DNA+Function
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
name the 2 types of nucleic acids and where they are found.
DNA-deoxyribonucleic acid in the nucleus
RNA-ribonucleic acid in the nucleolus of the nucleus
Describe the 3 main functions of DNA.
Controls cellular activity
Makes exact copies of itself
Undergoes Mutations
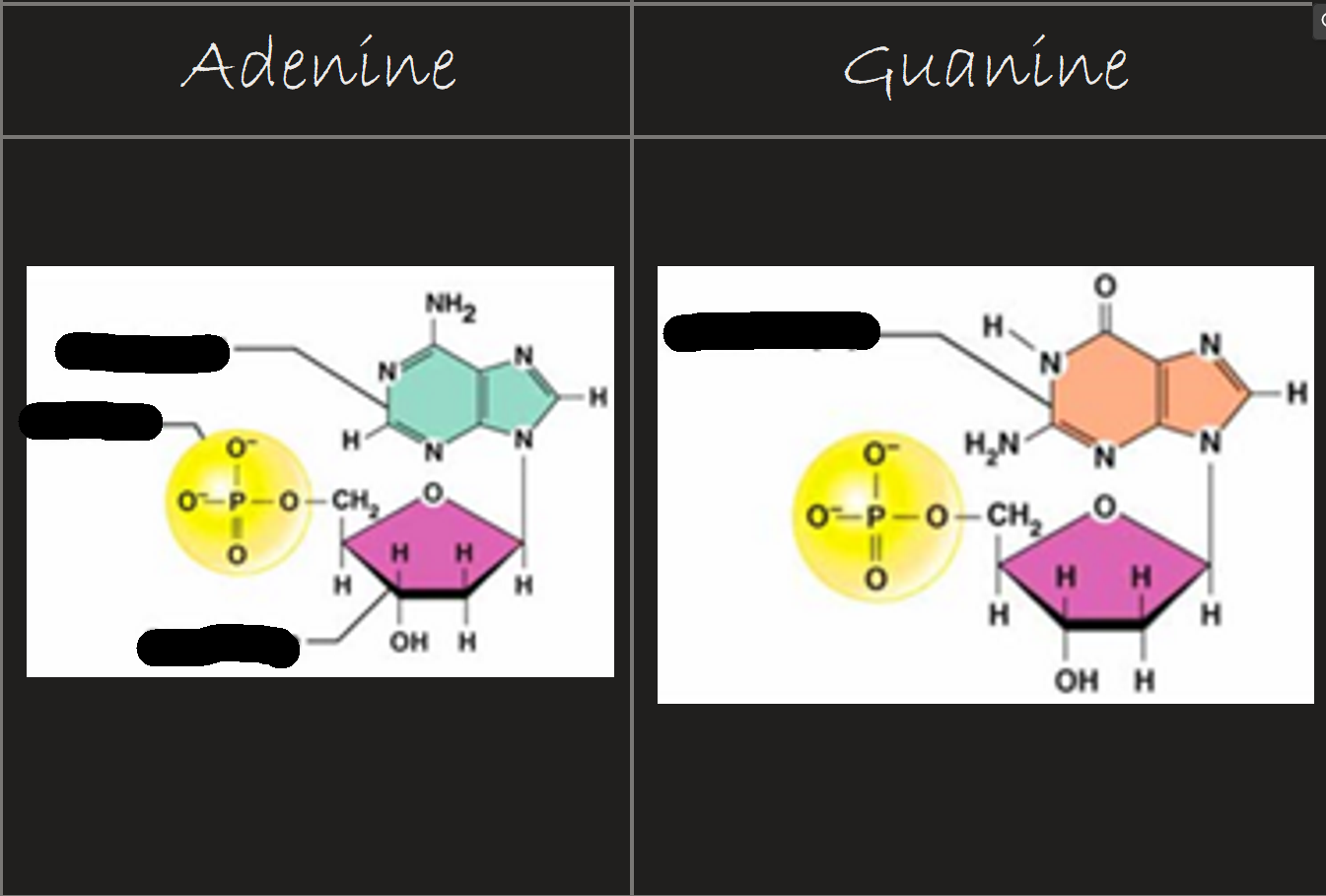
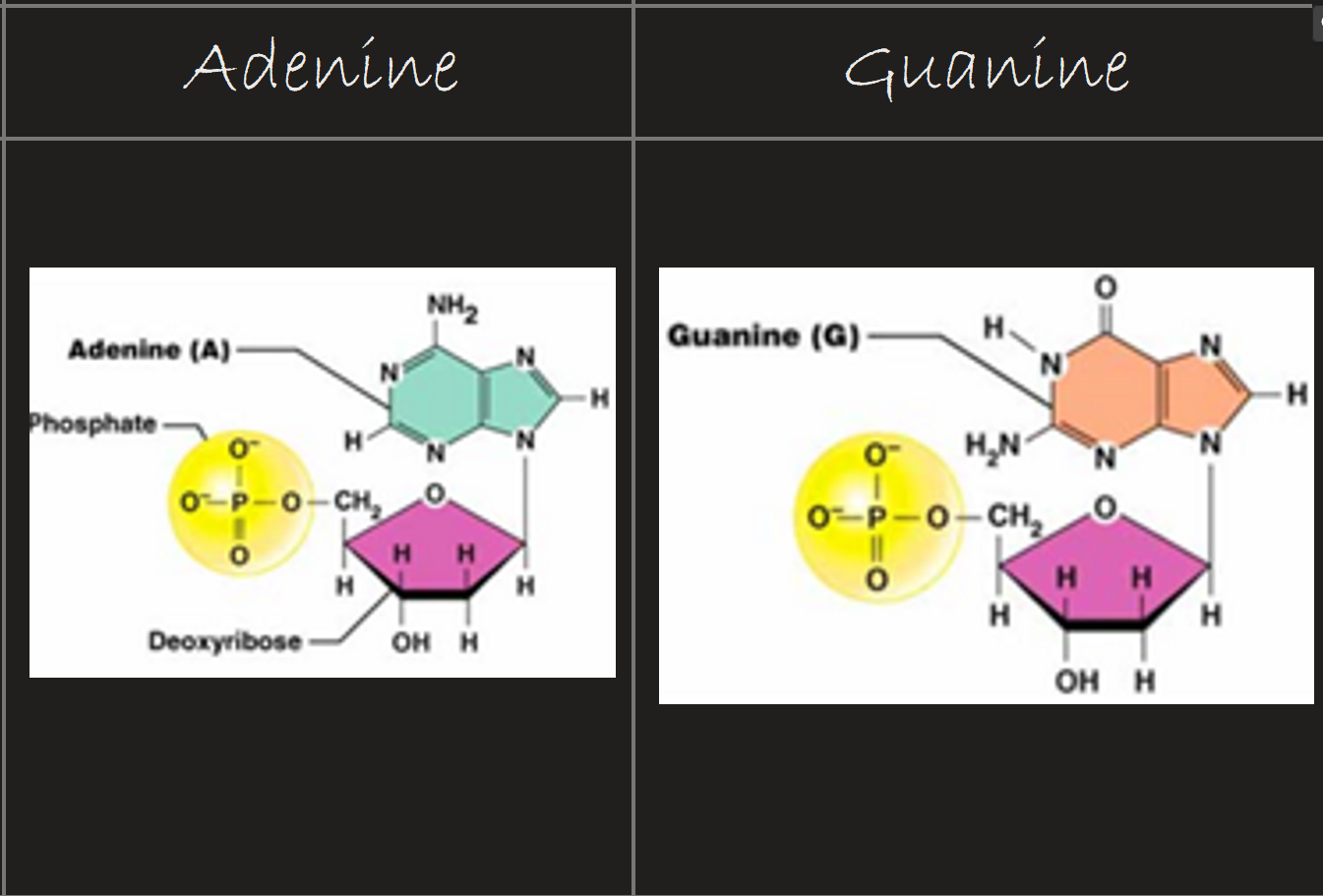
Label the purine Diagram
Describe the structure of DNA using the following terms: nucleotides, double helix, complementary base pairing, hydrogen-bonding, anti-parallel, 3', 5', sugar-phosphate backbone.
DNA has a double helix made of nucleotide monomers. Each strand has a sugar phosphate backbone. Has bases extending inwards, complementary base pairing (A-T G-C) held with h-bonds. The two strands are anti-parallel meaning one runs 3’ to 5’ while the other runs 5’ to 3’
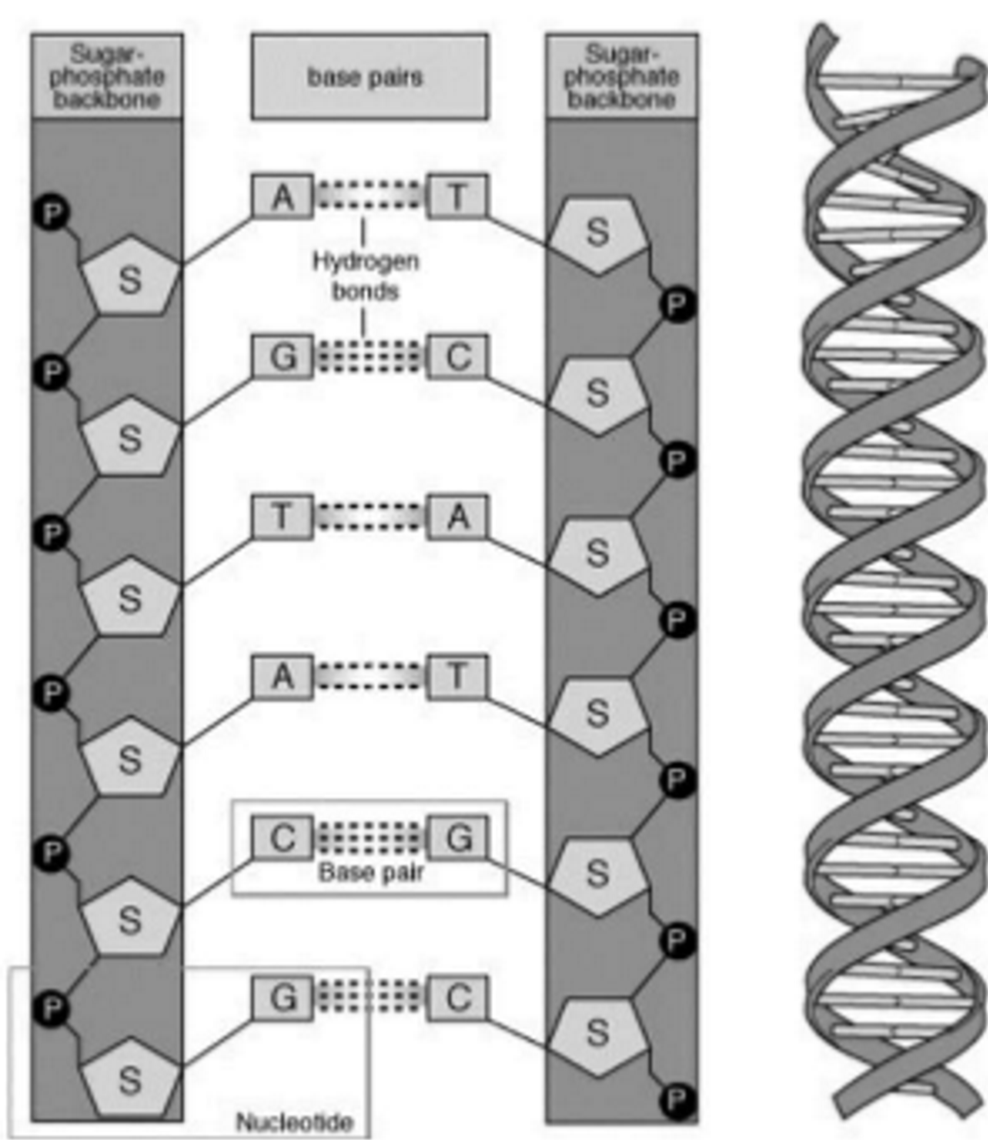
What exactly does complimentary base pairing mean?
Bases only h-bond with their specific base; a purine will always pair with a pyramidine.
Why must A always pair with T and C always pair with G
Because it is the only combination that can form H-bonds
Clearly explain the differences between genes and chromosomes.
A gene has DNA info to build a polypeptide, while a chromosome contains many genes
Explain how the structure of DNA and complementary base pairing promotes the continuity of life.
The structure of DNA ensures continuity of life by acting as a template to allow complementary base pairing during cell replication. Garnerin daughter cells to receive identical genetic info to the parent cell.