Cell Theory, Organelles, Organelles, Cell Theory
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
cell
what all living things are made of
microscope
first evidence for the cell theory - that cells exist

unicellular
made of just one cell
multicellular
made of more than one cell
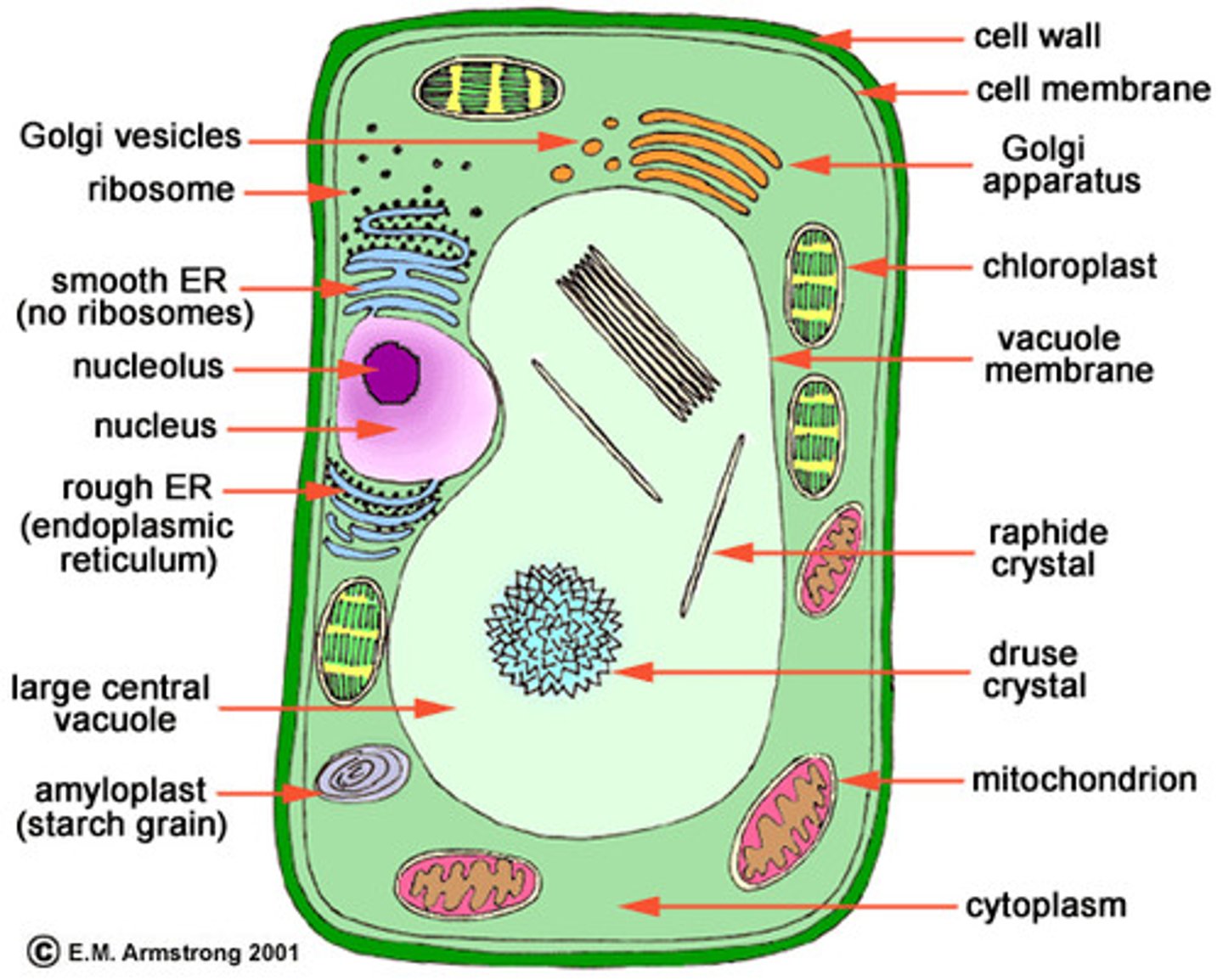
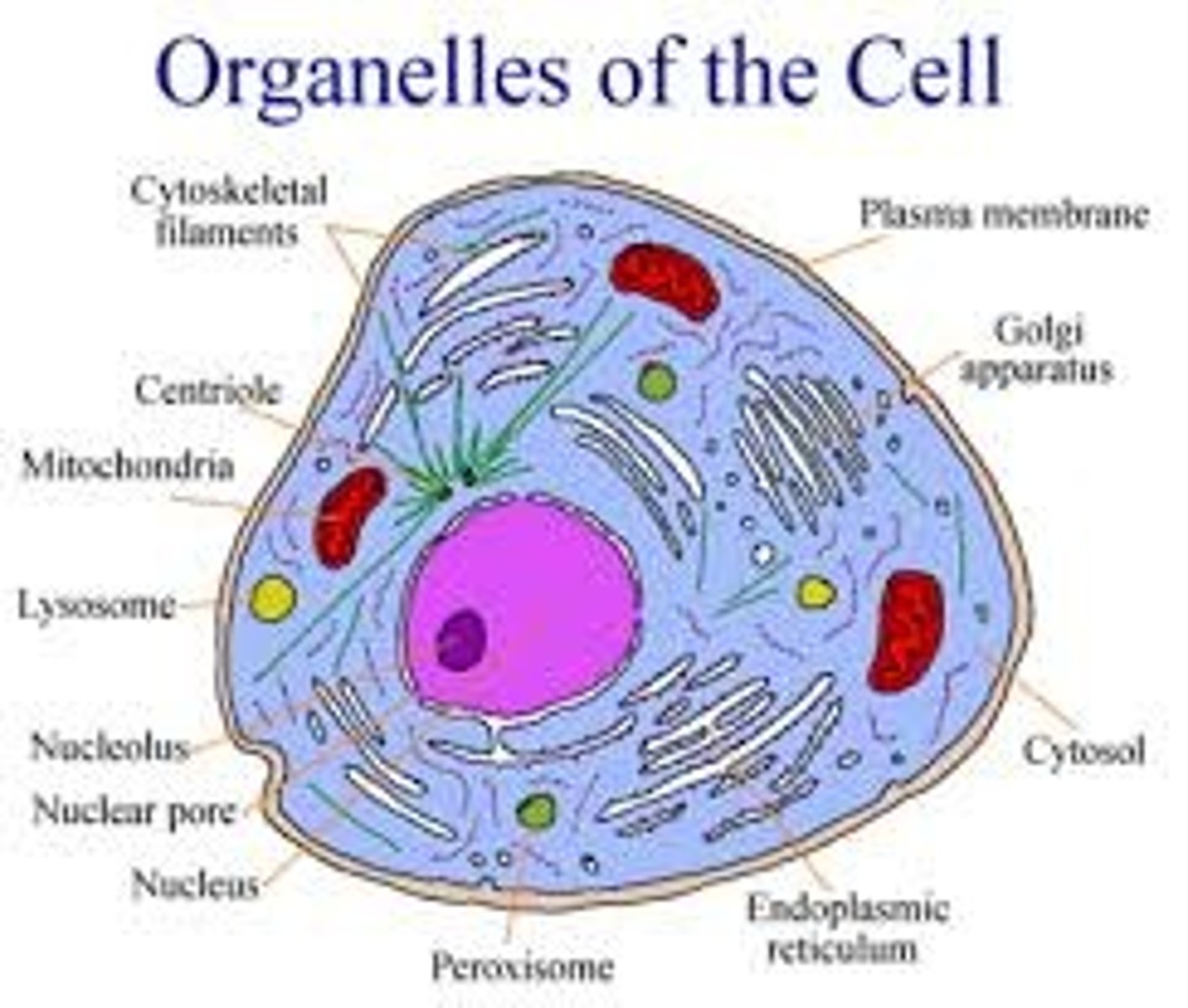
organelles
"small organs" of the cell that do different jobs

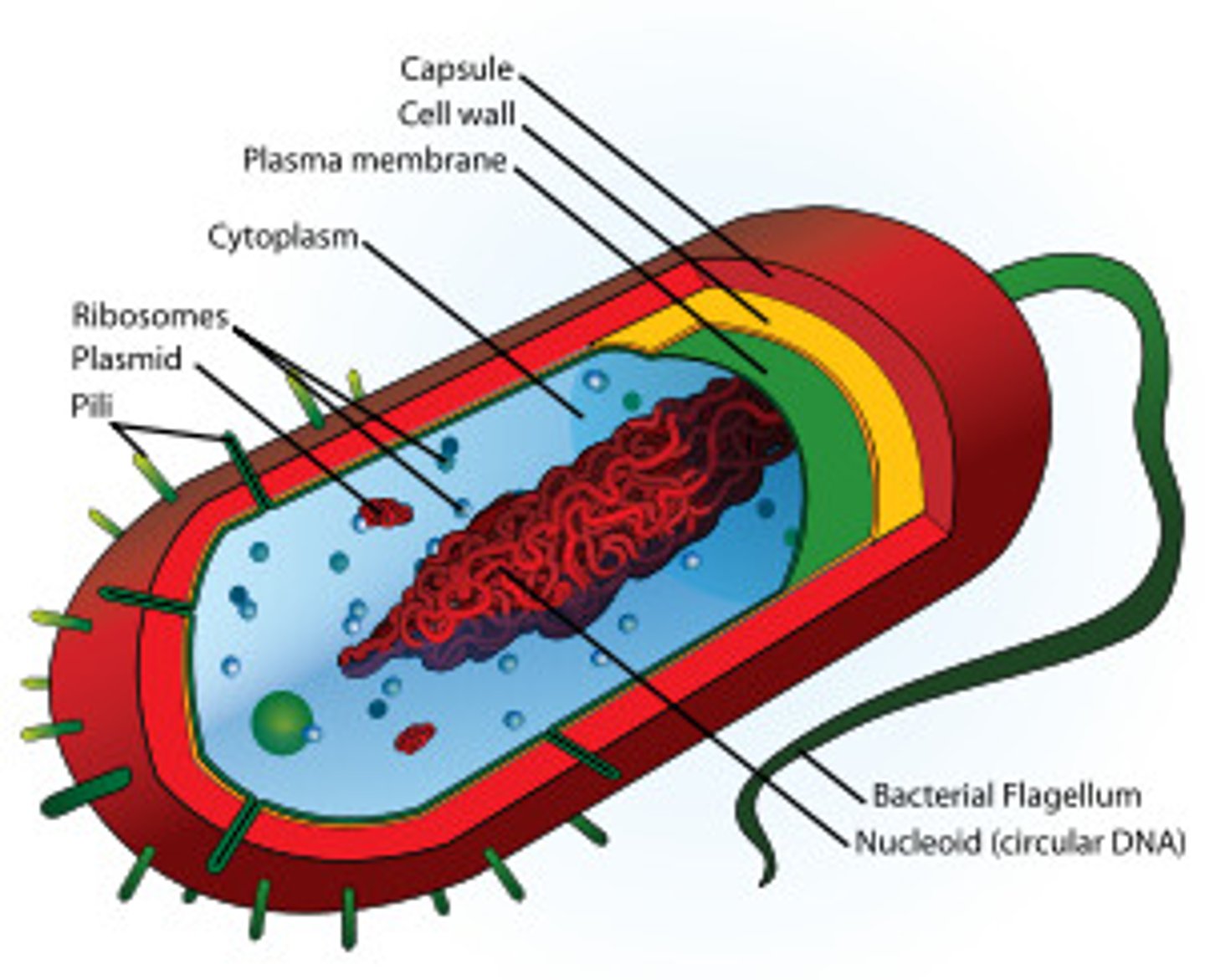
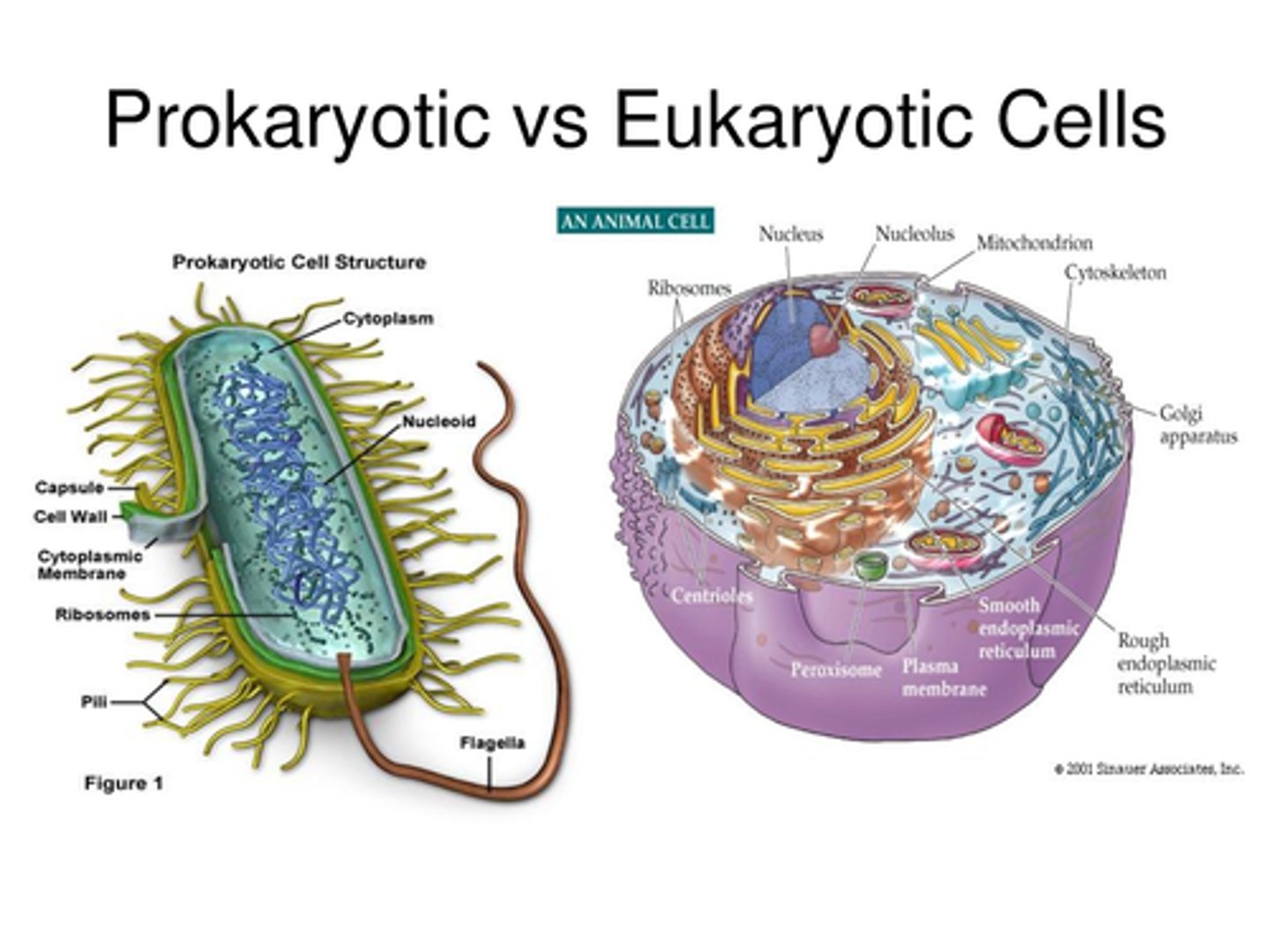
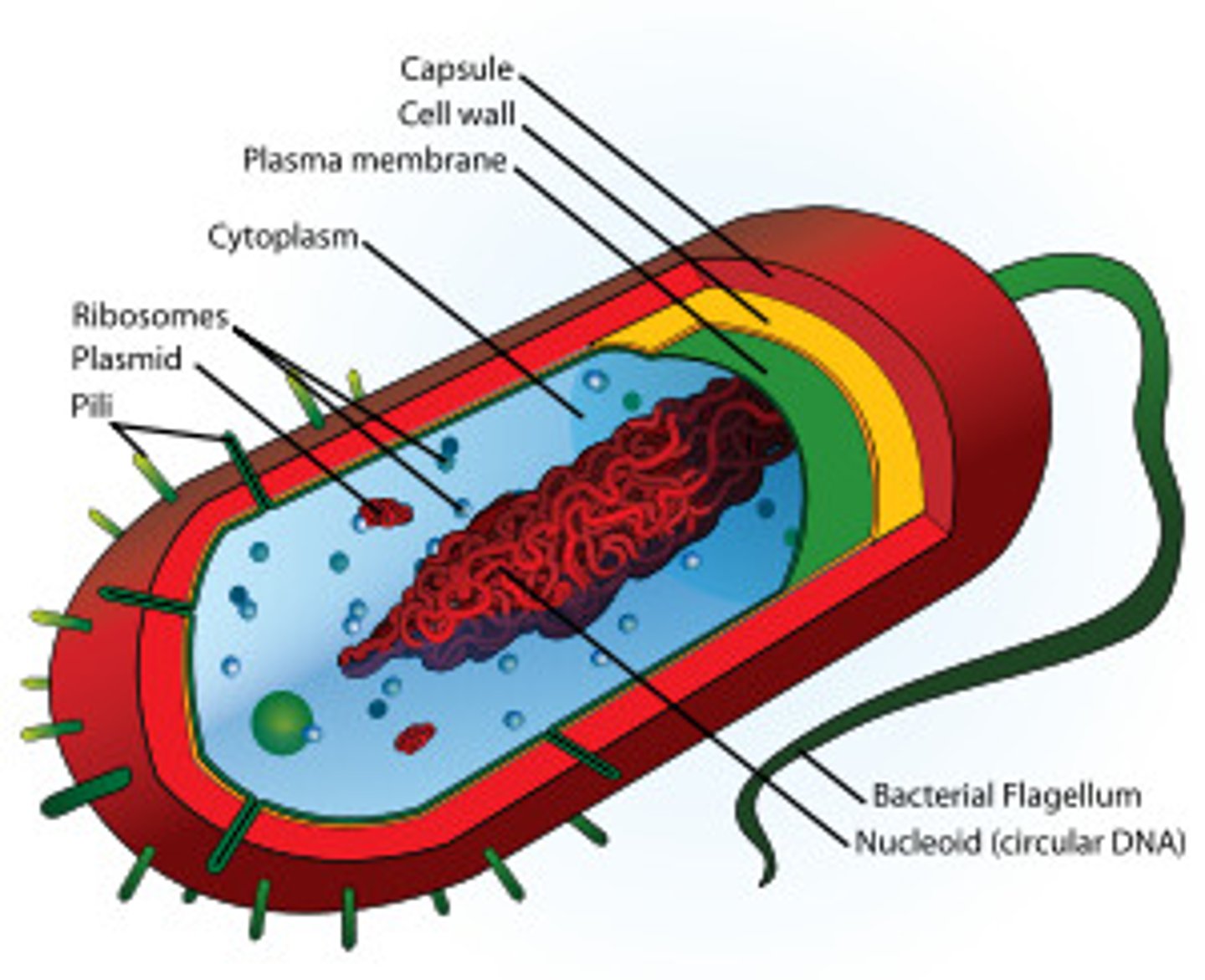
prokaryote
type of organism that is unicellular and has no nucleus or membrane bound organelles (ex. bacteria)
eukaryote
type of cell that has a nucleus and membrane bound organelles (ex. animals and plants)
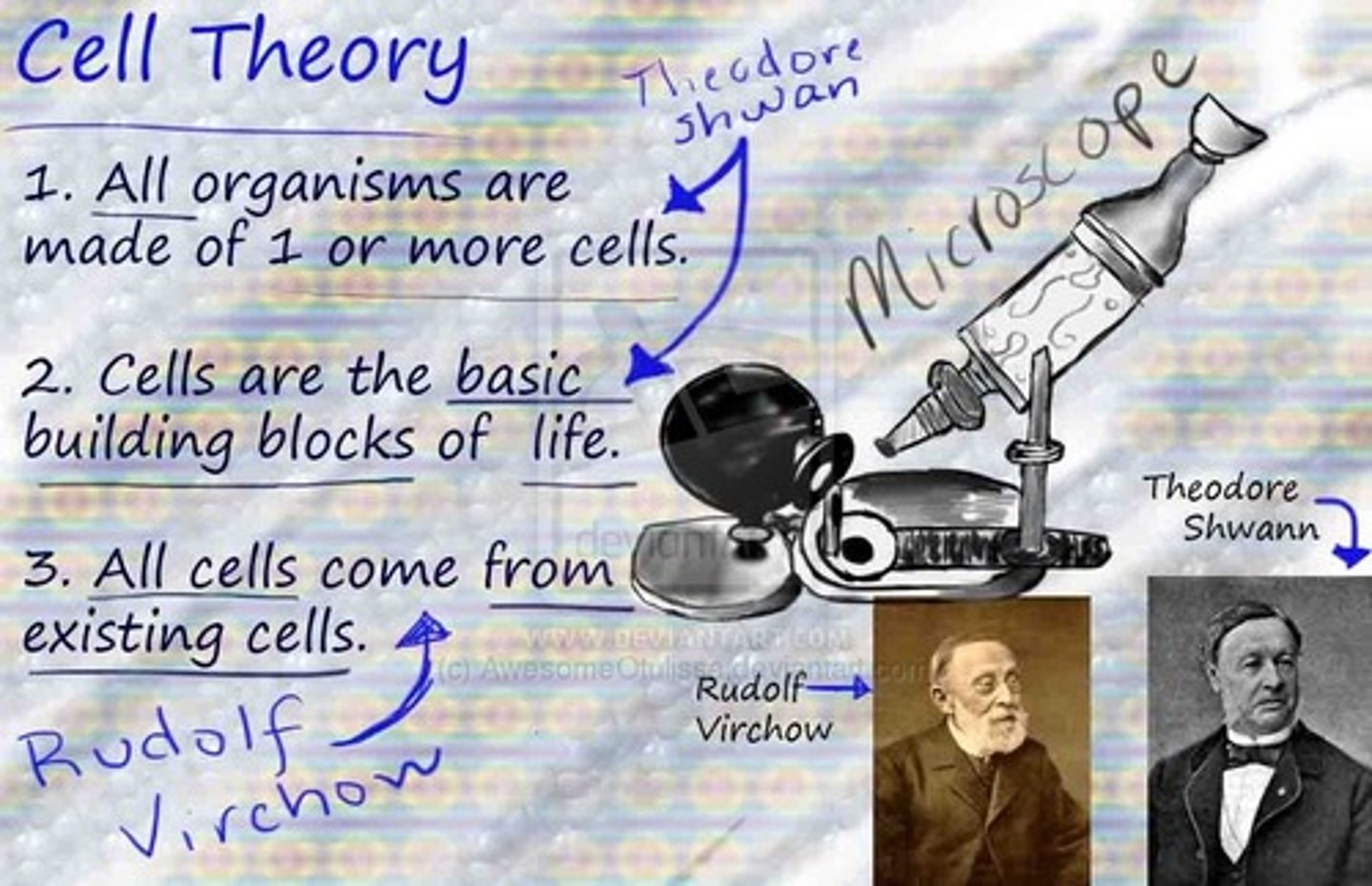
Cell theory
idea that all living things are composed of cells, cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things, and new cells are produced from existing cells
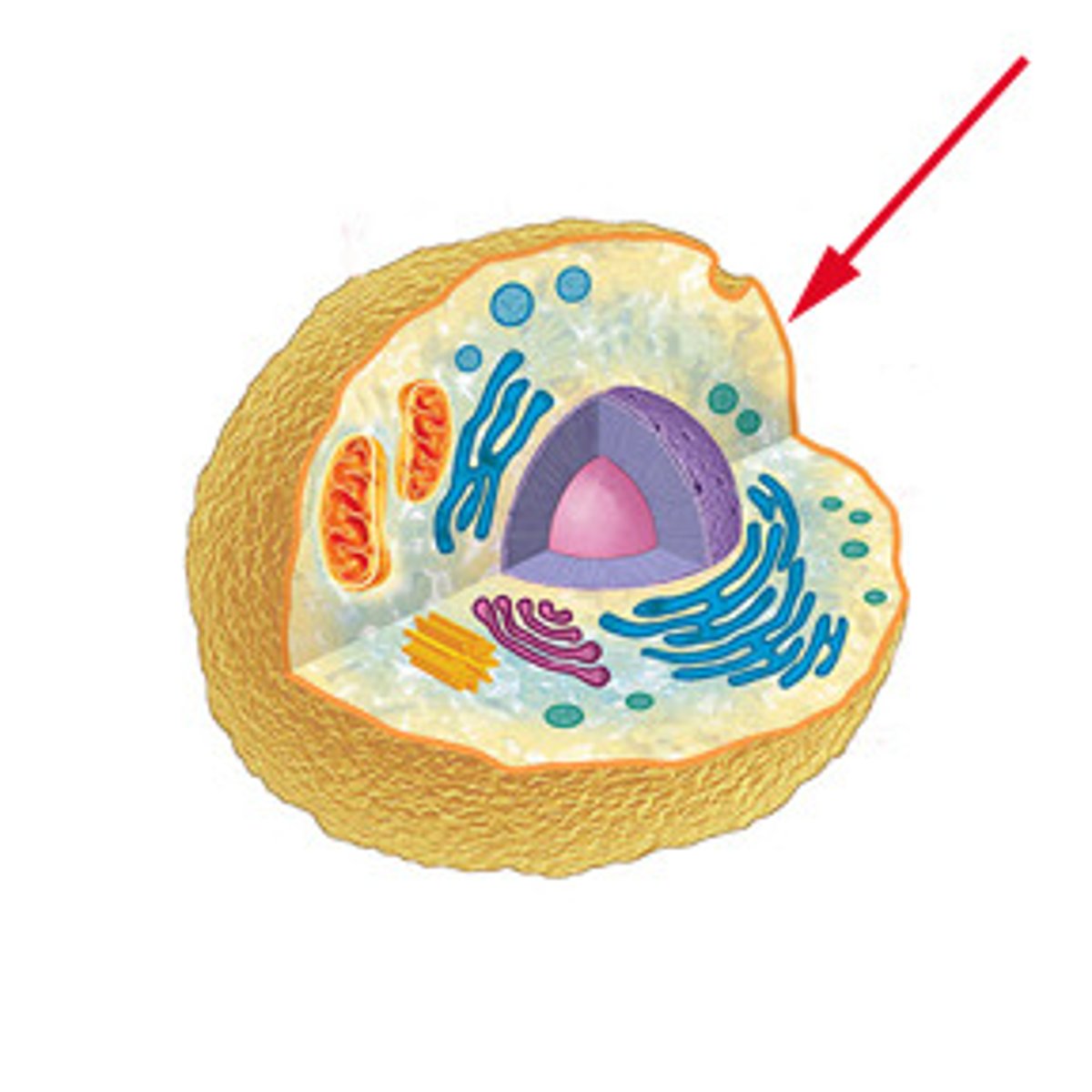
Cell Membrane
Controls what comes into and out of a cell; found in plant and animal
Cell Wall
Ridged outer layer of plant cell
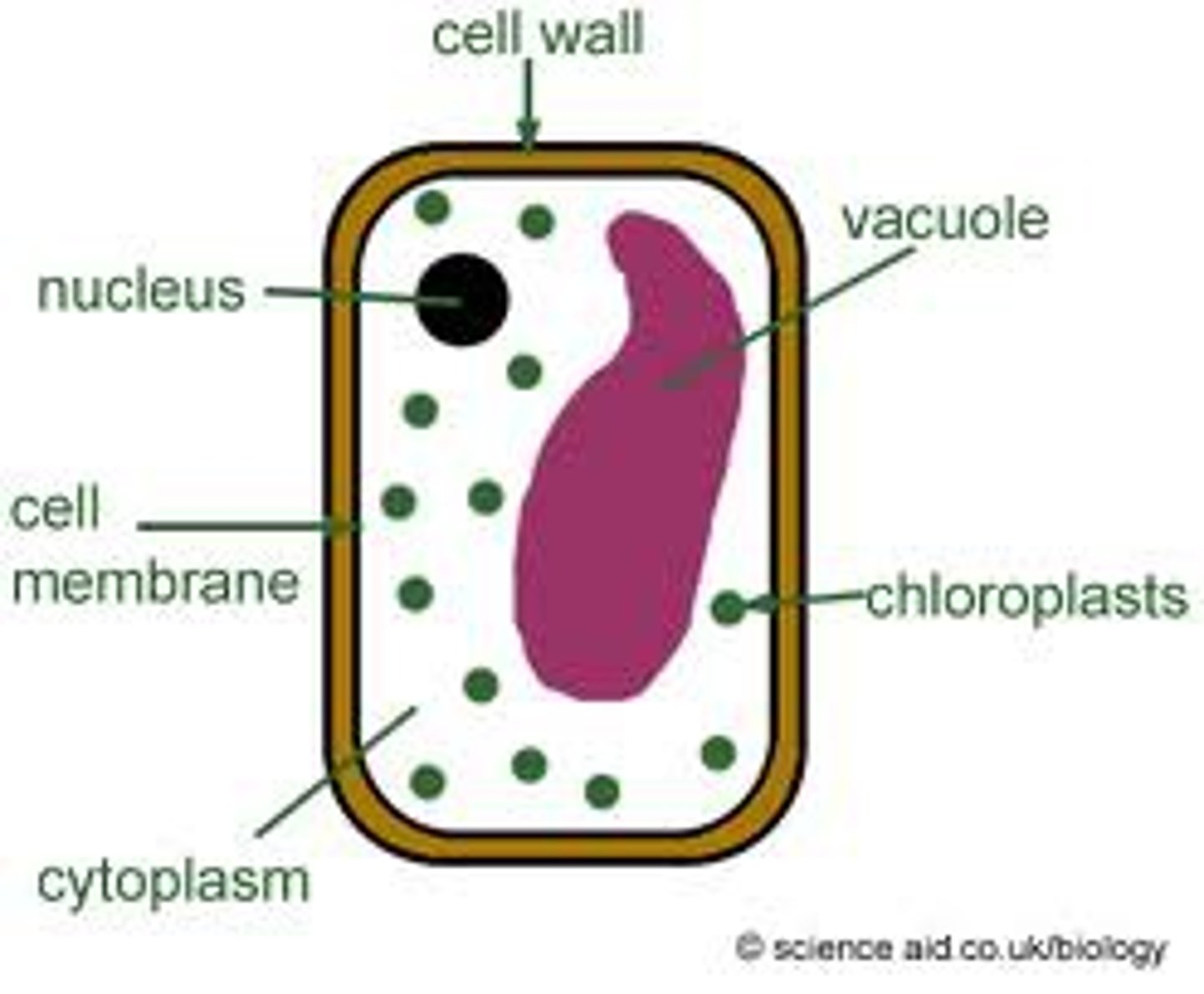
Cytoplasm
Gel-like fluid where the organelles are found
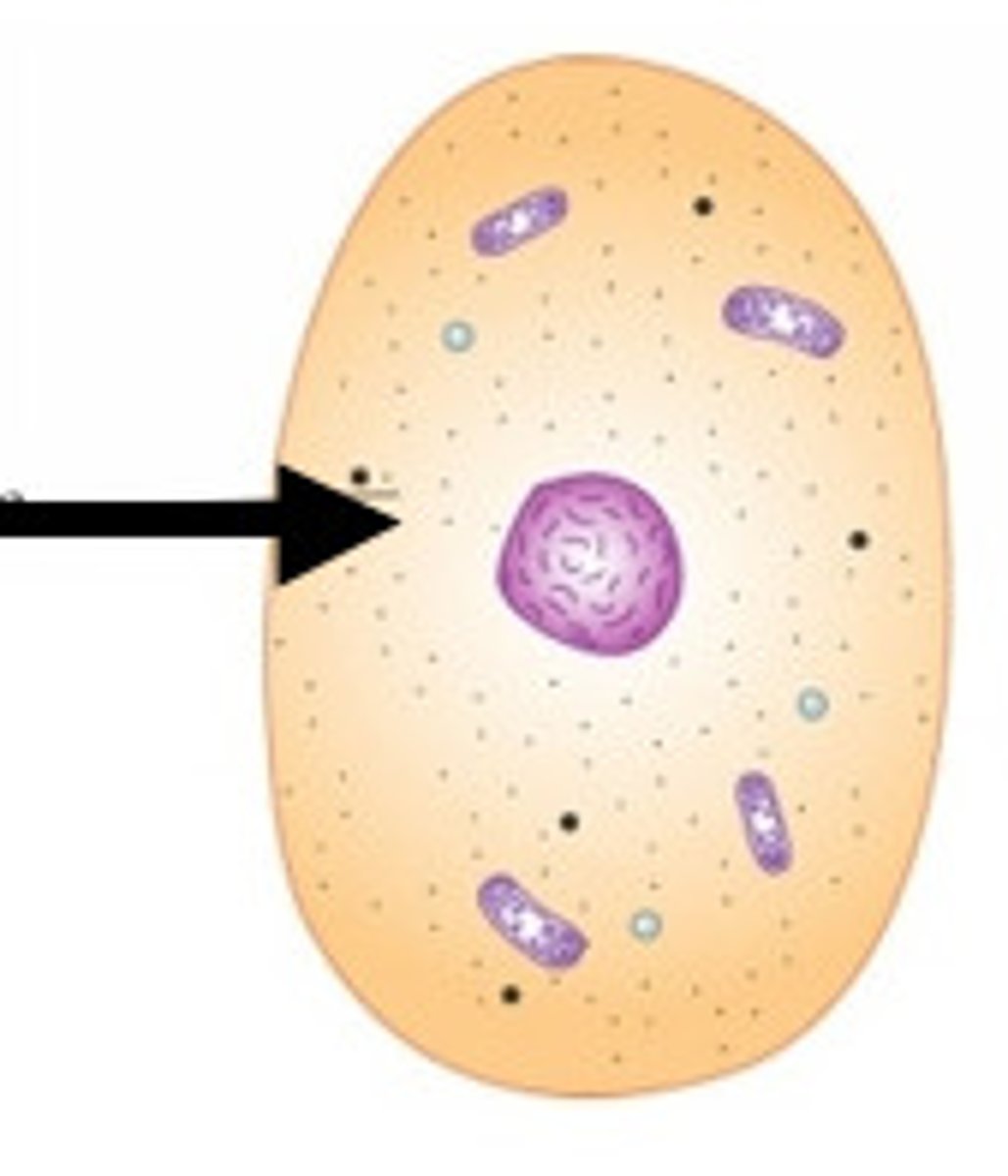
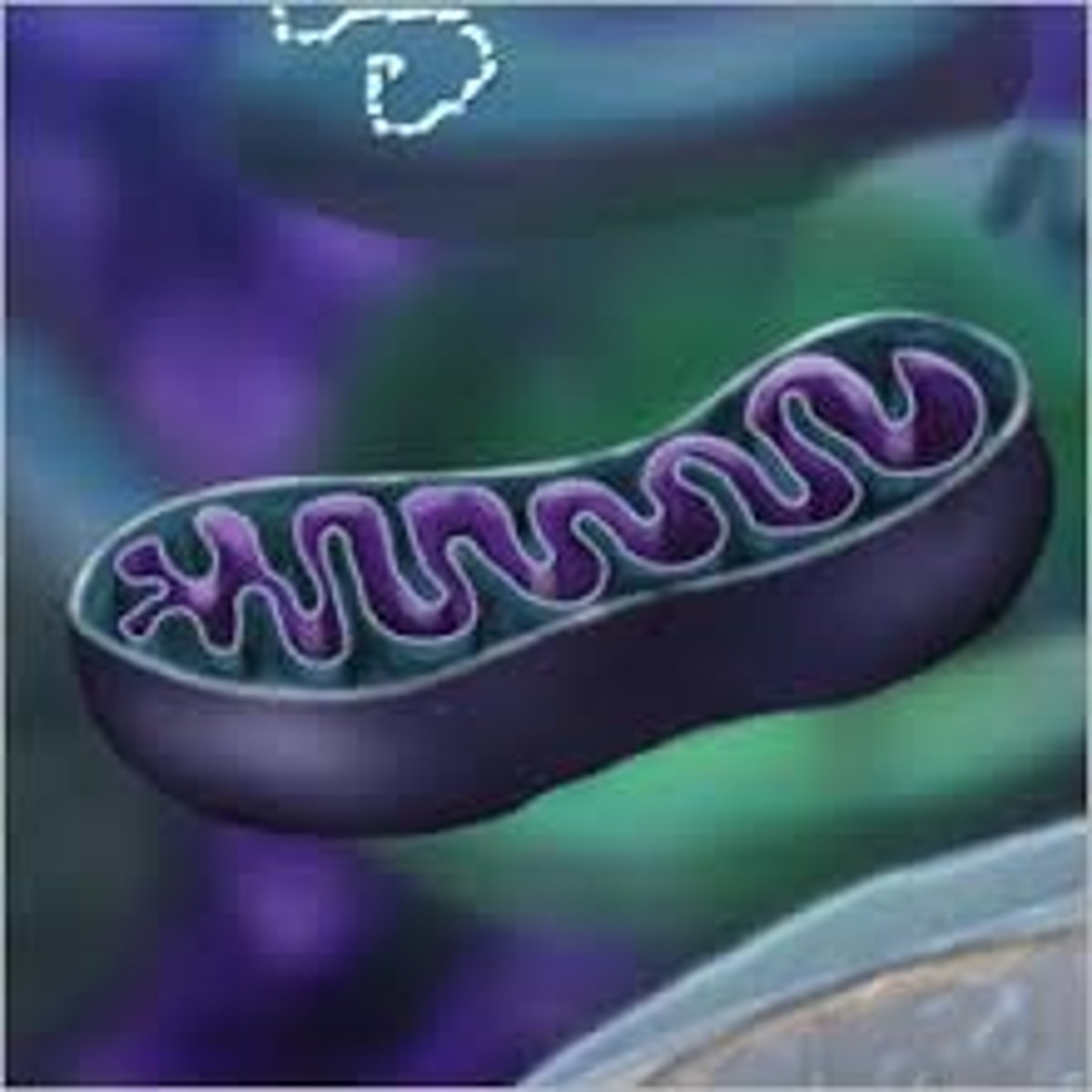
Mitochondria
Produces the energy a cell needs to carry out its functions

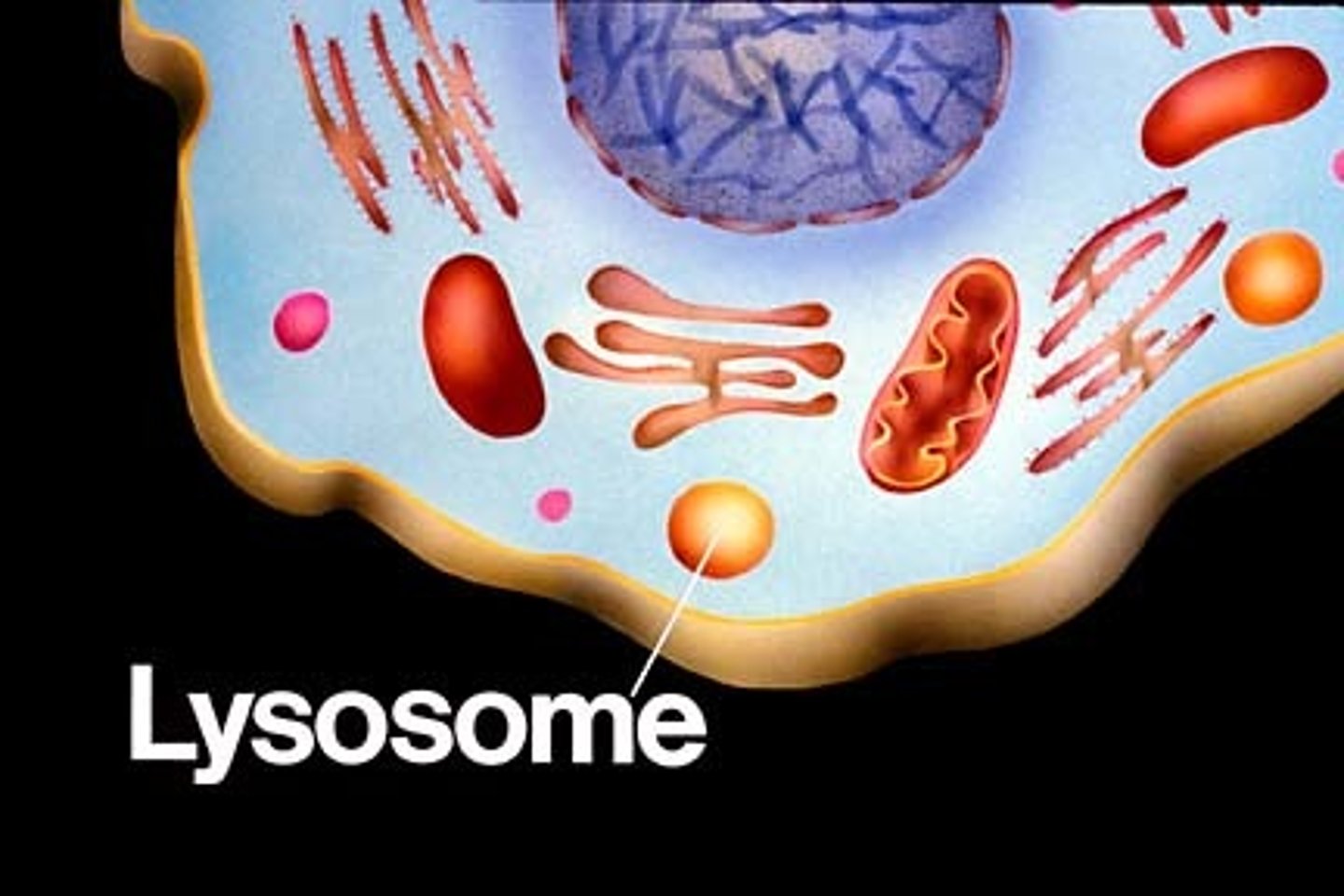
Lysosomes
Uses chemical to break down food and worn out cell parts
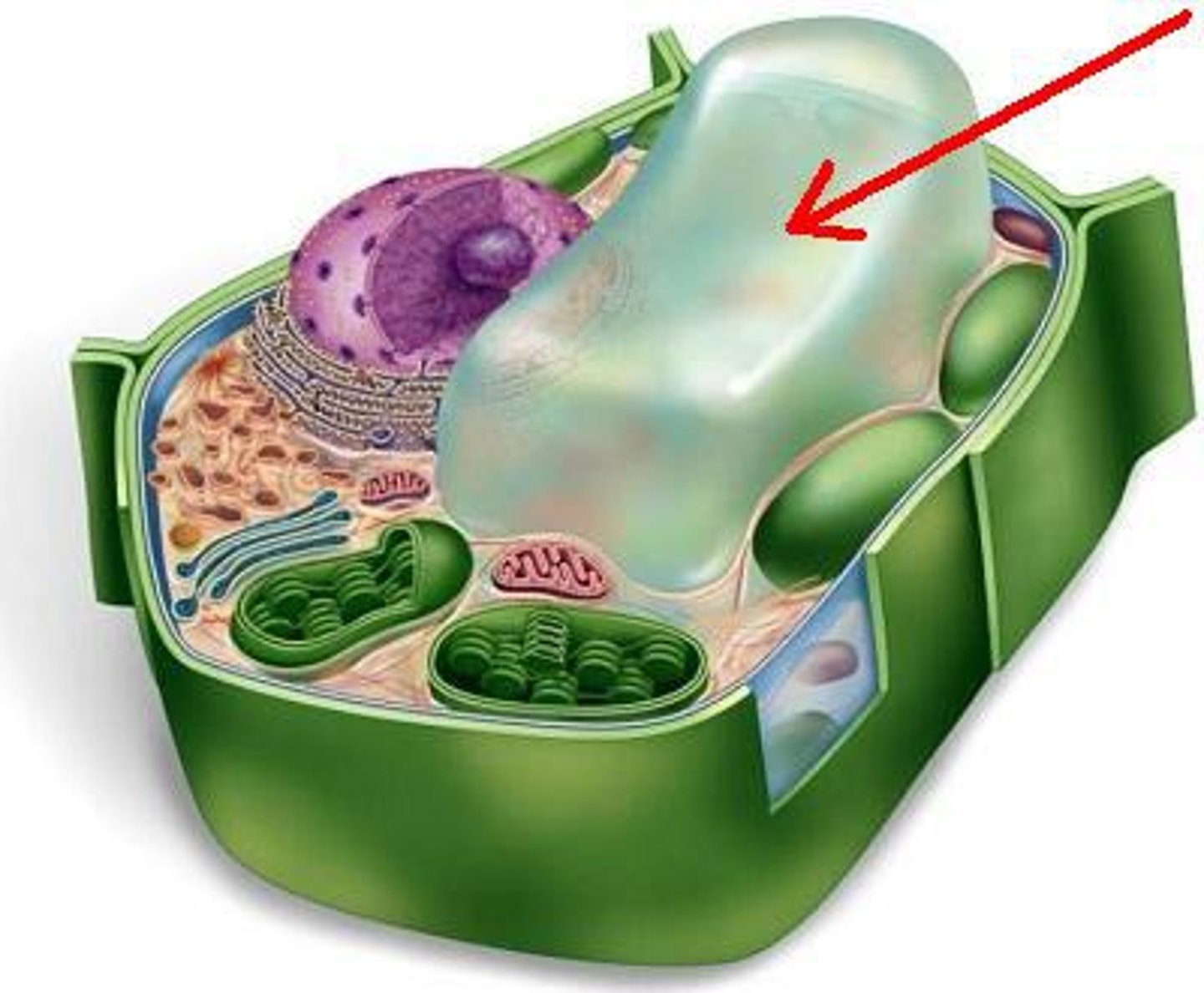
Vacuoles
Stores food, water, wastes and other materials in plant cells
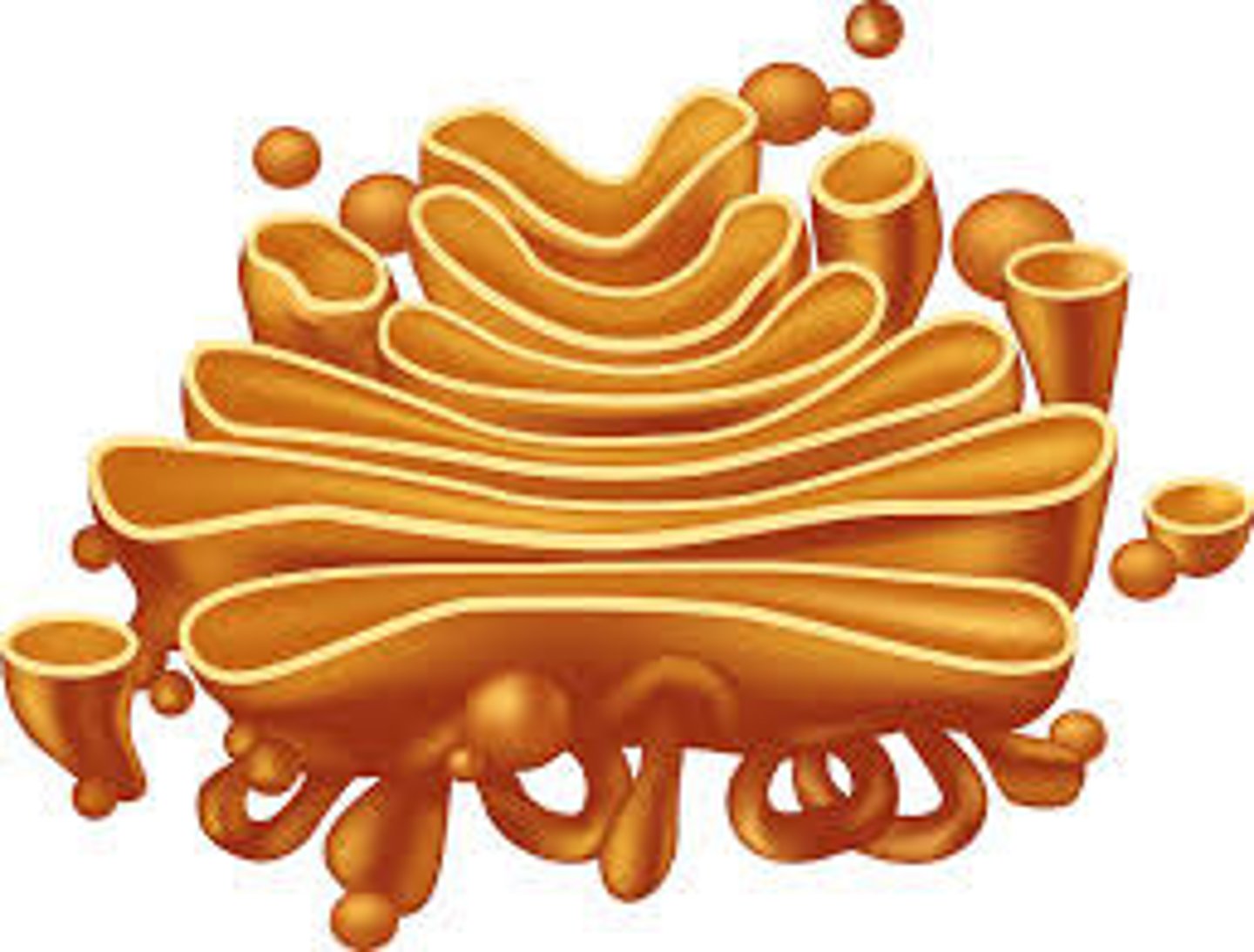
Golgi Bodies
Receives proteins & materials from the ER, packages them, & distributes them

Chloroplasts
Captures energy from the sunlight and uses it to produce food in plant cells

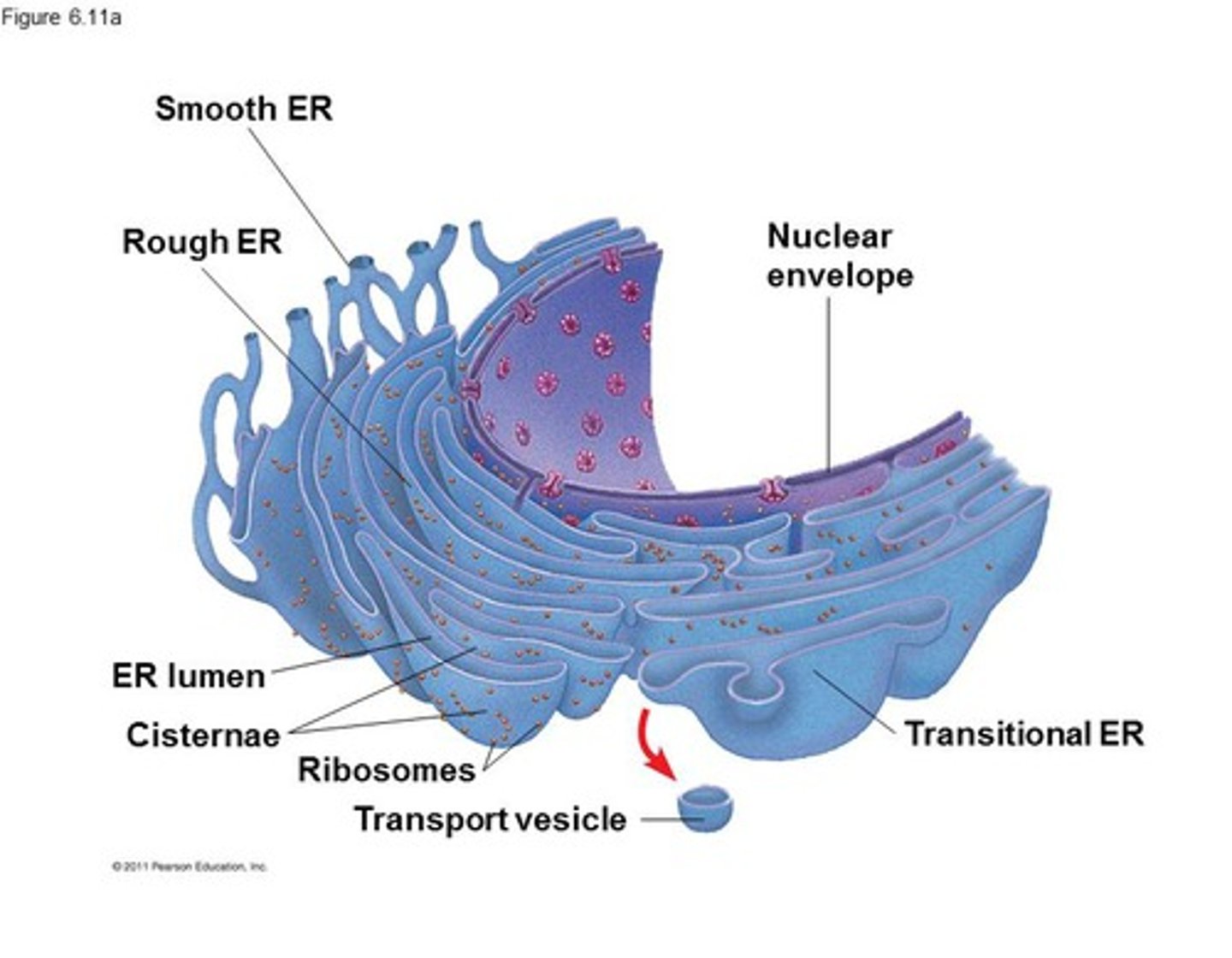
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Has passageways that assembles proteins, lipid components and other materials form one part of the cell to another
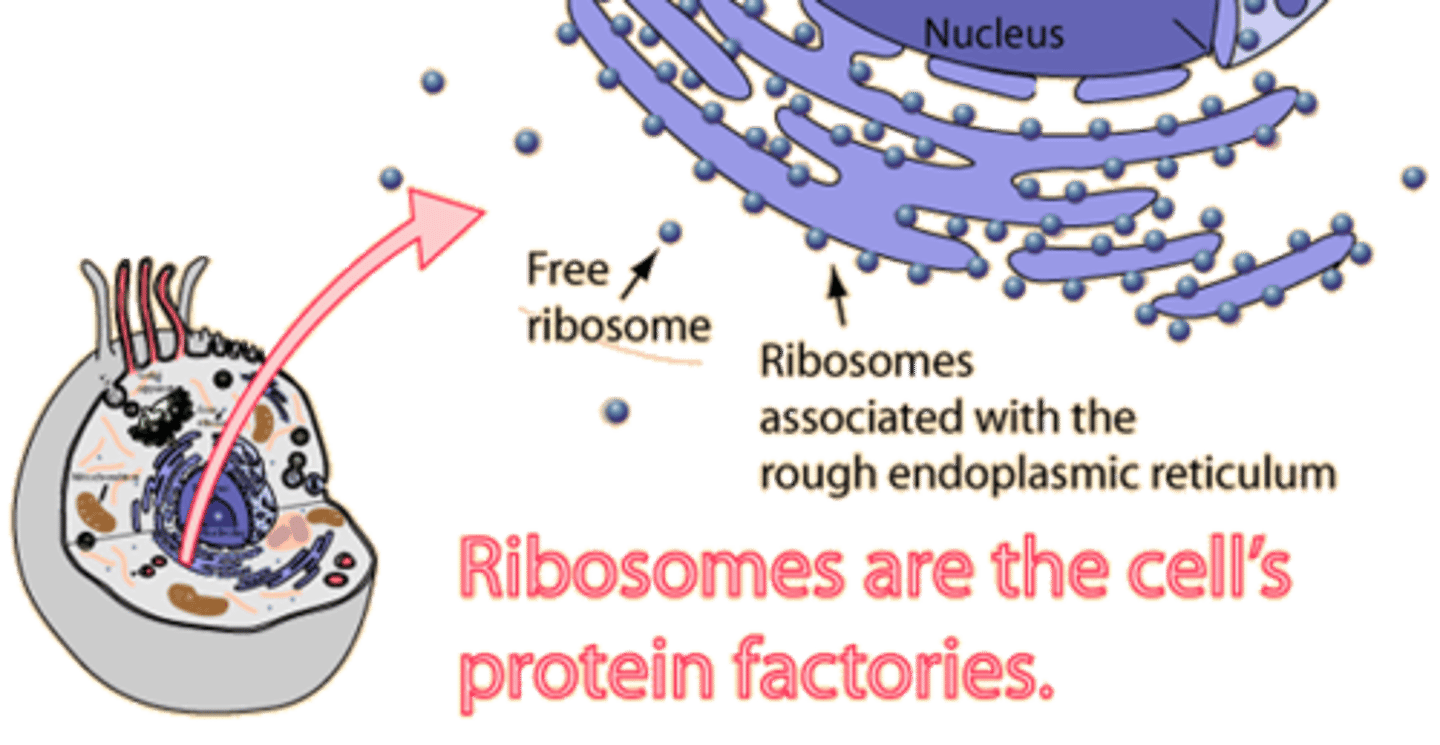
Ribosomes
Assembles amino acids to create proteins
Nucleus
Contain DNA, which controls the functions of the cell and production of proteins
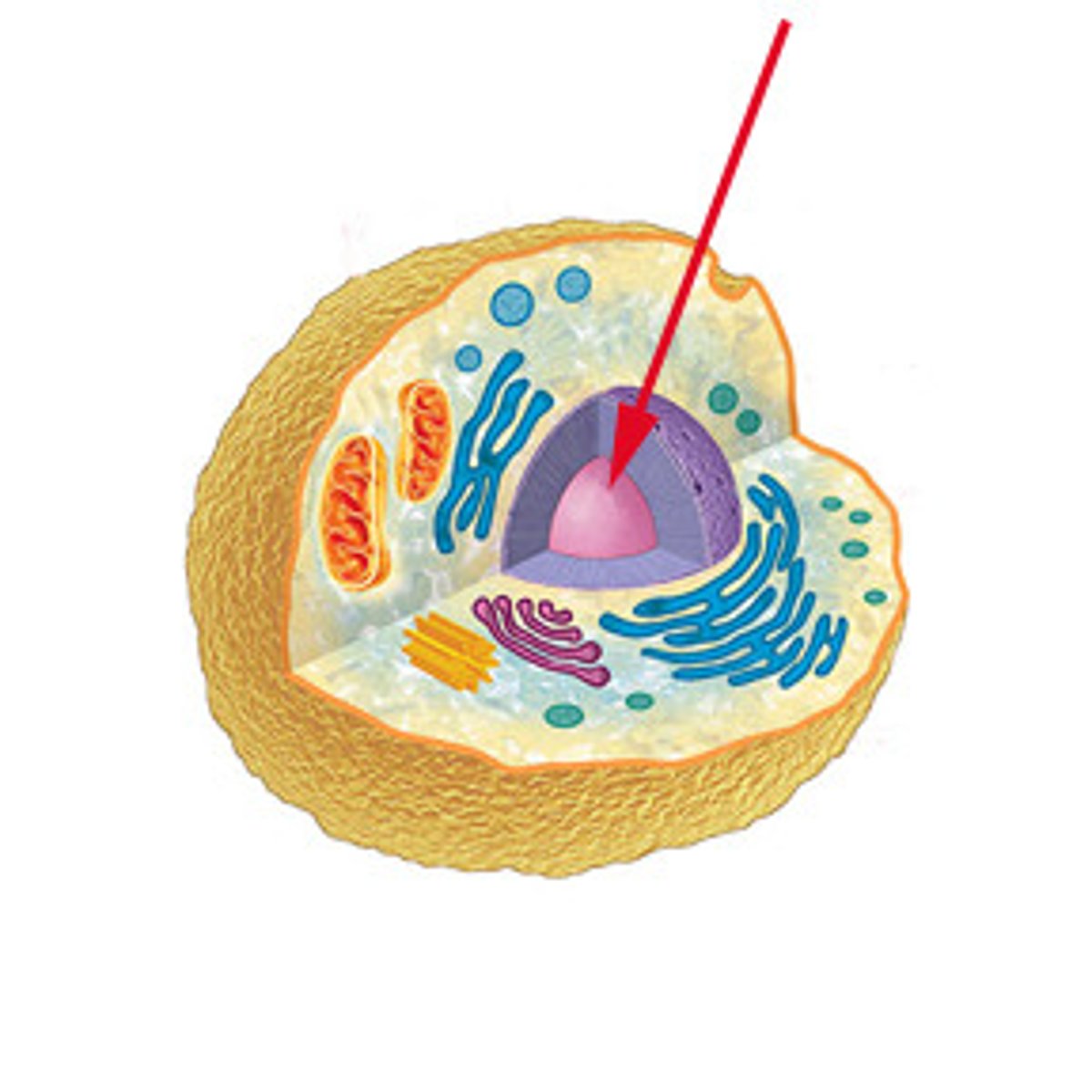
Nucleolus
Found inside the nucleus and produces ribosomes
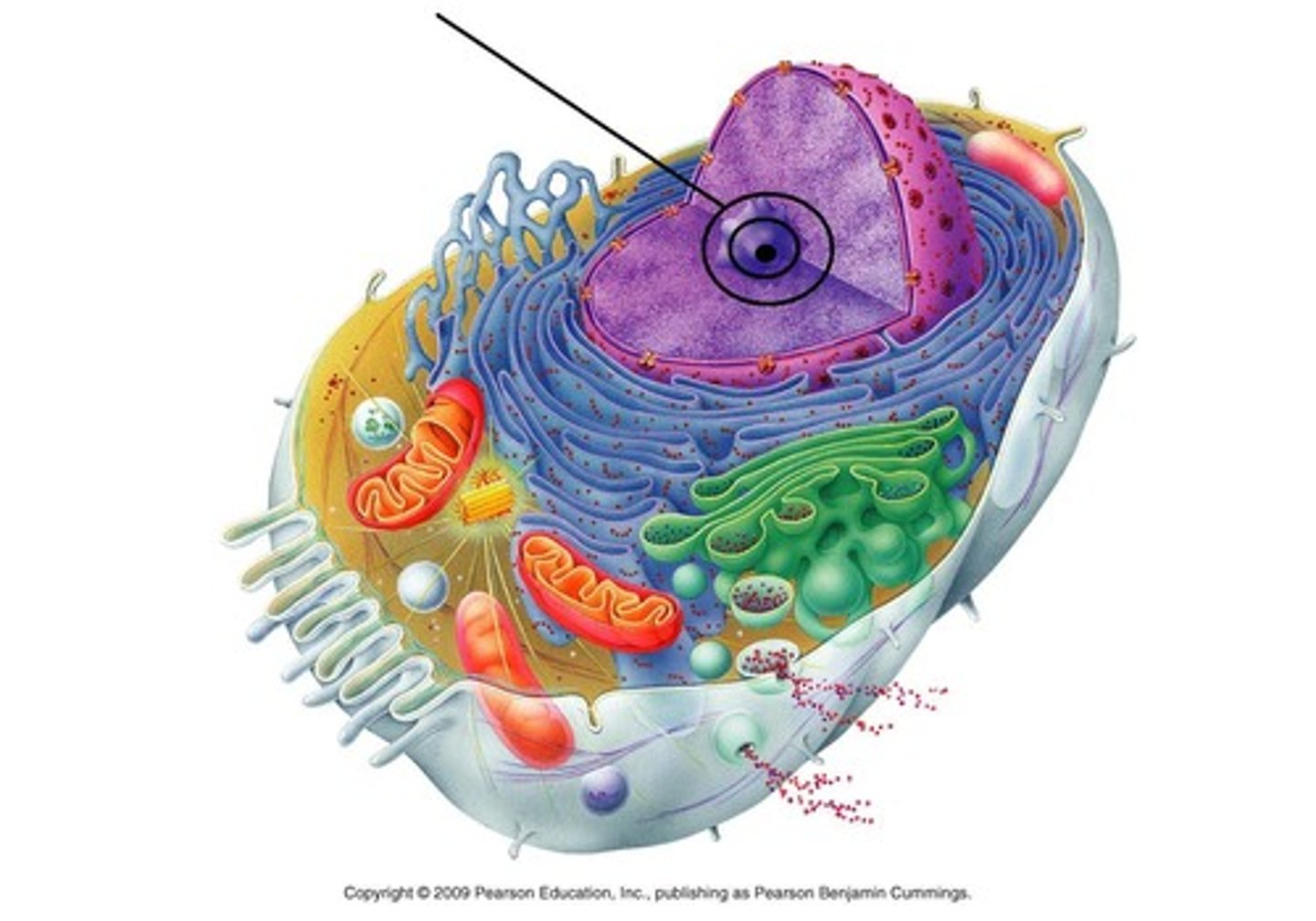
Chromatin
Tiny strands inside the nucleus that contains the instructions for directing the cells functions
Cell
Basic unit of life. All cell contain a cell membrane and DNA
Cell Theory
1.All living things are composed of cells.
2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things.
3. New cells are produced from existing cells
Eukaryote
Cells that contain nuclei
Complex
Example: animal cells, plant cells
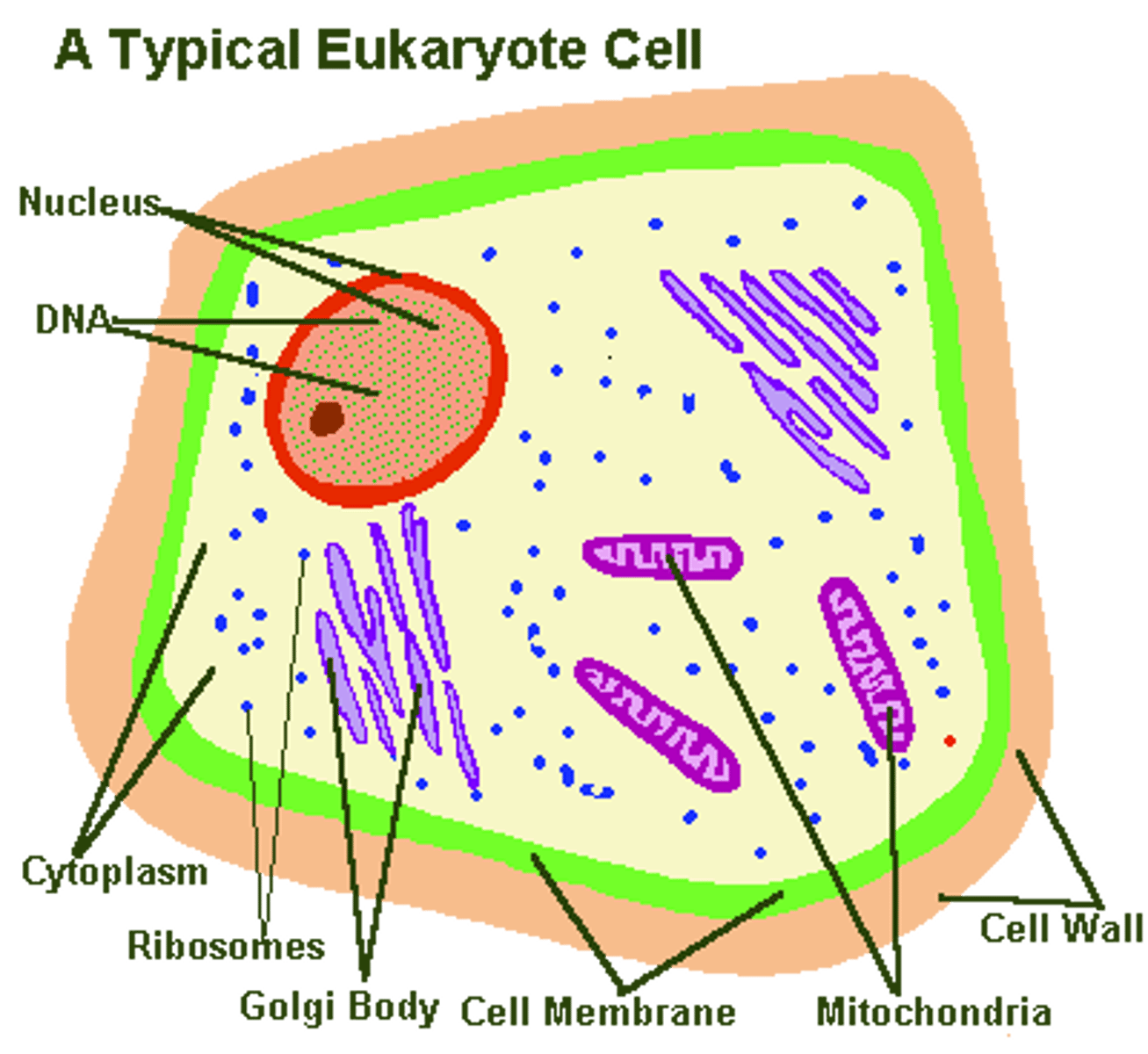
Prokaryotes
Cells that do not contain nuclei
Simple
Example: bacteria
Organelle
Specialized structure that performs important cellular functions within a eukaryotic cell
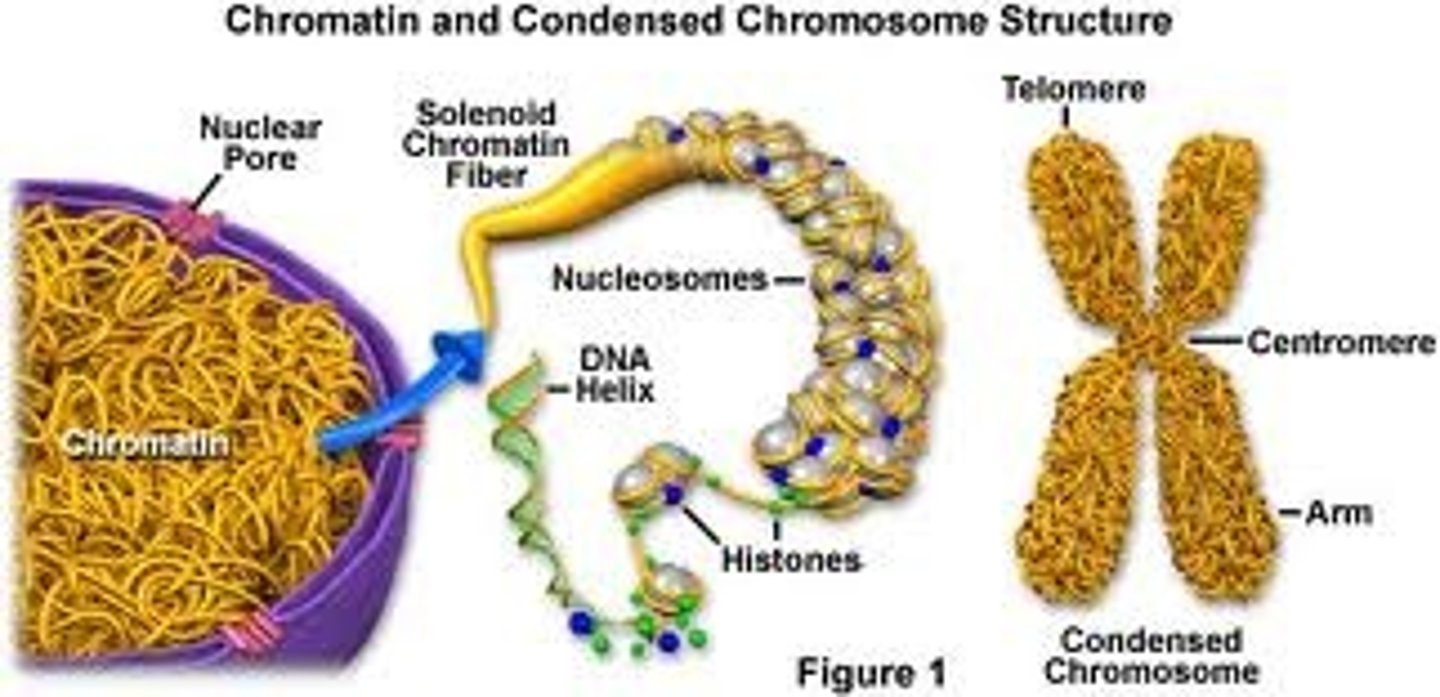
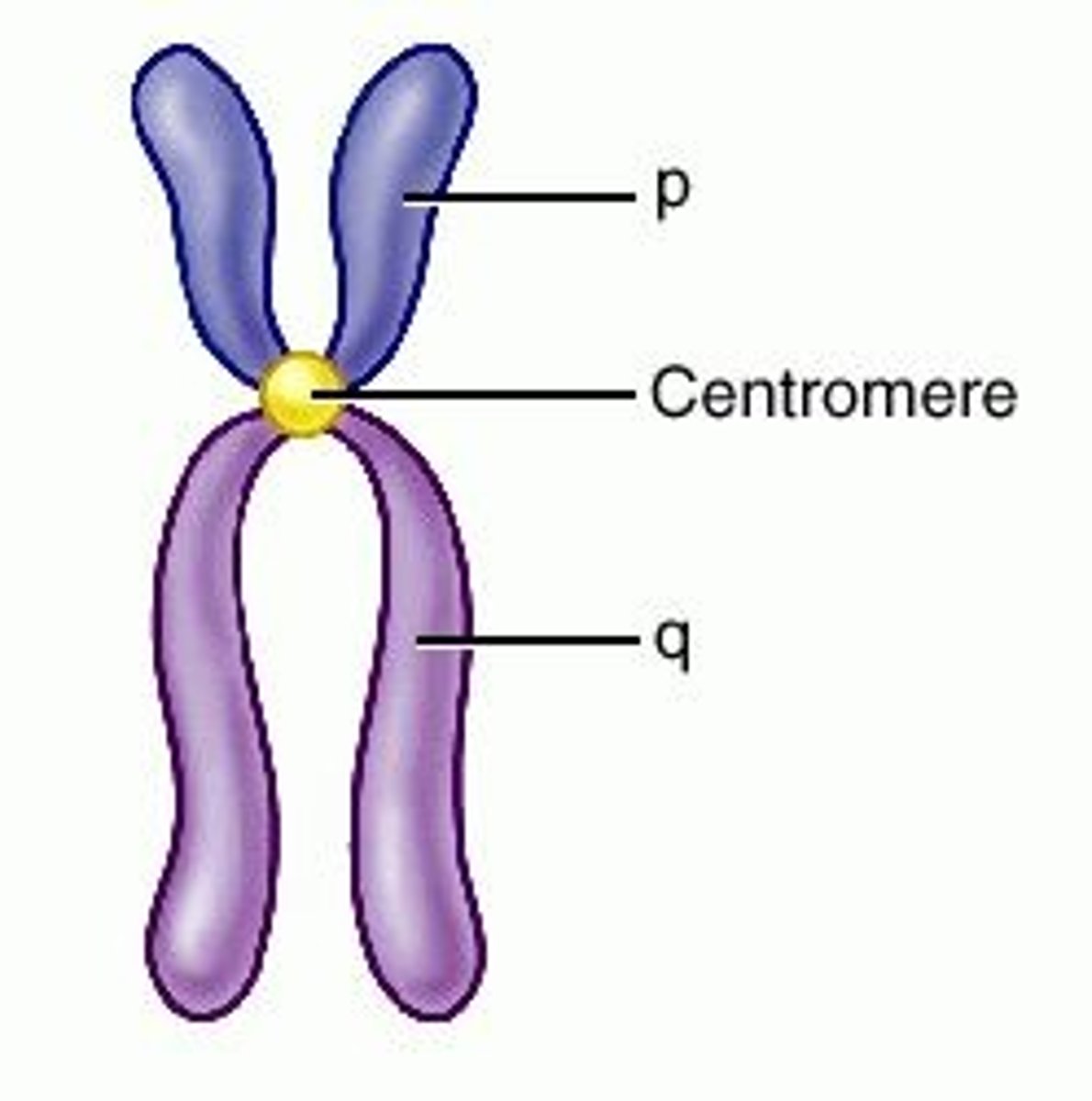
Chromosomes
Contain the genetic information that is passed from one generation of cells to the next.
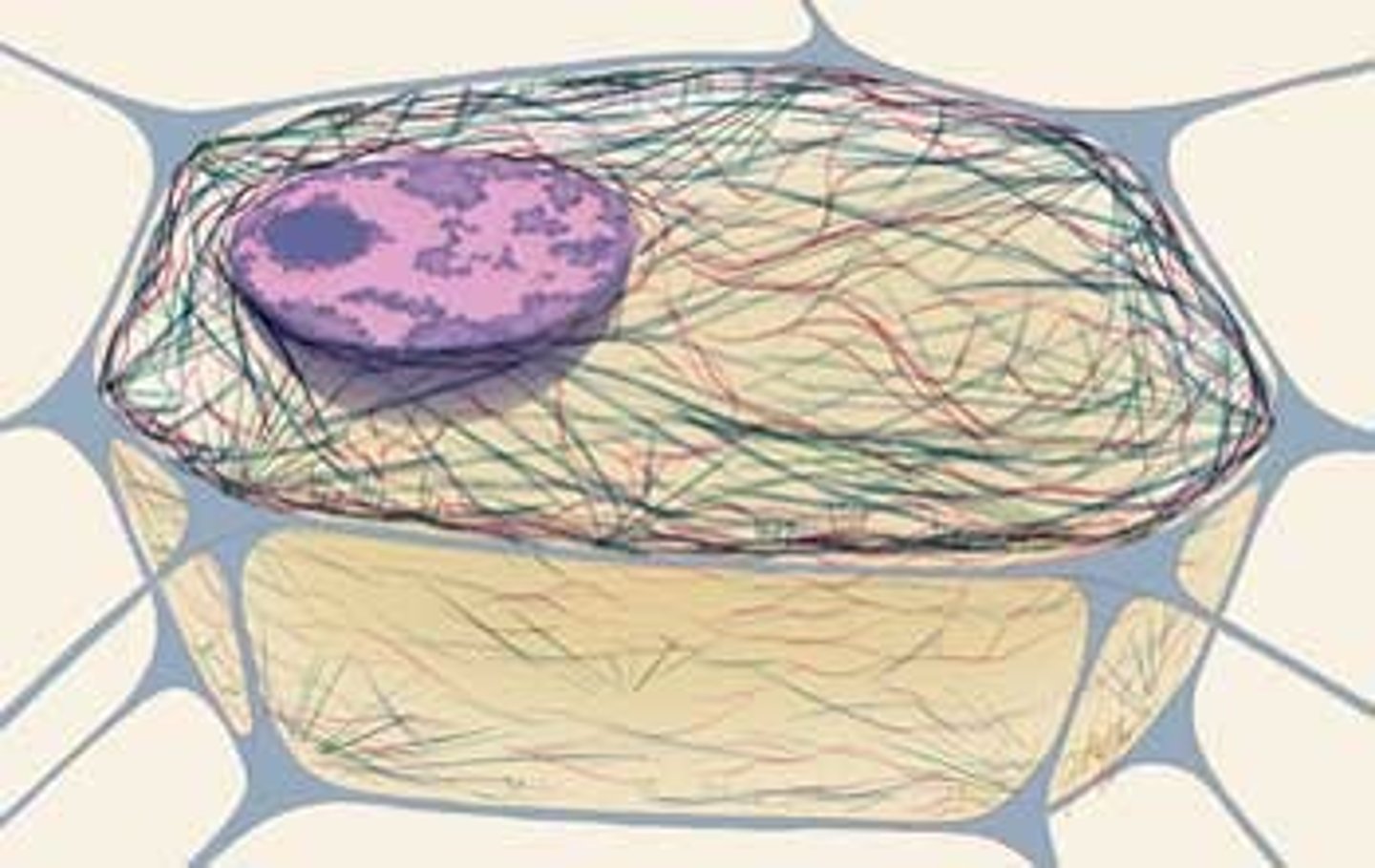
Cytoskeleton
Gives eukaryotic cells there shape and involved in movement. A network of protein filaments made up of microfilaments and microtubules.
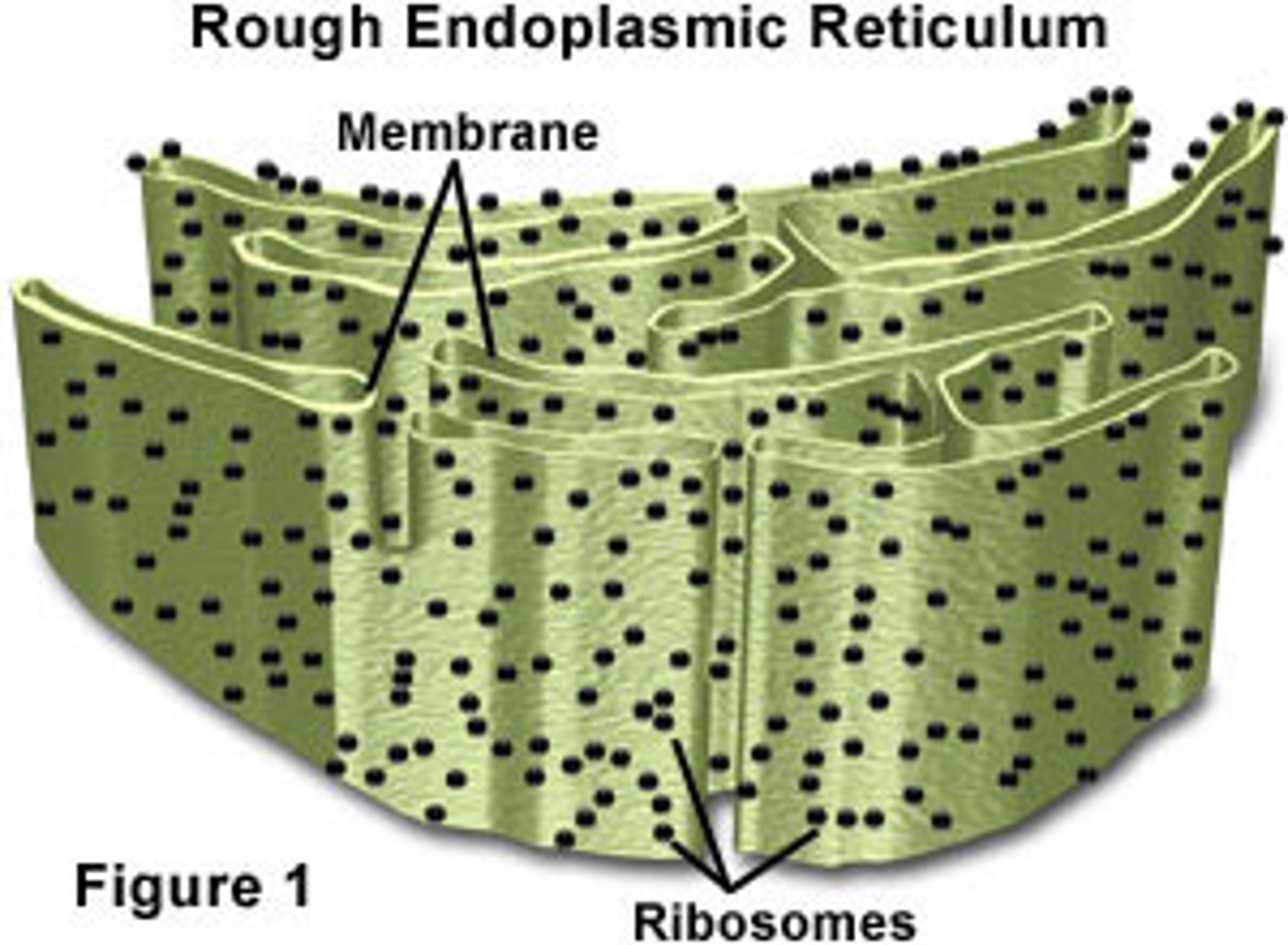
Rough ER
Ribosomes are on the surface and involved in protein synthesis
Smooth ER
Contain enzymes for synthesis lipids and detoxication of drugs
Ribosome
Makes proteins
Cell Membrane
It surrounds the outside of the cell and controls what materials enter and exit the cell.

Cell
The basic unit of life. It is the basic unit of structure and function.
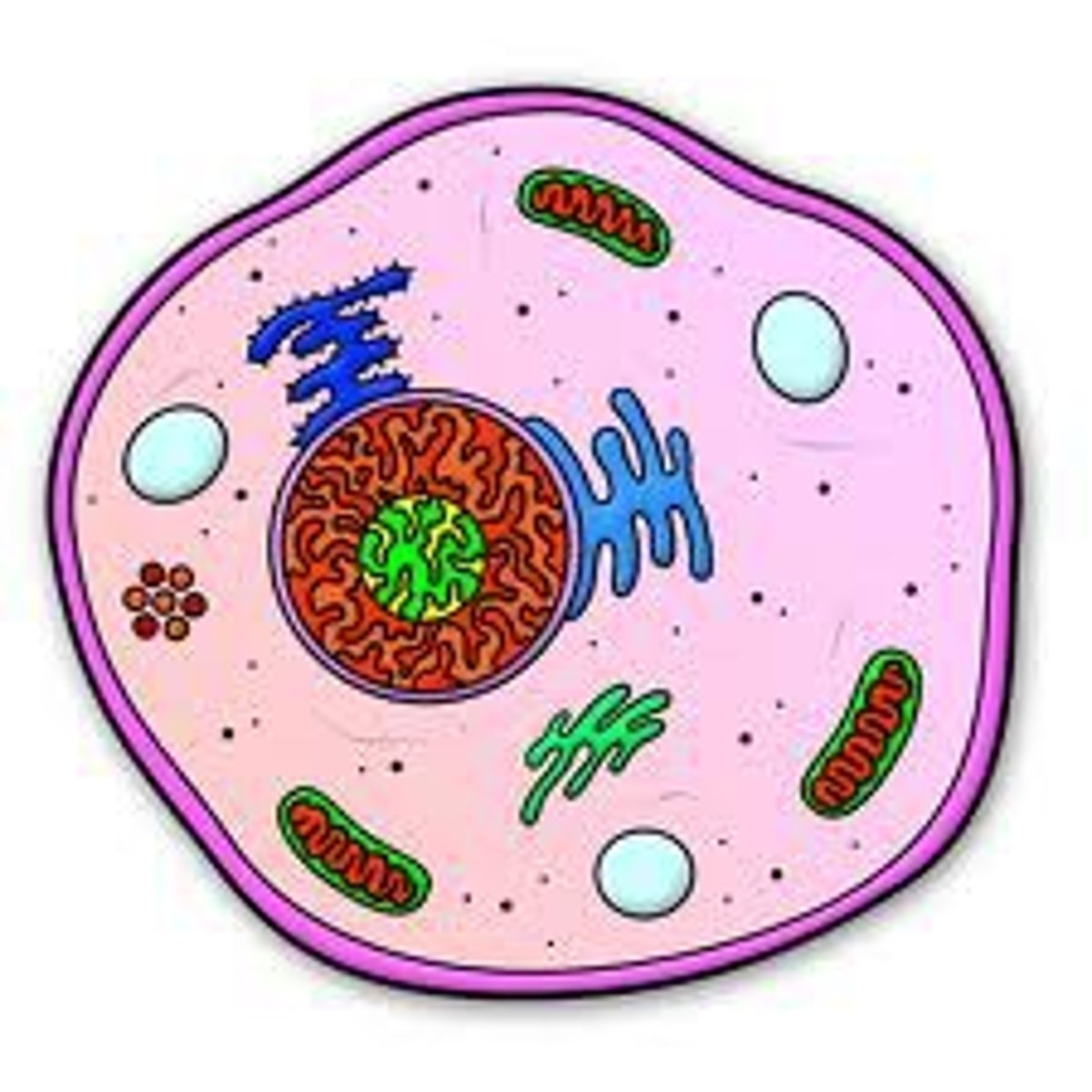
Organelle
A small structure within a cell that performs a specific job.
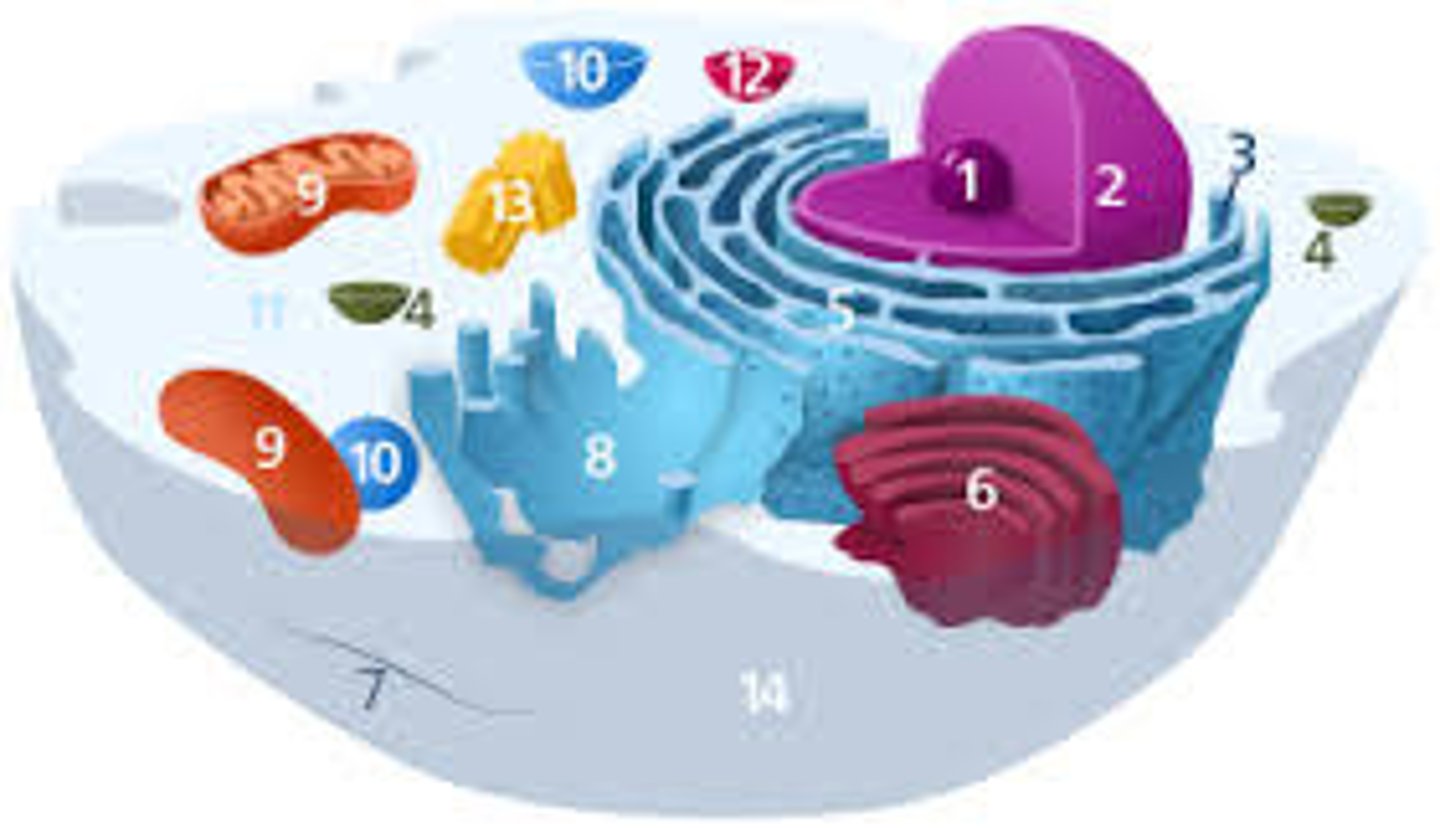
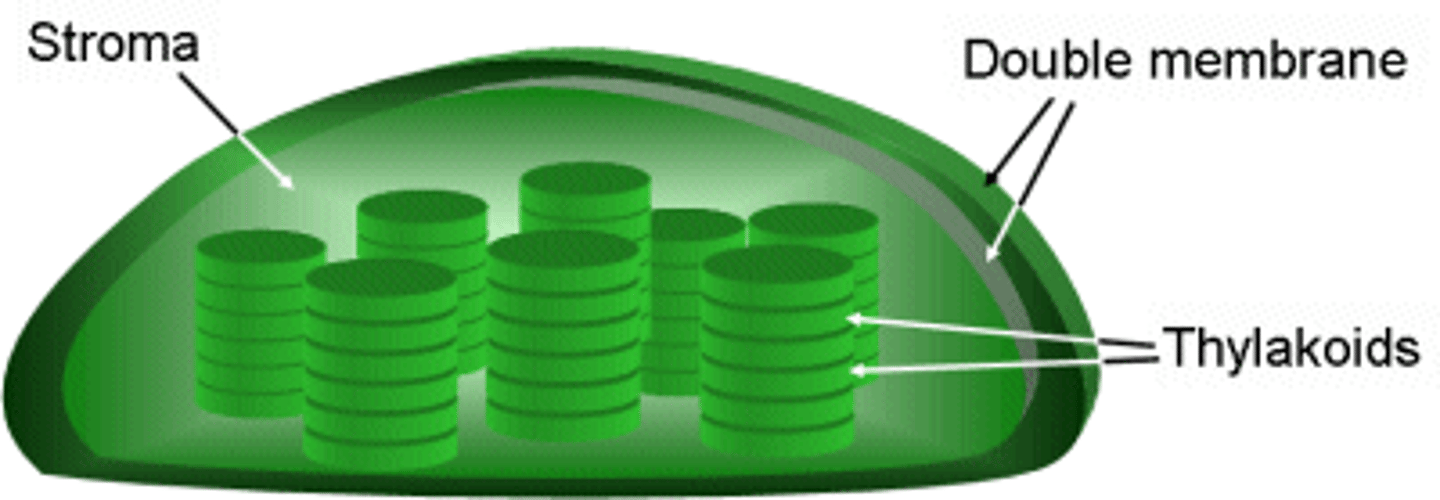
Chloroplast
Uses the sun's energy to make food for the plant cells. This is also the site of photosynthesis
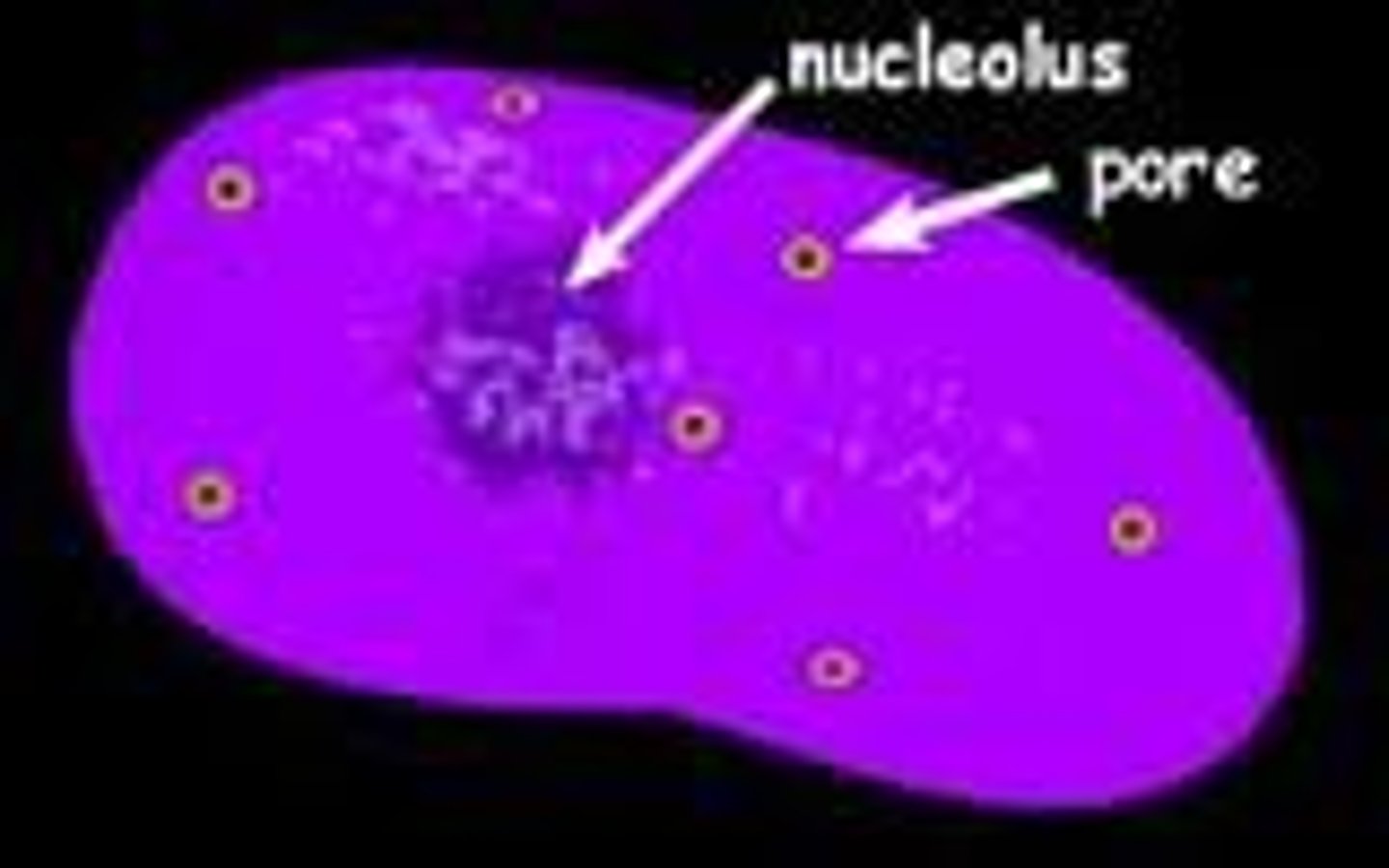
Nucleus
The "brain" of the cell and controls all cell functions. It contains the cell's DNA.
Smooth ER
This organelle does NOT have ribosomes attached to it. It helps to make fats.

Rough ER
This organelle has ribosomes attached to it. It transports materials through the cell. It helps to make proteins.

Vacuole
Store food, water, or waste
Golgi Body
This organelle sorts, packs, and ships proteins. This is known as the post office of the cell.
Lysosome
The organelle that digests old organelles and breaks down large food particles. Sometimes called the "Garbage Collector"

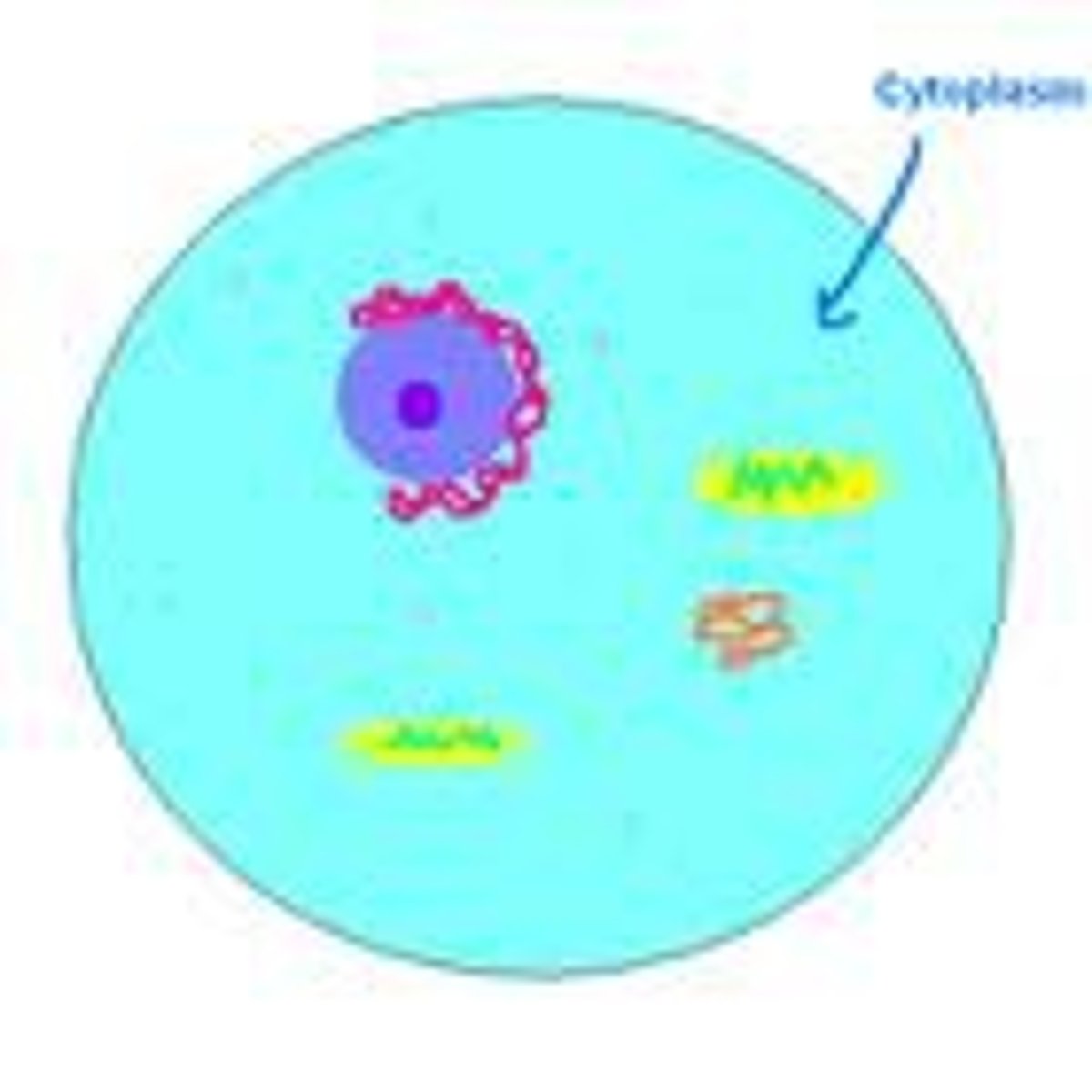
Cytoplasm
Cell fluid; jellylike liquid that fills the cell.
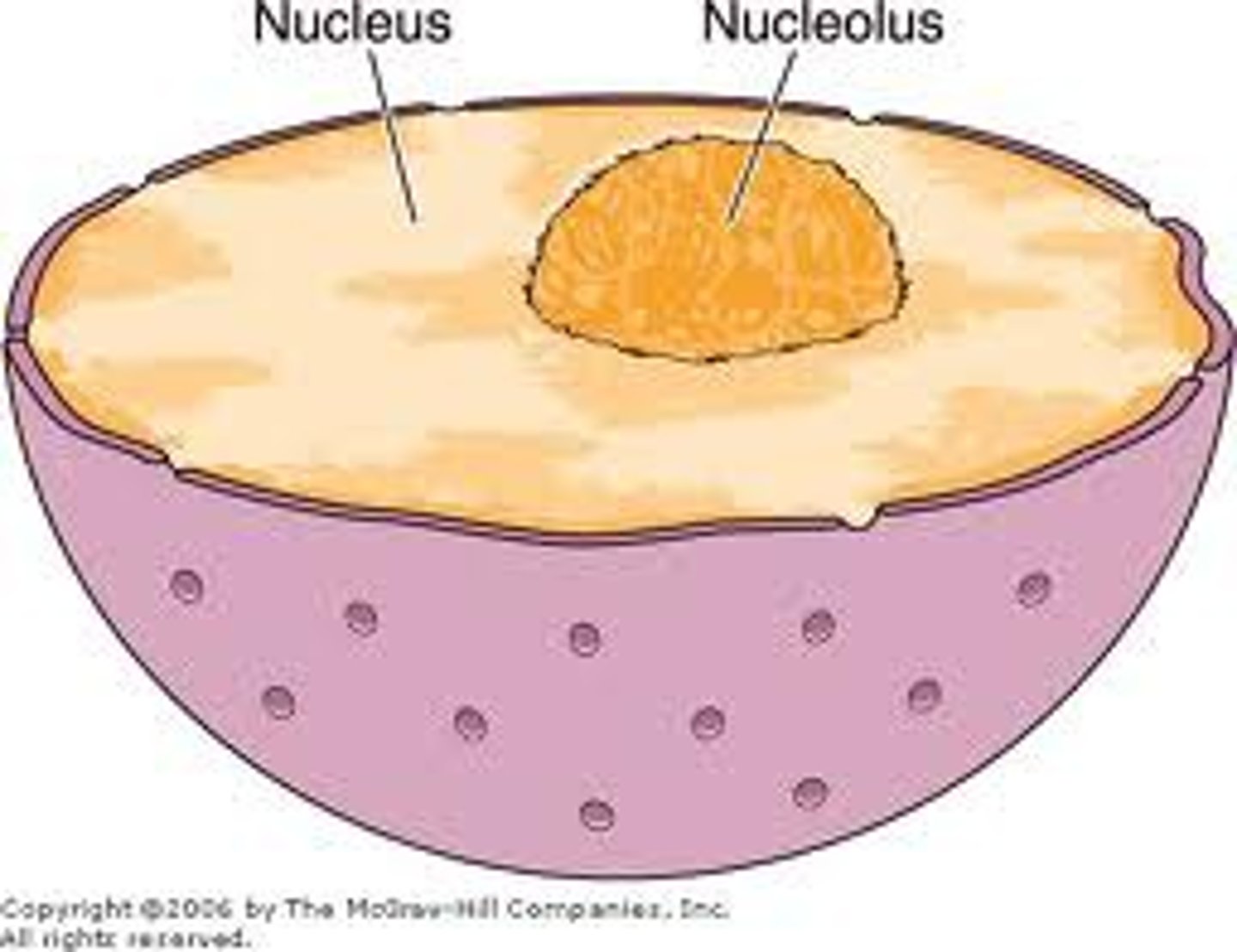
Nucleolus
The location inside the nucleus where ribosomes are made.
Cell Wall
The rigid or inflexible boundary found in plant cells. It is made of cellulose an provides support and structure to the cell.
Mitochondria
Breaks down food for energy. It is called the "Powerhouse" of the cell.
What are cells?
Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things.
What is the structure of cells?
The structure of a living thing in a determined by the amazing variety of the ways cells are put together.
What are cells involved in?
Cells are involved in living, growing, reproduction.
What is the cell theory?
Cell theory is a widely accepted explanation of the relationship between cells and living things.
What is a microscope?
A microscope is a instrument that makes objects look larger.

Who is Virchow?
He is a german physician, he came to the conclusion that all cells come from preexisting cells.

What are the three basic parts of the cell theory?
1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells.
2.The cells is the basic unit of life in all living things.
3.The cells are produced by the division of preexisting cells.
What is a theory?
The best explanation of an event in nature supported by evidence gathered when testing a group of related hypothesis.
How has the cell theory been used?
Cell Theory have been used for vaccines, disease, cure for cancer, cloning, health, and medical research.
What is the first thing that the cell theory states?
All living things are composed of cells.
What is the second thing that the cell theory states?
Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things.
What is the third thing that the cell theory states?
All cells are produced from other cells.