Diagnostic Imaging- Exam 3: Abdomen PART 1
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
2 (VD/DV and lateral)
how many views should you always take for the abdomen?
9
you should use a grid when the abdomen is greater than ____ cm thick
low kVp and high mA
what kVp and mA should you use for the abdomen?
expiration
at what point, expiration or inspiration, should you take an abdominal radiograph?
1. evaluate technique
2. read entire image
3. describe image
4. prioritize differential diagnosis
5. next step (other diagnostics)
what are the steps to good film reading?
you DO see
do you usually see or not see these abdominal structures on radiographs:
-stomach, duodenum, small intestines, colon, cecum, spleen, falciform fat, bladder, pelvis
do NOT see
do you usually see or not see these abdominal structures on radiographs:
-adrenal glands, mesentery, omentum, gallbladder, ovaries, ureters
cranial pole of right kidney
which pole of which kidney do you not usually see on abdominal x-ray?
-gas
-fat
-fluid
-bone
what are the four radiographic opacities?
metal
which material is the most radiopaque?
fat, cat
what opacity is being shown? what species is this?
young, can see epiphysis
is this animal young or old?
air
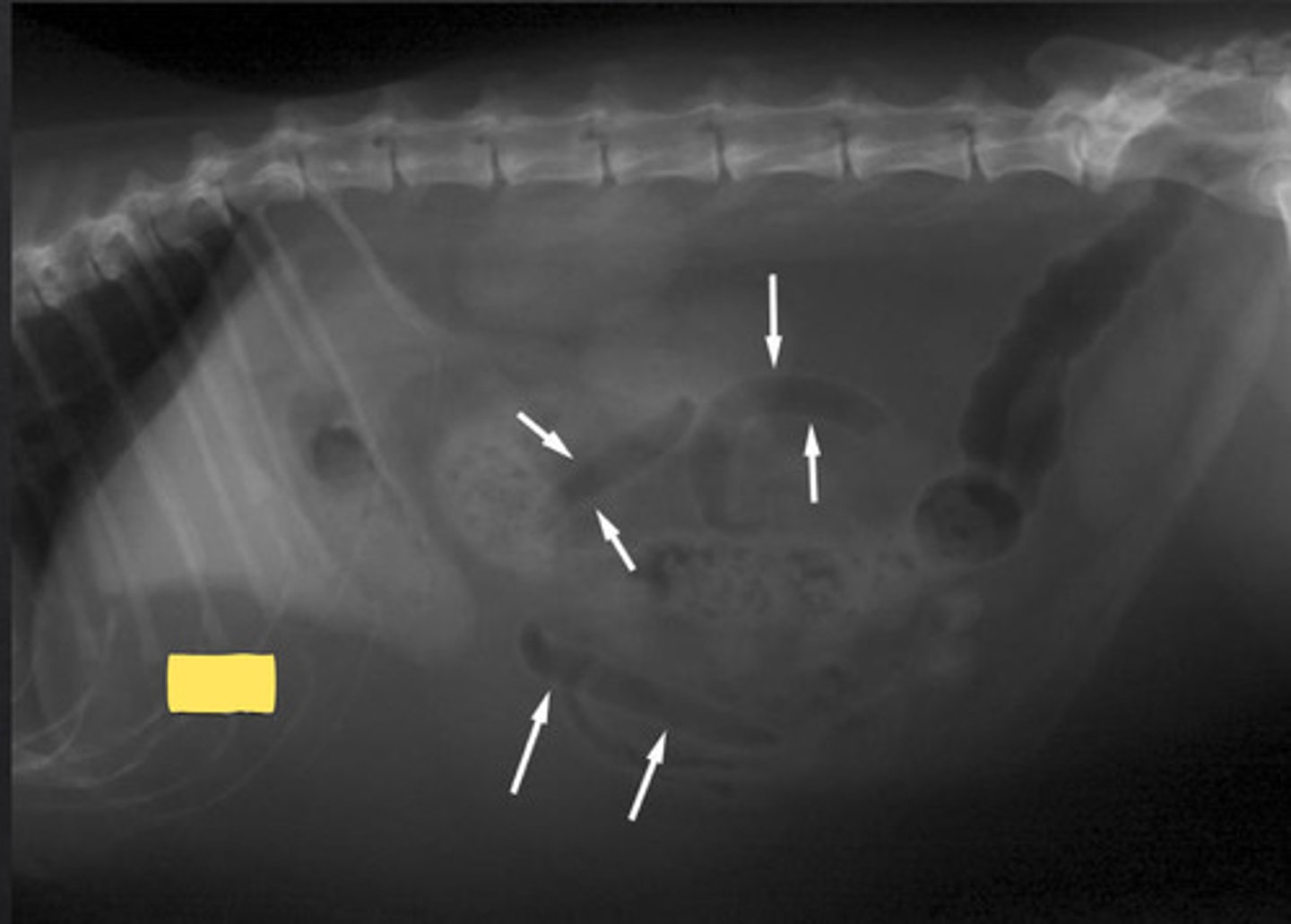
ID yellow, what is the opacity inside the bladder?
effacement
what is it called when two structures of the same opacity are in contact and the confluent borders cannot be distinguished?
poor
all abdominal organs are fluid opaque, thus, subject contrast is _____
intraluminal gas
what allows you to see intestinal loops?
serosal, radiopaque
if there is no fat or the fat is immature, _________ surfaces will not be seen and the radiograph will appear ___________
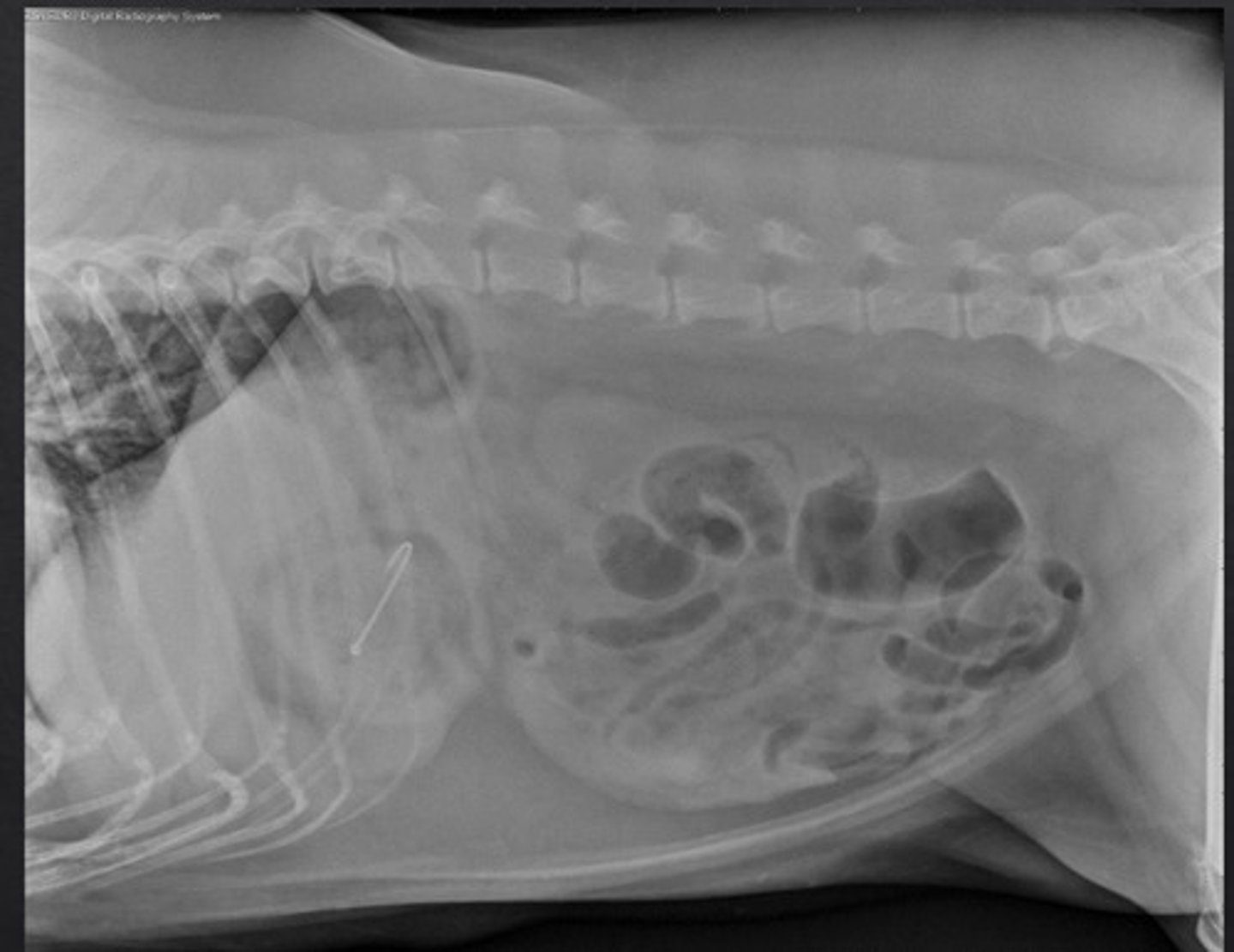
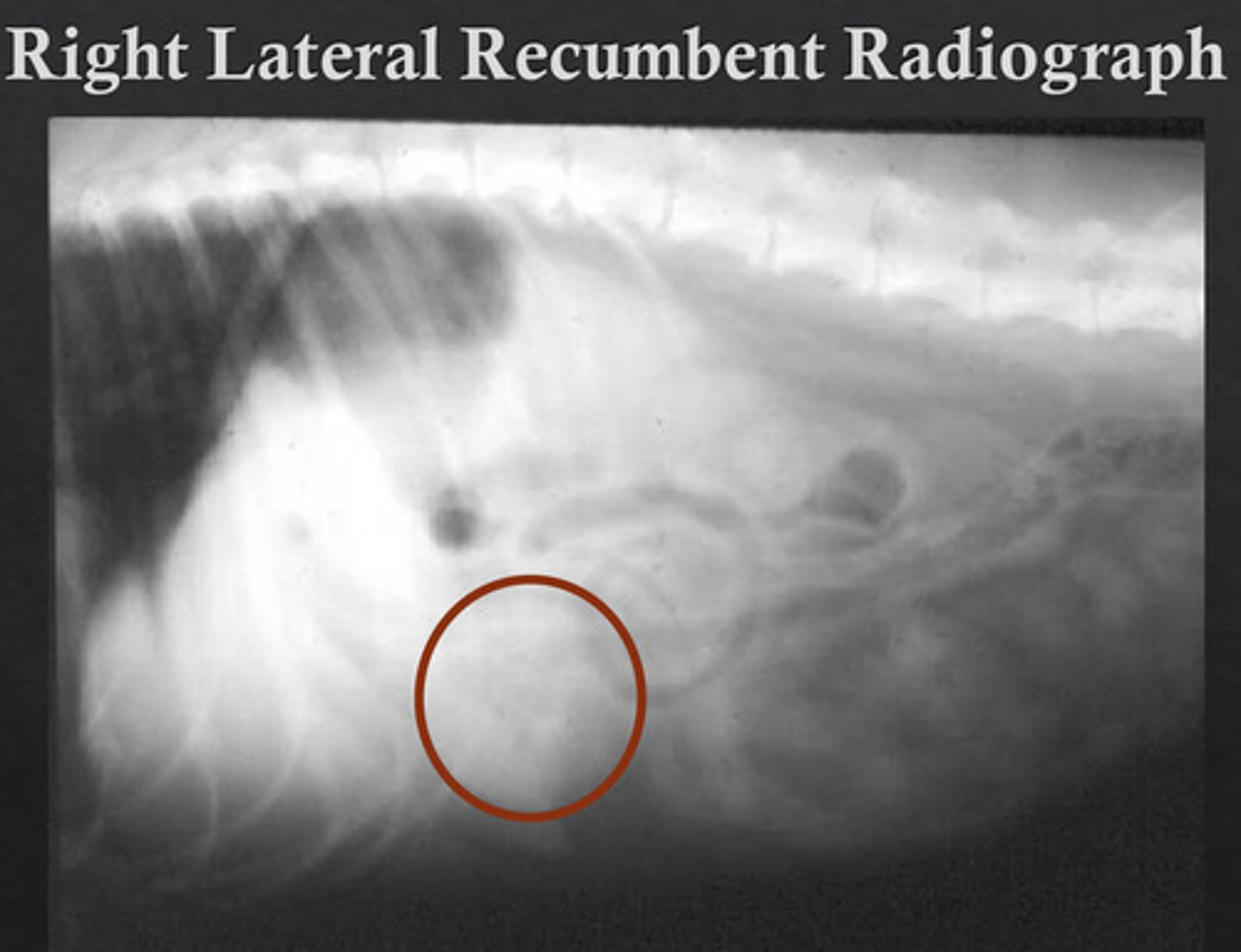
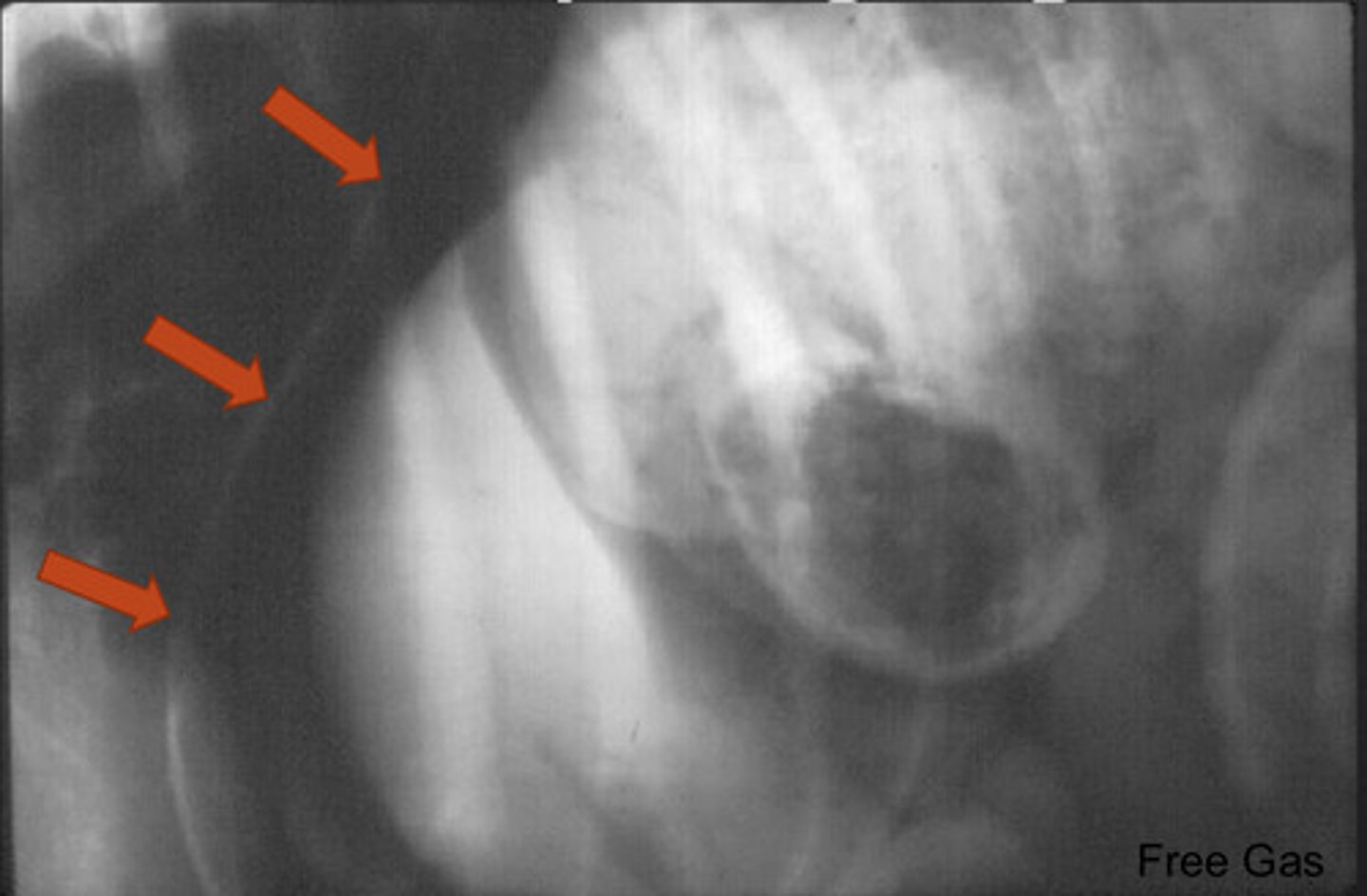
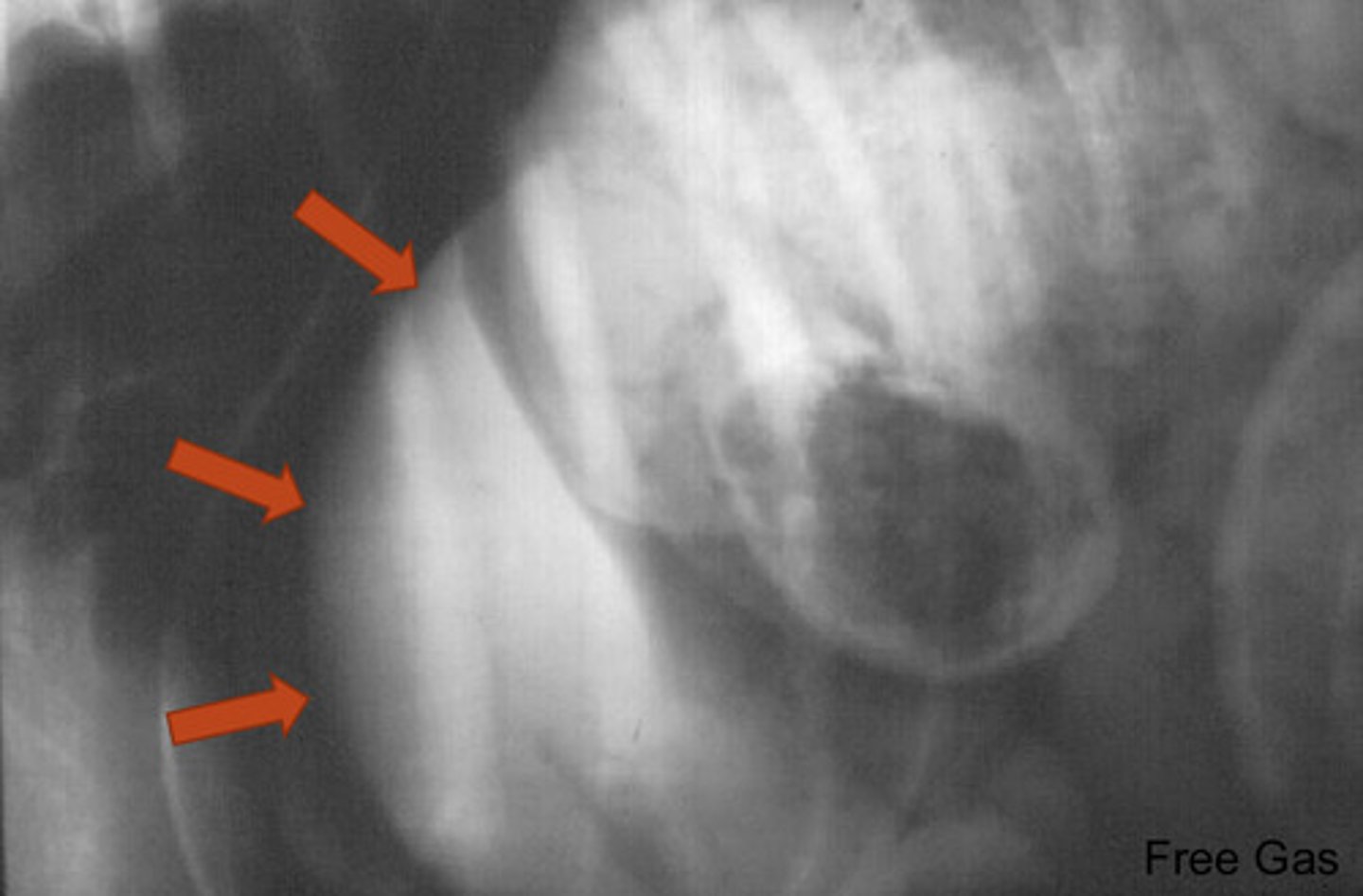
foreign body
what is abnormal about this radiograph?
-additional views
-Ultrasound, CT, MRI
-cystocentesis, biopsy
what could you do as your "next step" after doing abdominal radiographs?
left
what side is "down" on left lateral?
right
what side is "down" on right lateral?
we are observing a "shadow" of the patient on the film
the term "projection" is preferred in radiography because?
left!
in a lateral view, the cranial aspect of the animal is always on the ______?
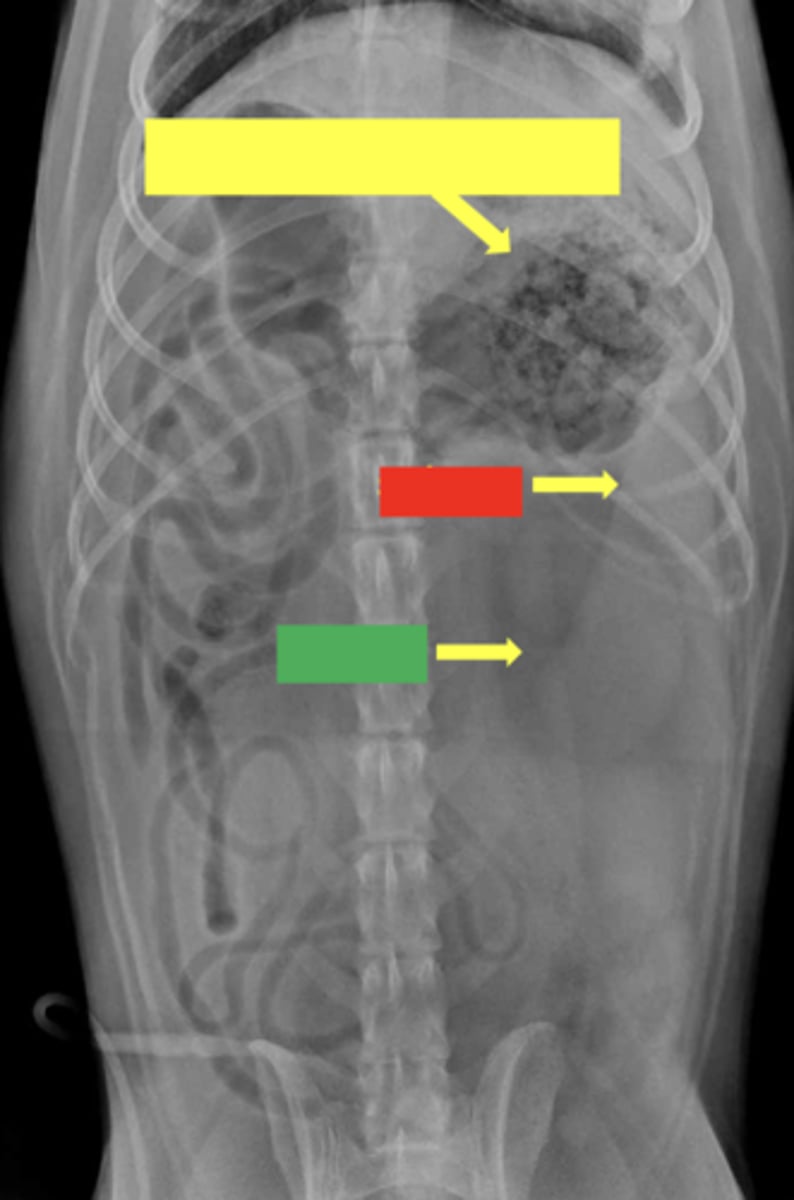
cardia
in left lateral recumbency, what parts of the stomach are "down"?
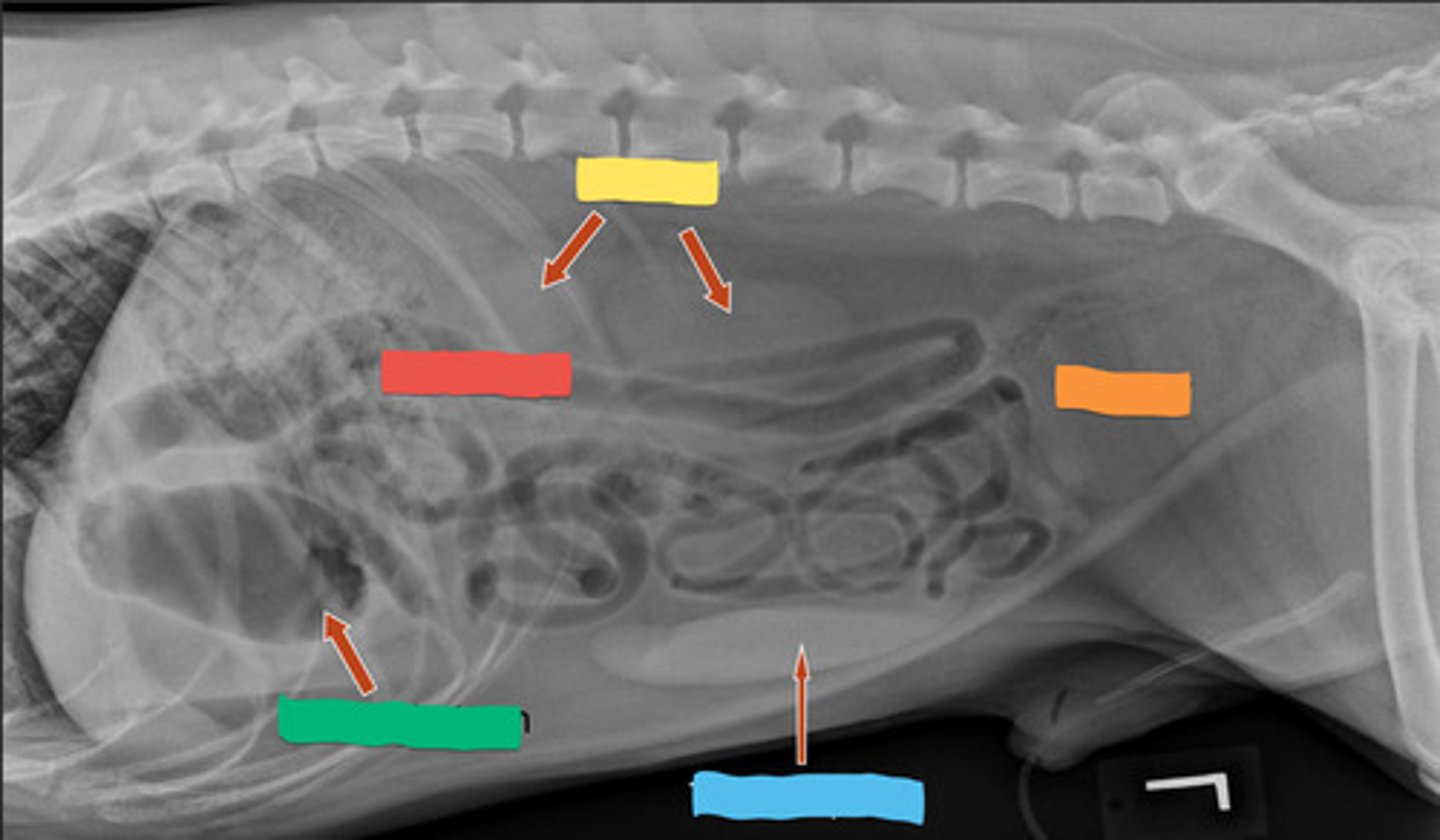
yellow- kidney
red- duodenum
green- pyloric antrum
blue- tail of spleen
orange- bladder
ID parts of abdomen
gas filled, because fluid moves "down"
on a left lateral view, why would the pyloric antrum be more radiolucent?
parallel
on left lateral view, the stomach axis is _________ to ribs or perpendicular to the spine
dependent or "down"
on right lateral view, the pyloric antrum is dependent or independent?
fluid-filled
what opacity will the pyloric antrum be on right lateral view?
stomach (pyloric antrum)
ID structure
ascending
at the caudal flexure of the duodenum become the _________ duodenum
left
VD or DV projections are viewed on the monitor with the right side to the viewer's _______
fluid opaque
the liver and diaphragm are both what opacity?
diaphragm
in a normal abdomen, the liver and ________ blend together
pylorus and fundus
which parts of the stomach tend to be more dorsal (in VD projection)
diaphragm
ID structure in abdomen
liver
ID structure in abdomen (right next to diaphragm)
fluid-filled cranial to the stomach
how does the liver appear (opacity) on x-ray and where (cranial/caudal) in respect to the stomach?
ventral
on lateral view of the liver, the _________ lobe margins should appear sharp
left
the caudal ventral border is formed by the ______ lateral lobe
barium
what can be placed in the stomach to aid in differentiating liver and stomach?
caudate lobe
in a VD/DV projection of the liver in the dog, the cranial border of the right kidney is buried in which lobe?
mineral
what opacity is this?
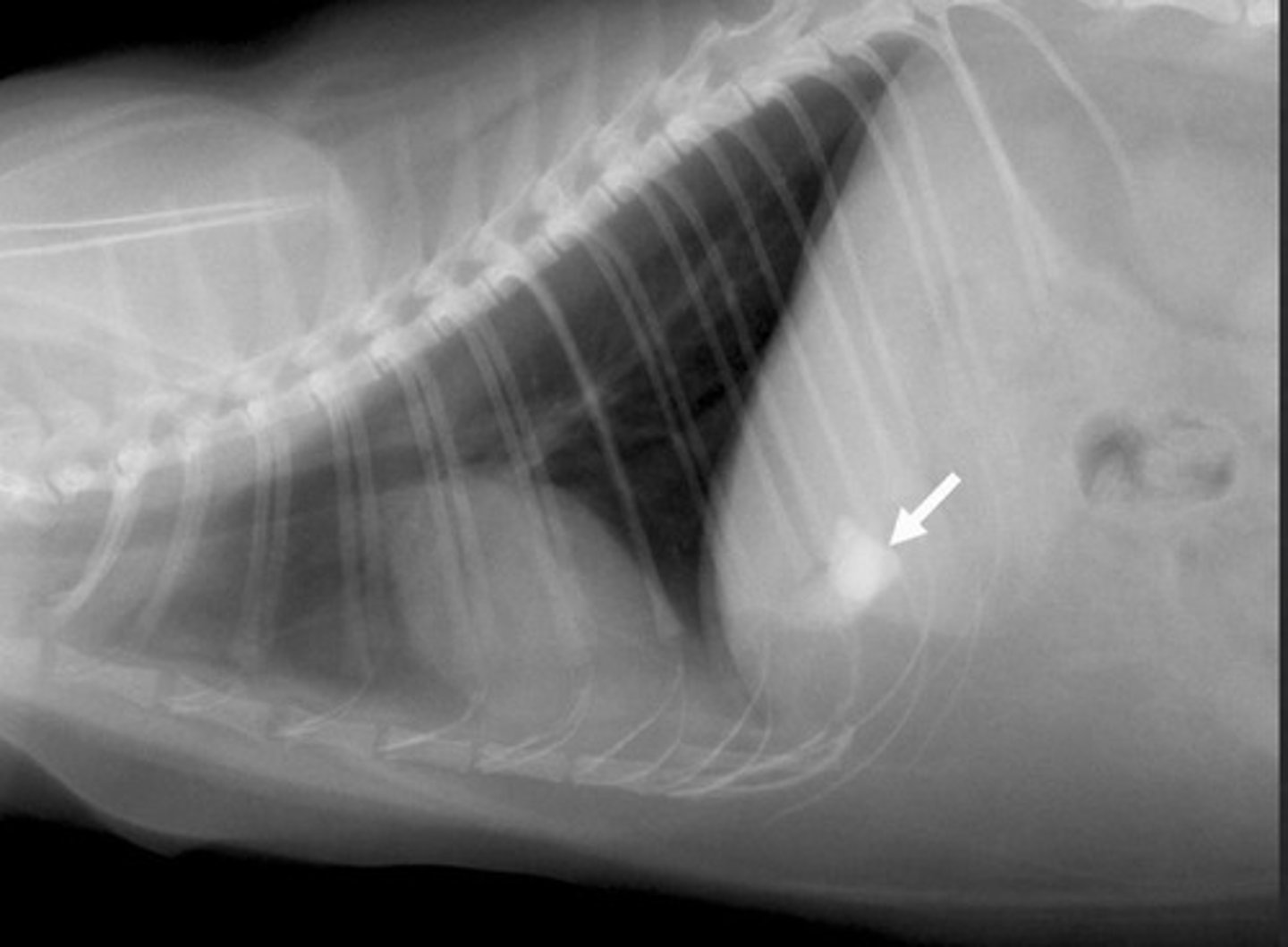
liver (technically gallbladder)
where is this mineral opacity located in the abdomen?
left and right lateral
in a VD/DV projection of the liver in the dog, the cranial duodenal flexure and fundus contact the ____ and ______ ______ lobes
adjacent
in a VD/DV projection of the liver in the dog, the medial and quadrate lobes are ________ to the lesser gastric curvature
right
on which side of the body is more liver seen?
FALSE
T/F: the body of the spleen will be seen in lateral recumbency
tail
the ______ of the spleen can be viewed on radiogrpahs
rounded to triangular shape soft tissue opacity on the floor of the abdomen
how does the tail of the spleen look on lateral projections?
left
the head of the spleen can sometimes be seen as a triangular opacity cranial to the _______ kidney
border effacement
why does the spleen appear to be attached to the body wall?
immobile
the spleen is immobile or mobile?
gastrosplenic ligament
what holds the spleen in place?
yellow- stomach
red- spleen
green- kidney
ID parts of abdomen
smaller and less visible
The feline spleen has a similar appearance radiographically but, is usually ________?
tail of the spleen
what part of the feline spleen do you usually not see on lateral view?
fat
______ in the retroperitoneal space allows the kidneys to be seen
13th
the right kidney is located at the level of which ribs?
cranial
the right kidney is cranial/caudal to the left?
caudate process of the caudate lobe
The cranial pole of the right kidney is buried in the ________________ of the liver and is poorly seen
summation
The caudal pole of the right kidney and the cranial pole of the left kidney are superimposed resulting in __________ creating a circular opacity
13th
in the VD view, the right kidney is bisected by the right ______ rib
caudally
in VD view, the left kidney is located more _______
2.5-3.5 x L2
(2.5 to 3.5 times greater length than L2)
what is the length of the kidney in the dog (VD view)?
more
the kidneys in the cat are more or less mobile?
caudal
-increased retroperitoneal fat
in the cat, the right kidney is located slightly more _______ than in the dog. WHY?
cranial pole
in the cat, which pole are you more likely to see of the right kidney?
2.4-3 x L2
in the cat, what is the length of the kidney?
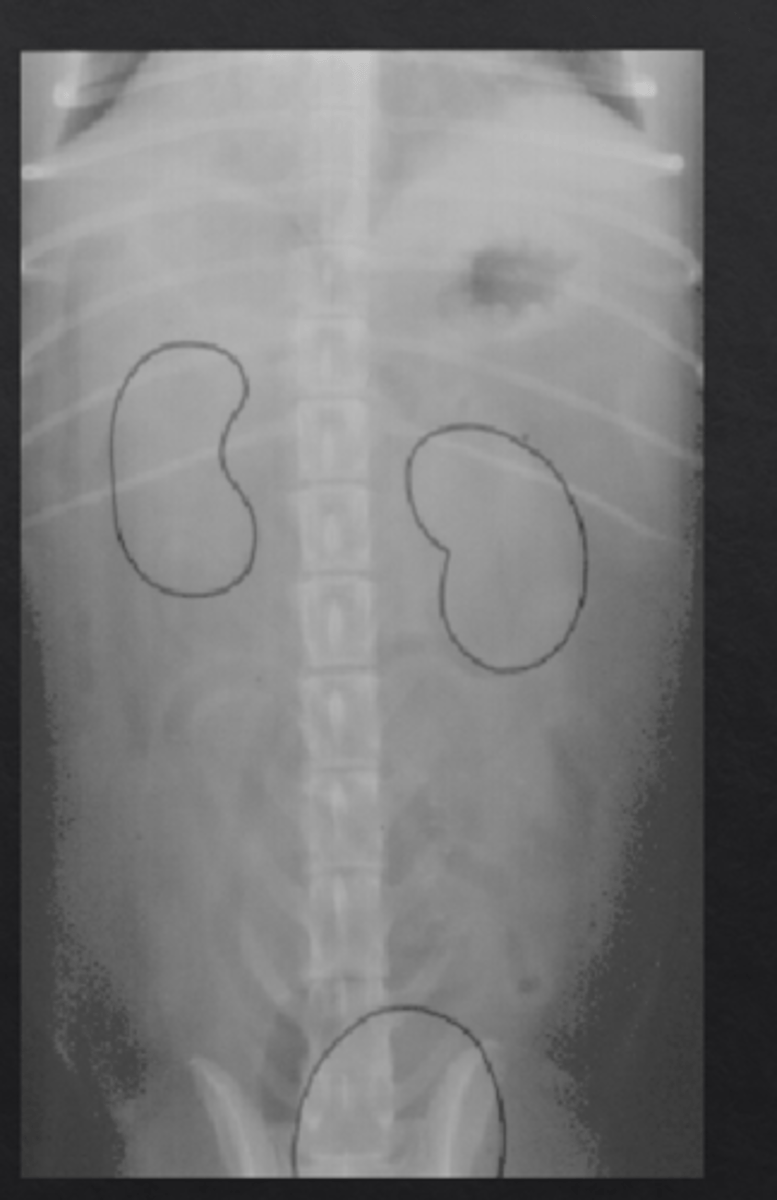
left- right kidney
right- left kidney
what is being outlined in the dog? (top two) which is right/left?
fluid-opaque
what opacity is the abdomen?
because of fat in the ventral and lateral ligaments and the omentum and mesentery
why can the bladder be seen?
pubis
in the dog, the neck of the bladder is near the ________
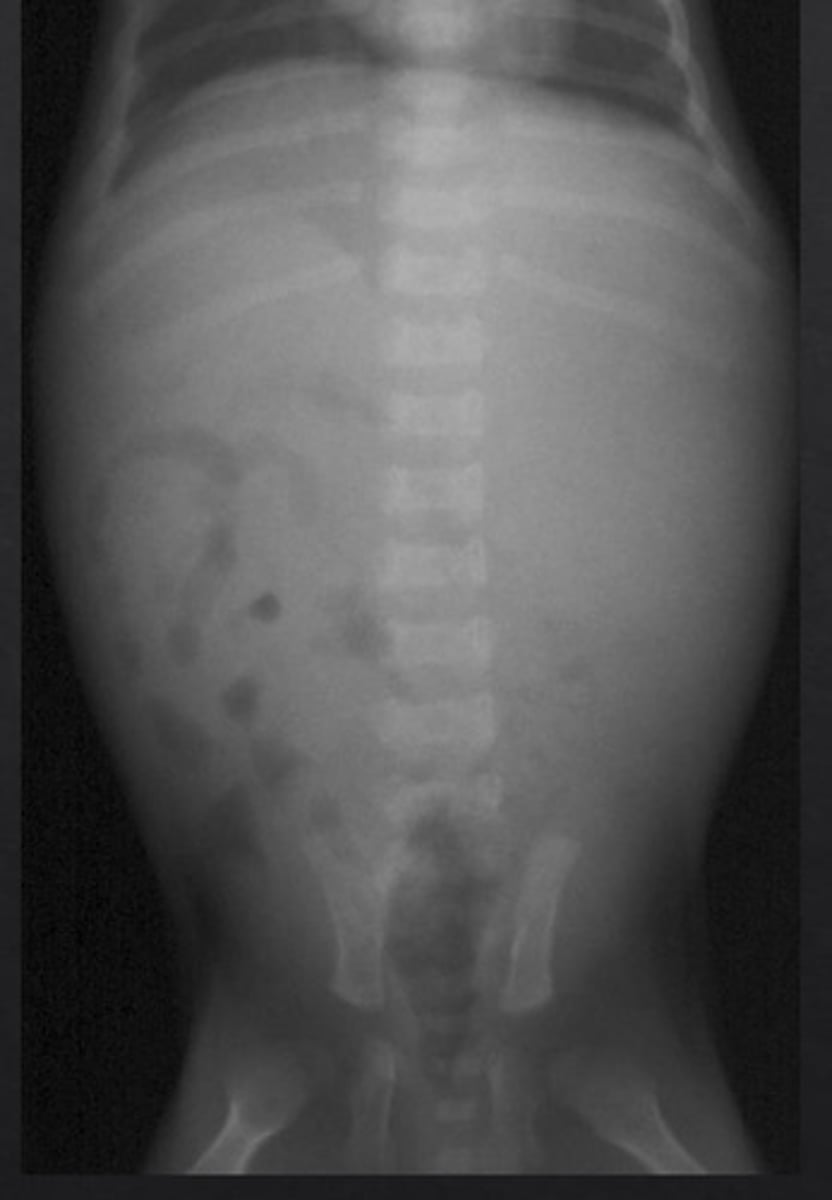
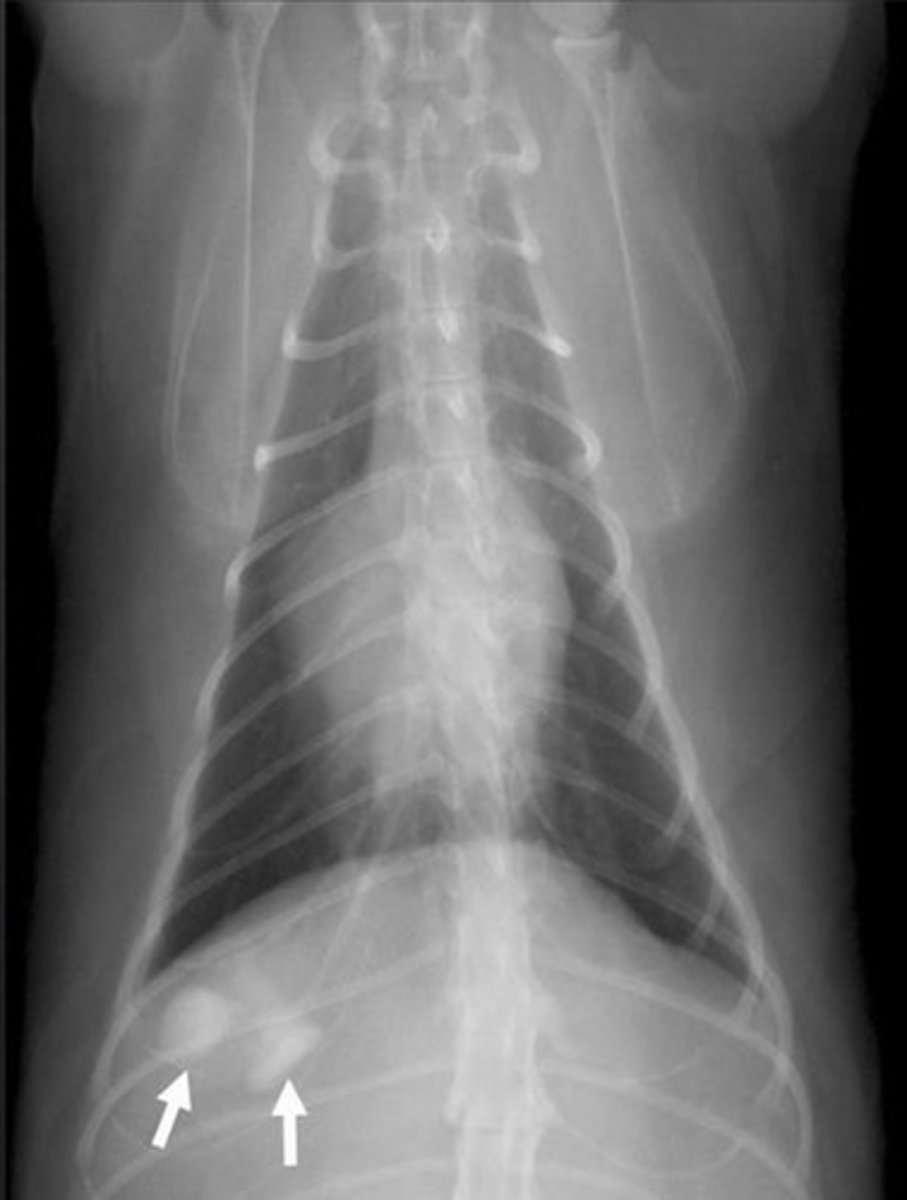
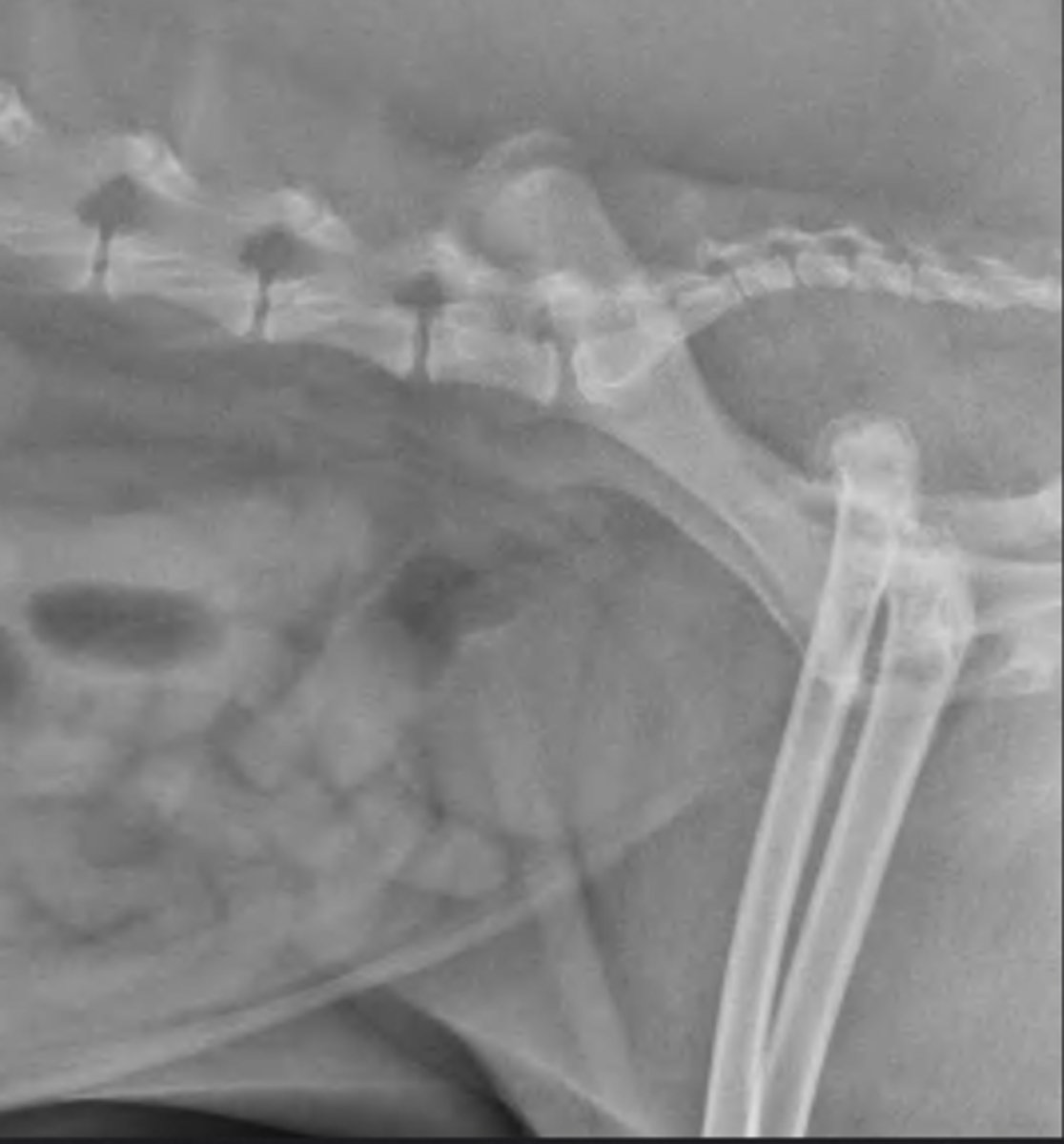
head of femur luxation
what is abnormal about this picture? (also be able to find the bladder)
-longer
-cranially
The feline bladder neck is _______ than that of the dog so that the bladder is located more _________
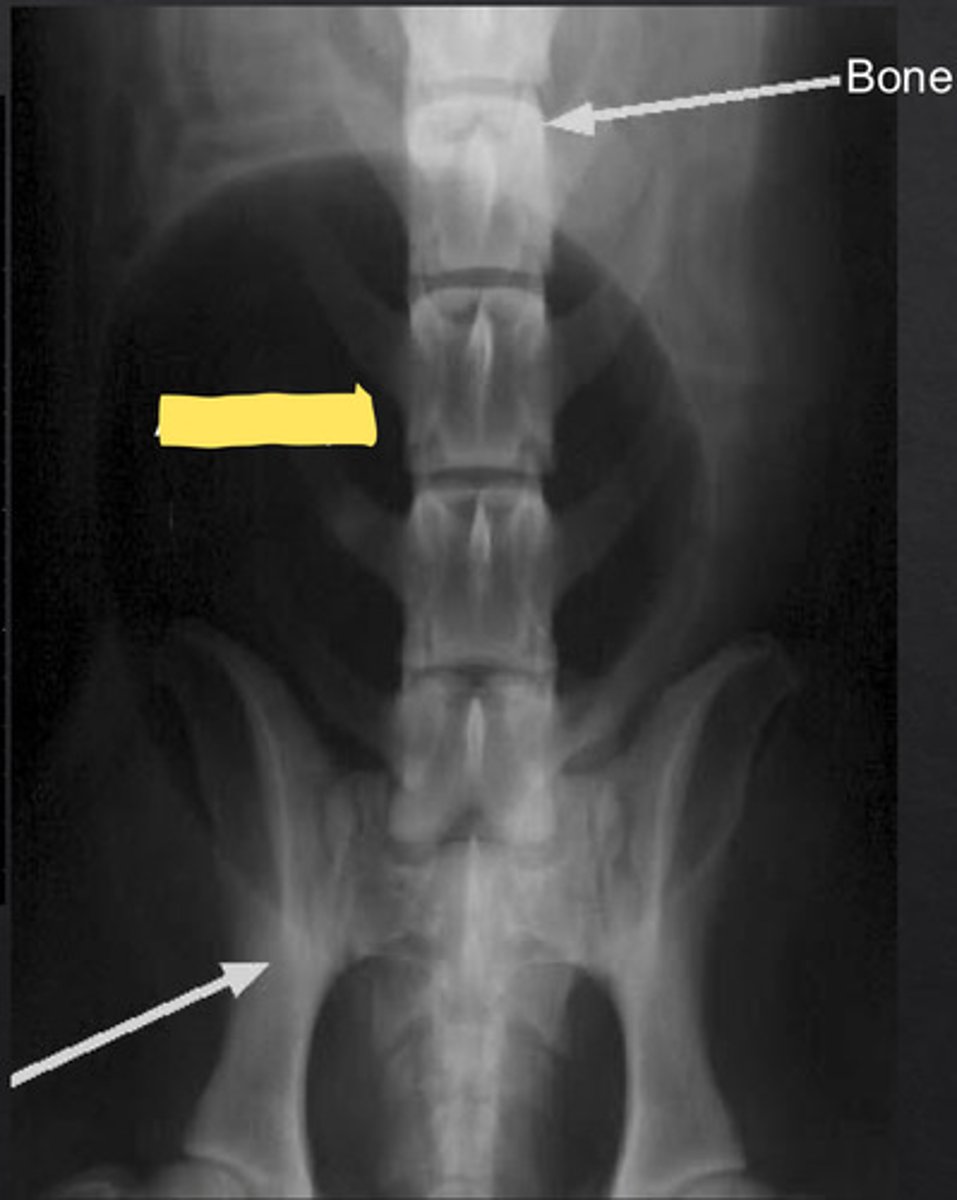
enlarged prostate
what is being shown in the radiograph?
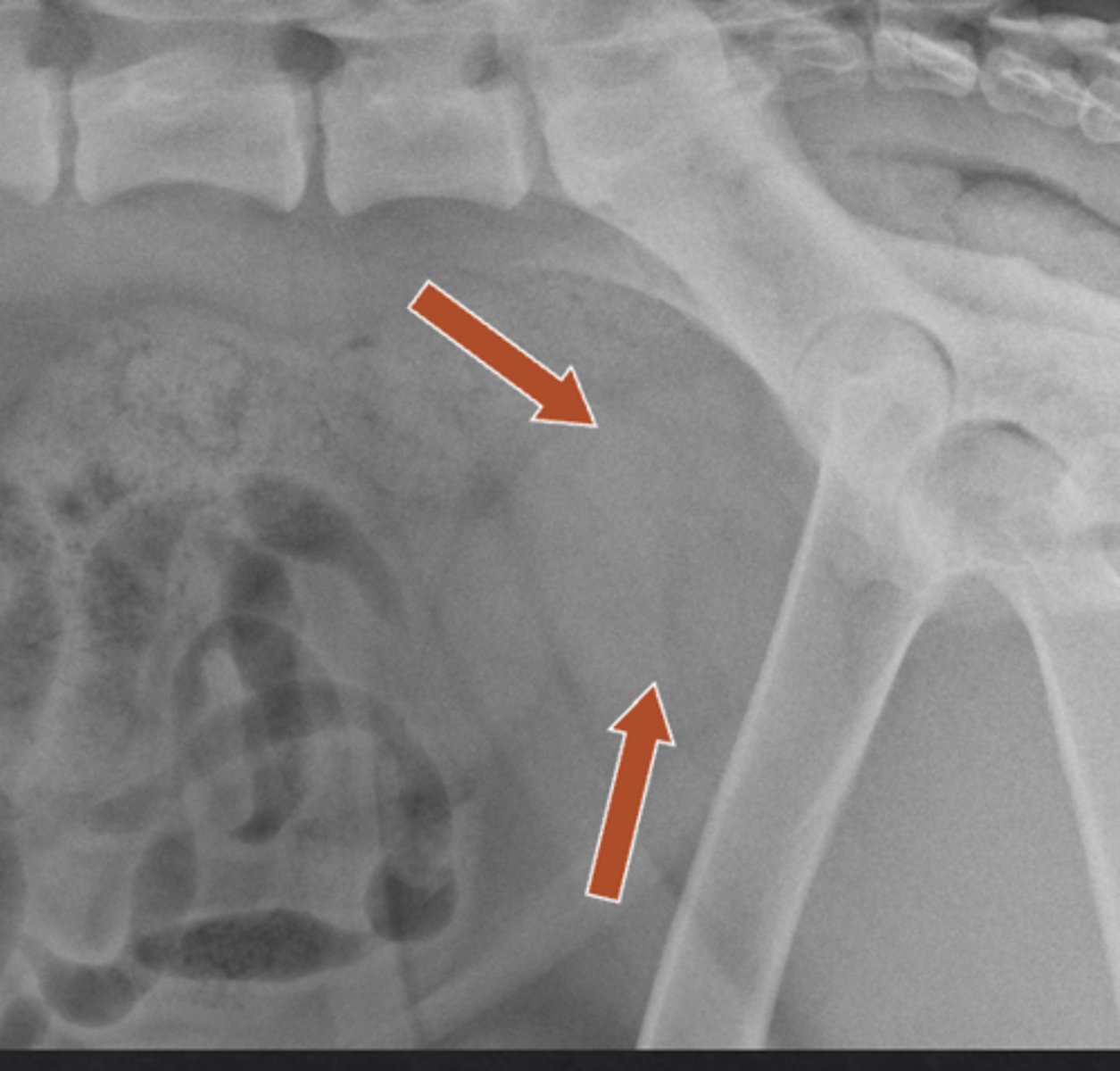
at neck of bladder
where is the prostate gland located?
the center
the urethra runs through what of the prostate gland?
prostate gland
In young or castrated dogs, the ____________ may be intrapelvic and may not be visible
prostate
ID what is being shown
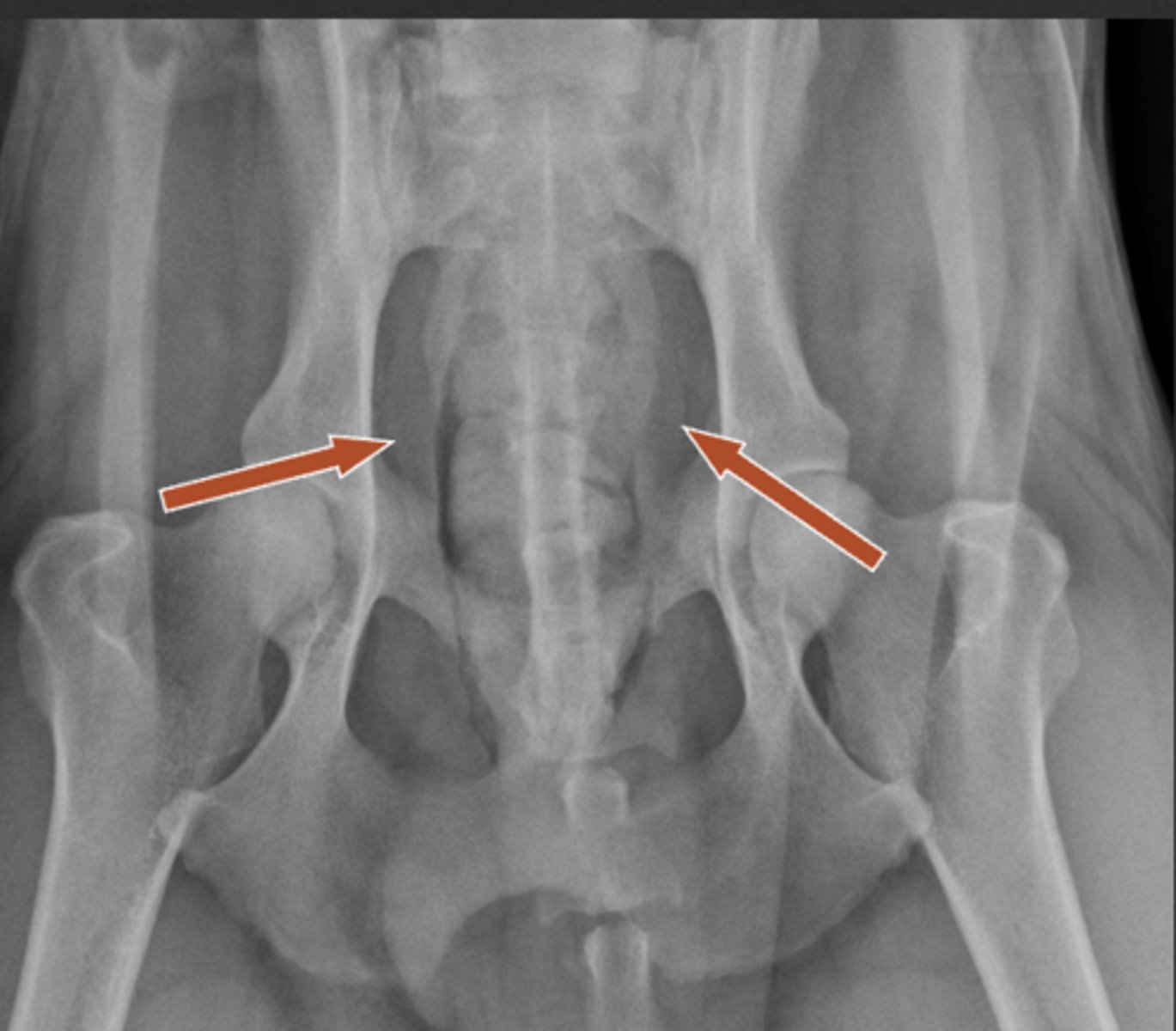
-fluid opacity
-cranial to pelvic brim
in older dogs, the prostate will appear as what opacity? where will it be located?
-pelvic brim
-ilial wings
In the ventrodorsal view, remember to look for the prostate cranial to the ____________ and not cranial to the
__________
NO
is the prostate gland visible in cats?
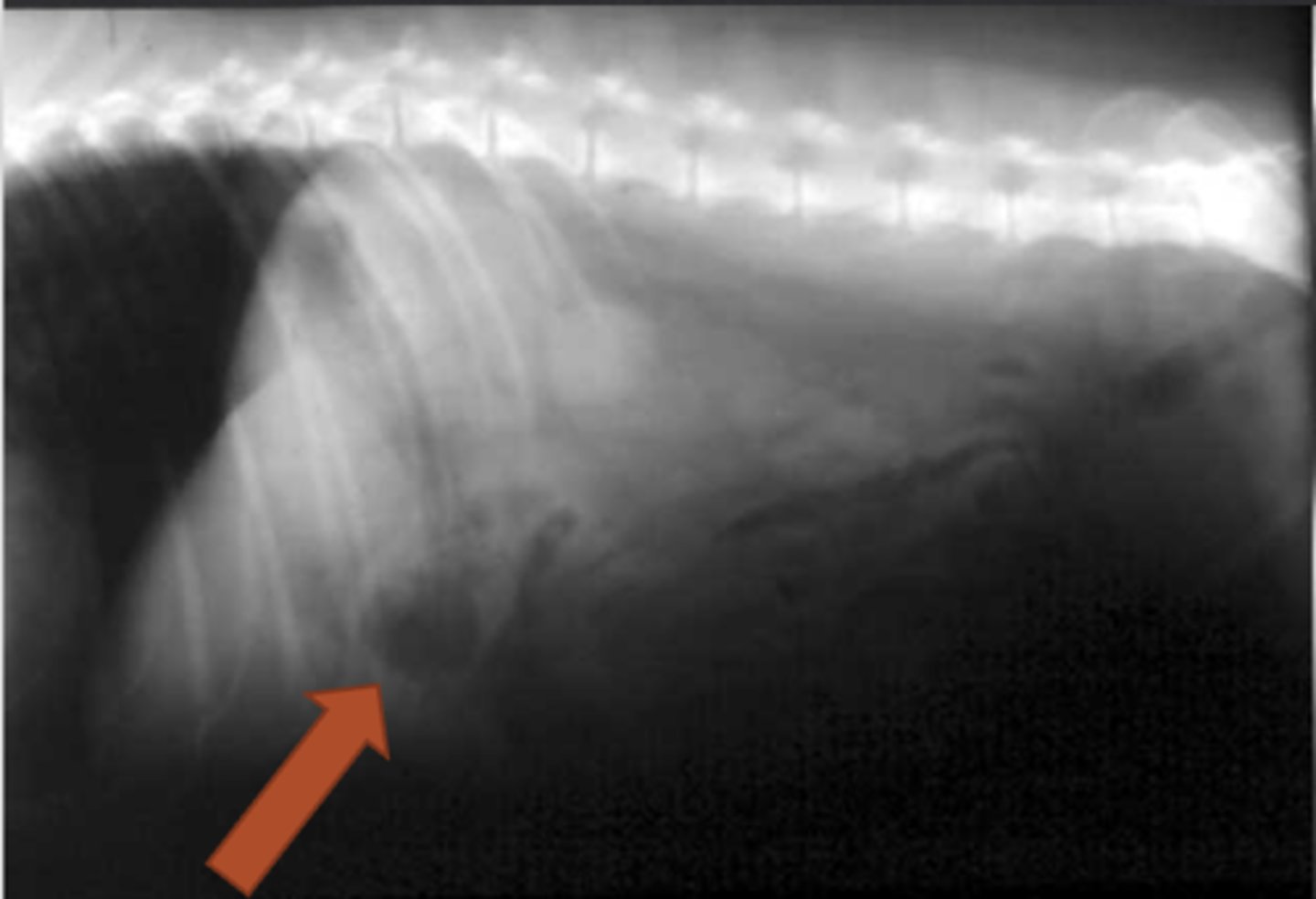
gas
in the dog, on left lateral view, the pyloric is ________ filled
stomach (pyloric antrum specifically)
what is being shown?
fluid
if the right side is down, the pyloric antrum is ______ filled
-stomach
-right
what is being shown? which side is down (R or L)?
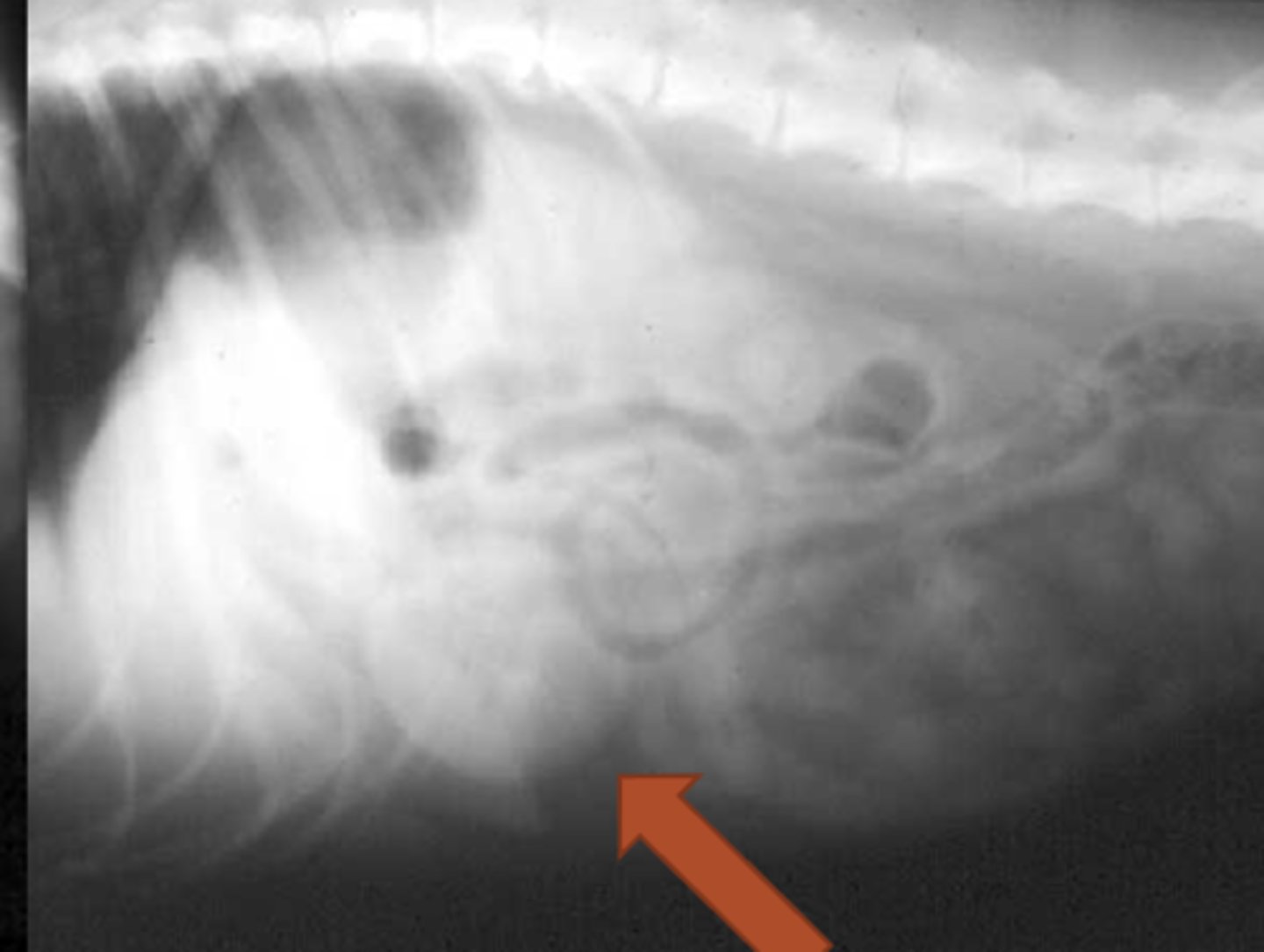
perpendicular
the stomach lies _______ to the spine across the abdomen
stomach
what is being shown?
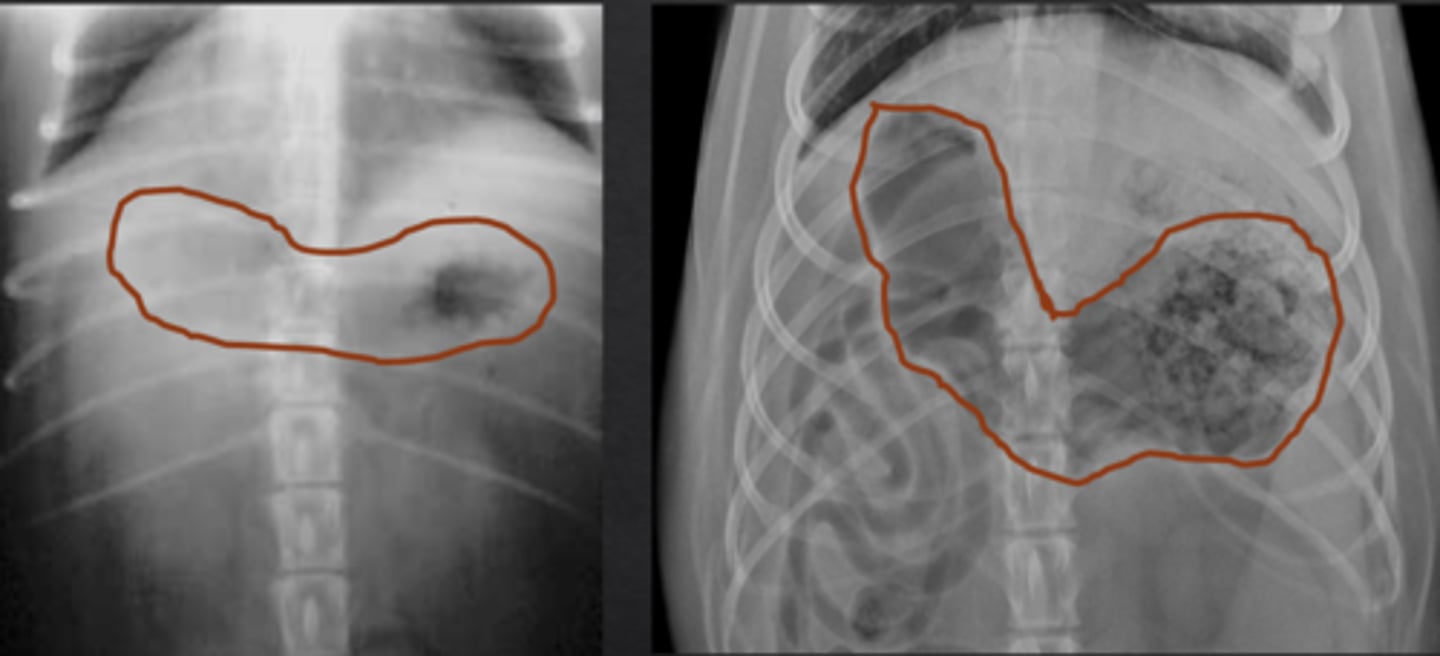
fundus
in dorsal recumbency, the _______ is dependent
gas
in dorsal recumbency, _______ moves to the body of the stomach
gastric body
in ventral recumbency, the ________ is dependent
fluid
in ventral recumbency, _______ moves to the body of the stomach
will fill the fundus
in ventral recumbency, where will the gas go?
large falciform fat pad
most cats have _______ that elevates the liver and stomach?
normal! its falciform fat pad
is this normal or abnormal?
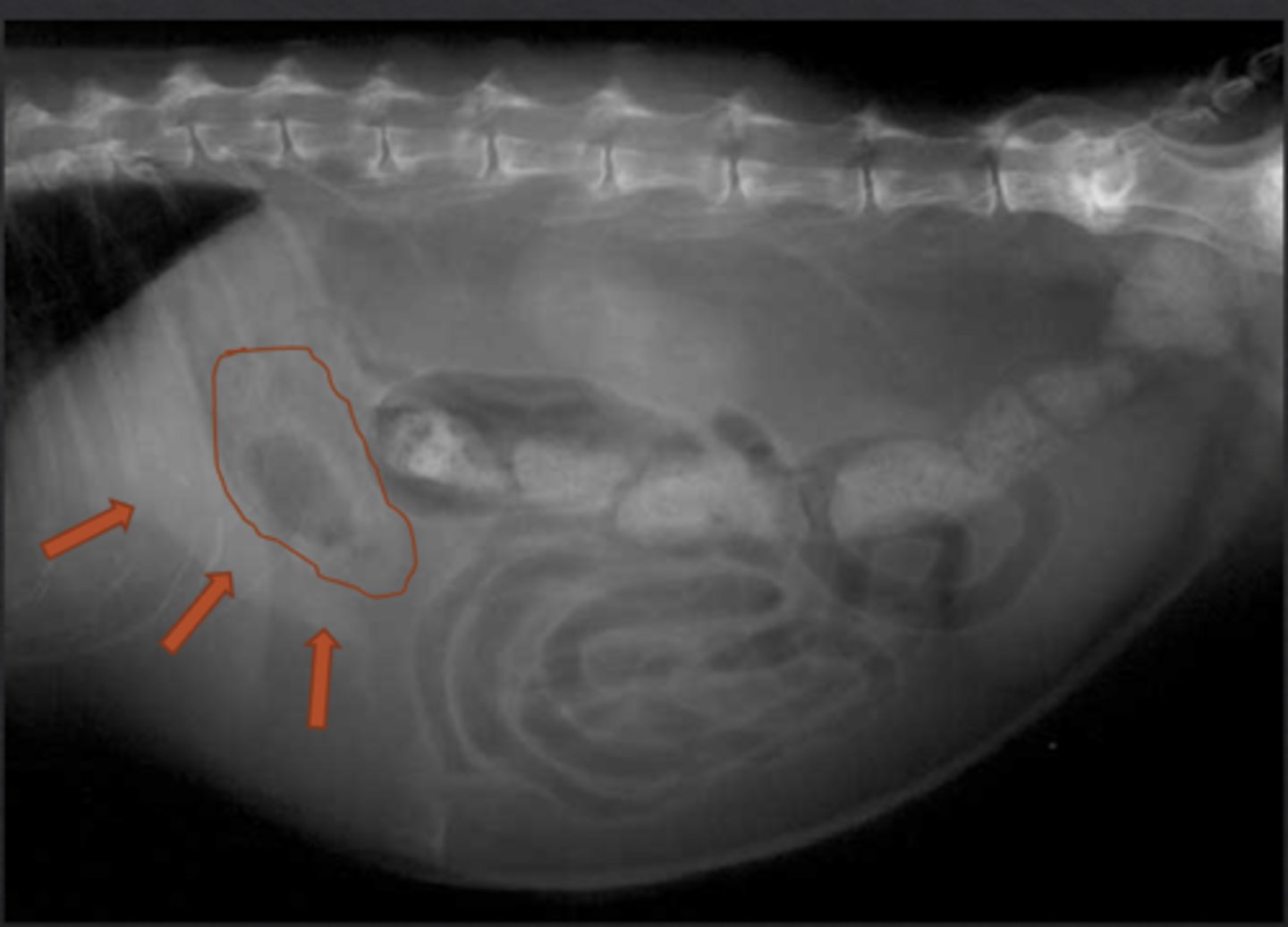
spine
in the cat stomach, the pylorus is superimposed on or to the right of the _______
cat, because of falciform and retroperitoneal fat
is this a cat or dog?
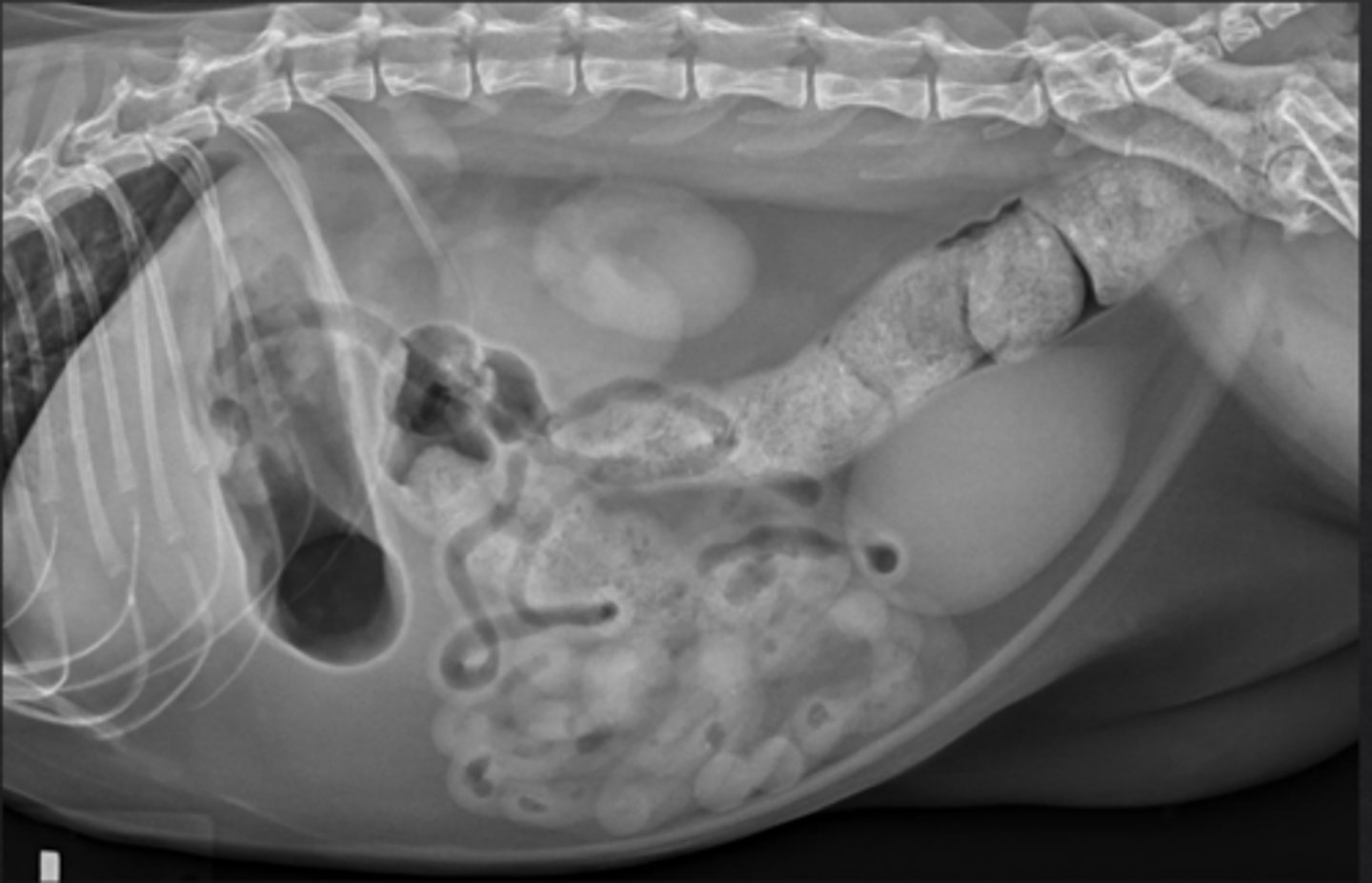
max of 12 mm serosal to serosa
in cats, the small intestine should be what size?
2 x the width of the last normal rib
in dogs, the small intestine should be what size?