exam2final
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
static
routes do not change or change slowly over time
dynamic
routes change more quickly
global information
all routers have compete topology, link cost info
decentralized information
router knows physically connected neighbors, link costs to neighbors
Dijkstra’s Algorithm
net topology, link costs known to all nodes
computes least cost paths from one node to all other nodes
iterative
split horizon
when a node sends a routing update to its neighbors, it does not send those routes it learned from each neighbor back to that neighbor
Count to Infinity problem
failures can cause DV to count to infinity, while seeking a path to an unreachable node
area border routers
summarize distances to nets in own area, advertise to other Area Border routers
backbone routers
run OSPF routing limited to backbone
boundary routers
connect to other AS’s
AS-PATH
contains ASs through which prefix advertisement has passed
NEXT-HOP
indicates specific internal-AS router to next-hop AS
gateway router receiving route advertisement uses ________ to accept/decline
import policy
policy intra/inter AS
inter-AS: admin wants control over how its traffic routed, who routes through its net
intra-AS: single admin, so no policy decisions needed
scale intra/inter
hierarchical routing saves table size, reduced update traffic
performance intra/inter
intra-AS: can focus on performance
inter-AS: policy may dominate over performance
Hot Potato Routing
suppose there are 2 or more best inter-routes, then choose route with closest NEXT-HOP
Multicast Routing Goal
find tree/tress connecting routers having local mcast group members
shared-tree
same tree used by all group members
source-based
different tree from each sender to rcvrs
Reverse Path Forwarding
rely on router’s knowledge of unicast shortest path from it to sender
DVMRP
distance vector multicast routing protocol
flood and prune
reverse path forwarding, source based tree
Where is the Link Layer Implemented
in each and every host
link layer implemented in “adaptor“
attaches into host’s system buses
flow control
pacing between adjacent sending and receiving nodes
half duplex full duplex
with half duplex, nodes at both ends of link can transmit but not at same time
Slotted Aloha Assumption
all frames same size
time divided into equal size slots
host start to transmit only at slot beginning
if 2 or more hosts transmit in slot, al hosts detect collision
Slotted ALOHA Operation
when host obtains fresh frame, transmit in next slot
if no collision: host can send new frame in next slot
if collision: host retransmits frame in each subsequent slot with probablilty p until success
polling
master host invites slave host to trainsmit in turn
typically used with dumb slave devices
polling concerns
polling overhead
latency
single point of failure (master)
MAC Address
32 bit IP address
network-layer address for interface
used for layer 3 forwarding
function: used ‘locally‘ to get frame from one interface to another physically connected interface
____ learns which hosts can be reached through which interfaces
when frame received, ____ learns location of sender: incoming LAN segment
switch
VLANS trunk port
carries frames between VLANS defined over multiple physical switches
MPLS Goal
high speed IP forwarding using fixed length label instead of IP Address
load balancer: application-layer routing
receives external client requests
directs workload within data center
returns results to external client
Cookies Four Components
cookie header line of HTTP response message
cookie header line in next HTTP request message
cookie file kept on users host, managed by users browser
backend database at website
____ acts as both client and server
typically ___ installed by ISP
cache
Why web caching?
reduce client request resposne time
reduce traffic on insitution access link
internet dense with caches: enables poor content providers to effectively deliver content
TDMA: time division multple access
access to channel in rounds
each station gets fixed length sloth in ecah round (length = pkt trans time)
unused slots go idle
ex. 6-station LAN, 1, 3, 4 have pkt, slots 2, 5, 6, idle
TDMA pros
variable user rate possible
no duplexer is needed for radio transmission
TDMA cons
precise synchronization required
for radio transmission equalization is necessary to combat ISI
bus/hub
popular through mid 90s, all nodes in same collision doman
star
prevails today
active switch in center
each spoke runs separate Ethernet protocol (nodes dont collide with each other)
DNS services
hostname to IP address transl
Why not centralize DNS?
single point of failure
traffic volume
distant centralized database
maintenance
RIP
included in BSD UNIX distribution 1982
distance vector algorithm
dist metric: # hops (max = 15 hops), each link has cost 1
DVs exchanged with neighbors every 30 sec in response message
each advertisement: list of up to 25 destination subnets
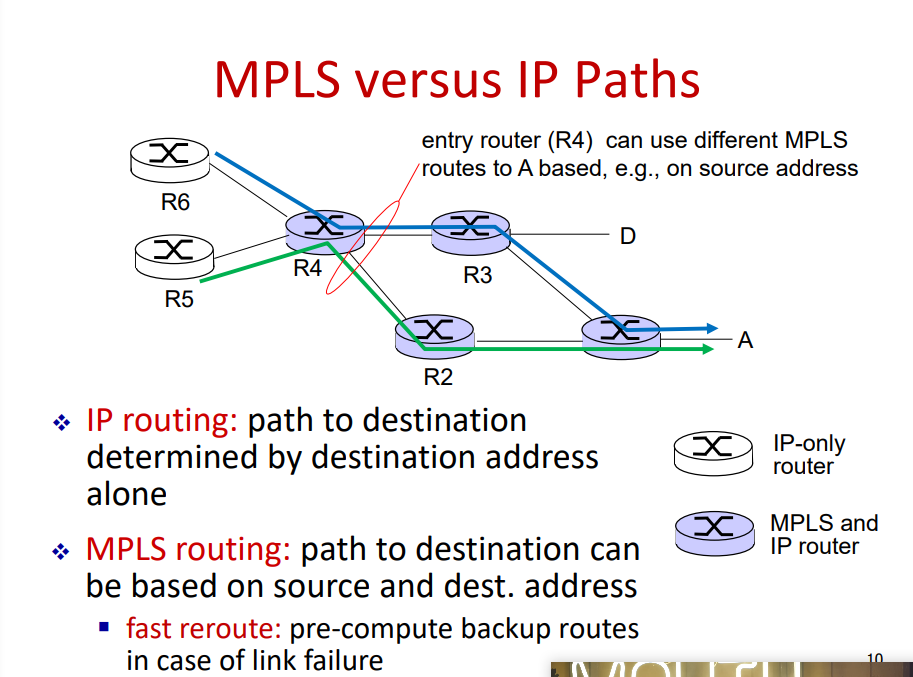
MPLS vs IP paths
IP routing: path to destination determined by destination address alone
MPLS: path to destination can be based on source and dest address
fast reroute: precompute backup routes in case of link failure