WC Prescription
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
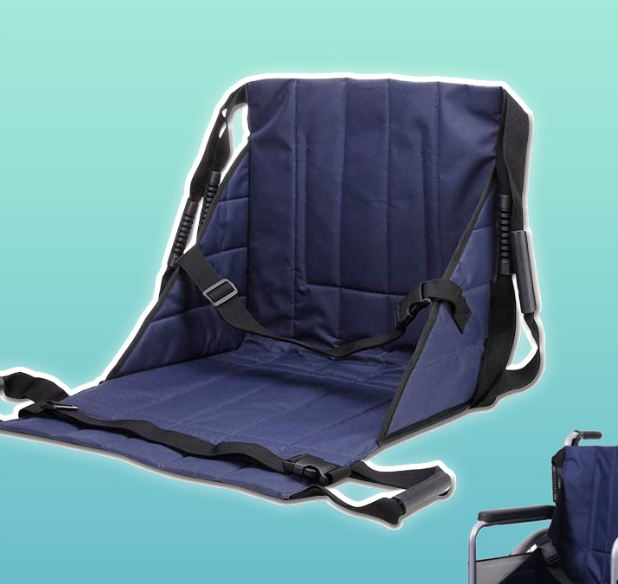

Parts of a WC: Seating
_______- standard on w/c
Disadvantage: hips tend to slide forward
Sling seat
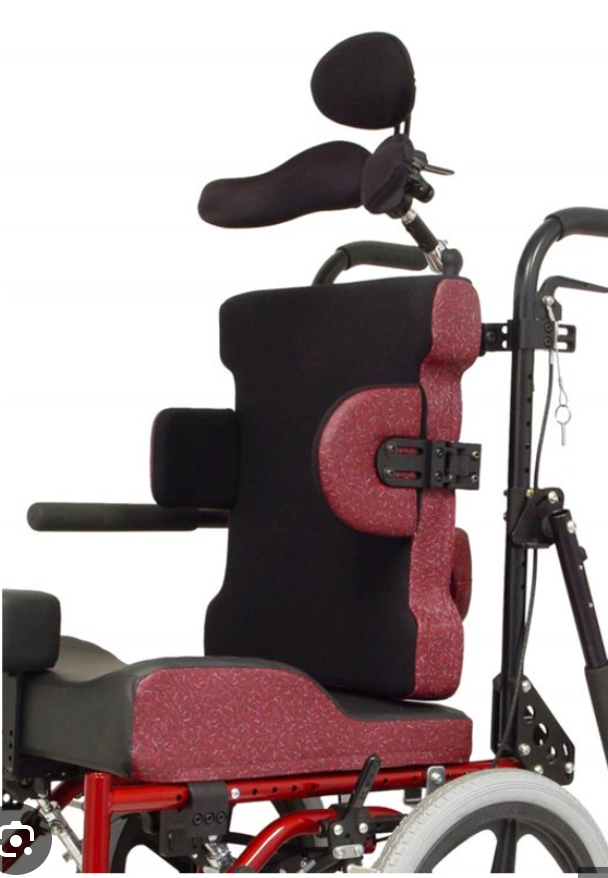

Parts of a WC: Seating
______ : Creates stable, firm surface
Improves pelvic position
Reduce tendency of pt sliding forward
Insert or Contour Seats
Parts of a WC: Seating
_______: Distributes WB pressures
Pressure - relief push ups are required every ______ mins
Seat Cushions
15-20 mins
Parts of a WC: Seat Cushions
______: most common
_________: Heaviest, efficient but high maintenance
_________: Light, expensive, high maintenance
Pressure-relieving foam
Pressure-relieving gel
Pressure-Relieving Air Cushion


Parts of a WC: Back
________: caters the midscapular region, Standard W/C
Mid-back rest

Parts of a WC: Back
________: poor trunk stability
High Back Rest

Parts of a WC: Back
________: Good to normal trunk stability
Low-Back Rest

Parts of a WC: Back
________: improves trunk extension and improves over-all alignment
Insert or Contour Backs
Parts of a WC: Back
________: Improve trunk alignment for patients with scoliosis
Lateral Trunk Support
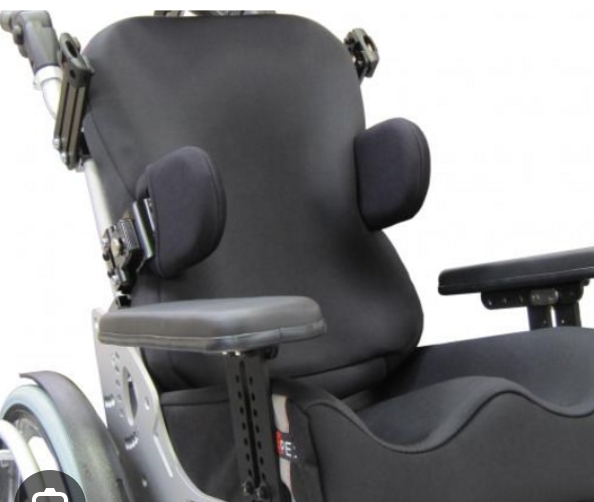

Parts of a WC: Arm Rest
________ : covers the whole length of the wheelchair
used for transfers in and out of wc
Full Length

Parts of a WC: Arm Rest
_________ : good for patient who goes to office
perfect for working on normal tables
Desk-Length
Parts of a WC: Arm Rest
______: fixed
Fixed-Height
Parts of a WC: Arm Rest
________: can accommodate STS transfers & better for UE
Adjustable- Height
Parts of a WC: Arm Rest
__________: To accommodate bed to w/c transfers
Removable
Parts of a WC: Arm Rest
________: used if pt needs a bigger arm rest or more cushion
Wrap Around (Space Saver)
Parts of a WC: Arm Rest
________: provides additional postural assistance
UE Support Surface

Parts of a WC: Leg Rest
______: Standard leg strap
______: Used for transfers
fixed
swing away
Parts of a WC: Leg Rest
________
Edema
CI: severe extensor spasticity
Elevating
Parts of a WC: Leg Rest
_______
Provides a resting base for feet
Foot Plates
Parts of a WC: Leg Rest
______: Prevents posterior sliding of the foot
______: To stabilize feet on foot plates
Heel loops
Straps

Other Types of Leg Rest

Parts of a WC: WC Frames
_______: Promotes mobility, easy transport and storage
Folding Type
Parts of a WC: WC Frames
______: Promotes stability, increases stroke efficiency, inc distance per stroke, independent w.c users
Rigid Type
Parts of a WC: WC Frames
________ : greater ease of use, sports, titanium made
Light Weight
Parts of a WC: WC Frames
_______: Active w/c user, good UE strength
Heavy Duty
Parts of a WC: Drive Wheels
T/F: Medium rear wheels used for propulsion
False → Large
Parts of a WC: Drive Wheels
_______: to facilitate propulsion in patients with poor hand grips
Projection Rims
Parts of a WC: Drive Wheels
_______: inc hand grip
Friction rim/Leather Gloves
Parts of a WC: Drive Wheels
________: Small front wheels, 8 in diameter
Caster Wheels
Parts of a WC: Drive Wheels
________: Spoke or spokeless
Wheel Construction
Parts of a WC: Tires
_______: Durable, low-maintenance
Standard Hard Rubber Tires
Parts of a WC: Tires
______
Provide smoother ride, inc shock absorption
Light-weight w/c, less durable
Pneumatic
Parts of a WC: Brakes
W/C Caregiver Propelled

Parts of a WC: Additional Attachments
_______
should grasp the pelvis at a 45° angle to the seat
Seat Belts (Pelvic Positioner)


Parts of a WC: Additional Attachments
_______
maintain alignment; adductor pommel, prevents adductor spasticIty
Seat Positioners

Parts of a WC: Additional Attachments
_______
add lateral trunk support
_____
posterior extensions attached to lower horizontal support
Seat Back Positioners
Anti-Tipping Device

Parts of a WC: Additional Attachments
_______
a mechanical brake that allows the chair to move forward, but automatically brakes when the chair goes in reverse.
Useful for patients who are not able to ascend a long ramp or hill
Hill-Holder Device

Specialized WC
_______
indicated for patients who are unable to independently maintain an upright posture
Reclining w/c
Specialized WC
________
Entire seat and back tipped backwards
Indicated for pt with extensor spasticity
Tilt in Space
Specialized WC
_______
drive mechanism is located on one wheel usually with two outer rims
is not recommended for patients with spatial deficits
One Arm Drive
Specialized WC
______
Designed to be low to the ground
Hemiplegic Chair
Specialized WC
_______
modified by placing the drive wheels posterior to the vertical back supports (~2 in backwards)
Amputee Chair
Specialized WC
________
heavy-duty, extra wide wheelchair designed for obese
Rear axle is displaced forward – allows more efficient arm push
Hard tires
Adjustable backrest accommodate excessive posterior bulk
Reclining wheelchair – accommodate excessive anterior bulk
Bariatric w/c
Specialized WC
________
Oblique wheels to inc stroke efficiency low back height for mobility rigid frame
Sports Wheel Chair
WC TYPES (Pierson & Fairchild)
_________
Designed for persons who weigh less than 200 lb and for limited use on rough surfaces; not designed for vigorous functional activities
Standard Adult
WC TYPES (Pierson & Fairchild)
_________
Constructed for persons who weigh more than 200 lb or for those who perform vigorous functional activities
Heavy Duty Adult
WC TYPES (Pierson & Fairchild)
_________
Designed to be lightweight, may have a rigid or folding frame, and can be made with titanium in a rigid or folding frame;
weighs from 12 to 30 lb
benefit is efficiency in propulsion and reduction in cumulative trauma in the UE; weight capacity to 300 lb
Ultralight wheelchair
WC TYPES (Pierson & Fairchild)
_________
Designed for persons with a body build smaller than that of an adult but larger than that of a child
Intermediate or junior
WC TYPES (Pierson & Fairchild)
_________
Designed to permit adjustments in the frame to accommodate the growth of the user
Growing
WC TYPES (Pierson & Fairchild)
_________
Designed for persons up to the approximate age of 6 y/o
Child or youth
WC TYPES (Pierson & Fairchild)
_________
Constructed for use indoors, with the larger drive wheels placed at the front of the chair and the caster wheels at the rear;
Functions better in confined areas
more difficult to propel and perform many functional activities
Indoor
WC TYPES (Pierson & Fairchild)
_________
The seat is lowered ~ 2 inches to allow better use of the user’s lower extremities to propel the chair
However, the lower seat may make it more difficult for the user to perform a standing transfer
Hemiplegic
WC TYPES (Pierson & Fairchild)
_________
The rear wheel axles are positioned ~ 2 inches posterior to their normal position to widen the base of support of the chair
Compensate for the loss of the weight of the user’s lower extremities
Amputee
WC TYPES (Pierson & Fairchild)
_______
Two hand rims are fabricated on one drive wheel, and the two drive wheels are connected by a linkage bar;
smaller hand rim propels the near drive wheel
large hand rim propels the far drive wheel
when both rims are moved simultaneously, both wheels are propelled
One Hand Drive
WC TYPES (Pierson & Fairchild)
_________
The chair is propelled by a deep-cycle battery system, and various types of controls are used to operate the chair (e.g., a joystick, a chin piece, or a mouth stick)
Externally powered
WC TYPES (Pierson & Fairchild)
_______
A low-profile, fixed frame, lightweight (15-24 lb) chair with features such as a low back, canted rear wheels, fixed or adjustable axles, and fixed or adjustable seat and backrest
can be bought or customized for various sports activities
Sports
WC TYPES (Pierson & Fairchild)
_________
Used for persons who need to partially or fully recline at some time when they are in the chair;
chair may be a semi-reclining or fully reclining chair
Semi-reclining chairs recline to ~ _____ ° from ____
Fully reclining chairs can recline to a ______ position
elevating leg rests and headrest extensions are necessary components for these chairs
Reclining Chairs
~30° from vertical
horizontal position
Submit for
PART 2 :000