Metals and Non-metals
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
Property of metals
Melting and Boiling Points- High (they are al solid at room temperature. except mercury which is a liquid
Malleability- Malleable (they can be hammered into different shapes without breaking)
Ductility- Ductile(they can be drawn out to make wires)
Heat Conductivity- Good
Electrical Conductivity- Good
Property of Non-Metals
Melting and Boiling Points- Lower than metals(bromine is a liquid at room temperature, and eleven others are gases)
Malleability- Brittle(they break or shatter when hammered)
Ductility- Not Ductile
Heat Conductivity- Bad
Electrical Conductivity- Bad (except graphite, a form of carbon)
Alloy definition
A mixture of metals with other elements
Alloy Examples- need to remember what its made out of
Its a mixture of:
Stainless Steel: Iron, Chromium, Nickel and Carbon (C).
Brass: Copper and Zinc
Why are alloy’s used instead of pure metals?
The alloy will have a different and improved set of physical properties from either of its “parent” metals
Example: Stainless steel is used in cutlery because of its hardness and resistance to rusting.
Alloys can be harder and stronger than pure metals
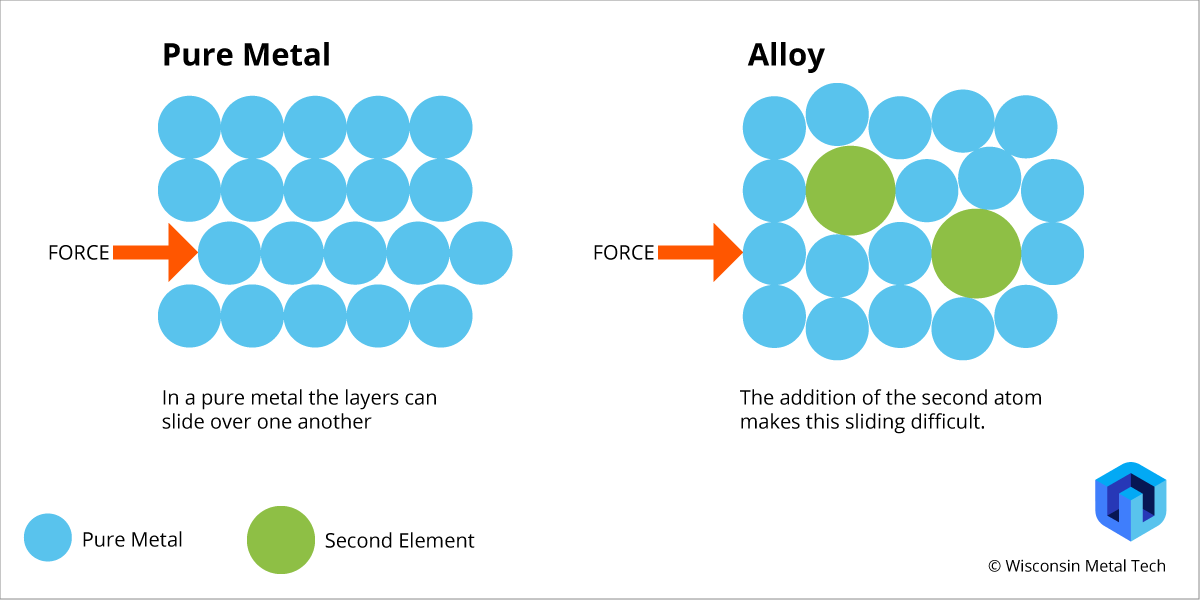
Structure of Metals vs alloys
Alloys can be harder and stronger that pure metals because of the different sized atoms in alloys means the layers can no longer slide over each other
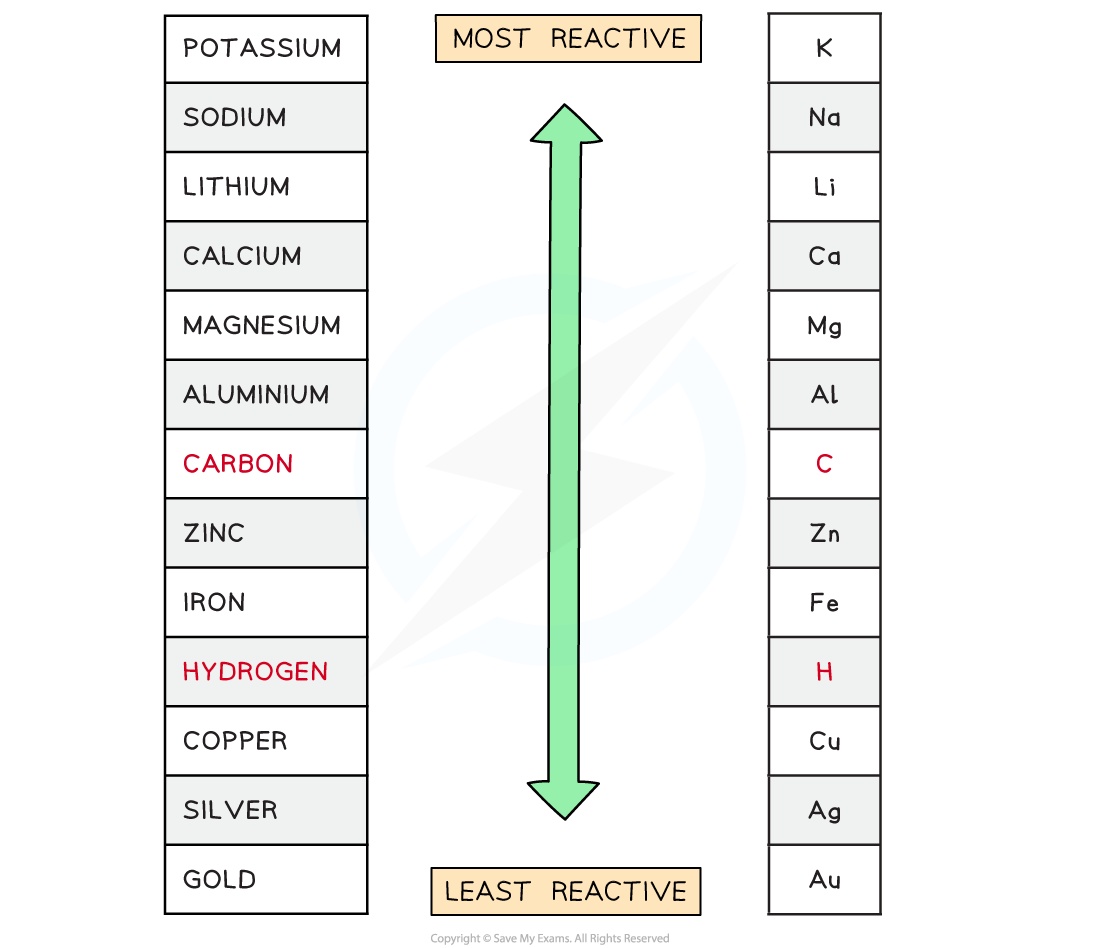
Reactivity Series of Metals-Including Carbon and Hydrogen
P - Please Potassium
S- Send Sodium
L - Lions Lithium
C - Cats Calcium
M - Monkeys Magnesium
A - And Aluminium
C - Cute Carbon
Z - Zebras Zinc
I - Into Iron
H - Hot Hydrogen
C - Countries Copper
S - Signed Silver
G - Gordon Gold
Reactions with Metals- Water
Potassium-Reacts with cold water
Sodium- Reacts with cold water
Calcium- Reacts with cold water
Magnesium- Reacts with cold water
Aluminium- Protected by an oxide layer
Reactions with Metals- Dilute hydrochloric acid
Magnesium-Reacts, but less vigorous
Zinc-Reacts, but less vigorous
Iron-Reacts, but less vigorous
Copper-No Reaction
Silver- No Reaction
Gold-No Reaction
General word equations-Reactions of metals
metal + oxygen = metal oxide
metal + water = metal hydroxide + hydrogen
metal + acid = metal salt + hydrogen
The salt formed depends on the acid used:
Hydrochloric acid= Chloride
Nitric acid= Nitrate
Sulfuric acid= Sulfate
Metals reactions with water and steam-Description
Potassium, Sodium, Calcium - Fizz giving off hydrogen gas and forming a metal hydroxide solution
Magnesium (STEAM) - Reacts giving off hydrogen has and forming magnesium oxide
Extraction of metals-Related to reactivity
The ease in obtaining metals from their ores is related to their position in the reactivity series:
the more reactive the metal the harder its to obtain
the less reactive the metal the easier its to obtain
Aluminium is extracted from its ore bauxite by electrolysis
.
Iron from hematite is extracted by reduction for iron(III) oxide in the blast furnace
.