Understanding Speciation and Evolutionary Processes
1/526
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
527 Terms
What is required for speciation to occur?
Interruption of gene flow.
What does the Dobzhansky-Muller model explain?
The evolution of genetic incompatibilities when a population is subdivided and evolves independently.
What happens to alleles in the Dobzhansky-Muller model?
New alleles become fixed at different loci in each lineage, leading to genetic incompatibility.
What is the result of genetic incompatibility between two isolated populations?
Hybrids have low fitness.
How can reproductive isolation develop?
It may take millions of years or can develop in just a few generations.
What are the two geographical patterns of speciation?
Allopatric speciation and sympatric speciation.
What is allopatric speciation?
Speciation when populations are separated by a physical or geographic barrier.
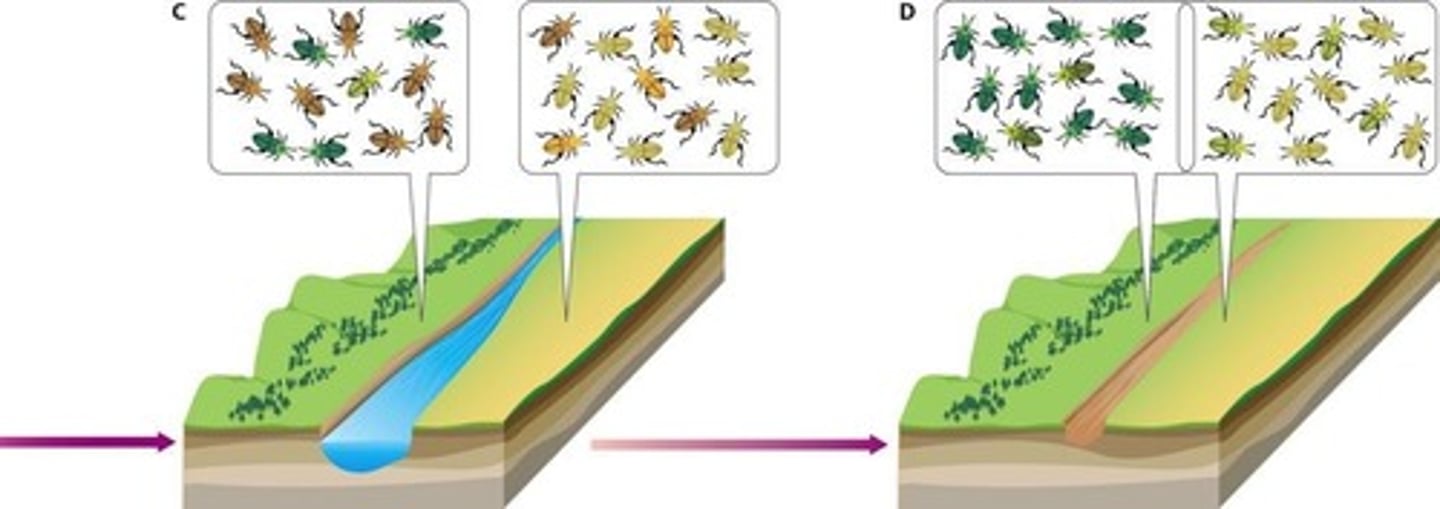
How do populations evolve in allopatric speciation?
Through genetic drift and adaptation to different environments.
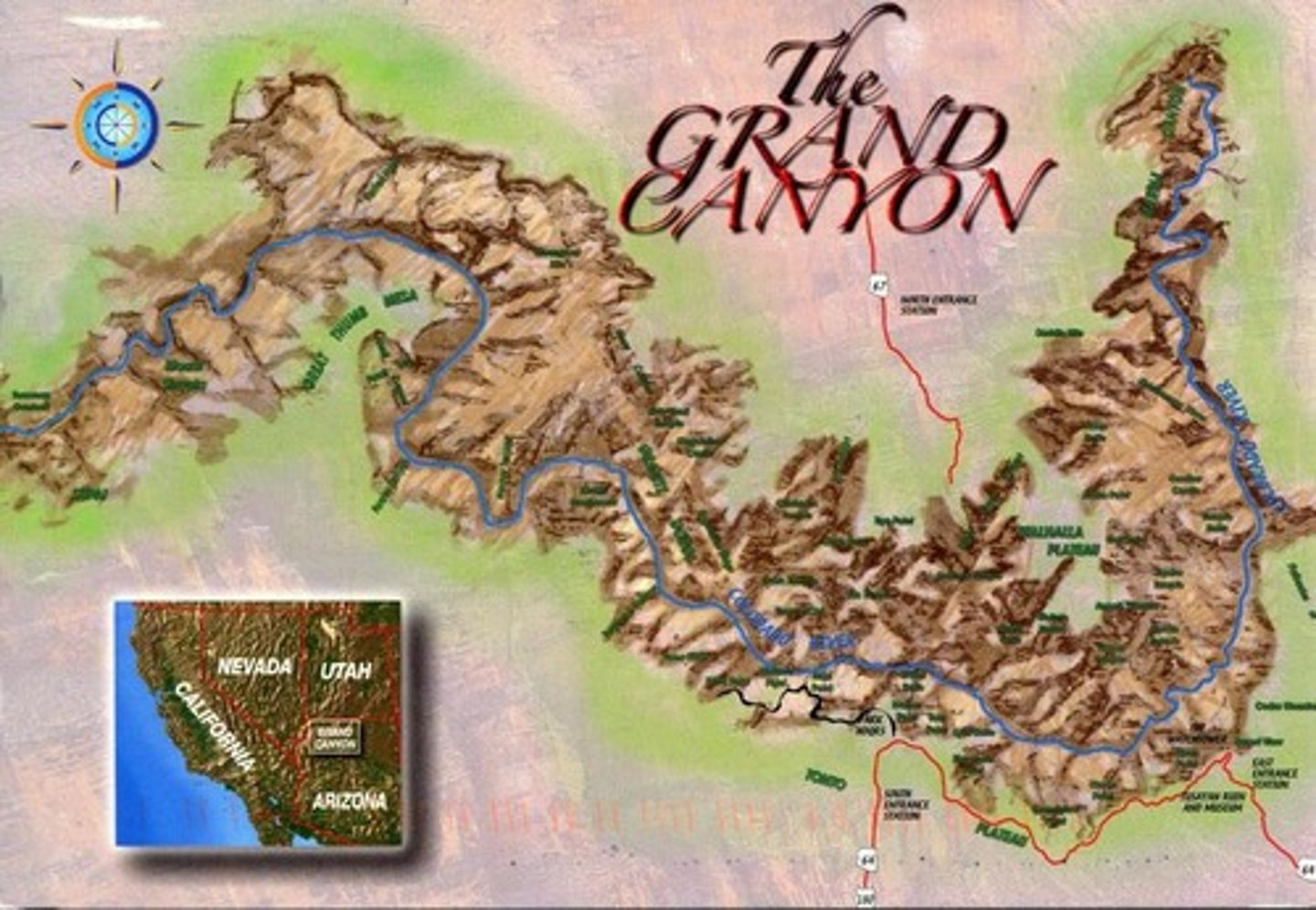
What is an example of allopatric speciation by vicariance?
The formation of the Grand Canyon, which separated populations.
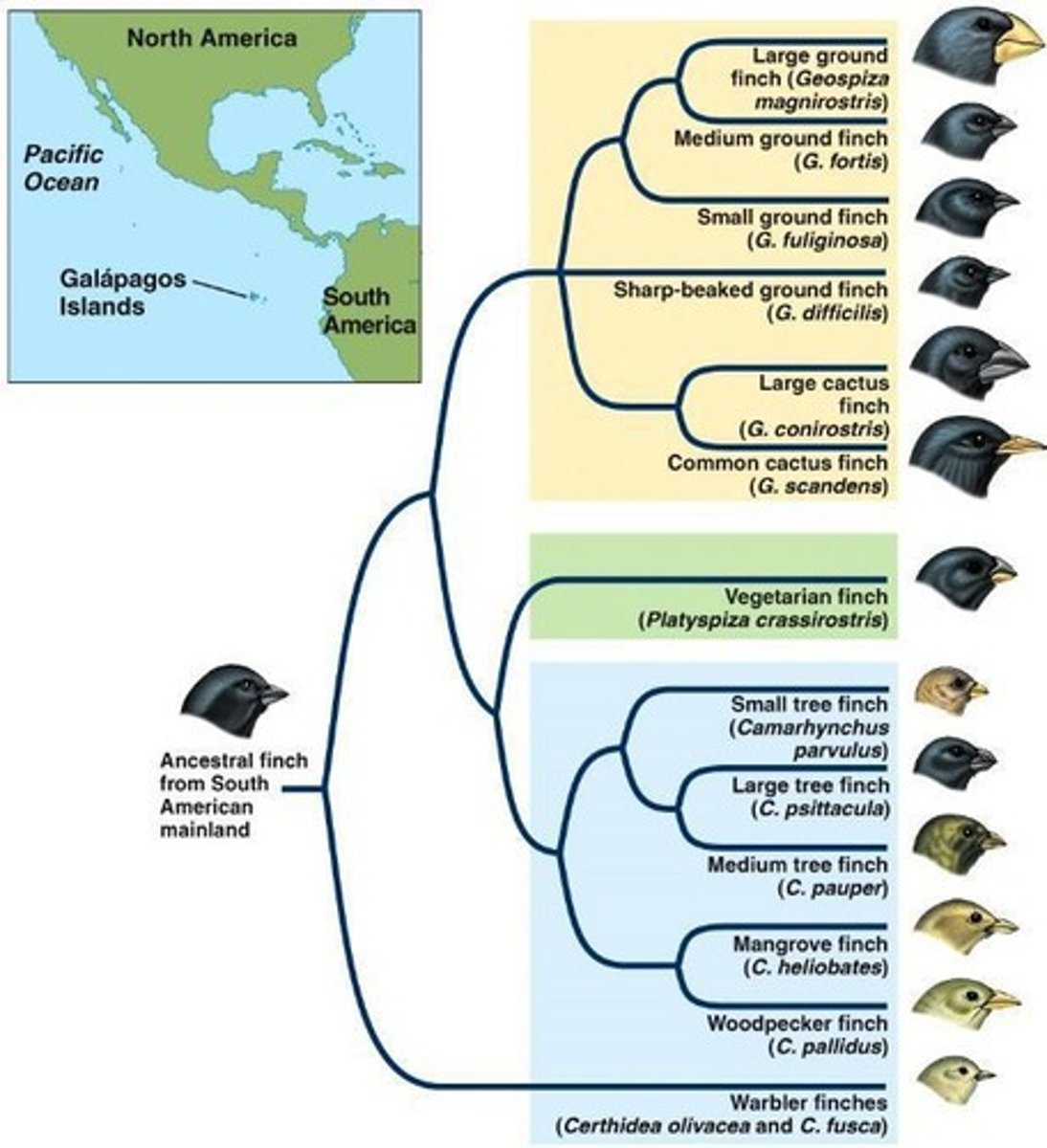
What is an example of allopatric speciation by dispersal?
Finch species in the Galápagos Islands evolved from a single South American species.
What is sympatric speciation?
Speciation that occurs without physical isolation.
How can disruptive selection lead to sympatric speciation?
Individuals with certain genotypes may prefer distinct microhabitats for mating.
What is assortative mating?
A mating pattern where members of subgroups preferentially mate within their own group.
What is the significance of the F1 hybrids in the Dobzhansky-Muller model?
They have reduced fitness due to genetic incompatibility.
What can increase reproductive isolation as species diverge?
Genetic divergence.
What is reinforcement in the context of speciation?
The process that strengthens reproductive isolation between incipient species.
What is the role of genetic drift in allopatric speciation?
It contributes to the divergence of populations after they are separated.
How does environmental adaptation influence allopatric speciation?
Populations adapt to different environments, leading to speciation.
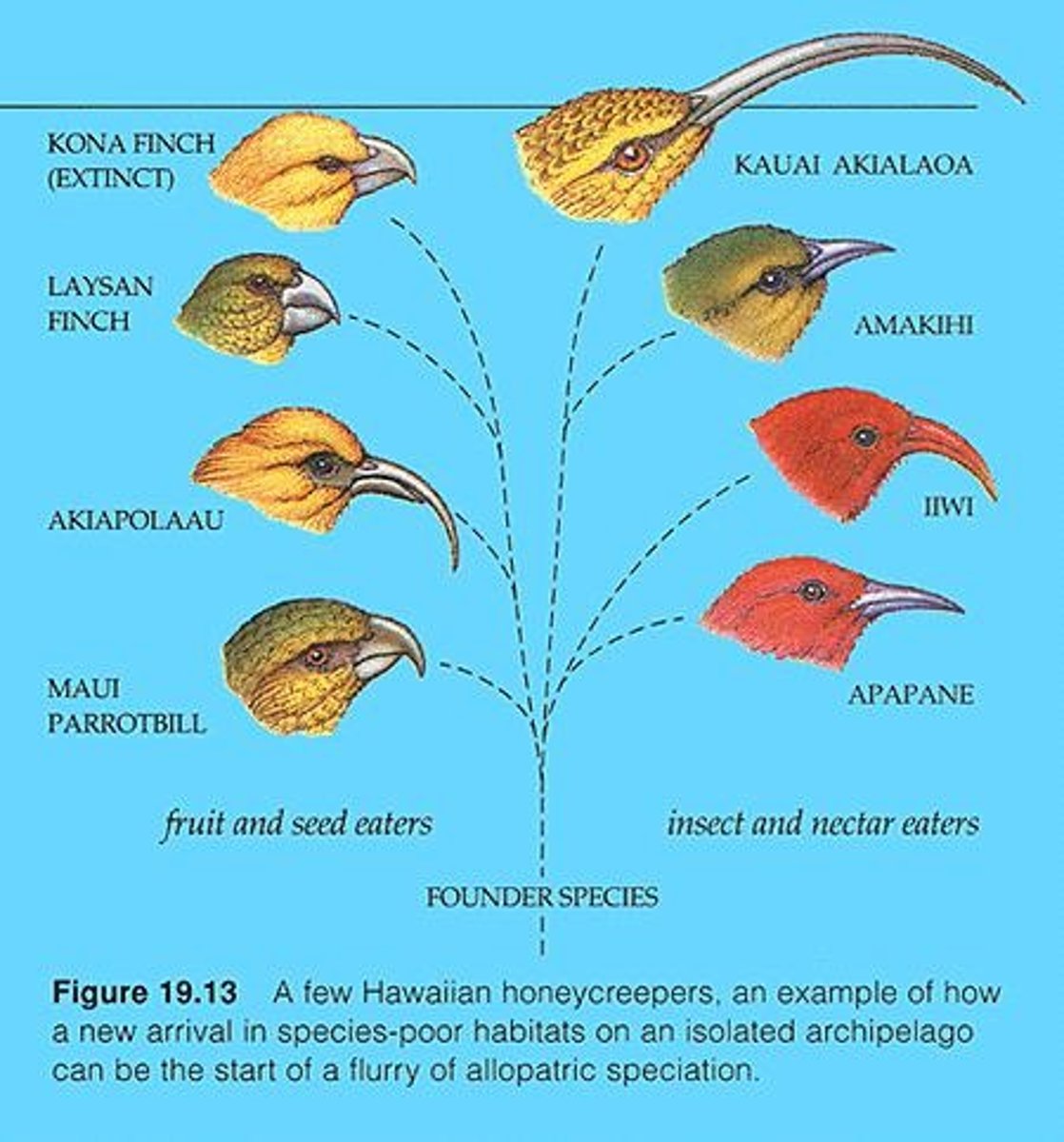
What is an adaptive radiation?
Multiple speciation events that occur when a single species colonizes a new environment.
Why is sympatric speciation considered less likely to happen?
Because it requires mechanisms like disruptive selection and assortative mating without physical barriers.
What is the relationship between genetic divergence and reproductive isolation?
As genetic divergence increases, reproductive isolation also increases.
What is a key factor that can lead to the development of new species in sympatric speciation?
Disruptive selection favoring different microhabitats.
What is the significance of the term 'incipient species'?
It refers to species that are in the early stages of divergence and may become reproductively isolated.
What is assortative mating?
Assortative mating is when members of subgroups preferentially mate within their own group, helping to further differentiate the groups.
What is the dominant mode of speciation among most groups of organisms?
Allopatric speciation is believed to be the dominant mode of speciation.
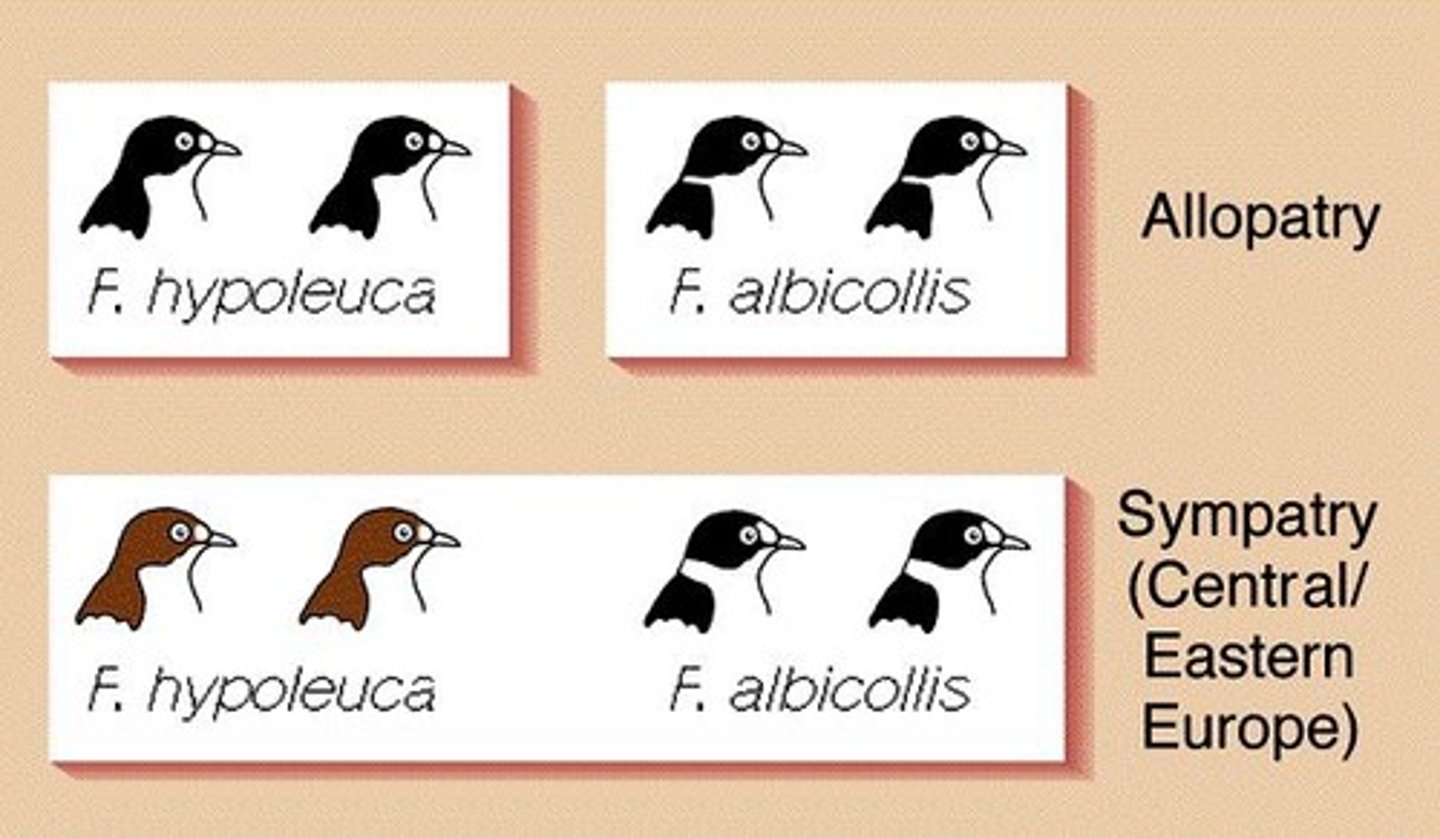
What is sympatric speciation?
Sympatric speciation is the process in which new species arise within the same location as a parent population.
What must be maintained for speciation to occur?
Reproductive isolation must be maintained, regardless of whether the mode of speciation is allopatric or sympatric.
What are incipient species?
Incipient species are populations that are in the process of diverging to the point of speciation but still have the potential to interbreed.
What happens when incipient species come back into contact and hybridization occurs?
If hybrids are equally fit, populations may merge back into a single species; if hybrids are less fit, postzygotic isolating mechanisms may reduce hybrid fitness.
What are postzygotic isolating mechanisms?
Postzygotic isolating mechanisms are genetic differences in diverging lineages that reduce the fitness of hybrid offspring, including reduced genetic compatibility, low hybrid zygote viability, low hybrid adult viability, and hybrid infertility.
What is reinforcement in the context of speciation?
Reinforcement is the process where individuals that do not interbreed with related species have more offspring in the long term, leading to the spread of alleles that contribute to prezygotic isolating mechanisms.
What are prezygotic isolating mechanisms?
Prezygotic isolating mechanisms are traits that prevent hybridization from occurring, such as mechanical isolation, temporal isolation, and behavioral isolation.
What is mechanical isolation?
Mechanical isolation refers to differences in sizes and shapes of reproductive organs that prevent mating.
What is temporal isolation?
Temporal isolation occurs when different species breed at different times of the year or day.
What is behavioral isolation?
Behavioral isolation happens when individuals reject or fail to recognize mating behaviors of other species.
How do sympatric populations evolve compared to allopatric populations?
Sympatric populations are expected to evolve more effective prezygotic reproductive barriers and have stronger reinforcement than allopatric populations.
What is an example of temporal isolation in frogs?
Closely related leopard frog species that breed at different times of the year are an example of temporal isolation.
How can pollinators affect hybridization in plants?
Whether plant species hybridize may depend on their pollinators, influencing reproductive isolation.
What is polyploidy and its role in speciation?
Polyploidy can lead to sympatric speciation in a very short time span, most commonly observed in plants.
What is the significance of hybrid sterility in speciation?
Hybrids that are sterile contribute to reproductive isolation, preventing gene flow between diverging species.
What is the role of postzygotic mechanisms in hybridization?
Postzygotic mechanisms result in selection against hybridization, reinforcing prezygotic isolating mechanisms.
What are some examples of prezygotic isolating mechanisms?
Examples include mechanical isolation, temporal isolation, and behavioral isolation.
What is the relationship between hybrid fitness and speciation?
If hybrid offspring have lower survival and/or fertility, this leads to selection for prezygotic isolating mechanisms.
What is the impact of reinforcement on allele spread?
Reinforcement leads to the spread of alleles that contribute to prezygotic isolating mechanisms within populations.
What is the significance of reproductive isolation in speciation?
Reproductive isolation is crucial for the divergence of species and the maintenance of distinct species over time.
What is the effect of hybridization on incipient species?
Hybridization can either lead to the merging of incipient species or reinforce reproductive isolation depending on hybrid fitness.
How do flower color and shape influence pollinators?
They attract specific pollinators and alter where pollen is deposited.
What are the main pollinators for different species of columbines?
Some are pollinated by hummingbirds, others by hawkmoths or butterflies.
What is habitat isolation in the context of reproductive isolation?
It occurs when closely related species evolve preferences for living or mating in different habitats.
Give an example of habitat isolation.
Apple maggot flies.
What is gametic isolation?
It is when the sperm and eggs of different species do not fuse, important for aquatic animals that release gametes into the water.
What happens when reproductive isolation is incomplete?
Hybrid zones may form where population ranges overlap.
What is a characteristic of hybrids in hybrid zones?
Hybrids suffer from a range of defects and are not as fit as purebred individuals.
What is an example of temporal isolation?
The spring field cricket and the fall field cricket, which mate in different seasons.
What is the Biological Species Concept?
It does not apply to organisms that reproduce asexually and is based on reproductive isolation.
What model of speciation is expected for Hawaiian fruit flies?
Allopatric speciation by dispersal.
How can you determine if phylogenetic trees show the same or different relationships?
By comparing the branching patterns and relationships depicted in the trees.
If the frequency of an allele is 0.5 in a population of 300 diploid individuals, how many copies of this allele are present?
300 copies.
In a population of 500 rabbits with p=0.2, what are the expected frequencies of black and white phenotypes?
0.64 black; 0.36 white.
What are the expected allele frequencies if 100 white individuals emigrated from the rabbit population?
p = 0.36; q = 0.64.
What are the three types of rock?
Igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic.
How are fossils formed?
Fossils form in sedimentary rocks under low temperature and anaerobic conditions, compressed over time.
What type of organisms are best preserved in the fossil record?
Aquatic organisms with hard skeletons.
Under what circumstances does preservation of soft tissue occur?
It occurs under rare circumstances.
What major forces shaped the history of life on Earth?
Geologic and atmospheric forces.
What is the significance of sedimentary rocks in paleontology?
Most fossils are formed in sedimentary rocks.
What is the general timeline for major events in Earth's history?
It includes significant transitions and events that can be identified through the fossil record.
What is the role of scientists in determining the ages of rocks and fossils?
They use various dating methods to establish the timeline of geological and biological events.
What rare circumstances allow for the preservation of soft tissue?
Preservation of soft tissue only occurs under rare circumstances.
How can sedimentary rocks be dated relatively?
Sedimentary rocks can be given relative dates by the principles of stratigraphy, where younger layers are deposited on top of older layers.
What is the order of fossil appearance in different outcrops?
Fossils appear in the same order in different outcrops.
What are the younger and older fossils mentioned in the notes?
Younger fossils include snails, brachiopods, clams, ammonites, and trilobites.
How are the relative ages of rocks determined?
Relative ages of rocks are determined by stratigraphy, where layers are young at the top and older at the bottom.
What is the role of radioisotopes in dating igneous rocks?
Igneous (volcanic) rock contains radioisotopes that are used for dating strata and the fossils they contain.
What is radiometric dating?
Radiometric dating determines actual ages of rocks using the predictable decay of radioisotopes.
What is half-life in the context of radiometric dating?
Half-life is the time in which half of the remaining radioisotope decays into another element.
How can we determine how long since a rock was formed?
By measuring the ratio of parent to daughter atoms.
What happens to the amount of carbon-14 in an organism after it dies?
The amount of 14C in an organism starts to decrease after it dies.
What is true about carbon-14 decay?
14C decays at a constant rate.
Why is carbon-14 not useful for dating fossils older than 250 million years?
14C would not be useful for fossils expected to have formed over 250 million years ago.
What fraction of a radioactive substance remains after 2,000 years if its half-life is 500 years?
One-sixteenth of the original material is left after 2,000 years.
What geological time scale is developed using various dating methods?
A geological time scale is developed using various dating methods and fossil stratigraphy, dividing Earth's history into eras and periods.
What do the boundaries between geological divisions indicate?
Boundaries between divisions are based on abrupt changes in fossil organisms.
What significant evolutionary event occurred around 3.3 billion years after the first appearance of life?
The expansion of multicellular life.
What is the state of the fossil record?
The fossil record is incomplete; most organisms decompose quickly after death.
What conditions favor fossilization?
Fossilization occurs only when organisms are at sites with no oxygen and where decomposition is very slow.
Which types of organisms are more likely to be preserved as fossils?
Marine organisms and those with hard shells or exoskeletons are more likely to be preserved.
What geological processes can affect fossil preservation?
Geologic processes can transform rocks and destroy fossils or bury them too deeply to be accessible.
What was Alfred Wegener's contribution to geology?
Alfred Wegener suggested the idea of continental drift in 1912.
What evidence supported Wegener's theory by the 1960s?
Evidence of plate tectonics convinced geologists that Wegener was correct.
How do plate tectonics influence Earth's environment?
Plate tectonics shapes the position and size of continents, influencing oceanic circulation patterns, global climate, and sea level.
What major environmental event can result from large volcanic eruptions?
Large volcanic eruptions can inject ash and SO2 into the atmosphere, blocking sunlight and causing cooling, which can lead to increased glaciation and mass extinctions.
What was the early atmosphere's oxygen concentration likely like?
It probably had little or no O2.
What significant role did cyanobacteria play in Earth's history?
Cyanobacteria formed stromatolites and released O2, allowing for oxidation reactions as an energy source for ATP synthesis.
How did the evolution of chloroplasts occur in relation to cyanobacteria?
Cyanobacteria were incorporated into eukaryote host cells as chloroplasts evolved.
What happened to organisms with aerobic metabolism as oxygen levels increased?
They replaced anaerobes in most of Earth's environments.
When did life first appear on Earth?
About 3.8 billion years ago.
When did eukaryotes evolve?
About 1.5 billion years ago.
What characterized the late Precambrian era?
Many kinds of multicellular soft-bodied animals evolved, some of which may have no living descendants.
What was the Cambrian explosion?
A rapid diversification of life known as an evolutionary radiation that occurred during the Cambrian period (542 - 488 mya).