Chromosomes Study Questions
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
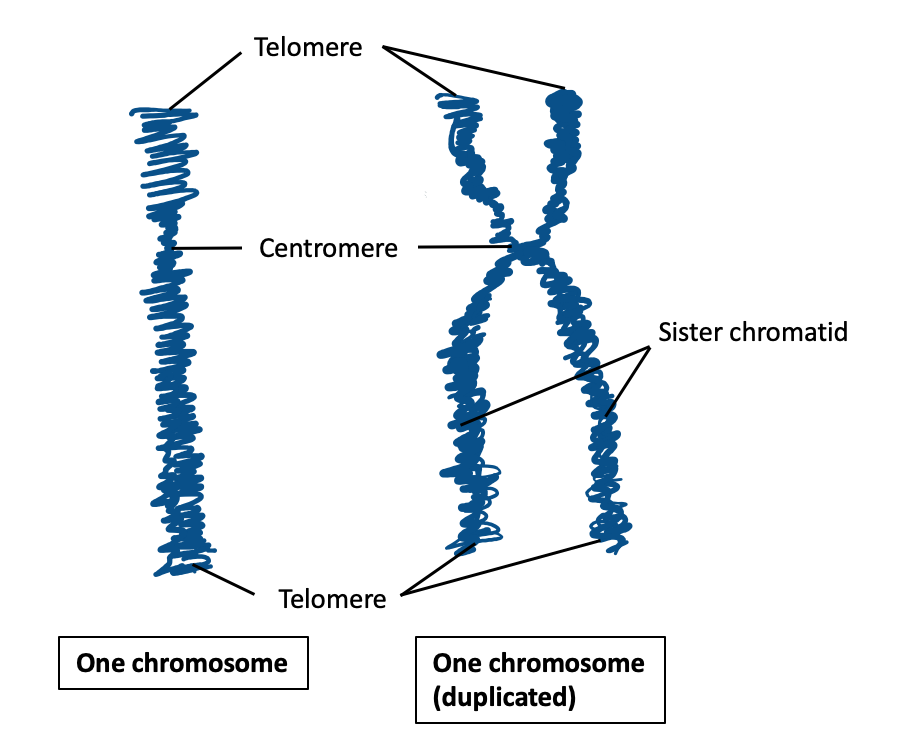
Locate the centromere and telomeres of a eukaryotic linear chromosome.
Telomeres are at the two “ends” of a chromosome, Centromeres are in the center of a chromosome
What are the differences between euchromatic and heterochromatic DNA?
Euchromatic DNA (Euchromatin) contains more active genes, is less compressed, and stains lightly compared to the rest of the chromosome. Heterochromatic DNA (Heterochromatin) is highly compressed, contains inactive genes, and stains darker than the rest of the chromosome.
What are the types of large scale chromosome rearrangements, how can we
visualize them and why do they matter?
Duplication - A segment of a chromosome is duplicated
Deletion - A segment of a chromosome gets deleted
Movement - part of one chromosome moves from one chromosome to another
Inversion - A portion of a chromosome gets “flipped” around
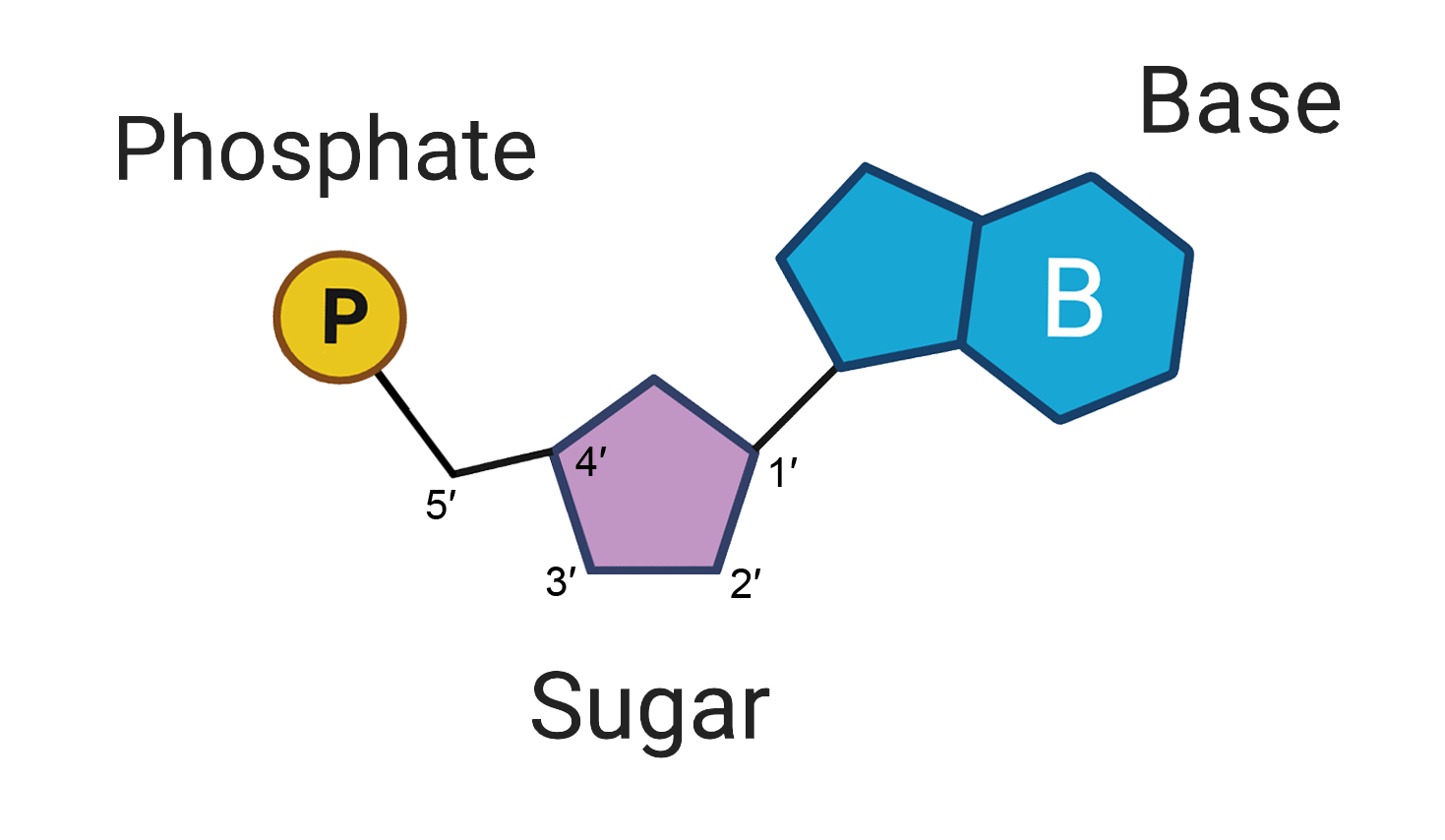
What is the structure of a DNA nucleotide?
A DNA Nucleotide contains a ribose sugar (Deoxyribose), a phosphate group, an OH group, and a nitrogenous base (A,C,G,T)
What properties determine which nucleotides base pair with each other?
A purine (oo) nucleotide will always pair with the pyrimidine (o) nucleotide that have the same amount of bonds.
Which nucleotides are purines vs pyrimidines.
G and A are purines, where as T and C are pyrimidines
Explain 5’ to 3’ orientation of a DNA strand.
The 5’ to 3’ orientation of a DNA strand is based on the positioning of the ribose sugar molecule. the direction that the 5’ carbon in the sugar molecule (The one closest to the phosphate group) will lead to the 5’ end of the DNA strand, and the end that the 3’ carbon is facing (The carbon closest to the OH group) will be the 3’ end. These are the “prime” carbons because the nitrogenous base consists of the normal numbered carbons, and the 1’ carbon is the carbon closest to the nitrogenous base, with the number increasing clockwise around the sugar.
What is the approximate size range for plant genome size? Do the # of genes vary?
the approximate size range for plant genome size is 61mbp to 149gbp. The # of genes do not vary.
What is the energetic consequence of a large genome?
the more base pairs, the more ATP it will take to produce the genetic material of each cell. For example, the largest plant’s genome of 149 GBP will require 149 billion ATP to produce a new cell’s genetic material, compared to a genome of 61mbp, which will take 61 million ATP to produce a new cell’s genetic material
What are the proteins that make up chromatin and what are their individual
functions?
Histones, which are structural proteins that bind DNA into nucleosomes using their positive charge and DNA’s negative charge.
Non histone proteins are involved in DNA metabolism, structure of the DNA, and regulate gene expression
How much is DNA compressed inside a cell? Why is this necessary?
What properties of DNA and histones facilitates their interaction?
What are matrix attachment regions of DNA?
Where does mitosis happen in a plant?