Biochemistry - Chapter 12 - Membrane Structure and Function - Review
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
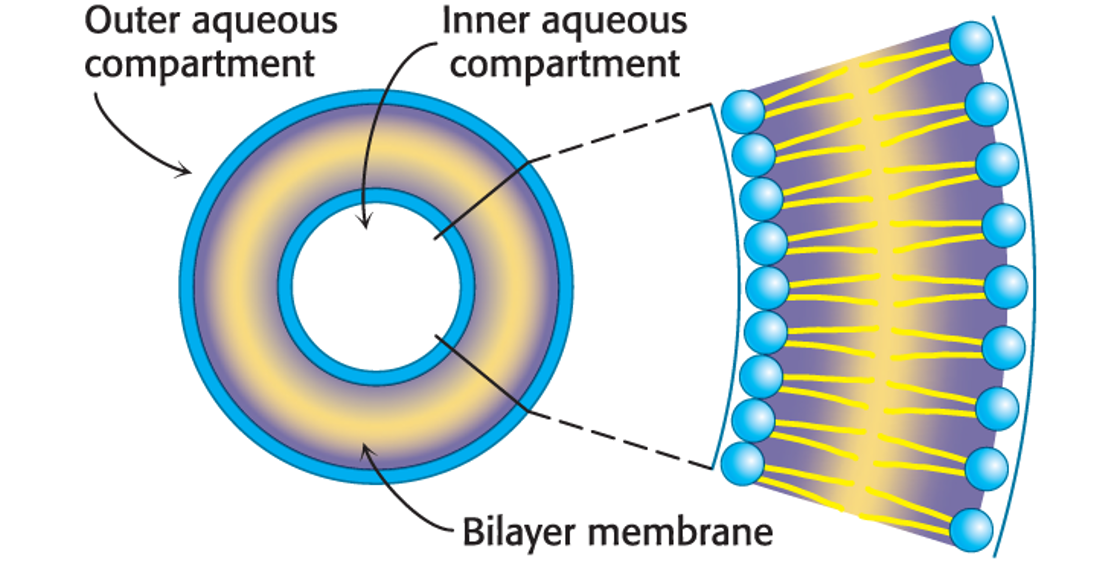
Liposomes, or lipid vesicle
Liposomes, or lipid vesicles, are aqueous compartments enclosed by a lipid membrane.
Lipid bilayers
Highly impermeable to ions and most polar molecules.
Cholesterol helps to maintain proper…
…membrane fluidity in membranes in animals.
Lipid soluble molecules such as __________ can cross the membrane but ______ and __________ and other cannot cross the membrane.
O2 and CO2
Ions (K+, Na+, Ca2+) and big molecules such as glucose
Although membrane lipids establish a permeability barrier, membrane proteins allow…
…transport of molecules and information across the membrane.
Integral membrane proteins
Proteins that are embedded in the hydrocarbon core of the membrane.
Peripheral membrane proteins
Proteins that are bound to the polar head groups of membrane lipids or to the exposed surfaces of integral membrane proteins.
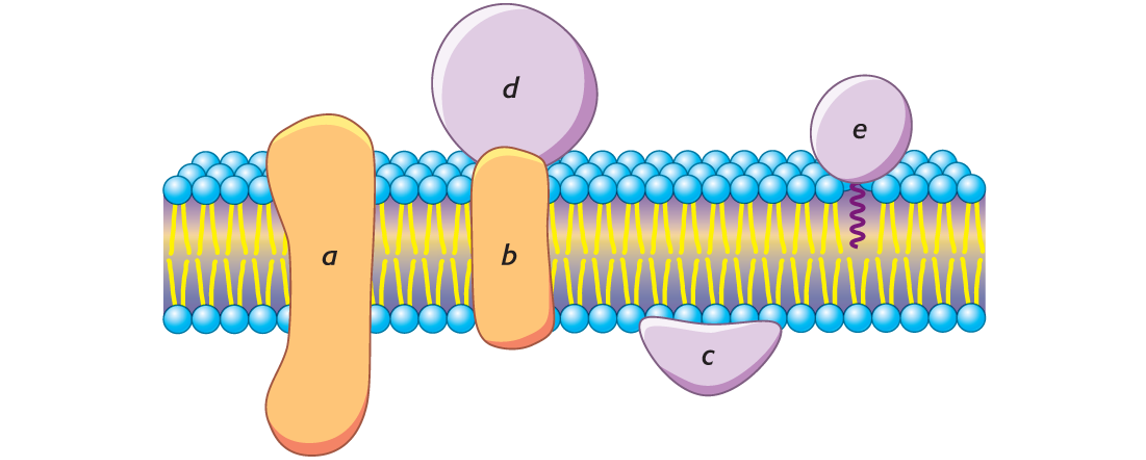
________________ interact extensively with the hydrocarbon region of the bilayer.
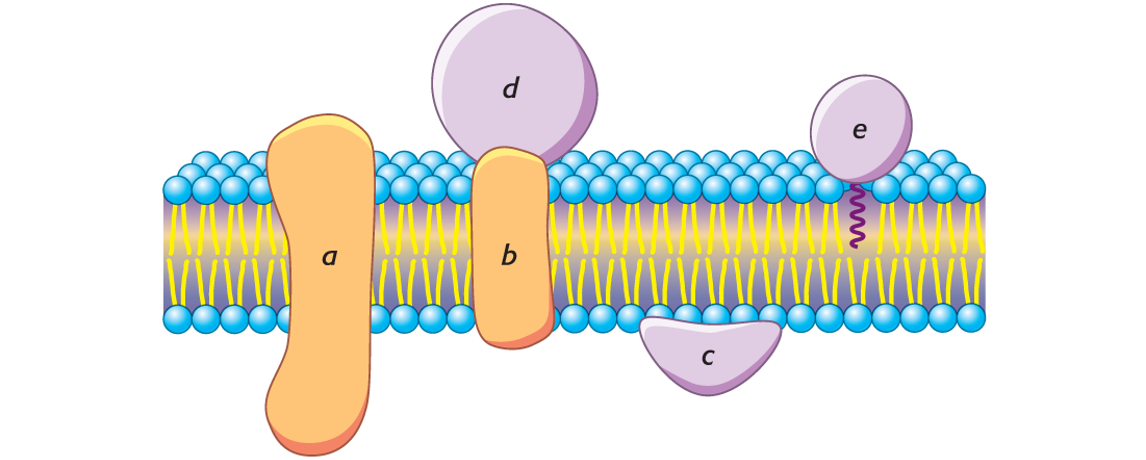
Integral membrane proteins (a and b)
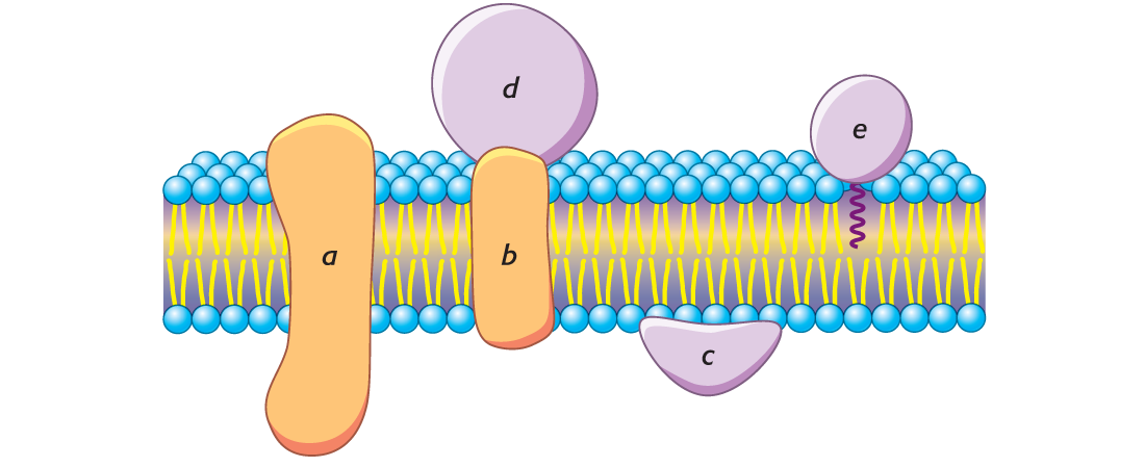
What are the 5 letters?
a) Integral membrane proteins
b) Integral membrane proteins
c) Peripheral membrane proteins (Interact with polar head groups of lipids
d) Peripheral membrane proteins (Bind to the surfaces of integral proteins)
e) Tightly anchored to the membrane (by a covalently attached lipid molecule.)
Transport Proteins
Proteins that function as pumps or channels or carriers to facilitate the flow of small molecules across the cell membrane.
Passive transport, or facilitate diffusion
It occurs when a molecule moves down its concentration gradient through a transport protein.
Active transport
Occurs when protein pumps use energy to move a molecule against its concentration gradient in the process.
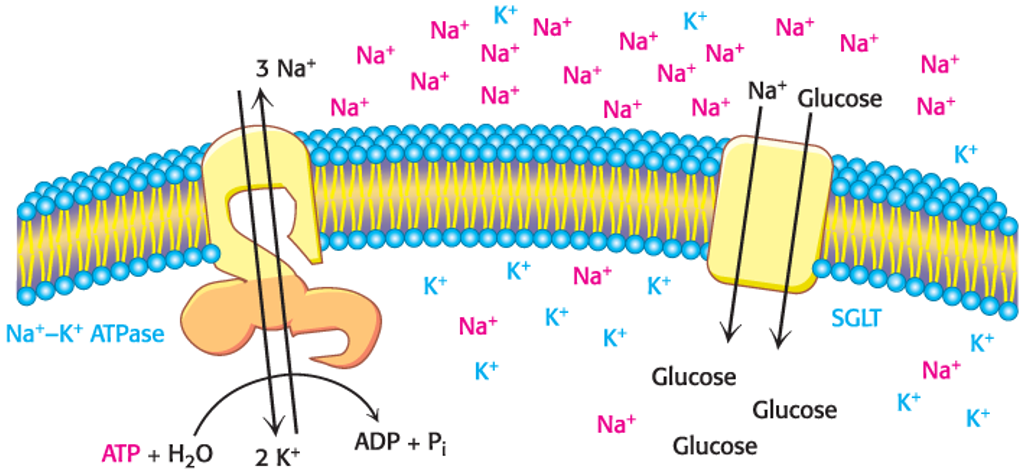
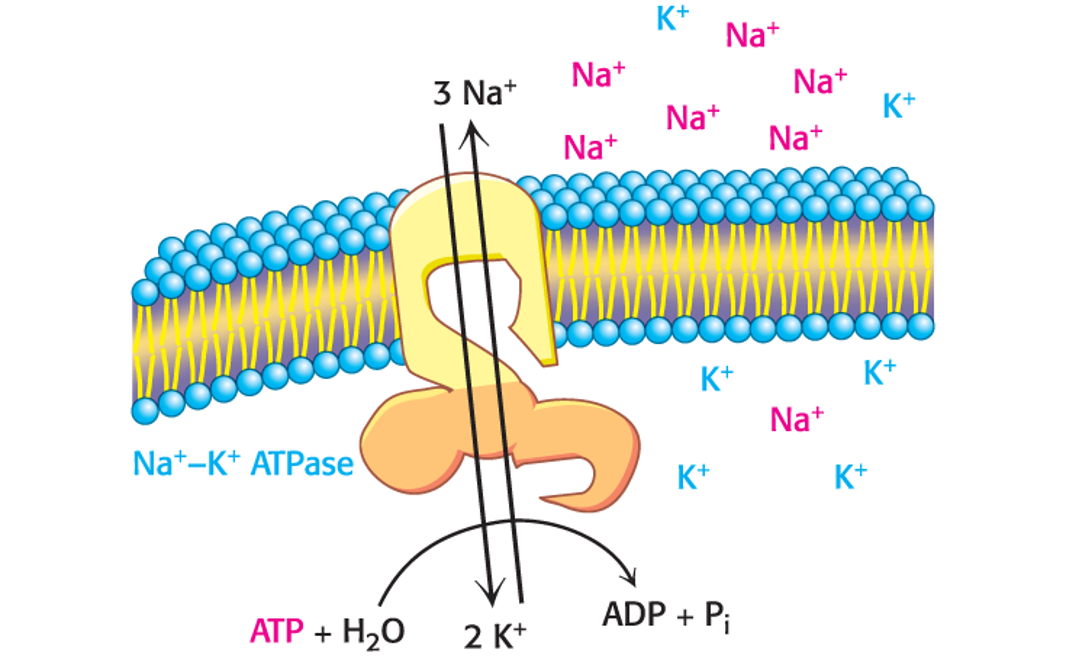
The Na+–K+ ATPase or Na+–K+ pump uses the energy of ATP hydrolysis to simultaneously pump three Na+ ions out of the cell and two K+ ions into the cell against their concentration gradients.
Pump three Na+ ions out.
Pump two K+ ions into.
Because the reaction includes an intermediate in which the enzyme is phosphorylated, such pumps are called P-type ATPases.
This type of transport is called primary active transport
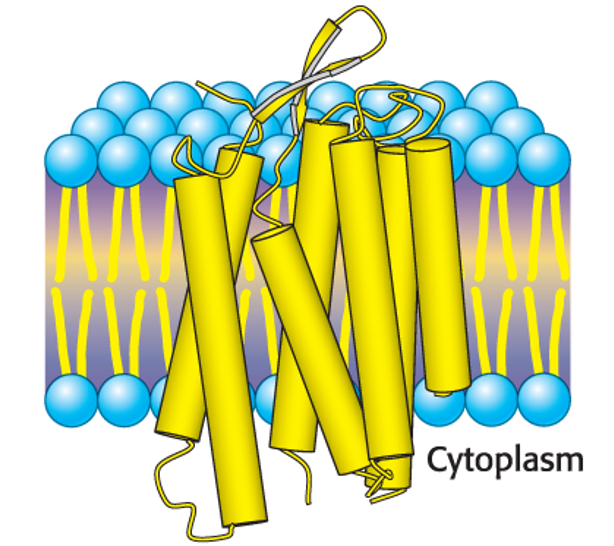
Membrane-spanning _________ are a common structural feature of integral memrbane proteins.
Membrane-spanning α-helices
What are examples of pores?
Porin
Nuclear Pore Complex
Aquaporin
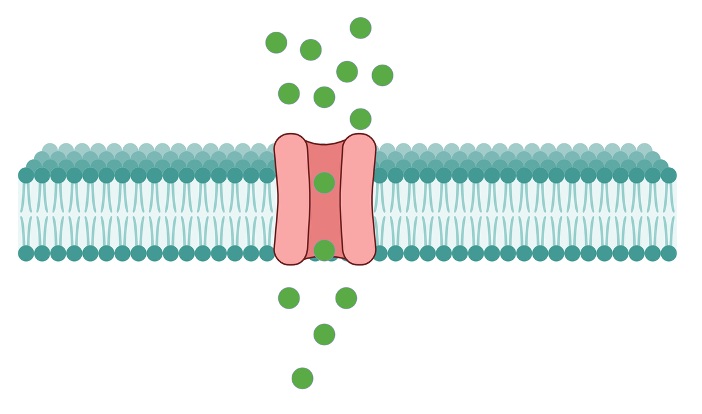
What are examples of gated channels?
Ligand-gated Channels
Voltage-gated Channels
Light-gated Channels
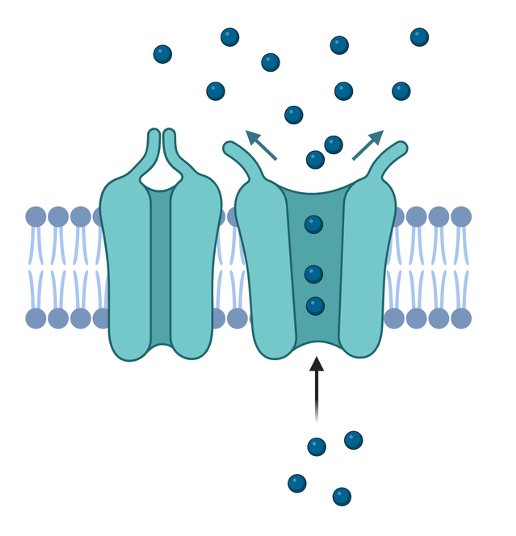
Ion channels
Passive transport systems that allow specific and rapid transport of ions down their concentration gradients.
Voltage-activated channels
Channels that can be activated by changes in the voltage across a membrane.
Ligand-activated channels
By binding specific molecules to the channels
Tetrodotoxin
, produced by the pufferfish, is a lethal inhibitor of the Na+ channel.
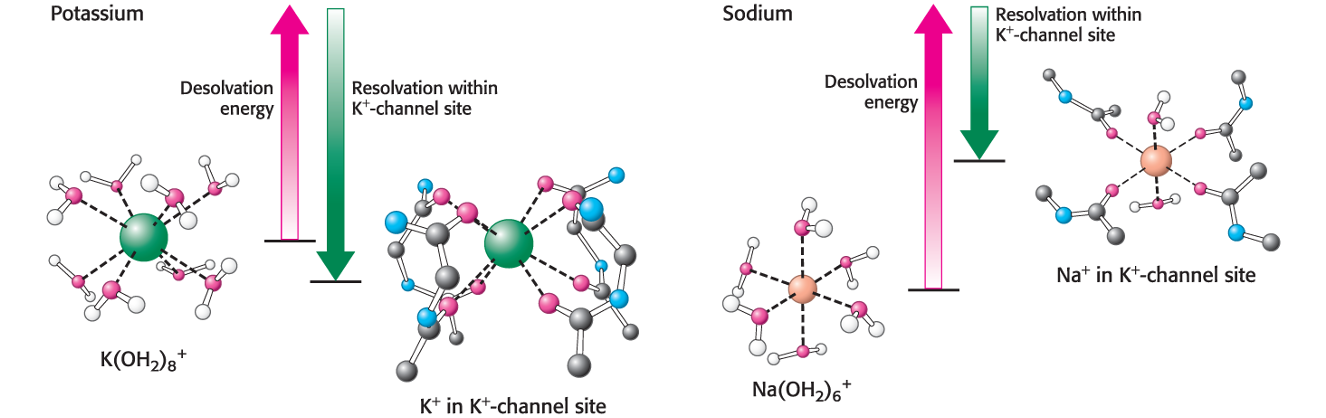
The potassium channel selectively and rapidly transports K+ across the cell membrane. Larger ions are not transported because… Smaller ions are excluded because
…because they are too big to enter the channel.
…because they cannot interact with the selectivity filter. Such ions are small enough that the nergy of desolvation cannot be compensated for by interactions with the selectivity filter.
Lipids rapidly diffuse ______ in membranes, although _______ diffusion or flip-flopping is very rare without the assistance of enzymes.
The prohibition of ______ diffusion accounts for the stability of membrane asymmetry.
laterally
transverse
transverse
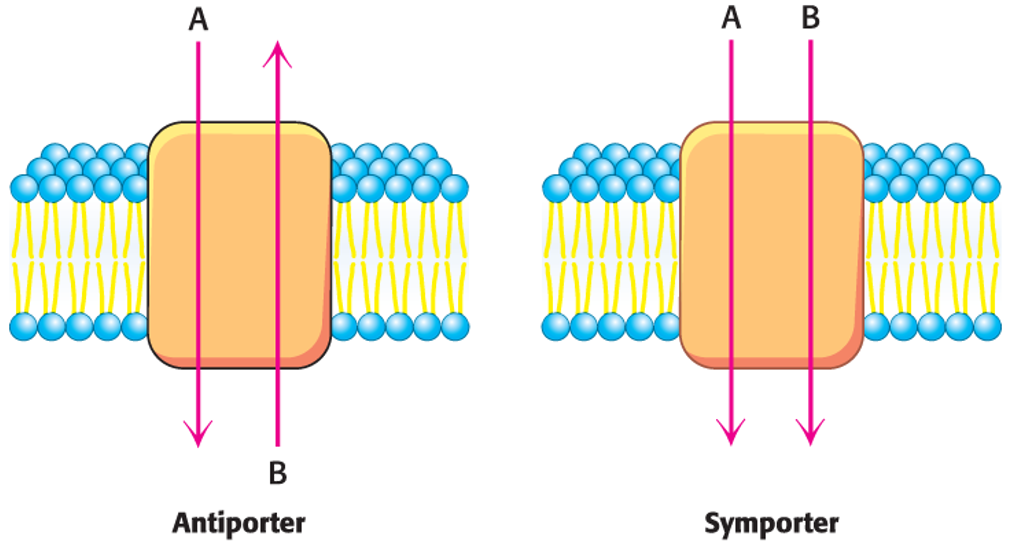
Secondary transporters
Use one concentration gradient to power the formation of another.
Examples: Symporters and Antiporters
Symporters
Power the transport of a molecule against its concentration gradient by coupling the movement to the movement of another molecule down its concentration gradient, with both molecules moving in the same direction.
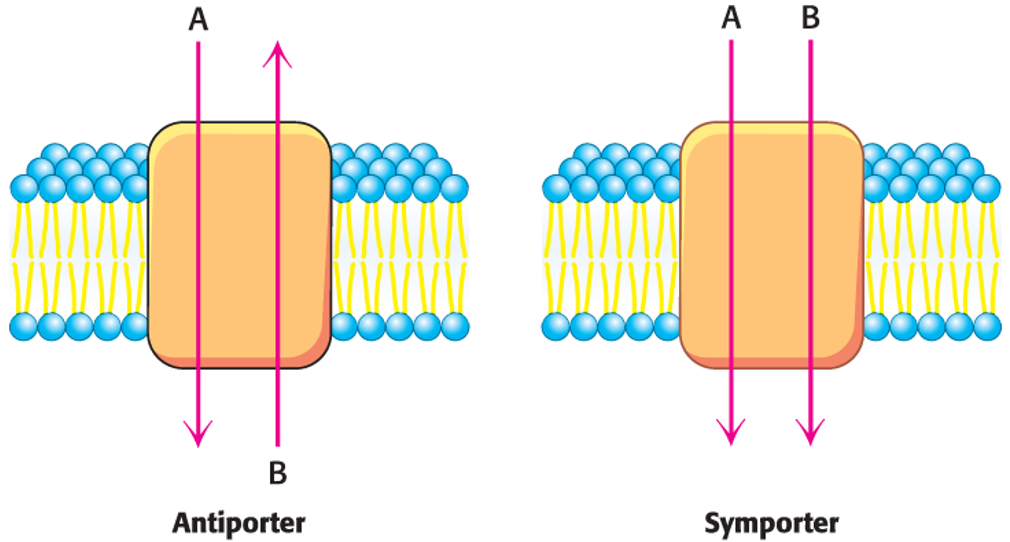
Antiporters
Also, use one concentration gradient to power the formation of another, but the molecules move in opposite directions.
Glucose is moved into some animal cells against its concentration gradient by a…
…symporter that is powered by Na+ ions moving down a concentration gradient.