FPSYC3400: Offender Profiling
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lecture 5
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Crime Scene Information → (blank) to Offender Characteristics
prediction
OP is blank and based on blank
speculative; criminal shadows
The rationale of OP relies on the uniqueness of blank & different blank types which presumably will be reflected in offending behaviour
experience; personality
OP - The assumption is that the blank reflects key characteristics of the offender’s blank
crime scene; personality
OP - What do we assume about the offenders personality?
will not change (much)
OP - What do we assume about the way crimes are committed?
will not change (too much)
OP - What do we assume about the frequency of when offenders commit crimes?
do not commit crimes at random
Role of OP
Assist in the evaluation of evidence
Summary of a case
Reduces the pool of suspects
Link similar crimes through unique indicators & behaviour pattern
Target intervention or resources on suspects/areas
Assist in developing interview strategies
Help gain insight into offender motivation
Assess the potential for escalation in crime seriousness and frequency
Provide investigators with potential leads and approaches
Canter suggests that OP is created for?
unknown persons
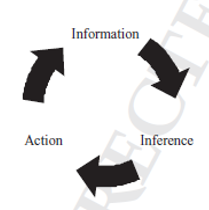
Where is OP in the investigative cycle?
Inferring a person’s characteristics from their actions, cognitions or motives dates as far back as the blank
Middle Age
Dr Thomas Bond (pathologist/coroner) inferred characteristics of blank
Jack the Ripper
James A. Brussel profiling the characteristics of the blank
Mad Bomber
The specific application of such inferences to criminal investigations gained interest as the FBI started publicizing their techniques in the blank
1970s
What are underlying assumptions of OP?
behavioural consistency
homology
2 Components of Behavioural Consistency
implies that an offender will show similar behaviours across their offences
but their actions will be different enough from other offenders that they can be differentiated
Where does support for behavioural consistency comes from?
the areas of case linkage, comparative case analysis, or linkage analysis
Research supports this assumption within a variety of crime types
Sexual assault
Homicide
Burglary
Robbery
arson
Behavioural Consistency - “blank”
necessary
Homology Assumption - “blank”
sufficient
Which assumption of OP has less conclusive support?
homology
What does homology assumption have some support in?
bivariate relationships
Examples: stranger rape & domestic burglaries
Behavioural consistency is not blank upon the assumption of homology being met or of it being valid
dependent
behavioural consistency is blank for offender profiling to work, the offender’s actions have to remain consistent for similarities to be found between their personal characteristics and behaviour.
necessary
the assumption of behavioural consistency would be blank if the assumption of homology is found to be valid
valid
Approaches to OP
criminal investigative
clinical
statistical
The Criminal Investigative Approach involves which approaches?
pragmatic
theory-led
FBI 1970s – led by the work of Howard Teten; joined by Patrick Mullany, Robert Ressler, John Douglas, Alan Burgess
Founders of modern-day profiling
Frustrations that forensic evidence (i.e., blood, fingerprints) is only valuable when you have a suspect
FBI provides behavioural-based investigative and operational support through the National Centre for the Analysis of Violent Crime’s (NCAVC) Behavioural Analysis Unit (BAU)
Slide 17 delete
Done
Stages of Profile Generation (Slide 17)
Done
Slide 18
how it differed offenders from the general population
Done
Slide 21
Done
Criminal Investigative Approach - Criticisms
More of an art vs science
Lack of psychological training
Based heavily on criminal investigative experience/intuition
Issues surrounding reliability, validity, & generalizability of methods & findings
Criminal Investigative Approach - Strengths
Origins – first systematic approach to profiling
Origins – first-ever quantitative study
In-depth study of sexual murderers
Later approaches started to incorporate theory (i.e., theories of aggression) and submit their work to be peer-reviewed
Now we see a mixture of science and experience
Pragmatic – most definitely
Scientific? It’s improving
blank was the 1st systematic approach to profiling and first-ever quantitative study
Criminal Investigative Approach
The Clinical Approach includes which approach?
individualistic
Clinical Systematic Approach - Principles
custom made
specific to that case
interactive
pitch the advice to their level of sophistication
reflexive
“knock on” effect
evolving
reconsideration about new information
need to see how it effects other factors
Clinical Systematic Approach - Dangers
Desire to please
Influence
Un-kept records
supposed to write everything down and collect information
Misinterpretation
10 Step Procedural Model
Done

4 Types of Sexual Murders
sexually motivated
sexually triggered
grievance motivated
neuropsychological dysfunction sexual
Clinical Approach - Criticisms
idiosyncratic
Based on knowledge & experience
Little guidance as to HOW to produce a profile; inferences are intuition driven
Ambiguous nature of statements made in the profile
Confirmation bias; Barnum (Forer) effect
Pragmatic usefulness/relevance of some inferences?
Clinical Approach - Strengths
Deep understanding and training in human behaviour
Positioned well to help with multi-aspects of the case
Can educate others without psychological background
The Statistical (Academic) Approach - 5 Main Factors
Residential location
Criminal biography
Domestic/social characteristics
Personal characteristics
Occupational/educational history
The Statistical (Academic) Approach is often called blank
Statistical Profiling
Investigative Problems
Salience of behaviours
Consistency
Distinguishing between offenders (Differentiation)
Inferring characteristics
Linking offences
Statistical Profiling Process
there is none (lol)
outline relevant information
why you’re doing this
what is being asked for
keep detailed records of what you have done and how you have done it
make it specific to the case
evaluate risk of offender
how risky their offence is
make investigative
look into previous research
plug in statistical analyses
make inferences
Radex of Criminal Behaviour - Differentiation
Victim as Object
Victim as Vehicle
Victim as Person
Radex of Criminal Behaviour – Salience & Differentiation: Level of Violation/Severity/Intensity
Personal
Physical
Sexual
Slide 33
uses SSA
measured as a ‘yes’ or ‘no’
victim is treated as an object
Done
Statistical Approach - Criticisms
Statistics alone do not predict the future
Use of stats does not mean the inferences will be valid or reliable
Question over the use of MDS as replication using similar variables has not been successful
Differences between recorded and reported crime
Sources of data
Investigative use?
Statistical Approach - Strengths
Rooted in the scientific method
Models are based on theory
Dimensional understanding of offending behaviour
rather than continuum or categorical
(meant to be) Pragmatically useful
More than just profiling (links with the 10 operational questions)
Slide 35
Done
Concerns Regarding Profiling in General
Not always scientific
Used in different ways
Not always of investigative use
Different techniques
Used when police have no motive or understanding of the offender
No standardized way to write profiles
‘Professional organizations’ popping up
Little or no credentials besides ‘say so’
Interpretation of profiles can be biased
Should be based on Scientific principles
Falsifiable, Evidence, Competence, Scientific
Cultural differences and research sources