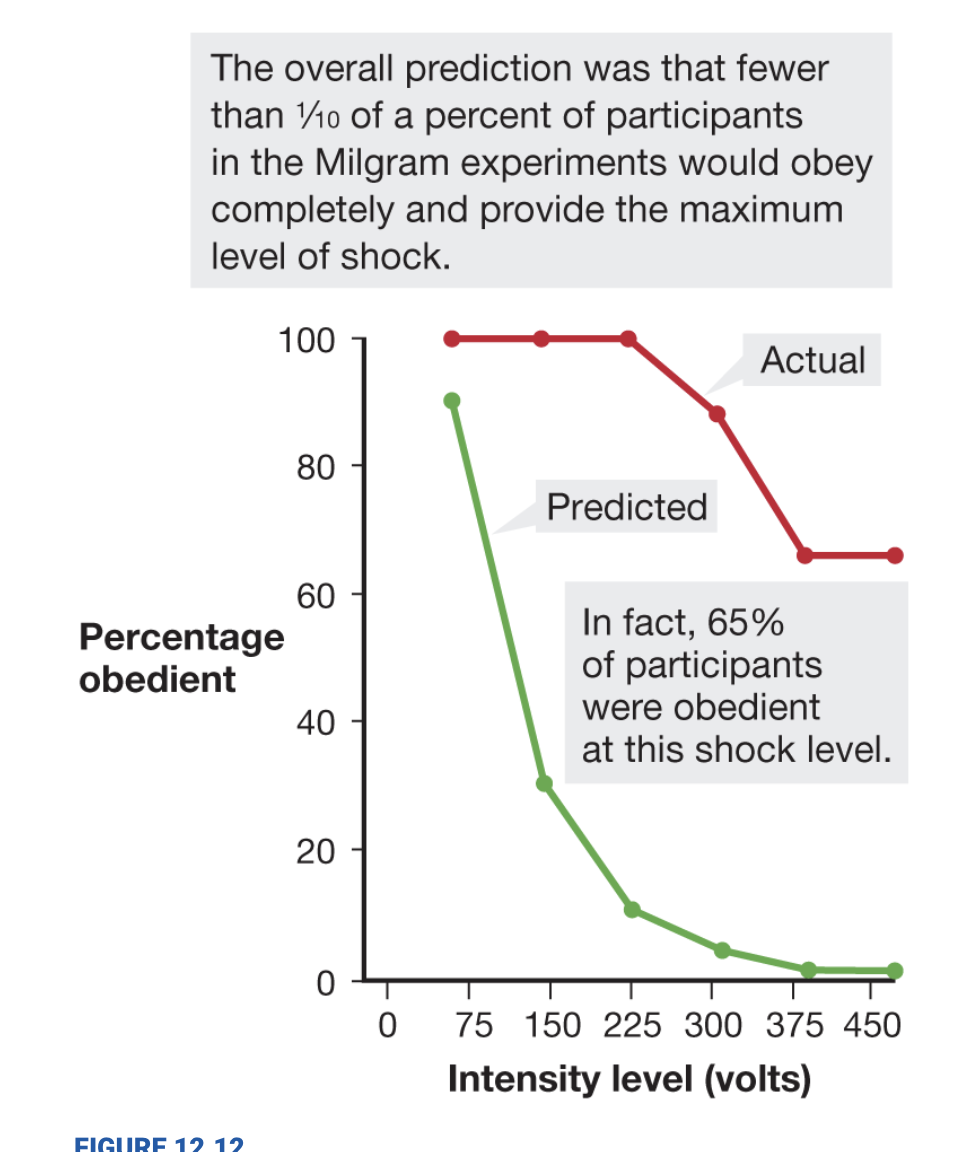
teachers were more likely to shock learners
if they were told they had no choice, if study was conducted at prestigious university, if there was credibility given to experiment
teachers were less likely to shock learners
if teachers could see learner or touch them
people will
rationalize away actions when they can
need to belong can also lead to
altruism and generosity
aggression
behaviors with the intention to harm someone else
agression is more common in
the heat — more crimes occur over the summer
situations inducing negative emotions
can trigger more physical aggression
testosterone
modest correlation with physical aggression but not directly tied to it, more related to social dominance
serotonin
regulates aggression
culture of honor
culture encouraging boys and men to protect their reputation through physical aggression
collaboration can
reduce outgroup bias
superordinate goals, or those that require people to cooperate
reduce hostility
competition can create ____, collaboration can create _____
enemies, friends
not always true depending on situation
prosocial behaviors
actions that benefit others
strengthen relationships
altruism
providing help when needed without any reward for doing so
inclusive fitness
Explanation for altruism that focuses on the adaptive benefits of transmitting genes, such as through kin selection, rather than individual survival
kin selection
seeing family members thrive and supporting their wellbeing so they can develop and genes can thrive
reciprocal helping
the idea that someone might help another person so they can return the favor later
bystander intervention effect
the failure to offer help by those who observe someone in need
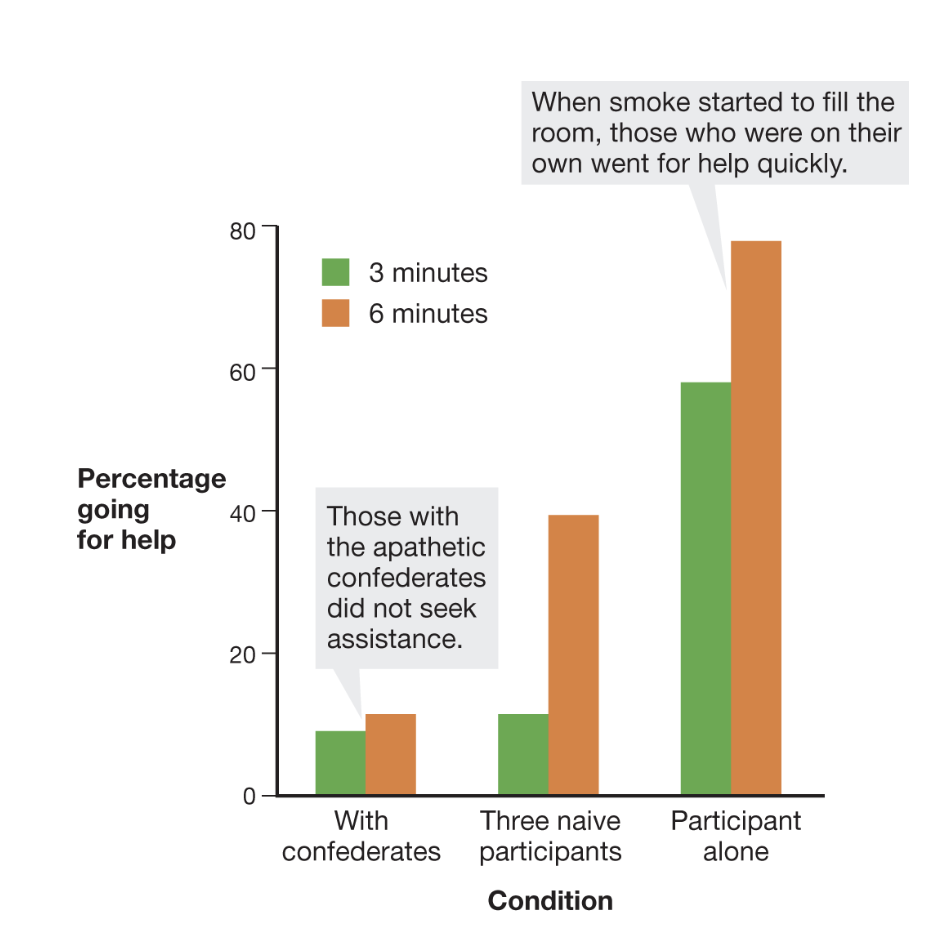
reasons for bystander effect
diffusion of responsibility, social blunders, desire to keep anonymity, harm
diffusion of responsibility
bystanders expect other bystanders to help
harm in helping
people will weigh how much harm they risk to themselves and what benefit they receive by not helping
attitudes
people’s evaluations of other people, objects, or ideas
people develop
negative attitudes more quickly than positive ones
stems from sense of danger
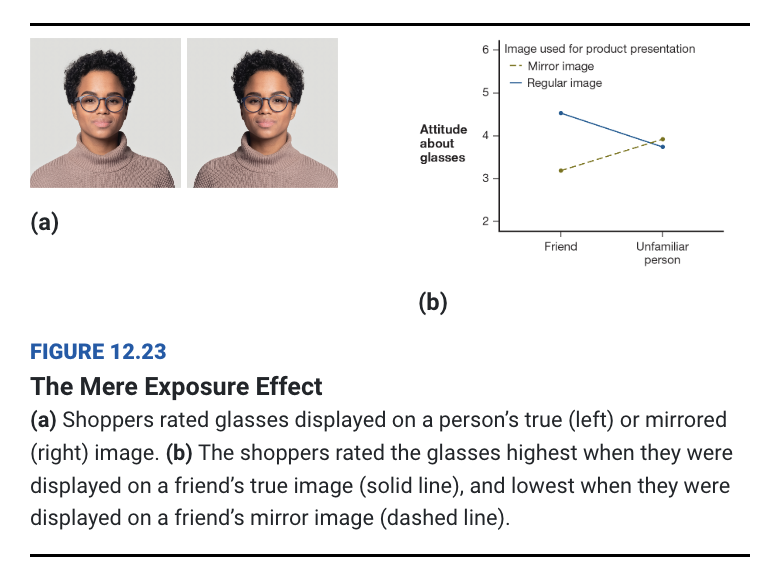
mere exposure effect
greater exposure to a stimulus leads to greater liking of it
people prefer
seeing mirrored versions of themselves bc that’s what they see in the mirror
attitudes will remain stable and predict behavior
when they are stronger, more specific, and personally relevant/related to personal experience
attitude accessibility
the ease or difficulty a person has retrieving an attitude from memory
explicit attitudes
attitudes you can report to other people
implicit attitudes
attitudes influencing feelings and behavior at an unconscious level
implicit attitudes work like
implicit memories - quicker to access and make it easy to perform action, such as buying a product if you’ve already seen a celebrity use it
implicit association test
found that people who have an implicit association between female and bad would have an easier time categorizing words they think are female or bad than someone with an association between female and good
controversial but sometimes meaningful test
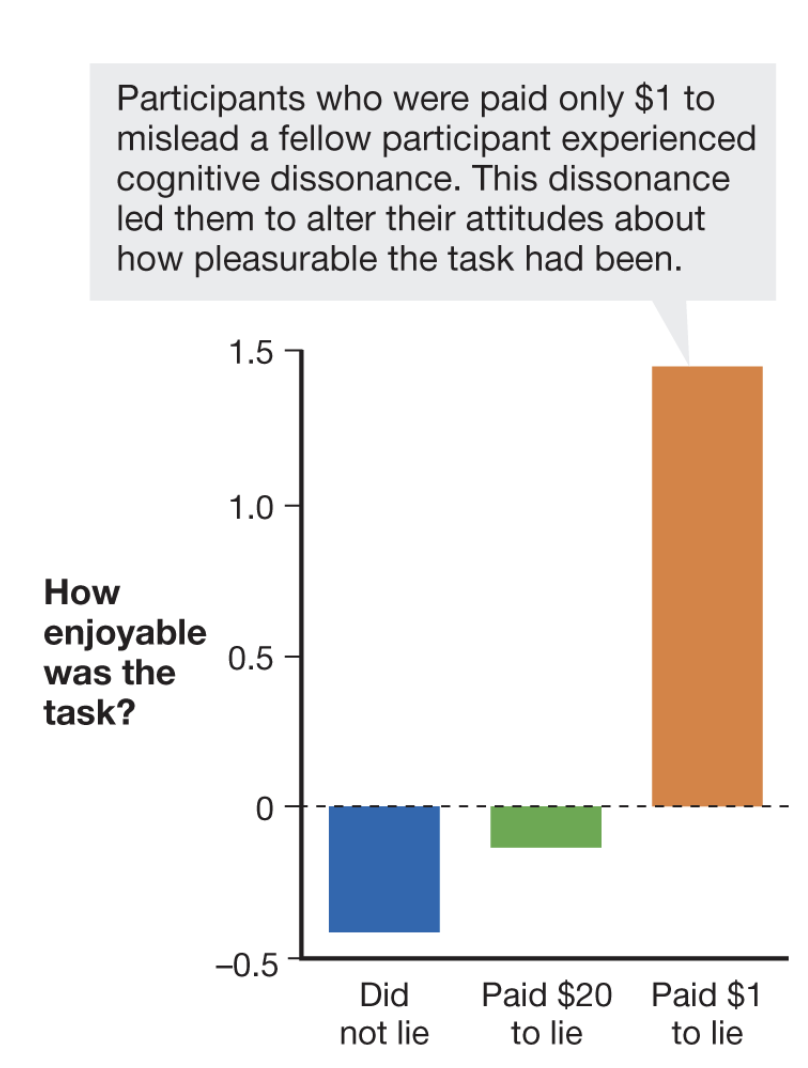
insufficient justification
people like to consider themselves honest so they may change their attitudes to what they say
people who were paid $1 liked the test more because they were insufficiently justified - why are you lying about $1
people experience dissonance when
they put themselves through pain, embarrassment, or discomfort to join a group
post decisional dissonance
motivates the person to focus on the chosen choice’s positive aspects and the other choice’s negative aspects
someone can have positive opinions about two schools when they apply to college, but will experience this when they choose one
persuasion
the active and conscious effort to change an attitude or behavior, usually with a message of some kind
persuasiveness of a message
source, content, and receiver
where it’s from, what it is, and who receives it - ideally someone similar to themselves
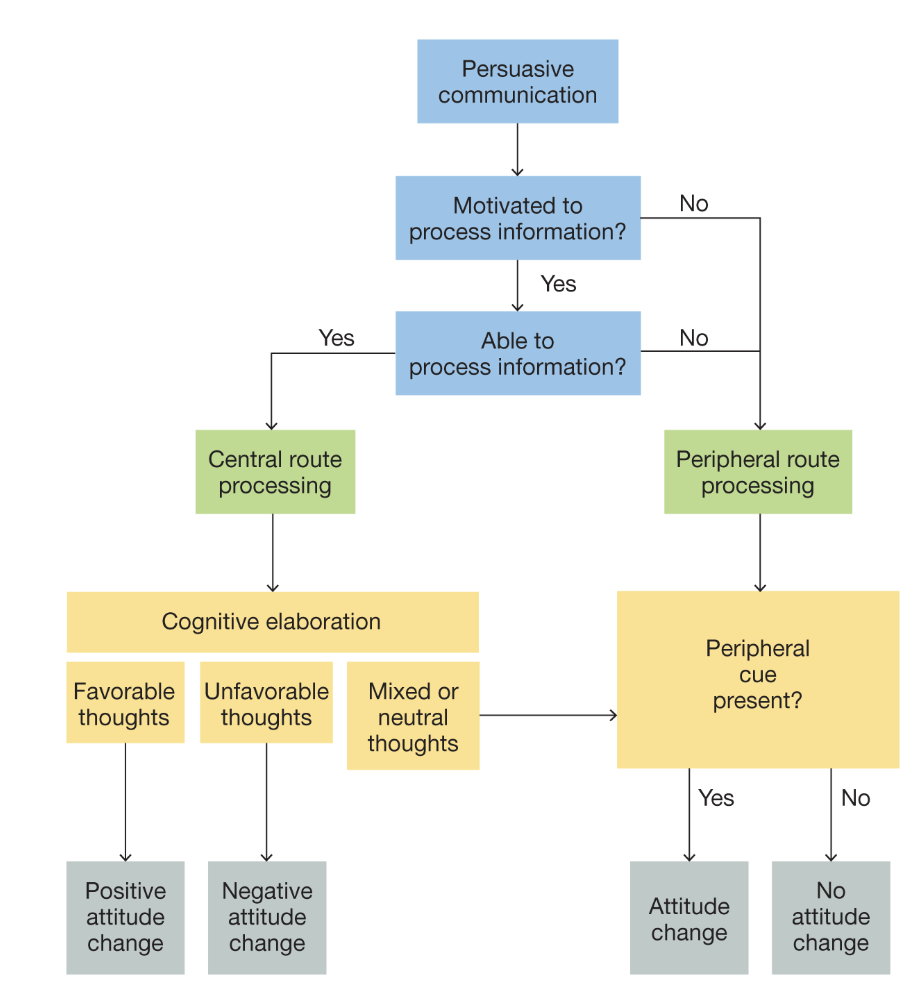
elaboration likelihood model
the idea that persuasive messages can change attitude in 2 ways:
via peripheral route
via central route
central route
when people are motivated and able to process information
paying attention to arguments, information, using rational cognitive processes
strong, lasting attitudes people will defend
peripheral route
when people minimally process a message, leading to more impulsive action
cues include attractiveness/status of source
elaboration likelihood model
compliance
the tendency to agree to do things requested by others
compliance influenced by
buttering up, having a reason for request, foot in door, door in the face, lowballing
foot in the door
if you agree to a small request now, you are more likely to comply with a large request later
door in the face
if you refuse a huge request first, you are more likely to comply with a smaller request
lowballing
when you agree to buy a product for a certain price, you are more likely to comply with a request right after to pay more for the product
faces are important
for first impressions
nonverbal behavior
body language, or the facial expressions, gestures, mannerisms and movements by which one communicates with others
thin slices of behavior
people can make accurate judgements based on only a few seconds of observation
attributions
people’s explanations for why events or actions occur
personal attributions
explanations of people’s behaviors based on internal characteristics, such as abilities, traits, moods or efforts
situational attributions
explanations of people’s behavior on external events, such as weather, luck, accidents, or people’s actions
fundamental attribution error
in explaining other people’s behavior, the tendency to overemphasize personality traits and underemphasize environmental factors
actor/observer discrepancy
the tendency to focus on situations to explain one’s own behavior but focus on dispositions to explain others’ behavior
from a psychological standpoint stereotypes are
neutral and meant to produce efficiency, but can be positive or negative in content
occur from limits in mental resources
illusory correlations
seeing relationships that do not exist because of noticing only information that confirms stereotypes
subtyping
when people who encounter someone who does not fit a stereotype and places them in a special category/as an exception
prejudice
negative feelings, opinions, or beliefs associated with a stereotype
discrimination
the differential treatment of people based on their group membership
prejudice, discrimination, stereotypes
negative Affect, Biased Behavior, Cognitive thoughts/beliefs (ABC)
shooter bias
participants more likely to assume objects held by Black people are guns or weapons even when they’re not
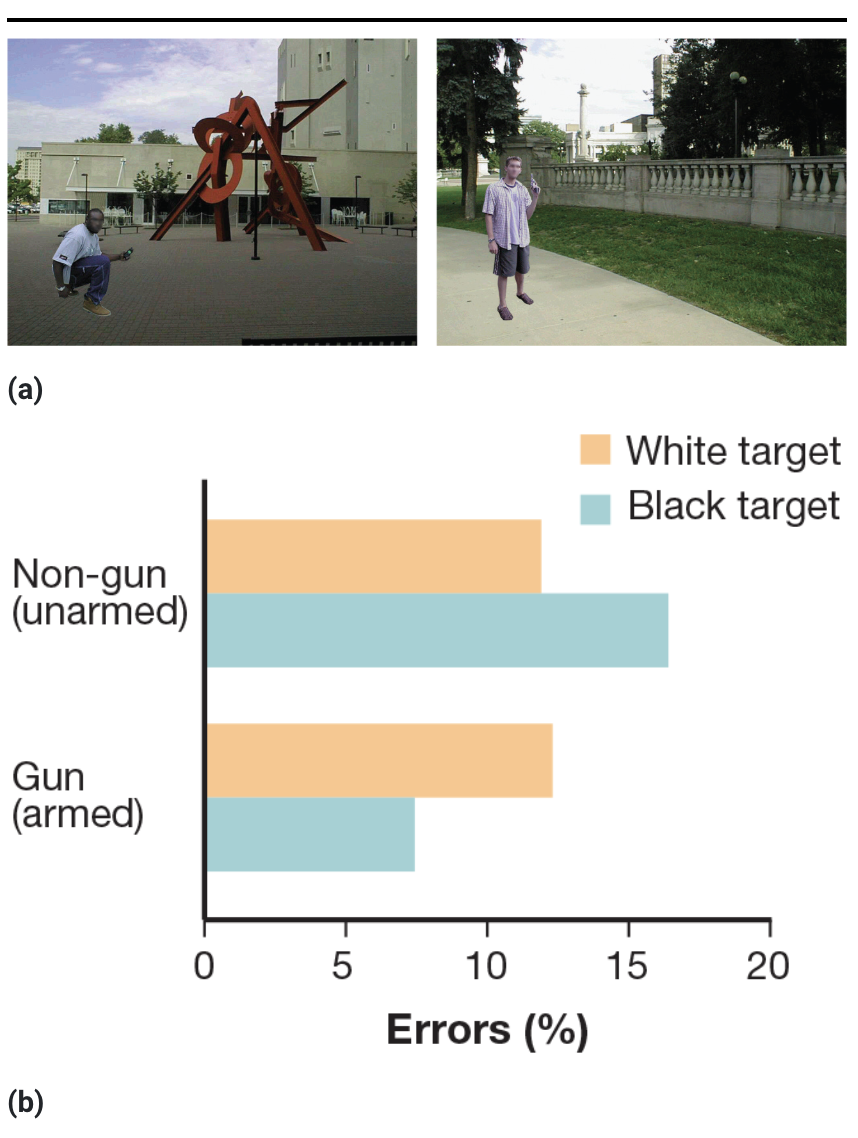
modern racism
subtle forms of prejudice that exist alongside the rejection of racist beliefs
belief that discrimination is no longer a serious problem and that minority groups demand too much change to traditional societal values
indirectly endorsing actions/policies that have the same effect as overt discrimination without labeling them as such
stereotype threat
fear or concern about confirming negative stereotypes related to one’s own group, which in turn impairs performance on a task
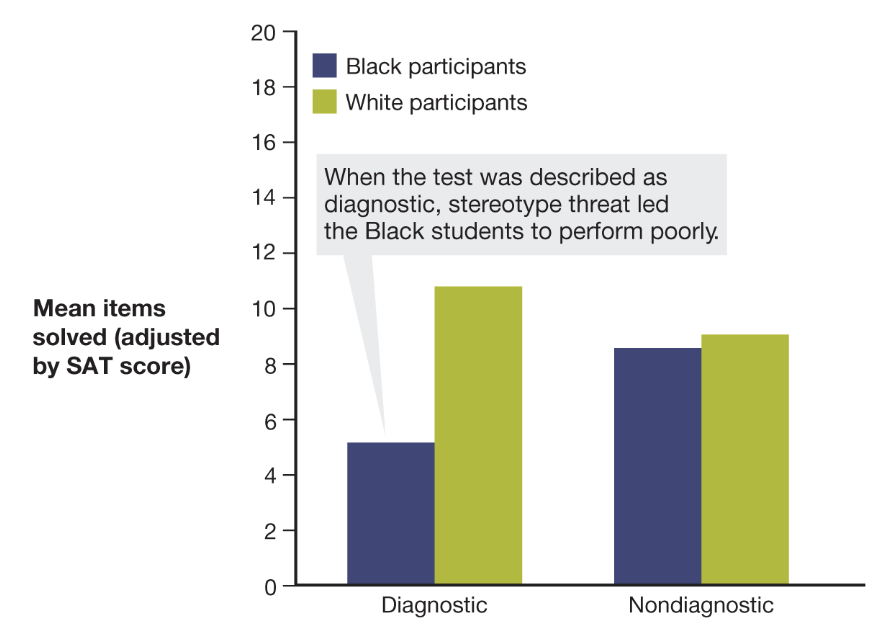
when people are primed about stereotypes that are related to them
they tend to perform in those manners, good or bad
stereotype threat is counteracted when
people are warned about it
use reframing and self labeling
perspective taking
actively contemplating the psychological experiences of other people
reduces racial bias, stereotyping
perspective giving
when people share their experiences being targeted by discrimination
perspective and attitude changes
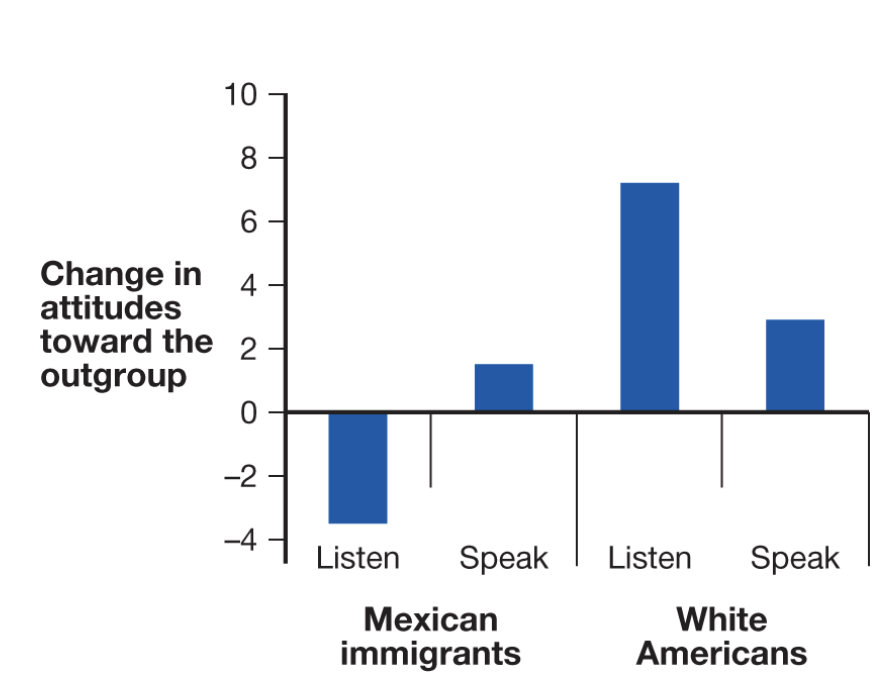
the more people come into contact
the more likely they are to be friends