4.1 Amorphous Solids
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What is a glass?
A disordered non crystalline (amorphous) solid
Does glass have SRO or LRO
SRO only
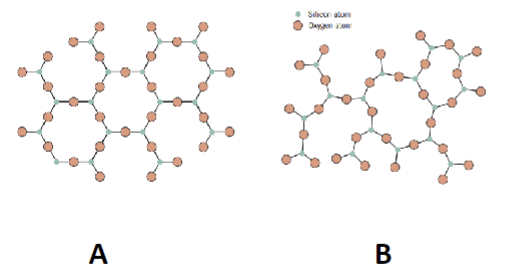
Which one is the amorphous structure?
B
True/False: SRO and LRO are found in every material
False
LRO is only found in crystalline materials
When you do x-ray diffraction of an amorphous solid what does the picture show?
It shows a hump instead of a bunch of peaks in the graph
Why do we use x-ray scattering?
It reveals information about the property of the material including bond length and information about crystallinity
When a liquid is cooled, atoms lose their thermal energy making atomic motion more difficult. What increases?
Viscosity
How does a glass form?
Thermal energy is lost, and atoms become liquid “frozen” reaching a “denser” solid statewithout long-range order, resulting in an amorphous structure.
True/False: All solids are thermodynamically favored to solidify into a crystalline solid
True because the crystalline solid is a lower energy state
What is Tg
Transition temp at pseudo-equilibrium (slowest cooling)
What is Tf
Fictive tempat which the structure of the glass would be in equilibrium if it were crystalline. It represents the temperature below which the material behaves as a solid.
True/False: Slower cooled glass is more dense
True
What does a higher Tf mean?
Faster cooling temp & lower density
What does a fast cooling mean?
It has the least time to rearrange, so it locks in density closer to liquidand retains a more disordered structure.
What is refractive index?
Electron density of a material
When light slows down…
refractive index increases
What does refractive index depend on?
Atomic density & atomic number of elements
Higher density means…
higher refractive index
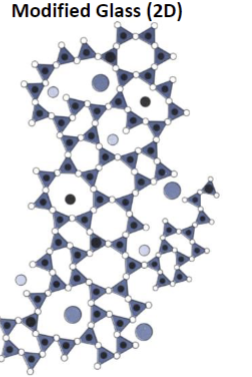
What do modifiers do in a glass network?
Disrupt the network
What are modifiers?
Elements that don’t form 3+ covalent bonds with oxygen.
What do modifiers form?
Non-directional, weaker, ionic bonds w/higher coordination number
Why do modifiers bond w/higher coordination numbers?
It adds more “wiggle room” to the network
Ex: Soda Lime Glass
Sodium —> Na2O
Calcium —> CaO
What happens when you add a modifier?
Tg decreases because the modifier lowers the energy barrier (atoms can keep moving at lower temps)
Why do we care about a lower Tg and Temp?
More fluid like at lower temps, can process at lower temps, and uses less energy, is cheaper, and easier to manufacture
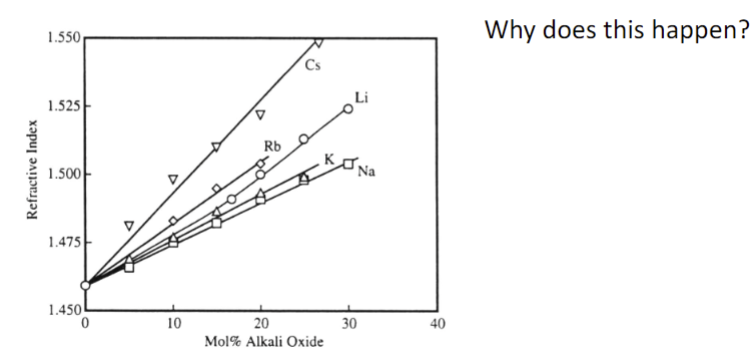
Why does this happen?
A higher atomic number means a bigger difference in refractive index (n)
If we wait a long time, will glass window panes flow and get thicker at the bottom?
No
Why do older windows have thicker glass at the bottom?
They were processed by spinning, and the outer radius is thicker when it’s processed in that way