Platyhelminthes (Digeneans, Monogeneans, Cestodes)
1/71
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Quiz 3 + Test 3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
Platyhelminthes
-Has acoelomate
-Bilateral symmetry
-Definite anterior end
-Flattened dorso-ventrally (with exceptions)
-Hermaphroditic (with exceptions)
-Tegument (covers surface of worm)
Digeneans
Trematodes
Digenean
-Type of Platyhelminth
-Consists of flukes
-Polyembryony>sporocysts>cercariae
-Eggs have miracidium
-Sporocysts have rediae
Liver flukes
Consists of:
1) Fasciola
2) Dicrocoelium
3) Clonorchis
Liver flukes
These flukes infect the bile ducts. Larvae move through the lumen/tissue.
Fascioliasis (Liver rot)
What disease does Fasciola hepatica cause?
Ruminant (cow/sheep)
What is the definitive host for Fasciola hepatica?
Snail
What is the intermediate host for Fasciola hepatica?
Fasciola hepatica
What parasite has this life cycle?

Accidental host
What do humans serve as in the life cycle of Fasciola hepatica?
Acute Fascioliasis
-Pre-adult migration
-Large number of metacercariae at once
-Hemorrhagic tracts and inflammation
-Sudden death during pre-patent period (~8 weeks)
-No clinical symptoms
Chronic Fascioliasis
->12 weeks
-Ingestion of moderate amount of metacercariae
-Damage in liver
-Fibrosis, blockage, inflammation
-Leads to anemia, “bottle jaw”, and progressive weakness
Dicrocoeliasis
What disease does Dicrocoelium dendriticum cause?
Dicrocoelium dendriticum
Parasite is also called little liver fluke/lancet fluke.
Dicrocoelium dendriticum
What parasite has this life cycle?
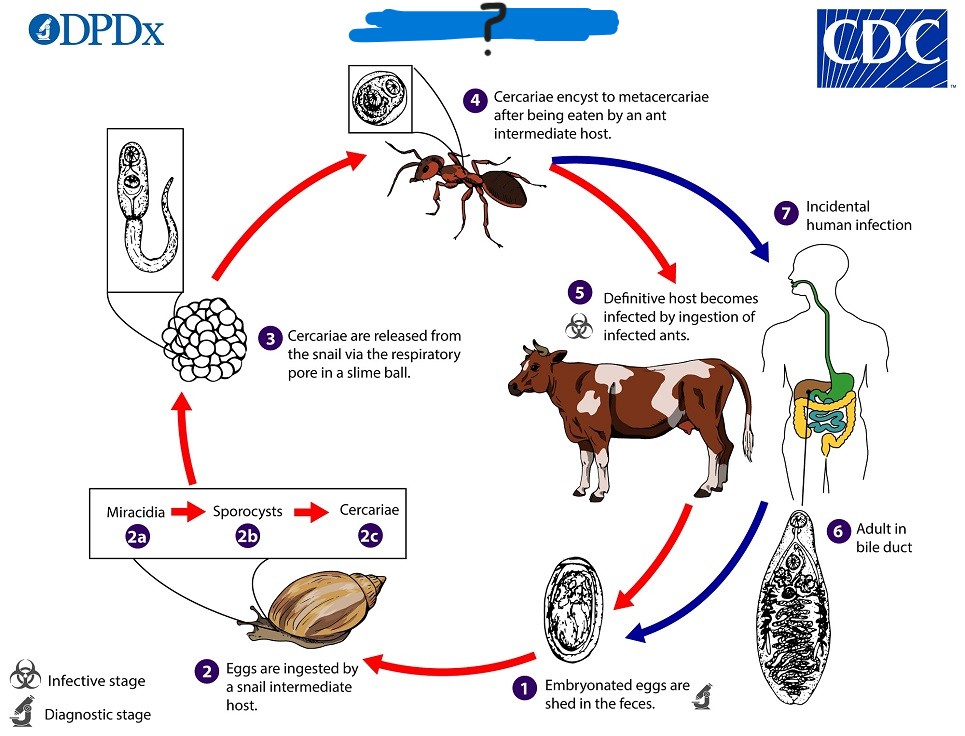
Dicrocoeliasis
-Uses common bile duct
-Duct becomes inflammatory
-Pathology is burden-dependent
-Granulomas/cirrosis
Clonorchis sinensis
Parasite also known as human liver fluke.
Clonorchiasis
What disease does Clonorchis sinensis cause?
Clonorchis sinensis
What parasite has this life cycle?
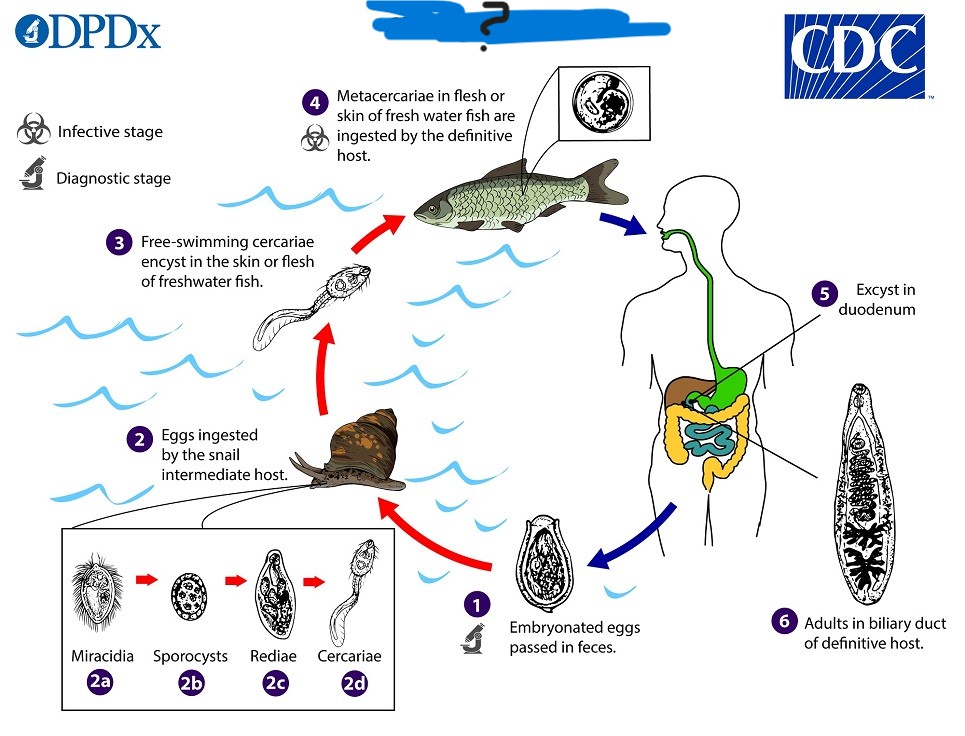
Cats
What can act as a reservoir host for Clonorchis sinensis?
Clonorchiasis
-Symptoms depend
-Pathogenesis: mechanical damage of the liver due to movement of worm
-Excretory-Secretory products>mitogenic>hyperplasia
-Immune-mediated
-Creates environment for cancer development
Heterophyes heterophyes
What parasite has this life cycle?
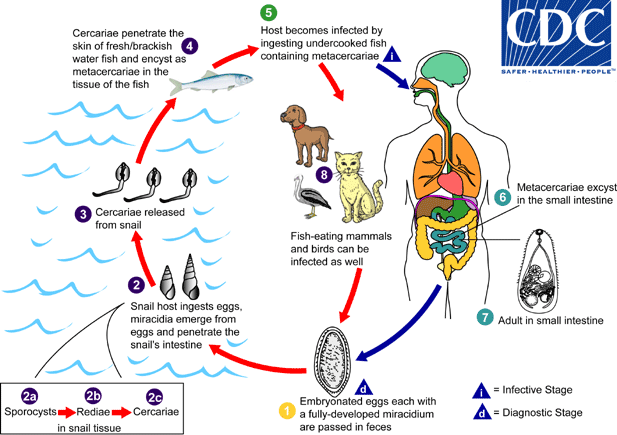
Heterophyiasis
What disease does Heterophyes heterophyes cause?
Heterophyiasis
-Ectopic infection in brain, lymph nodes, and myocardium
-Diarrhea and abdominal pain
-In Philippines, 15% myocardiatic
Ribeiroia ondatrae
What parasite has this life cycle?
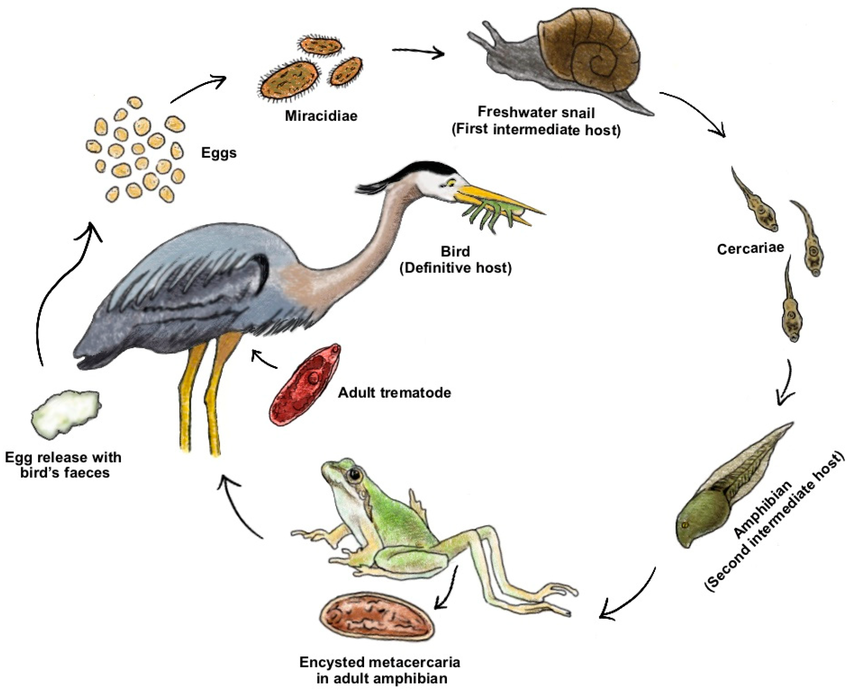
Ribeiroia ondatrae
This parasite has an additive effect with pollution and causes frogs to grow additional limbs.
Blood flukes
Consists of:
-Cardicola
-Schistosoma
-Trichobilharzia
Blood flukes
These flukes are endoparasites that live in the circulatory system. They release eggs through blood vessels and create granulomas.
Schistosoma spp.
What parasite has this life cycle?
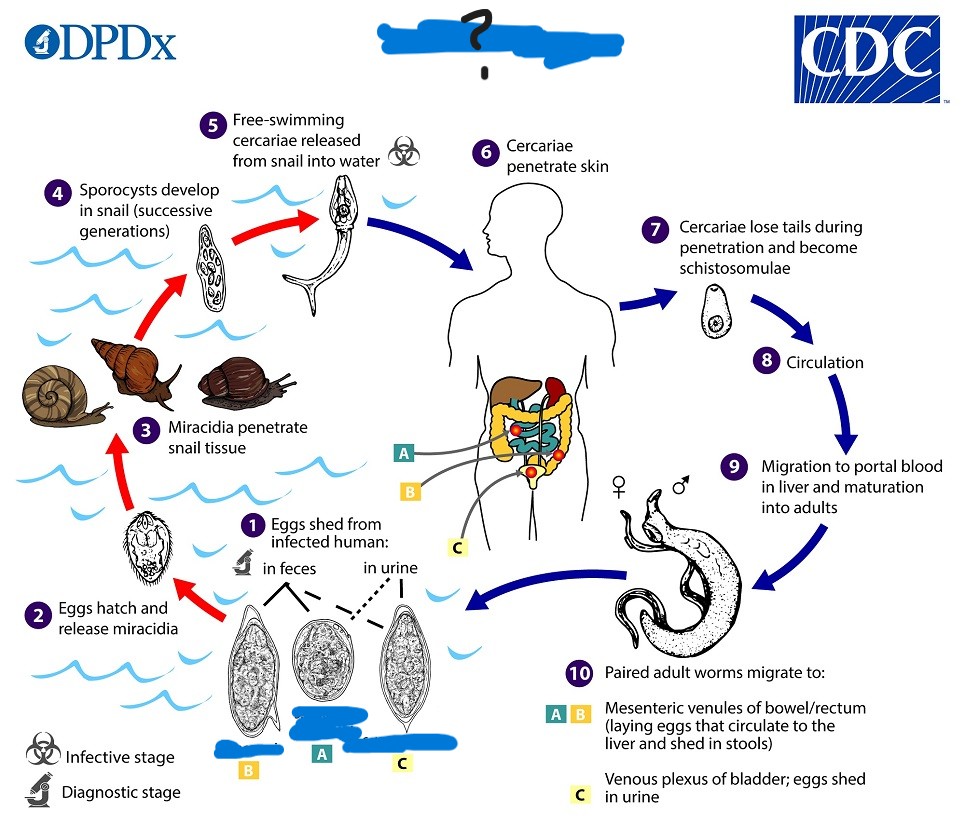
S. mansoni
This species of Schistosoma:
-Lives in mesenteric veins that connect to large intestine (eggs shed in feces)
-RH=Monkeys and rodents
-Range:Africa, Caribbean, South America
S. japonicum
This species of Schistosoma:
-Lives in mesenteric venules that connect to small intestine (eggs shed in feces)
-RH=Horses, dogs, cats, etc.
-Range=Asia
S. haematobium
This species of Schistosoma:
-Lives in veins of urinary bladder and uterus (eggs shed in urine)
-No RH
-Range=Africa
Gastropods
Immune evasion in ________:
-Immunosuppression
-Molecular mimicry of host antigens
Vertebrates
Immune evasion in ________:
-Eggs use granulomas to survive and move through walls of gut via degradation of host tissues to exit
Schistosomiasis
What disease does Schistosoma spp. cause?
Migratory phase
What disease phase of Schistosomiasis is being described below:
-Penetration of cercariae
-Cutaneous allergy to parasite’s products (hives, dermatitis)
-Migration of schistosomules to lung capillaries
-May be asymptomatic
Acute phase
What disease phase of Schistosomiasis is being described below:
-Maturation of parasite
-Oviposition
-Can be asymptomatic or symptomatic
-Signs include fever, diarrhea, prostration
-Immune response
Chronic phase
What disease phase of Schistosomiasis is being described below:
-Cell mediated response to eggs creates granulomas
-Can cause fibrosis, hepato-splenomegaly, ascites
PZQ, yes
What is the only drug available for Schistosomiasis? Is there resistance?
Cercal dermatitis (Swimmer’s itch)
What disease is being described:
-Humans serve as unsuitable definitive hosts
-Penetrates skin and creates itching rash
-Present throughout the world
Haptor
What is the morphological feature for Monogeneans?
Gyrodactylus spp.
All Monogeneans are oviparous, except for which spp.?
Oncomircidium
What life cycle stage is unique to Monogeneans?
Monogeneans
Consists of:
-Dactylogyrus spp.
-Gyrodactylus spp.
-Diplozoon spp.
Polystomes
Consists of:
-Pseudodiplorchis americanus
Dactylogyrus spp.
-DH=Freshwater or marine fishes
-Distrubution=Worldwide
-Habitat=Gills
-Pathogenesis=Mucus on gills, acute infections (short period of dyspnea)
-Oviparous
Gyrodactylus spp.
-DH=Salmon, eels, etc.
-Habitat=Skin, gills, fins
-Pathogenesis=Mucous, epithelium
-Ovoviviparous
Diplozoon spp.
-Fused adults (two diporpa fuse into 1 adult)
-DH=Cyprinid fish (freshwater)
-Habitat=Gills
-Distribution=Europe, Africa
Pseudodiplorchis americanus
-DH=Spadefoot (desert) toad
-Habitat=Urinary tract
-Life cycle of parasite is synced with host’s
-Oncomiracidium live in lungs/respiratory system when host is a tadpole, then migrate to urinary tract as host becomes an adult frog
Monogenean
-Type of Platyhelminth
-1 oral sucker
-Blind bifurcated intestine
-Monoxenous
-Oviparous (with exception)
-Hermaphroditism
Cestode
-Type of Platyhelminth
-All mesoparasites
-All intestinal worms as adults
-All parasitic
-DH=Vertebrates
-Habitat=Intestinal
-No digestive tract
Scolex
What is the morphological feature of cestodes?
Cestodes
Tapeworms
Proglottid
What is the segments of a tapeworm called?
Coracidium
Free-living hexacanth (only in aquatic species)
Humans
These parasites infect who? :
-Taenia saginata
-Taenia solium
Animals (Zoonosis)
These parasites infect who? :
-Echinococcus granulosus
-Diphyllobothrium latum
-Diphyllobothriid spp.
Taenia saginata
This Taenia spp. uses a cow as its intermediate host.
Taenia solium
This Taenia spp. uses pigs as its intermediate host.
Taenia spp.
What parasite has this life cycle?
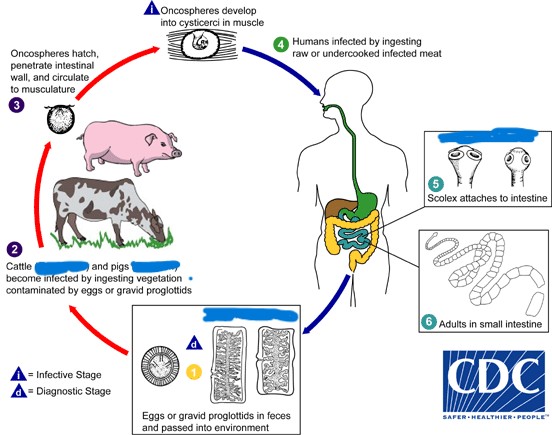
Taenia solium
What Taenia spp. causes Cysticercosis?
Taeniasis
-Caused by ingesting raw or undercooked meat
-Can be asymptomatic or symptomatic based on burden
-Passage of migrating proglottids
Cysticercosis
-Caused by humans ingesting eggs of parasite
-Humans act as accidental, unsuitable “intermediate” hosts
-Cysticerci develop in brain and lead to neurocysticerci
-Re-emerging disease
Diphyllobothrium latum
-DH=fish-eating mammals
-Broad fish tapeworm
-Two IHs
-Stages include procercoid and plerocercoid
Intermediate/Paratenic host
What do humans serve as in the life cycle of Diphyllobothrium latum?
Diphyllobothriasis
What disease does Diphyllobothrium latum cause?
Diphyllobothriasis
-Can be asymptomatic
-Vague abdominal discomfort
-Diarrhea
-Avitaminosis B12 (pernicious anemia)
Diphyllobothrium latum
What parasite has this life cycle?
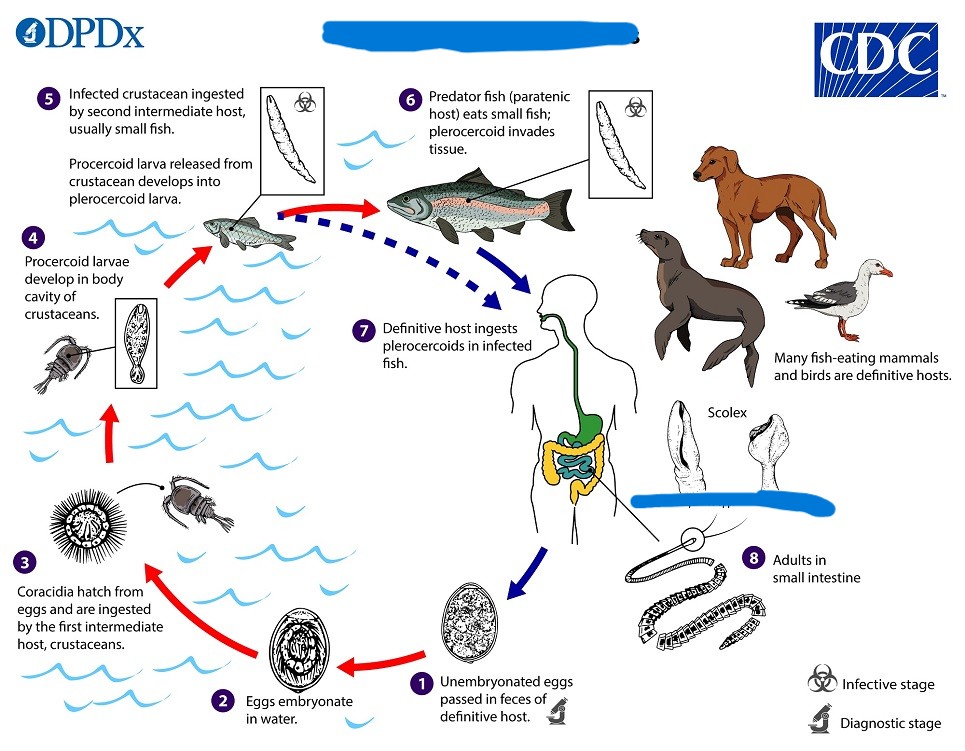
Sparganosis
-Caused by drinking water contaminated with infected copepods
-Zoonosis disease
-Caused by migrating sparganum
-Can be cutaneous or cerebral
-Inflammation
Echinococcus granulosus
What parasite causes hydatid disease?
Echinococcus granulosus
What parasite has this life cycle?
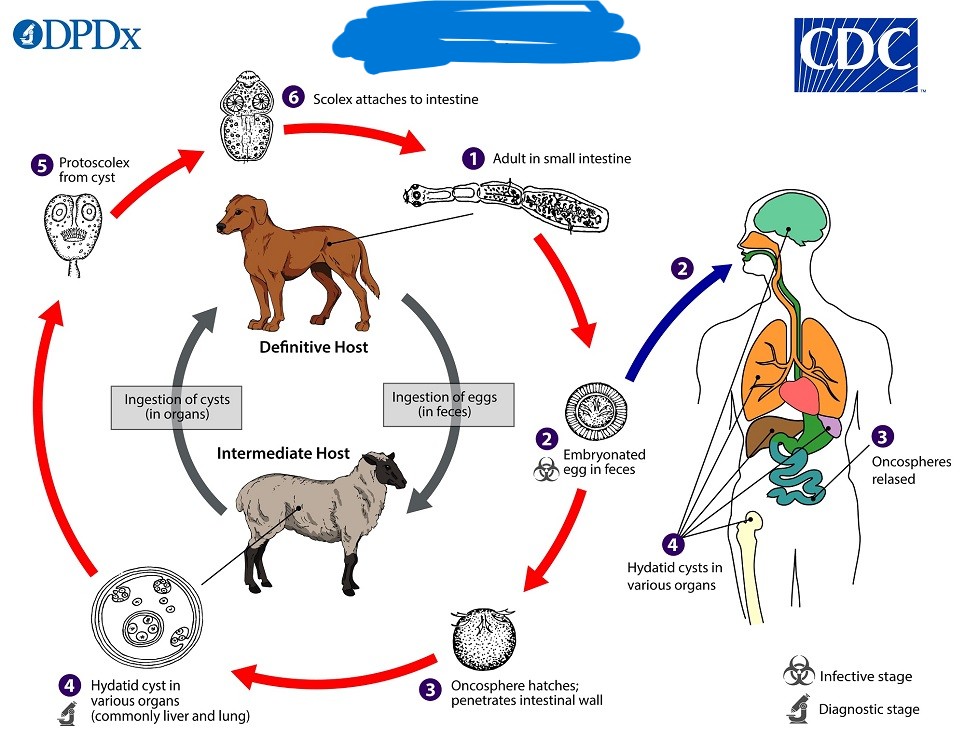
Intermediate hosts
What do humans serve as in the Echinococcus granulosus life cycle?