ch. 14 federal reserve system
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
open market operations is the primary tool to change ____ ___
monetary supply
Buying Securities:
Increases money supply
Banks' reserves are credited, allowing more lending
Selling Securities:
Decreases money supply
Money is taken out of circulation as banks pay
Impact on Interest Rates:
Increased reserves lower interest rates (cheaper borrowing)
Decreased reserves raise interest rates
define asset
anything that can depreciate in value
cash is the most liquid in assets
wealth =
assets - liabilities
define liquidity
ability to change an asset into cash
2 biggest categories in money supply
currency in circulation
cash held by public
checkable bank deposits
bank account on which ppl can write checks
define money supply
total value of financial assets in economy
define medium of exchange
something people accept as payment for goods and services
coincident indicator: reflects the current state of the economy, moving up or down; used to assess current economic conditions and inform decisions
double coincidence of wants: a situation in a barter system where 2 parties must both want what the other has to offer for a trade to occur
store of value
money is means of holding purchasing power over time
saving
unit of account
money provides yardstick for measuring & comparing the values of a wide variety of goods & services
commodity money
a good, normally gold or silver, used as a medium of exchange that has intrinsic value in other uses.
intrinsic value
commodity-backed money
medium of exchange with no intrinsic value; the ultimate value is guaranteed by a promise that it can be converted into valuable goods
fiat money
money whose value derives entirely from its official status as a means of payment.
$20 is intrinsically worth less than $1
Monetary aggregate
an overall measure of the money supply
treasuries
CDs
money in bank; savings & checking account (have $10k saved);
savings earns interest
2 measures of money supply
M1
includes only the most liquid forms of money. Money in circulation, demand deposits, and other checkable deposits
M2
includes M1 plus near-moneys: financial assets that can’t be directly used as a medium of exchange but can readily be converted into cash or checkable bank deposits
Which of these assets would you classify as being the most liquid?
demand deposits
small-time deposits
a house
gold bullion
demand deposits
T/F: state banks can’t go brankrupt
T
Net worth represents
the value of the firm to its stockholders or owners
total reserves =
required + excess
"reserves" is implied that it's total
define required reserve ratio & provide formula
percentage of its total deposits that a bank must keep as reserves at the Fed Reserve
RRR = (Commercial bank’s Required reserves) / (Commercial bank’s Checkable-deposit liabilities)
T-account
a tool for analyzing a business’s financial position by showing the business’s assets and liabilities.
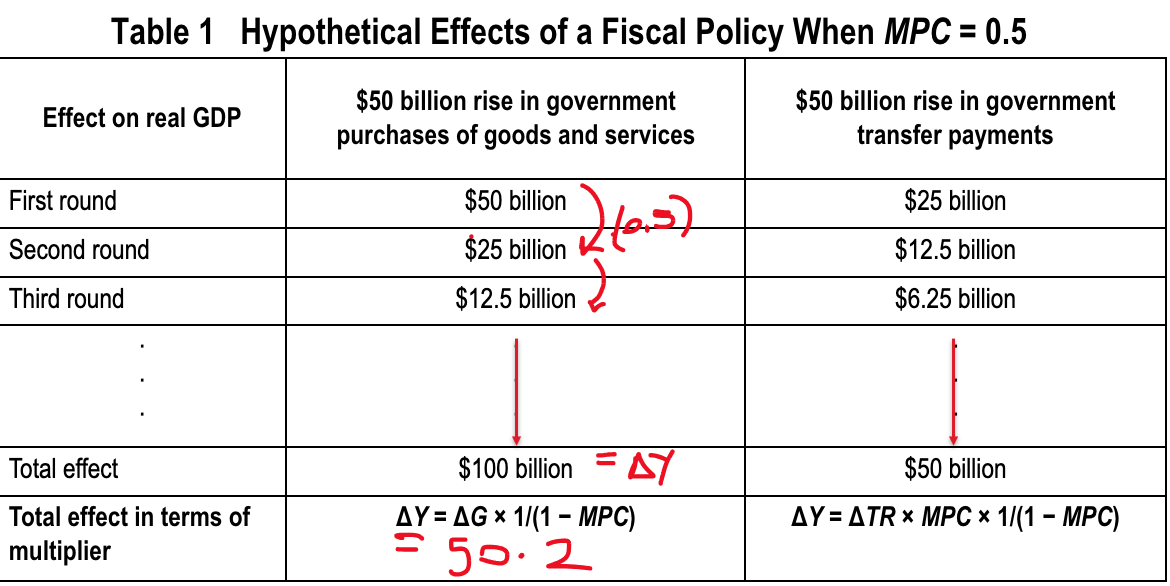
reserves (total) = ?
reserve ratio = ?
Reserves (Total) = $100,000 / Assume excess reserves = 0
Reserve ratio: the fraction of bank deposits that a bank holds as reserves ($100,000/$1,000,000 = 10%)
define bank run
everyone runs to bank & pulls everything out
withdrawing funds (defaulting on funds)
example:
lending out my money; percieve that bank has high default rate, take money out; run on the bank (bank run)
econoic decline
FDIC
independent fed agency insuring deposits in US banks and thrifts in the event of bank failures
maintain public confidence and encourage stability in the financial system through the promotion of sound banking practices.
Monetary multiplier formula
1 / R
R = required reserve ratio
private banking
biggest concern is making sure they get their money back; loaners have most productive use for it; no competition; give money out to those who have connections; diminishes economic growth