GW PUBH 1101 Henry: Chapter 1 (Public Health Approach)
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
vulnerable populations
group at a higher risk of disease or of bad outcomes from a disease
population health
composed of health issues (mental/physical health, genetics), populations (geography), shared health concerns (healthcare, exposure), and vulnerable groups (maternal/child/elderly groups)
social justice
arose during hygiene movement from 1840-1870s; idea that disease emerges from social conditions of inequality
interventions
strategies that protect health and prevent disease, disability, and death
high-risk approach
focuses on those with a high probability of developing disease and wants to decrease risk levels
risk factors
range of exposures that can increase the probability of disease
improving-the-average approach
focuses on entire population and wants to reduce risk of disease for everyone
contributory causes
immediate causes of disease; produce disease, disability, and death
determinants
identifies the factors or causes of disease that look at greater forces that can develop years before a disease appears
BIGGEMS
the 7 main determinants of disease
behavior
B in BIGGEMS; actions that increase exposure to factors that can produce disease or protect individuals from disease; Ex: smoking, drinking determine disease
genetics
G in BIGGEMS; contribute to development and progression of disease; rarely the most prominent disease determinant
infection
I in BIGGEMS; the direct cause of disease; exposure to this can contribute to development of or protection from a disease; Ex: early exposure to polio could reduce disease
geography
G in BIGGEMS; affects frequency and disease presence; there are special locations to produce disease; Ex: malaria, Lyme disease can show up in confined areas, you could be in area w high levels of radon/area w high altitude leading to sickness & frostbite
environment
E in BIGGEMS; world around us can cause disability & death; Ex: natural disasters (earthquakes, iodine deficiencies) and there can be toxins brought about by human activities
Medical care
M in BIGGEMS; access to this can allow for protection of many groups and can prevent disability & death if accessible; Ex: treating infectious diseases can reduce spread, helping smokers quit
Socioeconomic-cultural
S in BIGGEMS; the education, income, occupational status of an individual; those in lower status groups can be more at risk of a disease than those in a higher status; Ex: high rates of breast cancer in low SES
social determinants of health
how people are born into their environment/how we live; includes 1) neighborhood, 2) health/healthcare (ensure accessible insurance), 3) social/community context (where you like, walkability), 4) education (high/low level? based on residential area), 5) economic stability (medical bills/debt), 6) food (food deserts leading to food insecurity)
demographic transition
impact of falling childhood death rates & extended life spans on size & age distribution in a population; Ex: low childhood mortality rates from birth-5 yrs old indicates high public health standards
built environment
physical environment built for use by humans; part of Environment; could produce indoor air pollution & highway hazards that contribute to health determinants
rapid population growth
what would happen if there were high birth rates paired with low death rates
population pyramids
display changes in age distribution over time; display males vs. females in each age group
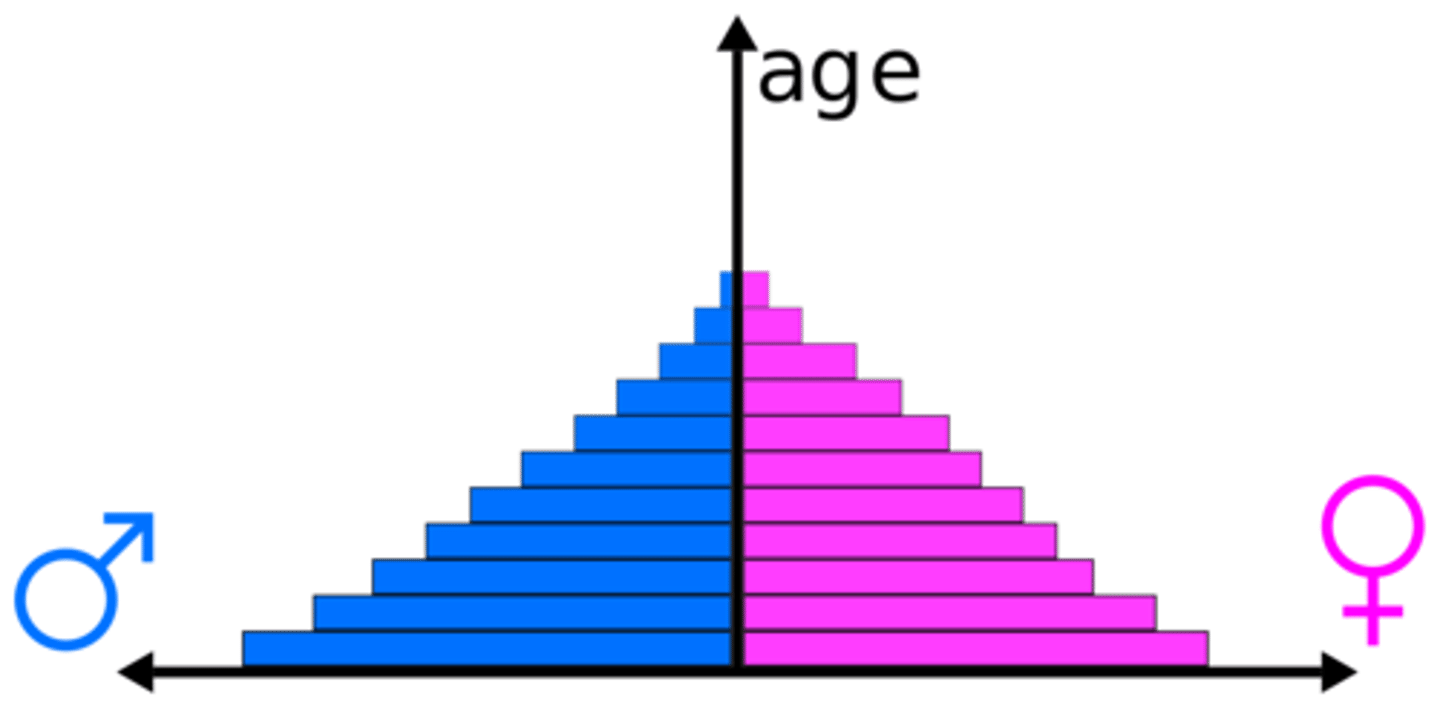
epidemiological transition
public health transition; there is social and economic development so different diseases become more prominent; Ex: developed countries have high rates of chronic disease, developing have communicable diseases
nutritional transition
countries move from poorly balanced, malnourished diets to diets w highly processed foods
optimal health determinants
social and economic factors are 40% of this (health = wealth!), health behaviors is 30% (exercising, putting right behaviors into practice), clinical care is 10% (physicians encourage people to seek care)