chapter 24- microbial diseases of the respiratory system
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:13 PM on 5/4/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
1
New cards
what are the 4 structures found in the upper respiratory system
nose
pharynx
middle ear
eustachian tubes
pharynx
middle ear
eustachian tubes
2
New cards
… and … protect mucosal surfaces in the upper respiratory system
salvia and tears
3
New cards
what are the 4 structures found in the lower respiratory system
larynx
trachea
bronchial tubes
alveoli
trachea
bronchial tubes
alveoli
4
New cards
… moves particles toward the throat via ciliary action
ciliary escalator
5
New cards
… destroy microorganisms in the lungs
alveolar macrophages
6
New cards
… protects mucosal surfaces in the lower respiratory system
respiratory mucus
7
New cards
what is the medical term for sore throat
Pharyngitis
8
New cards
what are the three microbial disease attaining to the lower respiratory system
bronchitis
bronchiolitis
pneumonia
bronchiolitis
pneumonia
9
New cards
for the common cold there are over … different viruses identified
200
10
New cards
what is the main type of virus associated with the common cold
rhinovirus
11
New cards
rhinoviruses thrive in temperatures … than body temperature
lower
12
New cards
what are the two modes of transport for influenza virus
droplet
indirect contact
indirect contact
13
New cards
what are the 4 main symptoms of influenza flu
chills
fever
headache
muscle aches
fever
headache
muscle aches
14
New cards
annual deaths in the United States is usually between … to …. for the influenza flu
3,000 to 50,000
15
New cards
what are the 3 main strains of influenza flu
avian
swine
mammalian
swine
mammalian
16
New cards
… spike binds to the sialic acid of the epithetic cells
hemagglutinin
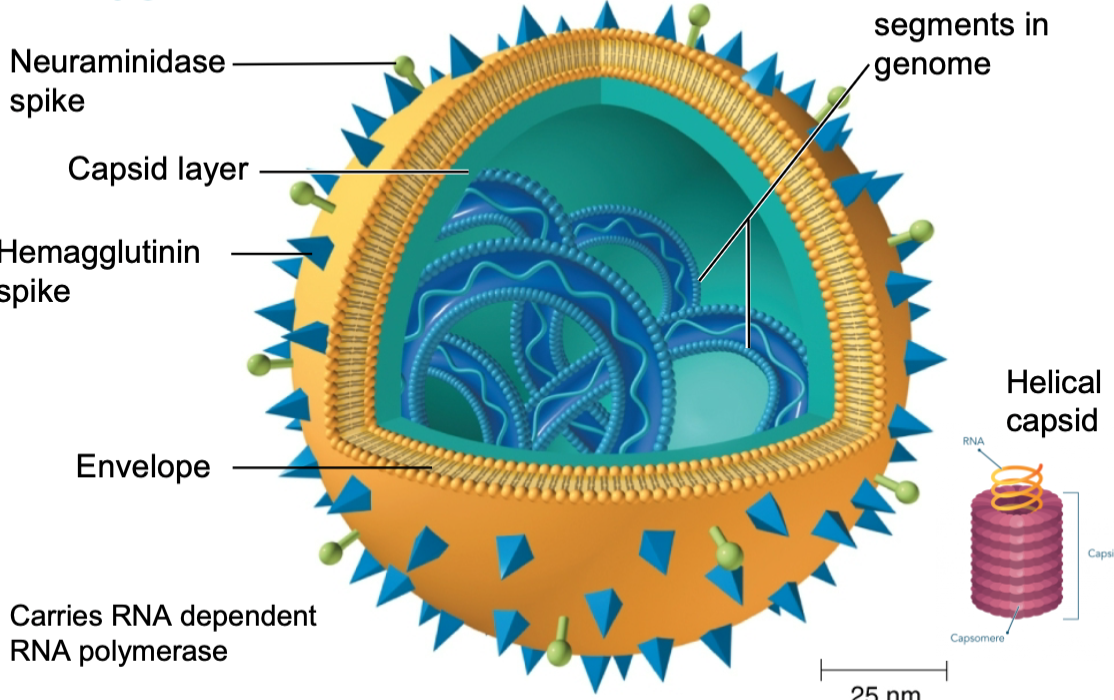
17
New cards
… spike will then remove sialic acid when the virus leaves the cell
neuraminidase
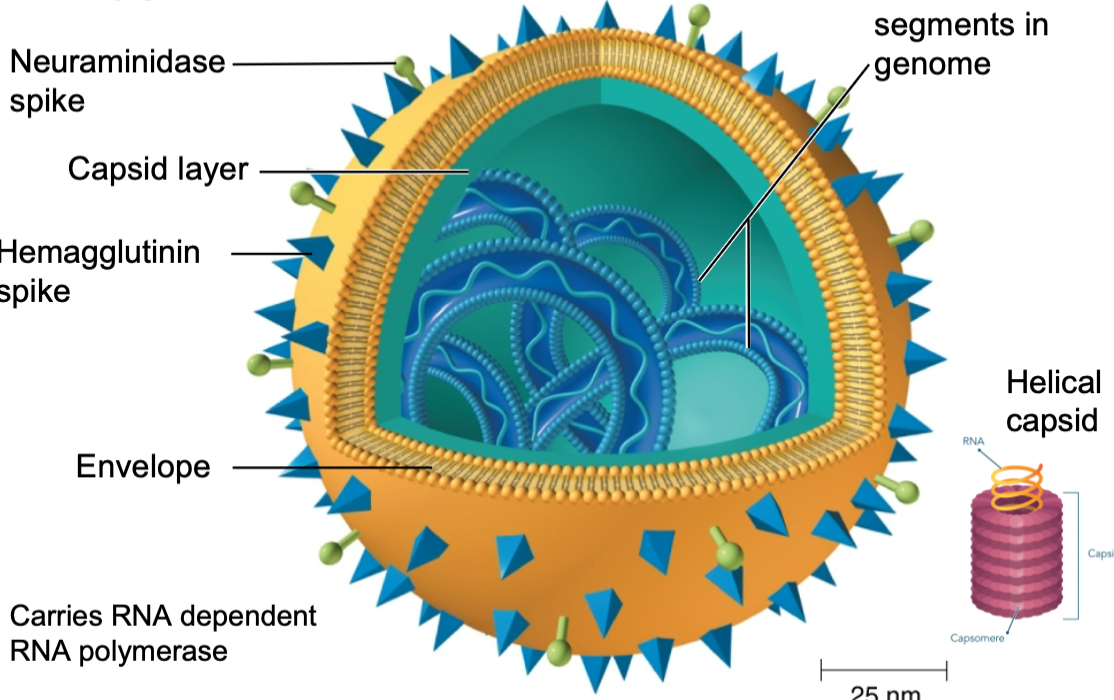
18
New cards
influenza virus has … genomic RNA segments
8
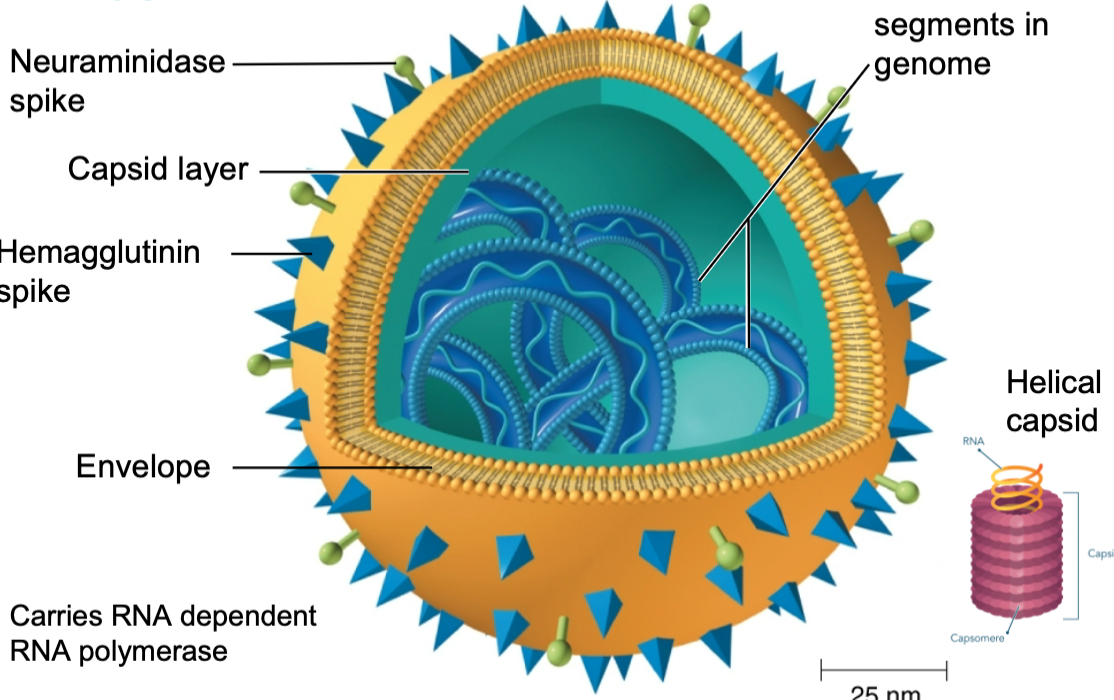
19
New cards
each RNA virus has a … surrounding it
capsid
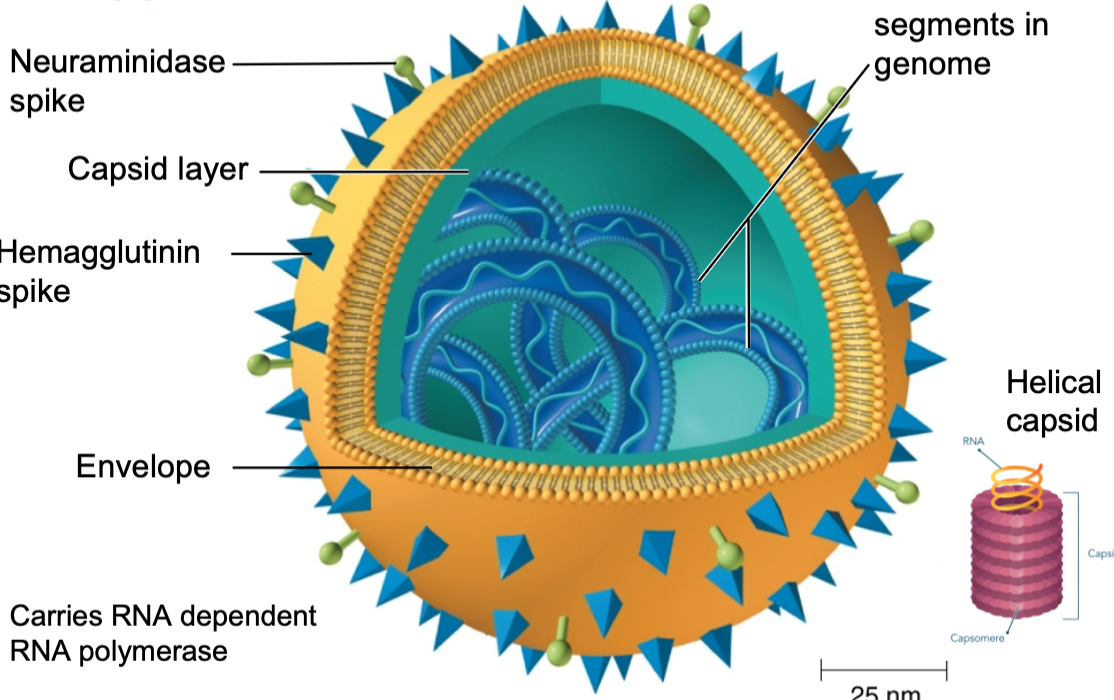
20
New cards
(SHORT ANSWER QUESTION) explain the influenza virus pathway
1. adhesion via hemagglutinin spike protein to sialic acid
2. endocytosis
3. fusion and un-coating
4. RNA dependent RNA polymerase assists with replication to produce mRNA and vRNA
5. protein synthesis
6. assembly
7. budding
8. release, neuraminidase spike protein will remove sialic acid on way out
21
New cards
antigenic drift is minor … changes
antigenic
22
New cards
antigenic drift allows the virus to elude … host Immunity but antigenic shifts changes are great enough to evade … immunity
some, most
23
New cards
an example of antigenic drift in the influenza virus
minor antigenic changes in HA and NA
24
New cards
an example of antigenic shifts in the influenza virus
reassortment of the eight RNA segments
25
New cards
what are the three branches of Orthomyxoviridae
influenza virus a
influenza virus b
influenza virus c
influenza virus b
influenza virus c
26
New cards
influenza a host
wide range of hosts
27
New cards
influenza b host
humans only
28
New cards
influenza c host
humans and swine
29
New cards
which subtype of influenza is the mildest
influenza c
30
New cards
influenza reservoir
wild water birds
domestic chickens
domestic chickens
31
New cards
swine is known to be an …
antigenic mixer
32
New cards
antigenic … is the cause of pandemic strains
shift
33
New cards
antigenic … is not good for vaccines as they are regularly unanticipated
shift
34
New cards
what is the one subtype of influenza virus we should know
H1N1
35
New cards
… pandemics of influenza normally occur every century
3
36
New cards
the influenza vaccine is known to be a … vaccine (for the most important strains)
multivalent
37
New cards
composition of the influenza vaccine is determined annually by the..
identification of circulating viruses
38
New cards
name 5 preventions for the spreading of influenza virus
wash your hands
wear a face mask/ respirator
wear a nanomask
clean surfaces frequently
cook your chicken and eggs properly
wear a face mask/ respirator
wear a nanomask
clean surfaces frequently
cook your chicken and eggs properly
39
New cards
what bacteria causes tuberculosis
__mycobacterium tuberculosis__
40
New cards
__mycobacterium tuberculosis__ is … (two morphology characters)
acid fast
rod shape
rod shape
41
New cards
mycobacterium tuberculosis is an obligate …
aerobe
42
New cards
…-hour generation time
20
43
New cards
what in the cell wall of mycobacterium tuberculosis makes it resistant to drying and antimicrobials
lipids
44
New cards
what is used for treatment primarily for tuberculosis
antibiotics
45
New cards
what is the skin test called for tuberculosis
Tuberculin
46
New cards
how does the tuberculin skin test work
t-cells react with purified protein derivative from TB bacterium
47
New cards
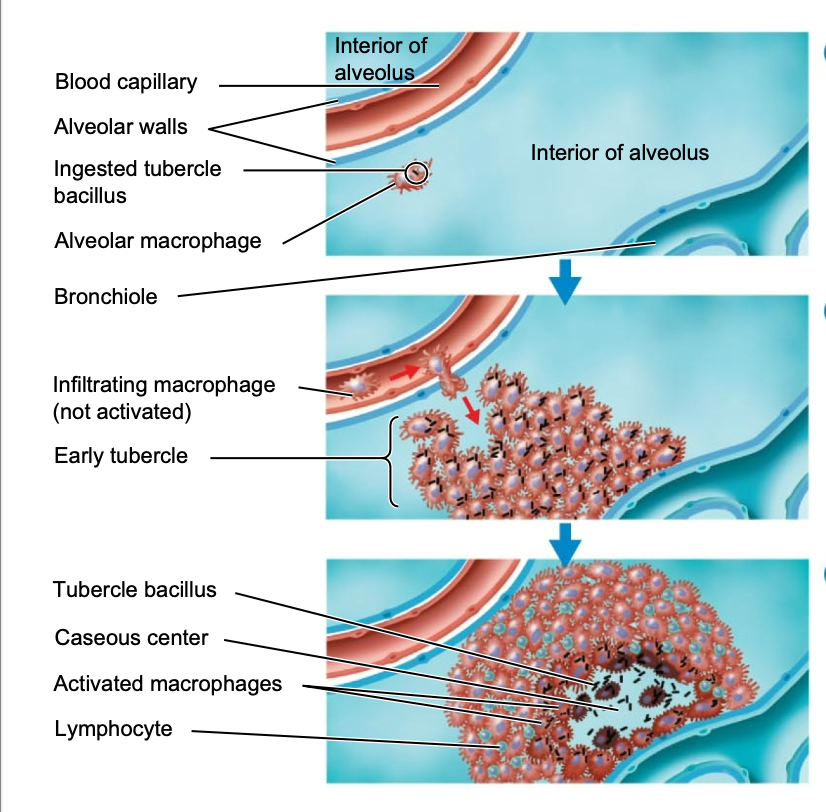
tubercle bacilli that reach the alveoli of the lung are then ingested by …
macrophages
48
New cards
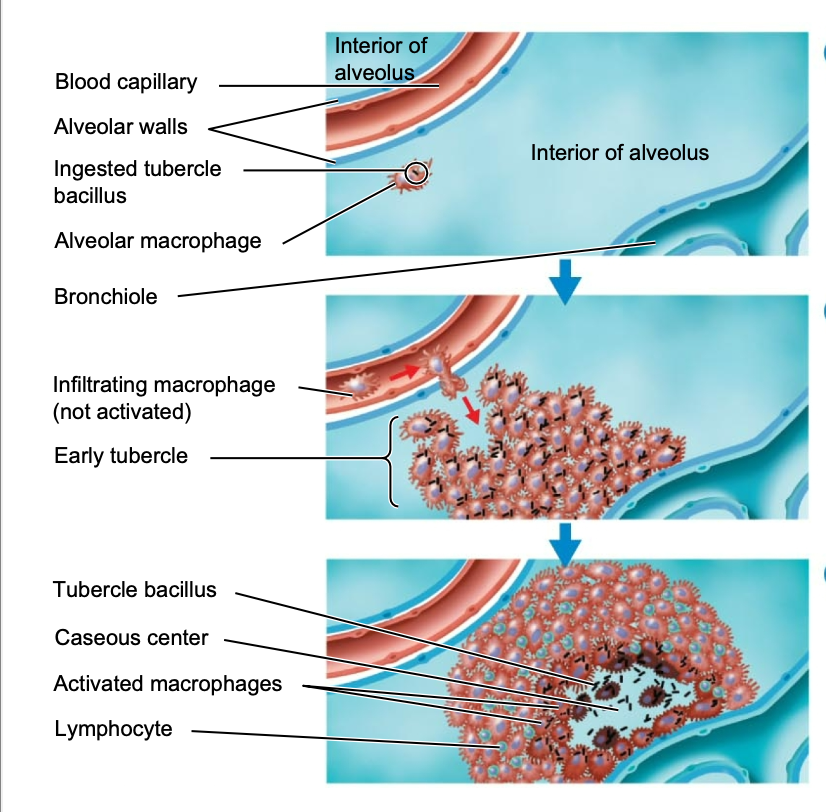
… in the cell wall of the macrophage stimulates an inflammatory response
mycolic acid
49
New cards
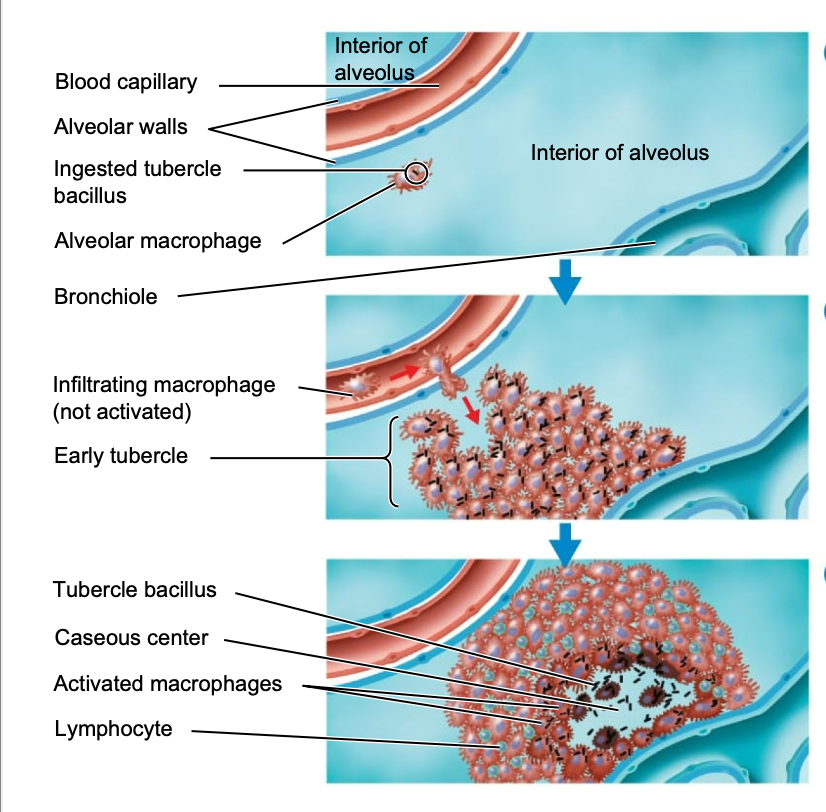
additional macrophages and other defensive cells respond to the area which form a surrounding layer, and in turn, form an early…
tubercle
50
New cards
after a while the tubercles will heal and become …
calcified
51
New cards
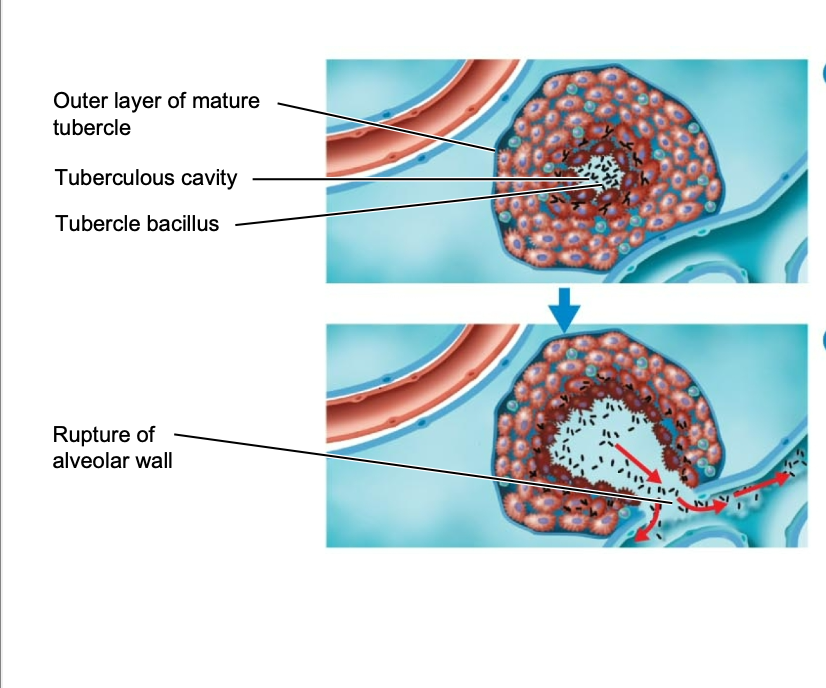
what is this calcified tubercle called
Ghon’s complex
52
New cards
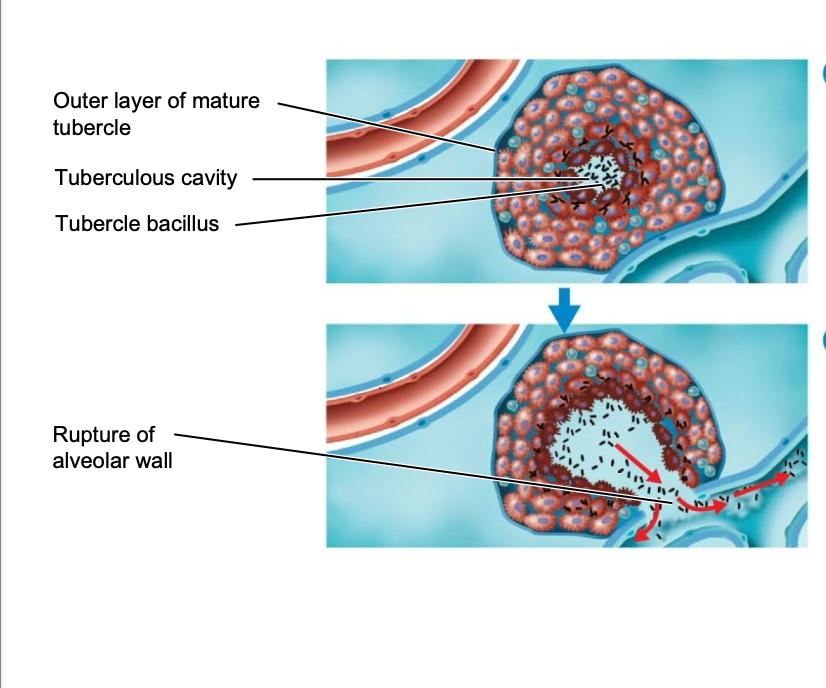
eventually the tubercle will break down, releasing … into the lungs, cardiovascular and lymphatic system
bacteria
53
New cards
military tuberculosis means…
disseminated infection
54
New cards
what is meant by latent TB
where the tubercle bacilli remain dormant and serve as a basis for later reactivation of the disease