IB (Part 2)
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Levels of Strategy
Corporate-level Strategy
Business-level Strategy
Operational-level Strategy
Corporate-level strategy
Quest for Economies of Scale
How value is added by the different businesses of the entire organization
ex. Disney leveraging its characters across movies, theme parks..
Business-level strategy
Quest for Competitive Advantage
How single business unit positions itself against rivals
Operational-level strategy
Quest for Operational Effectiveness
How functional components of an organization contribute to corporate and business level strategies in terms of resources, processes & people
ex. HR systems improving employee capability & retention
Paths for companies to diversify
Different industries
Geographies
Within-industry diversification
Different industries
Reduce dependency on a single industry
Spread risk
Leverage existing resources & capabilities across industries
Geographies
Access new customer base
Benefit from global economies of scale
Reduce exposure to local market risks
Within-industry diversification
Product diversification
Customer-segment diversification
Vertical integration
Horizontal integration
Globalization
Globalization of markets: Merging oh historically distinct national markets into a single global marketplace
Globalization of production: Sourcing G&S from around the world to take advantage of cost and quality differences (i.e. Apple designs in the US manufactures in China and sells globally)
Key Drivers of Globalization
Technology Change
Trade Liberalization
Global Institutions
Global Competition
Pro’s of Globalization
Expands economic growth & job opportunities
Increases consumer choice & lowers prices
Encourages innovation & international collaboration
Con’s of Globalization
Potential job losses in developed economies
Environmental degradation & resource strain
Cultural homogenization & loss of local identity
Growing income inequality in some regions
International business challenges
Cross-Cultural Differences: Strategies effective in one country may fall in another
Varying Political, Legal, and Economy Systems: Political risk and policy instability can affect strategy and performance
Global Coordination & Strategy: Need to balance global efficiency with local responsiveness
Ethical & Social Responsibility Issues
Value creation & Appropriation along the vertical chain
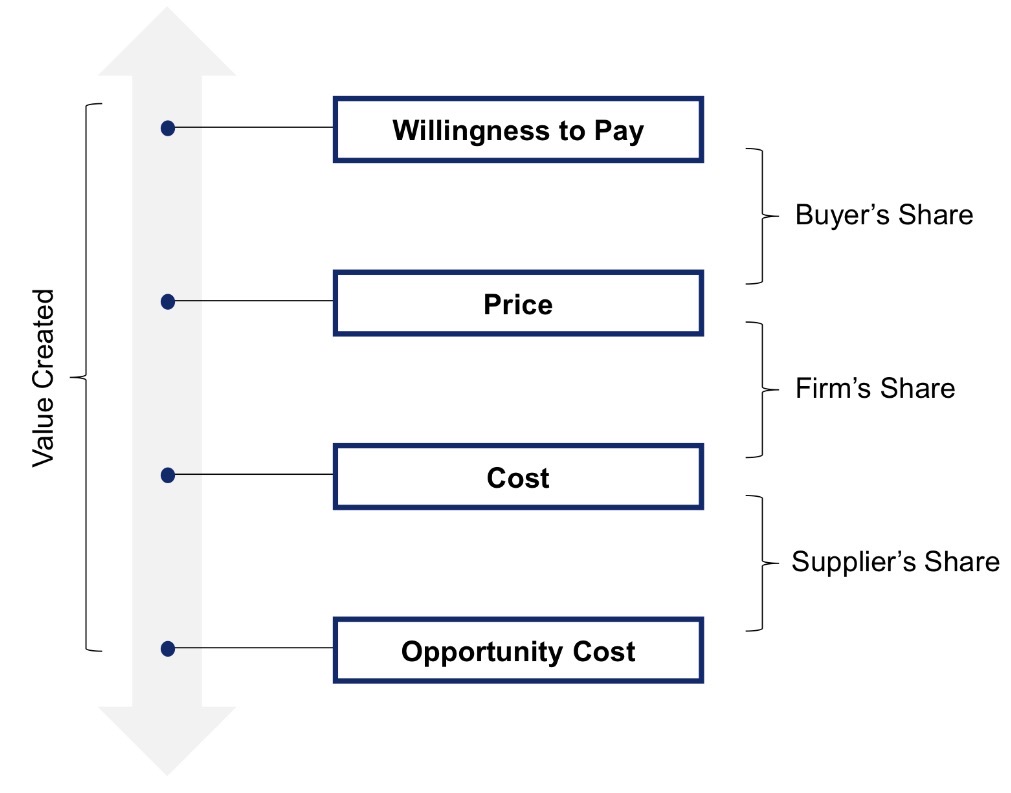
Buyer’s Share
Willingnes to pay (WTP): Firms can increase by improving product quality, customer experience, or offering unique features
Price
Price > WTP: Potential customer does not buy
Price < WTP: Potential customer byuys + captures a non-zero value
Supplier’s Share
Identify resources used & quantity of each resource
Negotiated cost rate vs Opportunity cost rate per unit of resource
Cost = Quantity of resource * Negotiated Cost per unit of resource
Opportunity cost = Quantity of resource * Opportunity Cost per unit of resource
Add up all costs
Generic Strategies for Going Abroad
Deployment
Development
Deepening
Deployment
Replication of competitive advantage from home country
Mechanism of creation of value is by aggregating demand
Target homogeneous segments (needs) of market across regions
Standardization of services or products
Development
Identifying where potential new capabilities reside
Goal is to get integrated competitive advantage
Locations should be different enough rather than too different
Deepening
Widen competitive advantage, without changing primary business strategy
Increase WTP by adjusting to local tastes
Decreasing costs by aggregation of demand (non-buyers turning to buyers)
Being internationally dispersed has value for stakeholders
Challenges in New Markets
Liability of being a foreigner
Paradix of being consistent
Liabilities of being a foreigner
Local laws favor domestic firms
Import/Export costs
Cultural differences
Caps on foreign investment
Seperate time zones can be a liability
Different contract structures
Paradox of being consistent
Need for market adaptation
Loss on internal consistency
Dilution of competitive advantage
Complex decision-making
Risk of strategic misalignment
Strategy
Actions that managers take to attain the goals of the firm
Determinants of Enterprise value
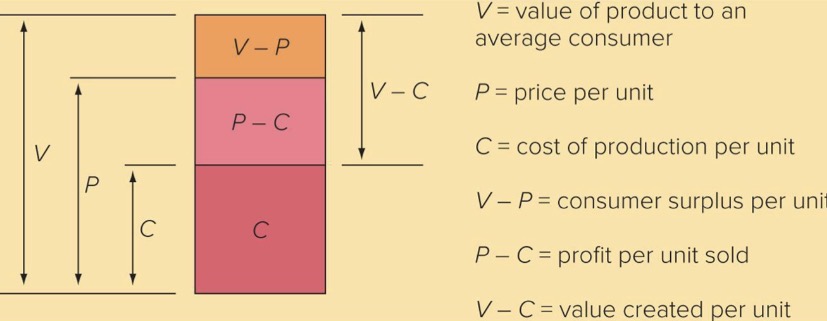
Value Creation
Measured by difference between a firm’s costs of production and the quality that consumers receive in its products
More value customers place on a firm’s product = high price firm can charged (V - C)
Porter’s strategies for creating value & attaining a competitive advantage
Low cost
Differentiation
To maximize profitability (Porter)
Pick a position on the efficiency frontier that is viable
Align internal operations to fully support that position
Ensure firm has right organization structure in place to execute its strategy
Consistency across strategy, operations & organizations is essential for competitive advantage & superior profitability
International firms are able to
Expand potential size of market for domestic products
Realize location economies
Realize greater cost economies from experience effects
Earn greater return-on-investment
Expanding the market
Successful firms transfer core competencies to foreign markets where indigenous competitors lack comparable competencies
Location economies
Performing a value-creationg activity in the optimal location to lower costs or add value
Cost reduction
Differentiation
Global web: Disperse value chain stages worlwide to maximize value or minimiza costs
Challenges:
Transportation costs
Trade barriers
Political & economic risks
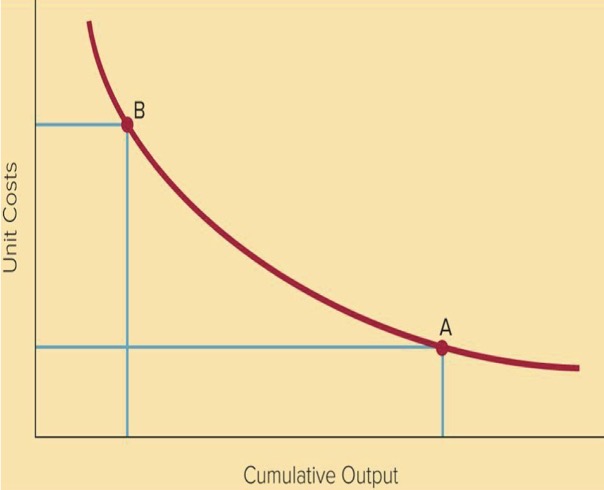
Experience effects
Experience curve describes how firm’s production costs decrease over the life of a product as the firm gains more experience producing it:
A: Learning Effects - Labor productivity improves & Management becomes more efficient
B: Economies of Scale - Producing more units spreads fixed costs over a larger output, reducing unit costs
Leveraging Subsidiary Skills
Using valuable skills developed in foreign subsidiaries and applying them across the firm’s global network to create value
Key steps for managers:
Recognize valuable skills can emerge anywhere
Incentivize local employees to acquire new skills
Identify when new skills are created
Facilitate skill transfer across the firm
Pressures for Cost Reductions
Requires a firm to try to lower the costs of value creation
Greater in industries producing commodity-type products (universal needs) & industries where major competitors are based in low-cost locations
Pressures for Local Responsiveness
Differences in Customer Tastes & Preferences
Differences in Infrastructure and Traditional Practices
Differences in Distribution Channels
Economic & Political demands by host-country governments
Rise of Regionalism (tendency toward the convergence of tastes, preferences… with a broader region composed of 2 or more nations; i.e. EU, North America, Latin America)
4 basic strategies
International strategy (low pressures for local responsiveness & low pressures for cost reductions)
Global Standardization strategy (low pressures for local responsiveness & high pressures for cost reductions)
Localization Strategy (high pressures for local responsiveness & low pressures for cost reductions)
Transnational Strategy (high pressures for local responsiveness & high pressures for cost reductions)
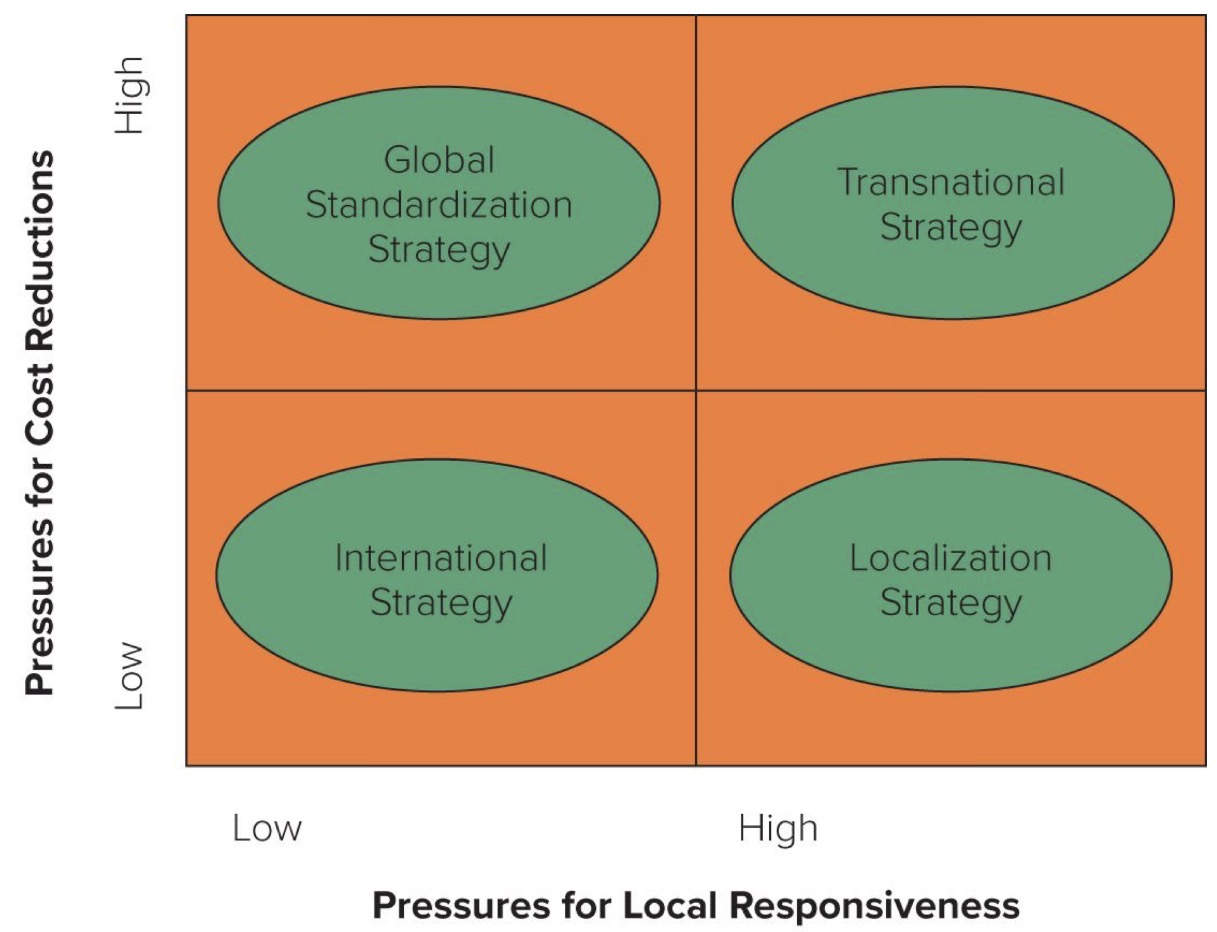
Global Standardization strategy
Goal: Achieve low cost globally by standardizing products
Concentrate productio, R&D and supply chain in a few lowest-cost locations
Use economies of scale, learning effects, and location economies
Avoid customization across countries
Use when: High pressur for cost reductions & low demand for local responsiveness
Localization strategy
Goal: Customize products to match local tastes & preferences in each national market
Customization reduces ability to gain cost savings from mass production
Use when: Large differences in consumer preferences across countries & low cost pressures
As competitors emerge, it will become less viable and would need to shift to a transnational strategy
Transnational Strategy
Goal: Achieve low costs while differentiating products to meet local market needs
Balance local customization with cost reduction is difficult
Requires complex coordination and management
Encourages multidirectional skill transfer between subsidiaries
Use when: Both cost pressures & local responsiveness is high
International strategy
Goal: Sell domestic products abroad with minimal customization
R&D and product development centralized at home
Manufacturing and marketing in each foreign market
Low local adaptation
Duplication of activities can raise cost
Use when: Cost pressures are not too high & low local responsiveness
As competitors emerge, it becomes less viable and would need to shift to global standardization or transnational strategy
Global strategy challenge
Companies must choose the right strategy for competing on a global stage
3 key strategies
Aggregation
Adaptation
Arbitrage
Aggregation
Achieving economies of scale by standardizing operations across regions
Adaptation
Customizing processes and offerings to meet local market needs
Arbitrage
Exploiting differences, such as offshoring to countries with lower labor costs
Basic Entry Decisions
Which markets to enter?
When to enter those markets?
On what scale?
Choosing foreign markets
Factors for entry:
Market size
Spending power
Costs & risks
Value creation potential
Suitability of its products to that market
Nature of indigenous competition
Choosing timing of entry
First-mover advantages:
Peempt rivals & build brand
Capture demand & customer loyalty
Build sales volume & experience curve
Create switching costs
First-mover disadvantages:
High learning costs
Risk of business failure
High promotion & customer education costs
Choosing Scale
Large-scale entry: Shapes competition, high risk, less flexible
Small-scale entry: Learn market gradually, lower risk
Strategic commitment: Long-term, difficult to reverse
No right scale: Depends on risk-reward tradeoff
Modes on entry
Exporting
Turnkey projects
Licensing
Franchising
Joint ventures
Wholly owned subsidiarie
Pro’s & Con’s of Exporting
Pro:
No establishment costs
Experience curve and location economies
Con:
May be costly if cheaper production abroad exists
High transport costs
Tariff/import barriers
Pro’s & Con’s Turnkey projects
Pro:
Less risky than FDI
Con:
No ongoing interest in foreign market
May create competitors
Risk of giving away proprietary knowledge
Pro’s & Con’s Licensing
Pro:
No development costs & risks
No barriers to investment
Good use of existing intellectual property
Con:
No control over operations
Limits firm’s ability to coordinate strategic moves
Risks losing technology
Pro’s & Con’s of Franchising
Pro:
Lower costs & risks
Helps build a global presence quickly
Con:
Set up subsidies
Quality Control
May inhibit firm’s ability to take profits out of one country to support attacks in another
Pro’s & Con’s Joint Ventures
Pro:
Local partner’s knowledge of the host country
Shared costs and risks
Political considerations
Con:
Loss of technology control
Lack of control over subsidiaries
Can lead to conflicts and battles for control between investing firms
Pro’s & Con’s Wholly Owned Subsidiaries
Pro:
Reduces risk of losing control over technology
Tightly control operations in different countries
Location and experience curve economies
100% share of profits
Con:
Bear full cost and risk
Problems associated with acquisitions
Acquisition
Firm seeks to enter a market where there are already well-established incumben enterprises
Global competitiors also interested in establishing presence
Pro:
Fast market entry
Can preempt competitors
Often less risky than building from scratch
Con:
Often produce disappointing results:
Risk of overpaying
Culture clashes during integration
Greenfield ventures
No incumbent competitors to be acquired
Good when competitive advantage relies on transferring unique routines or capabilities
Pro:
Full control over building the subsidiary
Con:
Slower to establish
Risky but less risky than aquisitions
Preemption by competitors
Factors influencing a mode of entry choice
Core competencies and entry-mode
Pressures for cost reductions and entry mode
Core competencies and entry-mode
Technological Know-How:
Licensing or joint venutres are risky since foreign partner could learn the technology & become a competitior
So company prefer wholly owned subsidiaries to protect their
Only license it if tech becomes outdated quickly
Management Know-How:
Franchising or ventures are safe enough
Less risk
Pressures for Cost Reductions and Entry Mode
High cost pressures prefer exporting and wholly owned subsidiaries
Allows tight control over global operations
Enables using profits from one market to support competition in another market
Strategic alliances for internationalization
Pro:
May facilitate entry into a foreign market
Allow firms to share the fixed costs
Brings together complementary skills and assets
May help the firm establish tech standards for the industry that will benefit the firm
Con:
May give competitors a low-cost route to new tech and markets
Partner selection
A good partner:
Helps the firm achieve its strategic goals
Has capabilities the firms lacks
Is unlikely to try to opportunistically exploit its partner
Choosing a partner:
Collect as much info as possible
Gather data from informed third parties
Get to know the potential partner before committing
Alliance Structure
Reduce the risk of giving away too much to partner
Use contractual safeguards
Agree in advance to swap skills and technologies
Cross-licensing agreements
Managing the Alliance
Be sensitive to cultural differences
Build trust
Build relational capital