Bot-Lec (Sem-1) - Chapter 9: Gymnosperms
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
seed
a reproductive body consisting of a young, multicellular plant and food reserves, enclosed by a seed coat (testa); reproductively superior to spores
radicle; cotyledon; testa; arils; embryo; haploid gametophyte
parts of a gymnosperm seed
radicle
part of a gymnosperm seed; embryonic root
cotyledon
part of a gymnosperm seed; embryonic leaves
testa
part of a gymnosperm seed; seed coat; parental sporophyte tissue
aril
part of a gymnosperm seed; an extra seed-covering, typically colored and hairy or fleshy
embryo
part of a gymnosperm seed; daughter sporophyte (diploid)
haploid gametophyte
part of a gymnosperm seed; food supply
scale
part of a pine cone; from where the ovules (which develop into seeds) are borne
spores
a single cell with minimal food reserves to sustain the plant that develops from a germinating spore
ovule
structure in seed plants that develops into a seed following fertilization
integument
outer layer of an ovule that develops into a seed coat following fertilization
gymnosperm
any of a group of seed plants in which the seeds are not enclosed in an ovary; seeds are either totally exposed or borne on scales of cones; produce wind-borne pollen grains
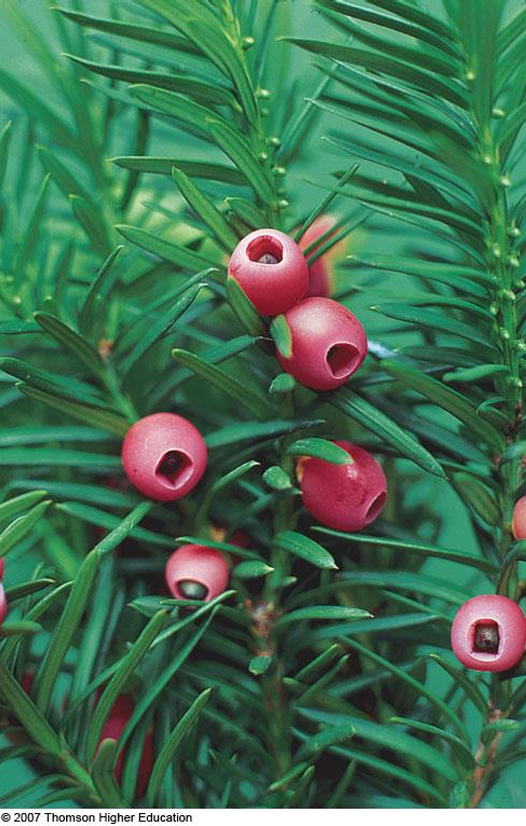
Taxus baccata
European yew/yew berries; gymnosperm that is often mistaken for an angiosperm due to the fleshy aril of the seeds

pollen grain
structure in seed plants that develops from a microspore into a male gametophyte
coniferophyta (conifers); cycadophyta (cycads); ginkgophyta (ginkgoes); gnetophyta (gnetophytes)
four phyla of gymnosperms
coniferophyta (conifers)
woody trees and shrubs with needlelike, mostly evergreen leaves, and seeds in cones; mostly monoecious; the most predominant trees (about 35% of the world’s forests)
strobilus
an aggregation of sporophylls resembling a cone (as in the club mosses and horsetails)
evergreen
a plant which has foliage that remains green and functional throughout the year
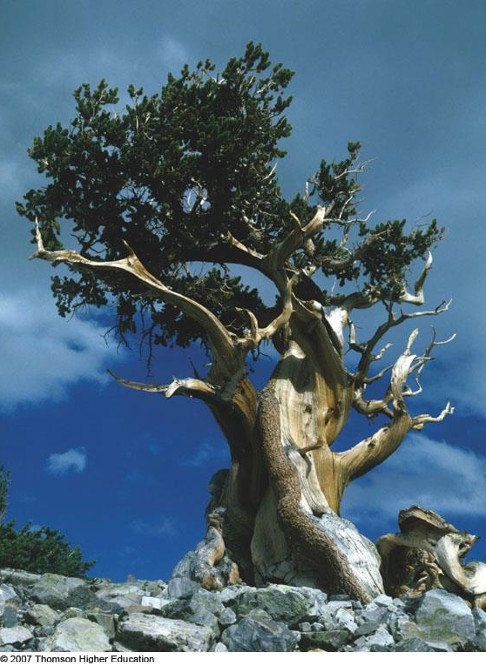
Pinus longaeva
conifer; bristlecone pine; one of the longest-living species of tree on Earth (world record: approx. 5,000 years old)

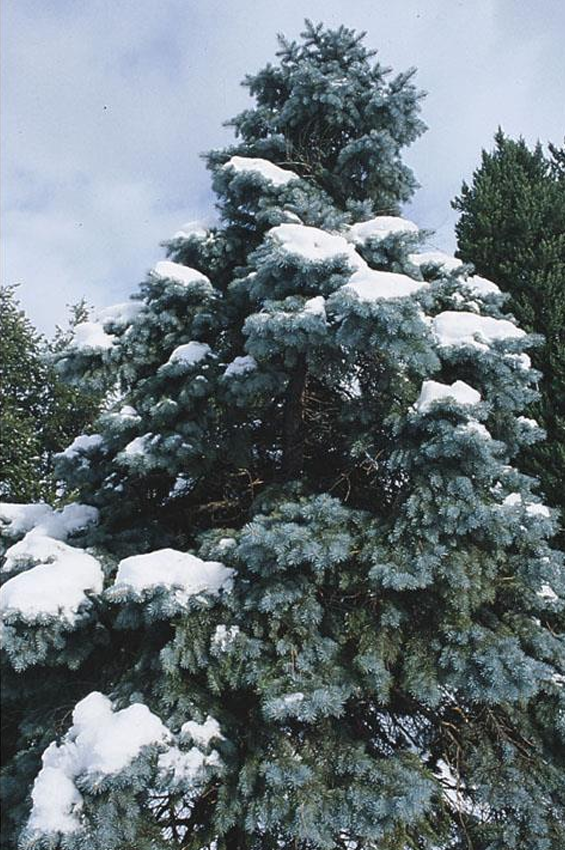
Picea pungens
conifer; Colorado blue spruce

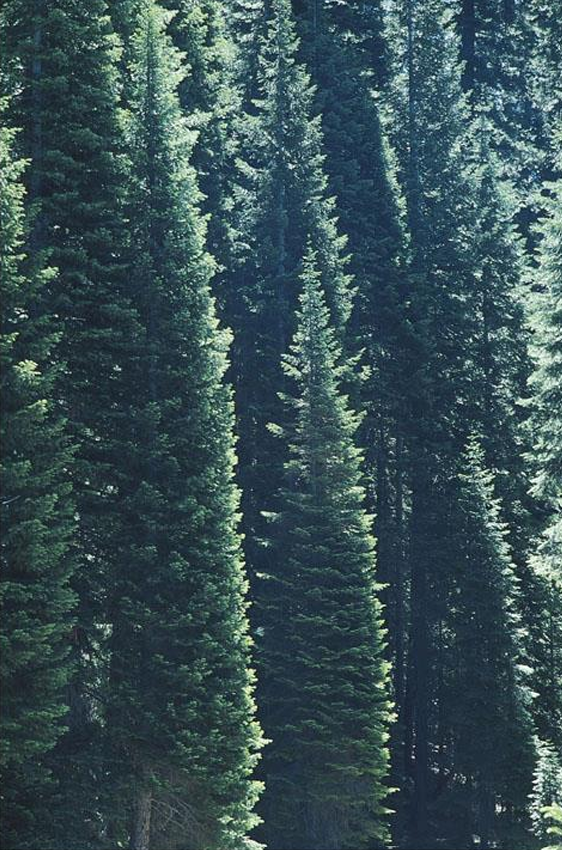
Abies concolor
conifer; white fir

Pinus strobus
conifer; white pine; leaves are long, slender needles that occur in clusters of five
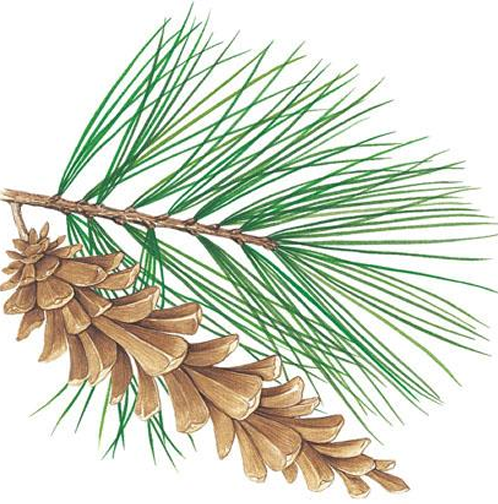

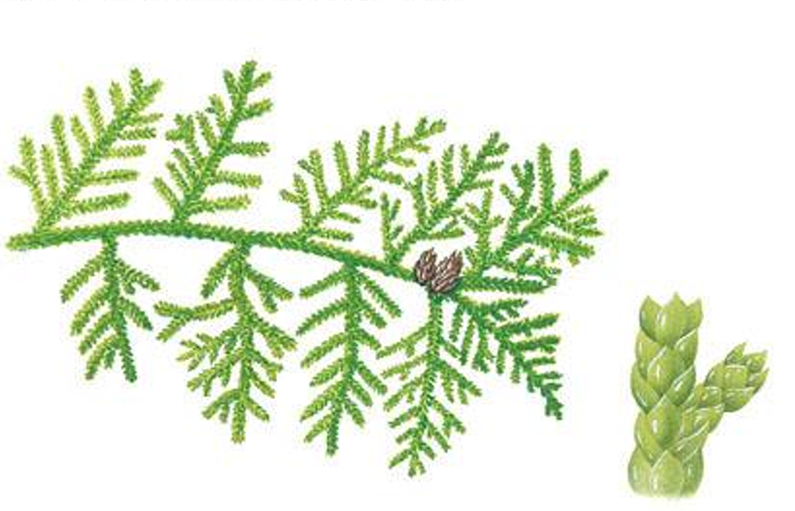
Thuja occidentalis
conifer; American arborvitae; leaves are small and scale-like
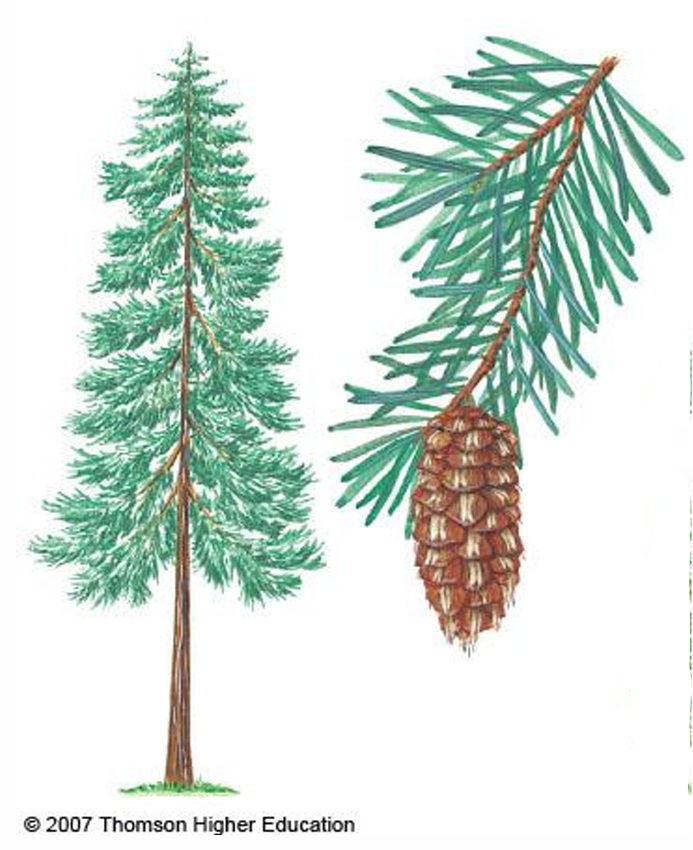
Pseudotsuga menziesii
commercially important conifer; Douglas fir; grows along the Pacific coast and in the Rocky Mountains
Picea rubens
commercially important conifer; red spruce; found in eastern Canada and the northeastern United States (also extends southward to the Great Smoky Mountains)

Pinus taeda
commercially important conifer; loblolly pine; widely distributed through the southeastern United States
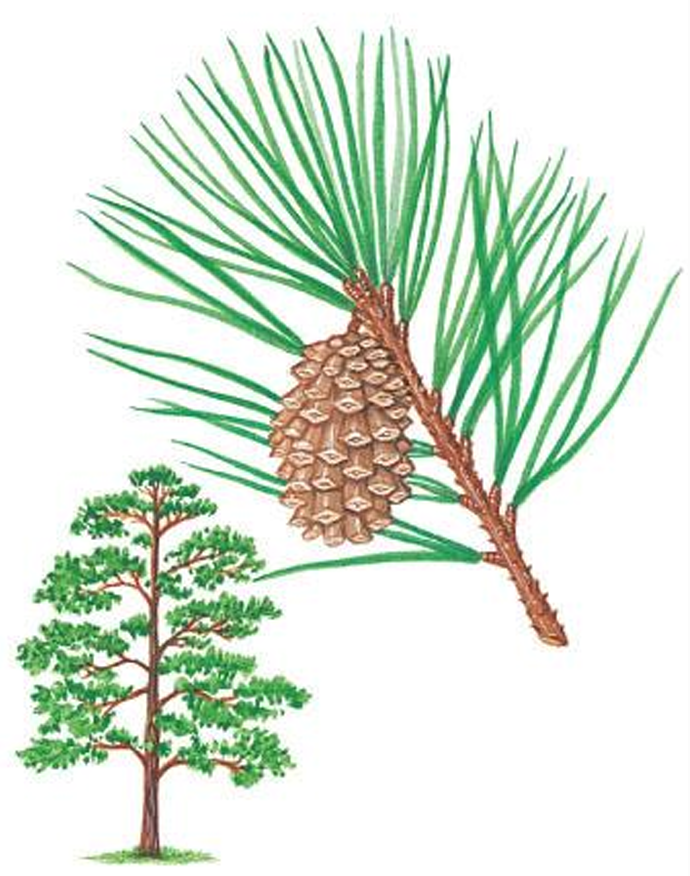
cycadophyta (cycads)
palm-like or fern-like in appearance; pollen and seeds in cone-like structures; relatively few living members; dioecious
Encephalartos transvenosus
cycad; Modjadji’s palm/cycad; localized distribution in South Africa; grows to approx. 9.2 meters (30 feet) and resembles a palm

Zamia integrifolia
cycad; coontie/sago cycas; native to southeastern United States, the Bahamas, Cuba, the Cayman Islands, and Puerto Rico; usually short (under 2 meters tall)

ginkgophyta (ginkgoes)
has only one surviving species; deciduous; produce fleshy seeds directly on branches; dioecious
deciduous
a tree or shrub that sheds its leaves annually
Ginkgo biloba
ginkgo; maidenhair tree; only surviving species of phylum ginkgophyta;
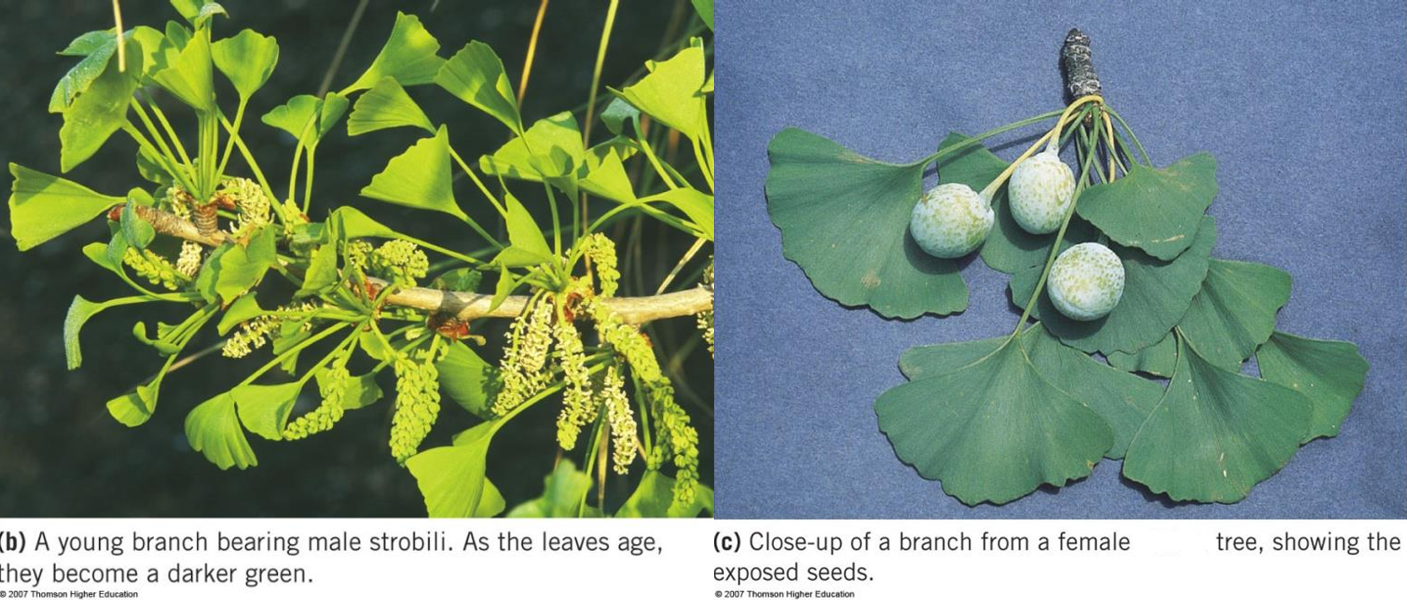
gnetophyta (gnetophytes)
share traits with angiosperms; more efficient water-conducting cells (vessel elements) in xylem; mostly dioecious
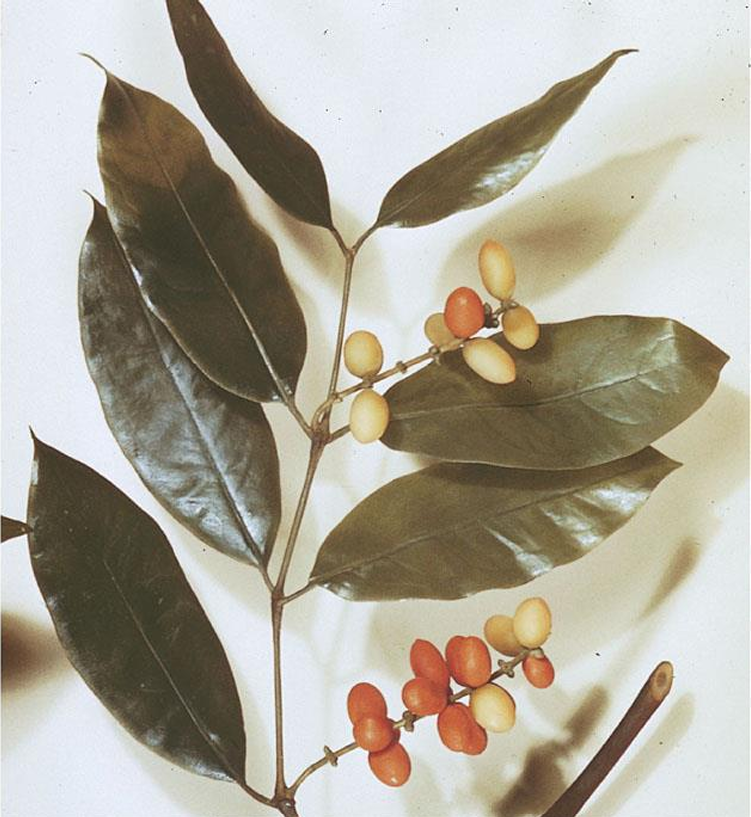
Gnetum gnemon
gnetophyte; melinjo/bago; resemble flowering plants due to fleshy exposed seeds that are yellow to red when ripe

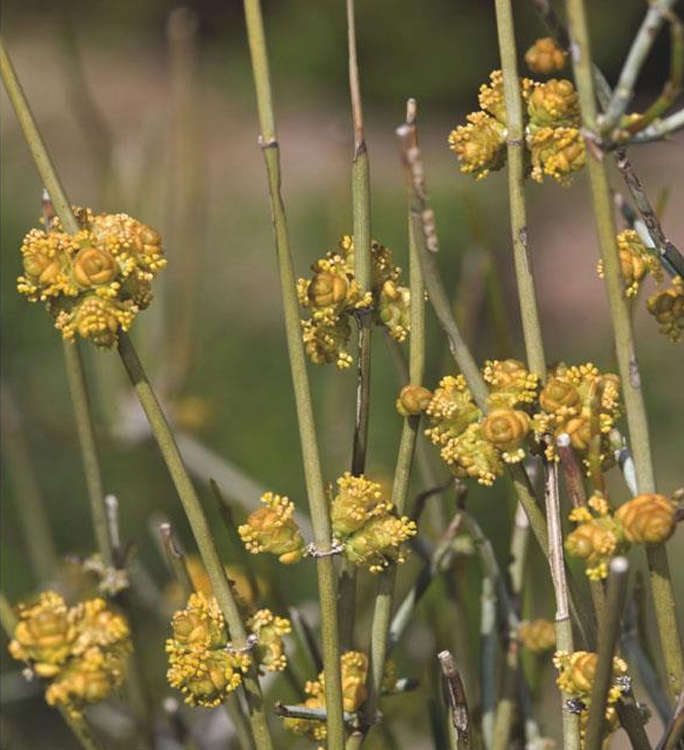
Ephedra
gnetophyte; jointfir; pollen clones cluster at nodes; European pioneers used species native to the American southwest to make Mormon tea

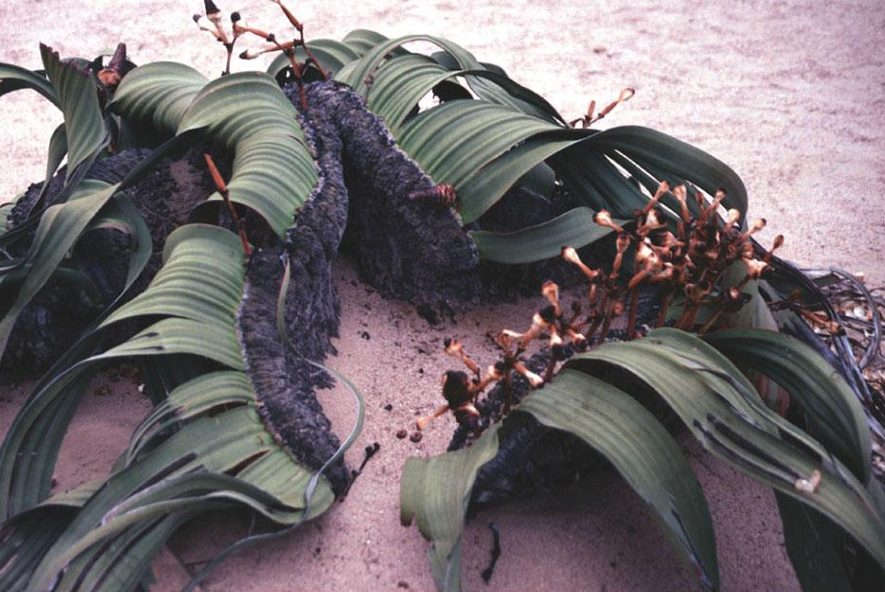
Welwitschia
gnetophyte; tree tumbo; native to deserts in southwestern Africa; survives on moisture-laden fogs that drift inland from the ocean

monoecious
having male and female reproductive parts in separate flowers or cones on the same plant
dioecious
having male and female reproductive structures on separate plants
sporpohyte
usually dominant; the diploid multicellular stage in the life cycle of a plant or alga which produces asexual haploid spores that develop into a gametophyte; e.g. pine tree
gametophyte
the gamete-producing and usually haploid phase, producing the zygote from which the sporophyte arises; the dominant form in bryophytes
pine gametophytes
extremely small and nutritionally dependent on sporophyte generation
heterosporous
the production of two types of spores (microspores; megaspores); e.g. pine
sporophyll
leaflike structure that bears spores within a sporangium (or sporangia)
microspores
produced by male cones; develop into pollen grains, which are carried by air currents to female cones
megaspores
produced by female cones; one of four produced by meiosis develops into a female gametophyte within an ovule
pollination
the transfer of pollen to female cones
pollen tube
after pollination; a tube that forms after the germination of a pollen grain and through which male gametes (sperm cells) pass into the ovule; grows through the megasporangium to the egg within the archegonium
watershed
an area of land that drains all the streams and rainfall to a common outlet
amber
fossil tree resin that has achieved a stable state through loss of volatile constituents and chemical change after burial in the ground; mostly produced by conifer trees
progymnosperms
seedless vascular plants that had megaphylls and “modern” woody tissue; probably gave rise to conifers and seed ferns, which likely gave rise to cycads and ginkgo
Archaeopteris
progymnosperm; existed about 370 mya; had some features in common with modern seed plants but did not produce seeds
Emplectopteris
seed fern; produced seeds on fernlike leaves; seed ferns existed from about 360 mya to 250 mya