CVA ch.2: origin of chordates
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
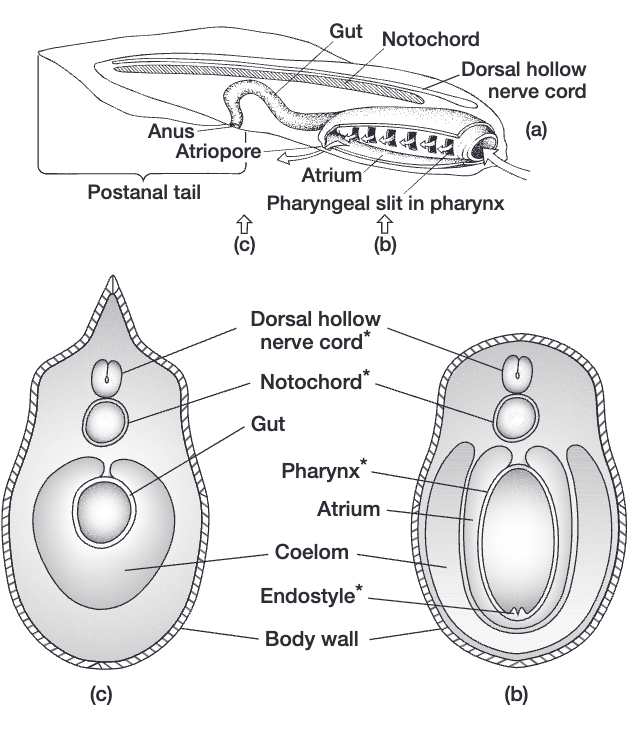
chordate characteristics (synapomorphies)
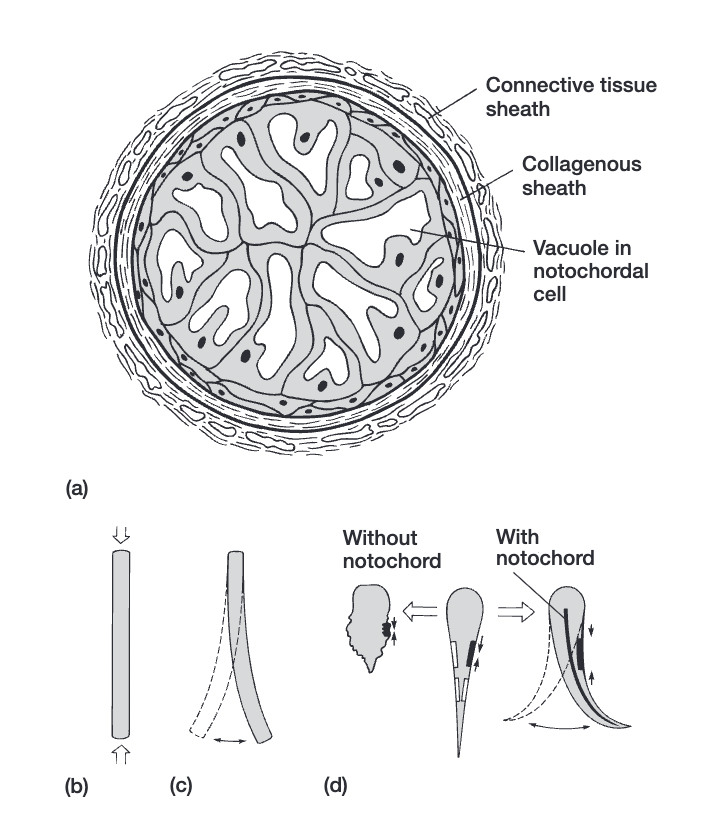
notochord (mesoderm)
pharyngeal slits (endoderm)
endostyle/thyroid gland (endoderm)
dorsal hollow nerve cord (ectoderm)
post anal tail and myomeres (mesoderm)
notochord (chordate synapomorphy)
mesoderm
provides scaffolding, above gastrointestinal tract
allows animal to flex it body left and right
all triploblastic animals have this in some point in their life history
in humans, it’s a gel-filled pad remnant in vertebral disk (nucleus pulposus)
mainly replaced by the vertebral column
hydrostatic organ w/ elastic properties

pharyngeal slits (chordate synapomorphy)
endoderm
slits in throat region that used to help us feed (suspension feeding), had mucus and cilia
helped early chordates filter feed
first formed as pharyngeal pouches along throat area
closed up more to form slits
in more derived vertebrate groups, goes on to form other things
endostyle/thyroid gland (chordate synapomorphy)
endoderm
grove that forms in bottom of the mouth/upper area of throat region depending on the animal
lined with cilia/mucus
young lamprey have endostyle, adult ones have thyroid
in our tracheal region, butterfly shaped soft tissue that secretes lots of hormones
dorsal hollow nerve chord
ectoderm
dorsal relative to GI tract (on top of it)
nerve cord is hollow, a lot quicker at propagating action potentials
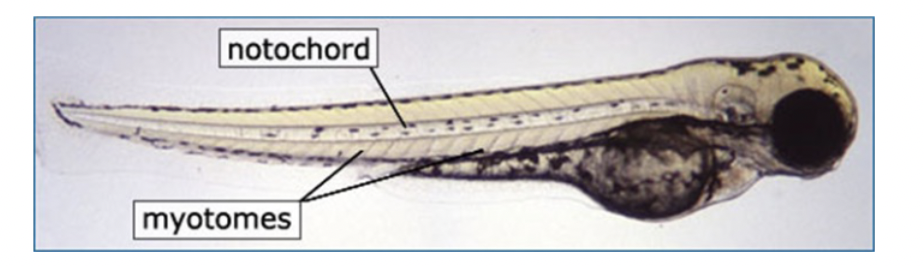
post anal tail + myomeres (chordate synapomorphy)
posterior elongation of the body extending beyond the anus
myotomes= cuts of muscle, delineate dif sections of muscle
myomeres= actual muscle bt each of the segments
myomeres/myotomes derived from mesoderm
chordates
“string + gut”?
541 mya
5 main characteristics
fluid filled internal body cavity called coelom
3 types:
urochordates (tail string gut)- tuncates/”sea squirts”
30-35 sp,
cephalochordates (head string gut)- amphoxi/lancets
2,000 sp
vertebrates (“verte”= articulations?)- fishes/amphibians/reptiles/mammals
66,000 sp
urochordates + cephalochordates are technically invertebrates
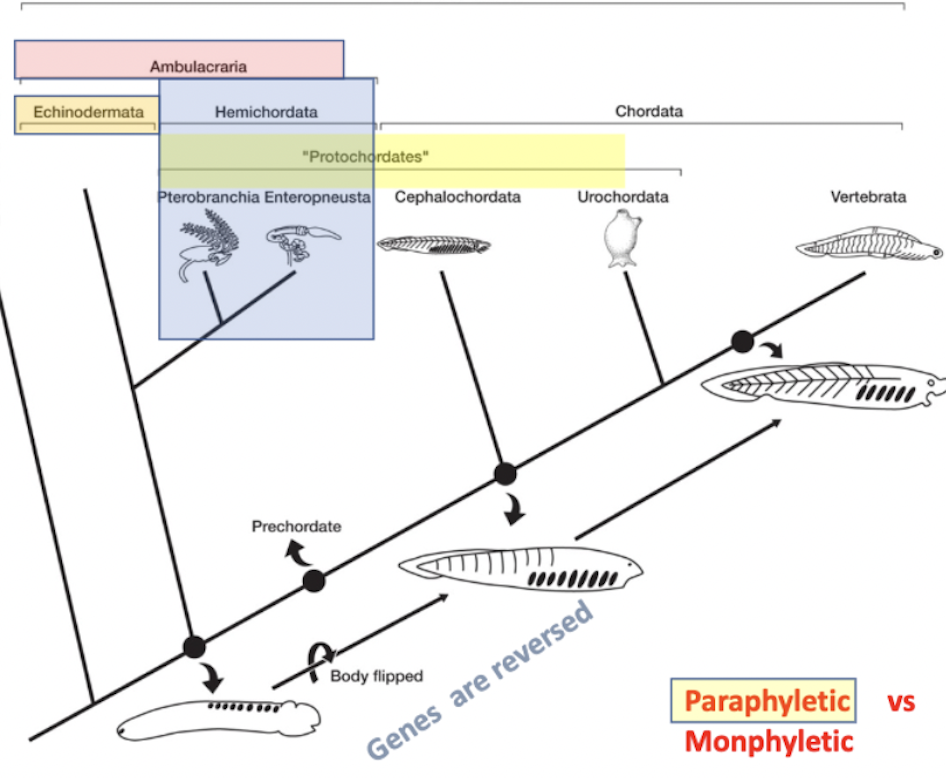
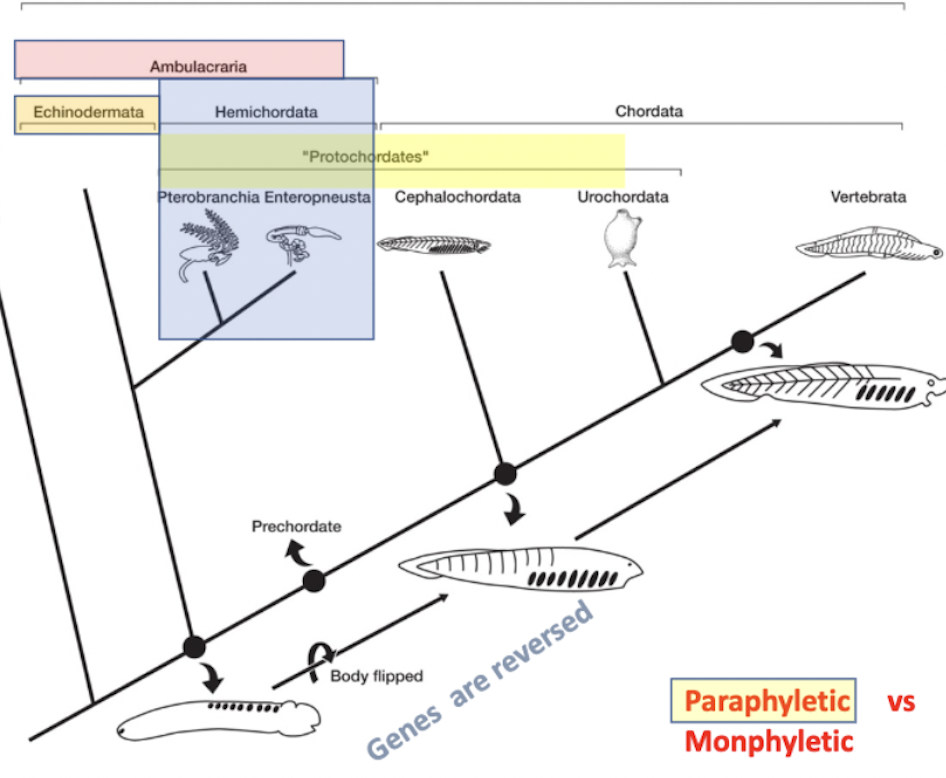
ambulacraria
deuterostome→ _______ → echinodermata + hemichordata
sister to chordata
sea stars + hemichordates
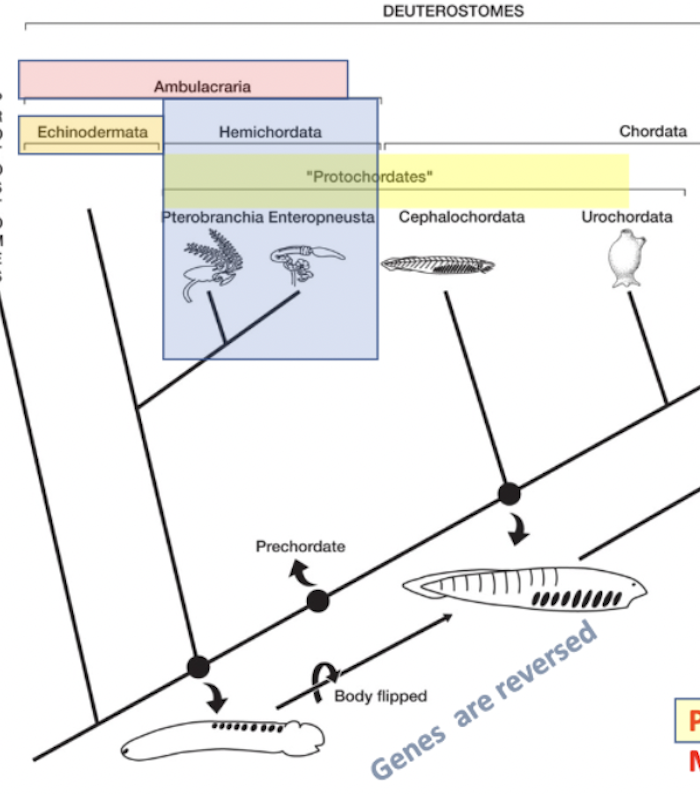
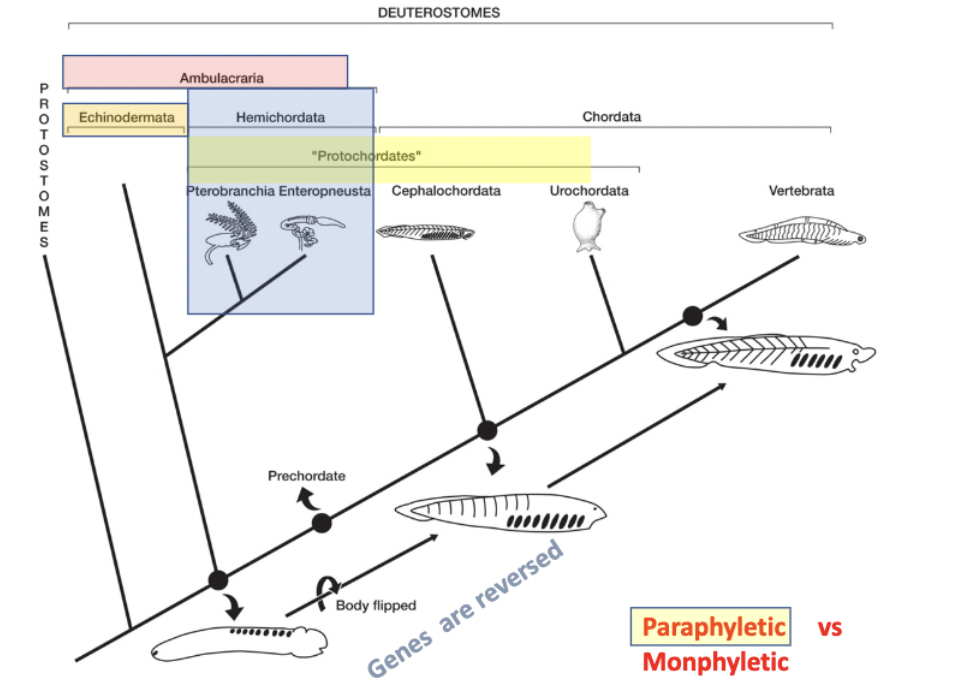
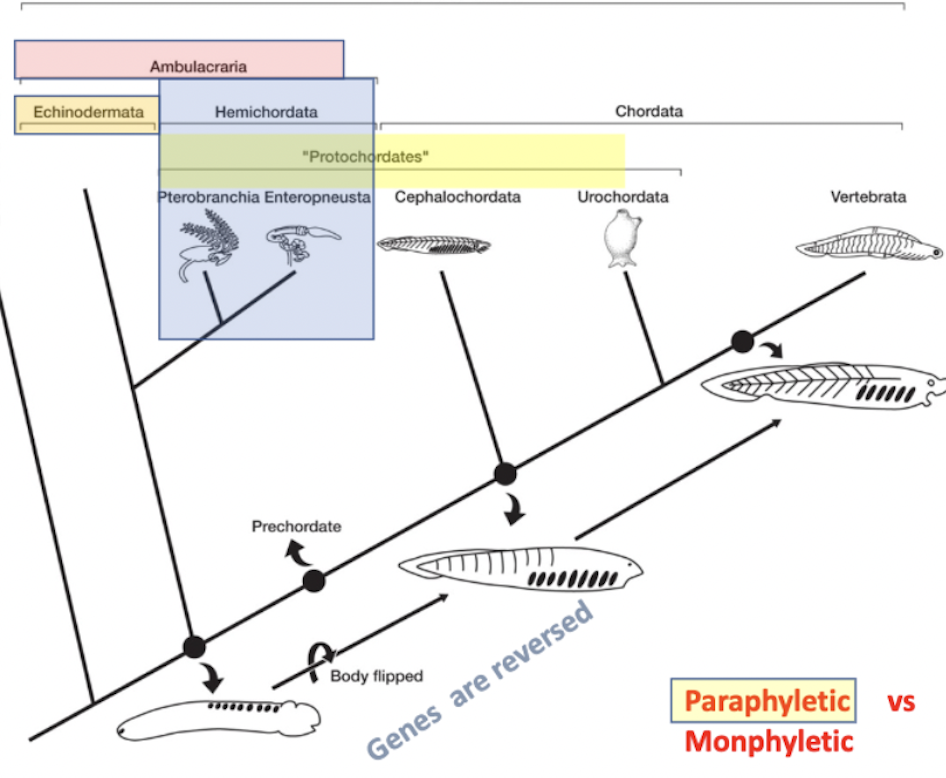
protochordates
“first chordates”
paraphyletic group- not looking at a mrca and all of its descendants, just some of them
leaves out vertebra and echinodermata
consists of:
hemichordata: pterobranchia + enteropneusta
chordata (only 2/3 lineages, actual chordates): cephalochordata + urochordata
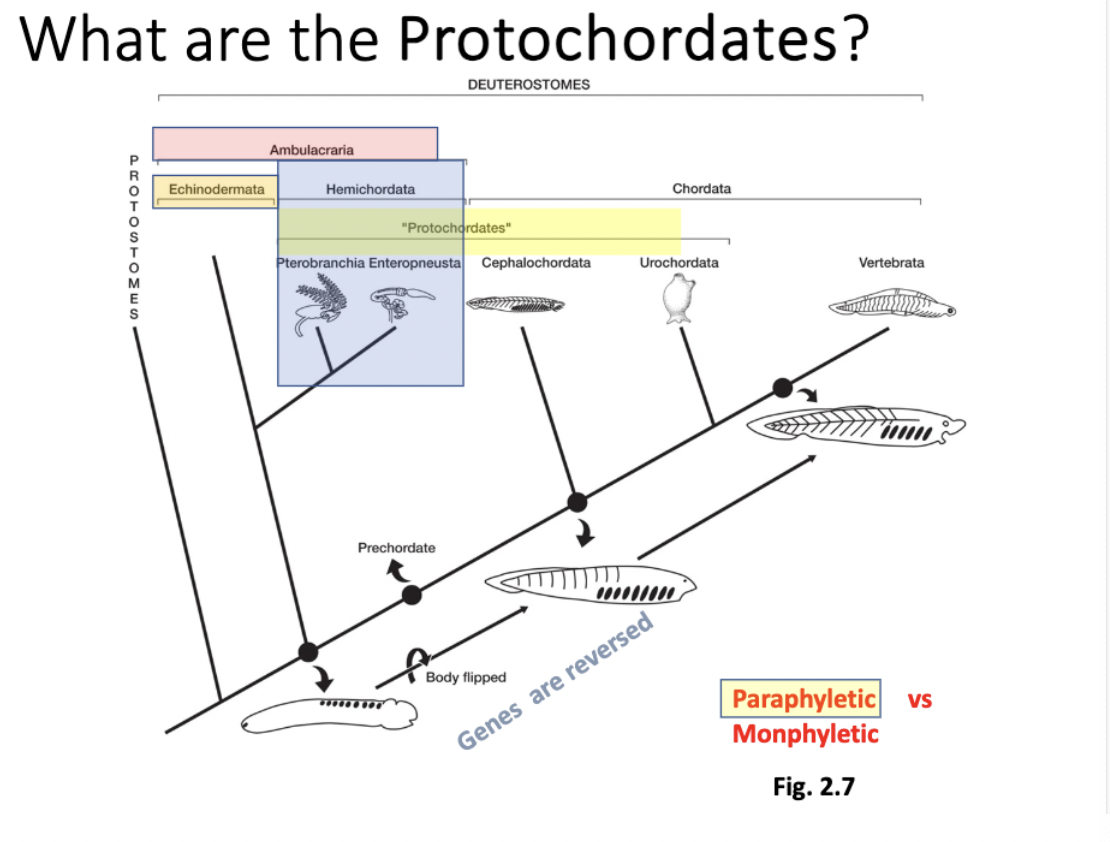
ceplalochordata
chordata→ ________ + urochordata + vertebra
pikia, mid-cambrian
had v tiny head
extant lancelets (Branchiostoma Amphioxus lanceolatus) have all 5 chordate traits + bigger head “protochordate”
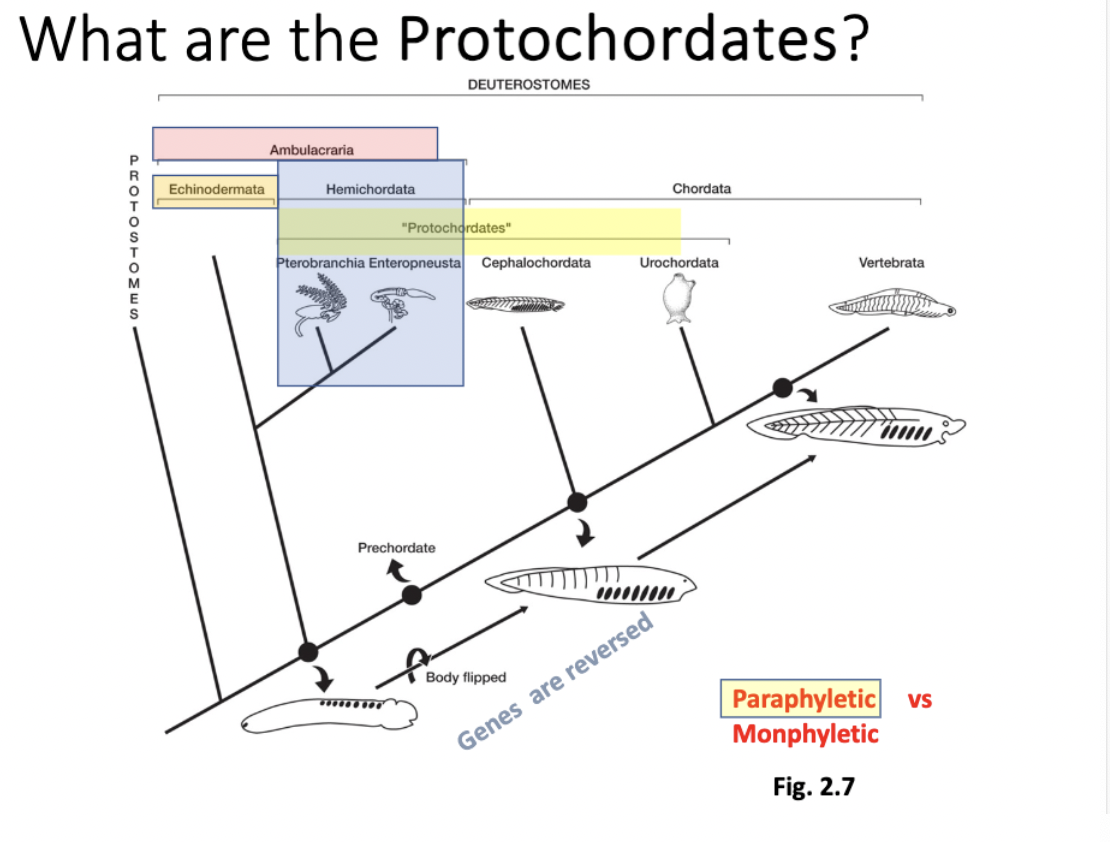
urochordata
chordata→ cephalochordata + ________ + vertebra
“tail backstring”
5 synapomorphies, during some portion of life history
marine suspension feeders
tunicates (tunic), ascidiacea (sea squirts)
larvae: ascidian tadpole (all synapomorphies simultaneously)
short-lived (hrs)
“protochordate”
sister group to vertebrates
hemichordata
ambulacraria → _______ → pterobranchia + enteropneusta
“marine worms”
sister to echinodermata
pharyngeal slits
postanal appendage in some, but not for movement
tornaria larvae (resembles auricularia larva of echinoderms), planktonic
proboscis, collar, trunk
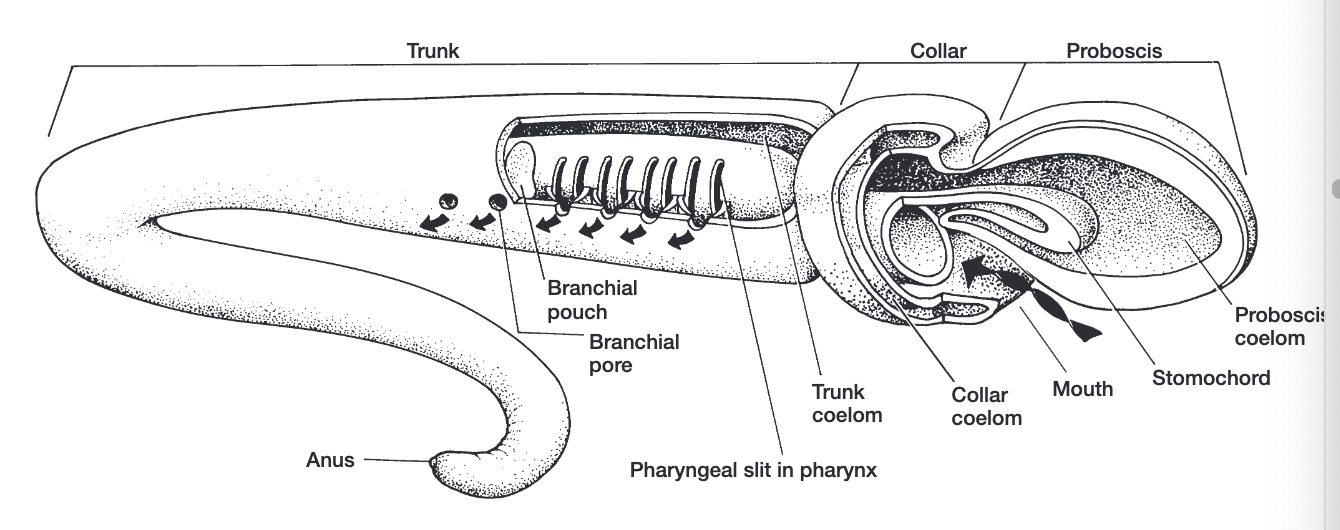
enteropneusta
ambulacraria → hemichordata → pterobranchia + _________
“acorn worms”
some thought to have a dorsal hollow nerve cord
proboscis, collar, trunk
pharyngeal slit
no notochord or thyroid/endostyle
close relatives of echinodermata
not colonial
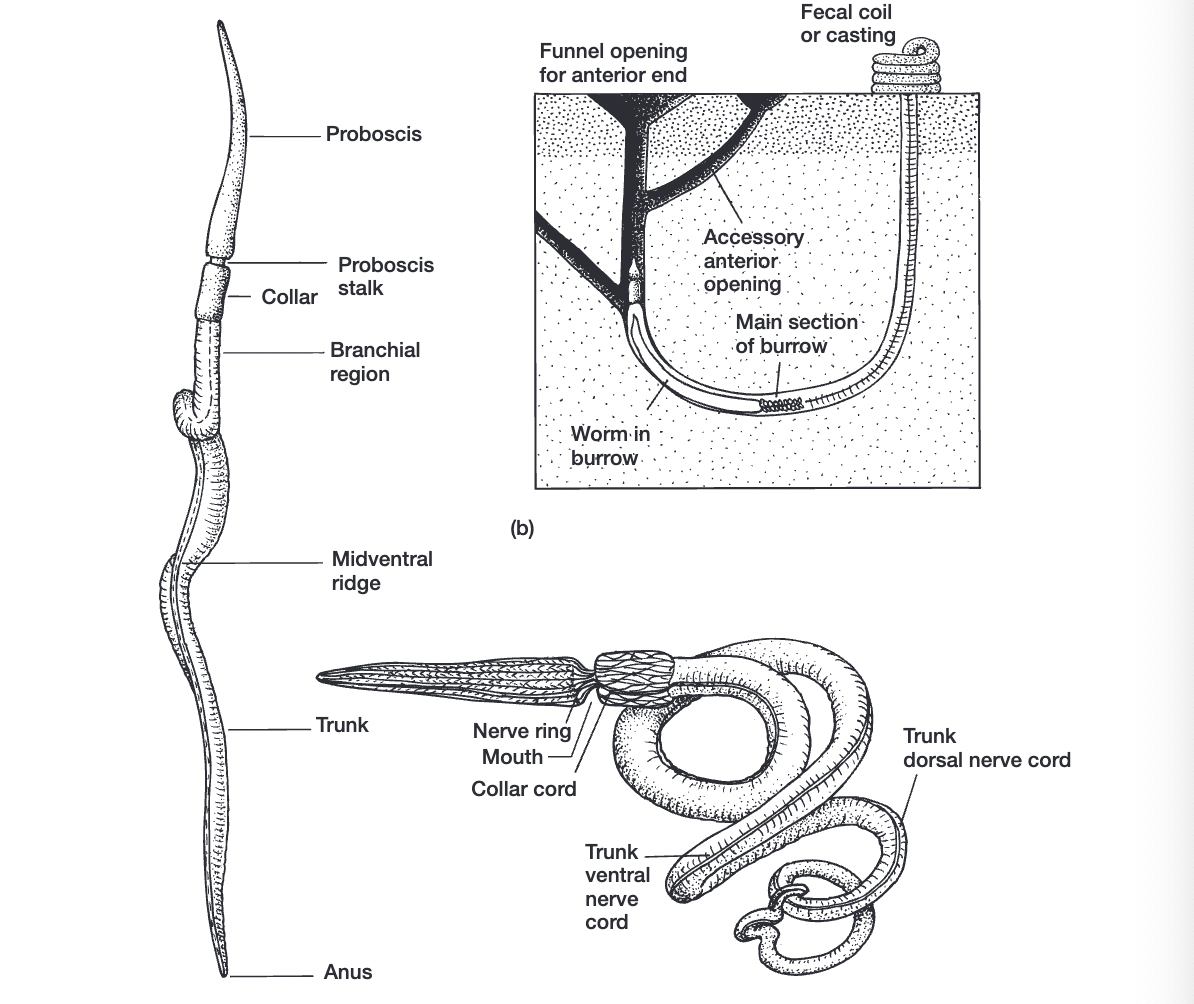
pterobranchia
ambulacraria → hemichordata → _________ + enteropneusta
evolved from acorn worms→ no, just say sister taxa or shared mrca
colonial (zooid)= start off as trunk but multiple animals sprout from it
proboscis, collar, trunk
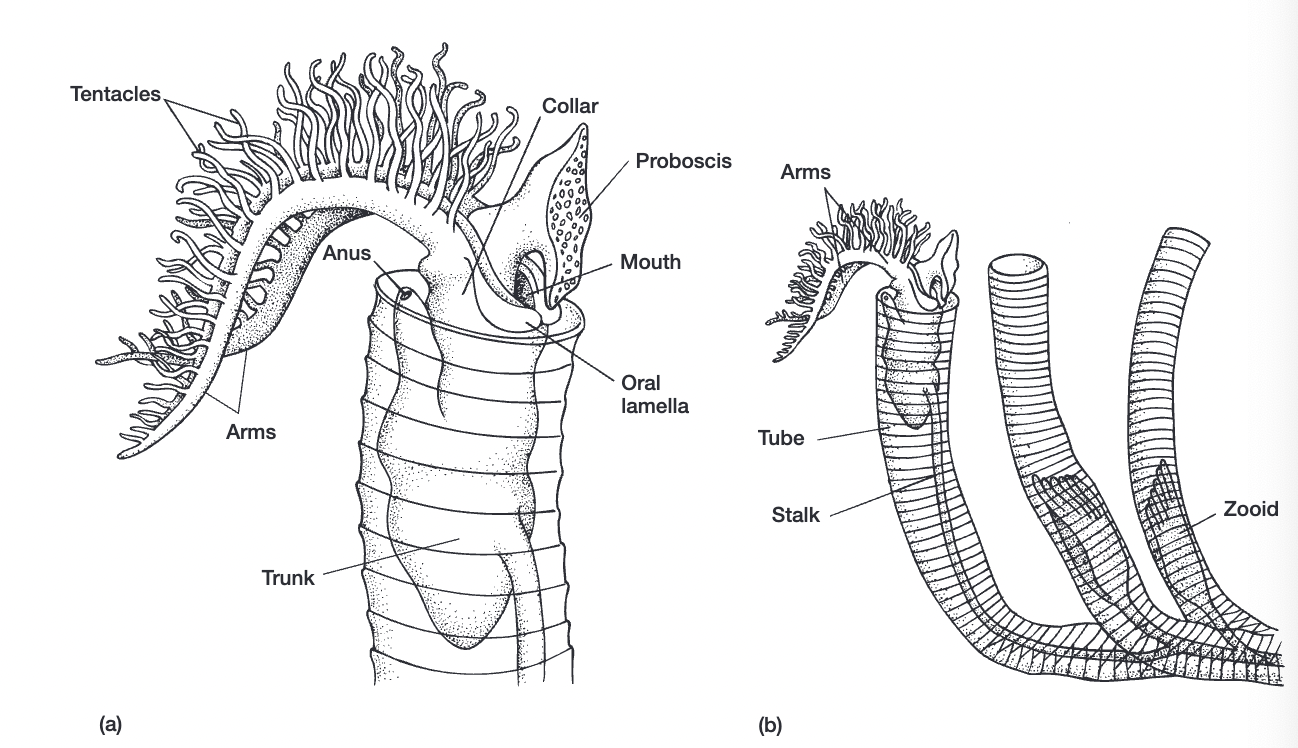
echinodermata
ambulacraria → _________
pentaradial, symmetrical body plan (sea stars)
endoskeleton of calcium carbonate, ossicles
water-vascular system, tube feet
in some fossils, pharyngeal slits present
synapomorphies
shared derived characteristics
parsimony
things usually connected/behave in the simplest/most economical way
occam’s razor: the simplest explanation has the least number of steps
(fill in the blanks)
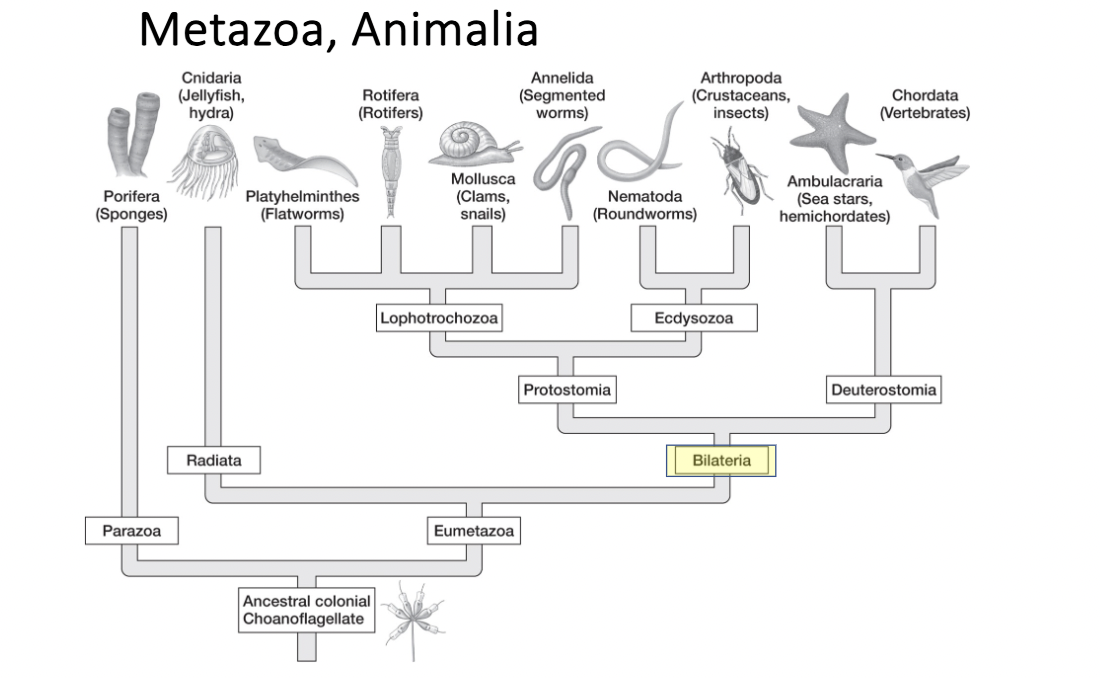
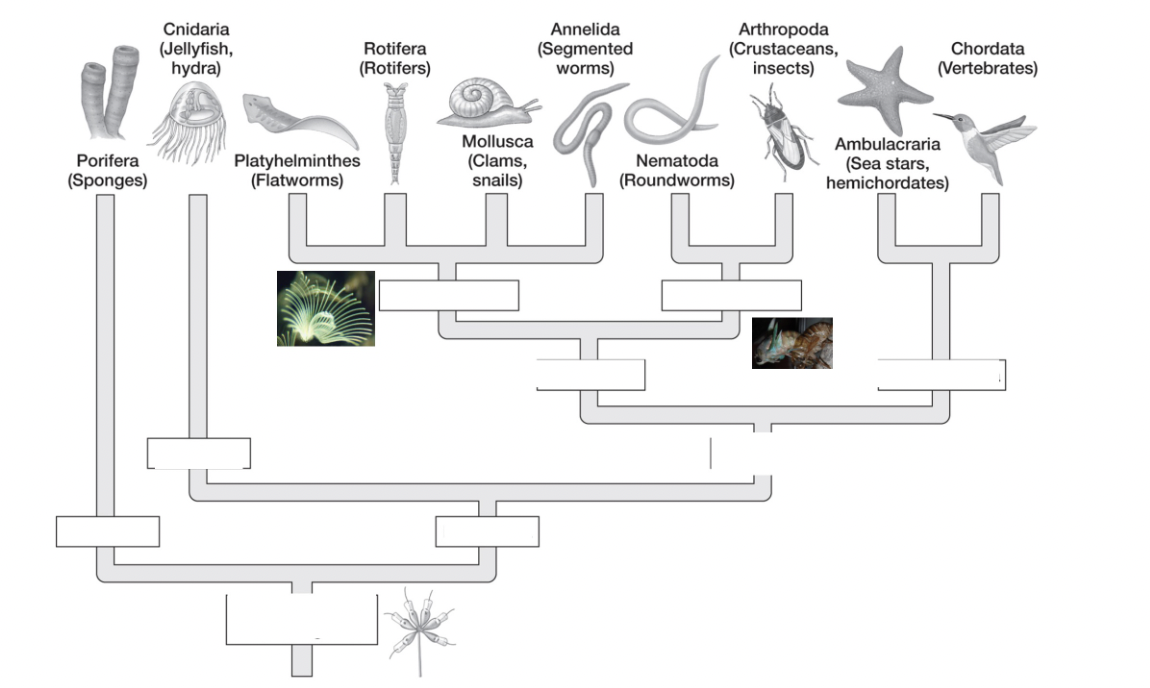
major metazoan groups (add?)
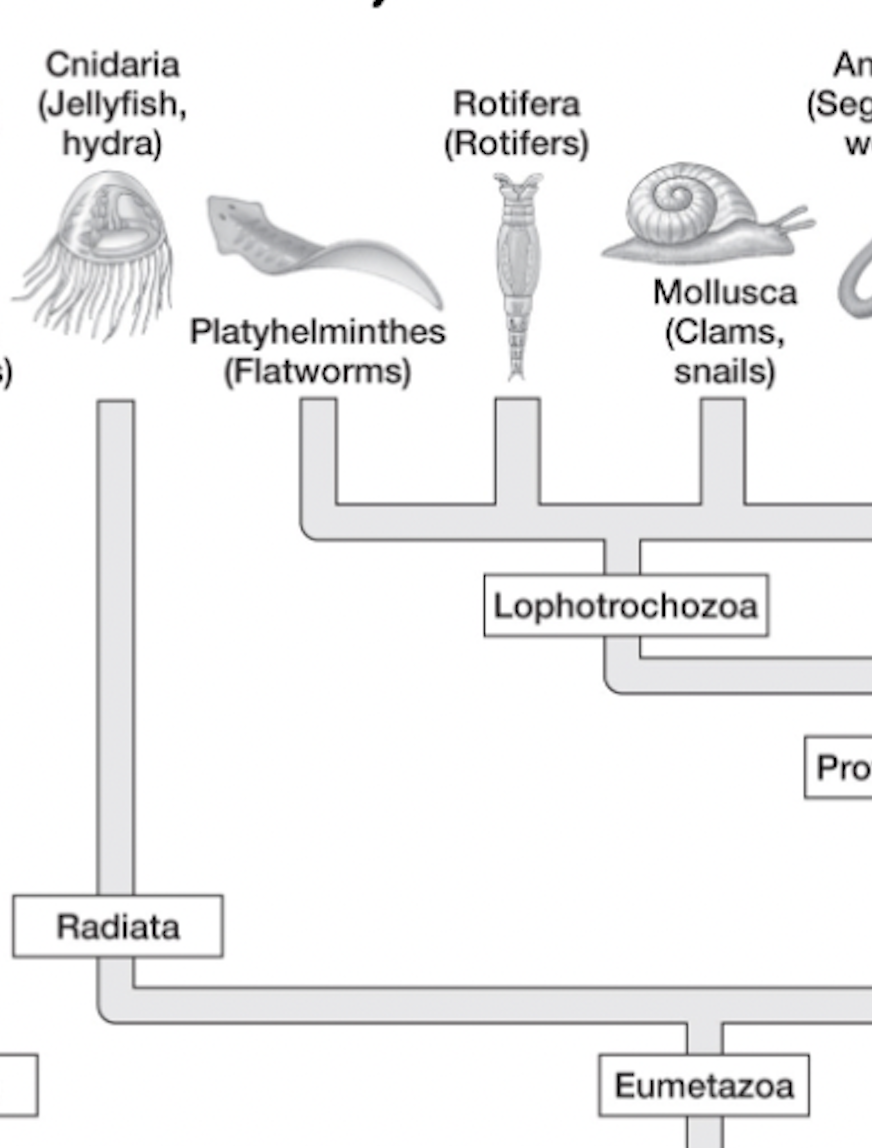
parazoa
eumetazoa
radiata
bilateria
protostomia
deuterostomia
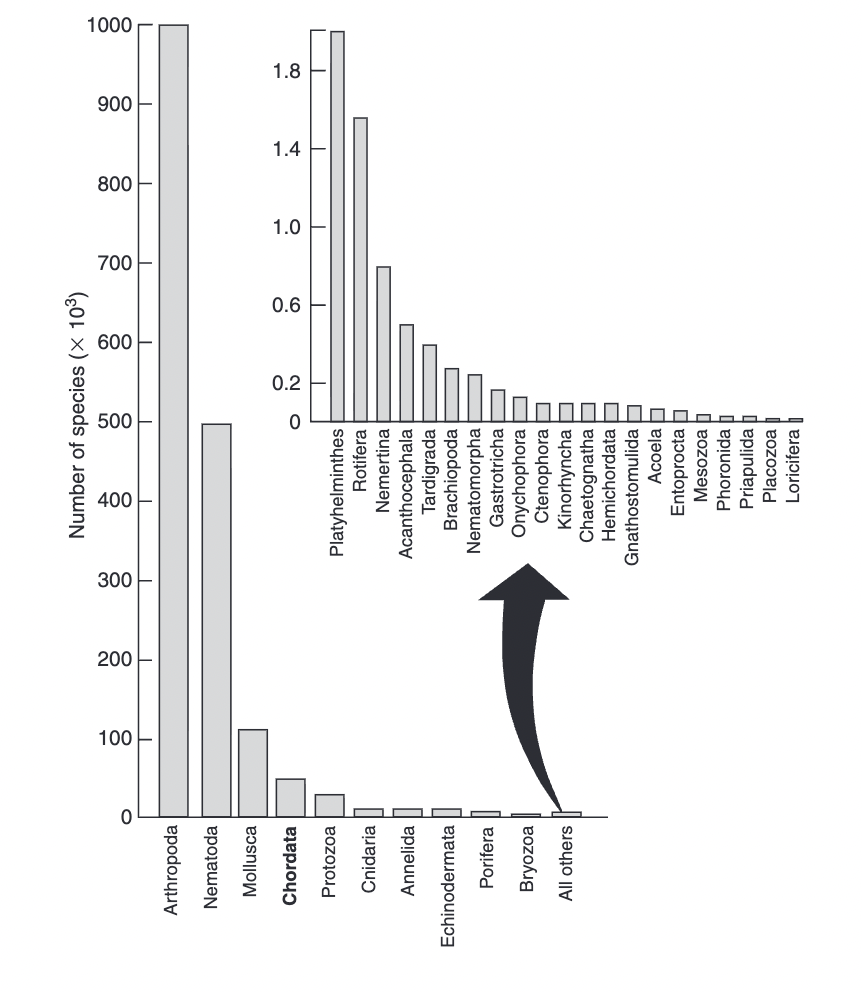
species diversity
arthropods (crustaceans/insects) most diverse (millions of species)
nematoda (roundworms) second most diverse (1/2 million species)
chordata (vertebrates + others) (~50,000 species)
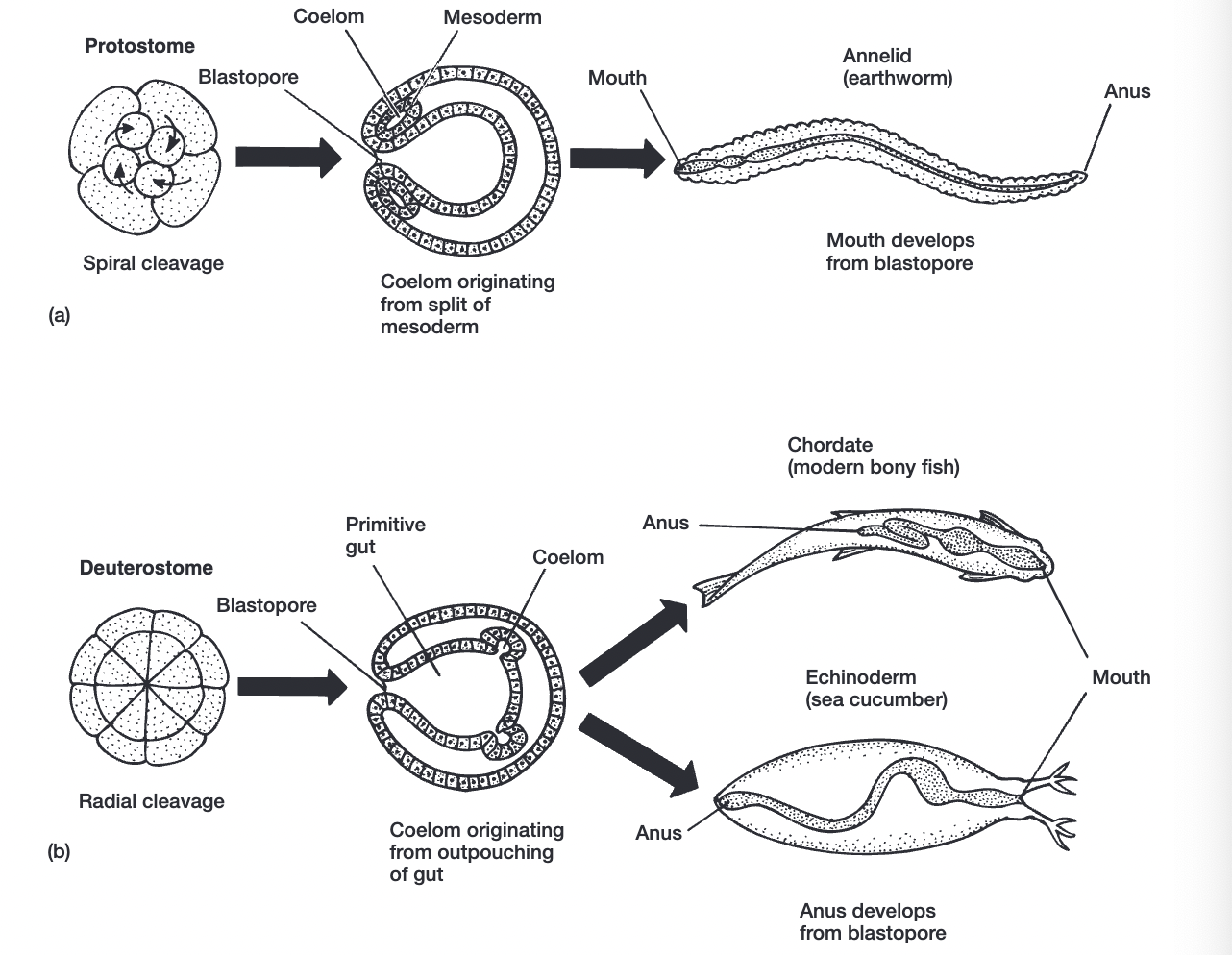
bilateria
eumetazoa → _________
left + right side
front + back
top + bottom
triploblastic= 3 germ layers
______ → deuterostomia= anus forms first from blastopore
______ → protostomia= mouth forms first from blastopore
bilateria development (protostomes + deuterostomes)
protostomes
blastopore forms mouth
spiral cleavage
schizocoelic coelom (cell clusters)
ectodermal skeleton
deuterostomes
blastopore forms anus
radial cleavage
enterocoelic coelom (outpouching)
mesodermal skeleton
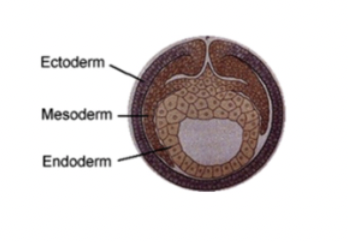
triploblastic
3 germ layers:
endoderm= inside, digestive tracts (liver + pancreas), all eumetazoa have this
mesoderm= middle, organs, blood, muscle, bones, heart
ectoderm= outside, nervous system (eyes + skin), all eumetazoa have this
bilateria are this
more complex, mesoderm gives rise to specific character traits
radiata
eumetazoa → _______ → cnidaria= jellyfish/hydra (nida=stinging)
diploblastic= 2 germ layers
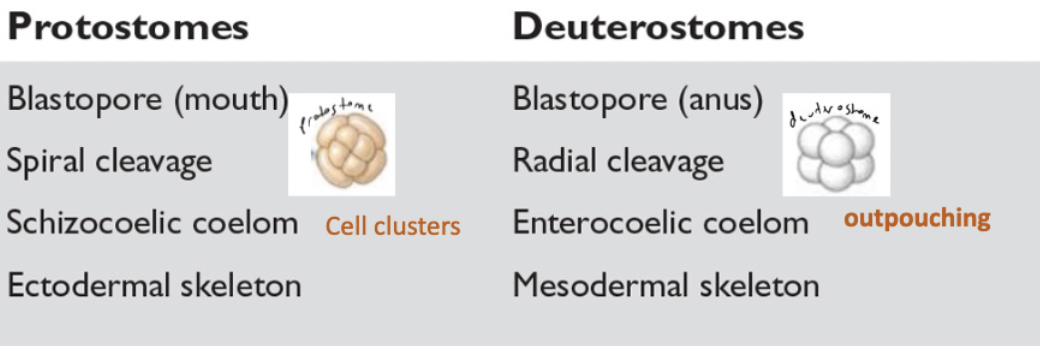
protostomes (ADDD)
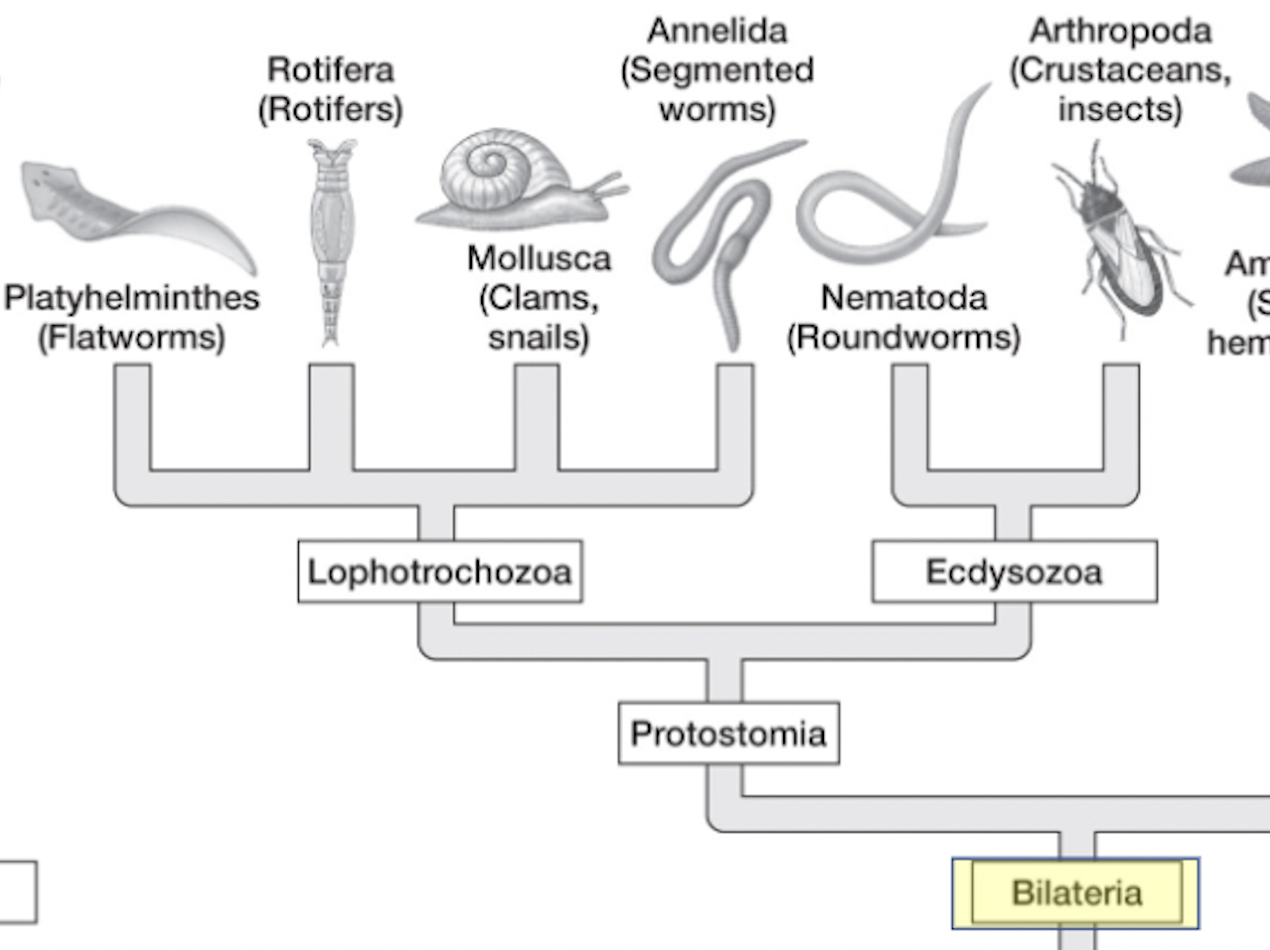
eumetazoa → bilateria → ______
“first mouth”
mouth arises from blastopore
molluscs, annelids, arthropods,
solid nerve cord
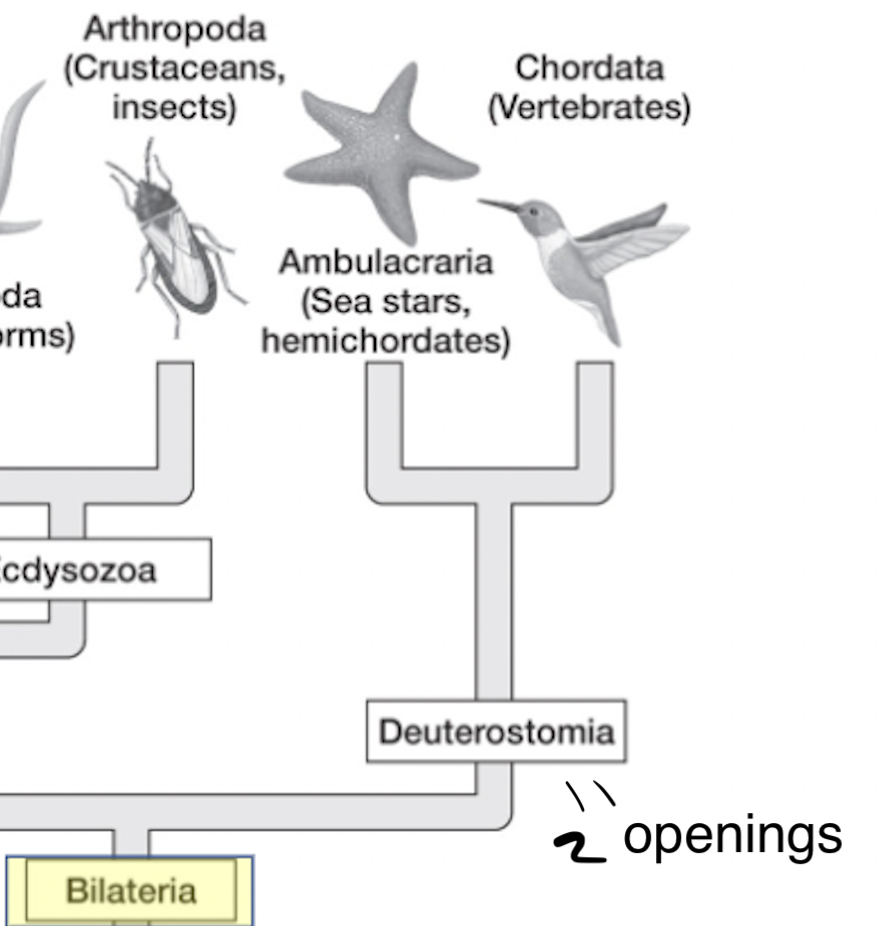
deuterostomes (ADDDDD)
eumetazoa → bilateria → ______
hollow nerve cord
“mouth second” → anus develops from blastopore as first opening, mouth forms later
ambulacraria (echinoderms + hemichordates) + chordates (cephalochordates, urochordates + vertebrates)
chordate origins (2 debated):
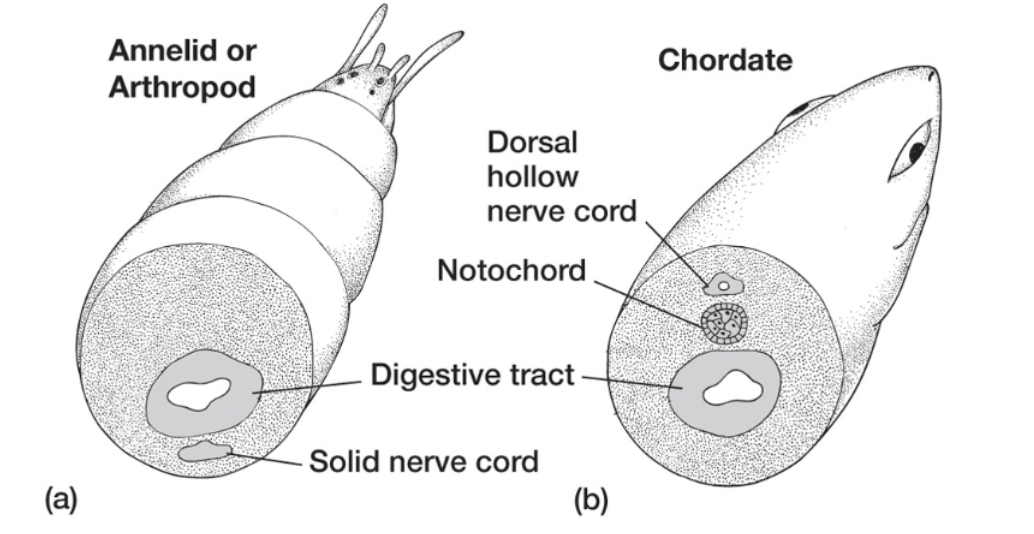
annelid or arthropod origin
echinoderm origin
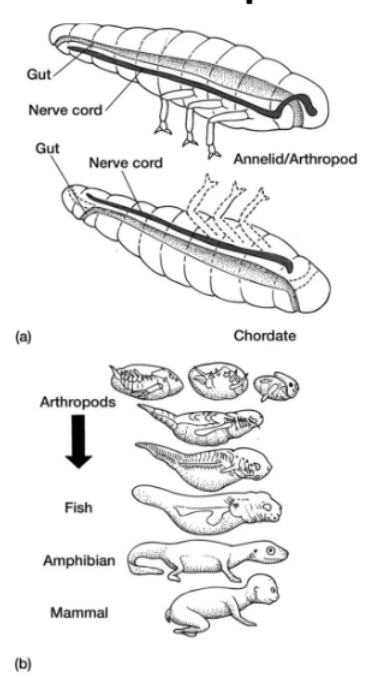
annelid or arthropod origin (chordate origin debate)
arguments:
segmented body
brain regionalization: forebrain, hindbrain
nerve cord and gut present
counter arguments:
nerve/gut flipped
nerve cord of chordates is hollow, in annelids/arthropods its solid
also develops a dif way in each
protostome vs deuterostome development
many of the supposed linking similarities between chordates and annelids or arthropods result from homoplasy rather than homology
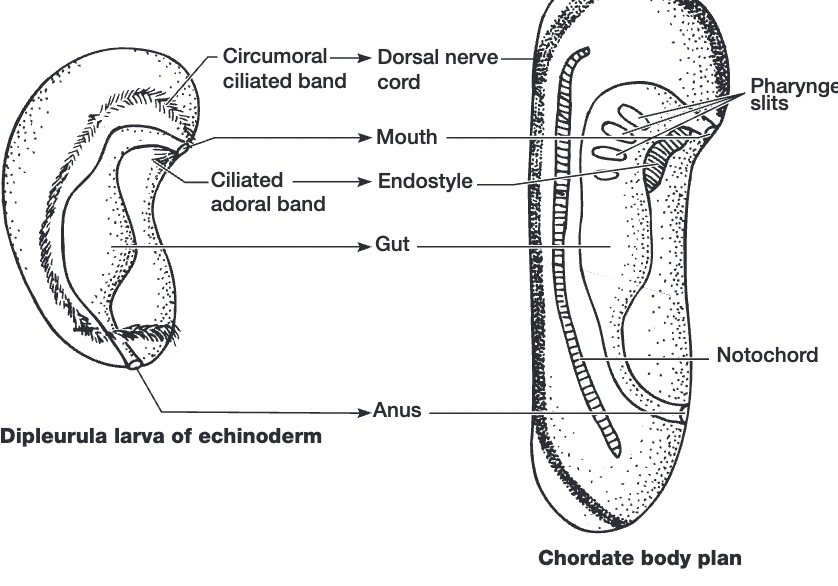
echinoderm origin (chordate origin debate) (idk)
W. Garstang’s arguments
deuterostomes
share embryonic similarities of cleavage + mesodermal/coelomic formation
auricularia hypothesis (appears similar to tornaria larvae?)
bilateral symmetry (left + right side)- echinoderm larvae + chordates
body elongation grew out of circumoral band (dorsal hollow nerve cord)
counter argument
larvae→ chordate plan?
W.Garstang’s argument
paedomorphosis- larval characteristics observed in adult form
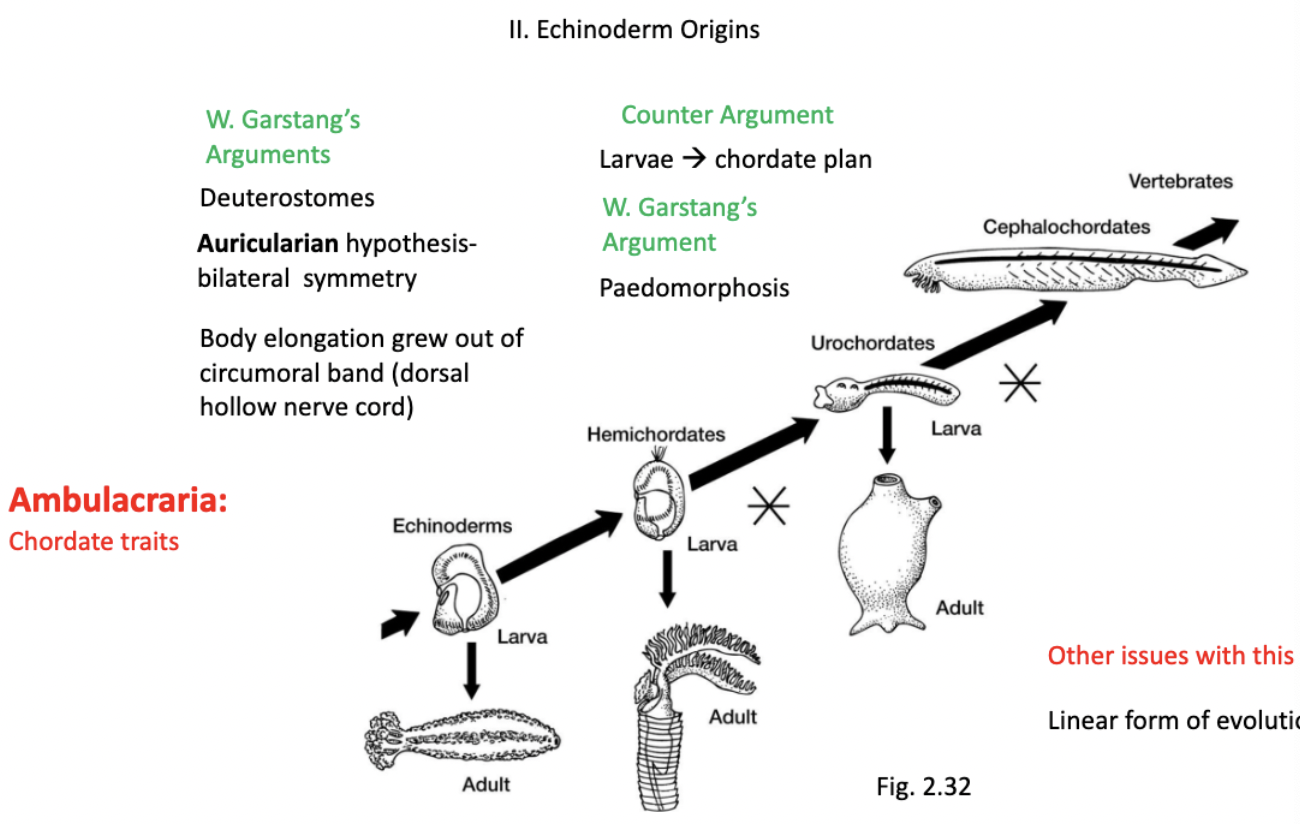
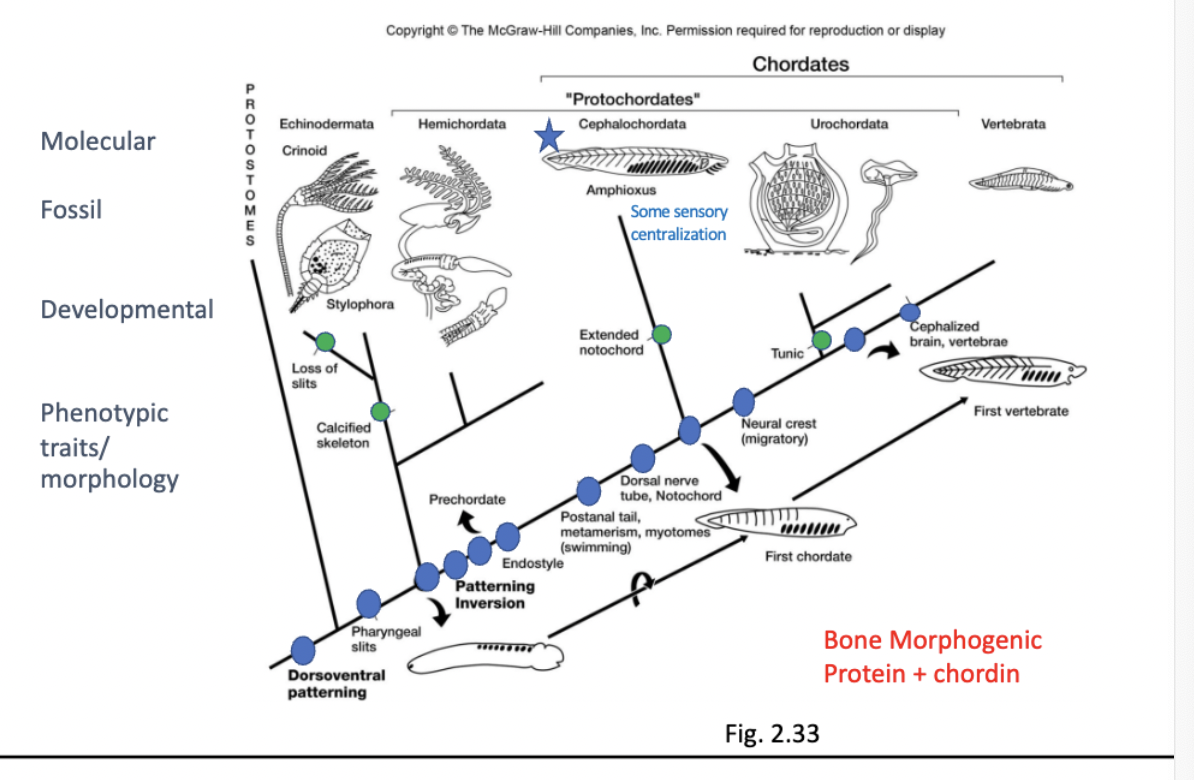
another phylogenetic tree to review
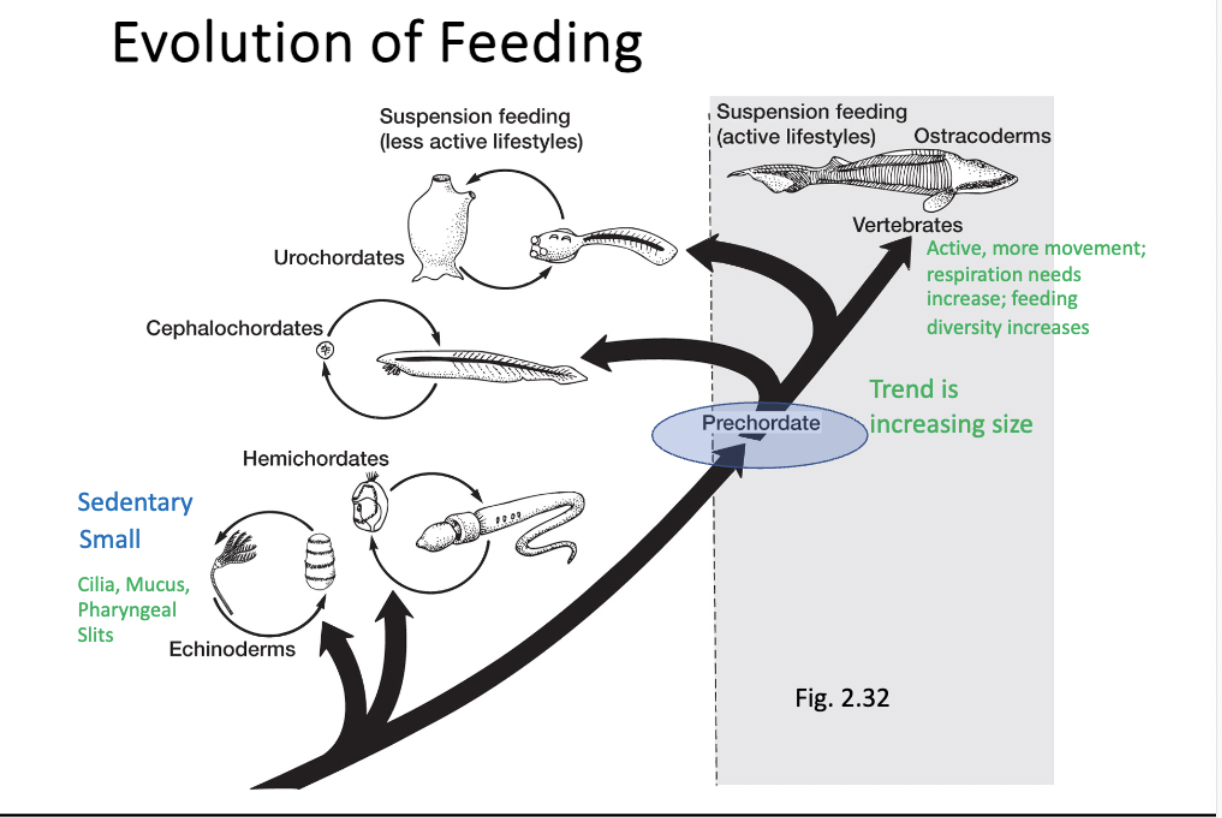
evolution of feeding image
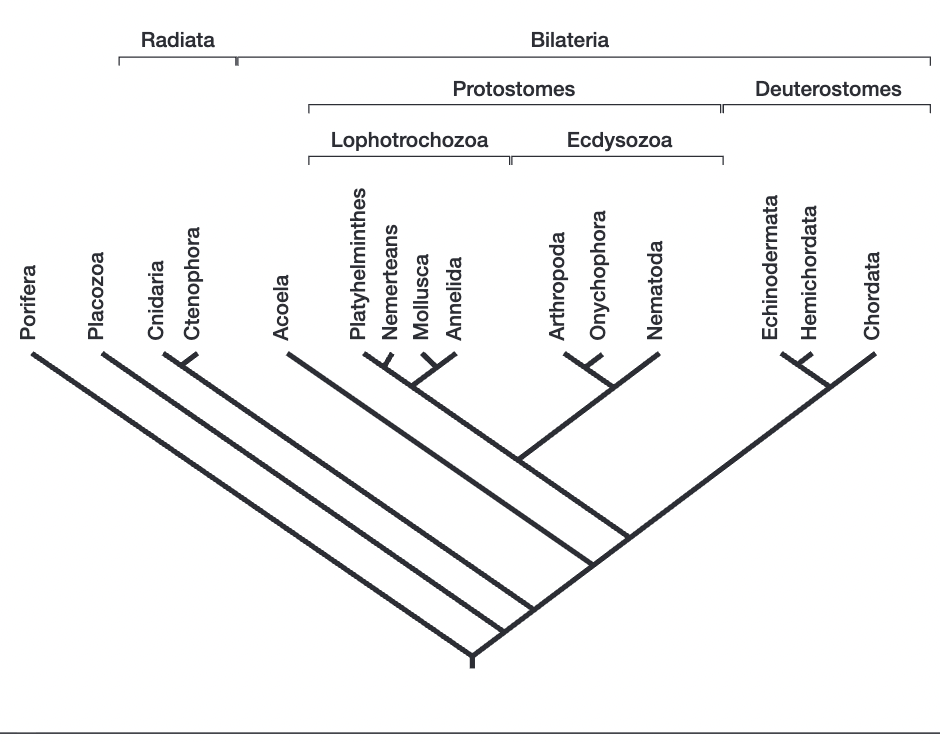
another version of the phylogenetic tree
(note that chordates are deuterostomes along with hemichordates and echinoderms,but the protostomes are a separate lineage)