Chapter 4: Earth Systems and Resources (copy) Revised
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/63
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:11 PM on 4/9/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
1
New cards
In 1915, ______ proposed that all present-day continents originally formed one landmass he called Pangaea.
Alfred Wegener
2
New cards
Subduction zones
These are areas on Earth where two tectonic plates meet and move toward each other, with one sliding underneath the other and moving down into the mantle.
3
New cards
Convergent Boundaries
These occur where two plates slide toward each other.
4
New cards
Divergent Boundaries
These occur when two plates slide apart from each other.
5
New cards
Transform boundaries
These occur where plates slide past each other in opposite directions.
6
New cards
Zone of leaching
Dissolved and suspended materials move downward.
7
New cards
Subsoil
Tends to be yellowish in color due to the accumulation of iron, aluminum, humic compounds, and clay leached from A and E horizons.
8
New cards
Weathered Parent Material
Partially broken-down inorganic materials.
9
New cards
Parent material
Refers to the rock and minerals from which the soil derives. The nature of the parent rock, which can be either native to the area or transported to the area by wind, water, or glacier, has a direct effect on the ultimate soil profile.
10
New cards
Extrusive igneous rocks
Solidify on or near the surface, cool quickly, and have a fine-grained smooth texture.
11
New cards
Metamorphic Rocks
These are formed by intense heat and pressure, high quartz content.
12
New cards
Sedimentary
These are formed by the piling and cementing of various materials over time in low-lying areas.
13
New cards
Gravel
* Coarse particles.
* Consists of rock fragments.
* Consists of rock fragments.
14
New cards
Sand
* Sedimentary material coarser than silt.
* Water flows through too quickly for most crops.
* Good for crops and plants requiring low amounts of water.
* Water flows through too quickly for most crops.
* Good for crops and plants requiring low amounts of water.
15
New cards
Loam
* About equal mixtures of clay, sand, silt, and humus. Rich in nutrients.
* Holds water but does not become waterlogged. Particle size can vary.
* Holds water but does not become waterlogged. Particle size can vary.
16
New cards
Silt
* Sedimentary material consisting of very fine particles between the sizes of sand and clay.
* Easily transported by water.
* Easily transported by water.
17
New cards
Clay
* Very fine particles.
* Compacts easily.
* Forms large, dense clumps when wet.
* Compacts easily.
* Forms large, dense clumps when wet.
18
New cards
Humus
It is the dark organic material that forms in soil when plant and animal matter decays.
19
New cards
Aeration
Refers to how well a soil is able to absorb oxygen, water, and nutrients.
20
New cards
Degree of Soil Compaction
It is measured by dry unit weight and depends on the water content and compaction effort.
21
New cards
Nutrient-Holding Capacity
The ability of soil to absorb and retain nutrients so they will be available to the roots of plants.
22
New cards
Pore Size
Describes the space between soil particles.
23
New cards
Size of soil and particles
It determines the amount of moisture, nutrients, and oxygen that the soil can hold along with the capacity for water to infiltrate.
24
New cards
Water holding capacity
It is controlled primarily by the soil texture and the soil organic matter content.
25
New cards
Soil texture
A reflection of the particle size distribution of soil.
26
New cards

Water holding capacity formula
27
New cards
Troposphere
The lowest portion of Earth’s atmosphere, 0–6 miles (0–10 km) above Earth’s surface.
28
New cards
Stratosphere
It is located 6–30 miles (10–50 km) above Earth’s surface.
29
New cards
Stratosphere
Ozone (O3) absorbs high-energy ultraviolet radiation from the sun and is broken down into atomic oxygen (O) and diatomic oxygen.
30
New cards
Convection
It is the primary way energy is transferred from hotter to colder regions in Earth’s atmosphere and is the primary determinant of weather patterns.
31
New cards
Air Mass
A large body of air that has similar temperature and moisture content.
32
New cards
Albedo
An expression of the ability of surfaces to reflect sunlight.
33
New cards
Cold Front
The leading edge of an advancing mass of cold air and is associated with thunderhead clouds, high surface winds, and thunderstorms.
34
New cards
Warm Front
The boundary between an advancing warm air mass and the cooler one it is replacing.
35
New cards
Stationary Front
A pair of air masses, neither of which is strong enough to replace the other, that tend to remain in essentially the same area for extended periods of time.
36
New cards
Latitude
The measurement of the distance of a location on Earth from the equator.
37
New cards
Moisture Content of Air
It is a primary determinant of plant growth and distribution and is a major determinant of biome type.
38
New cards
High-pressure weather systems
They have higher pressure at their center than around them, so winds blow away from them.
39
New cards
Trade Winds
These are the prevailing pattern of easterly surface winds found in the tropics near Earth’s equator, within the troposphere or lower portion of Earth’s atmosphere.
40
New cards
Coriolis Effect
A phenomenon wherein earth’s rotation on its axis causes winds to not travel straight, which causes prevailing winds in the Northern Hemisphere to spiral clockwise out from high-pressure areas and spiral counterclockwise toward low-pressure areas.
41
New cards
Hadley Air Circulation
* Air heated near the equator rises and spreads out north and south.
* After cooling in the upper atmosphere, the air sinks back to Earth’s surface within the subtropical climate zone.
* After cooling in the upper atmosphere, the air sinks back to Earth’s surface within the subtropical climate zone.
42
New cards
Ferrel Air Circulation Cells
* Develop between 30° and 60° north and south latitudes.
* The descending winds of the Hadley cells diverge as moist tropical air moves toward the poles in winds known as the westerlies.
* The descending winds of the Hadley cells diverge as moist tropical air moves toward the poles in winds known as the westerlies.
43
New cards
Polar cells
These cells originate as icy-cold, dry, dense air that descends from the troposphere to the ground.
44
New cards
Polar Vortex
A low-pressure zone embedded in a large mass of very cold air that lies atop both poles.
45
New cards
Hurricanes
Term used in the Atlantic and Northeast Pacific.
46
New cards
Cyclones
Term used in South Pacific and Indian Ocean.
47
New cards
Typhoons
Term used in Northwest Pacific.
48
New cards
Hurricanes
* _____ begin over warm oceans in areas where the trade winds converge.
* A subtropical high-pressure zone creates hot daytime temperatures with low humidity that allow for large amounts of evaporation, with the Coriolis effect initiating the cyclonic flow.
* A subtropical high-pressure zone creates hot daytime temperatures with low humidity that allow for large amounts of evaporation, with the Coriolis effect initiating the cyclonic flow.
49
New cards
Storm Surge
A rise in sea level that occurs during tropical cyclones, typhoons, or hurricanes.
50
New cards
Watershed management
It reduces pesticides and fertilizers that wash off farm fields and into nearby waterbodies by using land, forest, and water resources in ways that don't harm plants and animals.
51
New cards
Latitude
A measure of distance either north or south from the equator.
52
New cards
Tropic of Cancer
The northernmost latitude reached by the overhead sun.
53
New cards
Tropic of Capricorn
The southernmost latitude reached by the overhead sun.
54
New cards
The mountain range's _____ side is drier than the windward side because air on this side has less moisture.
leeward
55
New cards
Rain Shadow Effect
The drier situation which is directly responsible for the plants that grow there, which in turn affects the animals that live there.
56
New cards
Upwelling
It occurs when prevailing winds, produced through the Coriolis effect and moving clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere, push warmer, nutrient-poor surface waters away from the coastline
57
New cards
El Niño
* Air pressure patterns reverse direction, causing trade winds to decrease in strength.
* This causes the normal flow of water away from western South America to decrease “pile up.”
* This causes the normal flow of water away from western South America to decrease “pile up.”
58
New cards
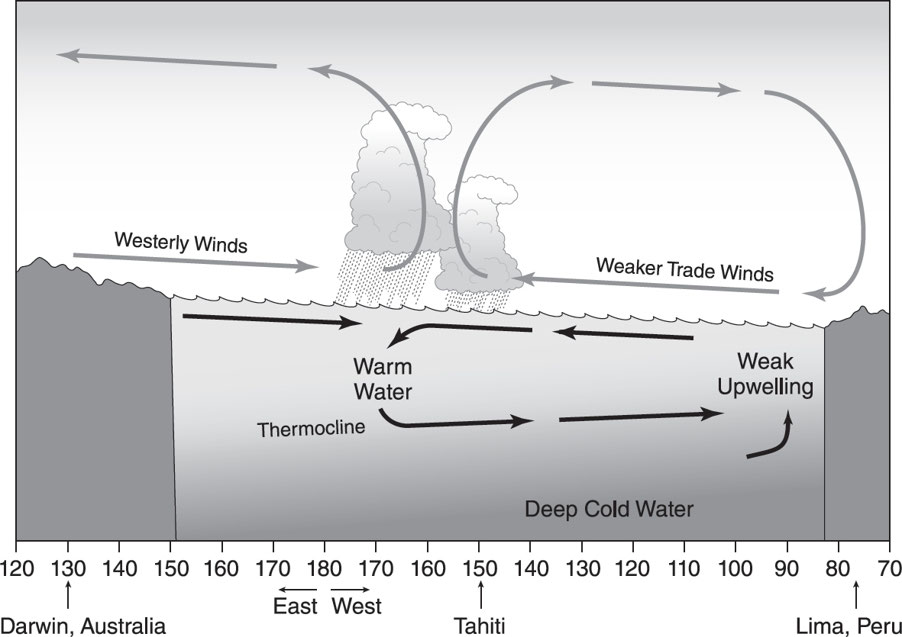
El Niño
59
New cards
La Niña
* Trade winds that blow west across the tropical Pacific are stronger than normal.
* This then results in an increase in the upwelling off of South America.
* This then results in cooler-than-normal sea surface temperatures off of South America.
* This then results in an increase in the upwelling off of South America.
* This then results in cooler-than-normal sea surface temperatures off of South America.
60
New cards
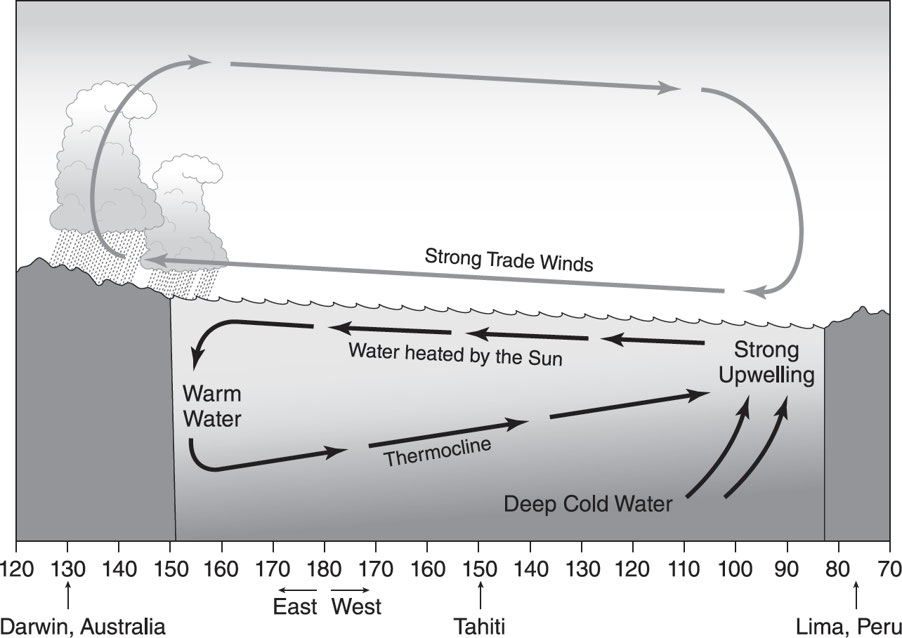
La Niña
61
New cards
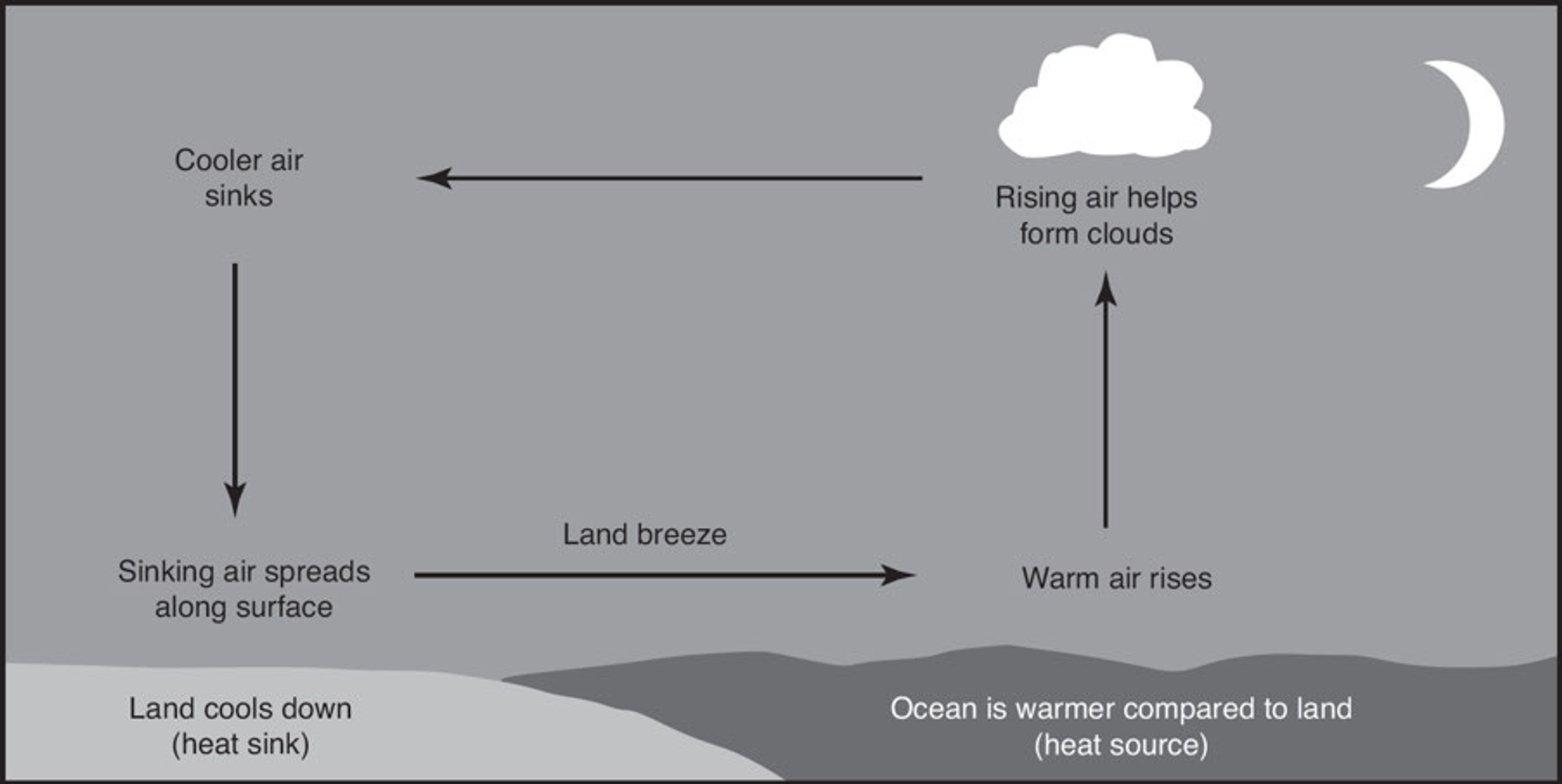
Land Breeze
62
New cards
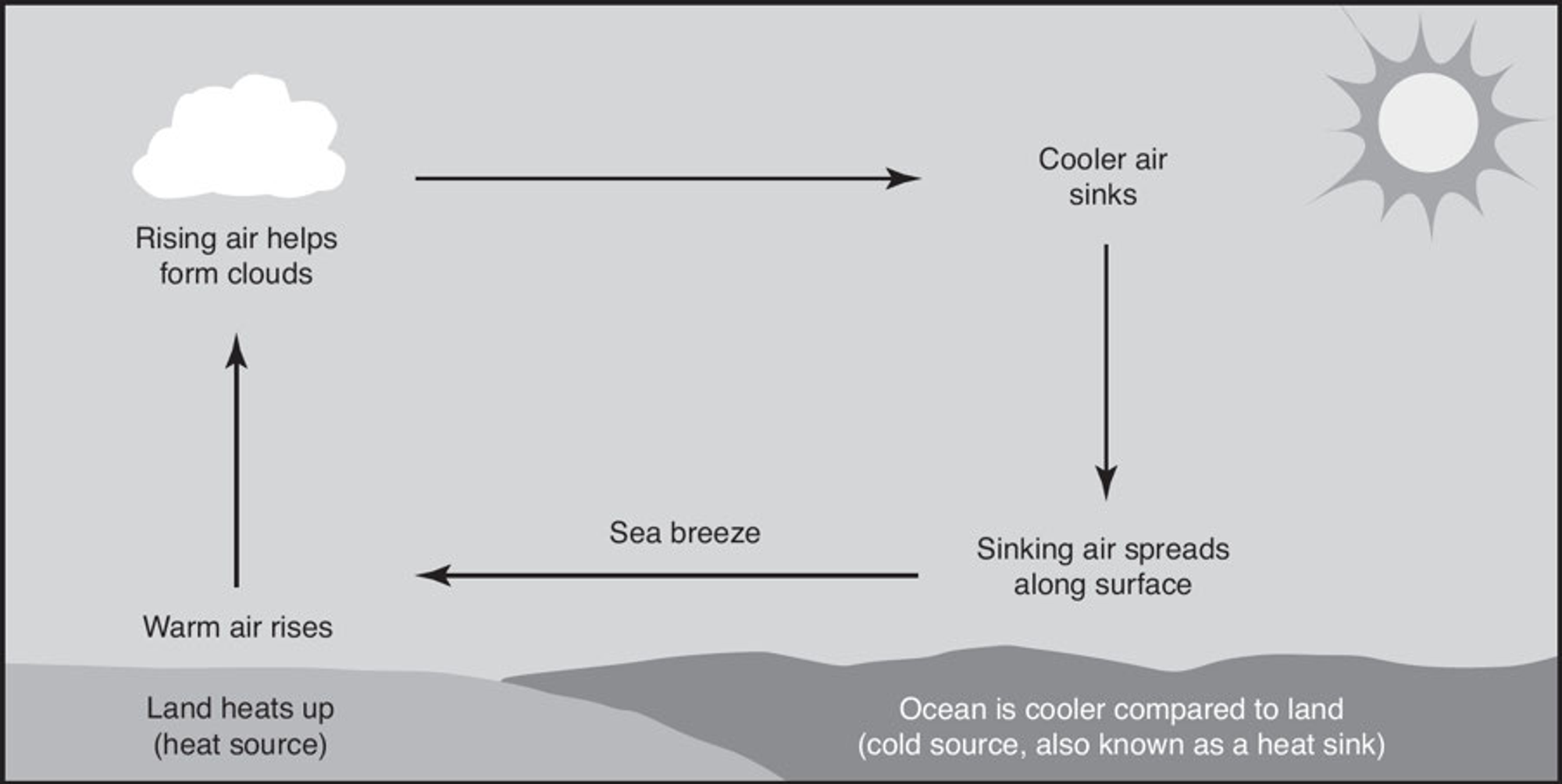
Sea Breeze
63
New cards
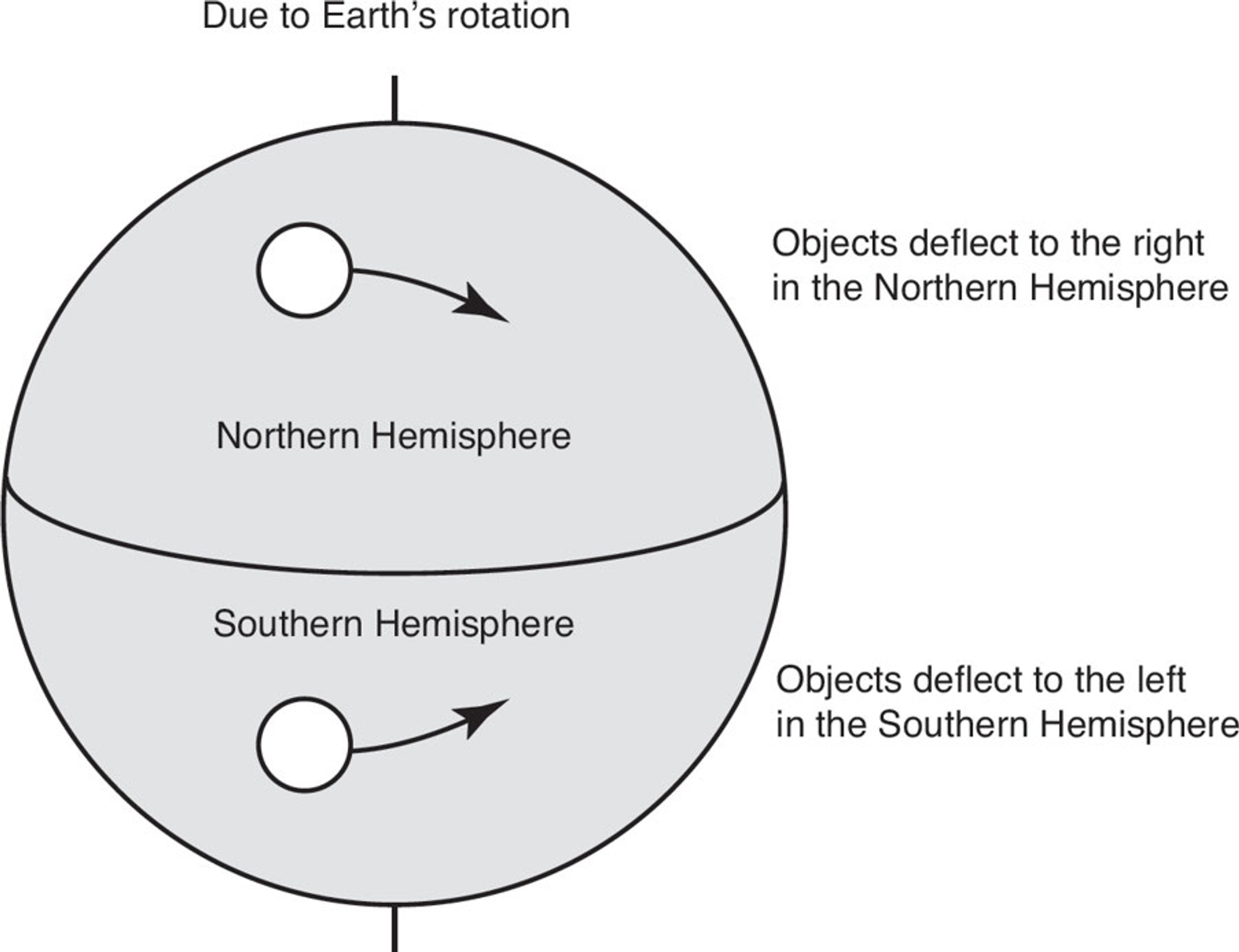
\
Coriolis Effect
64
New cards
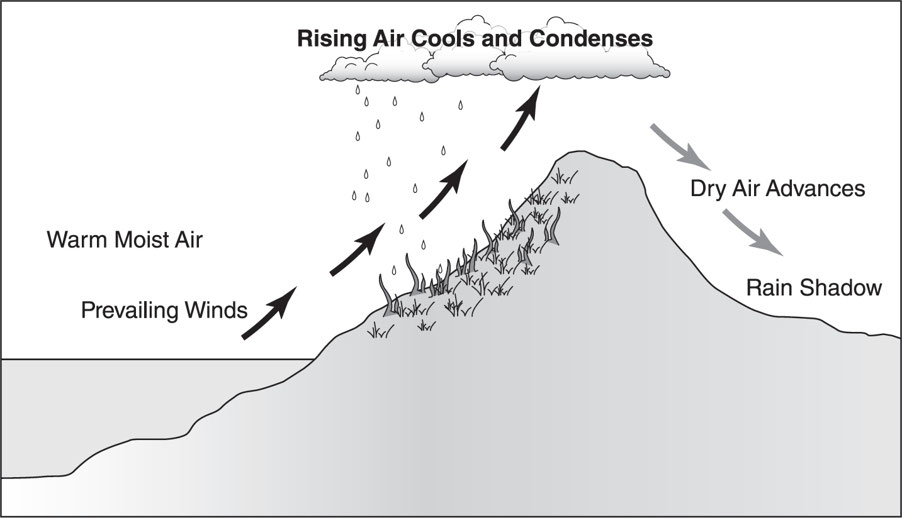
Rain Shadow Effect