Visual computing part 2
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/70
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 5:32 PM on 1/21/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
1
New cards
What is a solid model?
A model using implicit functions
2
New cards
What is a surface model?
A model using parametric functions
3
New cards
What is a voxel model?
Voxel models take 3d space and say whether each pixel has matter in it or not.
4
New cards
What are the advantages of solid modelling?
They allow you to combine shapes
5
New cards
What does a 1d/2d surface model mean?
1d takes 1 input, 2d takes 2.
6
New cards
How do you use scan conversion to render a surface model?
Take a set of parametric equations, and break the surface down into a set of pixels, then test at each pixel
7
New cards
What are particle models?
Particle models have each particle associated with a set of values and repeat the shape at each particle
8
New cards
What do we store in the face vertex data structure?
A list of faces (with face and then their vertices) and a vertex list (with vertex, x,y,z co-ordinates and their faces)
9
New cards
What does face-edge-vertex data structure store?
Each stores the two other for a complete representation.
10
New cards
What are the stages of the graphic pipeline?
* Vertex processing
* Clipping & rasterisation
* Fragment processing
* Frame buffer processing
* Clipping & rasterisation
* Fragment processing
* Frame buffer processing
11
New cards
What happens in vertex processing?
* Convert from object to world co-ordinates, then camera space and finally clip space.
* We workout vertex normals, for lighting
* We workout vertex normals, for lighting
12
New cards
What happens in clipping?
Get rid of anything that is not in the view of the eye. We create a frustum of what we can see to do this, and then do clipping for each plane of the frustum (6 times)
13
New cards
What is point-plane clipping?
We do the dot product with the plane normal and the point vector, if it is positive it is outside.
14
New cards
What happens in rasterisation?
We turn primitives into pixels, for each pixel we work out whether it is a triangle or not, this is called scan conversion
15
New cards
What happens in fragment processing?
This is where we compute the final fragment colours and shading, based on the texture mapping and lighting computations
16
New cards
What happens in frame buffer processing?
For every pixel we work out which fragment, or combination of fragments to use based of which is in front.
17
New cards
What are the painter’s and z-buffer algorithm
Painter’s algorithm, order all objects, paint from back to front overpainting when there’s a close object.
Z-buffer store the closest depth for each pixel, initially infinity then when drawing comprae new depth to this depth and paint if lower.
Z-buffer store the closest depth for each pixel, initially infinity then when drawing comprae new depth to this depth and paint if lower.
18
New cards
What is a pure diffuse reflection?
The surface scatters light equally in all directions.
19
New cards
What is a pure mirror reflection?
Line reflects along a line symmetrical about the surface normal
20
New cards
What are the three tpyes of lighting in the phon model?
1. Ambient
2. Diffuse (lambertian) lighting
3. Specular (phong) lighting
21
New cards
How do we work out diffuse relection?
diffuse reflectivity x light source intensity x cos angle (between light and surface normal)
22
New cards
How do we workout specular reflection?
specular reflectivity x light source intensity x cos angle (netween viewing ray and reflected ray ^ shininess coefficent.
23
New cards
What is the shininess coefficent
This describes the breadth of the angle of specular reflection, basically how much of an angle the viewing ray can be and still see the reflected ray. If this is smaller we have a broader angle and rougher objects. If this is larger we have a narrower angle and a smoother surface.
24
New cards
How do we workout ambient lighting?
ambient reflectivity x light source intensity
25
New cards
What can we replace cosine with for vector arithmetic?
Dot product of vectors, i.e theta is (l normal), phi is (reflection, viewing)^alpha
26
New cards
What are the different shading models, and how do they calculate light?
* Flat shading, per polygon
* Gourad shading, per vertex
* Phong shading, per pixel.
* Gourad shading, per vertex
* Phong shading, per pixel.
27
New cards
What do we call a model that uses a 4D function based on measurement to workout how much light is reflected?
Bidirectional reflectance distributions function (BRDF)
28
New cards
What are subsurface effects?
For translucent objects you have to work out the way light rays are absorbed, reflected inside and re-emited
29
New cards
What is a texture?
An image applied to a surface.
30
New cards
What are the two interpretations for workout out what part of the texture we want?
Forward and backward mapping (with bilinear interpolation)
31
New cards
What is bump mapping?
Where you perturb the surface normal to make it look bump.
32
New cards
What is displacement mapping?
Perturbing the surface height to physically change the shape of the object
33
New cards
What is environment mapping?
Surround the scene with a sphere, render the scene onto the sphere and colour the surface by reflection.
34
New cards
What are mipmaps?
Set of downsampled images of a texture, we choose fidelity basd on distance and move co-ordinates to get the right one.
35
New cards
What do we need to fit two polynomail curves together?
2 points, 2 gradients
36
New cards
What are hermite curves made up of?
Geometry matrix(2 points, 2 derivatives), blending matrix, parametisation
37
New cards
How do we create a basis function?
Combine blending matrix and pamatisation.
38
New cards
How do we work out the gradient in Bézier curves?
(0) = 3(p1 - 0)
(1) = 3(p3 - p2)
(1) = 3(p3 - p2)
39
New cards
What is the convex hull property?
The curve will never pass outsidethe convex hull formed by the four control points.
40
New cards
What is de catelajus algorithm, after seting the control points?
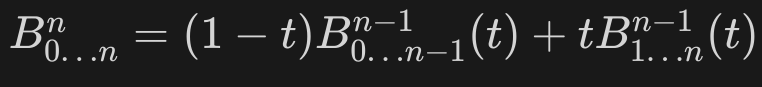
41
New cards
How do we ensure continuity in bezier splines?
ensure p(1) = q(0)
42
New cards
How do ensure smoothness in Bézier splines?
p’(1) = q(0)
43
New cards
What are the three ways of representing curves/surfaces?
* Explicit, one axis in terms of another.
* Parametric, from a parameter (t) to a point on the curve
* Implicit, point on the curve when f(x) = 0
* Parametric, from a parameter (t) to a point on the curve
* Implicit, point on the curve when f(x) = 0
44
New cards
What are the problems with explict?
* Cant represent vertical lines.
* Can’t represent a curve that outputs two values at a single point (e.g a cicle)
* Can’t represent a curve that outputs two values at a single point (e.g a cicle)
45
New cards
What are the benefits of a parametric representation?
Using a parameter makes it easy to iterate over all points on the surface
Makes it easier to handle outputting multiple values at one point.
Makes it easier to handle outputting multiple values at one point.
46
New cards
What values are inside, on and outside an implict surface?
47
New cards
What is the formula for an implict cone?
x^2 + y^2 - z^2
48
New cards
How can you specify size in an implict equation?
add a -w, which sets the size
49
New cards
How do we add (union) two implicit shapes?
Take the min of the two functions
50
New cards
How do we get the intersection of two implicit surfaces
Take the max of the functions
51
New cards
What is the zero set of an implicit function?
Surface exists if function = 0
52
New cards
What is the level set of an implicit function?
Function decays to 0 but dosen’t reach it, and includes a value we define.
53
New cards
What are benefits of level set?
We can add functions to combine instead of using min/max, create metaballs/blobs
54
New cards
What is marching squares/cubes?
A list of cases to tell you where to draw a line in a mesh based on which pixels are inside/outside of the implict surface
55
New cards
How do we convert an implicit surface to a mesh?
Marching cubes then interpolation to workout where the line cuts.
56
New cards
What are sudivision surfaces?
Surfaces that get better and better as we refine them, with continuity and a flexible level of detail.
57
New cards
What do we call the polygons we start/end with?
Control polygon and limit surface
58
New cards
What are the two ways we can do subdivision
1. Approximating where original vertices are moved
2. Interpolating where we add new vertices.
59
New cards
What is the difference between regular and irregular sampling?
Whether sampling interval is the same or not
60
New cards
What is aliasing?
Where we use a low sampling frequency for a high-frequency function, which means we can’t accurately depict it.
61
New cards
What is the Nyquist limit,
There needs to be two samples per weavelength, so limit is number of waves divided by two
62
New cards
What is the sampling theorem?
Assume band limited signal, to sample without alising we need to sample the highest frequency more than twice per period.
63
New cards
What is a band limited signal?
After a point (w) amplitude = 0
64
New cards
How can we reduce effect of aliasing on high frequency?
Low pass filter or add noise
65
New cards
How can we improve image sampling when downsizing?
Add a blur to reduce aliasing
66
New cards
What does an antialasing filter do?
Cut the signal at the Nyquist limit.
67
New cards
What is the implict form of a 2d line?
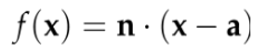
68
New cards
What do we call joining together multiple curves?
Piecwise modelling
69
New cards
What does C^0 continuity ensure?
0th order derivative is conitnous, so x points line up
70
New cards
What does c^1 continuity ensure?
1st derivate of the curves at each connection is continuous
71
New cards