EYES ASSESSMENT
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
2
a difference of more than— mm bet 2 eyes is abnormal
Exophthalmos
bulging eyes - could be a sign of thyroid gland problems; it can be treated but it needs to be checked quickly as your vision can be affected

graves
exophthalmos is a characteristic of what disease
AA, caucasian, 21 mm
the eyes of — protrude slightly than —, they have protruding eyes beyond
sunken eyeballs/ enopthalmos
“eyebags” sunk in your face. Family history, dehydration and lack of sleep. - Usual to severely dehydrated px”
ectropion, entropion, chalazion, hordeolum/stye, blepharitis, ptosis, Lagophthalmos, eye trauma
8 abnormal findings for the eyelids
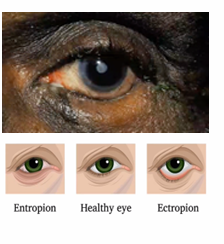
ectropion
where the lower eyelids droops away from the eye and turns outward - everted/outwardly turned lower eyelid
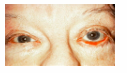
entropion
an inward turning of the eyelid margin and appendages such that the pilosebaceous unit and mucocutaneous junction are directed posteriorly towards the cornea and ocular surface.
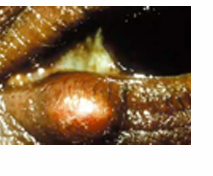
chalazion
a red bump on your eyelid (upper lid), infected meibomian gland
Hordeolum (stye)
an infection of an oil gland/hair follicle infection at the edge of the eyelid. (lower lid)
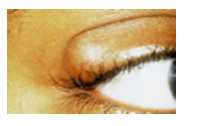
blepharitis
common eye condition that makes your eyelids red, swollen, irritated, and itchy. staphylococcal infection of eyelid
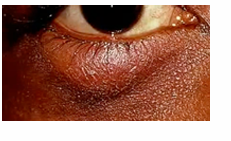
ptosis
drooping eyelids
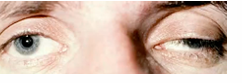
Lagophthalmos
incomplete or abnormal closure of the eyelids
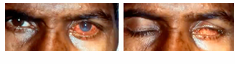
eye trauma
bruises, punctures, and scratches. They can result from accidents, exposure to chemicals, or foreign objects in the eye.
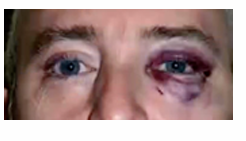
exophthalmos
protruding eyeballs and retracted eyelids
diffuse episcleritis
inflammation of sclera
oculomotor nerve damage, myasthenia gravis, weakened muscle, congenital disorder
ptosis may be attributed to 4
hyperthyroidism
retracted lid margins suggest?
corneal damage
failure of lids to close completely is risk for
xanthelasma
raised lower plaque loc near inner canthus is a normal finding assoc w/ high age and lipid levels
exposure and drying of conjunctiva
ectropion results in 2
conjunctivitis, pinguecula,Subconjunctival Hemorrhage, episcleritis
4 abnormalities in bulbar conjuctiva
Conjunctivitis
pink eye or piskat
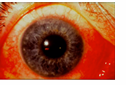
pinguecula
common type of conjunctival stromal degeneration in the eye. It appears as an elevated yellow-white plaque in their bulbar conjunctiva near the limbus. NORMAL in older client
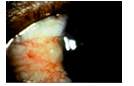
Subconjunctival Hemorrhage
occurs when a tiny blood vessel breaks just underneath the clear surface of your eye (conjunctiva); hypertension (HPN)
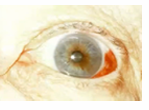
episcleritis
common, benign, self-limited cause of red eye, due to inflammation of the episcleral tissue. non infectious inflammation of sclera
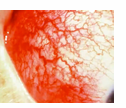
pallor
AB for palpepral
pallor
pale palpebral Conjunctivae; signifies anemia, low blood count, low blood pressure

hrt or lung disorder
cyanosis of lower eyelid suggest?
Dacryocystitis
lacrimal apparatus AB
Dacryocystitis
characterized as an inflammatory state of the nasolacrimal sac/ lacrimal apparatus - infection in lacrimal duct due to blockage
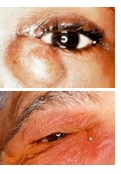
infectious/inflammatory condition
redness or swelling around puncta indicate
nasolacrimal sac obstruction
excessive tearing indicate
duct blockage
expressed drainage of puncta occurs w/
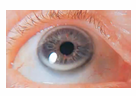
arcus senilis
normal variation in cornea and lens
arcus senilis
depositing of phospholipids and cholesterol in peripheral cornea - whitish ring surrounding the limbus or cornea around the iris; normal in aging, young high cholesterol level or lipids, no effect in vision
corneal scar, Pterygium, cataract
3 ab finding for cornea and lens
corneal scar
opacity of the cornea, graying/whitish, due to old injury/inflammation

Pterygium
pinkish triangular tissue growth in cornea treated with scraping - bulbar conjunctiva moves toward the cornea
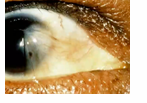
early pterygium
thickening of papebral c. extend nasal side
cataract
opacity of the lens, blurring of vision
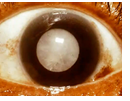
keratitis
inflammation of cornea infectios or non , accomp by redness, pain, decreased vision, discharge, photophobia
corneal ulcer
open sore of cornea
keratoconus
degenerative , cornea cone shape, distorted vision
corneal dystrophies
group of inherited disorders that cause abnormal deposits or growths in the corneal tissue
fuch and lattice
2 ex. of corneal dytrophies
nuclear cataract
appear gray when flashlight, appear black spot against red reflex thr ophthalmoscope
peripheral cataract
gray spokes point inward when flashlight, black spokes inward thru opthalmoscope
ectopia lentis, marfan syndrome, homocystinuria
lens become displaced fm its normal position due to trauma, genetic disorders like —- or —
spherophakia
lens abnormally small and spherical, leading to refractive errors such as myopia or lens dislocation
myopia
nearsightedness
hyperopia
farsightedness
hyphema, hypopyon
2 abnormal for iris
hyphema
pooling/ collection of blood inside anterior chamber of eye (space between cornea and iris) ; trauma
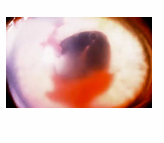
hypopyon
involving inflammatory cells in anterior chamber of eyes - the accumulation of white blood cells that form a whitish layer of fluid in the lower portion of the eye’s anterior chamber (front part); infection of internal eye.
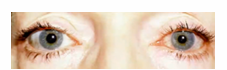
Pupils Equally Round, Reactive to Light Accommodation
PERLA procedure of pupil
miosis, aniscoria, mydriasis
3 AB of pupils
miosis
Small or constricted and fixed pupils; shrinking of pupils - Drug addicts; “pinpoint pupils”

anisocoria
pupil of one eye differs in size from the other - brain lesions.; pupil less than .5 mm 20% of clients
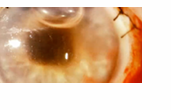
mydriasis
unusual dilation or widening of pupil - when the black center of your eyes are larger than normal (dilated pupils); high on drugs, coffee, or stimulants
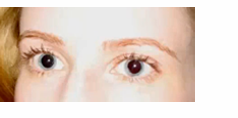
irreg shaped iris
causes shallow anterior chamber , increase risk of narrow/close angle glaucoma
impaired parasympathetic nerve, oculomotor nerve paralysis
anisocoria caused by 2
horner’s syndrome
if anisocoria is greater in dim light than bright light, it may be
pupillary rxn to light
test direct pupil rxn by shining a light obliqueqly to one eye
monocular blindness
when light directed to the blind eye results in no response to other pupil
corneal reflex test
this test assesses parallel alignment of eye
deviated alignment of eyes, muscle weakness, paralysis
asymmetric position of light reflex indicates — due to — and —
pseudostrabismus, strabismus/tropia
2 corneal reflex test abnormalities
pseudostrabismus
pupil appear at inner canthus due to epicanthic fold'; normal in children
strabismus/tropia
constant misalignmnet of eye axis, acc to direction towads which eye drifts and cause amblyopia
a. esotropia
b. exotropia
a. eye turn inward
b. eye turns outward
cover test
detects deviation in alignment or strength and slights deviations in eye movement
phoria
term used to describe misalignment that occurs only when fusion reflex is blocked
cardinal gaze test
assesses eye muscle strength and cranial nerve function
tropia, esotropia, exotropia, nystagmus
4 AB in cardinal gaze test
nystagmus
condition in which the eye makes repetitive, uncontrolled movements; inner ear problem
red green color blind/ deutranopia/protanopia
most common, client has difficulty distinguish bet red and green hues
blue yellow color blind/ tritanopia
unable to diff yellow and blue
complete color blindness/achromatopsia
client sees only shades of gray
myopia
a common vision condition in which near objects appear clear, but objects farther away look blurry (nearsighted)
amblyopia
also called lazy eye. A type of poor vision that usually happens in just 1 eye but less common in both eyes; legally blind. The lazy eye cannot see

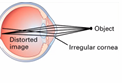
astigmatism
happens when your cornea (the clear front layer of your eye) or lens (an inner part of your eye that helps the eye focus) has a different shape than normal; irregular cornea
presbyopia
indicated when the client moves the chart away fm the eyes to focus on the print; common in 45 yrs of age
a. 70
b. 50
c. 90
d. 60
normal visual field degrees
a. inferior
b. superior
c. temporal
d. nasal