Age of Jackson
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
End of the Era of Good Feelings
More sectionalism, end of Post-Ghent nationalism
Return of Political Parties
United Republicans under era of good feelings split
National Republicans with Adams
Democratic Republicans with Jackson (renamed to Democrats under Jackson’s presidency)
Election of 1824
Last old-style election
James Monroe completed his second term; 4 new candidates all representing Democratic-Republicans
John Quincy Adams (Mass): highly intelligent, experienced, and aloof
Henry Clay (KT): the gamy and gallant “Harry of the West”
William H. Crawford (GA): an able though ailing giant of a man
Andrew Jackson (TN): gaunt, gutsy hero of New Orleans
Corrupt Bargain
Jackson called the election of 1824 a corrupt bargain because Jackson had the most votes and electoral votes, but not the majority
This made the election be thrown to the house of representatives where Henry Clay was the speaker
John Quincy Adams wins the election from the house of representatives and Jackson is mad about that
Adams’ Presidency
First “minority president” with difficulty winning the popular vote
Nationalist views
Most people swinging away from post-Ghent nationalist & toward states rights and sectionalism
Swung against the tide toward nationalism
First annual message urged Congress the construction of roads & canals
He renewed Washington’s proposal for a national university
Advocated federal support for an astronomical observatory
One of the least successful presidents
Entering White House under charges of “bargain”, “corruption”, and “usurpation”.
Henry Clay Secretary of State
Nationalist in a time of sectionalism, not keeping up with what was happening.
Wanted to treat the Cherokee Indians fairly since they’ve already been living there, and the citizens didn’t like that because they wanted more land.
Jackson Philosophy
Rewards loyalty, wanted the common man to have power and less in the national government. Jackson broke a lot of rules and he did that “in the interest of the common man.”
Spoils System
To the winner goes the spoils
Rewarding political supporters with public office
Was introduced to the federal government on a large scale
Jackson defined it on Democratic grounds:
“Every man is as good as his neighbor, perhaps equally better.”
Washington was due for a housecleaning
He fired a lot of the government workers and gave those jobs to his friends and supporters
Less about finding new blood than about rewarding old cronies
Scandals with this
illiterates , incompetents, and plain crooks were given positions of public trust
Important element of 2 party order
Gave jackson a ton of power because of loyalty
Fires ppl with disagreements and rewards ppl who agree with him
Anything Jackson wants
Election of 1828
Adams’ second presidential campaign began in 1825 when get was elected by the house
Adams only won some parts of New England, Jackson won everywhere else
Jackson had risen from adversity
Jackson’s inauguration
Symbolized the ascendancy of the masses
White House was thrown open for the first time
Tariff of 1828
The South hates tariffs because they dont make money off of their goods so South Carolina (BIG TARIFF), against what Jackson thought. SC didn’t want to pay these high tariffs and said they’d leave, and eventually Jackson comes with the army and by intimidation/force, and that they’re going to pay these tariffs regardless.
South Carolina Exposition
SC declared the Tariff of 1828 unconstitutional
Affirmed Calhoun’s “nullification theory”, where each state had the right to obey a national law or declare it void.
SC continued to increased tension by rejecting the Tariff of 1832 as well
Jefferson responded with military action and a Force Bill was passed giving Jefferson authority to act against SC
Tariff Compromise
Going in hand with the force bill, Henry Clay (the great compromiser) proposed an idea.
The tariff would start off high
Both sides (SC & National Government) thought they won because they would end up getting lower tariffs and the national government would get to keep South Carolina, meaning they wouldn’t leave.
Bank of the United States
Bank War:
When Daniel Webster & Henry Clay presented the congress with a bill to renew Bank of the US’ charter
Charter was not to expire until 1836, but Clay pushed for renewal 4 years early to make it an election issue in 1832
Clay’s scheme was to run a recharter bill through Congress and then send it to the white house
Supreme Court declared monopolistic bank constitutional in McCulloch v Maryland (1819)
Jackson’s veto message reverberated with constitutional consequences
Vastly amplified the power of presidency
He was arguing that he vetoed because he personally found it harmful to the nation
He was claiming for the president alone a power equal to ⅔ votes in the Congress
Destroying the Bank:
Charter denied, Bank of the US due to expire in 1836
Jackson was not one to let it die
He decided to bury the Bank by removing all federal deposits
Further proposed depositing no more funds
Death of the Bank of the US left a financial vacuum and kicked off a lurching cycle of booms and busts
Surplus of federal funds in state institutions – the so-called pet banks
No central control; the pet banks and smaller “wildcat” banks were more fly-by-night operations
Jackson tried to rein in the runaway economy
Authorized the Treasury to issue a Specie Circular – a decree that required all public land to be purchased with “hard” or metallic money
This drastic step slammed the brakes on the speculative boom, thus contributed to the financial panic and crash in 1837
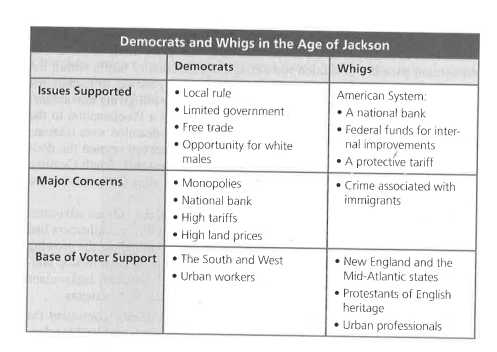
Whig Party
Whigs consisted of National Republicans & Anti-Masonic Party (people who didn’t like Jackson).
The Whig Party essentially had no other reason to gather together other than to hate on Jackson. So their connection as a party wasn’t as strong as the Democrats.
Others who joined the Whigs
Supports of Clay’s American System, southern states’ riggers, larger northern industrialists and merchants, and many evangelical Protestants
Whigs thought of themselves as Conservatives, yet progressive in their support of active government programs and reforms
Called for internal improvements like canals, railroads, telegraph lines, and support for institutions-prisons, asylums, and public schools.
NORTH & EAST: MORE WHIGS
SOUTH & WEST: MORE DEMOCRATS
Election of 1836
Whig’s Plan
Run 3 candidates
One from each section
No majority in the electoral college
Election decided in the House of Representatives
Van Buren wins (Whig’s Plan fails)
Intelligent, successful statesmen, wealthy
Van Buren’s problems as president:
He’s not Jackson
Jackson’s enemies
Anti-slavery
Texas annexations
Panic of 1837 economic depression
Divorce Bill
“Divorces” the government from banking
Treasury independence
No more investing
No more loans
Tippecanoe and Tyler too
Whig party motto in the Log Cabin and Hard Cider, Tippecanoe represented
Resulted in the victory of the Whig Party in the Election of 1840
William Henry Harrison & John Tyler
Jackson’s Beliefs
equal protection of the laws; an aversion to a moneyed aristocracy, exclusive privileges, and monopolies, and a predilection for the common man; majority rule; and the welfare of the community over the individual.
Increased Suffrage
Towards the end of Van Buren’s presidency, people started to recognize that the common man should have more rights.
Back then, in order to be able to do anything you had to be white, have land, etc.
However, people started advocating for more rights towards the common people, not just white, rich men.
Jacksonian Democracy
Pass legislation to the common man.
Emphasizing the empowerment of ordinary citizens against elite interests.
Sectional Differences
North & South:
North: favored their protective tariffs (helped manufacturing and businesses)
South: disliked tariffs, hurt more than help.
North more Whigs, south and west more Democrats
Jackson's Legacy
Had to appeal to the common man and way more voters
Ideology of the Democratic Republicans and the Whigs
Also called for internal improvements like canals, railroads, telegraph lines, and support for institutions-prisons, asylums, and public schools.