anatomy lab 3
1/217
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
218 Terms
what are the four major portions the brain can be divided into?
cerebrum, diencephalon, brain stem, and cerebellum
what is the cerebrum responsible for?
conscious thought process
what is the diencephalon responsible for?
relaying sensory and motor signals to the cerebral cortex and regulates sleep-wake cycle, body temperature, and appetite
what is the function of the brain stem?
make connections between the higher portions of the brain, the spinal cord, and the cerebellum and regulate breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure, and plays a crucial role in reflexes, sleep-wake cycles, and sensory/motor functions of the head and face
what is the function of the cerebellum?
coordination of movements and balance
what are the membranes that wrap the brain and spinal cord called?
meninges
what are cranial meninges?
three distinct layers of connective tissue that support and protect the soft tissue of the brain
what is the first layer of meninx found on the brain/spinal cord?
pia mater
what is pia mater?
a very thin and nearly transparent layer of areolar connective tissue that directly covers the surface of the brain
what is the layer after pia mater? why is it named that?
arachnoid mater; it has a web-like appearance
what is found between the pia mater and arachnoid mater? what is it filled with?
subarachnoid space; filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
what is the function of cerebrospinal fluid?
support and protect the brain, and also deliver nutrients to and remove waste from the brain
what is the outermost meninx called? what is it made up of?
dura mater; two layers of dense irregular connective tissue
what are the two layers of tissue found in the dura mater called?
there is a inner meningeal layer and an outer periosteal layer
what is the meningeal layer in contact with?
arachnoid mater
what does the periosteal layer do?
lines the inside of the cranium
what is the position of the cerebellum relative to the brain stem?
the cerebellum is posterior to the brain stem
briefly describe some problems a person might have if a stroke damaged his cerebellum.
the person would have issues with balance, movement, and coordination
between which of the cranial meninges is cerebrospinal fluid found?
pia and arachnoid mater, CSF is found in subarachnoid space
what is the layer of gray matter found on the surface of the cerebrum called?
cerebral cortex
what is found in the gray matter of the brain?
neuron bodies and unmyelinated axons
what do the neuron bodies in the cerebral cortex (gray matter of brain) help do?
form the conscious mind
what are the elevated parts of the cerebrum called?
gyri
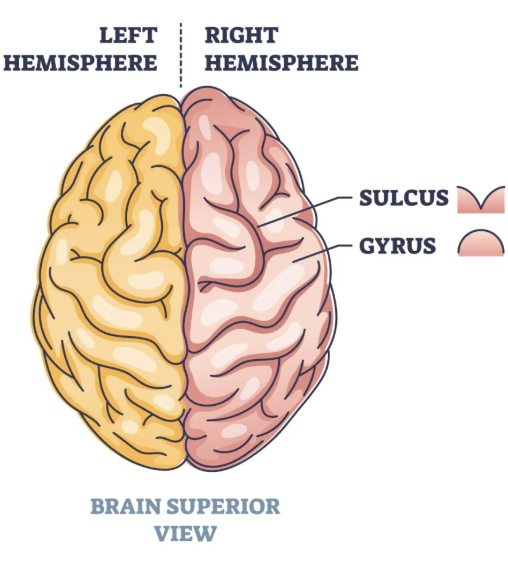
what are the depressed parts of the cerebrum called?
sulci
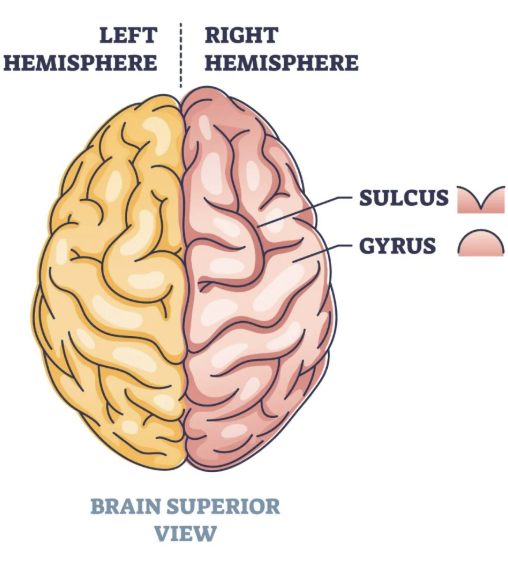
what do the gyri and sulci help do?
increase the surface area of the cerebral cortex and room for billions of neurons
what is the cerebrum divided into? what are they called?
left and right halves called cerebral hemispheres
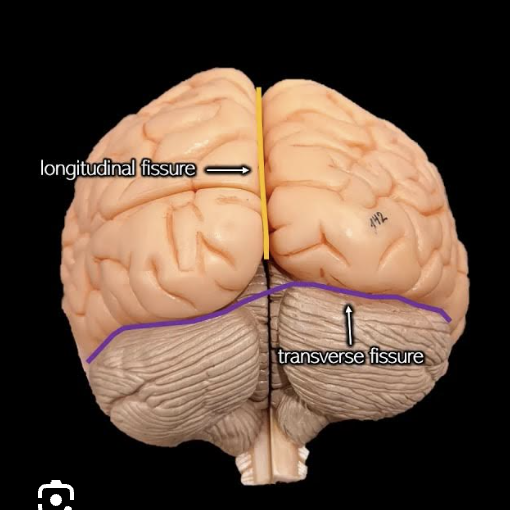
what divides the two hemispheres?
a deep midsagittal groove called the longitudinal fissure
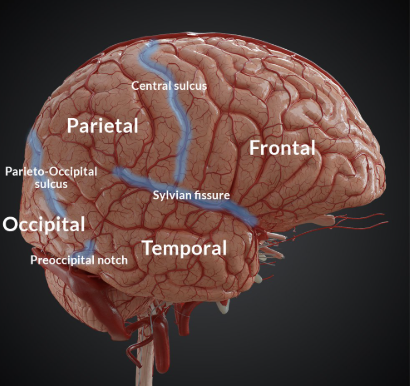
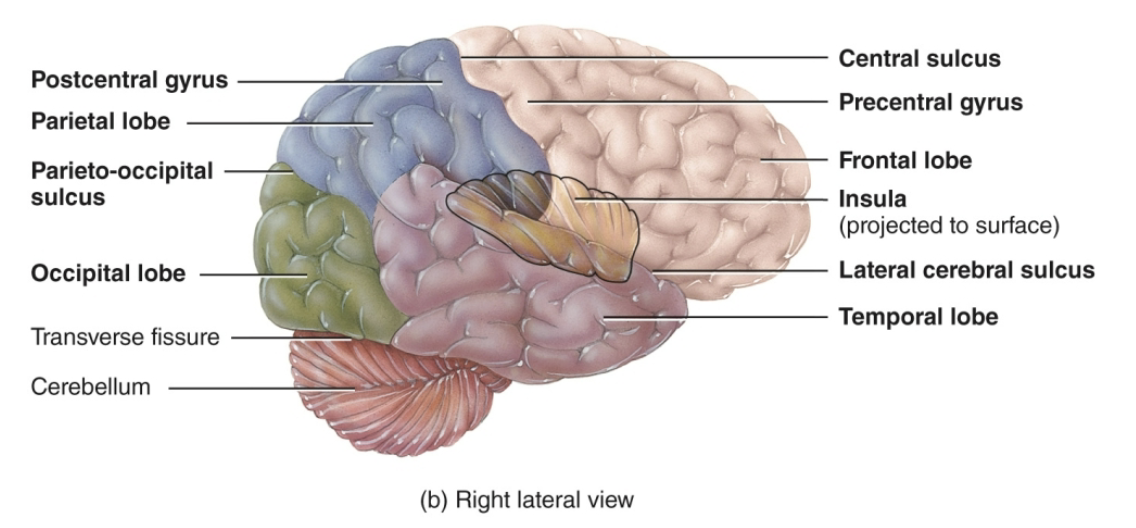
what are the four lobes that make up the cortex of both hemispheres?
frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital
what is the function of the frontal lobe?
personality, movement, back and forth eye movement, emotion, judgement, thinking
where is the precentral gyrus located? what is its function?
in the frontal lobe; responsible for directing somatic motor commands
what separates the frontal and parietal lobe?
central sulcus
what are the functions of the parietal lobe?
conscious processing of somatosensory information (ex. touch and body position) and language
where is somatosensory information processed?
in the postcentral gyrus located in the parietal lobe
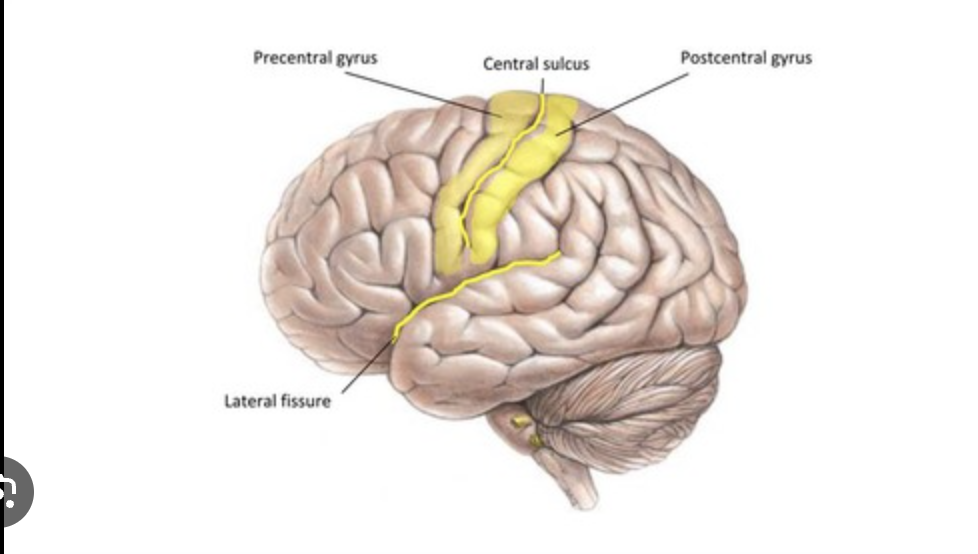
what separates the parietal and temporal lobe?
lateral sulcus
what are the functions of the temporal lobe?
processing auditory and olfactory sensations
what is the function of the occipital lobe?
processing visual information
what is the location of the insula? what is the function of the insula?
deep to the lateral sulcus; perception of taste, smell, digestion, visceral sensations (e.g., pain, hunger, thirst)
what make up the cerebral white matter?
myelinated axons
what is the function of the myelinated axons of the cerebral function?
they connect the billions of cortical neurons to each other and to lower portions of the CNS
what type of matter is found in the corpus callosum? what is its function?
white matter; its axons connect the two cerebral hemispheres to each other
what is the function of the fornix?
connects portions of the cerebrum and diencephalon
what thin membrane is between the corpus callosum and fornix? what is its function?
septum pellucidum; separates the two lateral ventricles
what are ventricles?
cavities in the brain that contain CSF
what visible structure seperates the frontal lobe from the parietal lobe?
central sulcus
what are the two main portions of the diencephalon?
thalamus and hypothalamus
what is the function of the thalamus?
collects various conscious senses (except smell), filters information, and directs important information to the appropriate area of the cerebral cortex
when you’re having a conversation in a crowded room, what does the thalamus do?
help process only important auditory information to the primary auditory cortex of the temporal lobe, allowing a person to focus on the conversation and not the background noise
what is the role of the hypothalamus?
the oversight of homeostasis within the body, relaying and filtering station for incoming olfactory information
what are the two small lumps that project from the underside of the hypothalamus?
mammillary bodies
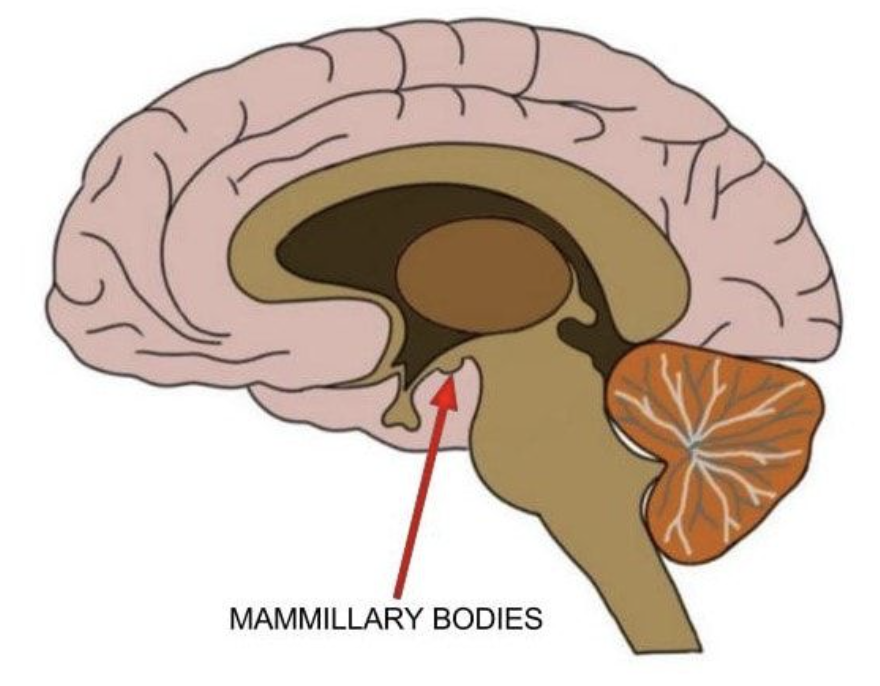
function of mammillary bodies
memory and olfactory sensation
what is the thin stalk structure that the pituitary gland attaches to?
infundibulum
what is the role of the pituitary gland?
homeostasis of the body
what are the hormones released by the pituitary gland?
growth hormone, follicle-stimulating hormone, and thyroid-stimulating hormone
what is the space between the right and left sides of the diencephalon?
third ventricle
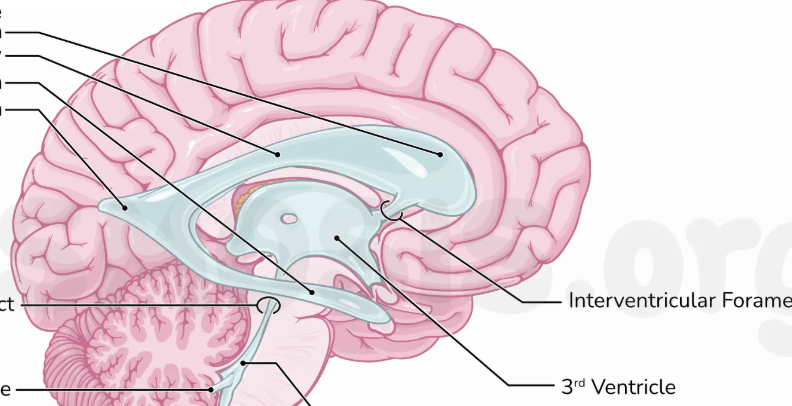
where is the choroid plexus located? what are their function?
superior to the third ventricle, inferior to the fornix; produces cerebrospinal fluid
name at least five specific functions of the hypothalamus
regulating body temperature, thirst, hunger, release of hormones, sleep-wake cycles, and maintaining homeostasis
what is the third ventricle associated with?
the diencephalon
what are the first and second ventricles and where are they?
they are the lateral ventricles; they can be found between the corpus callosum and fornix
what is the tectum? what is its function?
region of the midbrain made up of superior and inferior colliculus; associated with vision, hearing, motor control, sleep and wakefulness
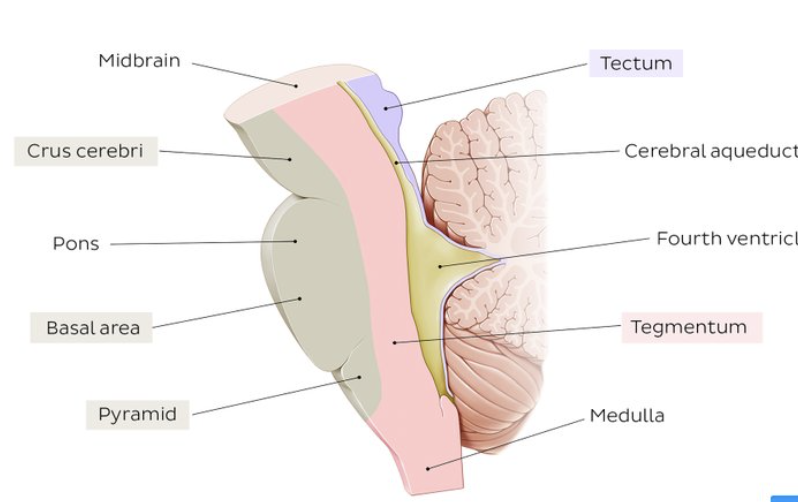
function of brain stem
form pathways between various structures such as cerebellum, diencephalon, and cerebrum
what is the superior part of the brain stem? what is it composed of?
midbrain; myelinated axons
what do the four lumps on the tectum of the midbrain make?
the corpora quadrigemina
what can the corpora quadrigemina be split into?
superior colliculi and inferior colliculi
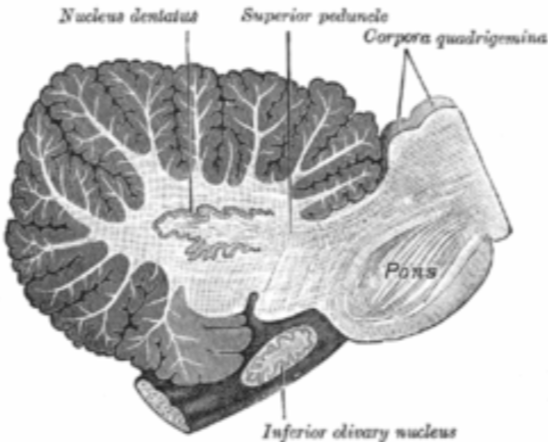
what is the superior colliculi for?
vision and visual reflexes
function of visual reflexes within superior colliculi
move your head and eyes to view moving objects
what is the inferior colliculi for?
hearing and auditory reflexes
function of auditory reflexes of the inferior colliculi
move your head in response to startling sounds
what is the arbor vitae and its functions?
the tree-like white matter tracts in the cerebellum that provide afferent and efferent (incoming and outgoing) sensory and motor information to and from the cerebellum
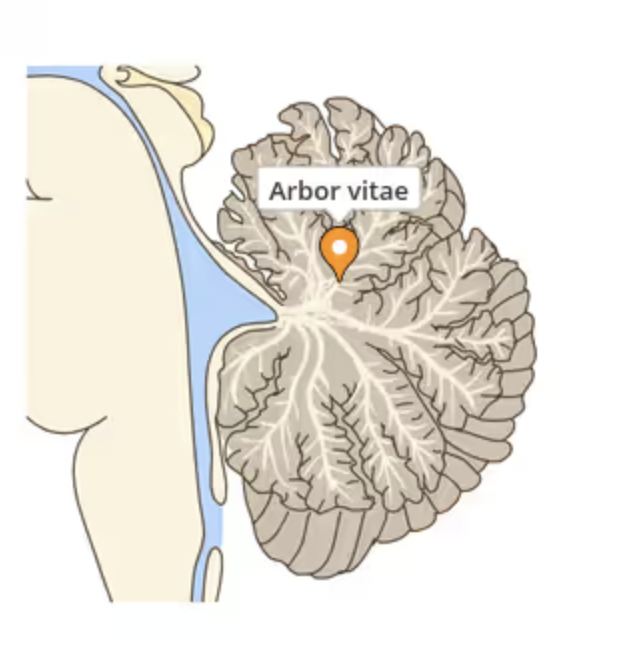
what does arbor vitae mean?
“tree of life”
what are the neuron bodies in the pons called and what are their function?
nuclei, they are involved in maintaining the rhythm of breathing
what do the descending tracts of axons running through ventral portions of the medulla do?
carry commands from the brain to motor neurons in the spinal cord
what do the ascending tracts of axons running through dorsal portions of the medulla do?
carry sensory information from the spinal cord to the brain
what do the nuclei in the medulla do?
exert control over the heartbeat
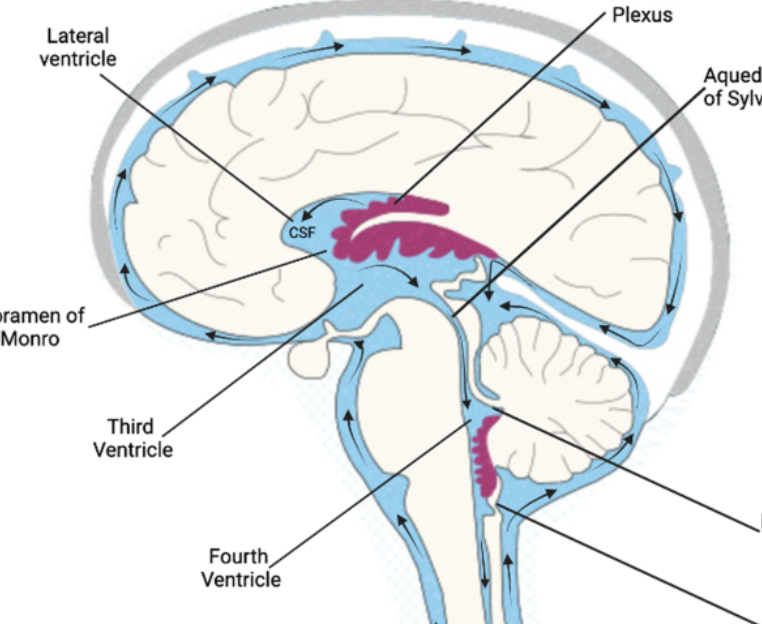
what structure connects to both the third and fourth ventricle?
cerebral aqueduct
function of cerebral aqueduct
pathway for the flow of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) throughout the brain and spinal cord
what are the four ventricles connected to? what flows through these spaces?
themselves, the central canal of the spinal cord, and the subarachnoid space that surrounds the brain and spinal cord; cerebrospinal fluid
a blow to the back of the head that damages the medulla oblongata may be fatal. why?
can obstruct and even cease regulation of breathing and heart rate, causing death
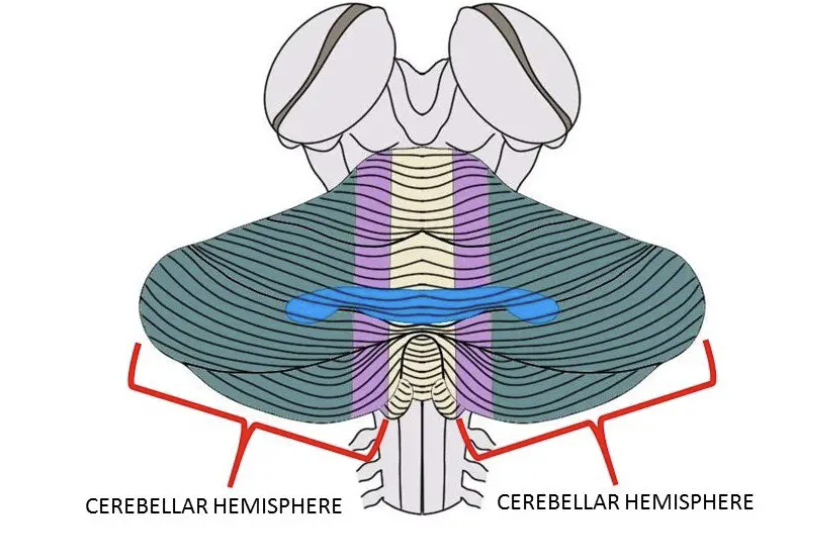
what separates the cerebrum and cerebellum?
the transverse fissure
what is the midsection of the cerebellum?
the vermis
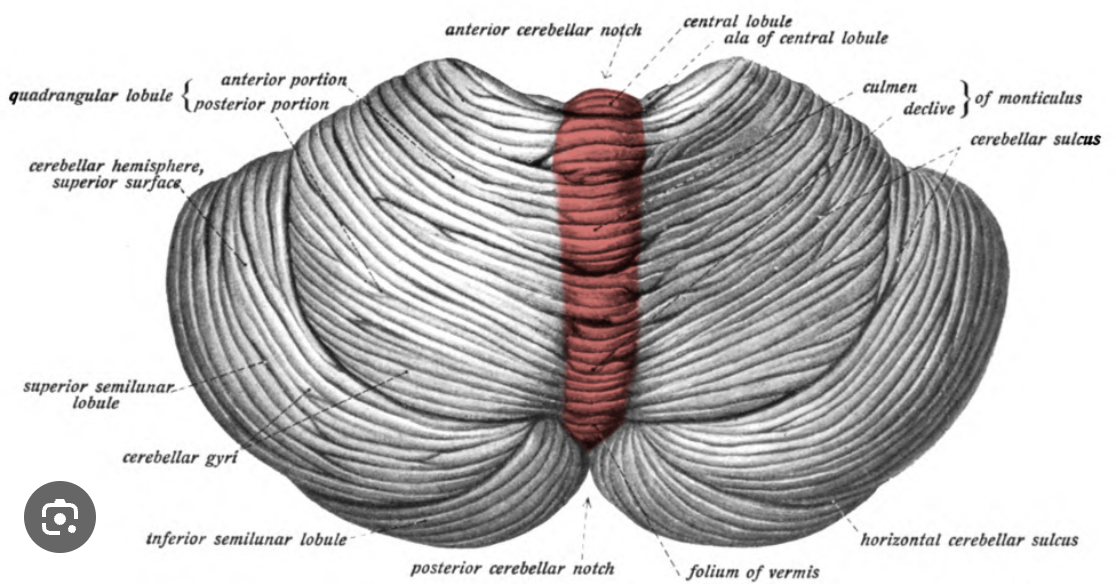
what are the lateral sides of the cerebellum called?
cerebellar hemispheres
what are the folds in each cerebellar hemisphere of the cerebellum called? what are they seperated by?
folia; shallow sulci
what is a nerve?
a bundle of axons located outside of the CNS
how many pairs of nerves are attached directly to the brain and what are they called collectively?
12 pairs, cranial nerves
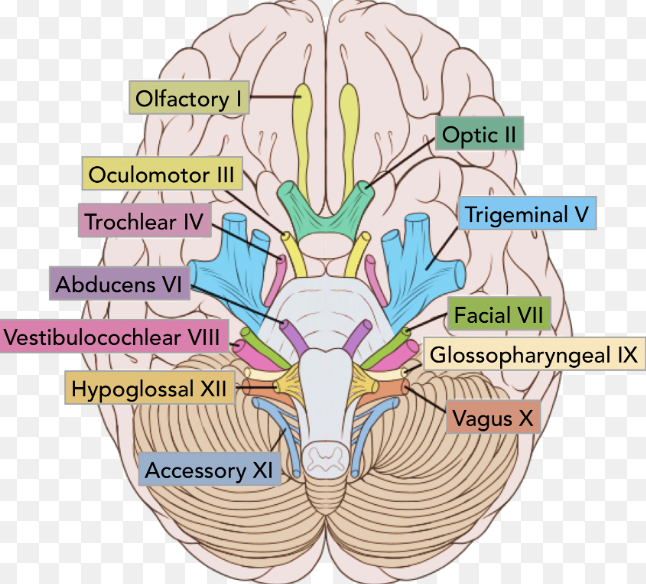
function of cranial nerves
carry information directly to and from the brain
what is another name for neurons that carry both sensory and motor information?
mixed nerves
what do cranial nerves attach to? what is the exception?
the brain stem; excluding the olfactory and optic nerves
cranial nerve I (name, type of nerve, major functions)
olfactory nerve, sensory, sense of smell
cranial nerve II (name, type of nerve, major functions)
optic nerve, sensory, sense of vision
cranial nerve III (name, type of nerve, major functions)
oculomotor nerve, motor, movement of eye
cranial nerve IV (name, type of nerve, major functions)
trochlear nerve, motor, movement of eye
cranial nerve V (name, type of nerve, major functions)
trigeminal nerve, mixed, sense of touch, pain, temperature, and proprioception; movement of chewing and middle ear muscles
cranial nerve VI (name, type of nerve, major functions)
abducens nerve, motor, movement of eye laterally
cranial nerve VII (name, type of nerve, major functions)
facial nerve, mixed, sensory impulse for taste, touch, pain, temperature, and proprioception, muscles of facial expression and middle; autonomic motor impulse for lacrimal (tears) and salivary (saliva) glands
cranial nerve VIII (name, type of nerve, major functions)
vestibulocochlear nerve, sensory, sense of hearing and balance
cranial nerve IX (name, type of nerve, major functions)
glossopharyngeal nerve, mixed, sensory impulse for taste, touch, pain, temperature, proprioception, swallowing; autonomic motor impulse to parotid gland (saliva)
cranial nerve X (name, type of nerve, major functions)
vagus nerve, mixed, sensory impulse for taste, touch, pain, temperature, proprioception, hunger, fullness, discomfort, speech, swallowing coughing; autonomic motor impulse for motility (movement of food through digestive tract), secretion, and decrease heart rate
cranial nerve XI (name, type of nerve, major functions)
accessory nerve, motor, movement of head
cranial nerve XII (name, type of nerve, major functions)
hypoglossal nerve, motor, movement of tongue
what problem would a person have if his oculomotor nerves were damaged? what if his optic nerves were damaged?
difficulty moving eyes; vision loss or blindness
what pair of cranial nerves also innervates various structures in the ventral body cavity? to what parts of the body is this nerve connecting the brain?
the vagus nerve (cranial nerve X); heart, lungs, stomach, and other organs in the chest and abdomen