Classification- Bacteria, Viruses, Protists, Fungus
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
Protists
eukaryotic, unicellular and multicellular organisms, autotrophic and heterotrophic organisms and don't fit in other kingdoms

Unicellular
organism is a single cell
Multicellular
organism is made up of many cells
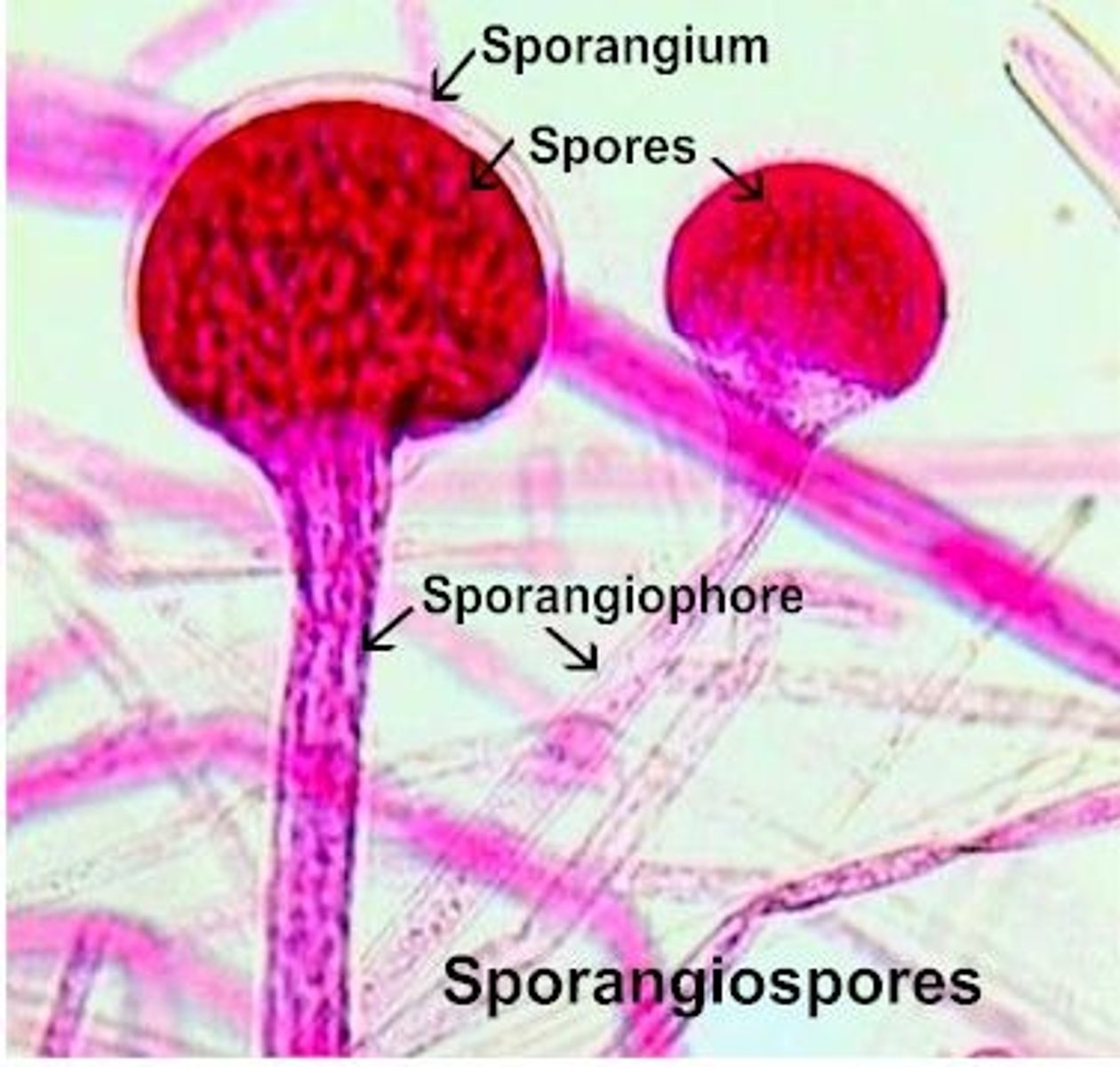
Fungi
A kingdom made up of eukaryotic organisms, reproduce by using spores, and get food through absorption (by breaking down food substances outside the cells and then absorbing the nutrients

Taxonomic Levels Acronym
KPCOFGS

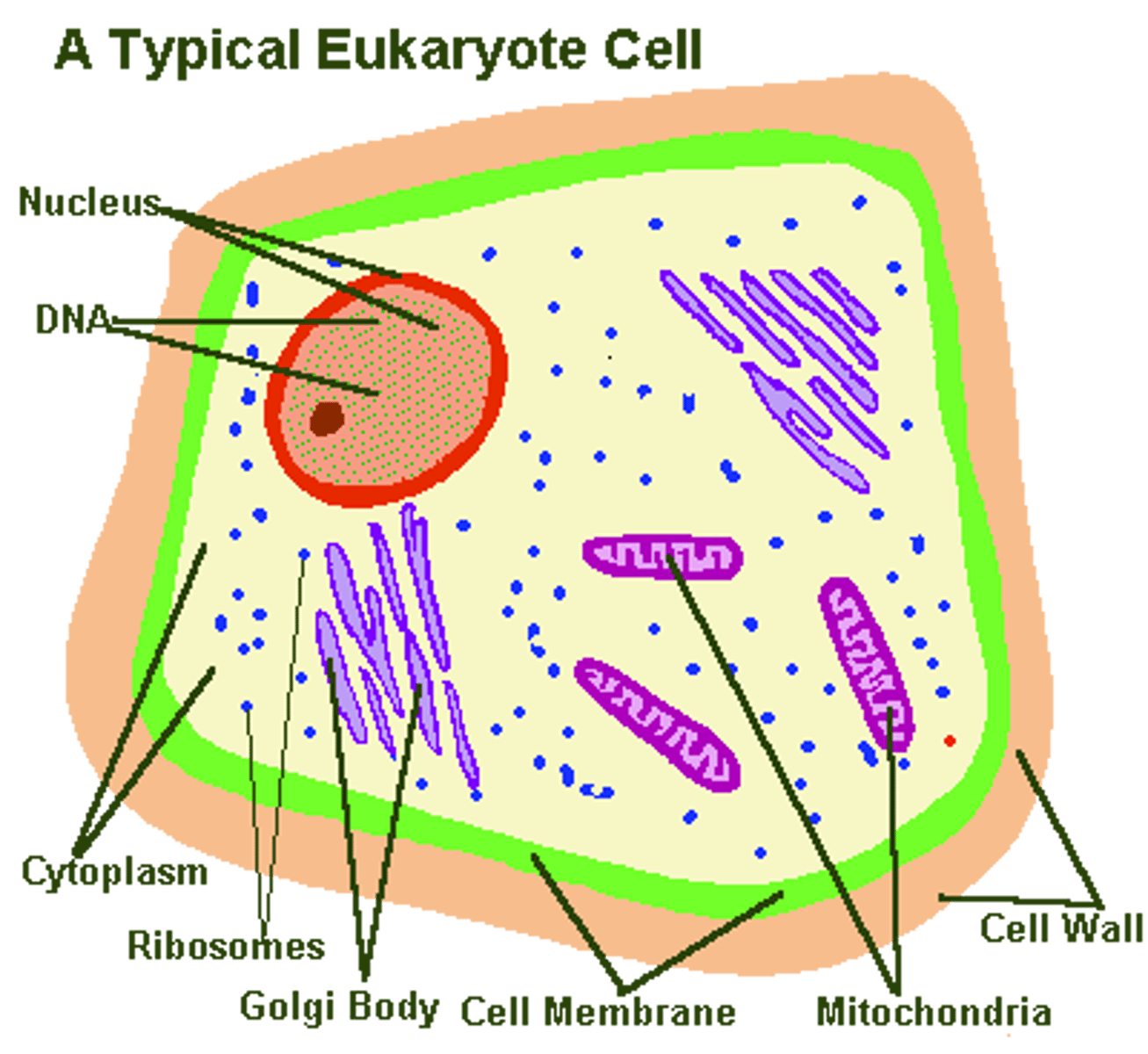
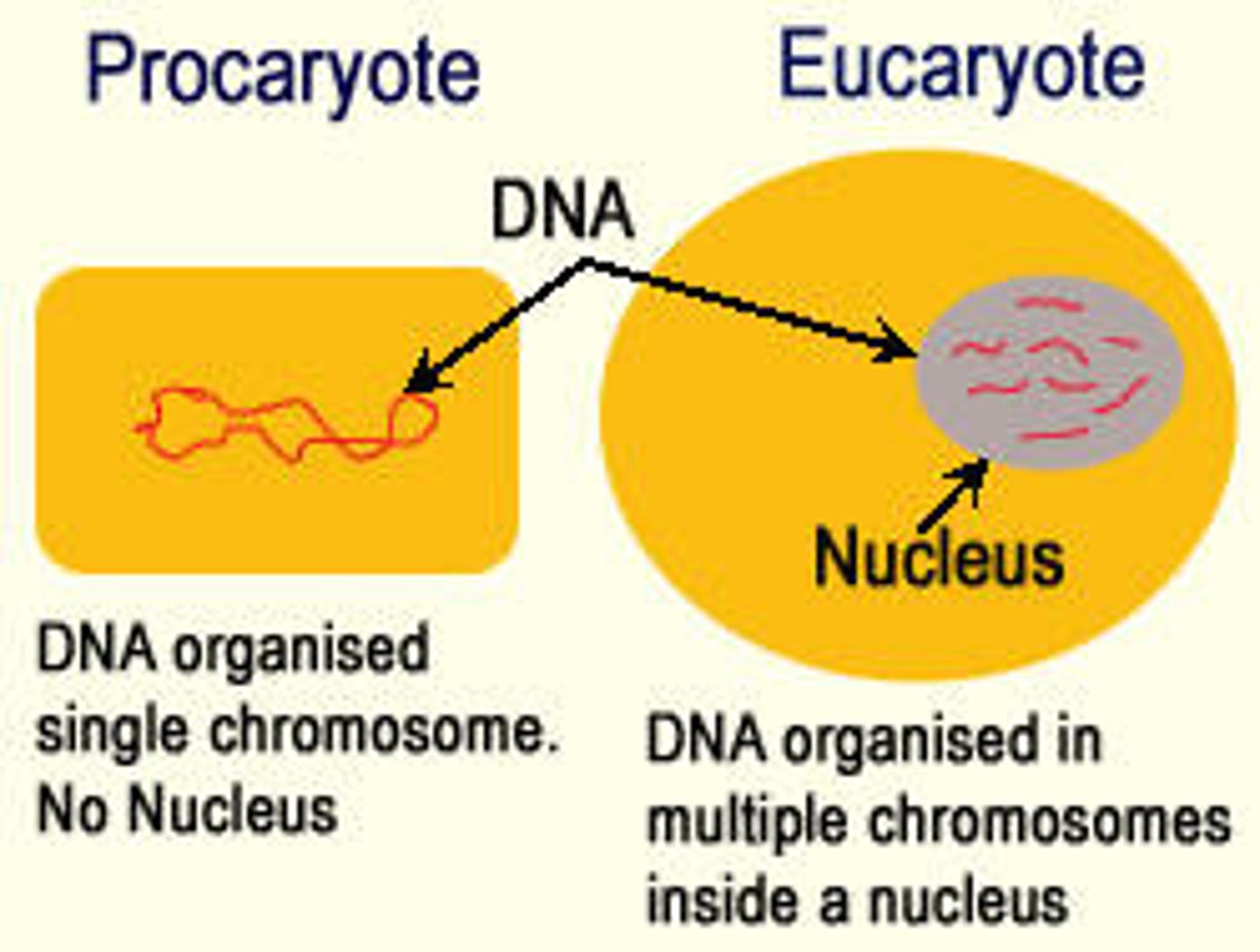
Eukaryote
A cell that contains a nucleus and membrane bound organelles
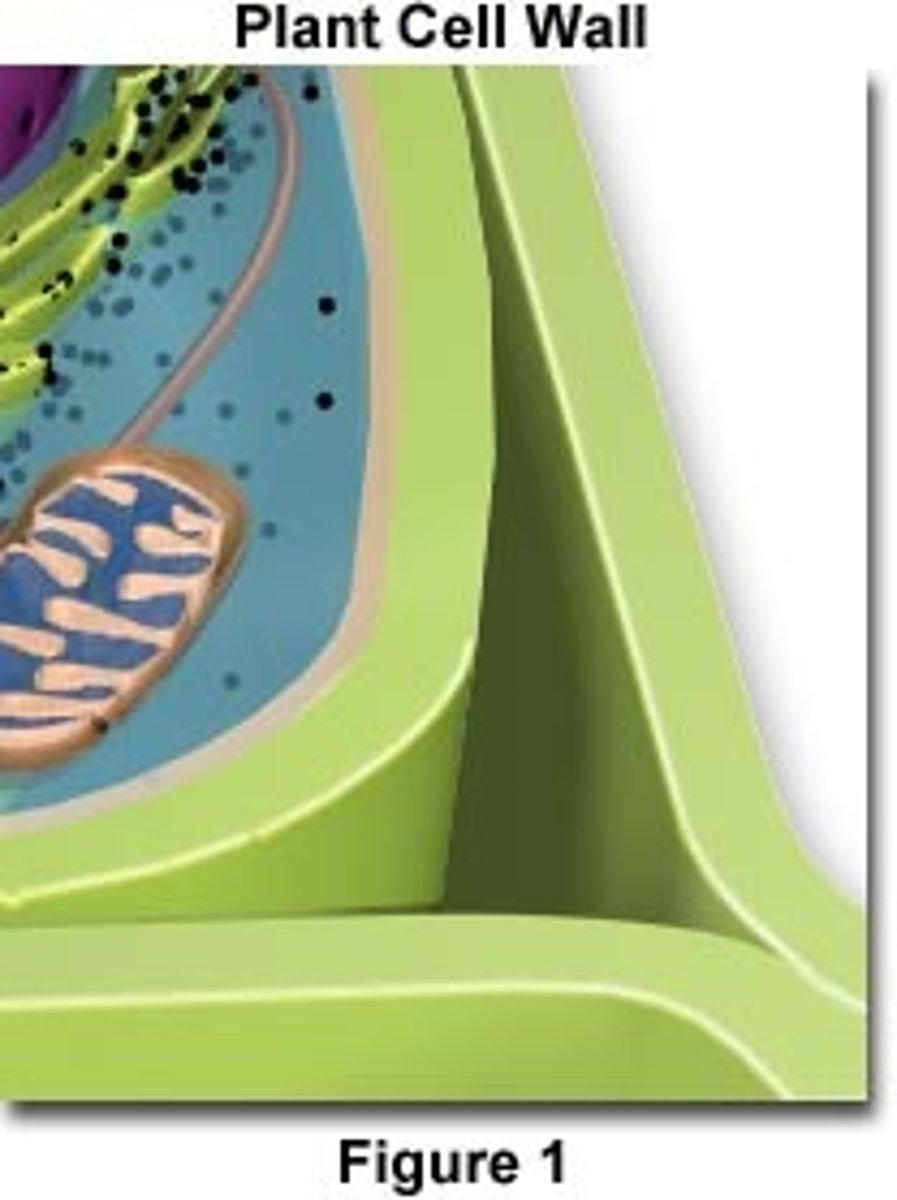
Cell wall
A rigid layer of that surrounds the cells of bacteria, some protists, fungus and plants. Animals and animal-like protists (protozoans) do not have cell walls
Genus
A classification level grouping that consists of a number of similar, closely related species

Heterotroph
An organism that cannot make its own food.

Autotroph
An organism that makes its own food

Eubacteria
A kingdom that contains prokaryotes. Bacteria that we normally come in contact with.
For example- E. coli and Salmonella
Species
A group of similar organisms that look similar, breed with each other and produce fertile offspring.

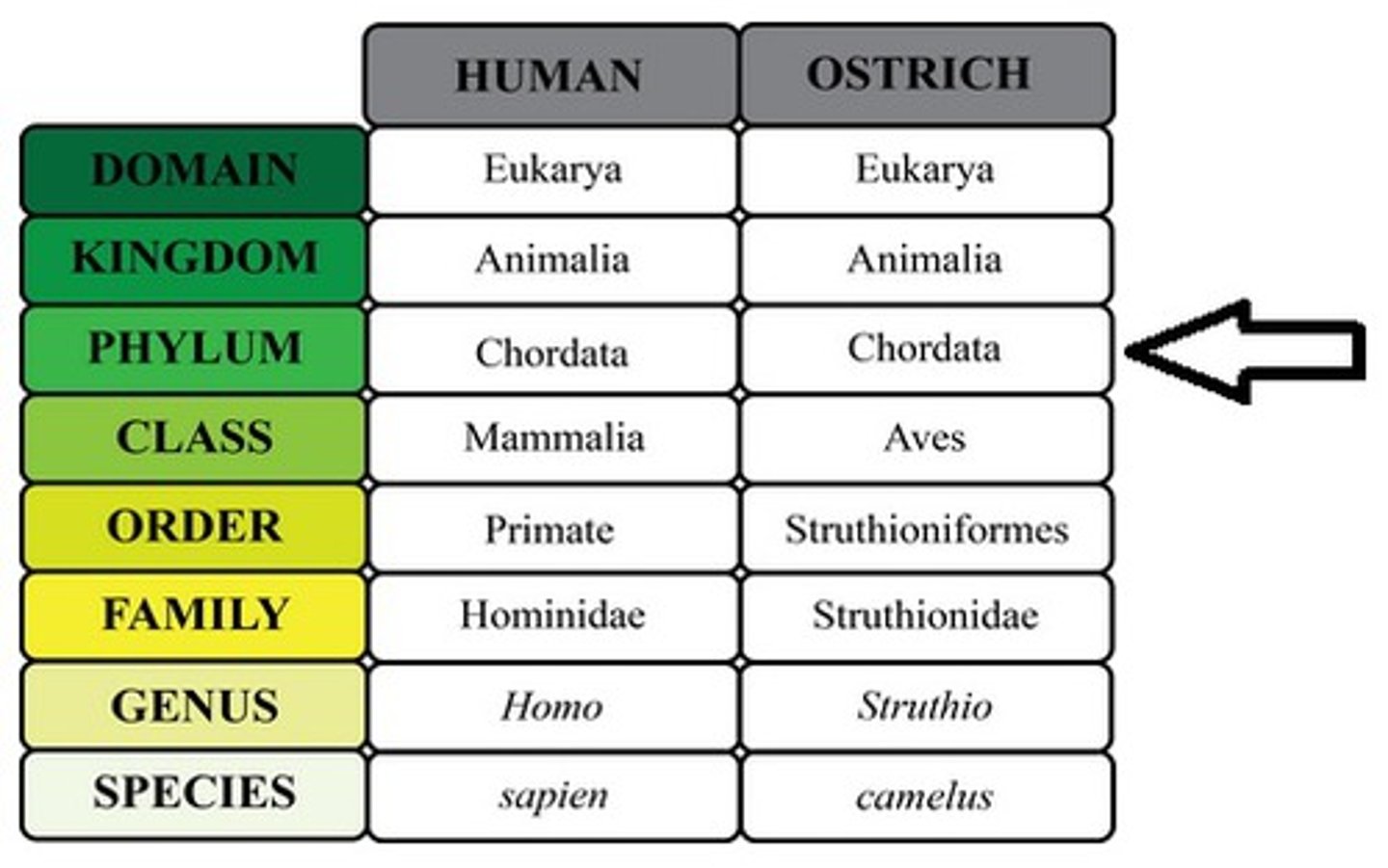
Phylum
Group of closely related classes
Archaebacteria
Kingdom of unicellular prokaryotes whose cell walls do not contain peptidoglycan. These bacteria live in extreme conditions (hot springs, acidic, high salt content, guts of ruminant animals)
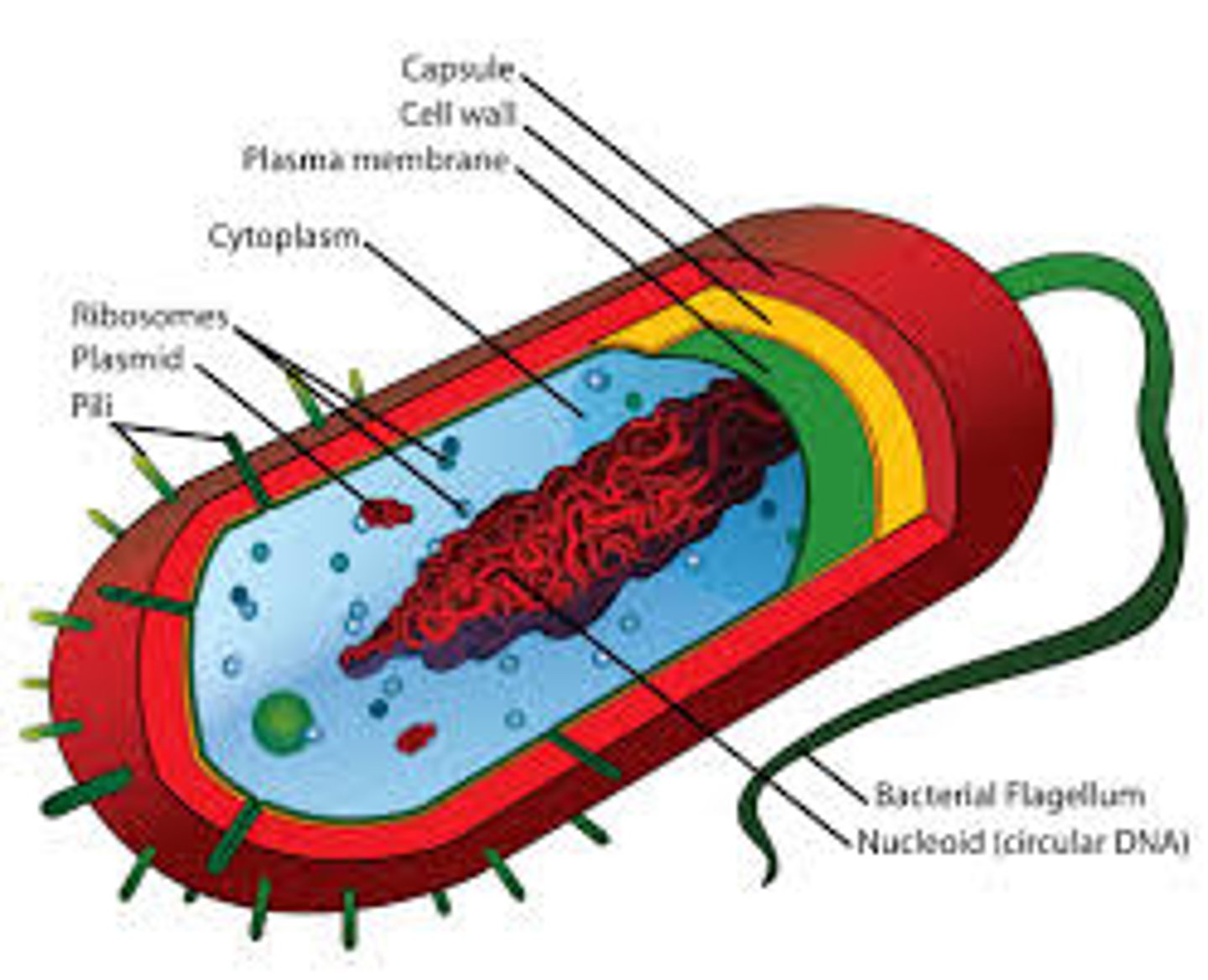
Prokaryote
A unicellular organism that lacks a nucleus and membrane bound organelles
Cocci Shape
circular shaped bacteria
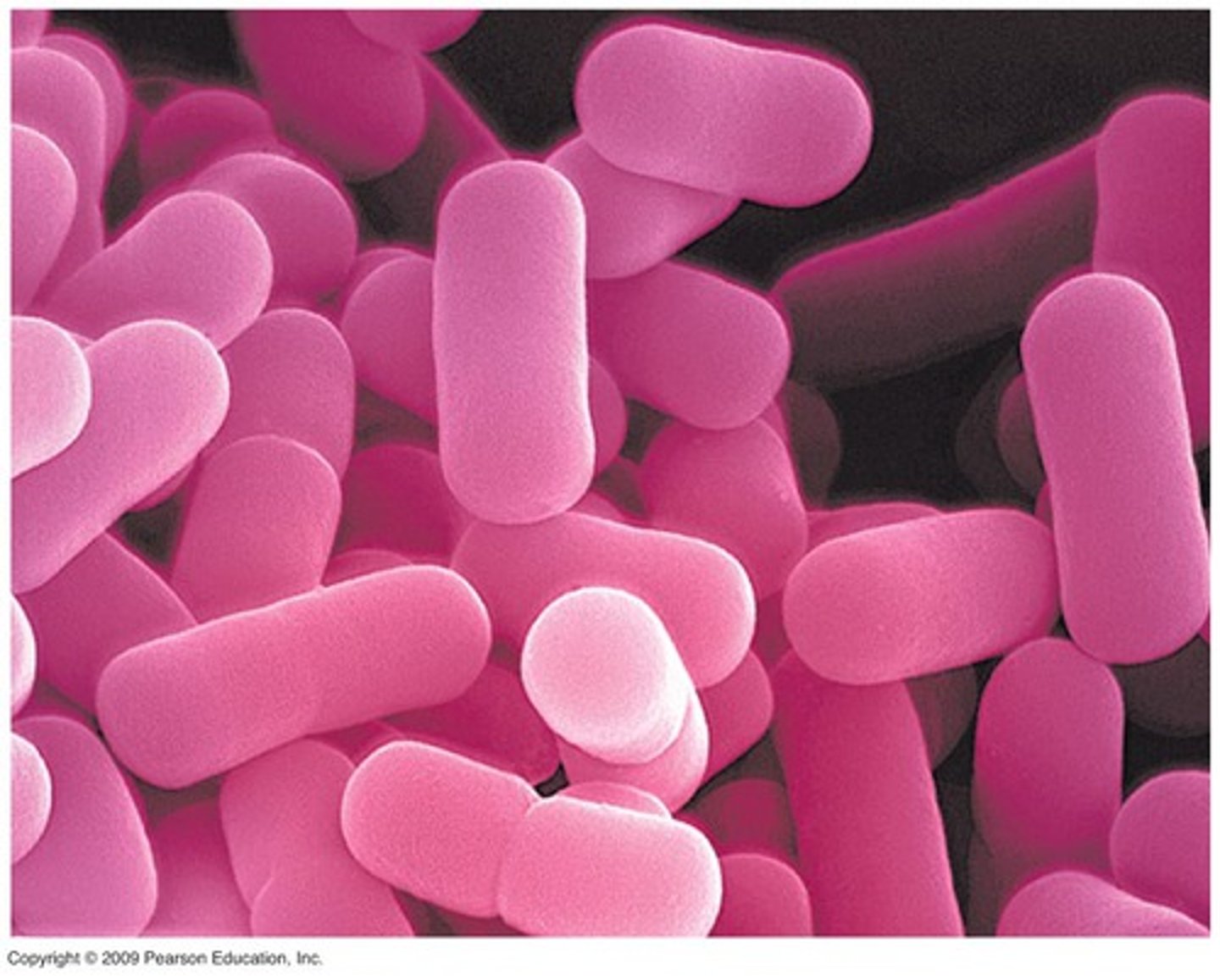
Bacilli Shape
Rod/Oval shaped bacteria
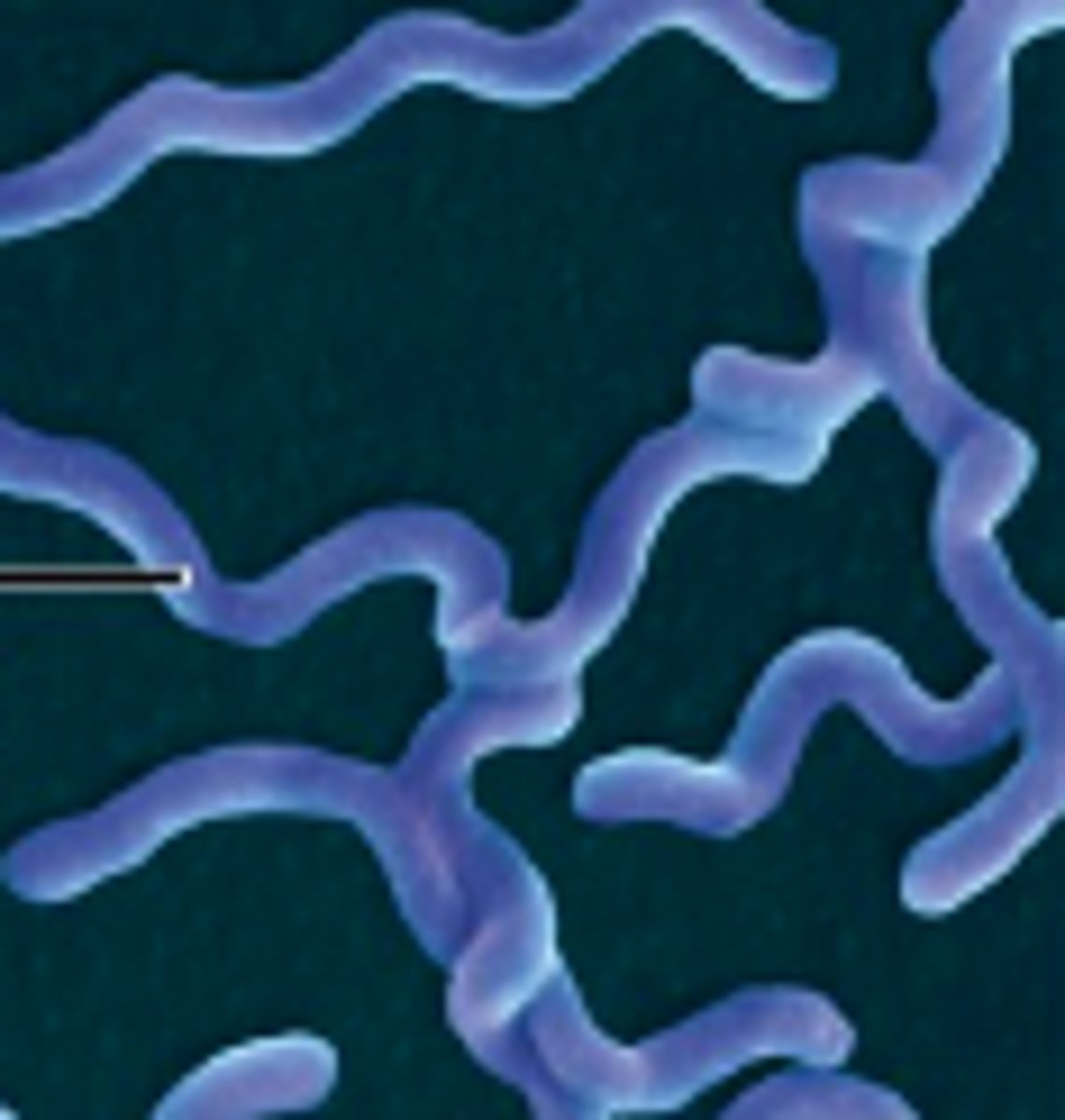
Spirilli Shape
spiral shaped bacteria
Diplo-
Two attached bacteria
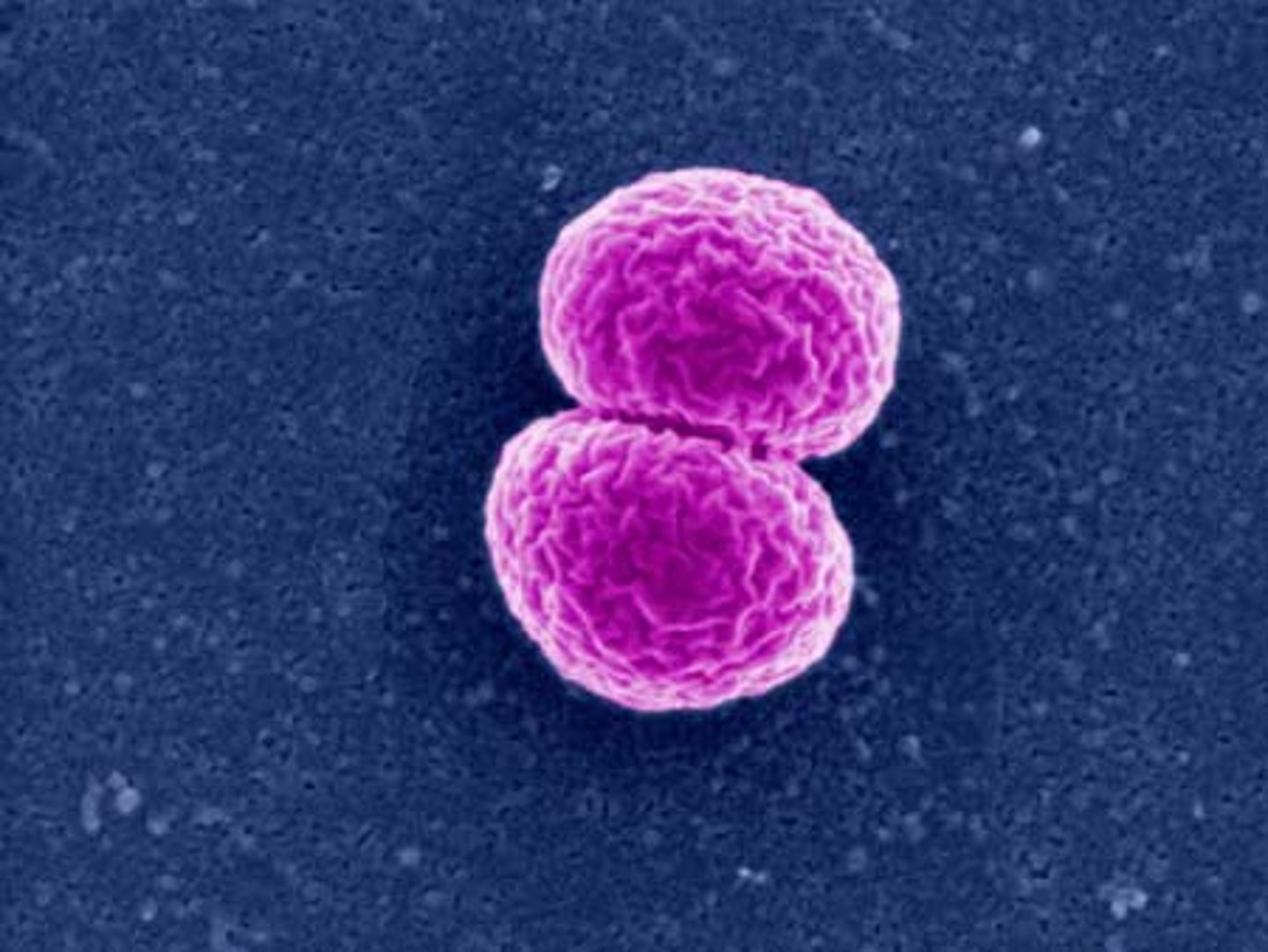
Strepto-
Long chain or filaments of bacteria
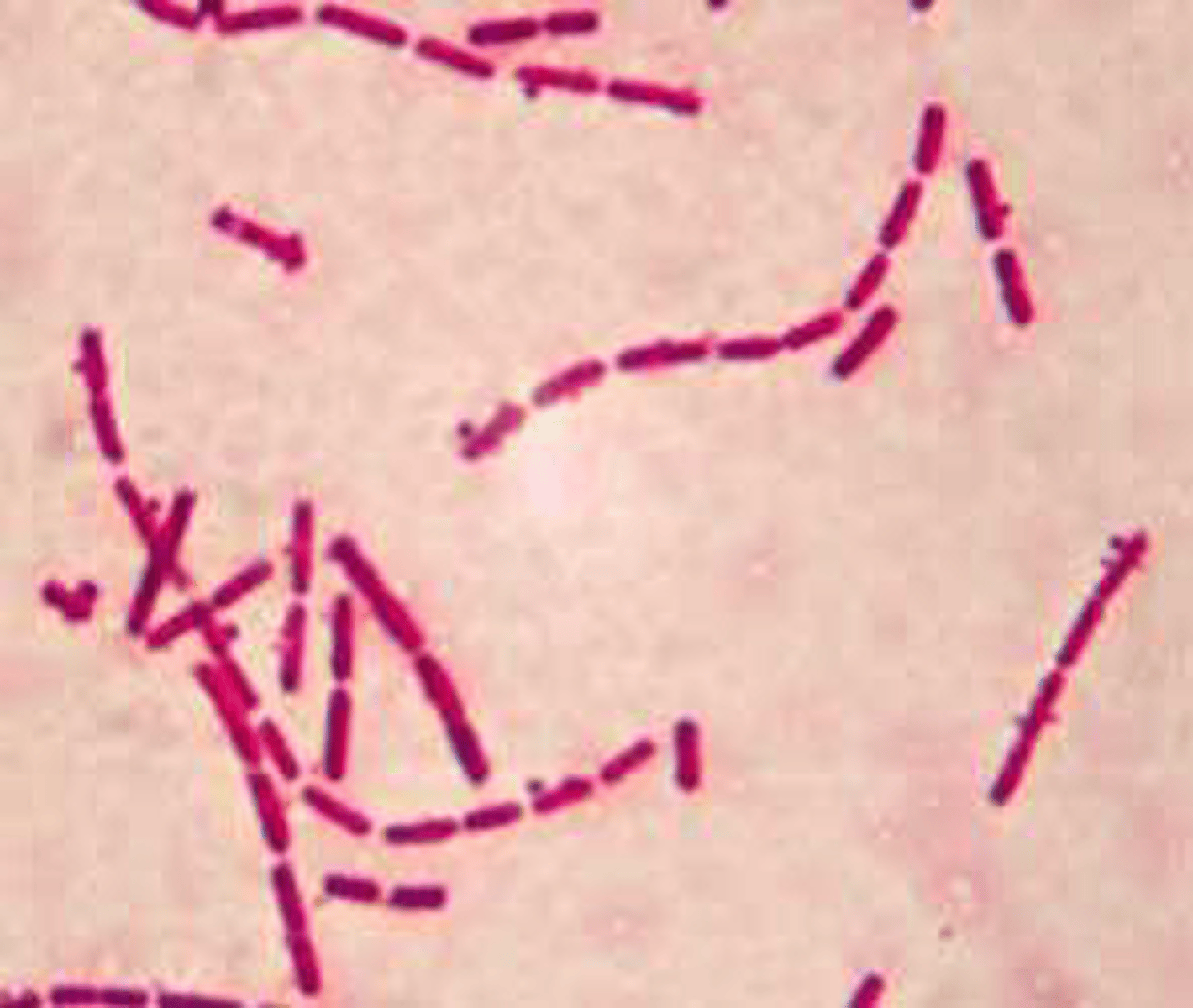
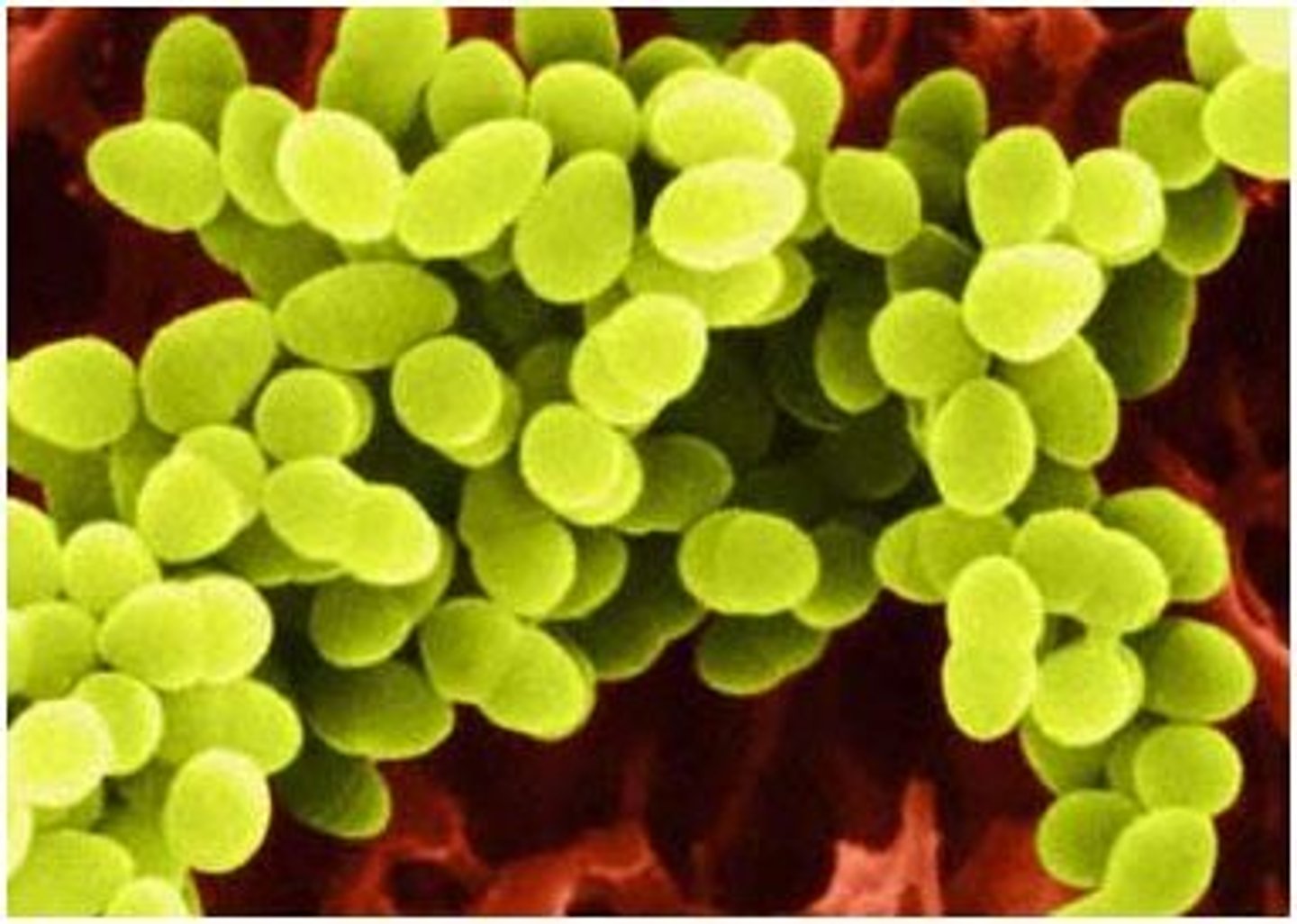
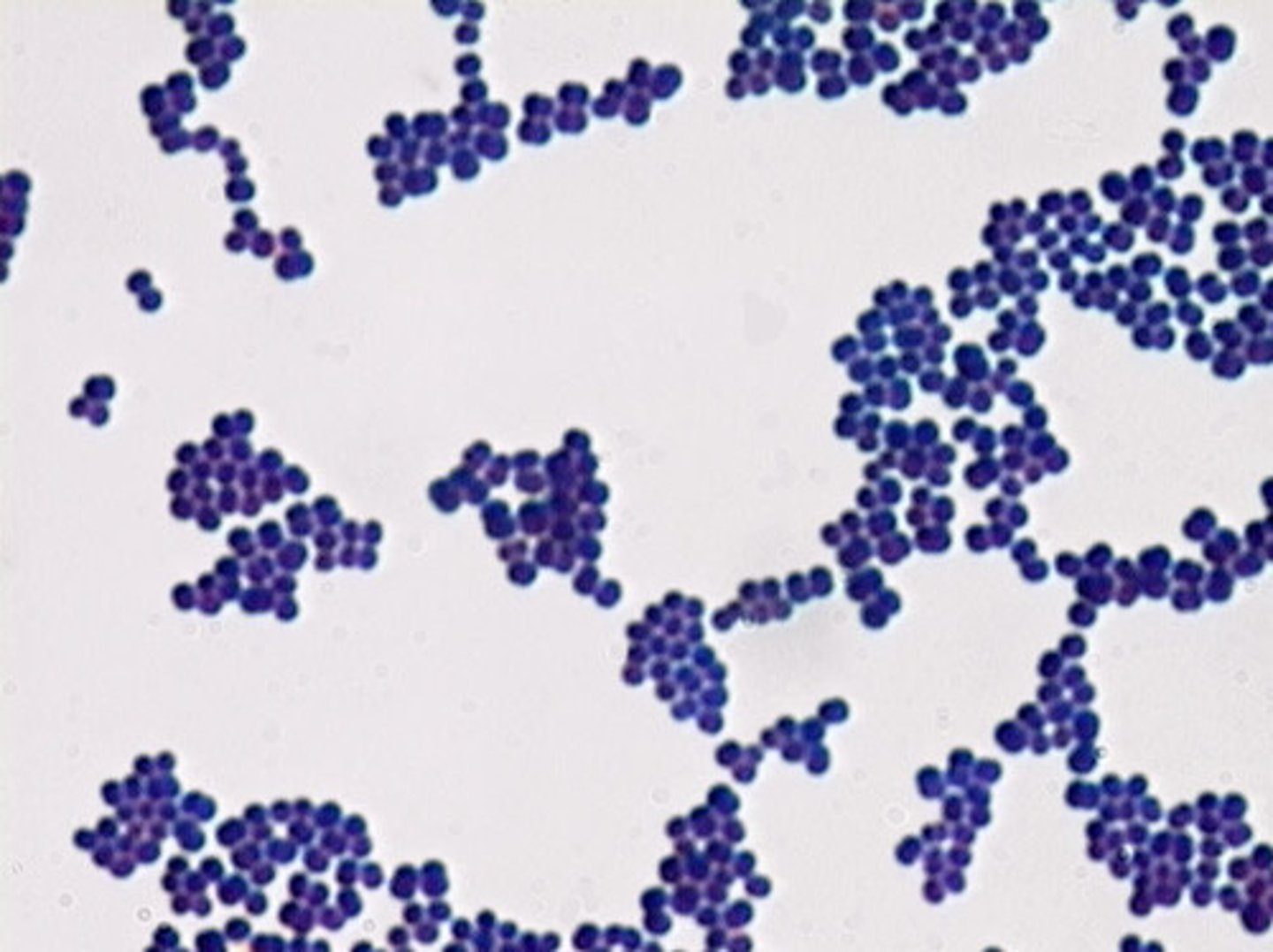
Staphlo-
cluster of bacterial cells

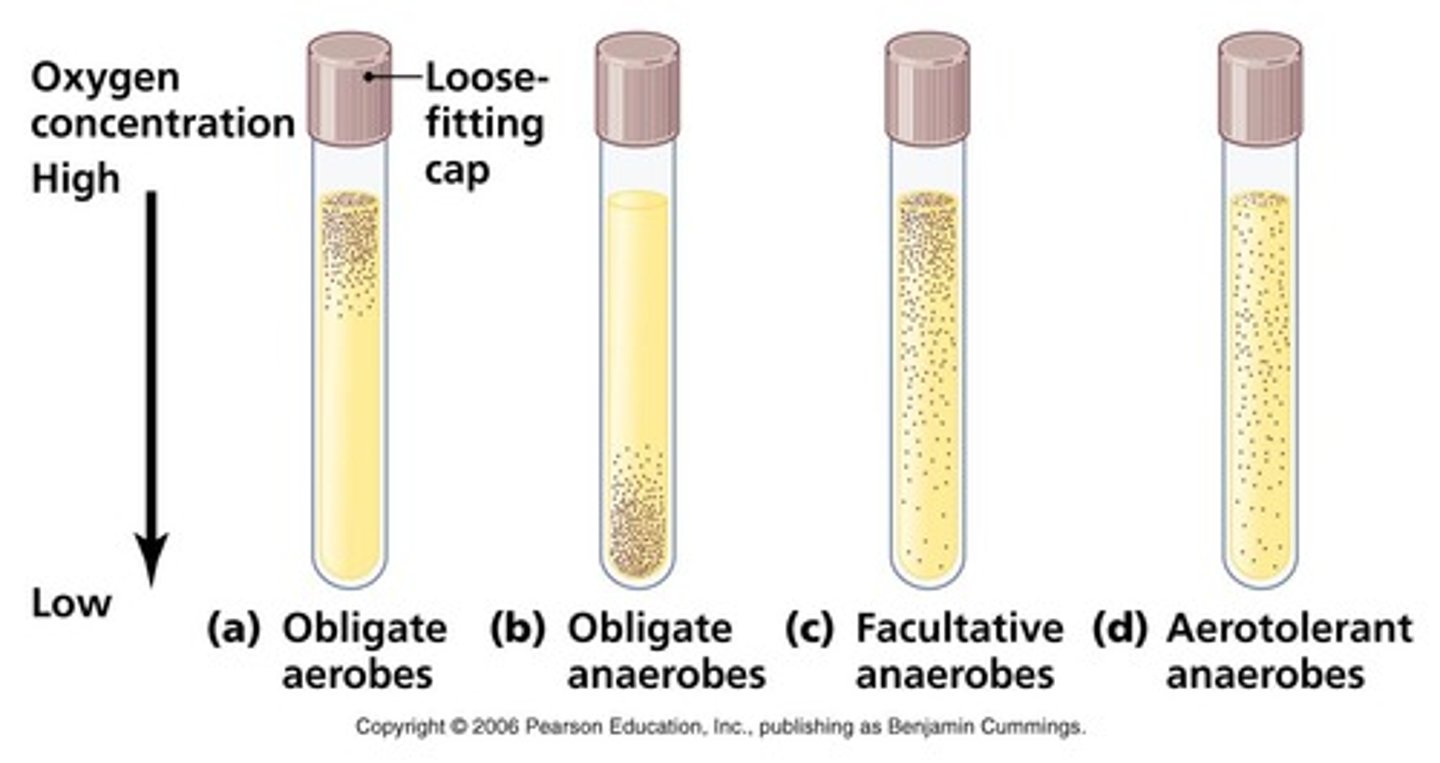
Obligate Aerobes
Bacteria that must have oxygen to survive
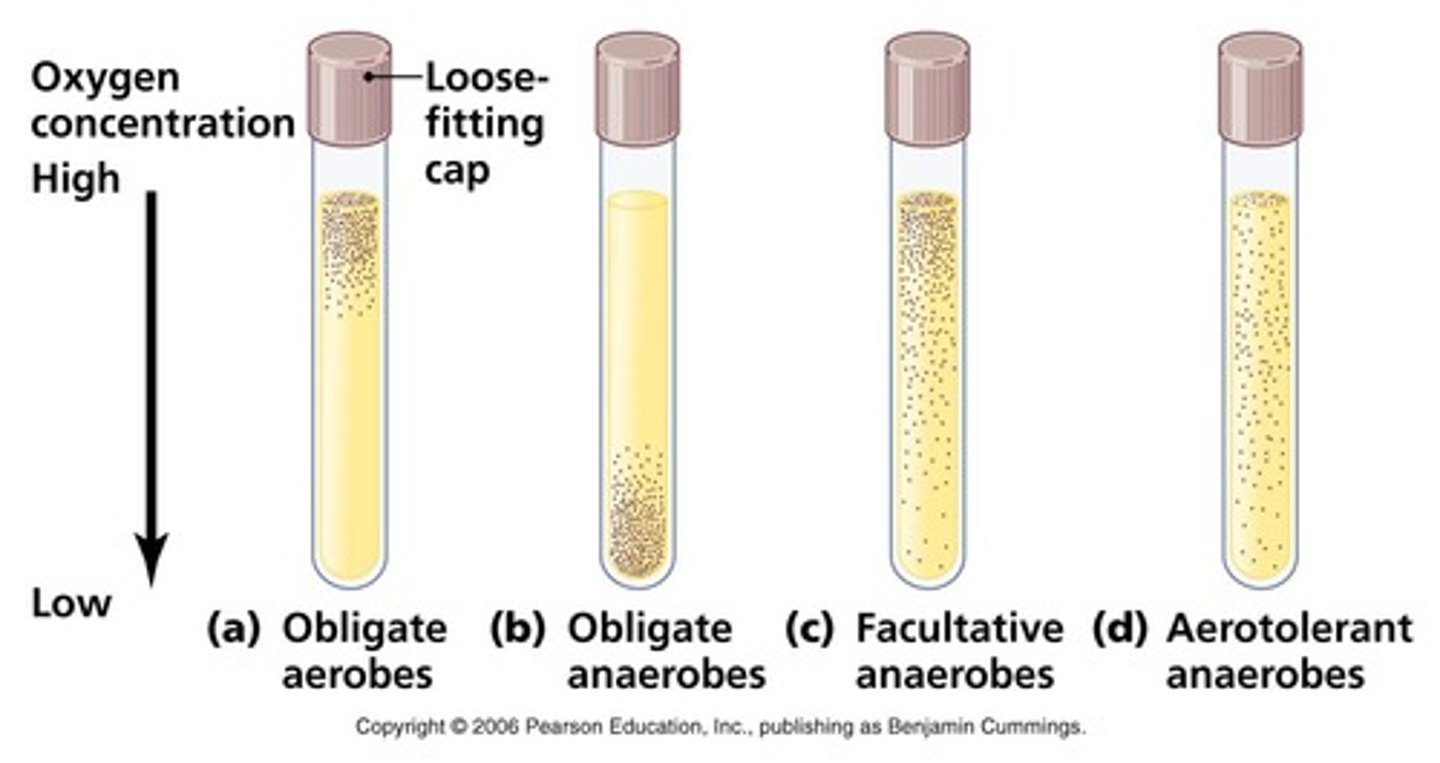
facultative anaerobes
bacteria that can survive with or without oxygen

Obligate Anaerobes
Bacteria that can't survive in oxygen
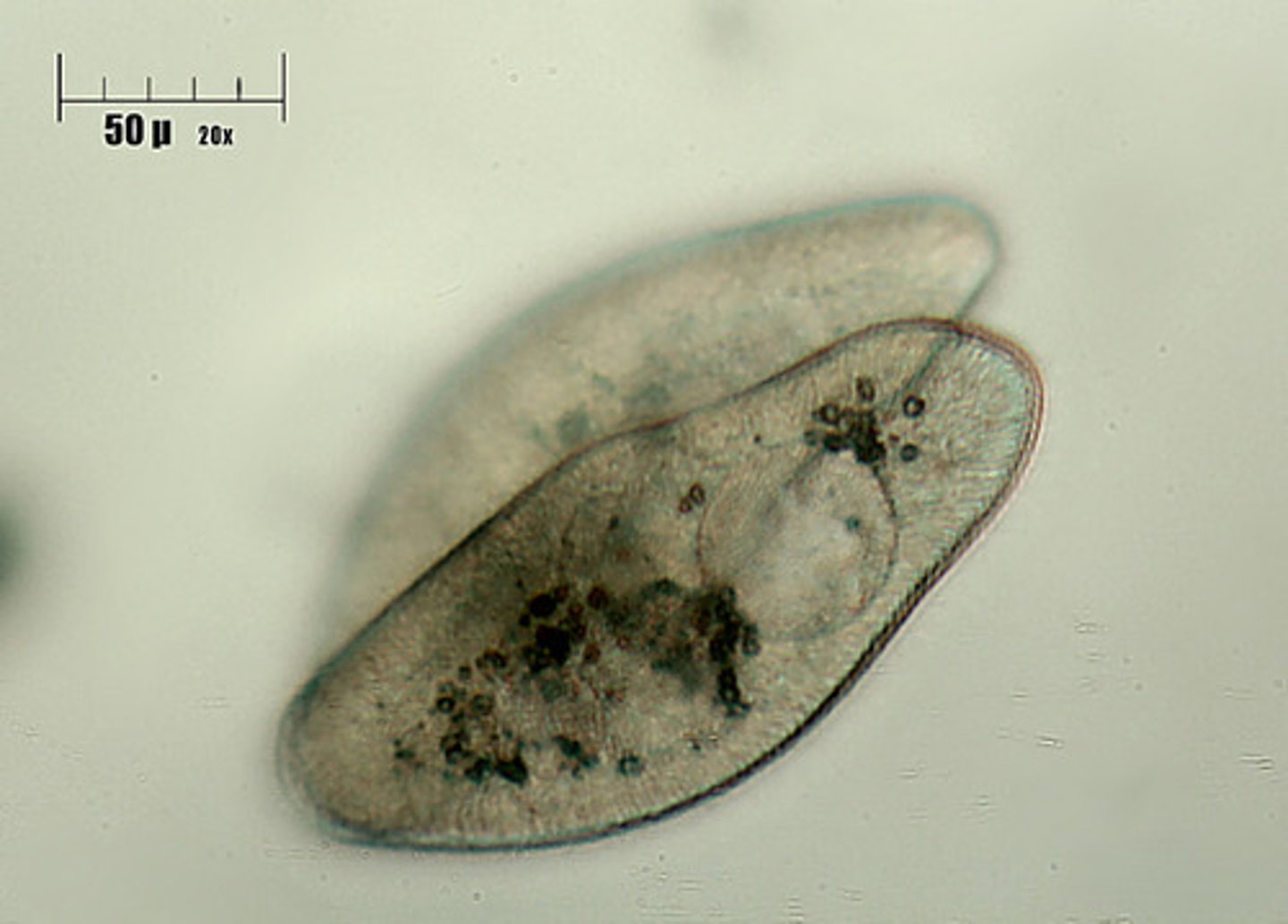
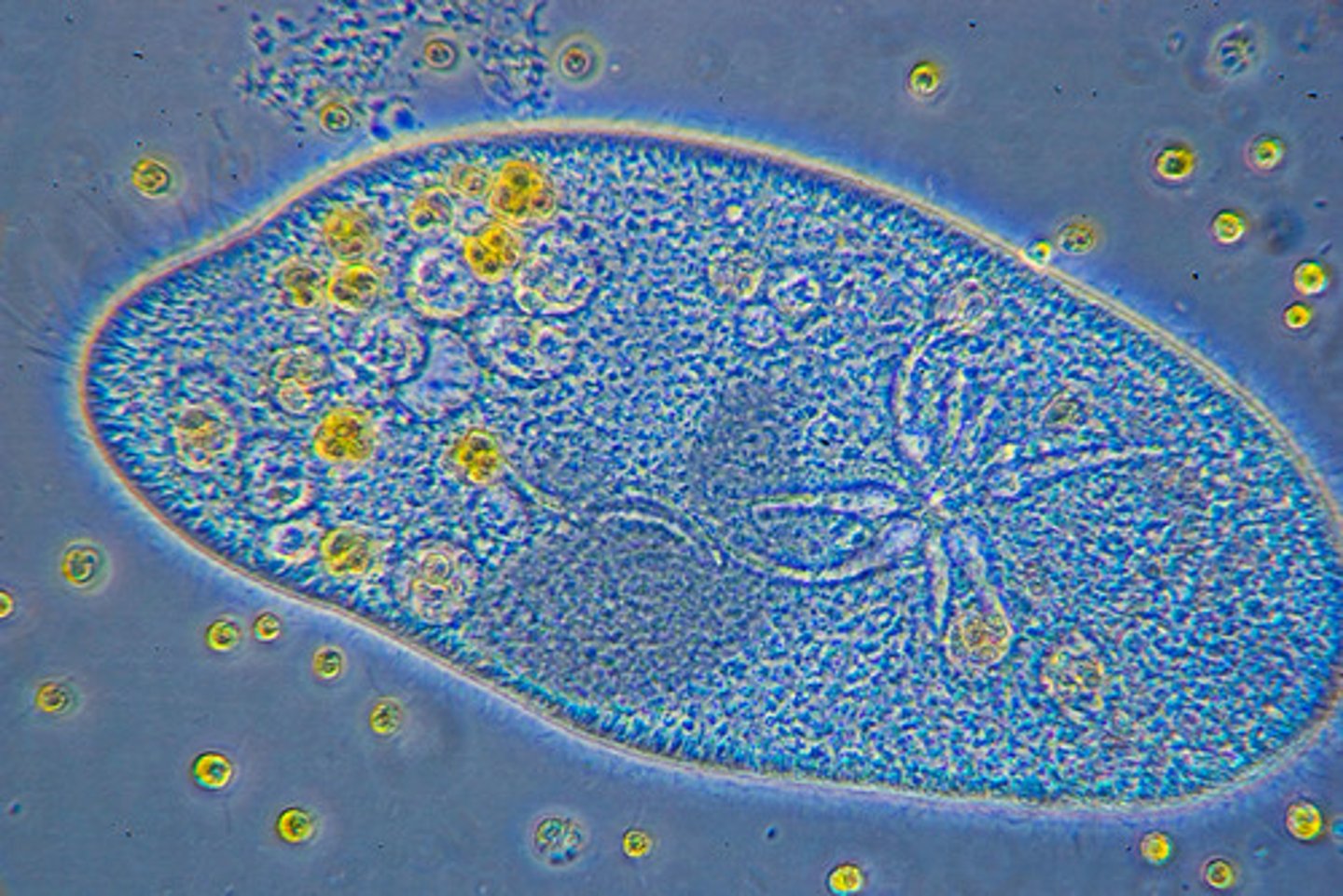
Protozoans
Animal-like protists-amoeba, paramecium
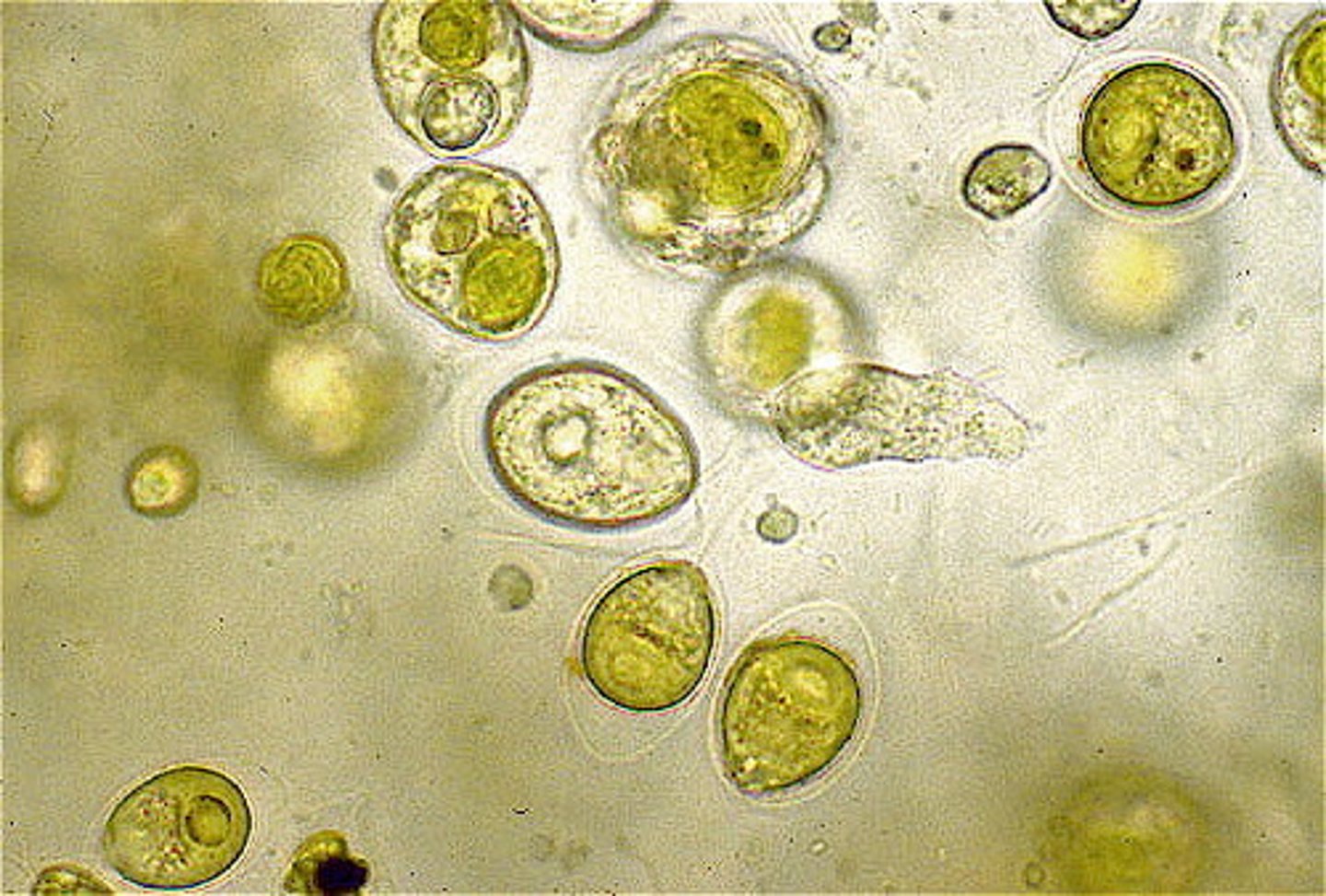
Algae- Plant-like protists examples
Algae-Chlorophyta, Phaeophyta, Rhodophyta, and Euglenophyta, Chrysophyta, Pyrrophyta
Why are fungus-like protists not fungi?
Have centrioles unlike actual fungus, can move, no chitin in cell walls

Fungus characteristics
Eukaryotic, Heterotrophic, Multicellular except for yeast , hyphae (except yeast), absorption of food, decomposers, chitin in cell walls
Harmful fungus examples
Ringworm, athlete's foot, yeast infections
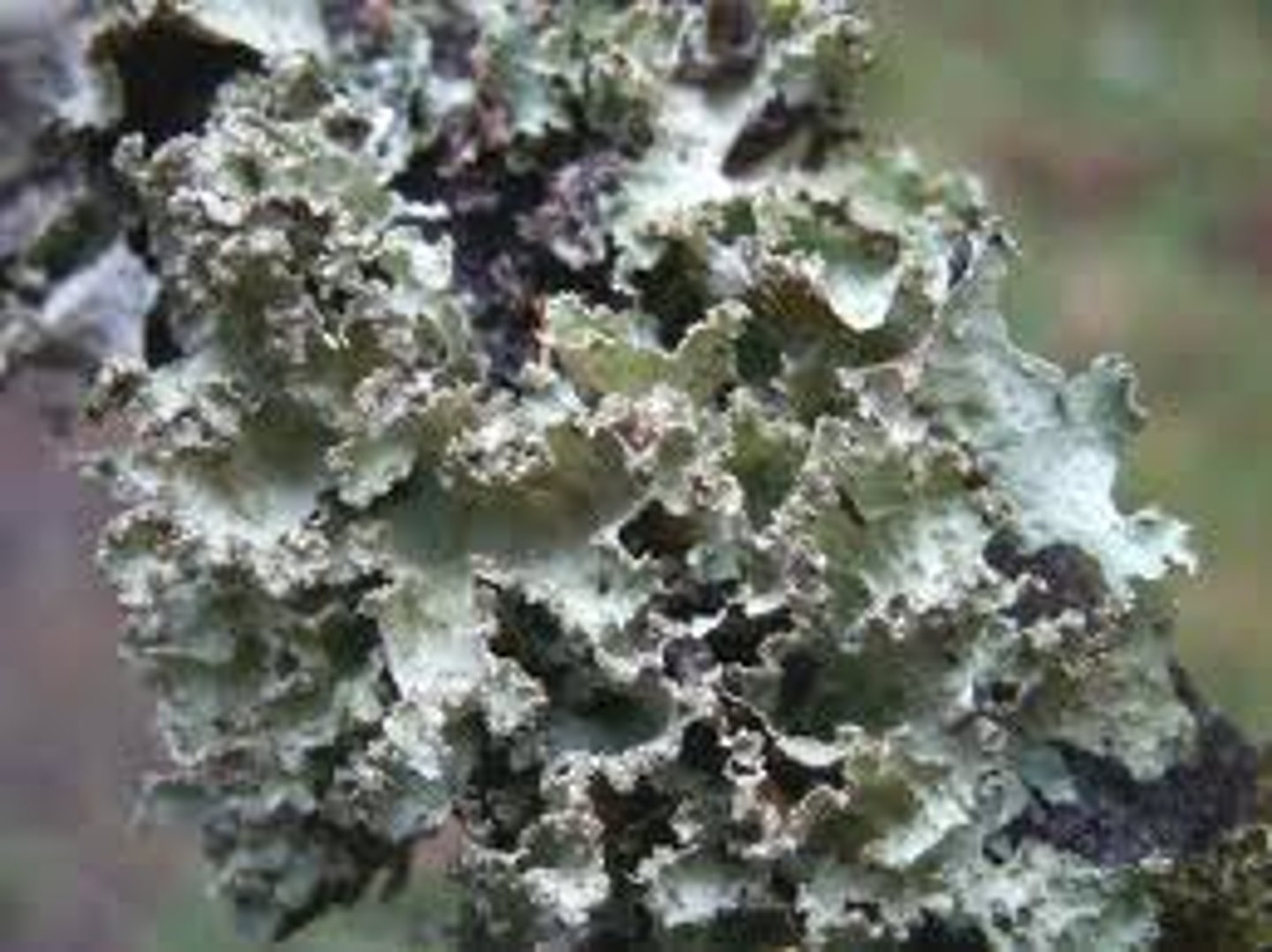

Zygomycota fungus
Bread mold (rhizopus)
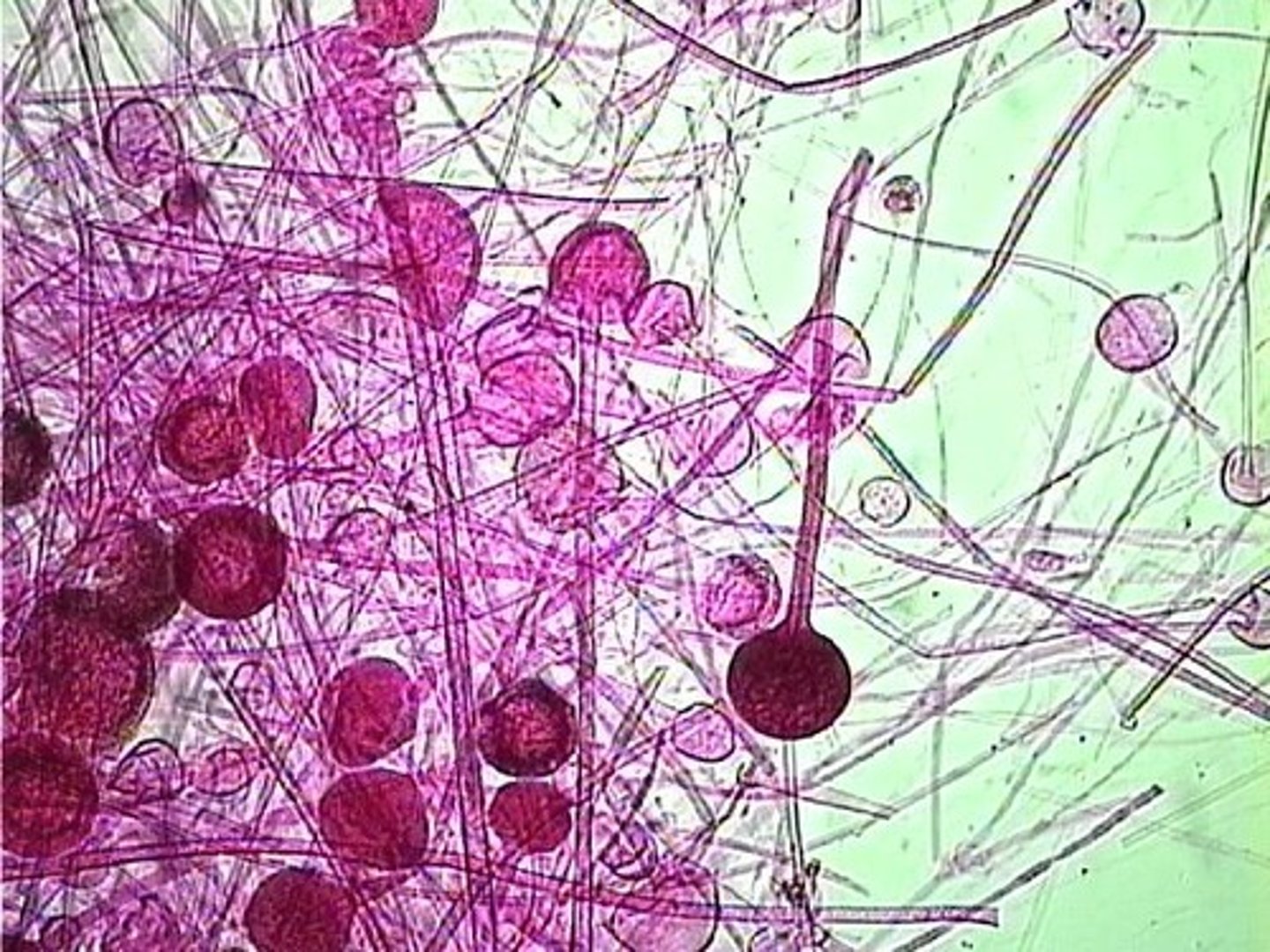
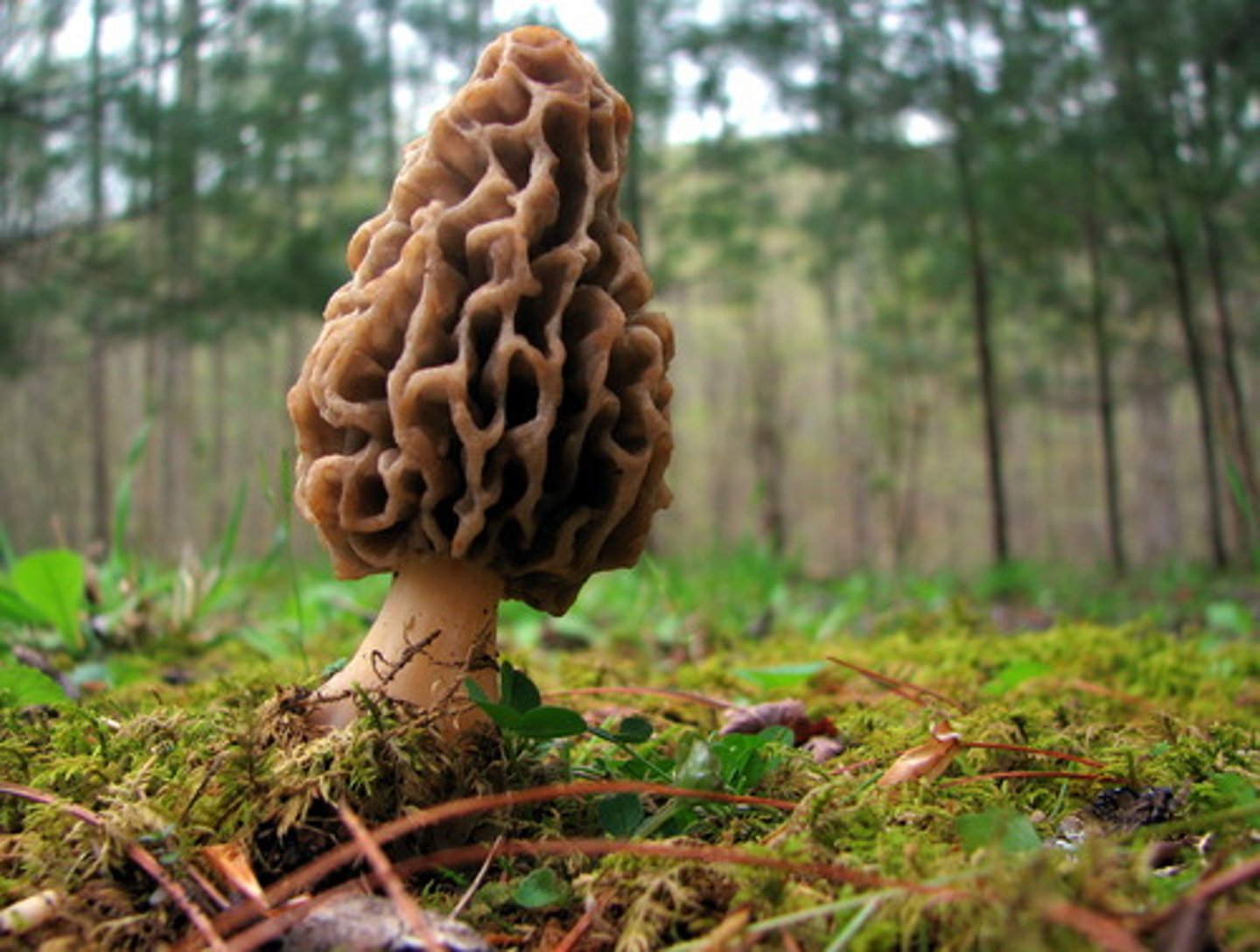
Ascomycota fungus examples
Morels, yeast, penicillium, ringworm

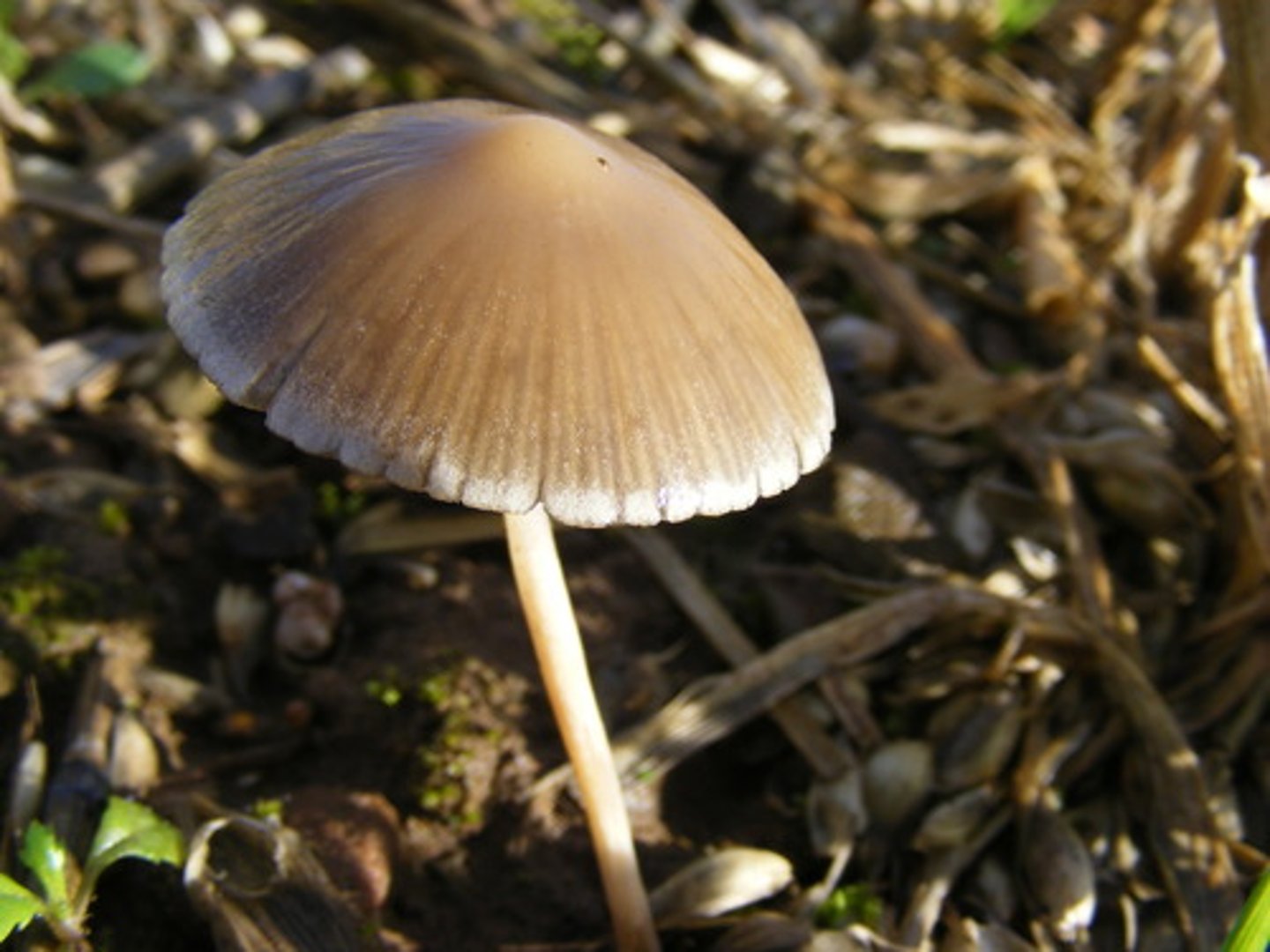
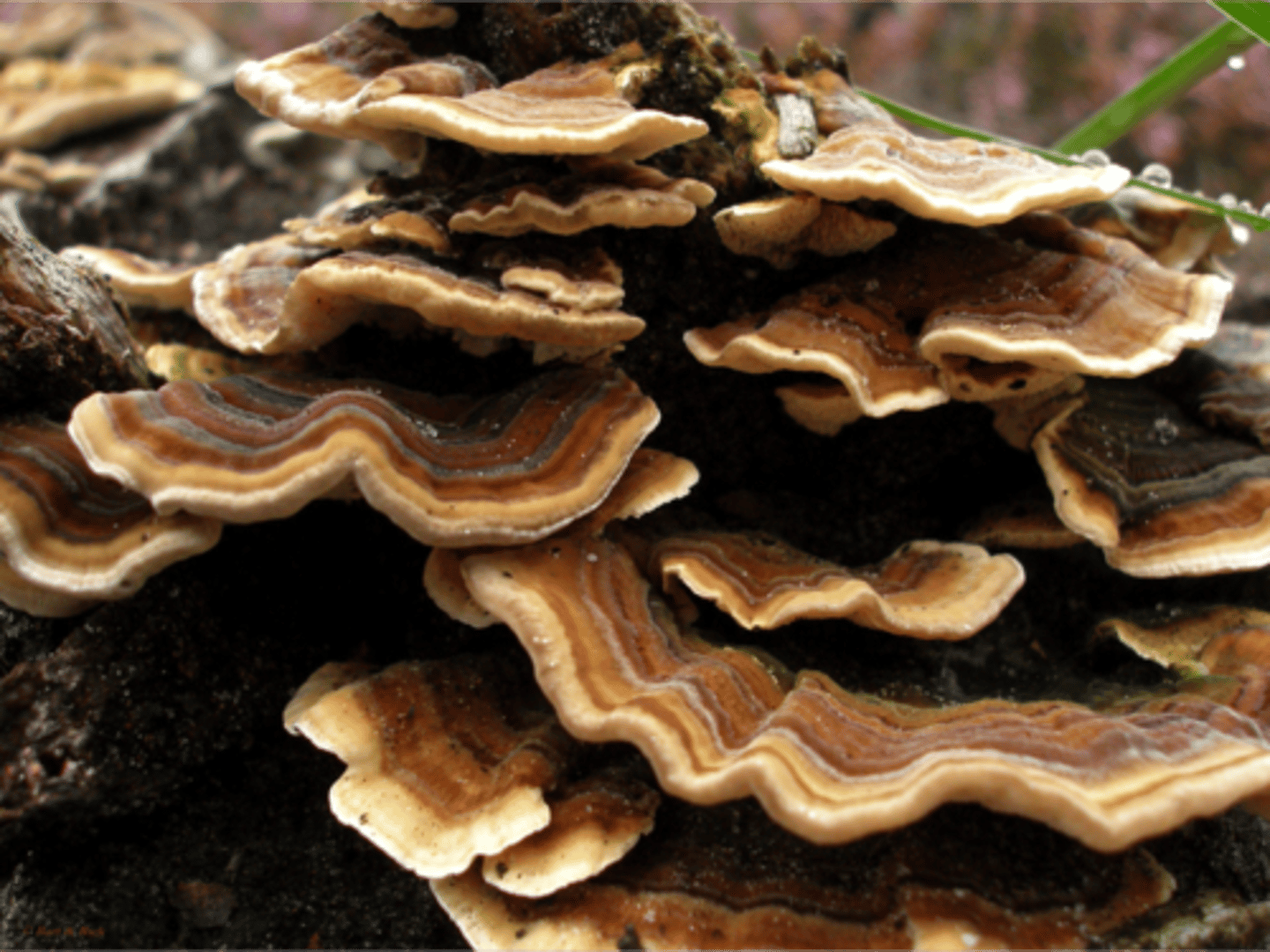
Examples of Basidiomycota Fungus
Mushrooms and shelf fungus

Chytridiomycota Fungus Examples
unique among fungi because they have a motile stage in their life cycle-the zoospores are a single flagellated cell (genus Rhizophidium)
How do fungus get food?
Absorption using hyphae- release enzymes outside of cell, food molecules broken down into smaller molecules that can then be absorbed into cells.
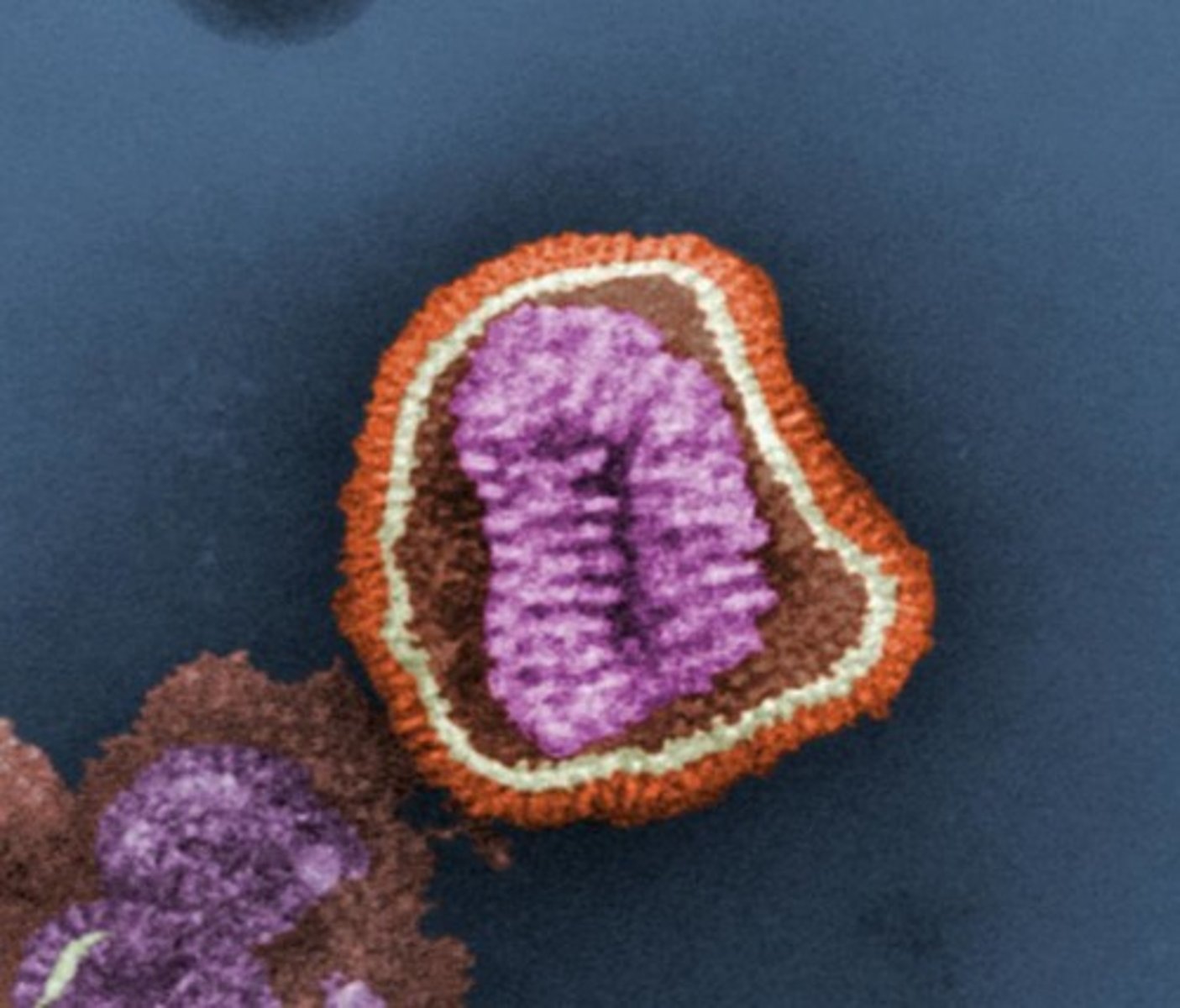
Why aren't viruses considered to be living?
No cell structures
No cell functions
No reproduction without host cell
doesn't have all the characteristics of living organisms
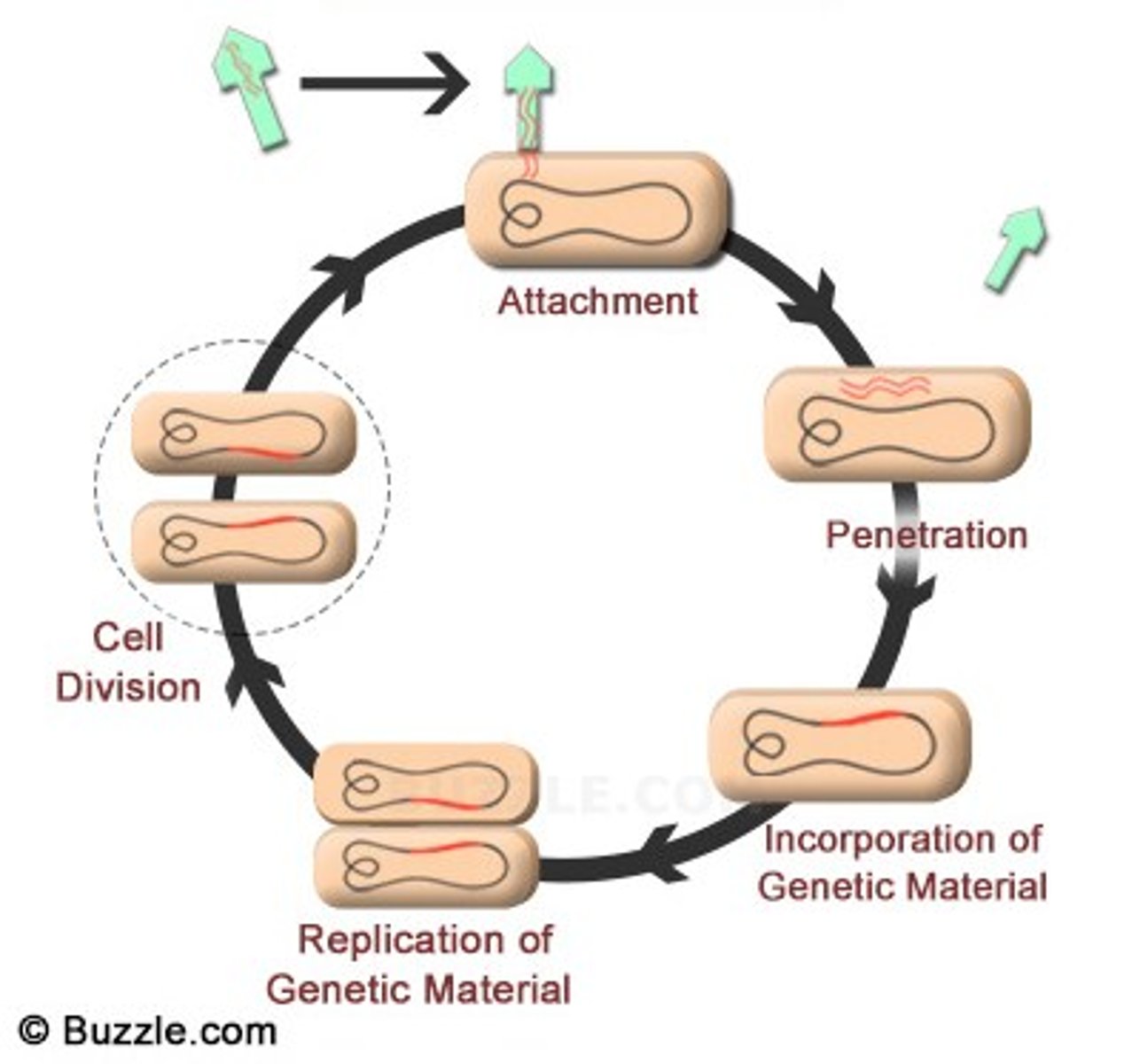
Lytic Cycle
Short virus cycle that quickly destroys host cell.

Lysogenic Cycle
Viral DNA becomes part of host DNA (provirus formation) Remains dormant and viral information is passed on to new cells. Eventually something triggers the virus to become lytic.
Lytic Cycle Virus Examples
Cold virus, flu, ebola
Lysogenic Cycle Virus Examples
HIV, Herpes, Chickenpox
scientific names (binomial nomenclature)
Genus and species level are used for a scientific name

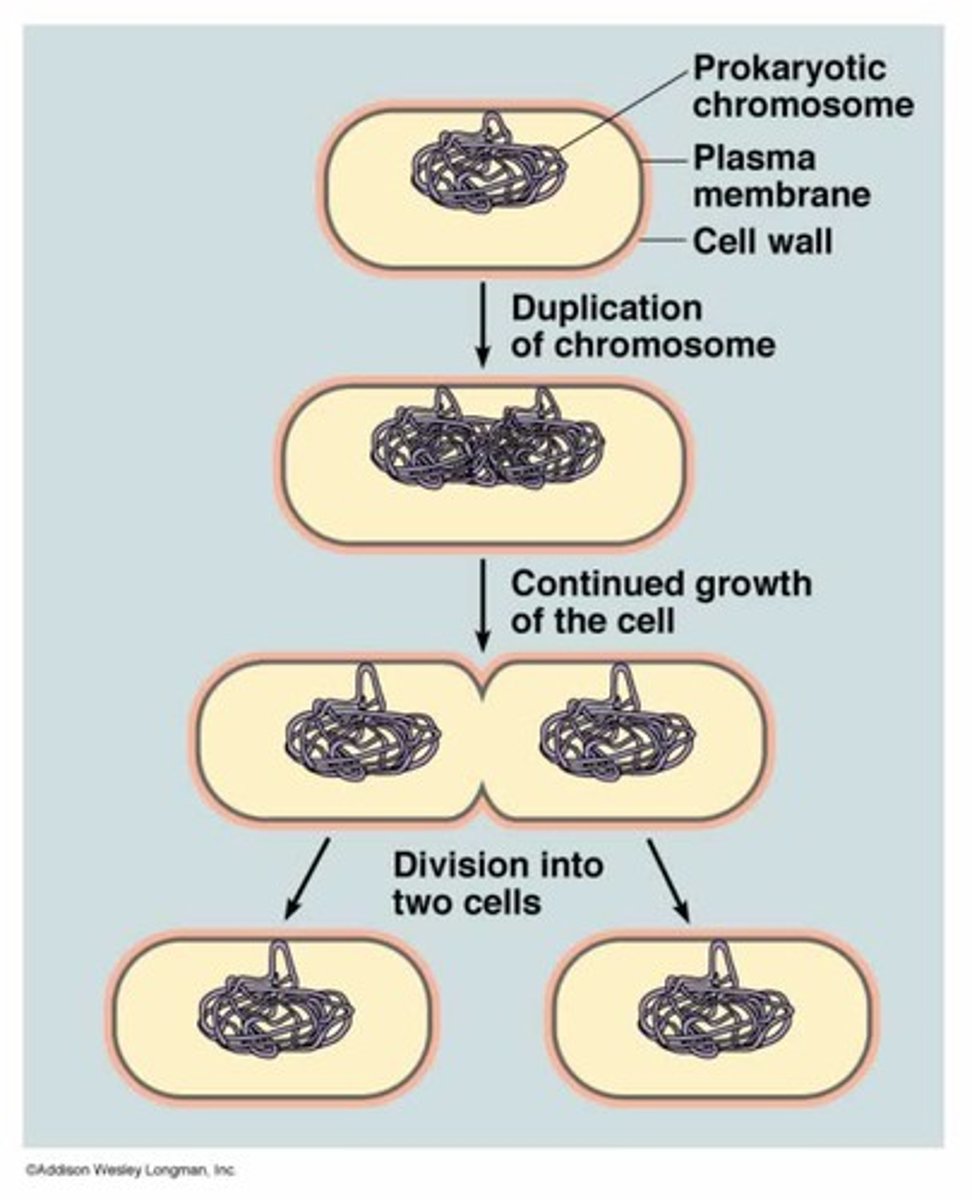
binary fission
A form of asexual reproduction in which one cell divides to form two identical cells.
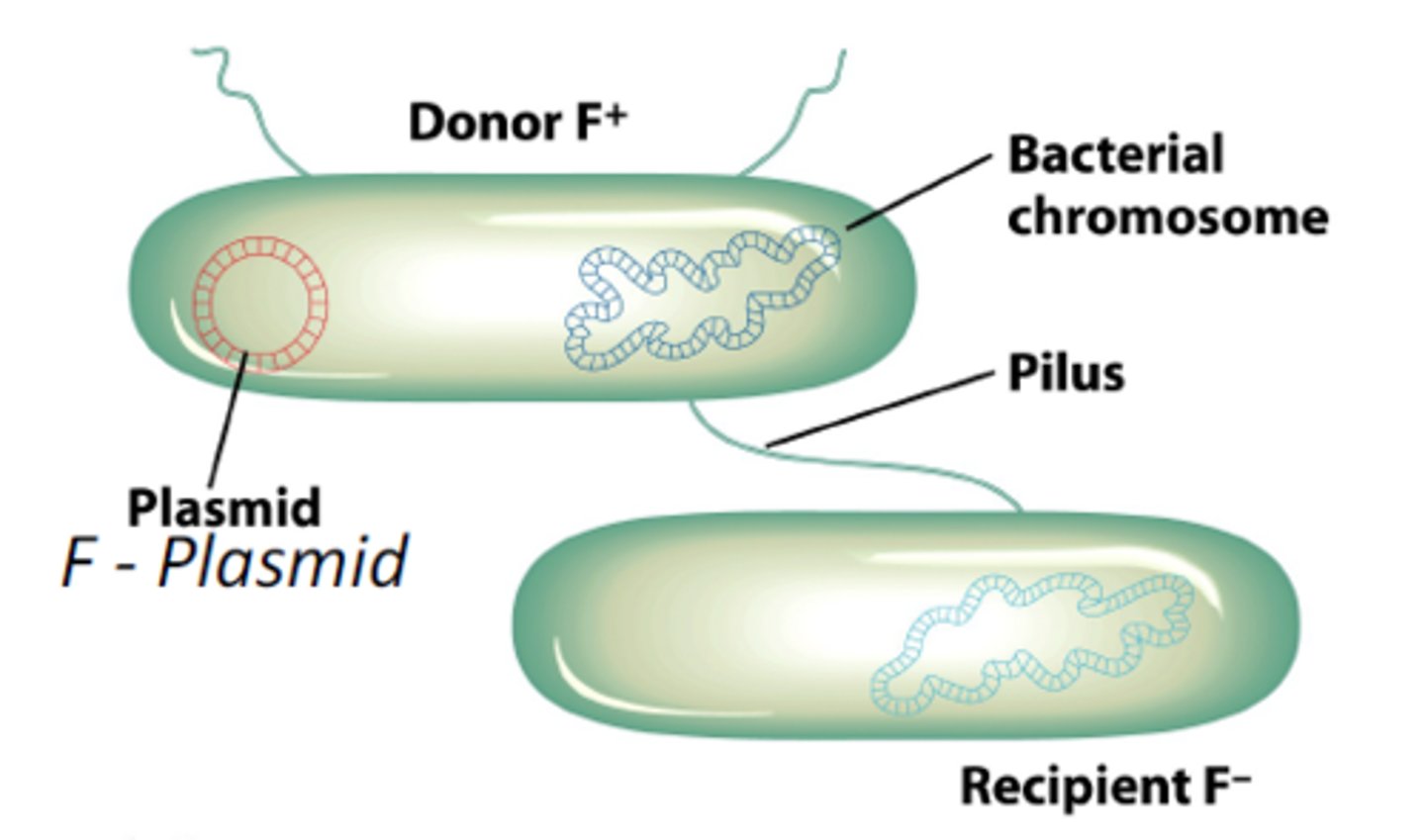
Conjugation
bacterial exchange of genes between individual cells- sexual reproduction
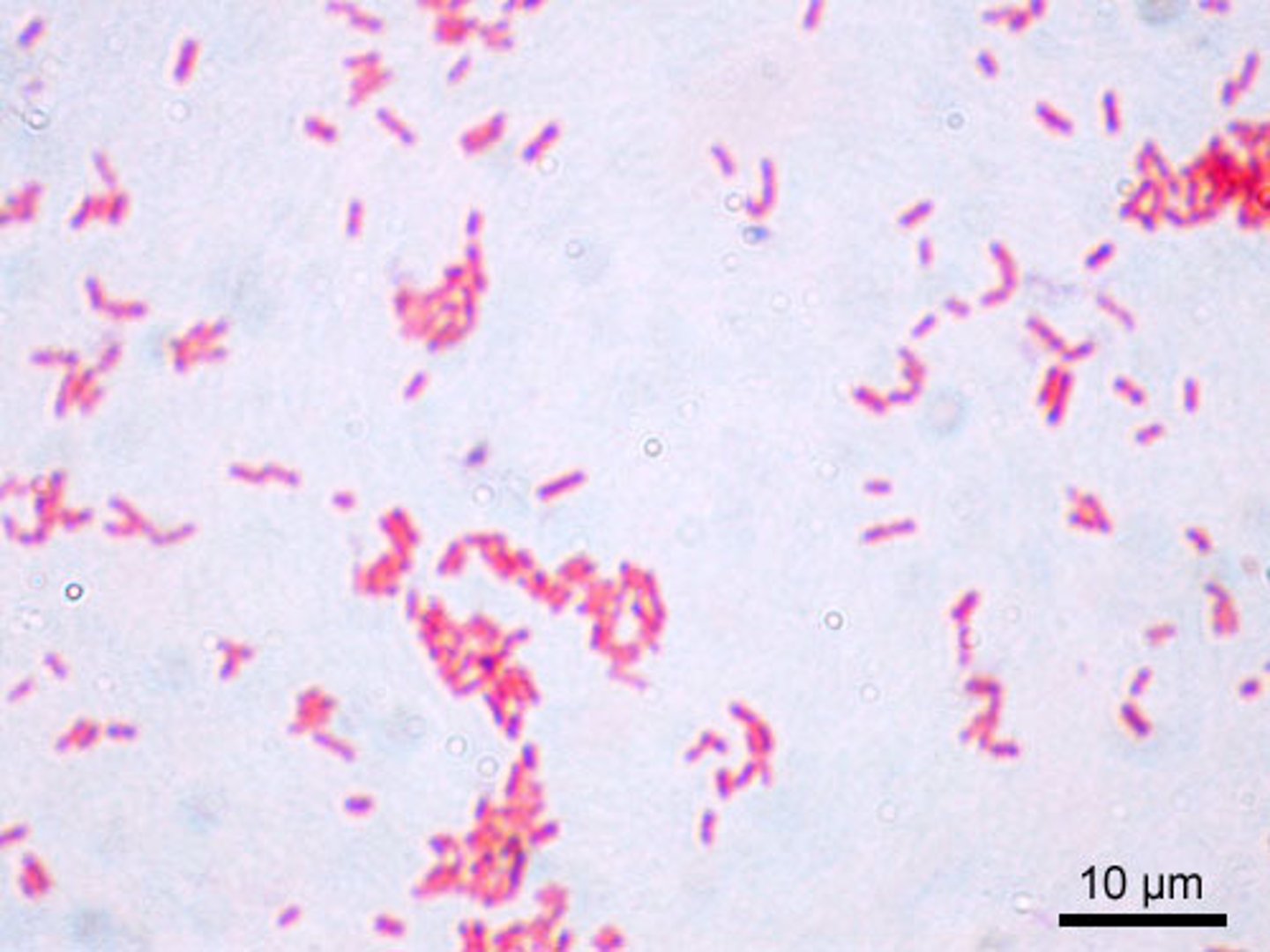
Gram-negative bacteria
type of bacteria that stain pink with Gram stain and have a thin cell wall with an outer membrane (capsule)
Gram-positive bacteria
Bacteria that have a thick peptidoglycan cell wall, and no outer membrane (capsule). They stain purple in Gram stain. Easier to treat with antibiotics
Mesophiles
bacteria that grow at moderate temperatures- our body temp included
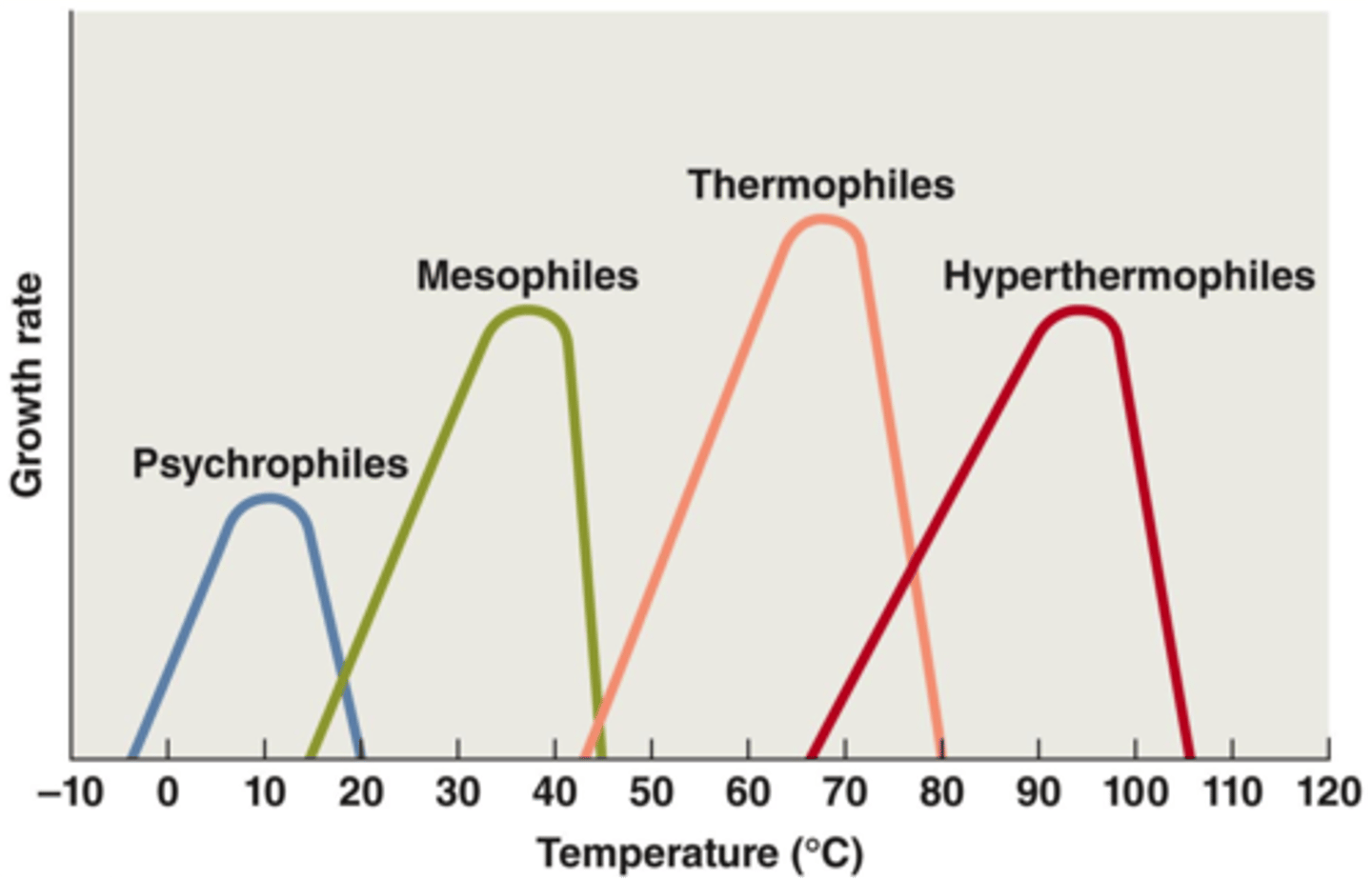
Thermophiles
bacteria that thrive at high temperatures such as Thermus aquaticus that live in hot springs.
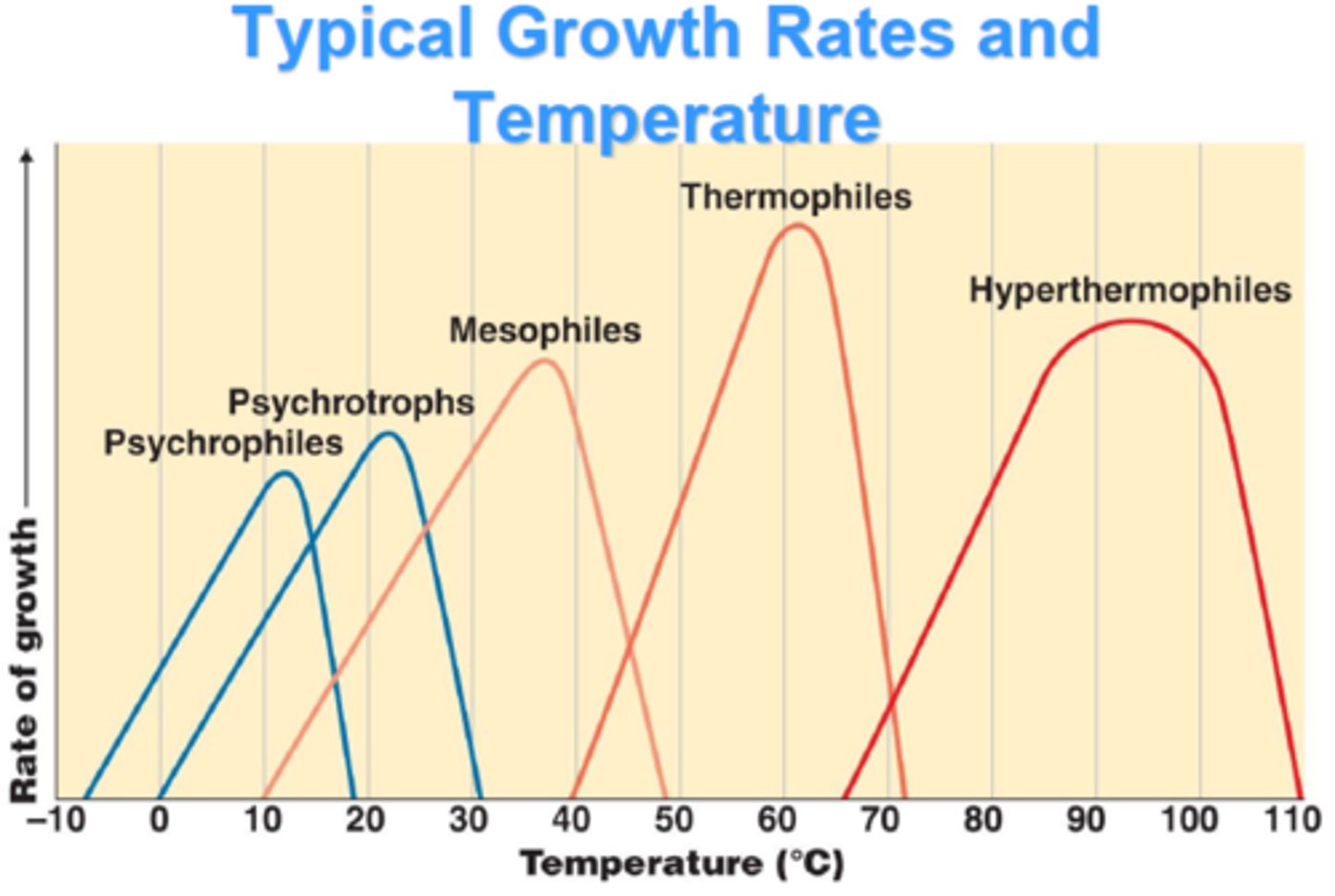
How are bacteria developing drug resistance?
Over prescribing antibiotics when they aren't needed, misuse of antibiotics by individuals not taking the medicine correctly, conjugation- bacteria acquiring resistance genes through sexual reproduction
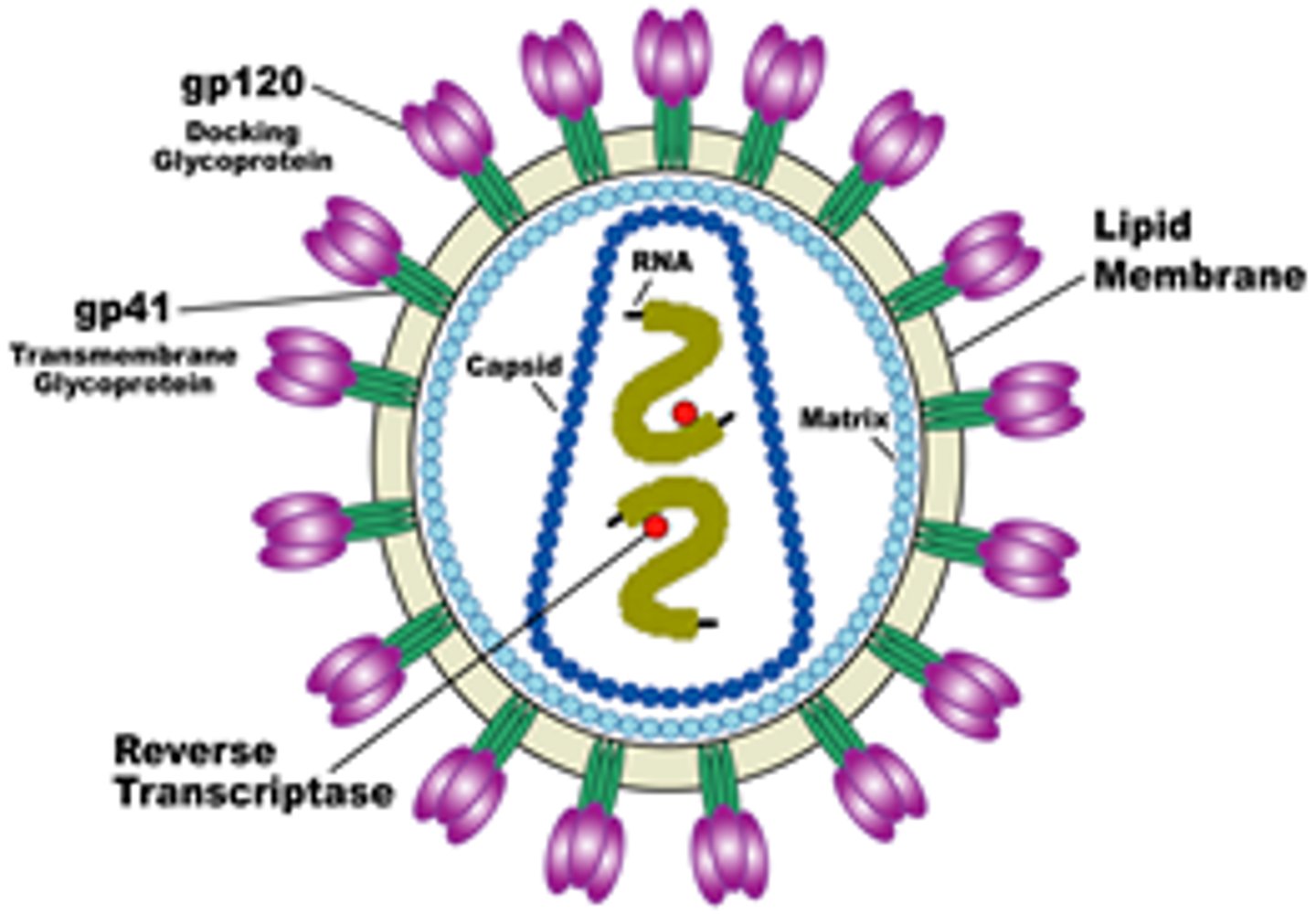
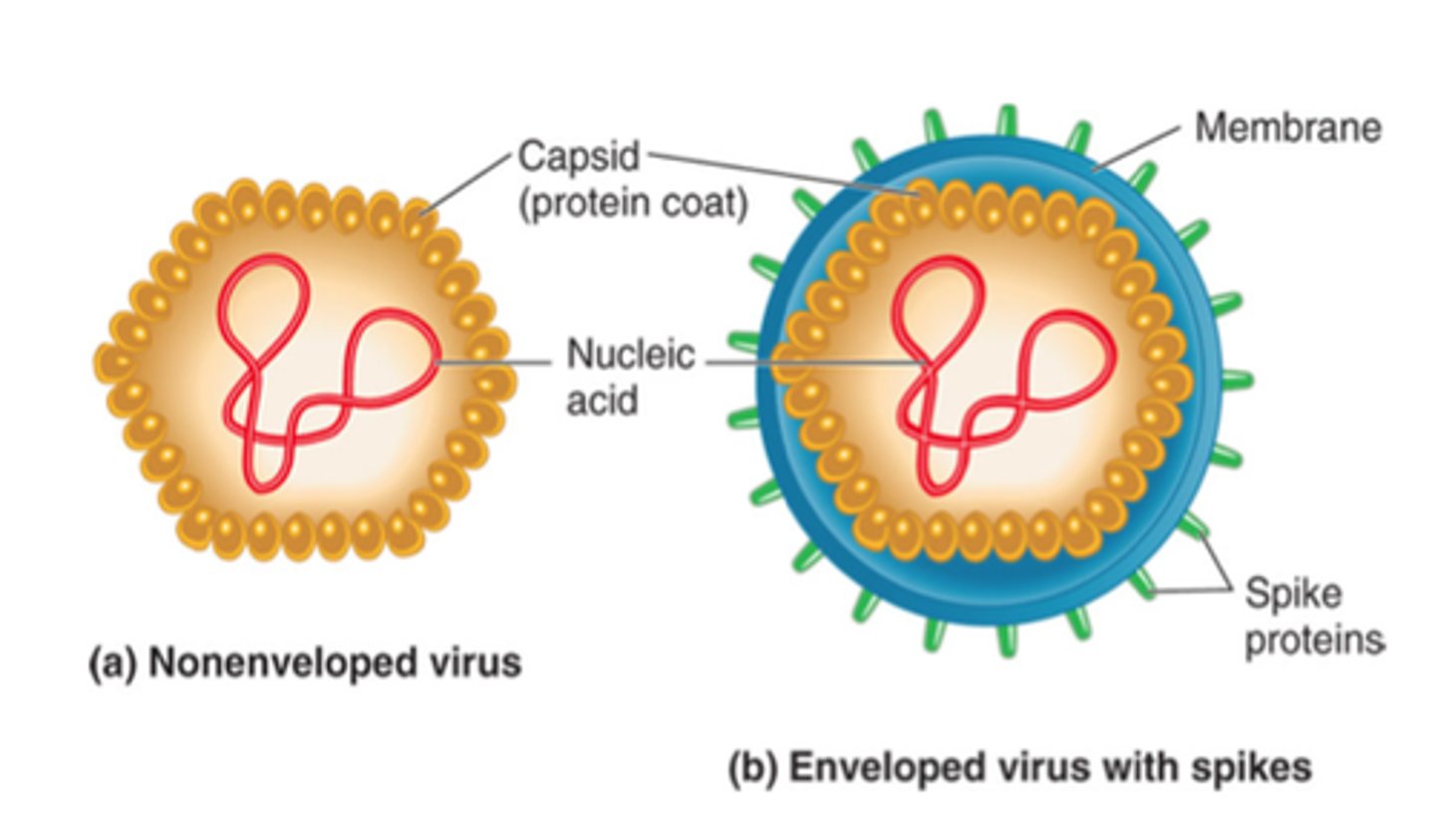
Basic Structures of Viruses
genome (DNA or RNA), capsid, attachment mechanism
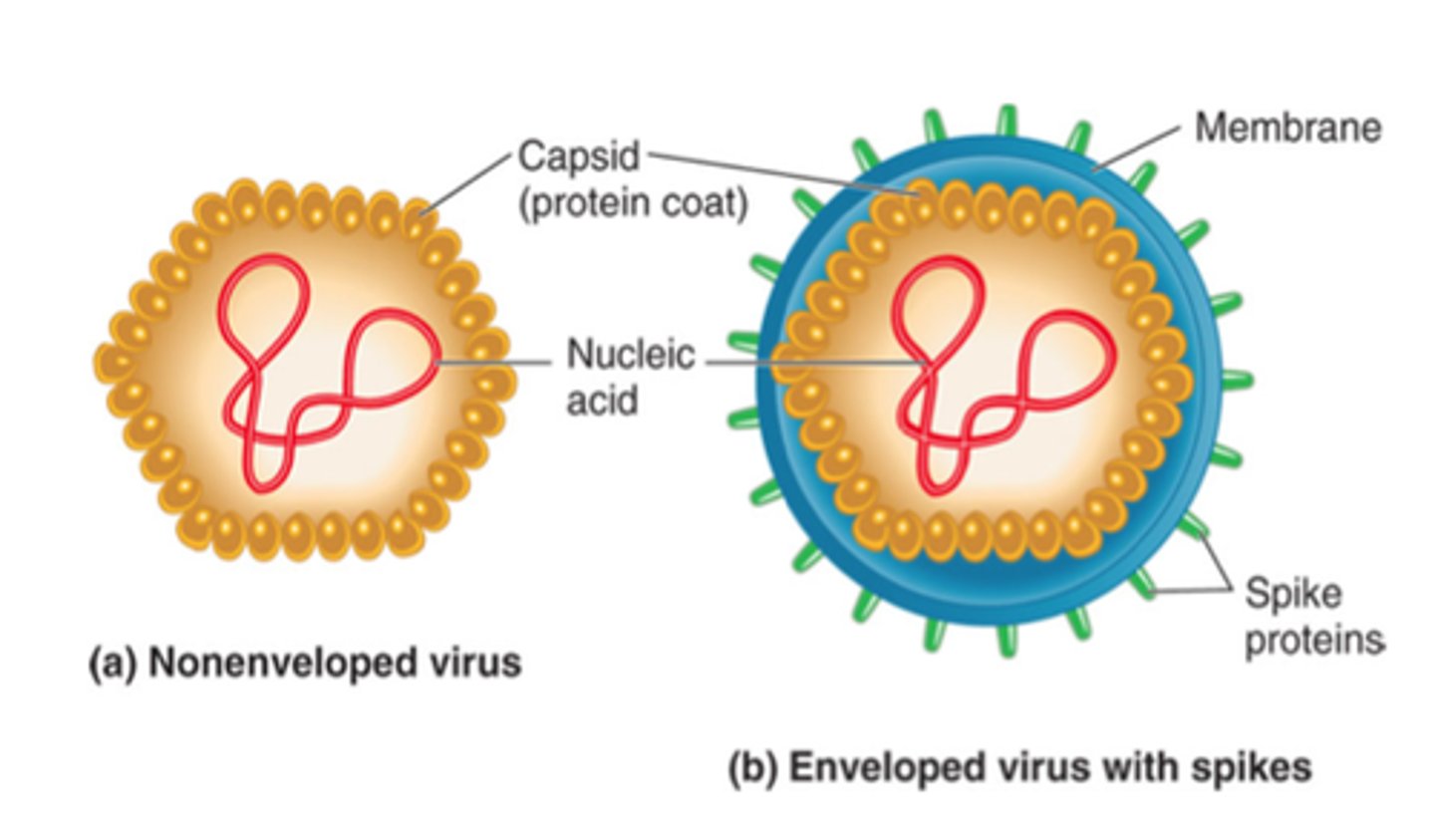
viral envelope
A membrane, derived from membranes of the host cell, that cloaks the capsid, which in turn encloses a viral genome.
Vaccines
used to stimulate an immune response against a pathogen without having to be infected
Main characteristic to classify protozoans is:
type of structure for movement
Main characteristic to classify types of algae is:
color (types of pigments)
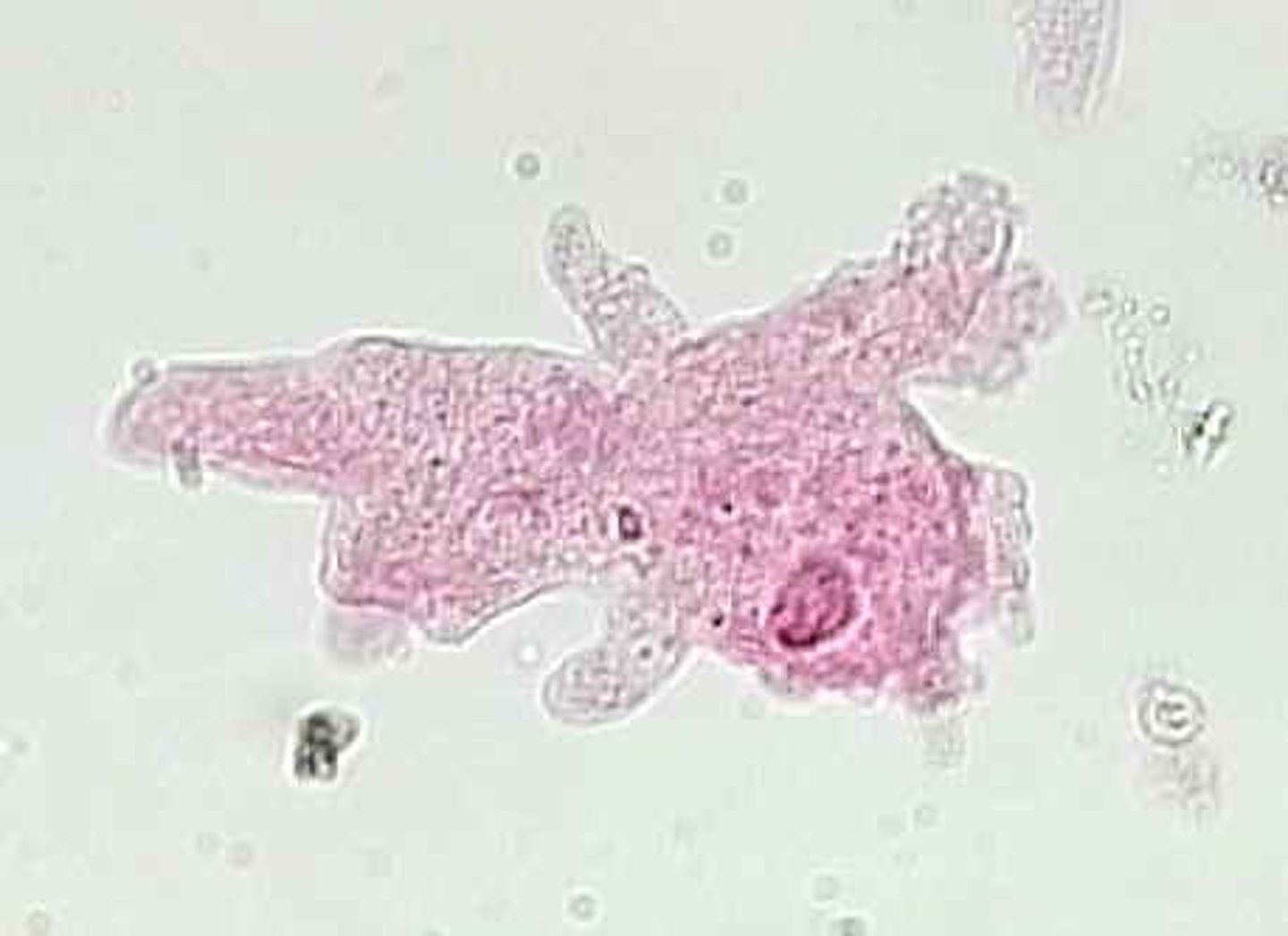
Amoeba
A type of protist characterized by great flexibility and the presence of pseudopodia.
Paramecium
A ciliated protist that lives in fresh water.

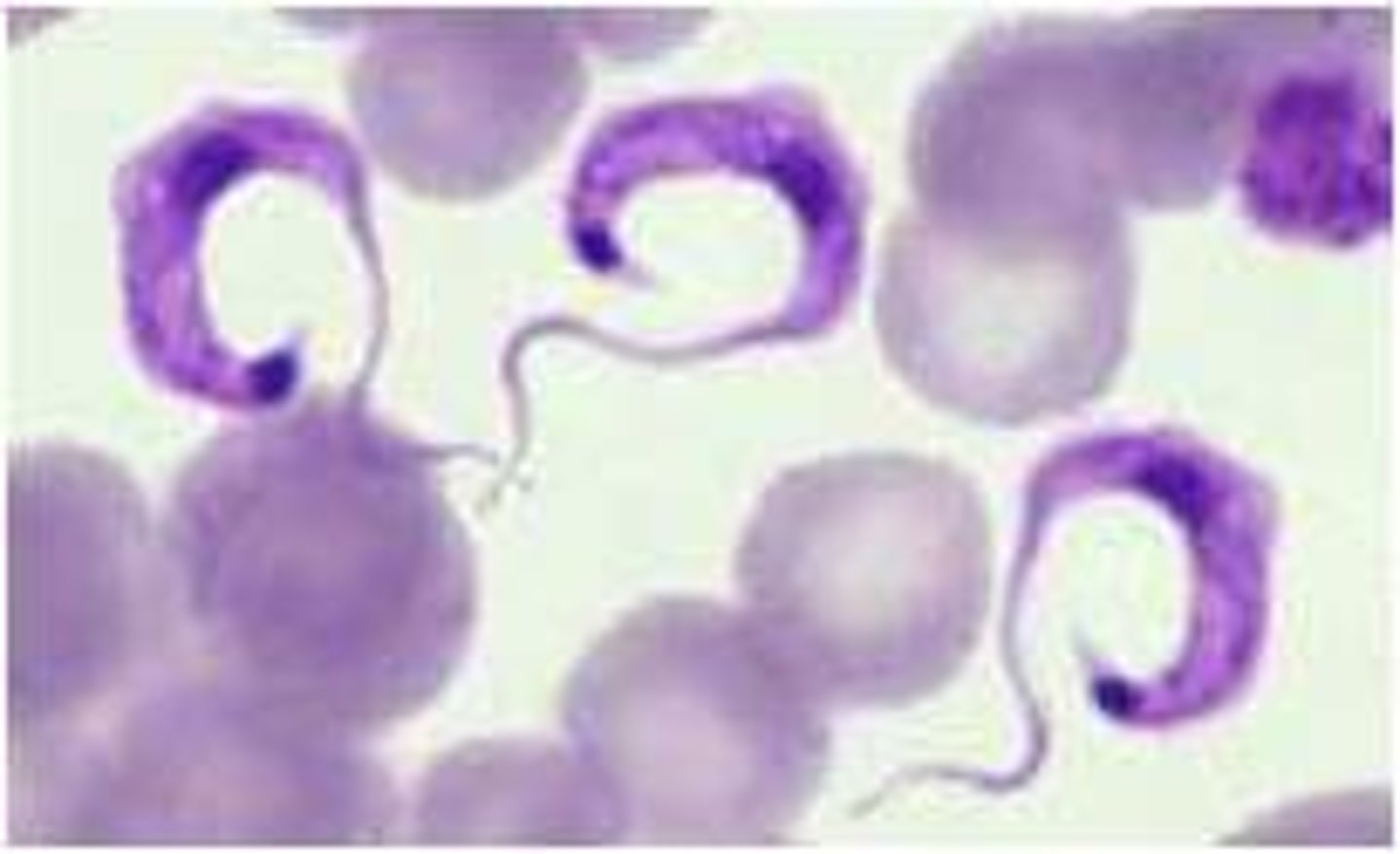
Trypanosoma
flagellate that causes African sleeping sickness
Plasmodium
sporozoan that causes malaria
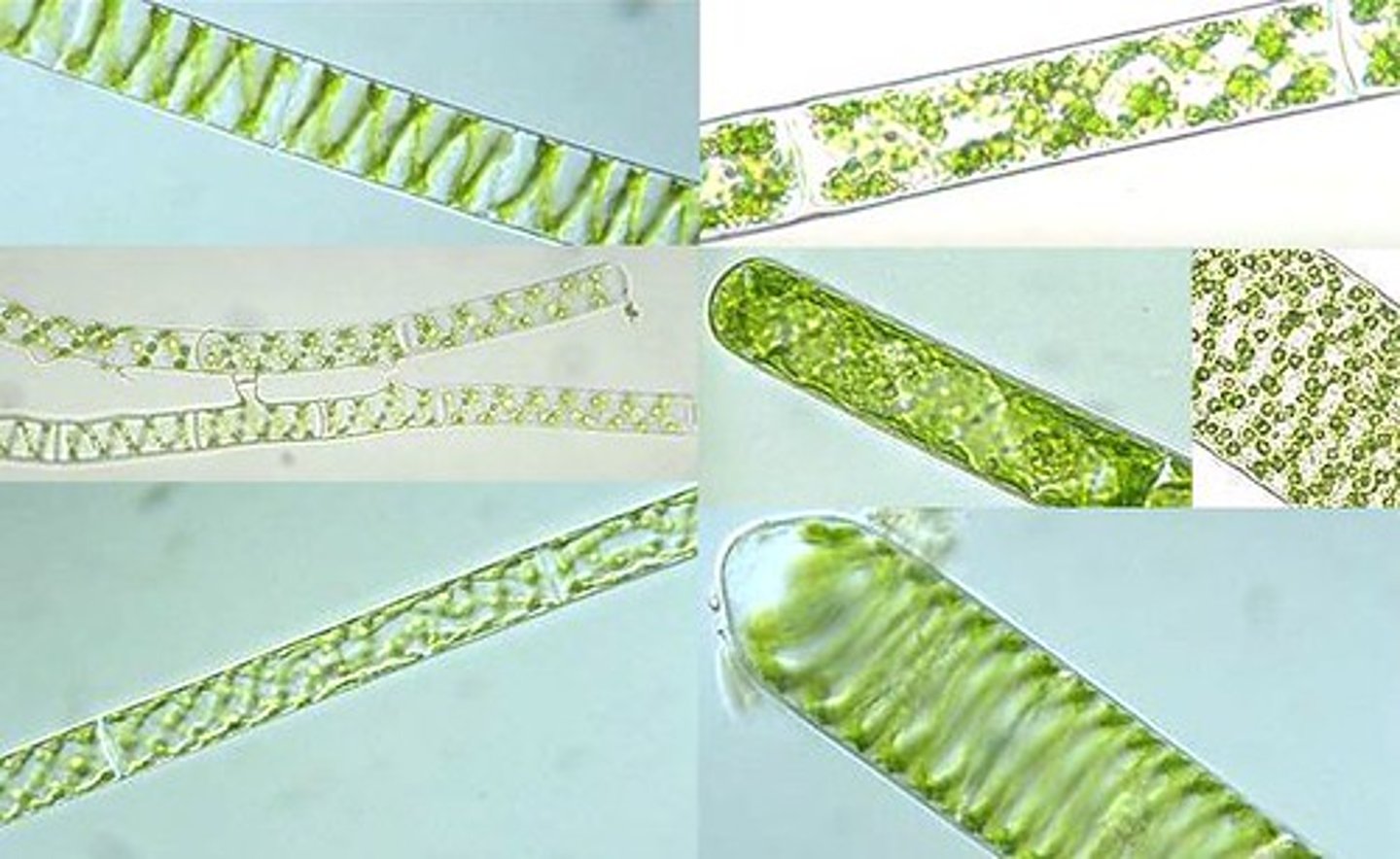
Chlorophyta
Green algae
Cellulose cell walls
Unicellular or multicellular
Chlorophyll a and b
Gave rise to plants
Phaeophyta
Brown algae such as kelp
Multicellular

Rhodophyta
red algae
live deeper in the ocean
multicellular

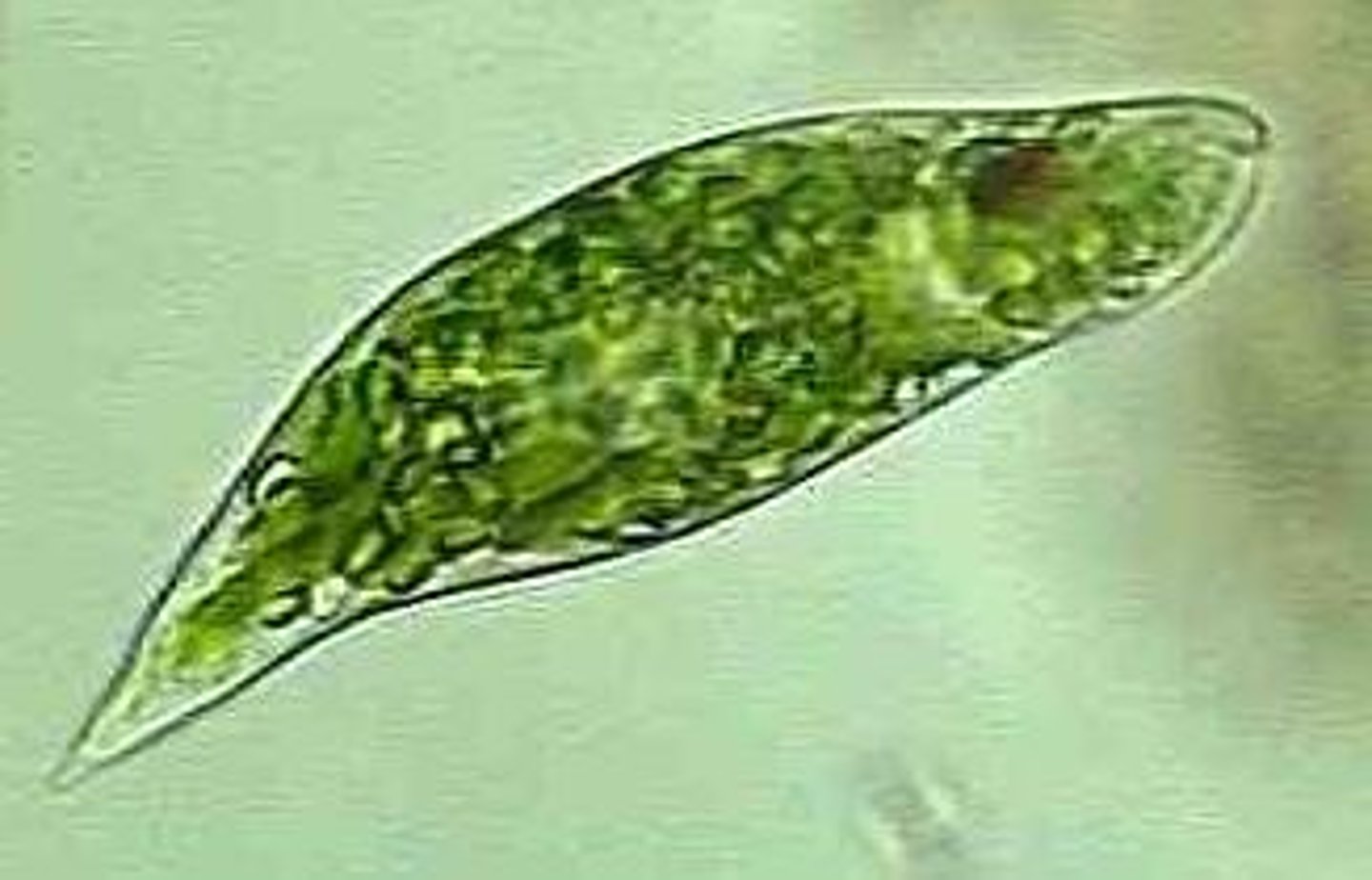
Euglena
has both plant-like (photosynthesizes) and animal-like characteristics (no cell wall, flagella for movement, can be heterotrophic)
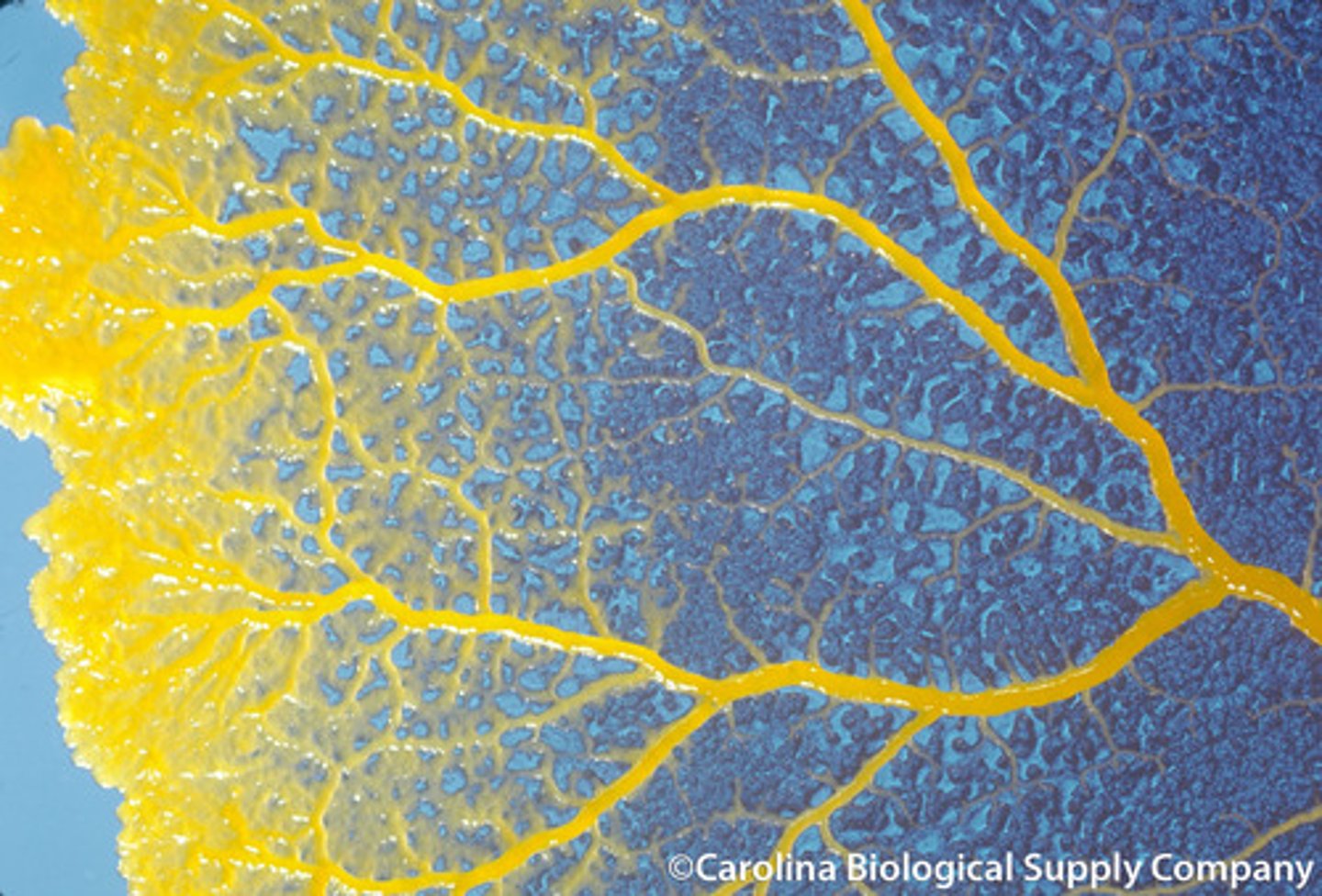
Acellular slime molds
slime molds that pass through a stage in which their cells fuse to form one large cell with many nuclei
Cellular slime molds
Types of slime molds that typically exist as individual cells and reproduce with binary fission; during stressful times, many of these cells will come together to form a fruiting body.
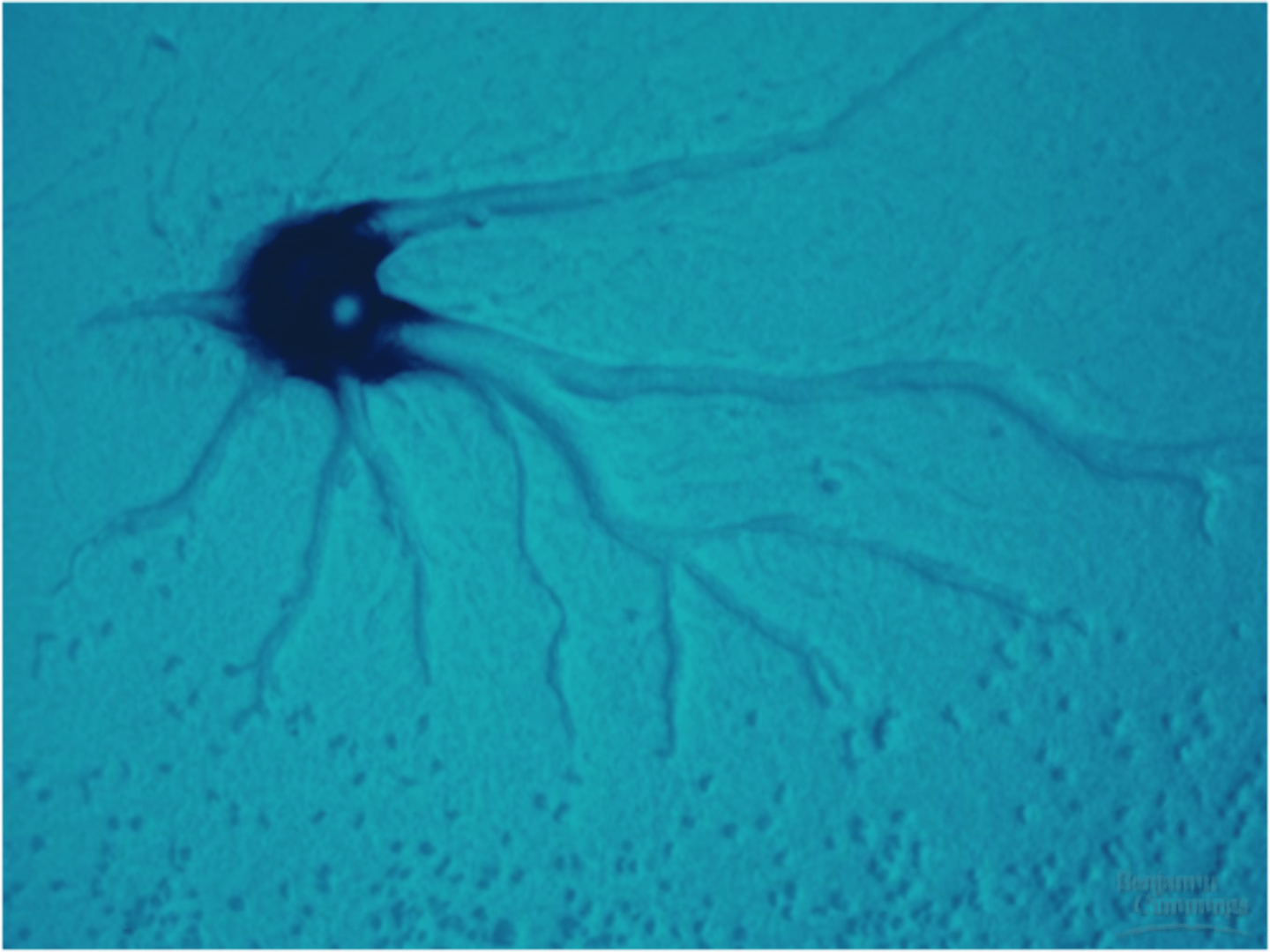
water molds
fungus-like protists that are made up of branching strands of cells- live in water or moist environments
Fungal Spores
reproductive cell capable of developing into a new organism (without fusion with another cell-asexual, with fusion from another cell-sexual)