PDA Lecture 25: Receptors, Neurotransmitters, and Medications of the Central Nervous System
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
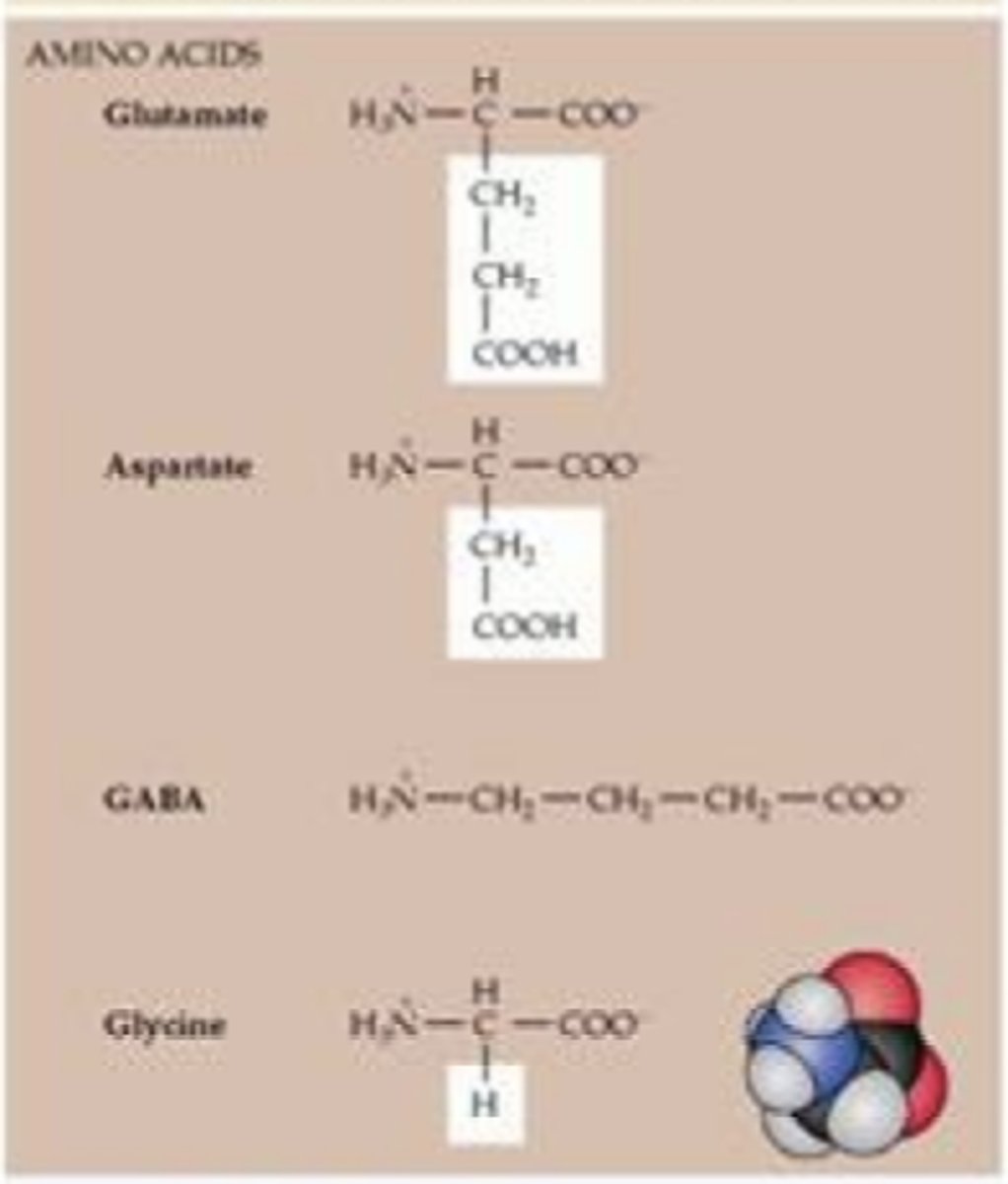
Amino acids
Organic compounds containing amine (-NH3) and carboxyl (-COOH) functional groups, along with a side chain (R group) specific to each amino acid
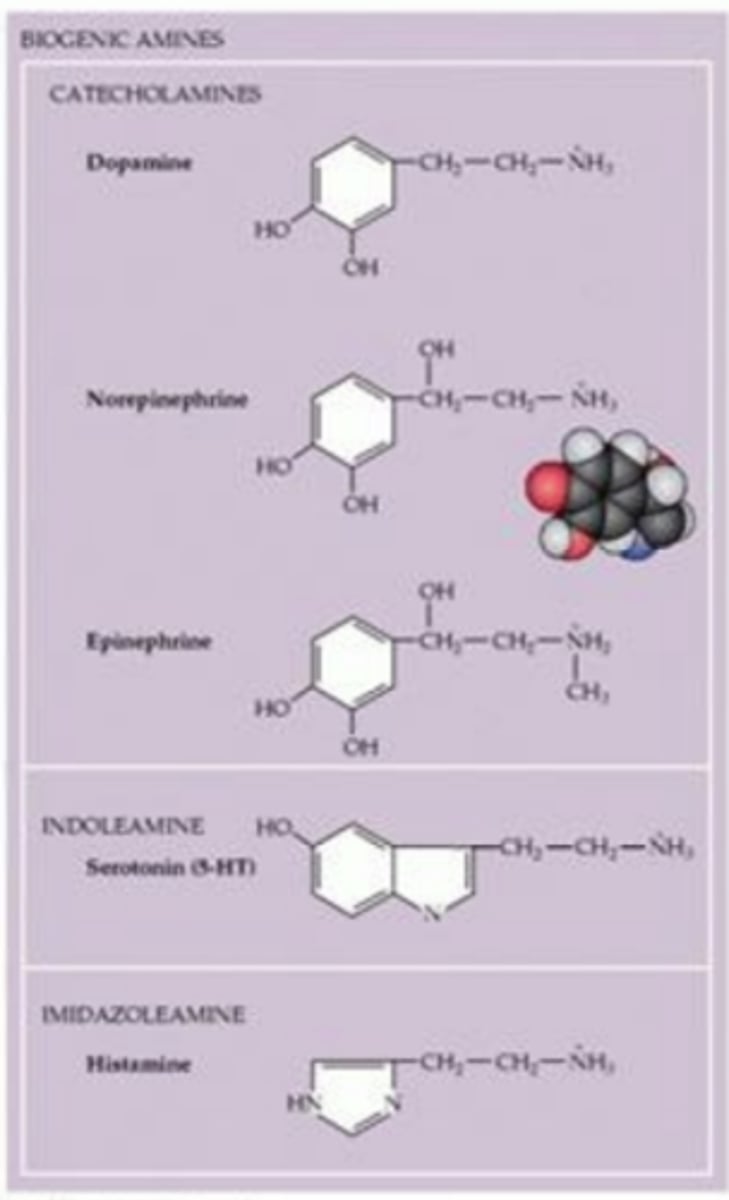
Biogenic Amines
Organic compound that has a benzene ring and a side-chain amine
- Includes catecholamines, indoleamines, and imidazoleamines
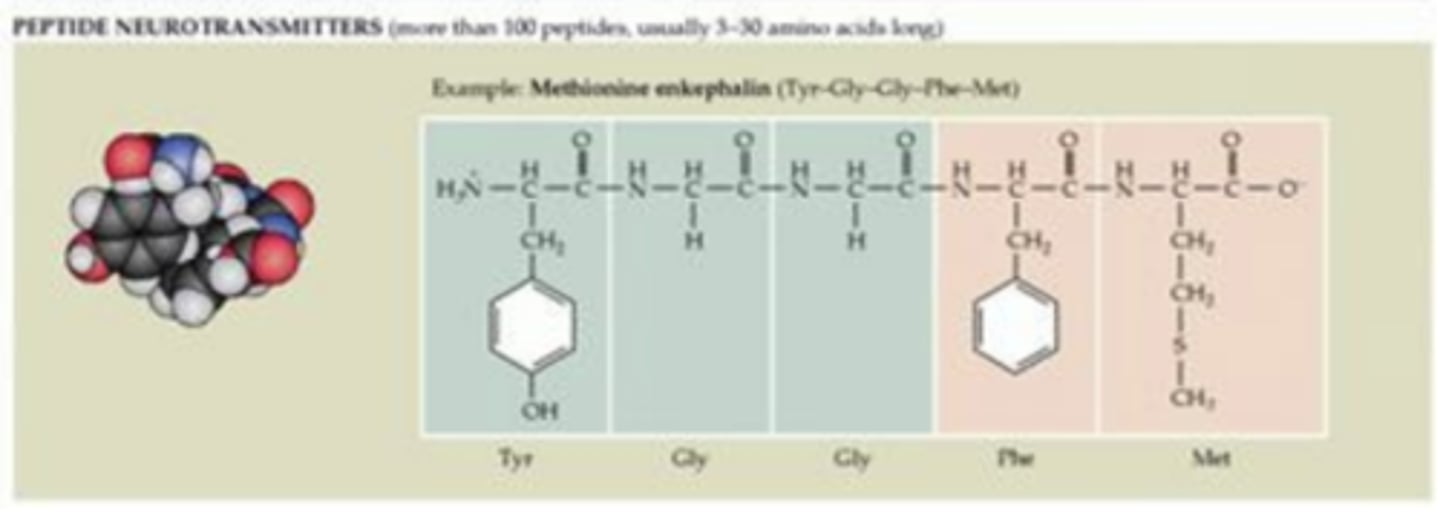
Peptides
Short chains of amino acid monomers linked by peptide bonds
Purines
Heterocyclic aromatic organic compound that consists of a pyrimidine ring fused to an imidazole ring
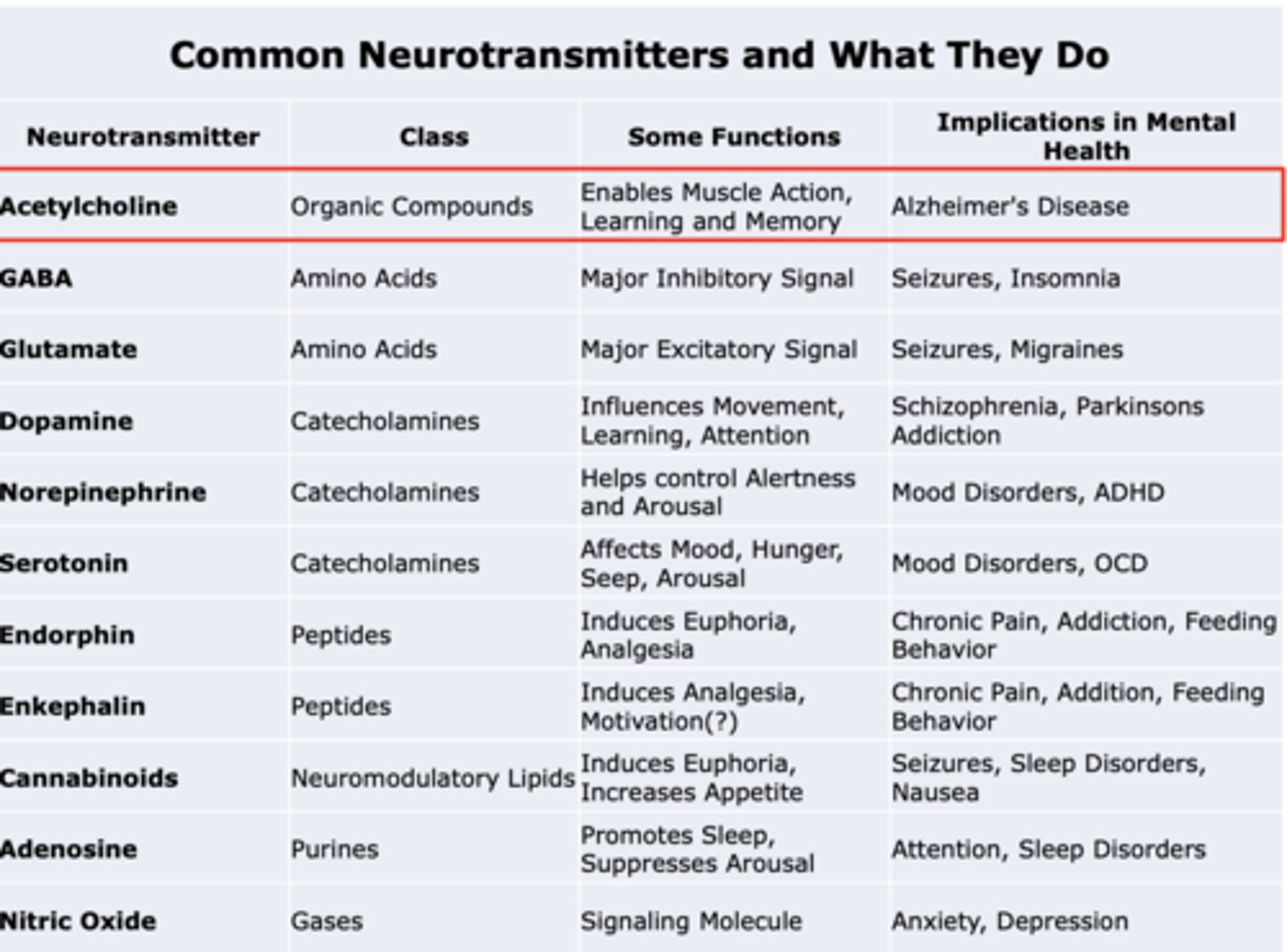
Acetylcholine
Class:
Some functions:
Implications in mental health:
Class: Organic compounds
Some functions: Enables Muscle Action, Learning, and Memory
Implications in mental health: Alzheimer's Disease
Nicotinic receptors are generally ____________ as a result of increased _____, ____, or _______ permeability
- excitatory
- Na+, K+, or Ca++
Nicotinic receptors: Note that α3β4 subtype is found on....
ANS ganglion
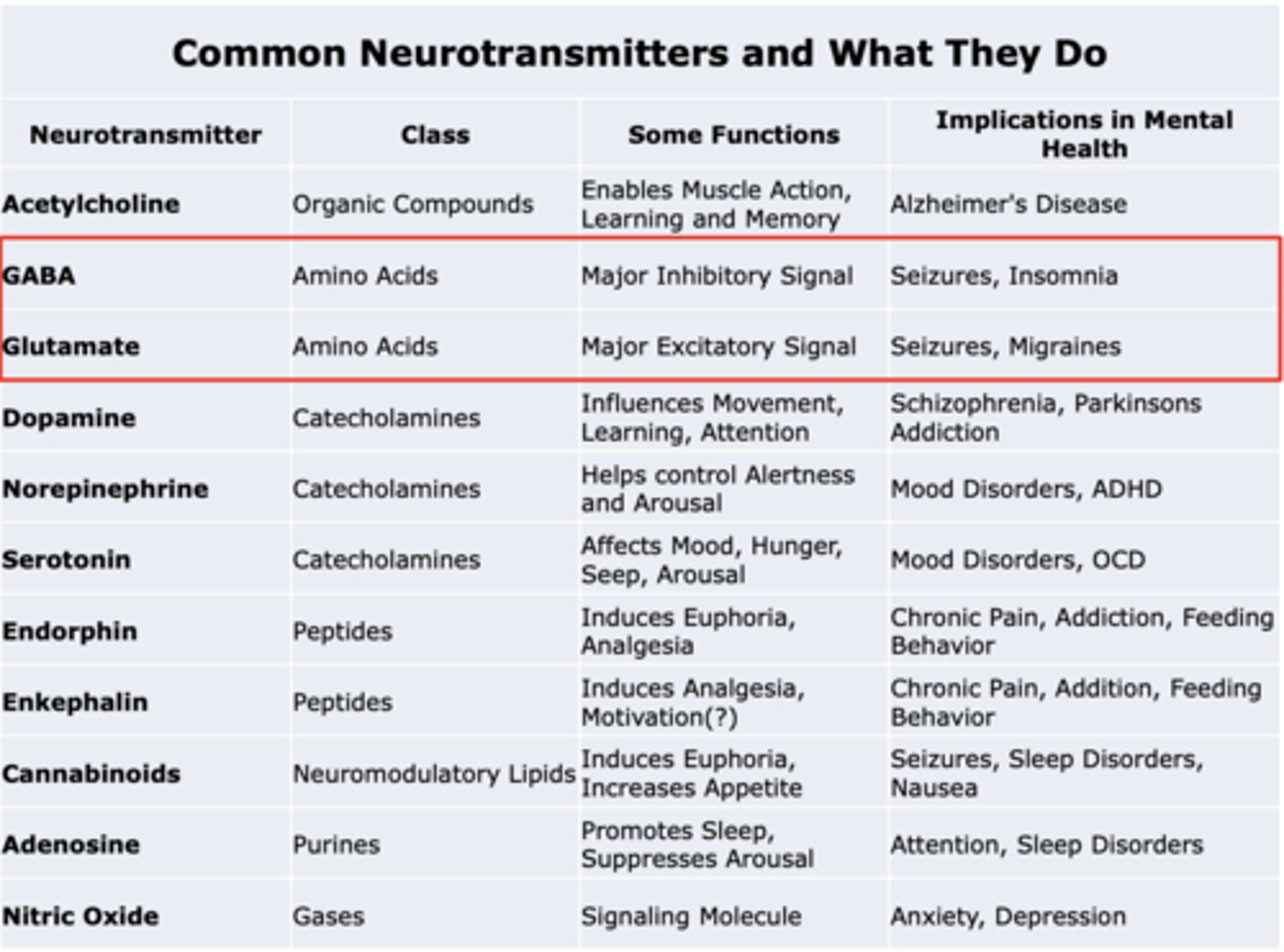
GABA
Class:
Some functions:
Implications in mental health:
Class: Amino Acids
Some functions: Major Inhibitory Signal
Implications in mental health: Seizures, Insomnia
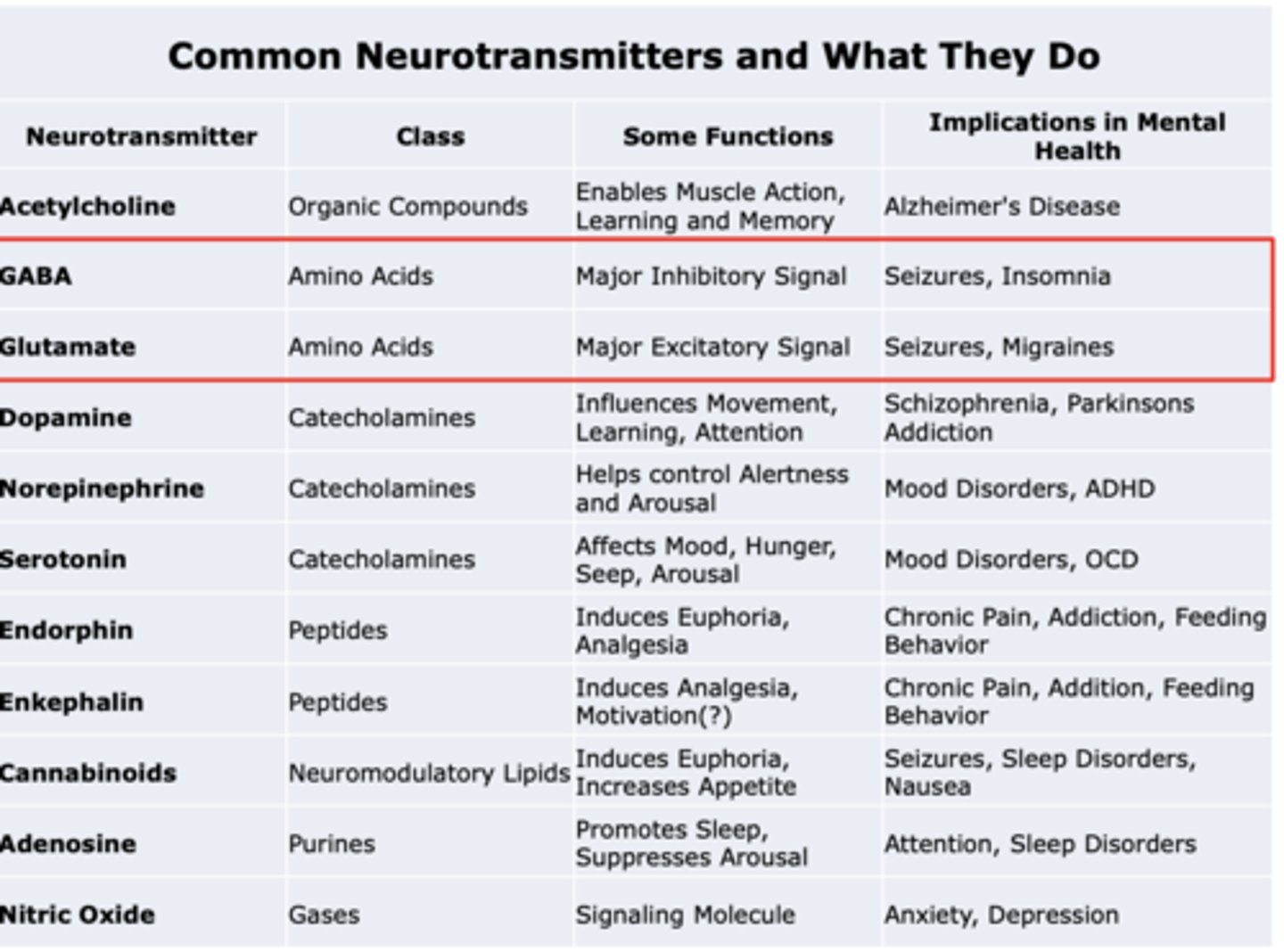
Glutamate
Class:
Some functions:
Implications in mental health:
Class: Amino Acids
Some functions: Major Excitatory Signal
Implications in mental health: Seizures, Migraines
Glutamate receptors
• NMDA Glutamate receptor (Ligand gated ionotropic)
• AMPA Glutamate receptors (Ligand gated ionotropic).
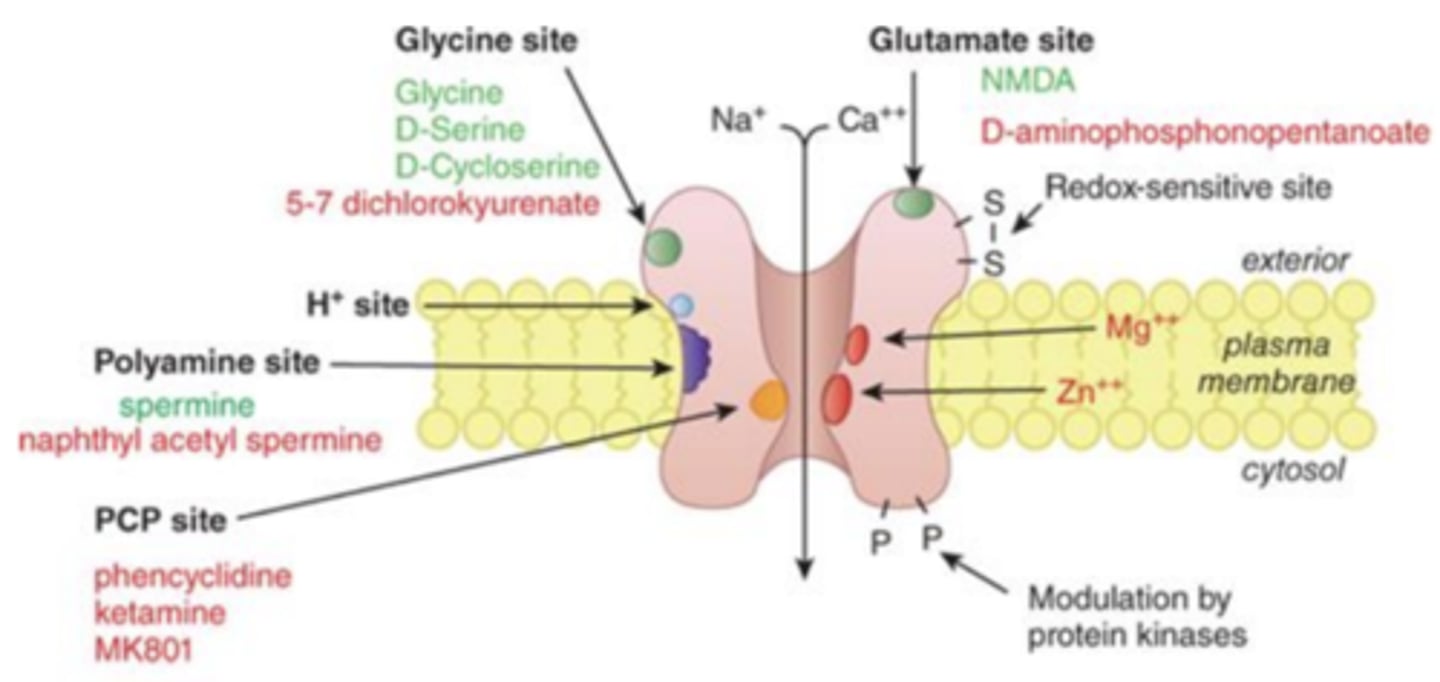
Glutamate is the primary _________________________ signal in the brain
primary endogenous excitatory signal
- increases the likelihood of action potentials firing
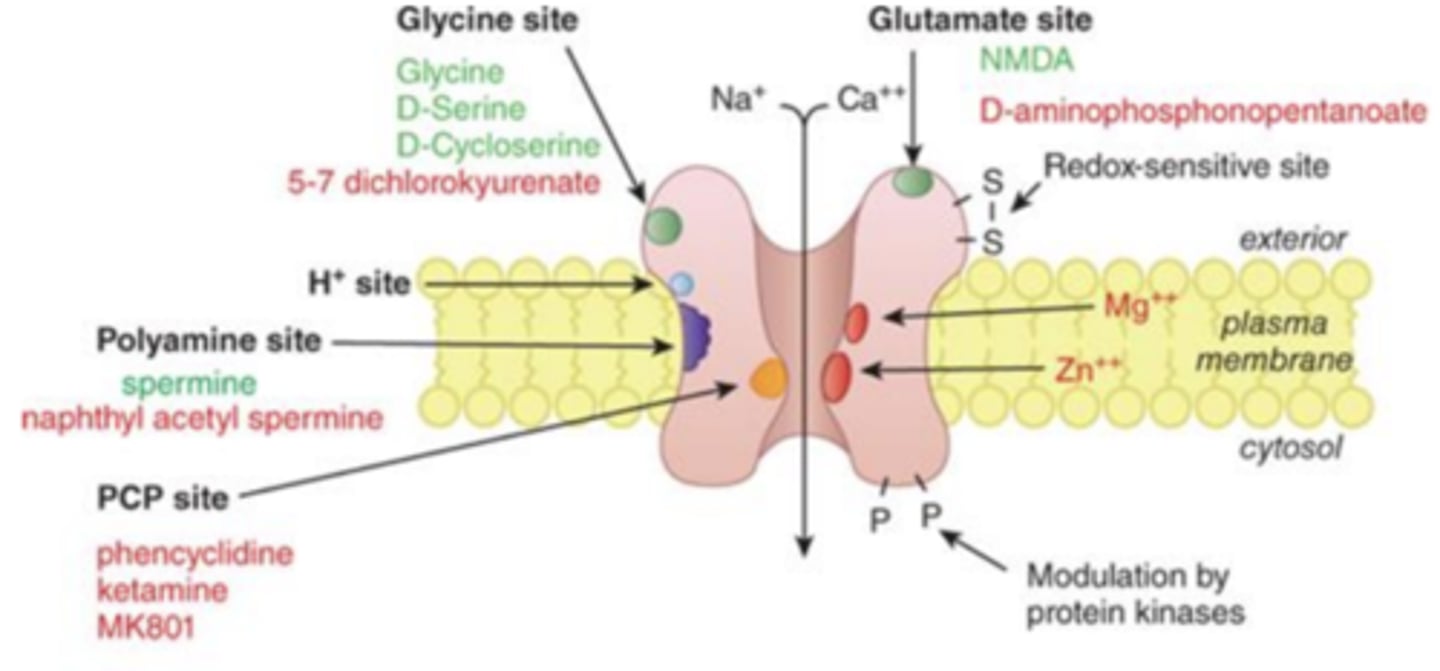
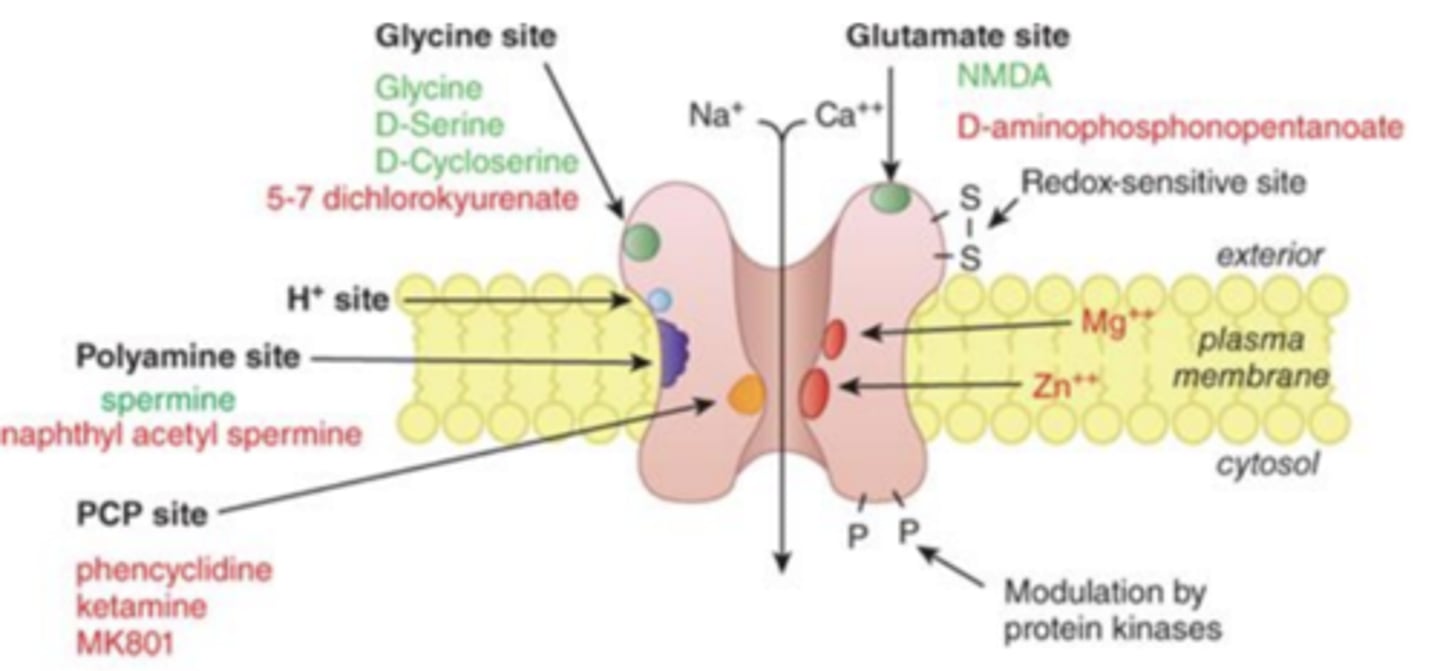
How do NMDA and AMPA work?
NMDA and AMPA work together for learning mechanism (long-term potentiation, LTP)
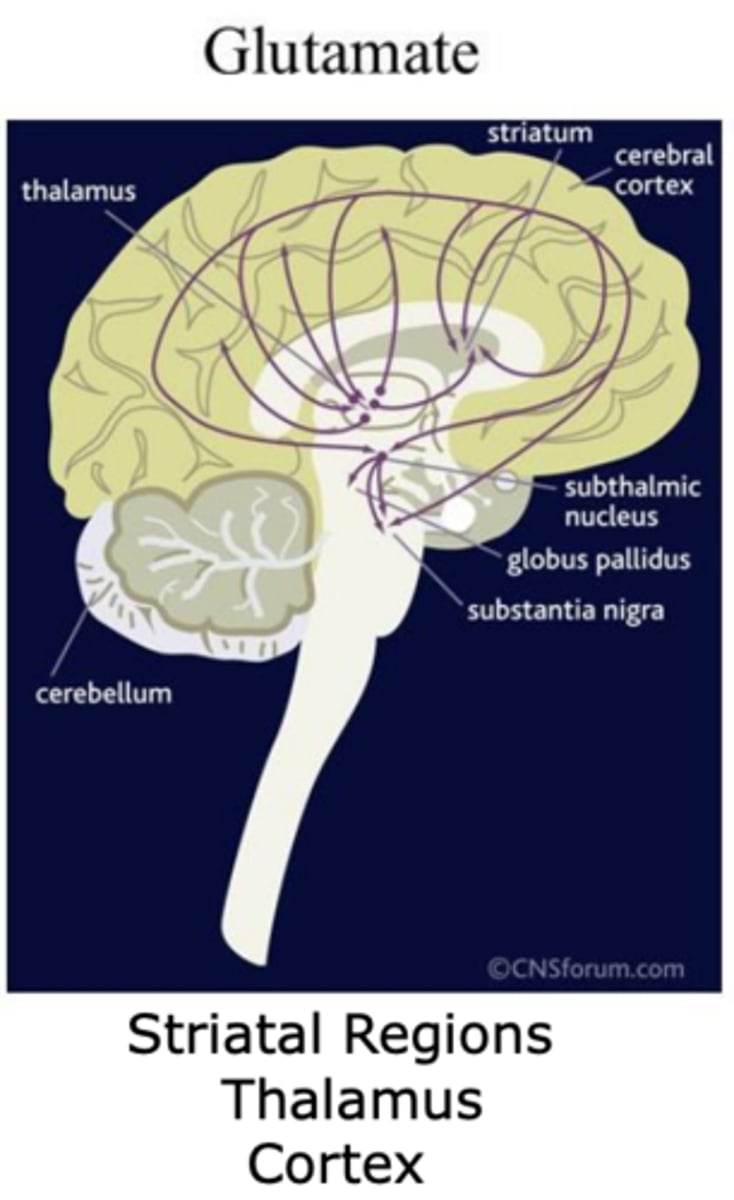
Glutamate projections in the brain (3)
- Striatal regions
- Thalamus
- Cortex
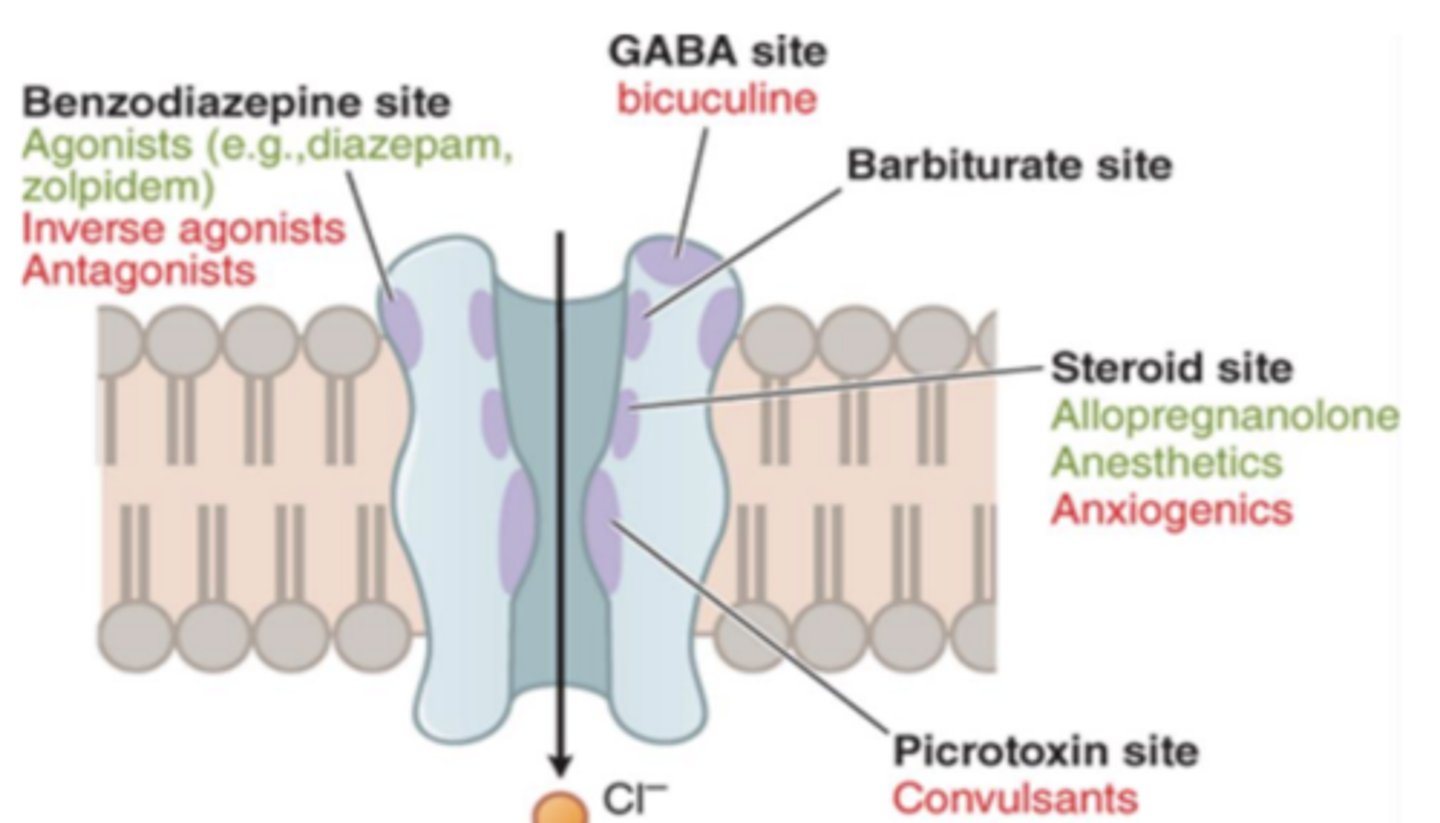
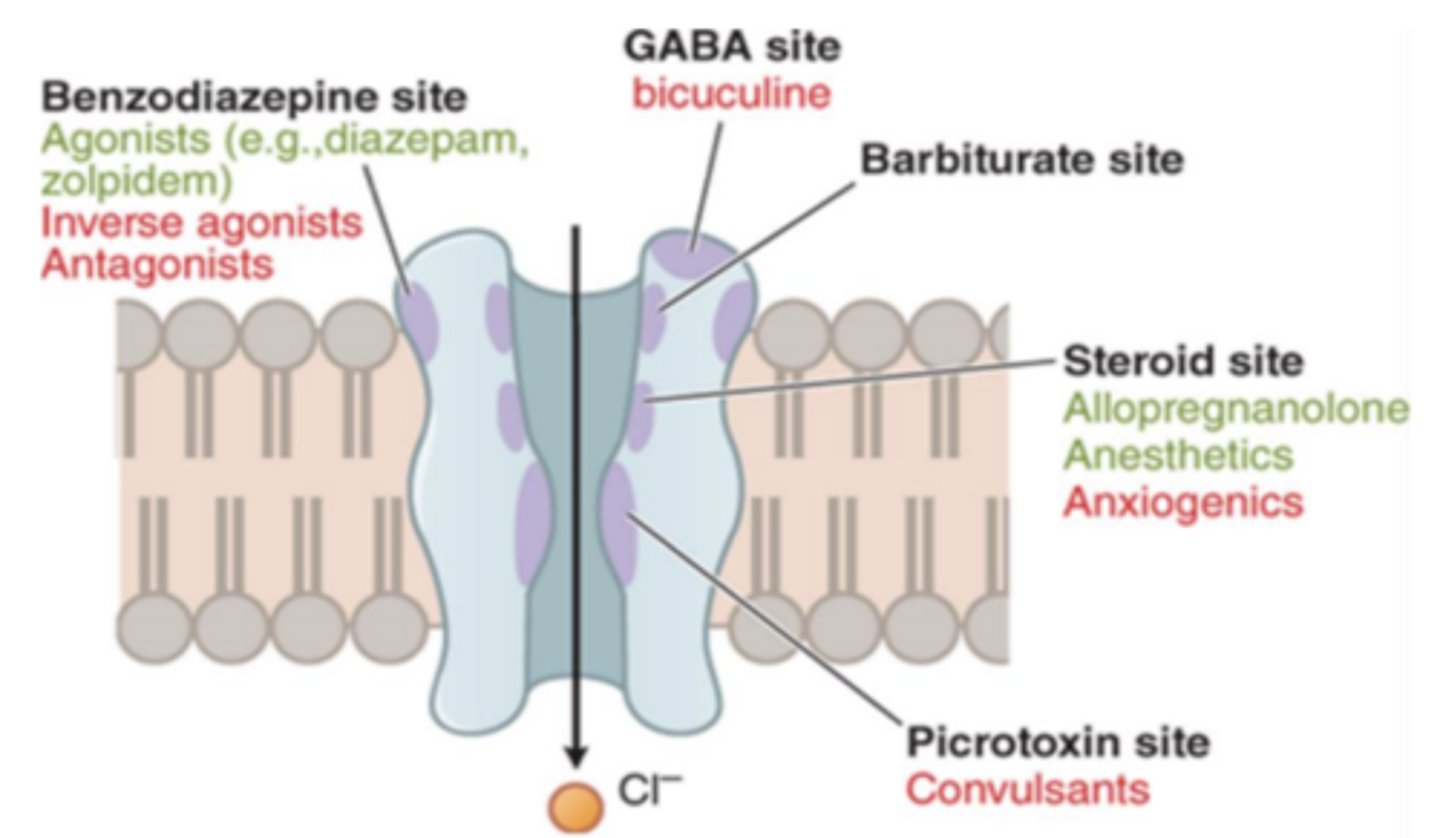
GABA receptors (2)
• GABAa receptor (Ligand gated ionotropic).
• GABAB receptor (G-protein coupled receptor)
GABA is the primary _________________ signal in the brain
primary endogenous inhibitory signal
- decreases the likelihood of action potentials firing
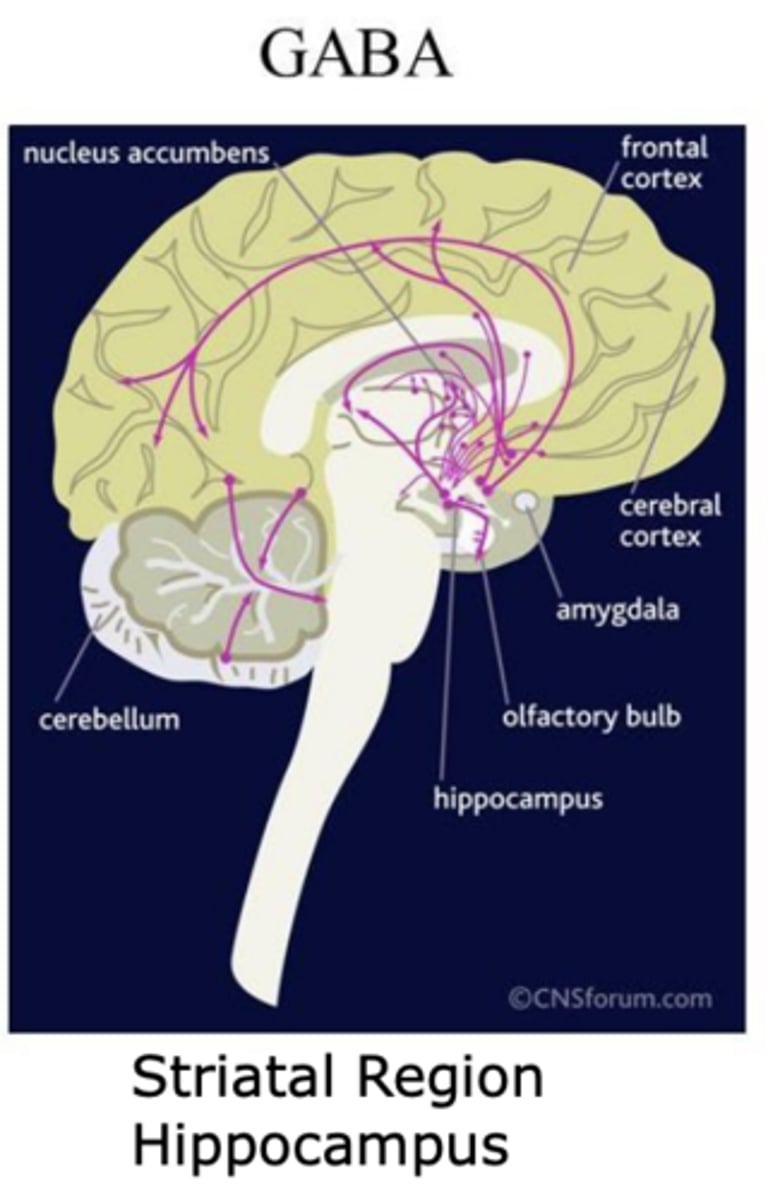
GABA projections in the brain (2)
- Striatal region
- Hippocampus
Dopamine
Class:
Some functions:
Implications in mental health:
Class: Catecholamines
Some functions: Influences Movement, Learning, Attention
Implications in mental health: Schizophrenia, Parkinsons Addiction
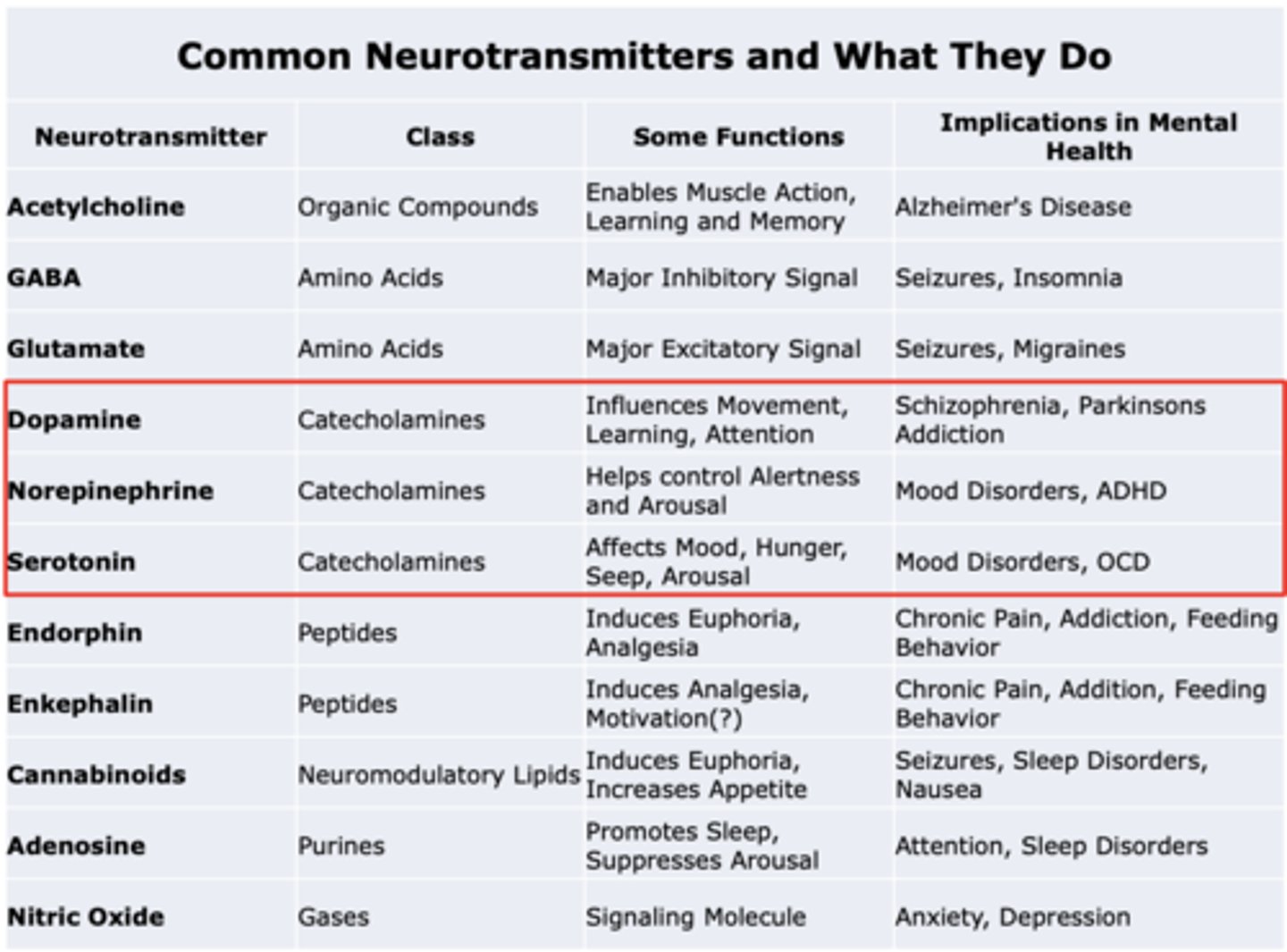
Norepinephrine
Class:
Some functions:
Implications in mental health:
Class: Catecholamines
Some functions: Helps control Alertness and Arousal
Implications in mental health: Mood Disorders, ADHD
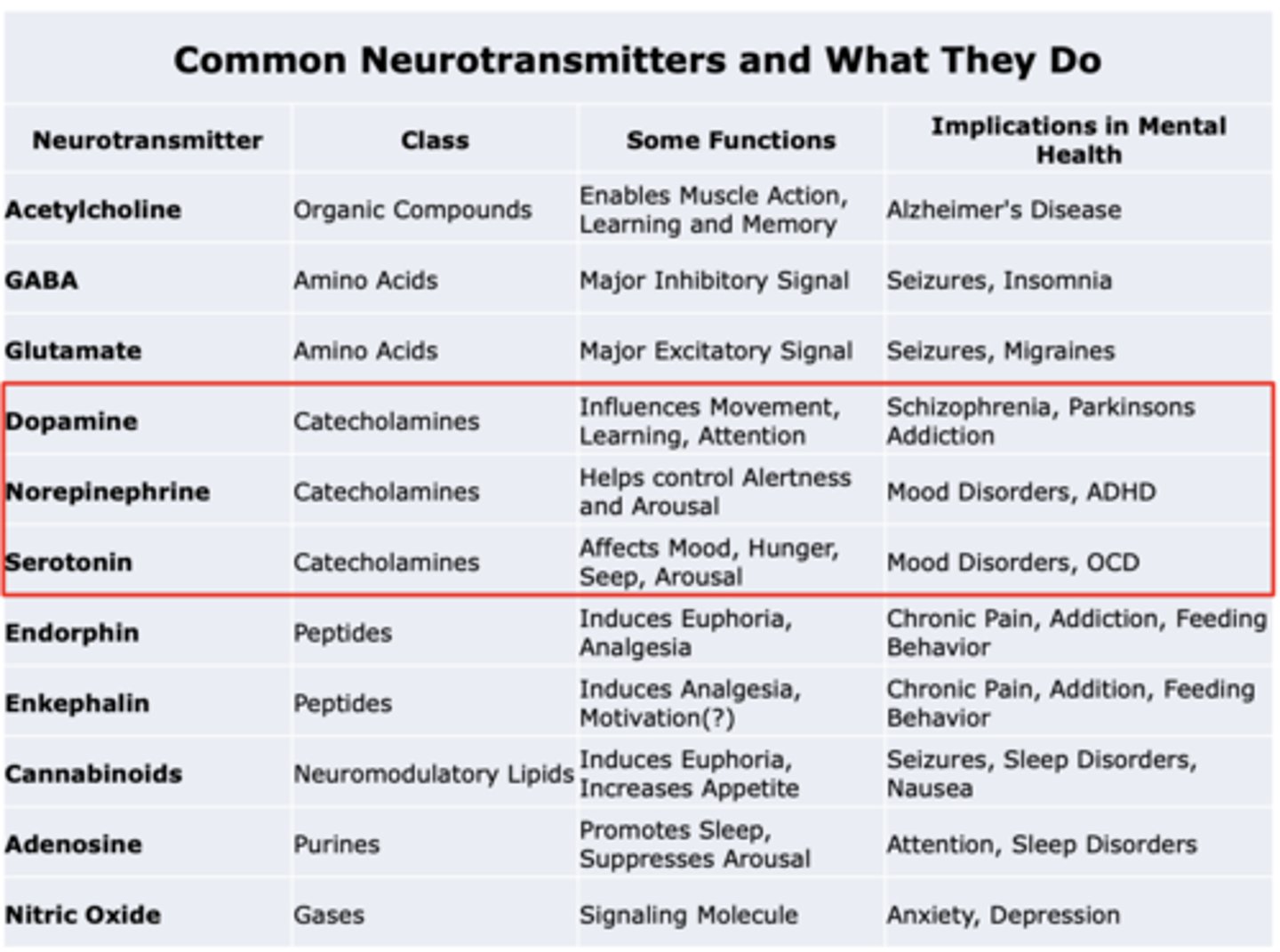
Serotonin
Class:
Some functions:
Implications in mental health:
Class: Catecholamines
Some functions: Affects Mood, Hunger, Seep, Arousal
Implications in mental health: Mood Disorders, OCD
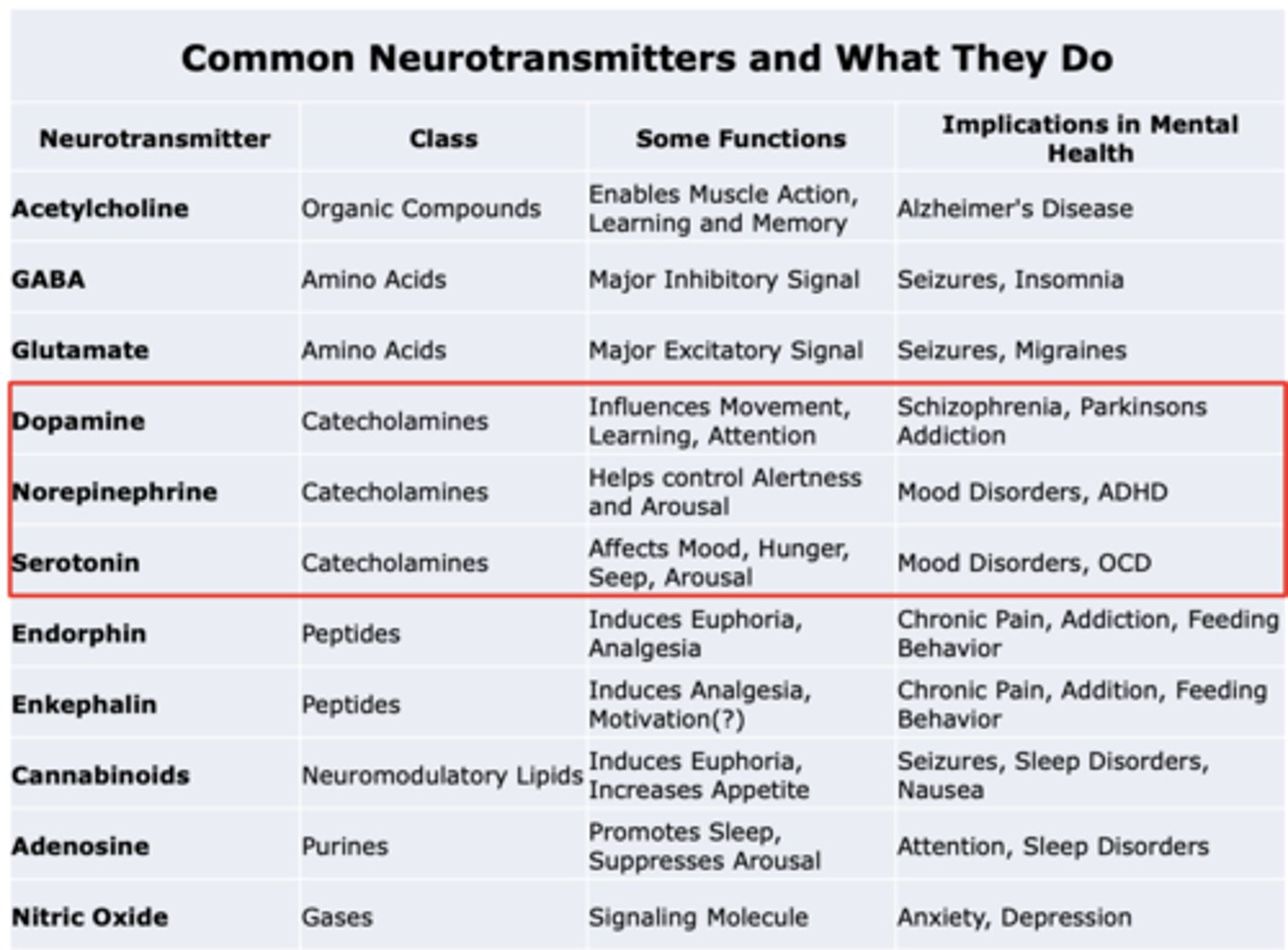
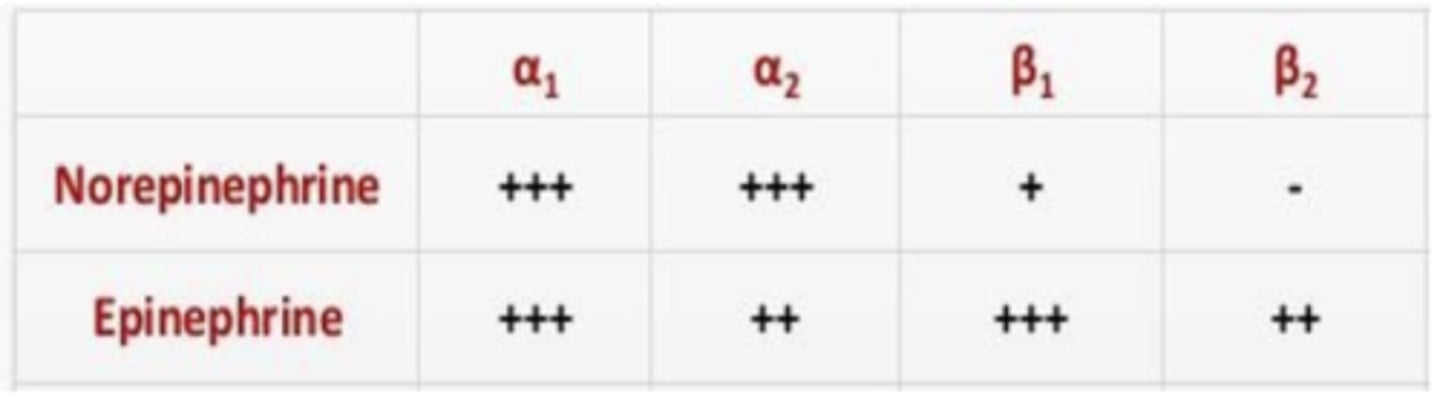
T/F: Adrenergic receptors are slower acting G-protein coupled receptors
TRUE
α1 -> Gq -> ___, ____, ____
α1 -> Gq -> α1A, α1B, α1D
activation of phospholipase C
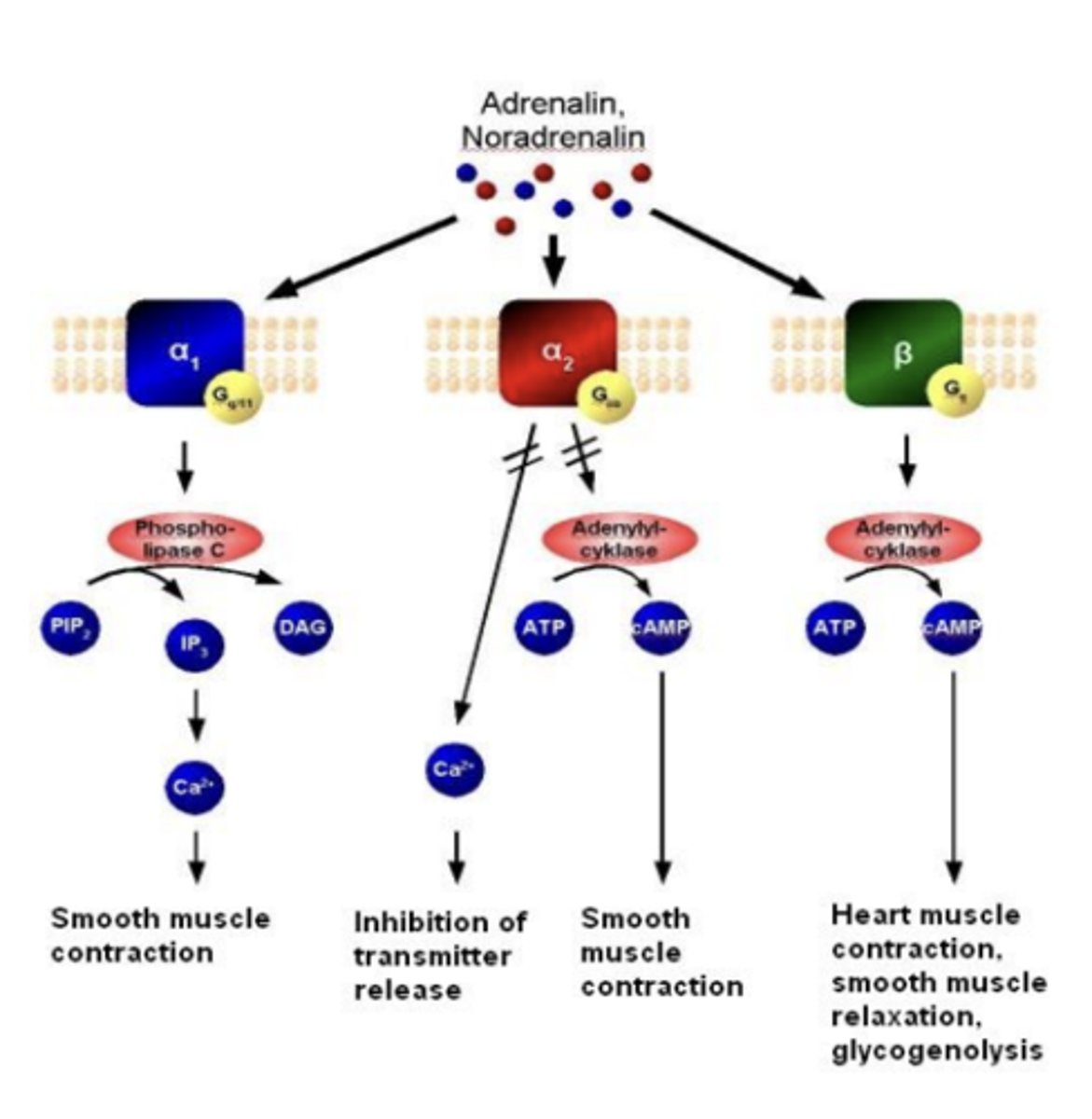
α2 -> Gi/o -> ___, ___, ___
α2 -> Gi/o -> α2A, α2B, α2C
inhibition of adenylate cyclase
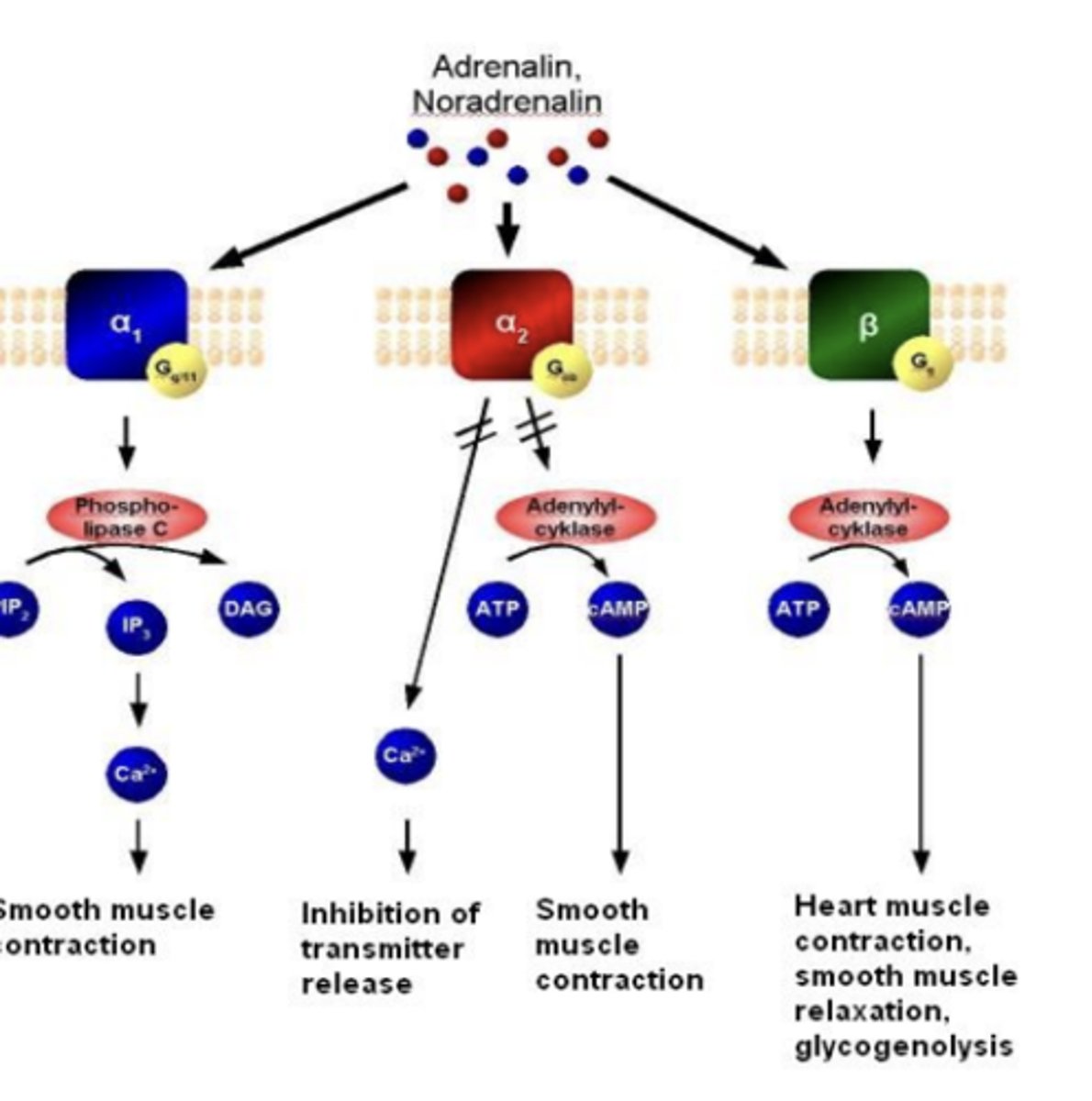
β -> Gs -> ___, ____, ___
β -> Gs -> β1, β2, β3
activation of adenylate cyclase
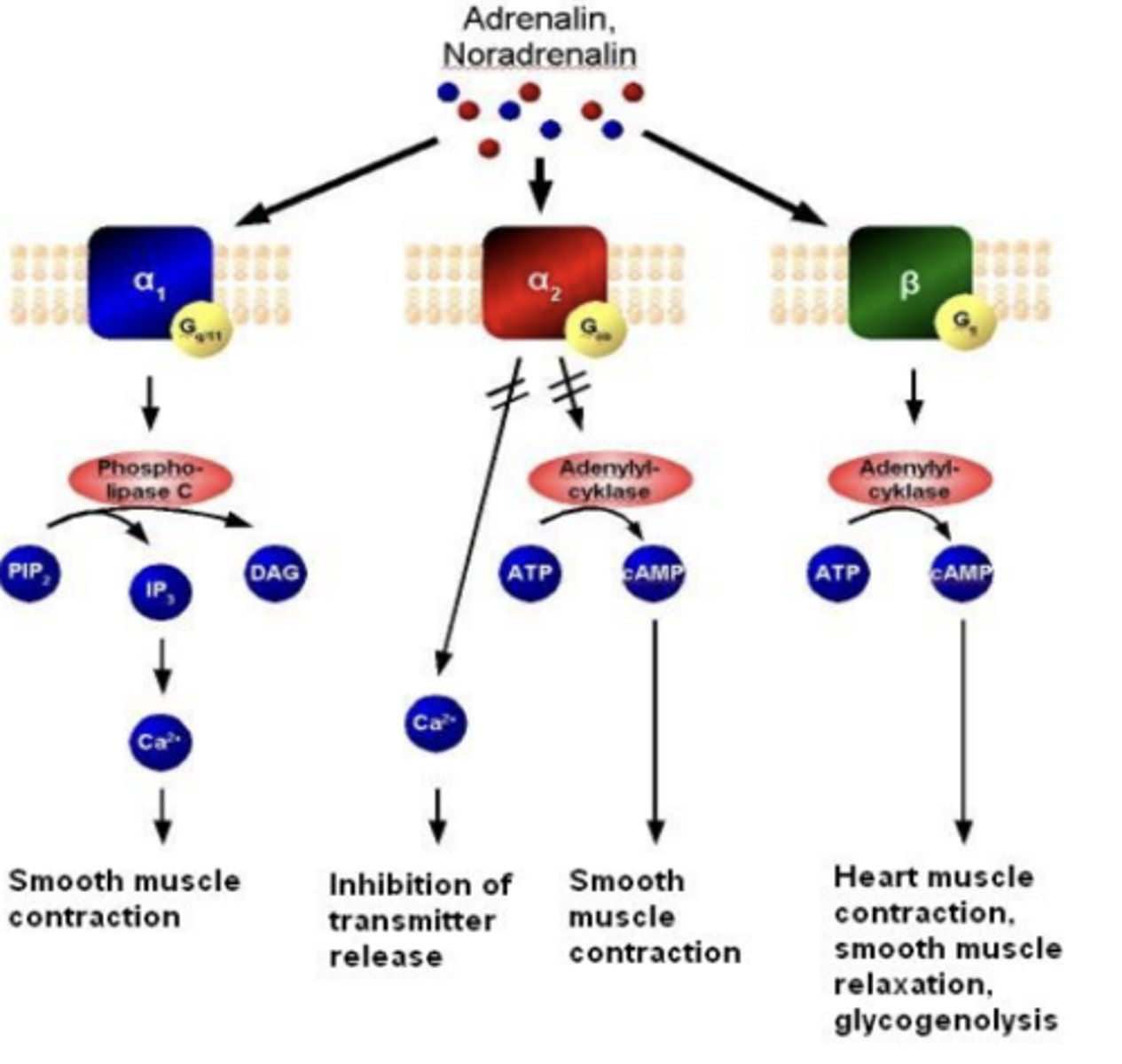
Adrenergic receptors are...
generally excitatory
Adrenergic receptors have varying sensitivities to....
norepinephrine and epinephrine
- a1 has equal sensitivity for both NE and EPI, a2 has more sensitivity for NE, but still sensitivity for EPI
- β1 and β2 have higher sensitivities for epinephrine. β2 has no sensitivity for NE
What kind of receptors are dopamine receptors?
G-protein coupled receptors
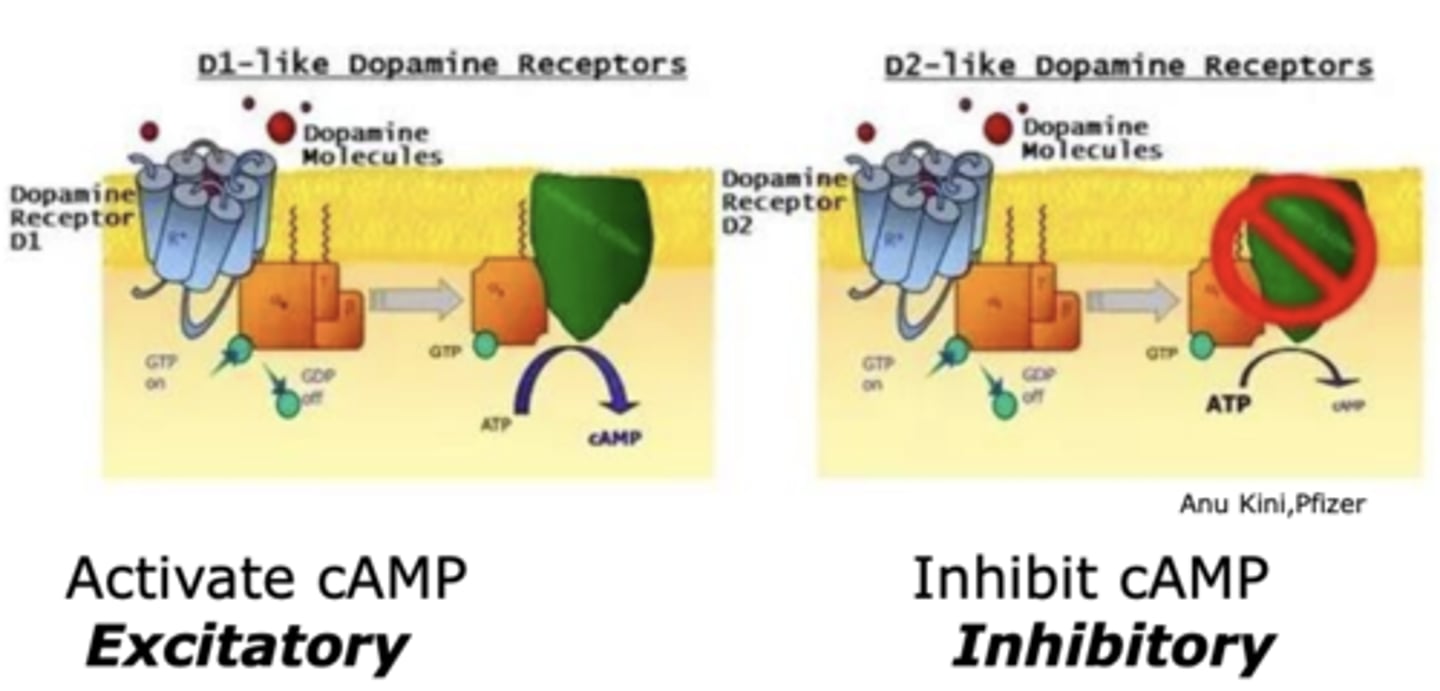
What effects do D1- and D2-like receptors have on neurons?
have opposite effects on neurons
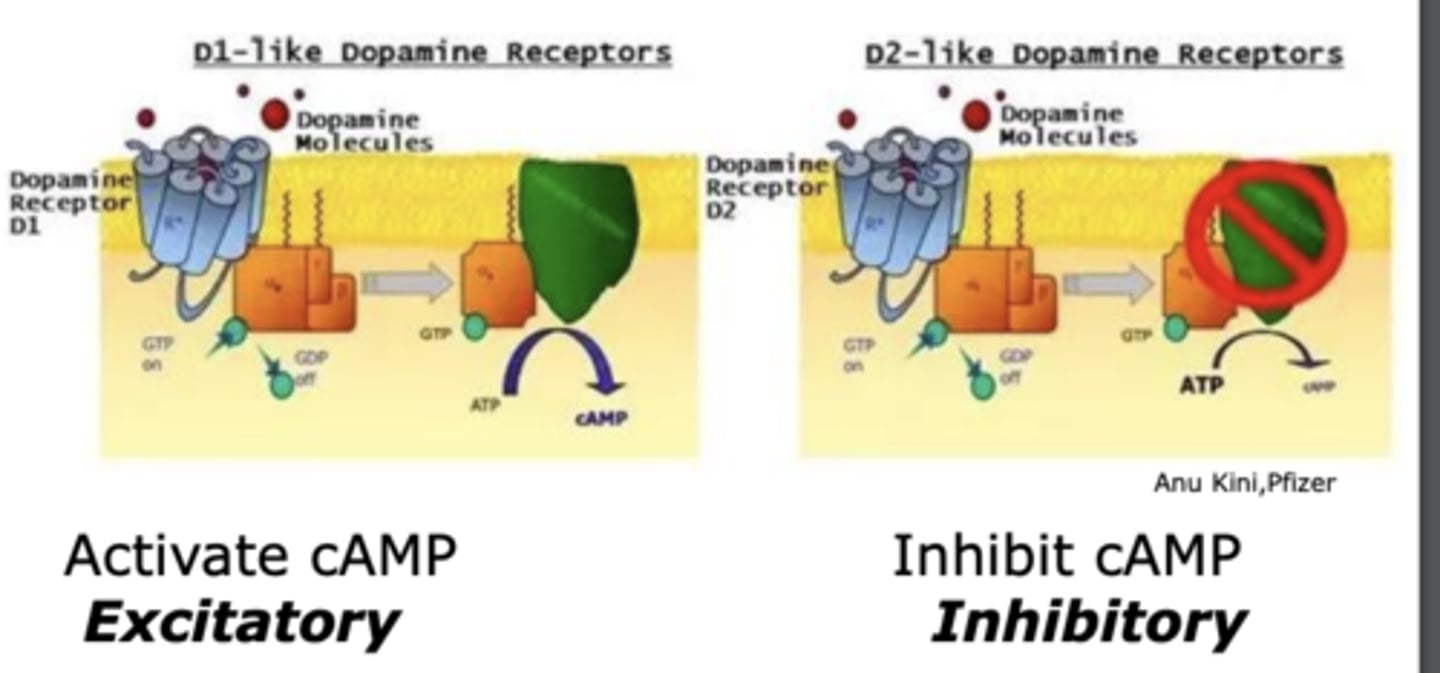
What dopamine receptors; D1- and D2-like receptors work together to regulate?
Work together to regulate reward and movement
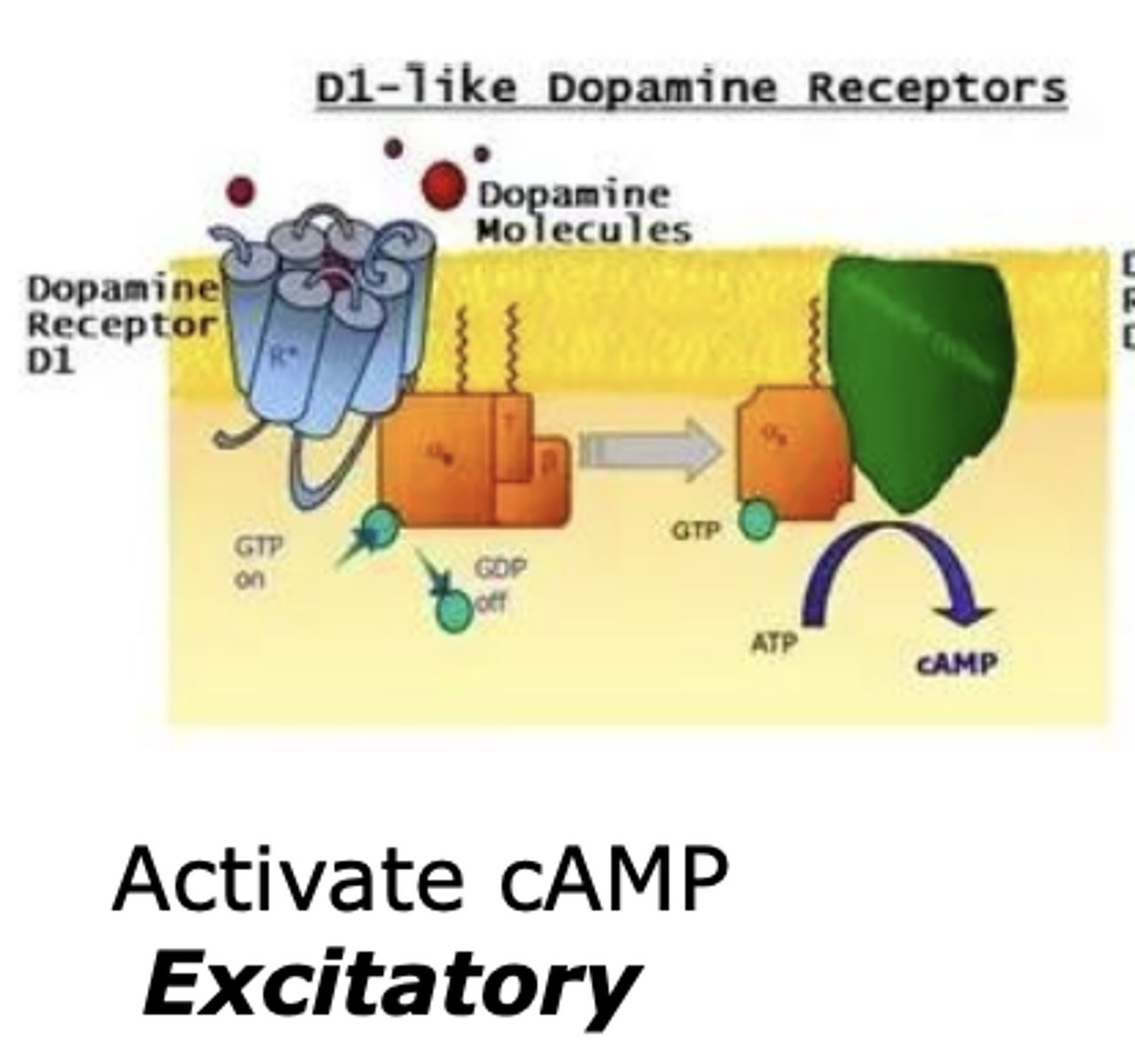
Which dopamine receptor activates cAMP?
D1-like dopamine receptor
- excitatory
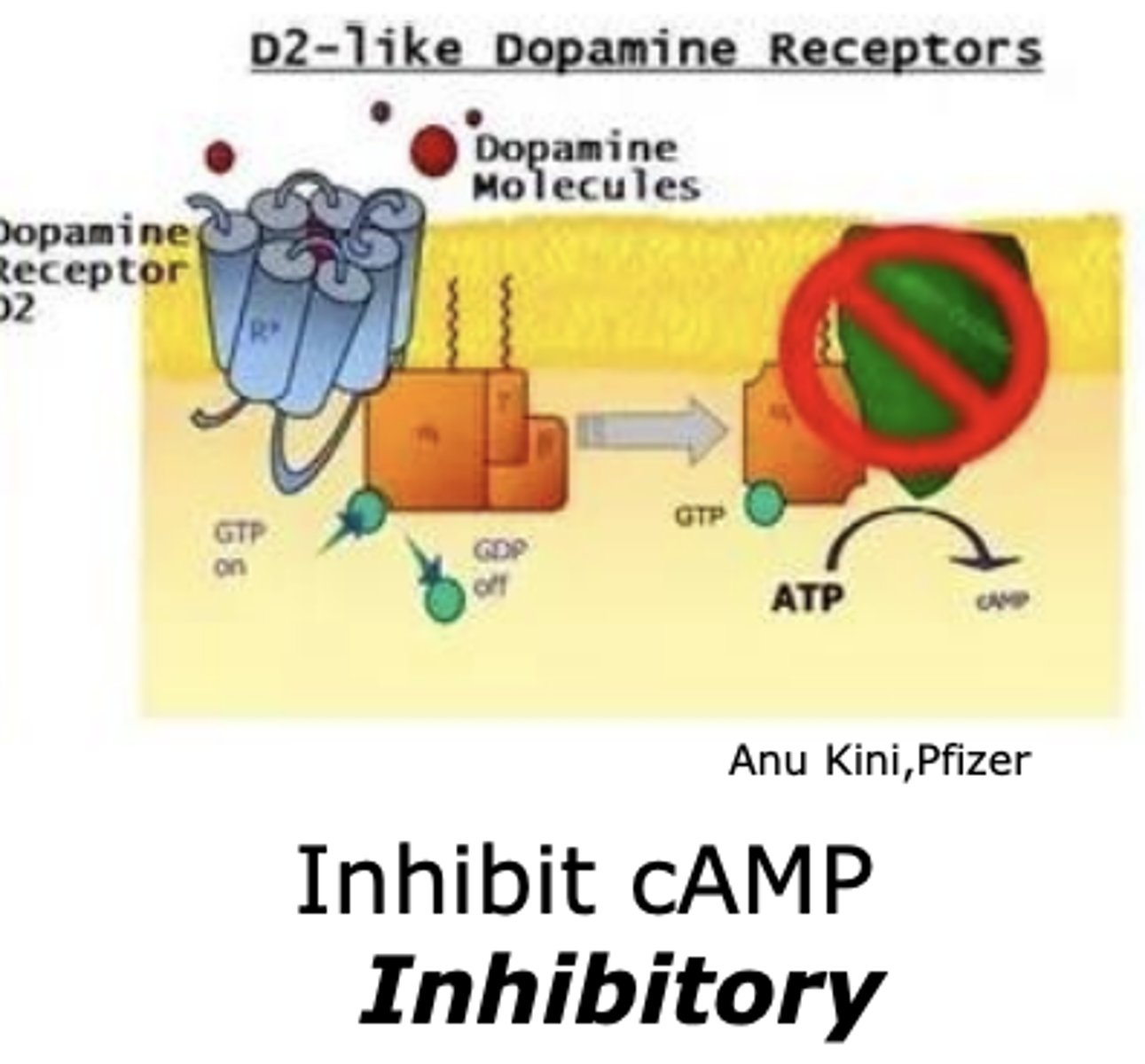
Which dopamine receptor inhibits cAMP?
D2-like dopamine receptor
- inhibitory
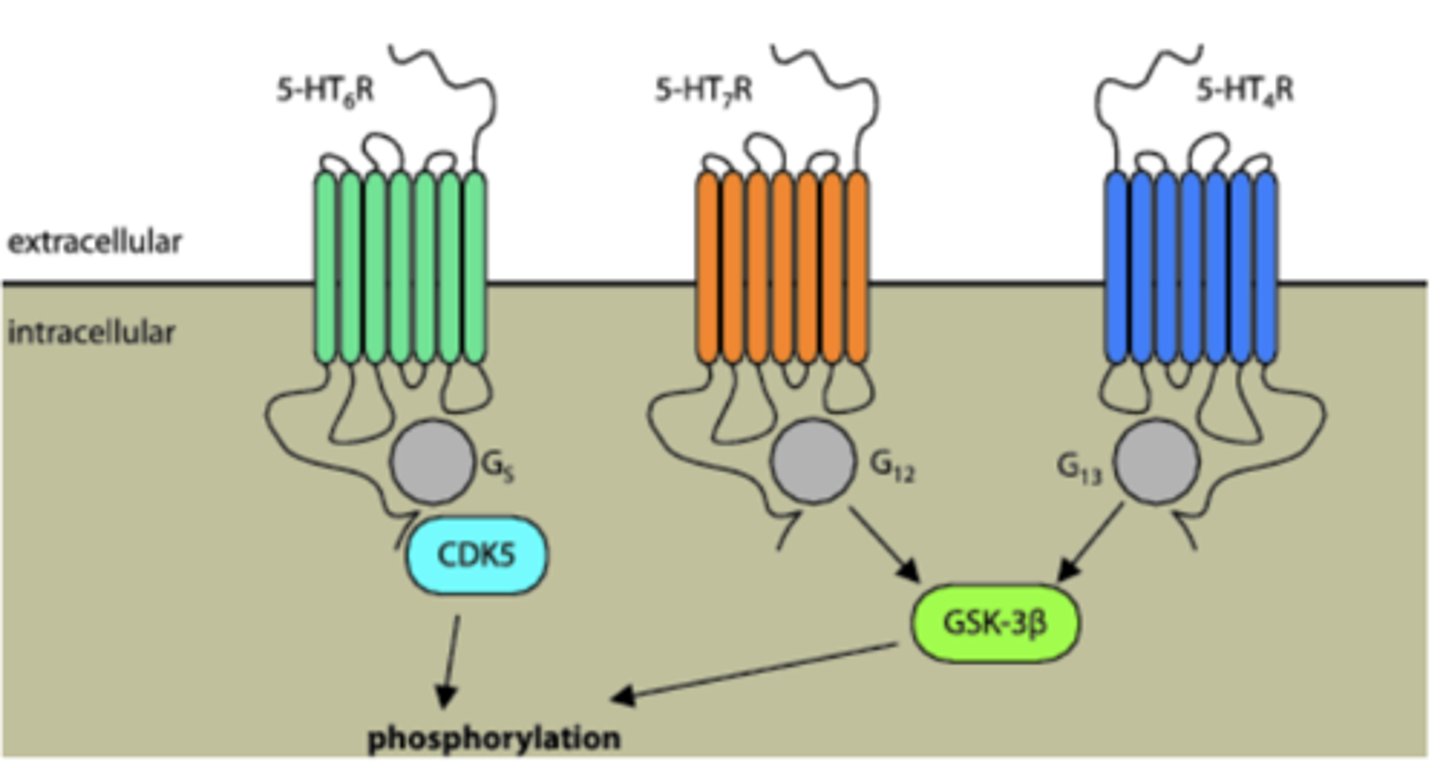
What kind of receptors are serotonin receptors?
G-protein coupled receptors
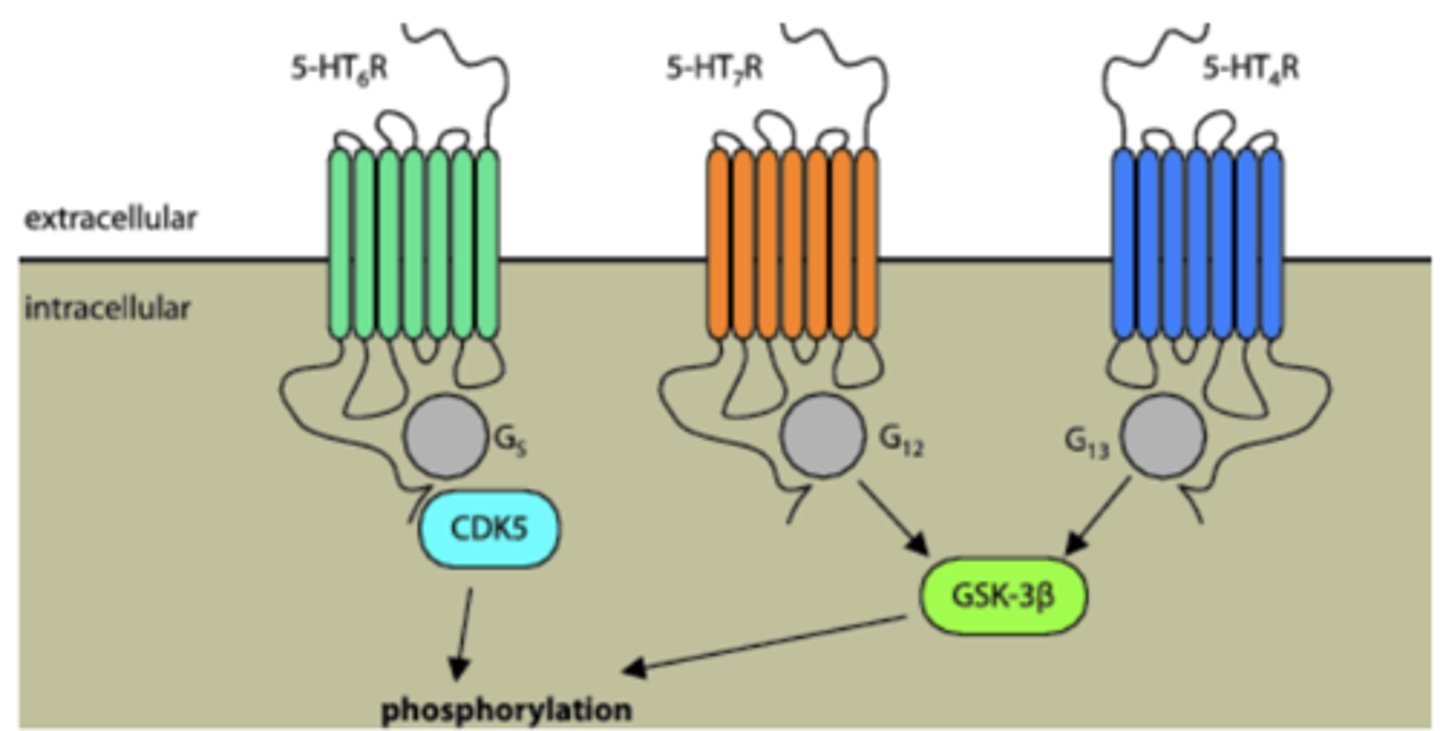
There are at least how many serotonin receptor subtypes?
at least 15
Serotonin receptors are implicated in....
mood disorders
Serotonin receptors have both ____________ and _______________ actions
excitatory and inhibitory
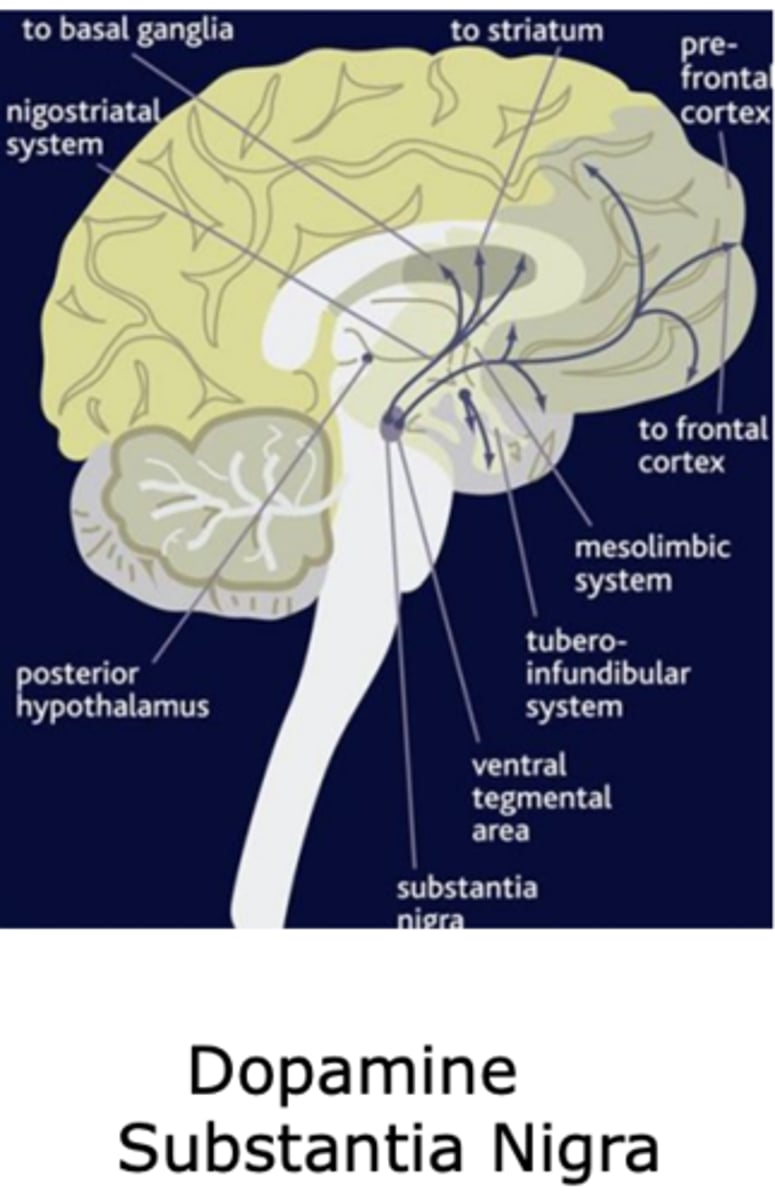
Dopamine origination and projections in the brain
Substantia nigra
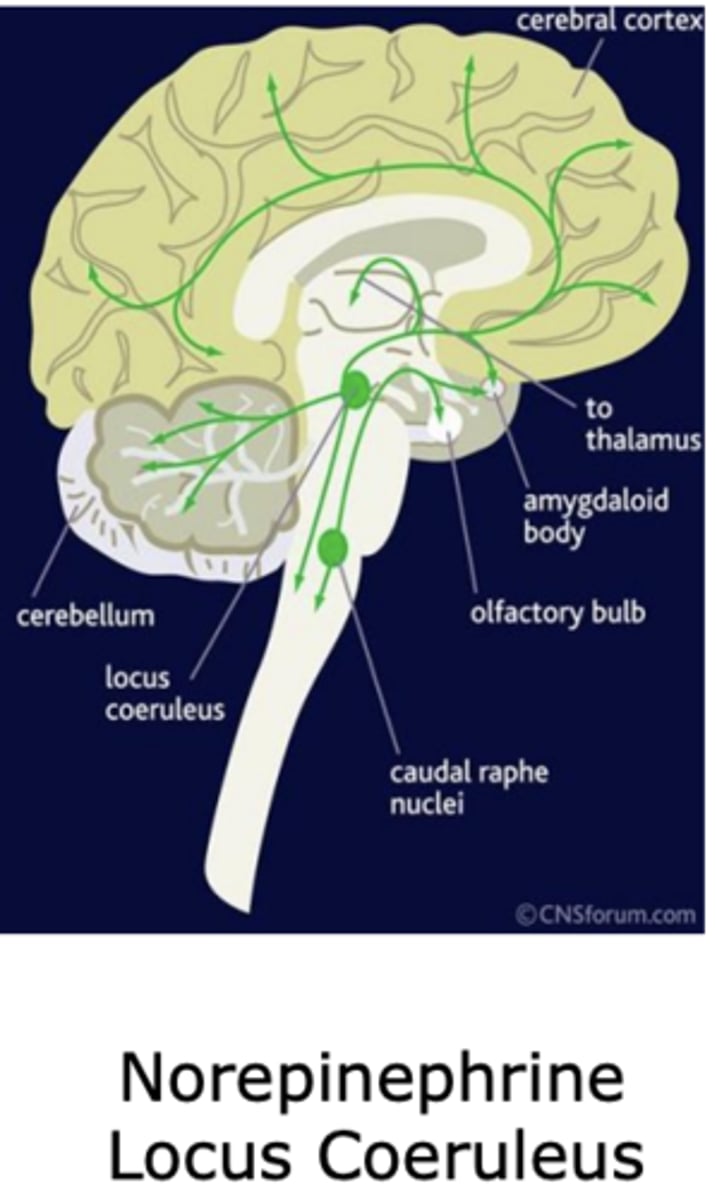
Norepinephrine origination and projections in the brain
Locus Coeruleus
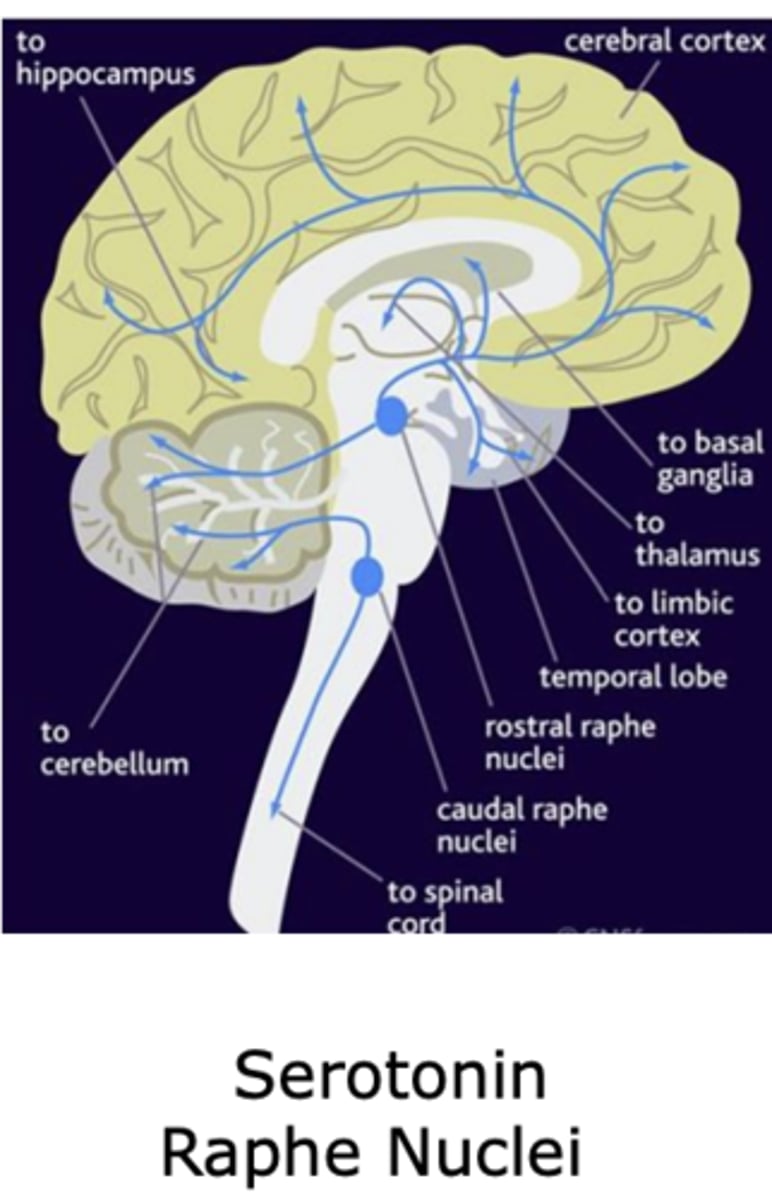
Serotonin origination and projections in the brain
Raphe Nuceli
Endorphin
Class:
Some functions:
Implications in mental health:
Class: Peptides
Some functions: Induces Euphoria, Analgesia
Implications in mental health: Chronic Pain, Addiction, Feeding Behavior
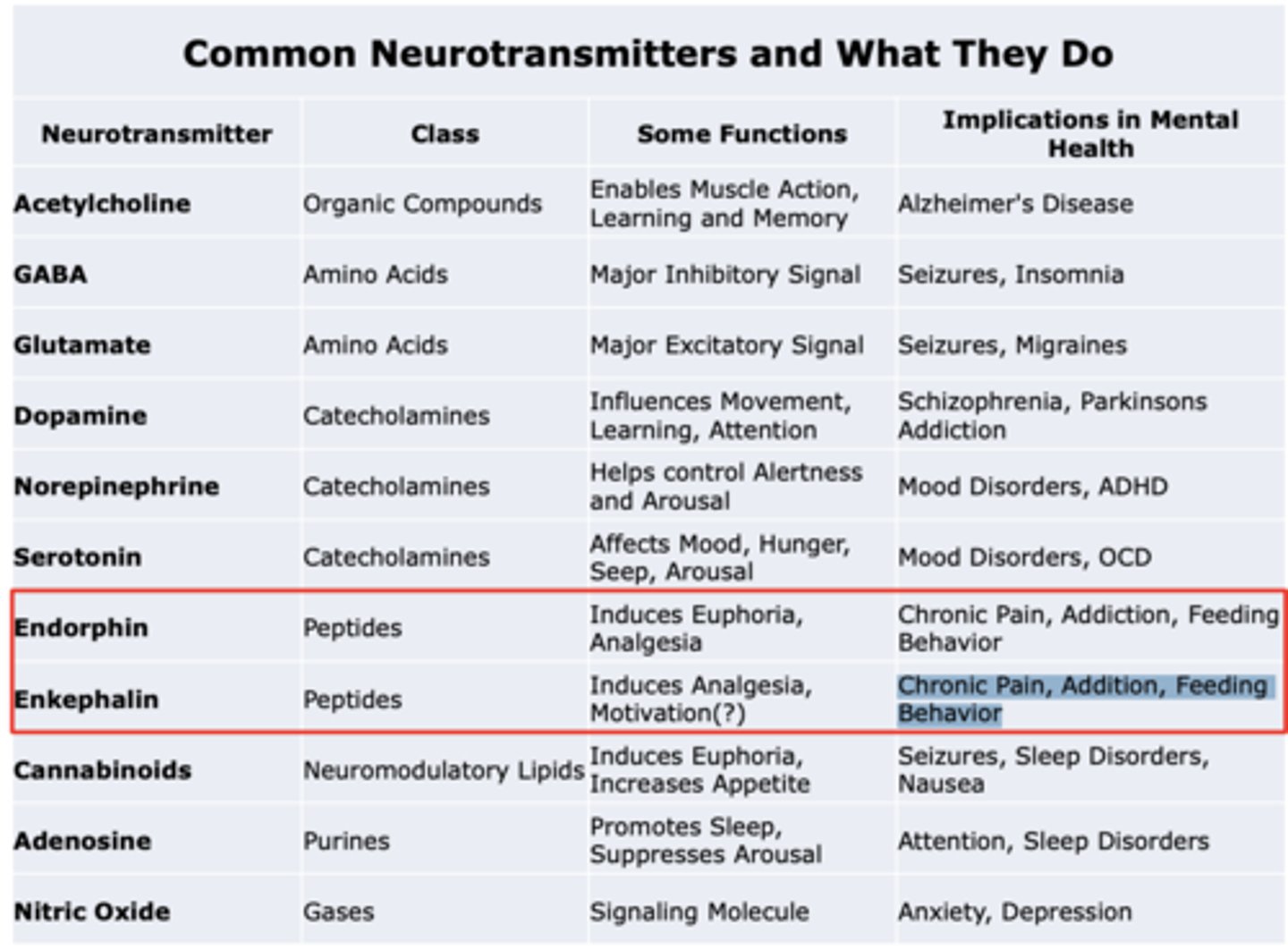
Enkephalin
Class:
Some functions:
Implications in mental health:
Class: Peptides
Some functions: Induces Analgesia, Motivation(?)
Implications in mental health: Chronic Pain, Addition, Feeding Behavior

The 4 major types of opioid receptors
Mu, Delta, Kappa, Nociceptin
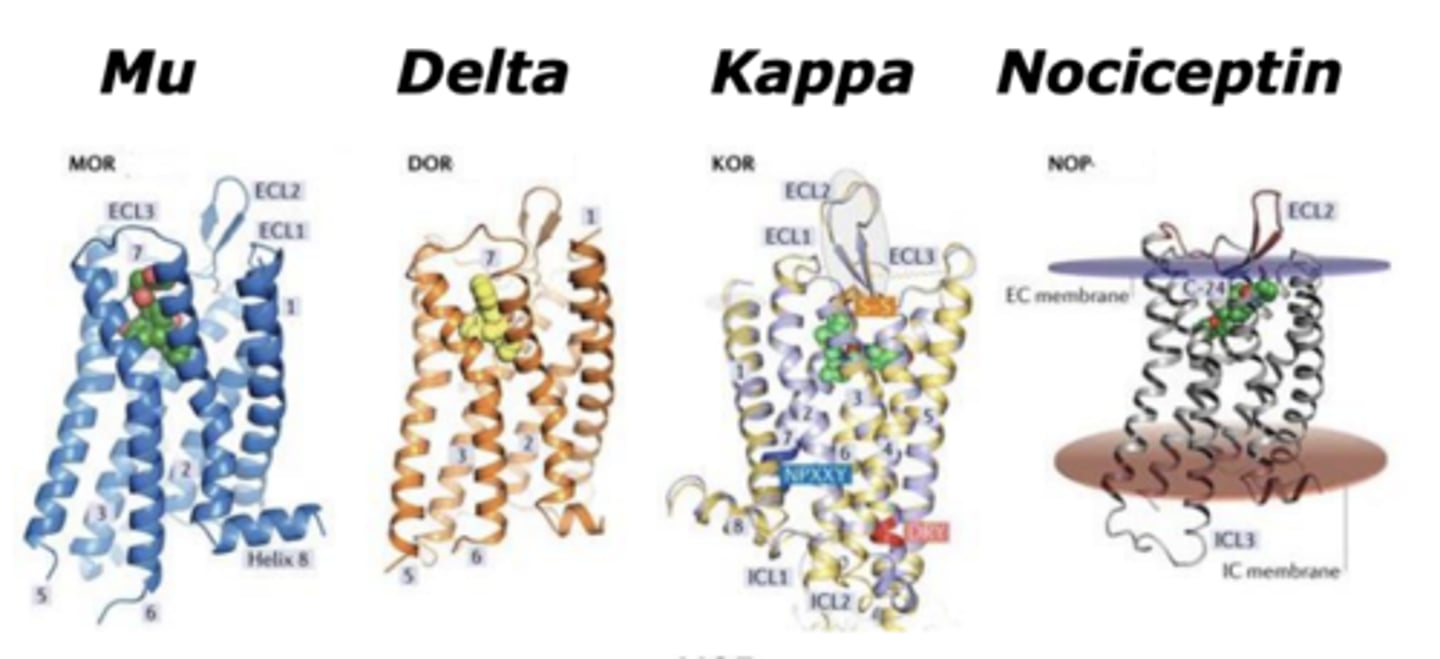
What kind of receptors are opioid receptors?
G-protein coupled receptors
What are opioid receptors implicated in?
Implicated in pain and hednoic impact (pleasure)
While _____ and _______ activation drives positive affect, _______ activation is implicated in dysphoria
- Mu and Delta
- Kappa
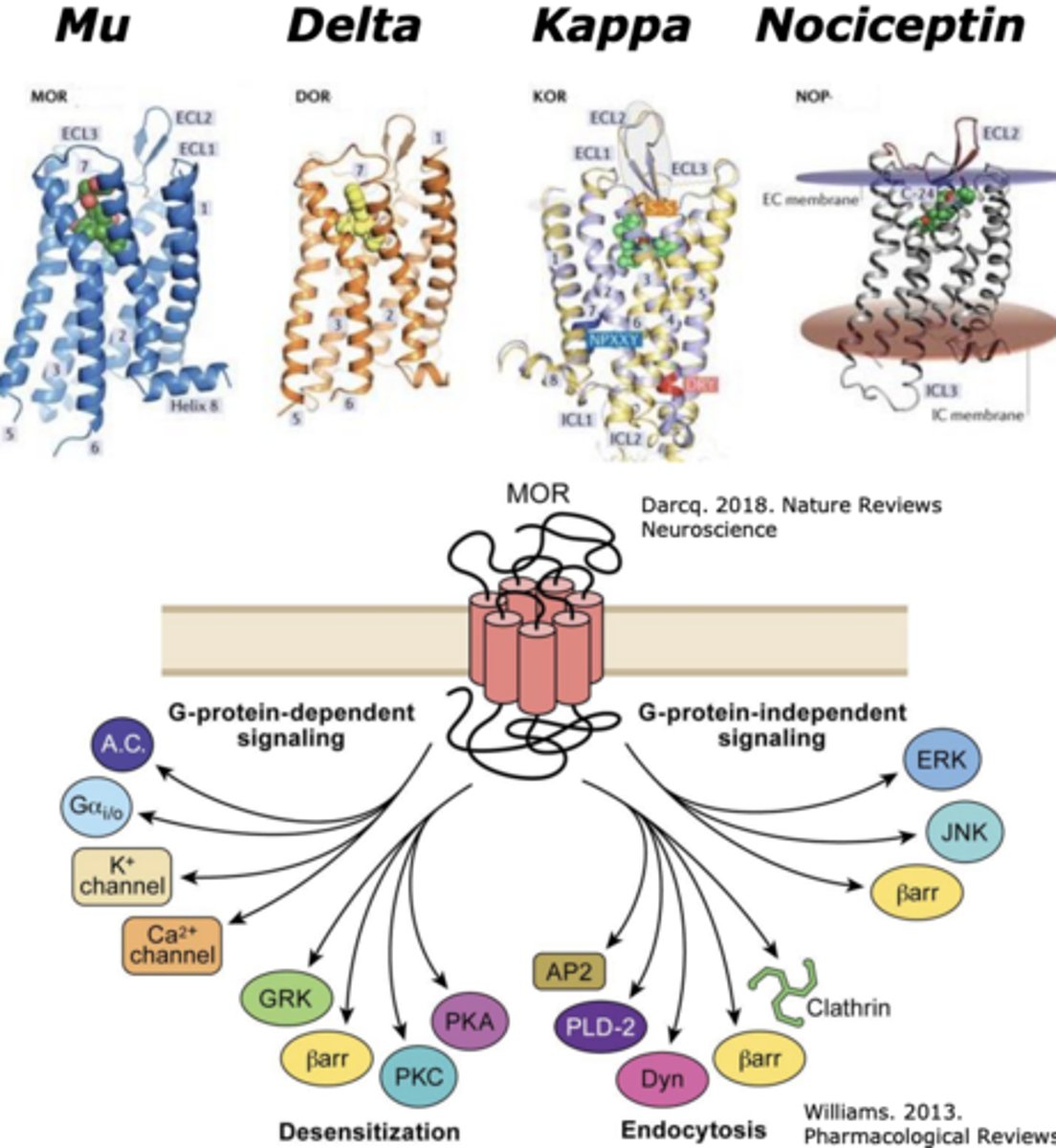
Opioid receptors have generally ______________ effects on neurons
inhibitory
Opioid projections in the brain:
pain pathways run up the spinal chord to the brain
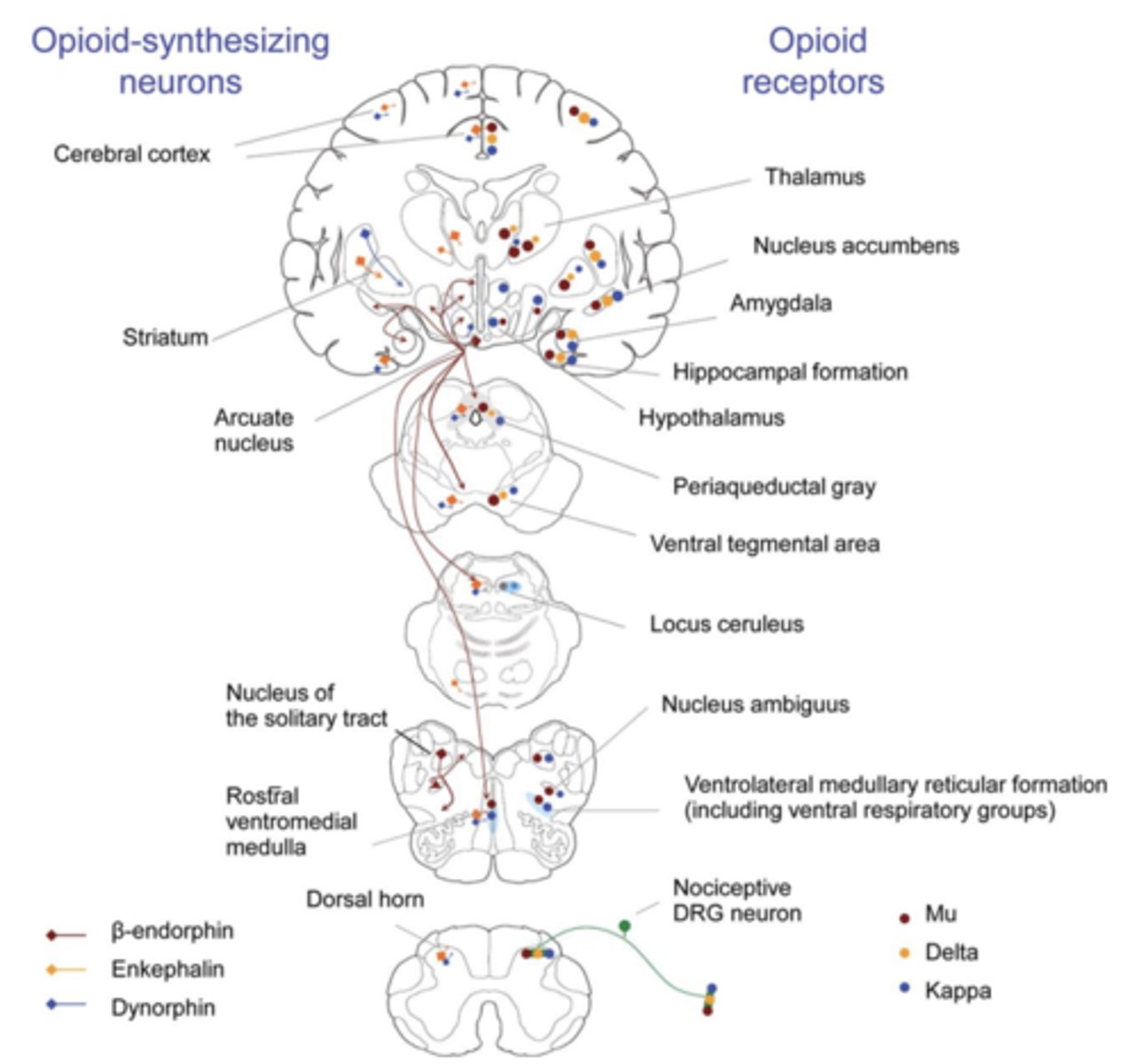
Opioid releasing neurons and opioid receptors spread throughout....
CNS
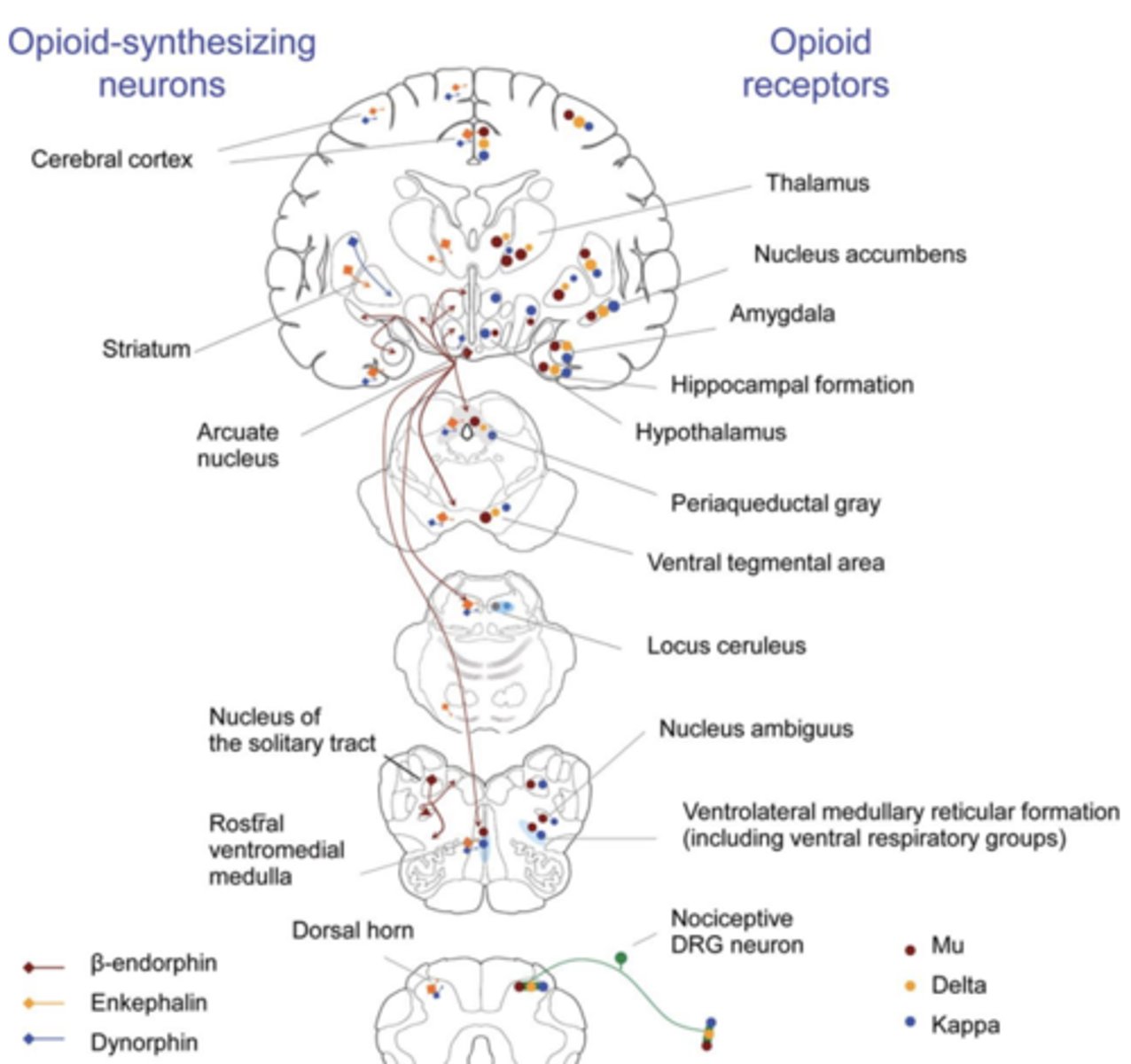
Activation of opioid pathways also inhibit....
respiratory system
Cannabinoids
Class:
Some functions:
Implications in mental health:
Class: Neuromodulatory lipids
Some functions: Induces Euphoria, Increases appetite
Implications in mental health: Seizures, Sleep Disorders, Nausea

T/F: Endocannabinoid system is one of the more complex signaling systems in the body
TRUE
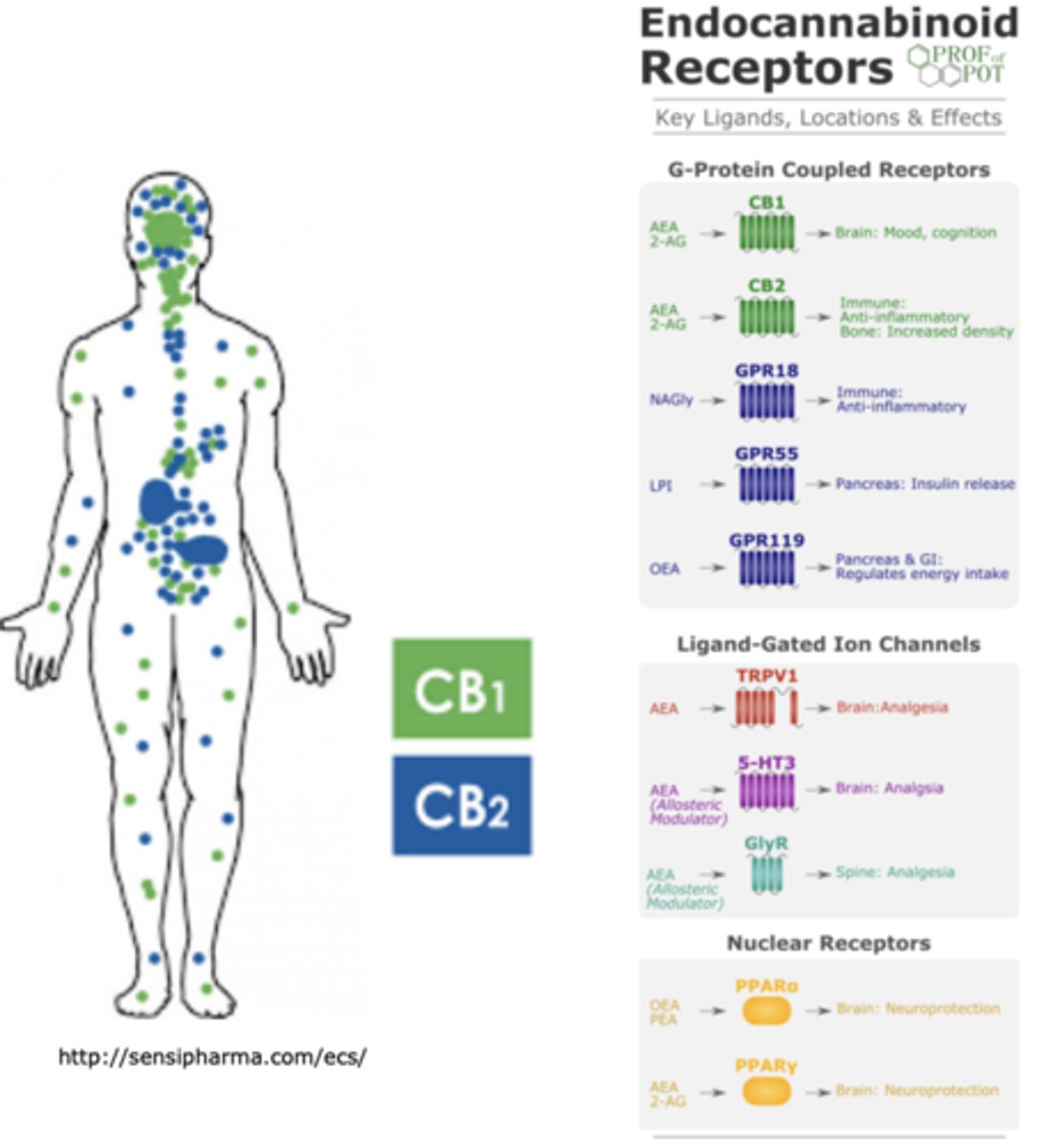
What are 2 major types of G-protein coupled cannabinoid receptors?
CB1 and CB2
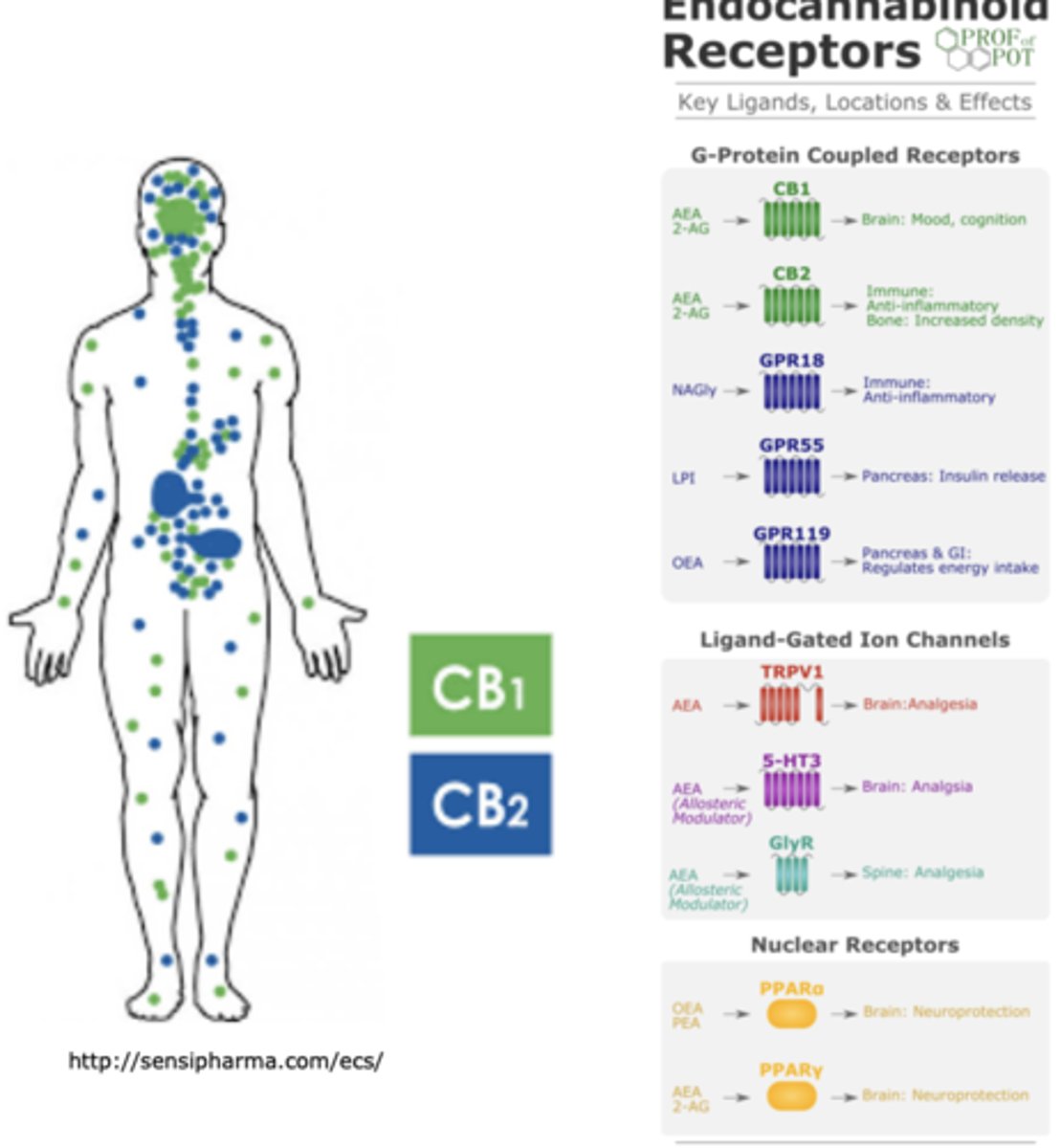
Cannabinoid receptors can also bind to other ______________, _______________, and __________________
- G-protein coupled receptors
- ligand gated ion channels
- nuclear receptors
The endocannabinoid Anandamide is synthesized on demand in.....
stimulated postsynaptic cells
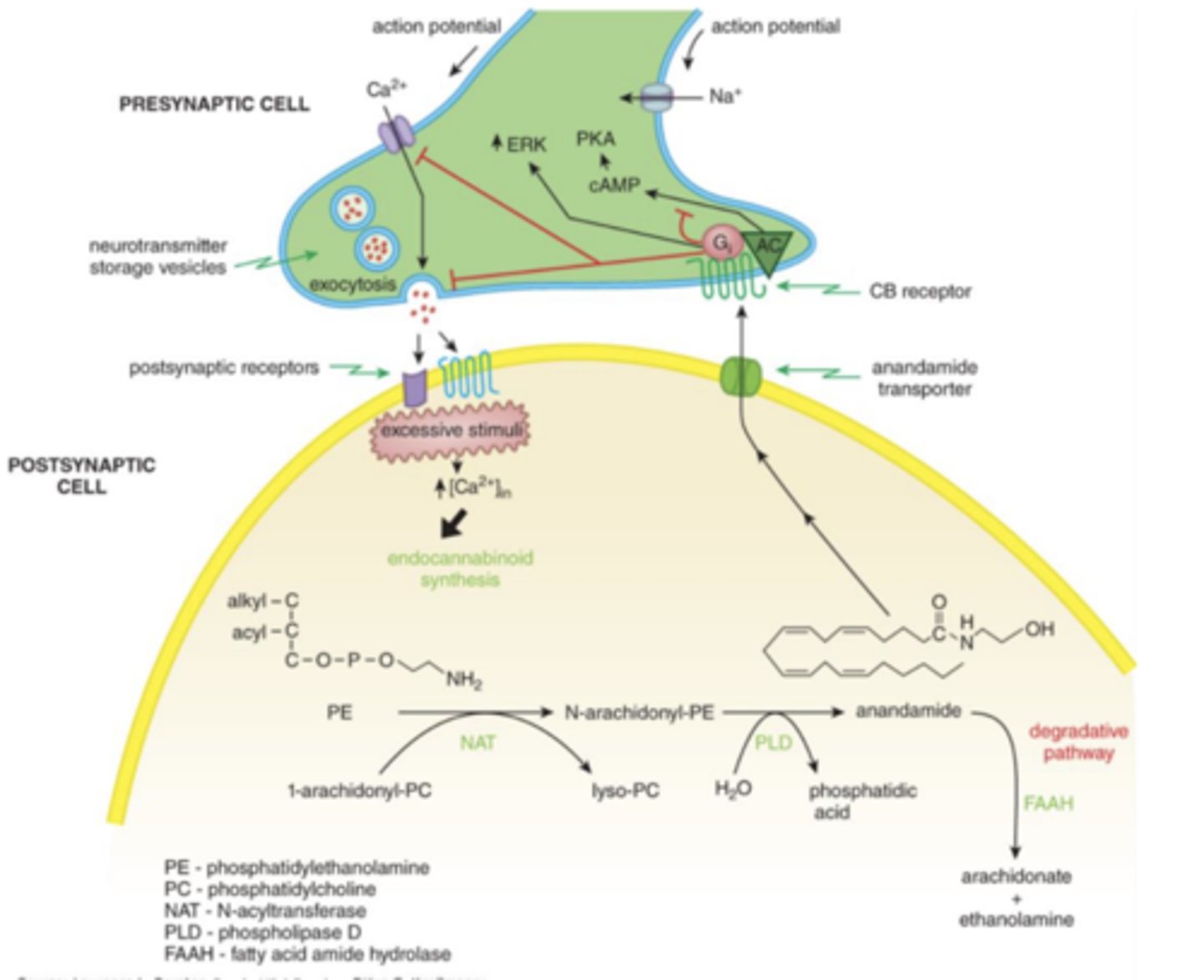
Cannabinoid receptors for negative feedback in the synapse
Function as a negative feedback system to limit further presynaptic transmitter release (inhibitory effect)
What have cannabinoid receptors been shown as an effective target for the treatment of?
nausea, glaucoma, and seizures
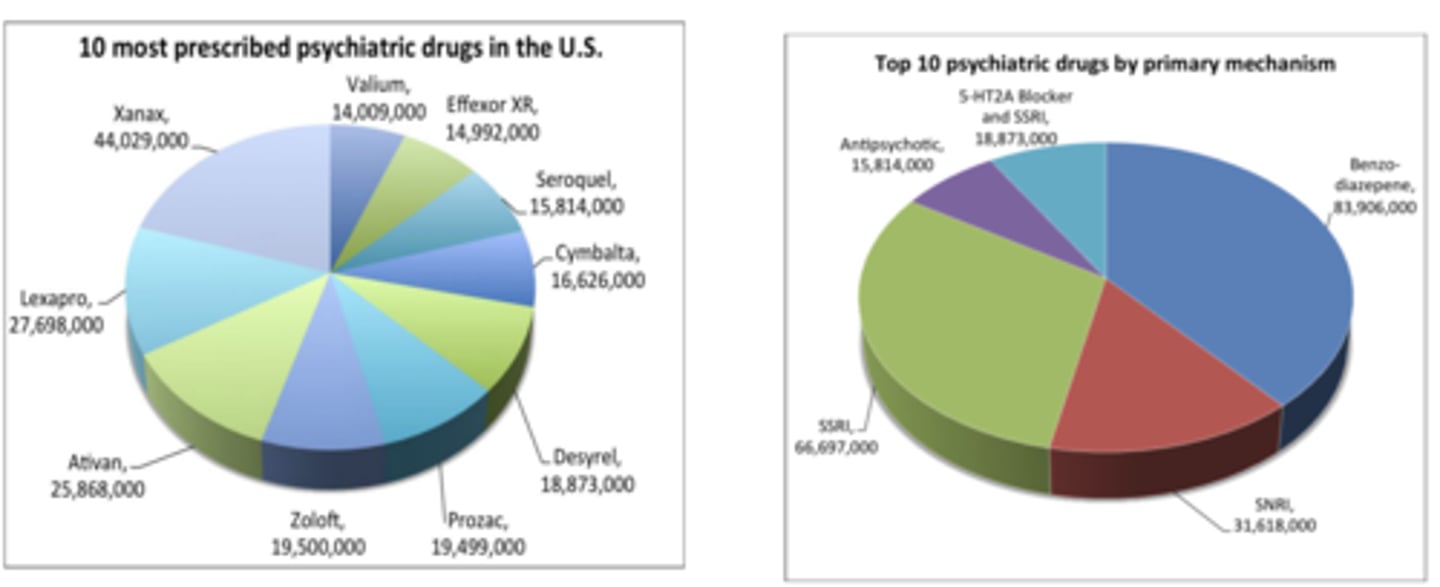
Most prescribed drugs are primarily used for the treatment of depression and anxiety
• Antidepressants
• Anxiolytics/Sedatives/Hypnotics
Antidepressants
• Enhance mood
• Have Selective Serotonin and Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitory properties (SSRIs, SNRIs)
• Ex: Prozac, Zoloft, Lexapro, Desyrel, Cymbalta, Effexor
Anxiolytics/Sedatives/Hypnotics
• Decrease Anxiety, have calming effect
• Benzodiazepines
• Ex: Xanax, Valium, Ativan
Benzos and barbiturates target....
the GABAa receptor
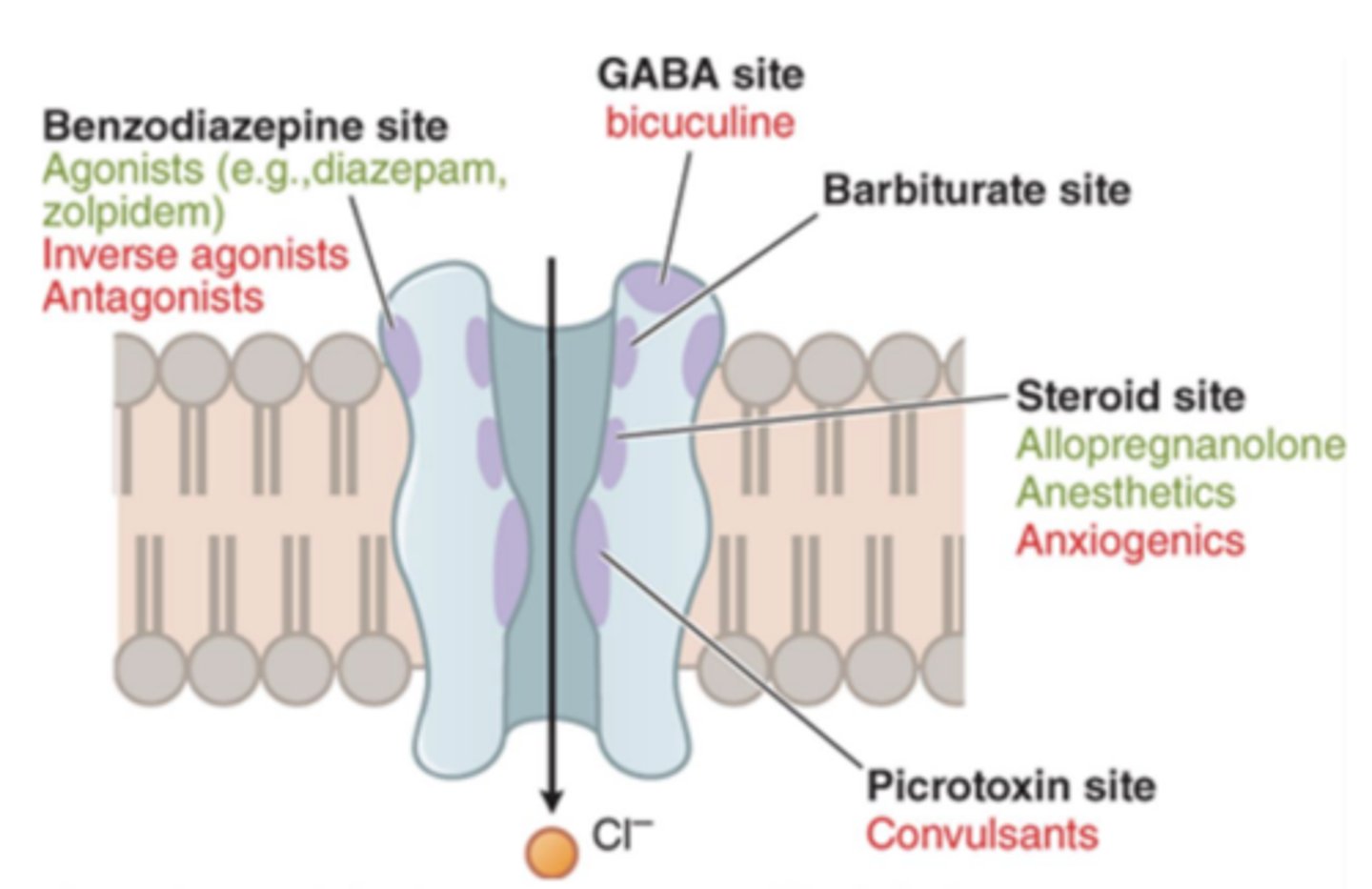
What are benzodiazepines and barbiturates? What are the commonly used for?
- CNS depressant
- commonly used for insomnia
- Benzos also have anxiolytic properties
- Barbiturates are useful for headaches
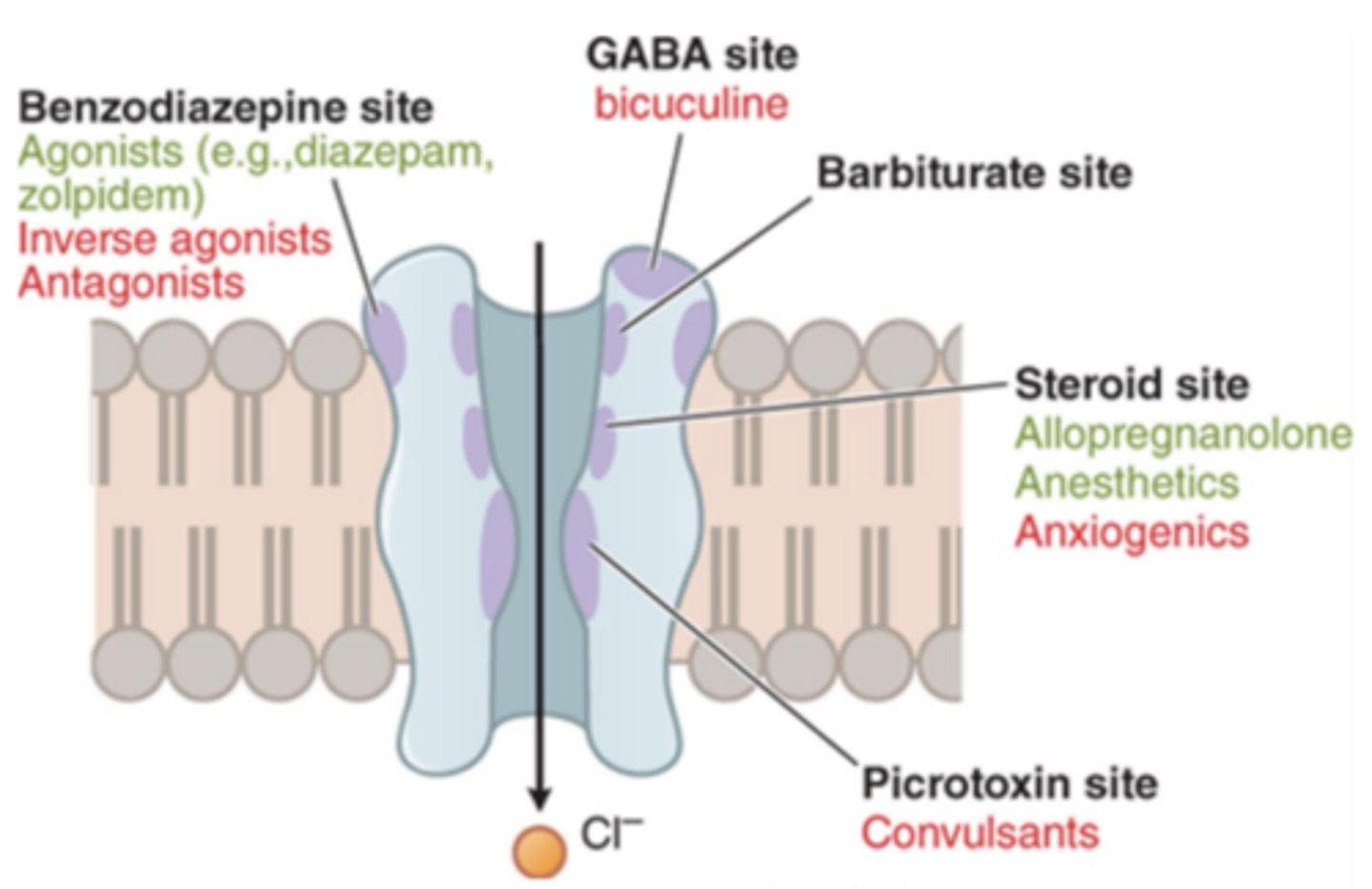
What are common side effects of benzos and barbiturates?
dizziness, headaches, stomach pains
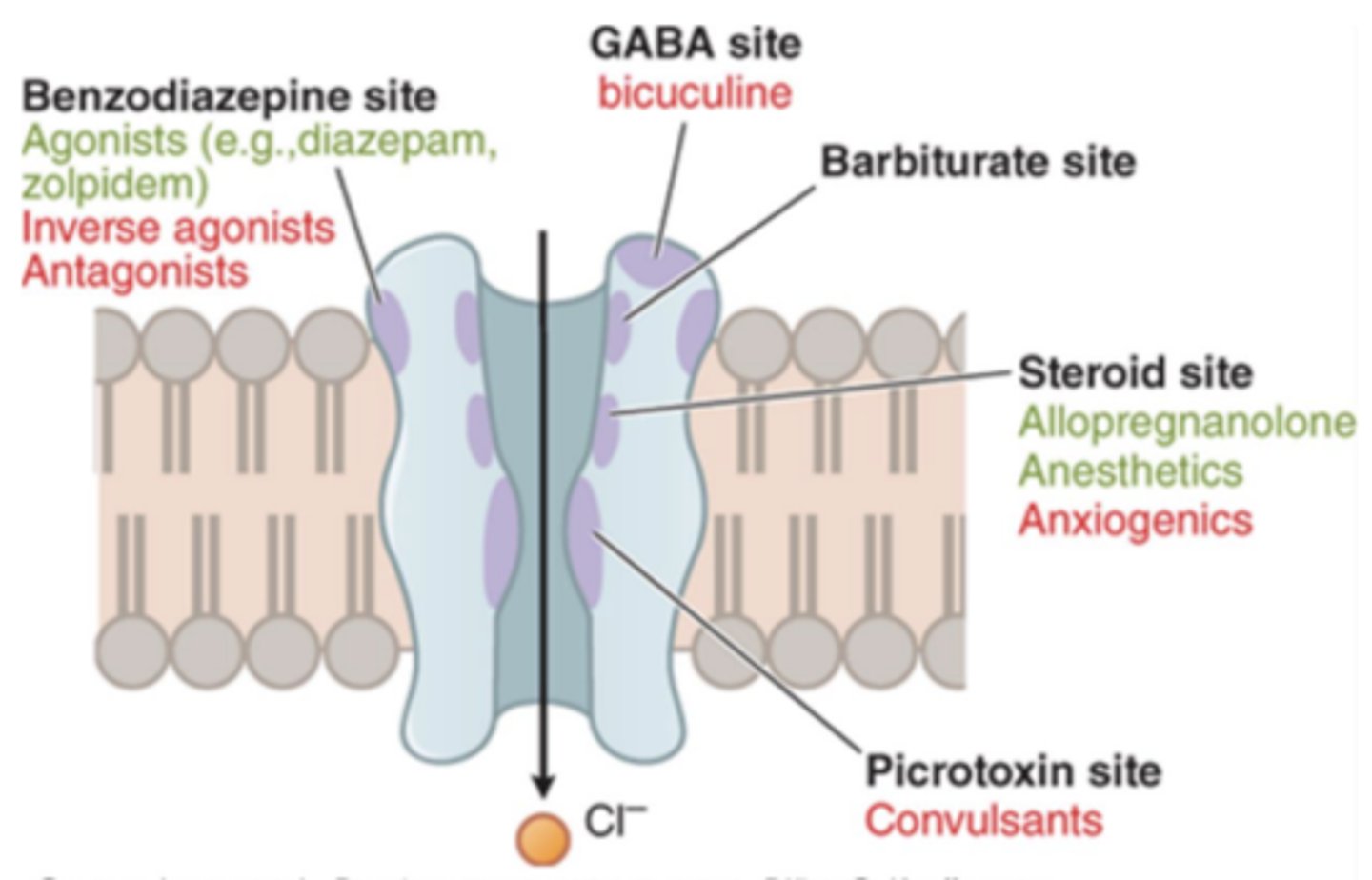
Alcohol affects _________ receptors; however, mechanism is still unclear
GABA
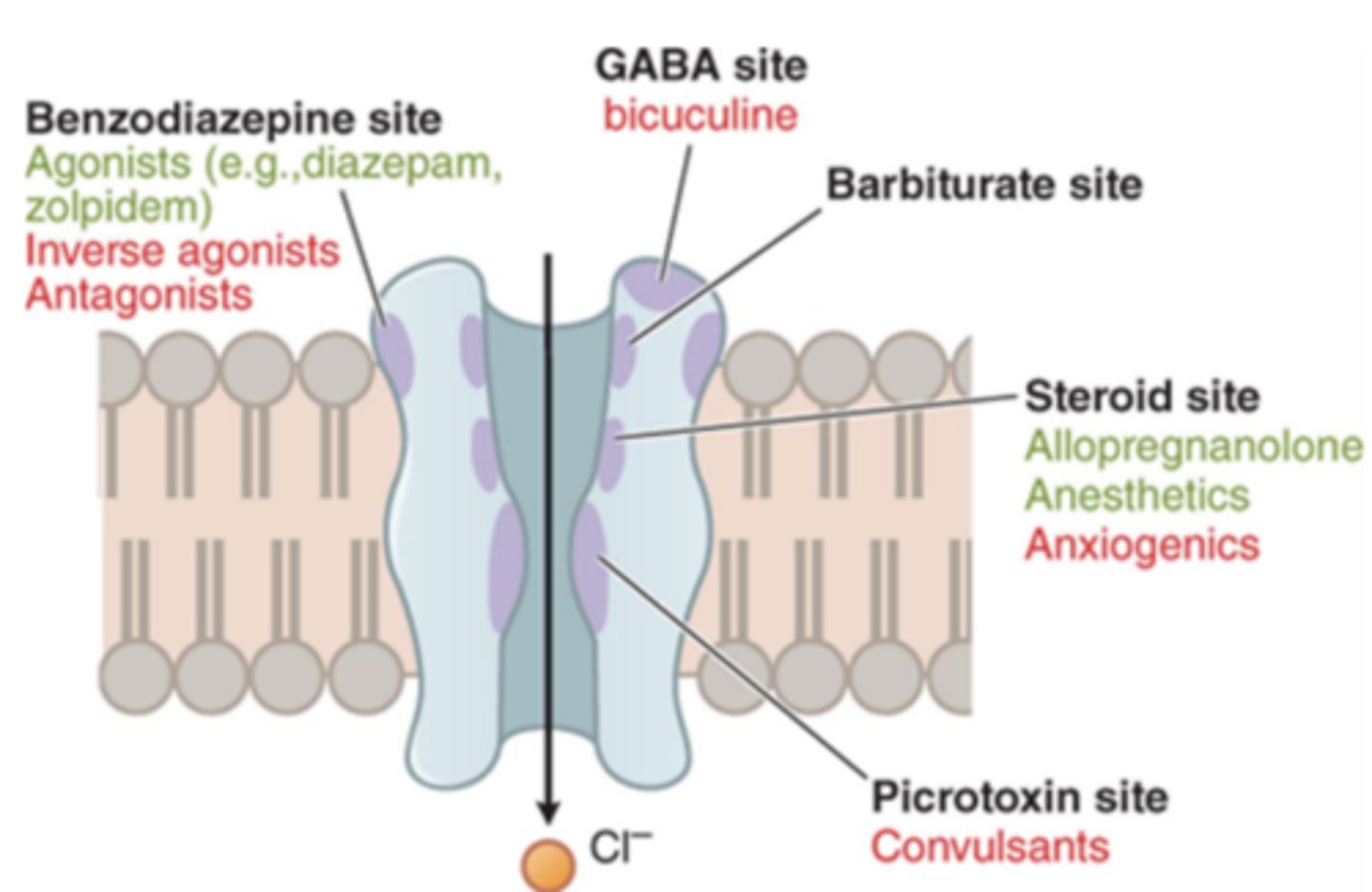
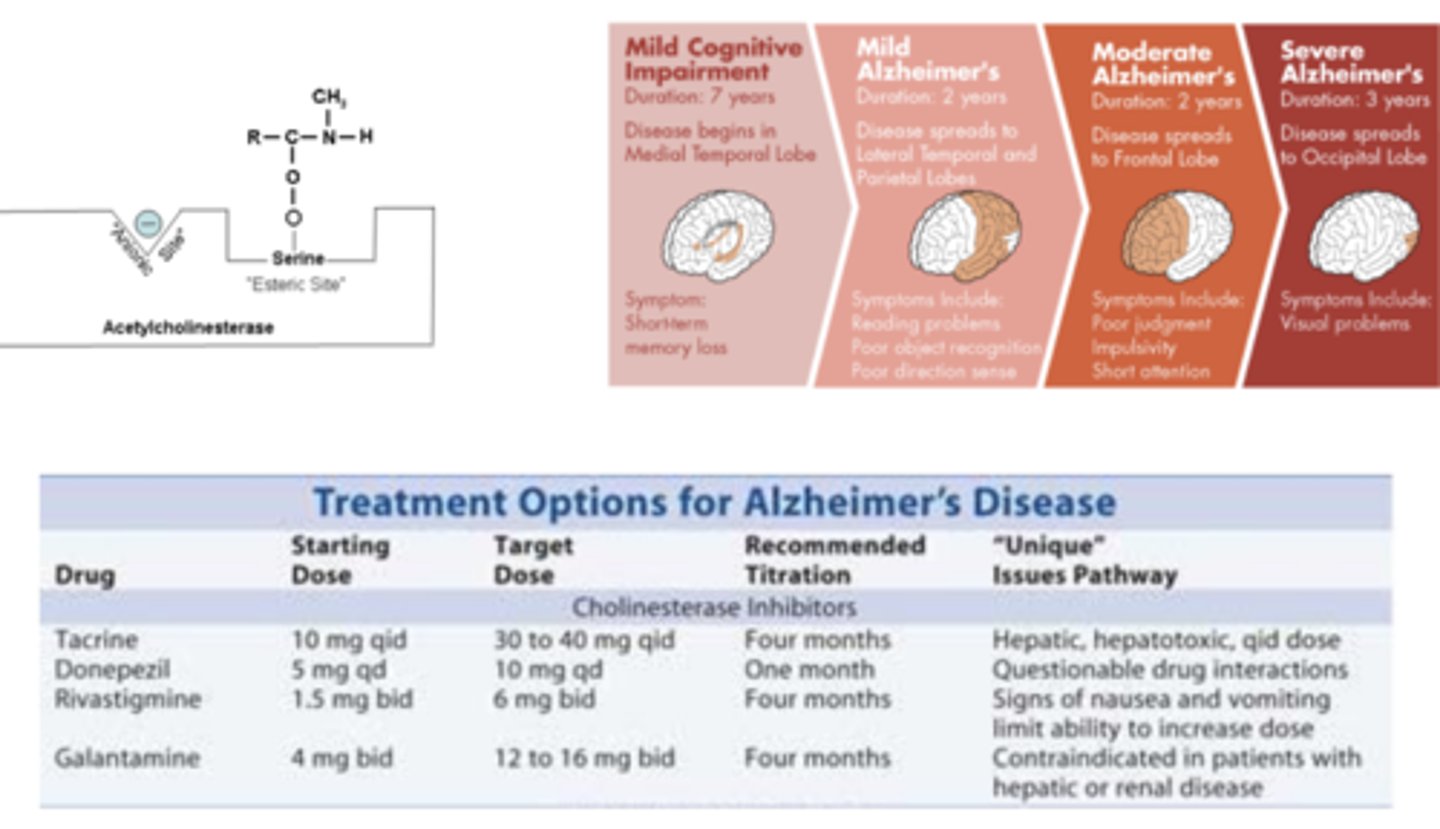
Pathophysiology of Parkinson's Disease
- Nigrostriatal dopamine pathway is part of a complex circuit that controls voluntary movements
- D1 and D2 type dopamine receptors in striatum work together to control movement
L-DOPA for the treatment of Parkinson's Disease
Pathophysiology of Alzheimer's Disease
- Mechanism is not well understood, but neuronal death caused by amyloid plaques and tau tangles is associated
- has been proposed that approximately 70% of risk is genetic
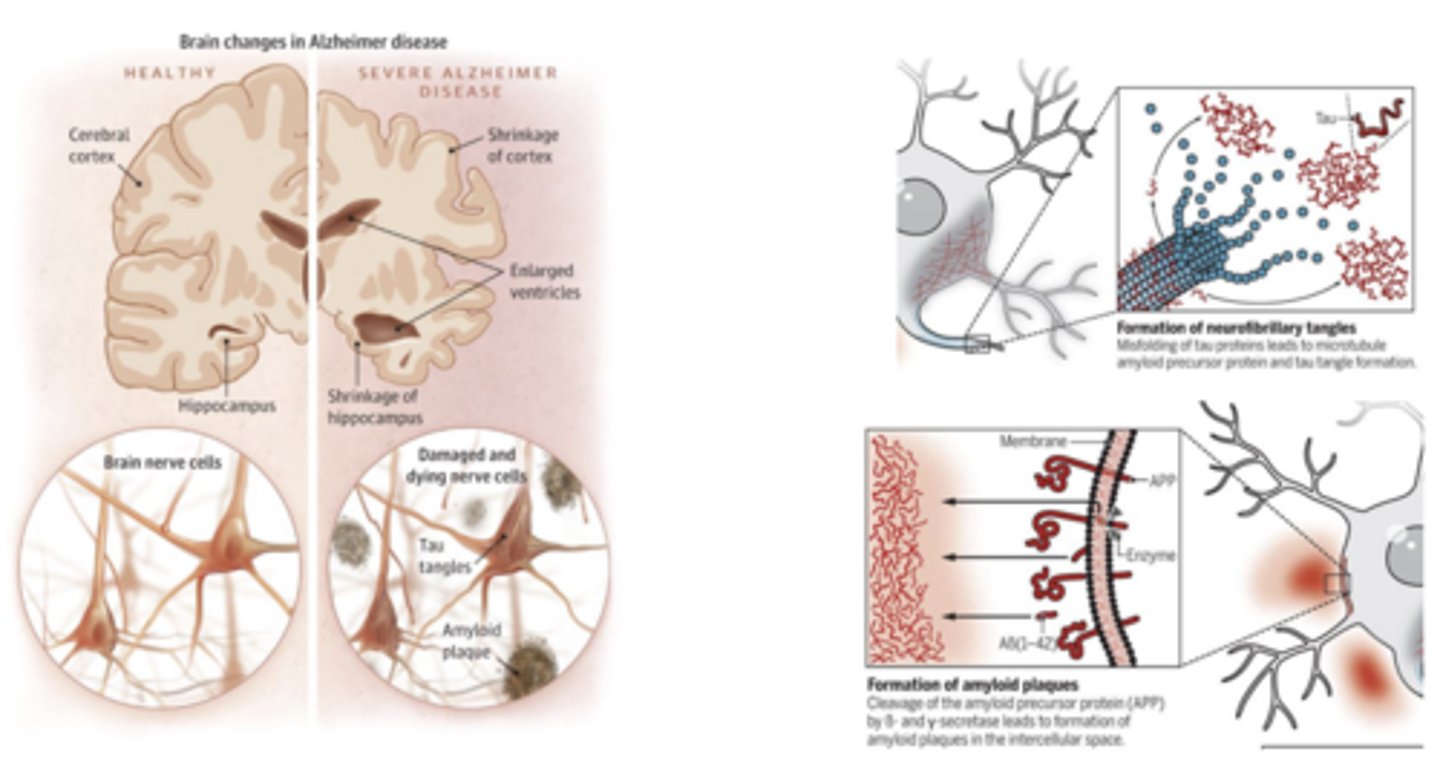
Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors work as ______________________ to temporarily offset symptoms of Alzheimer's Disease
- cognitive enhancers
- Good BBB penetration
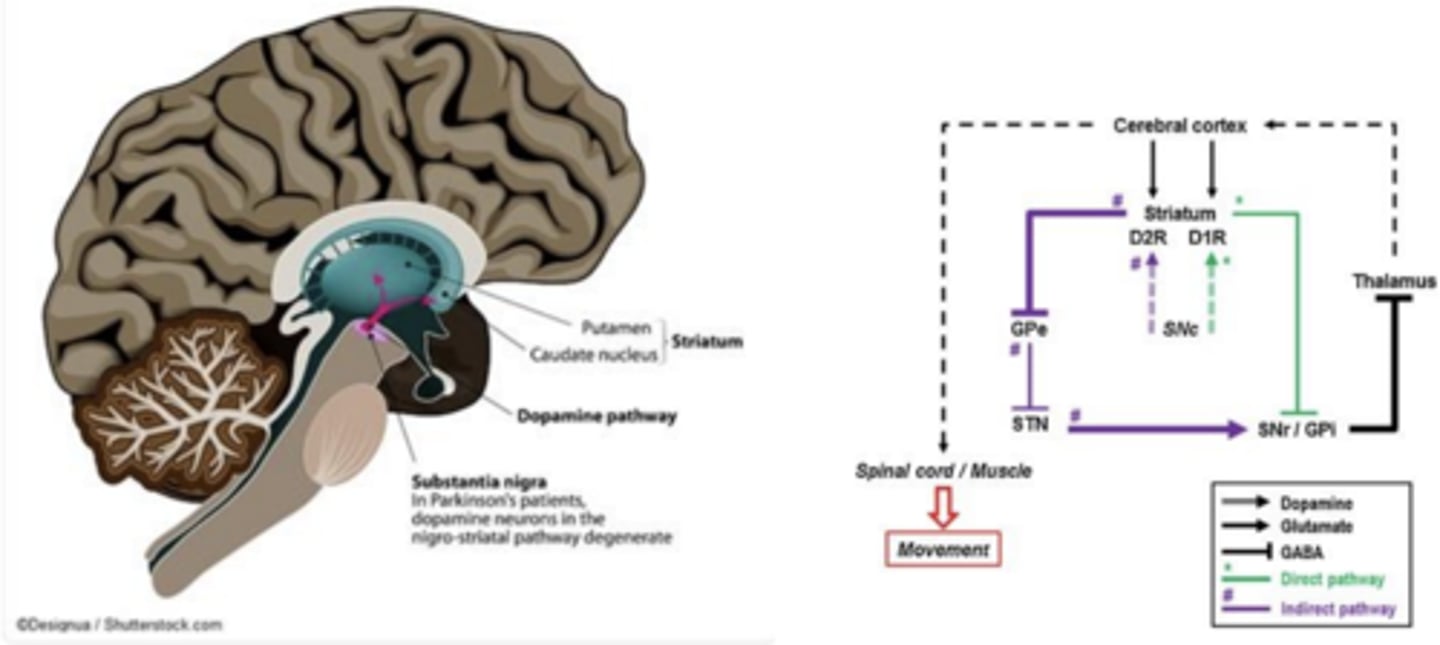
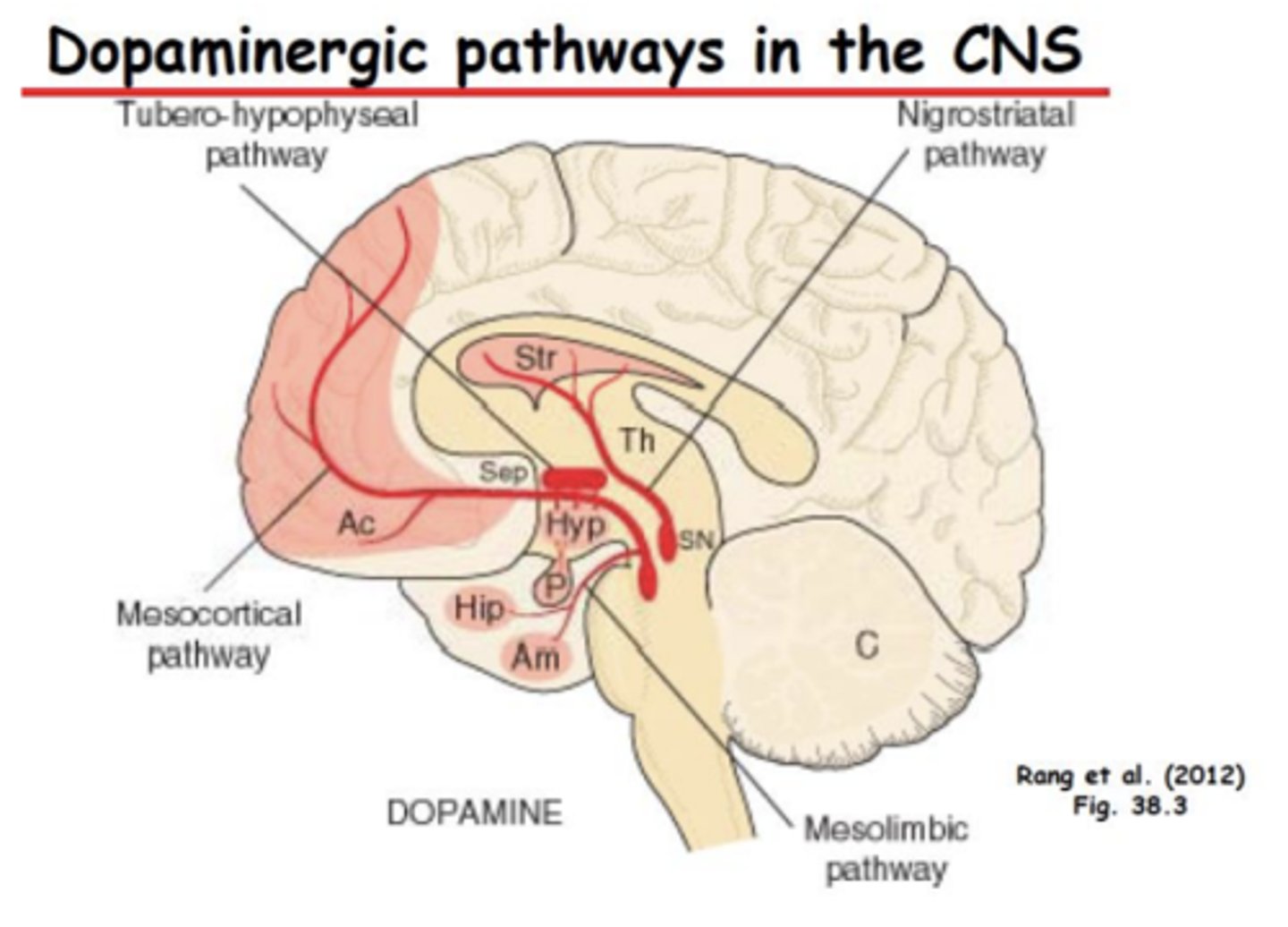
- Pathophysiology of Schizophrenia: Pathways (3)
• Mesolimbic Dopamine Pathway
• Mesocortical Dopamine Pathway
• Glutamatergic pathways from cortex to midbrain areas also implicated
Schizophrenia: Mesolimbic Dopamine Pathway
– Increase in DA causes positive symptoms
– Positive symptoms include disorganized thought, hallucinations
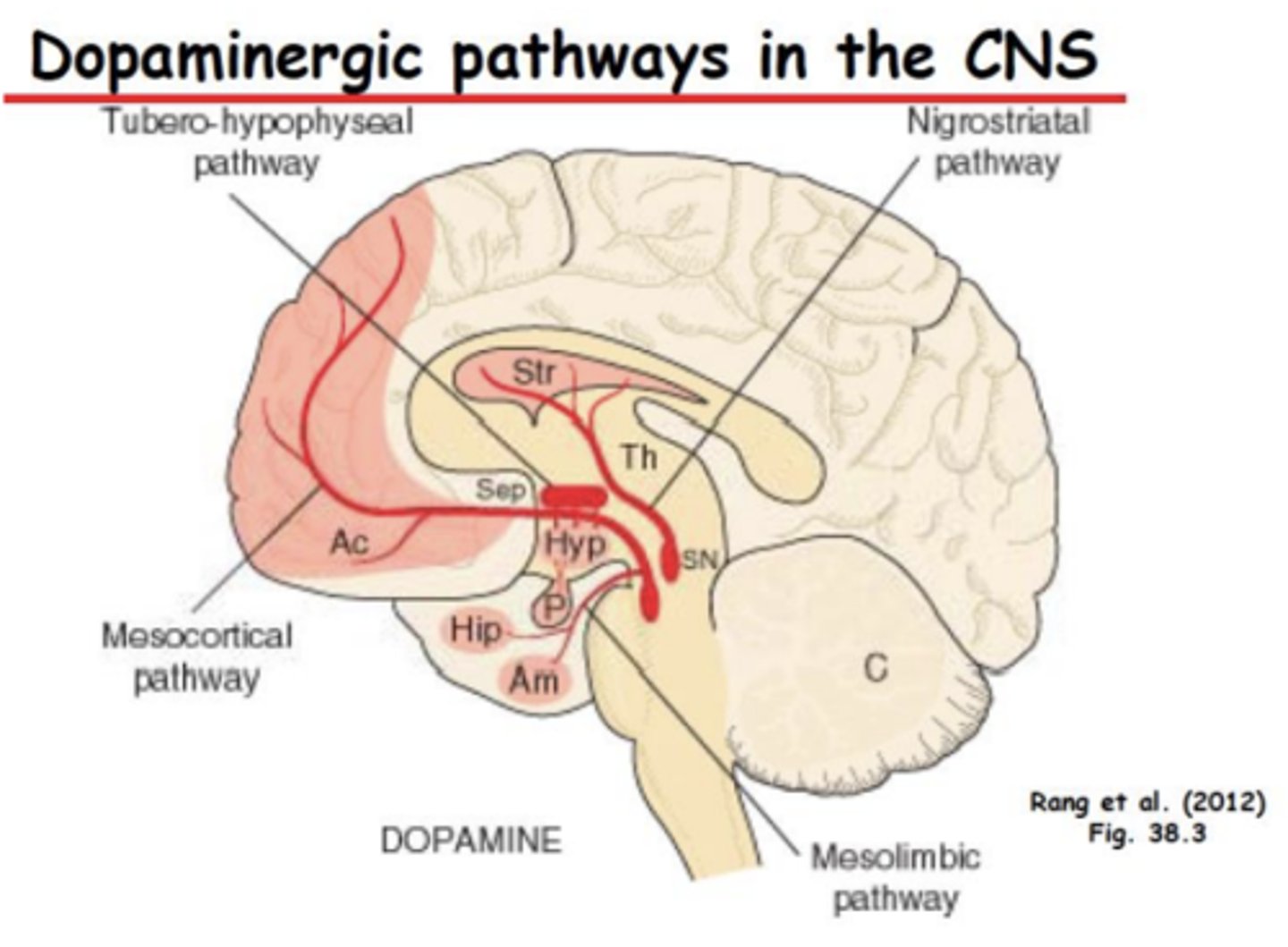
Schizophrenia: Mesocortical Dopamine Pathway
– Decrease in DA signaling causes negative symptoms
– Negative symptoms include decreased motivation, emotion, and pleasure. Attentional deficits
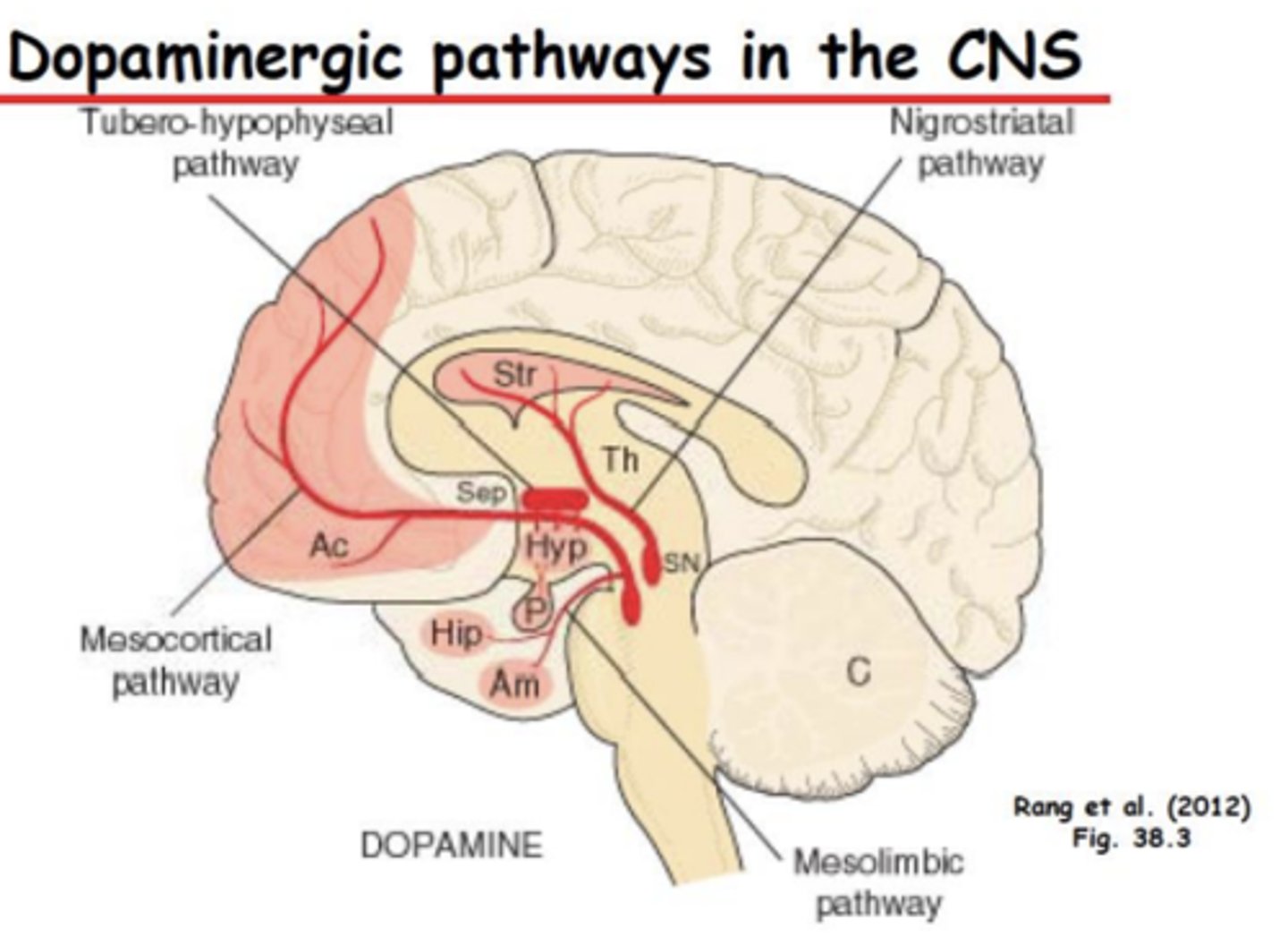
Schizophrenia: Glutamatergic pathways
- Activation of NMDA receptors controls mesolimbic and mesocortical pathways
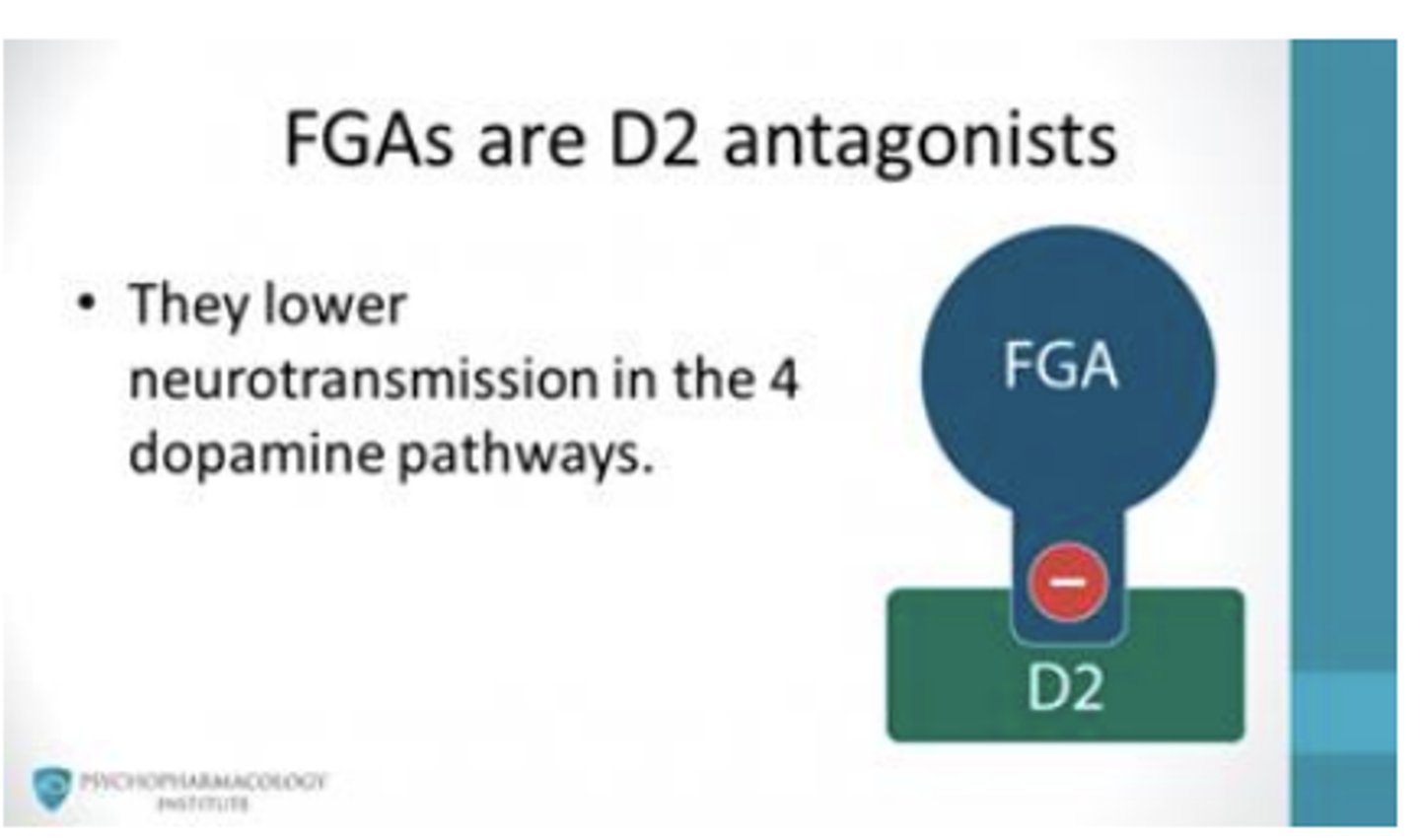
Antipsychotics for the treatment of Schizophrenia: First Generation Antipsychotics (FGA)
FGAs are D2 antagonists
- they lower neurotransmission in the 4 dopamine pathways
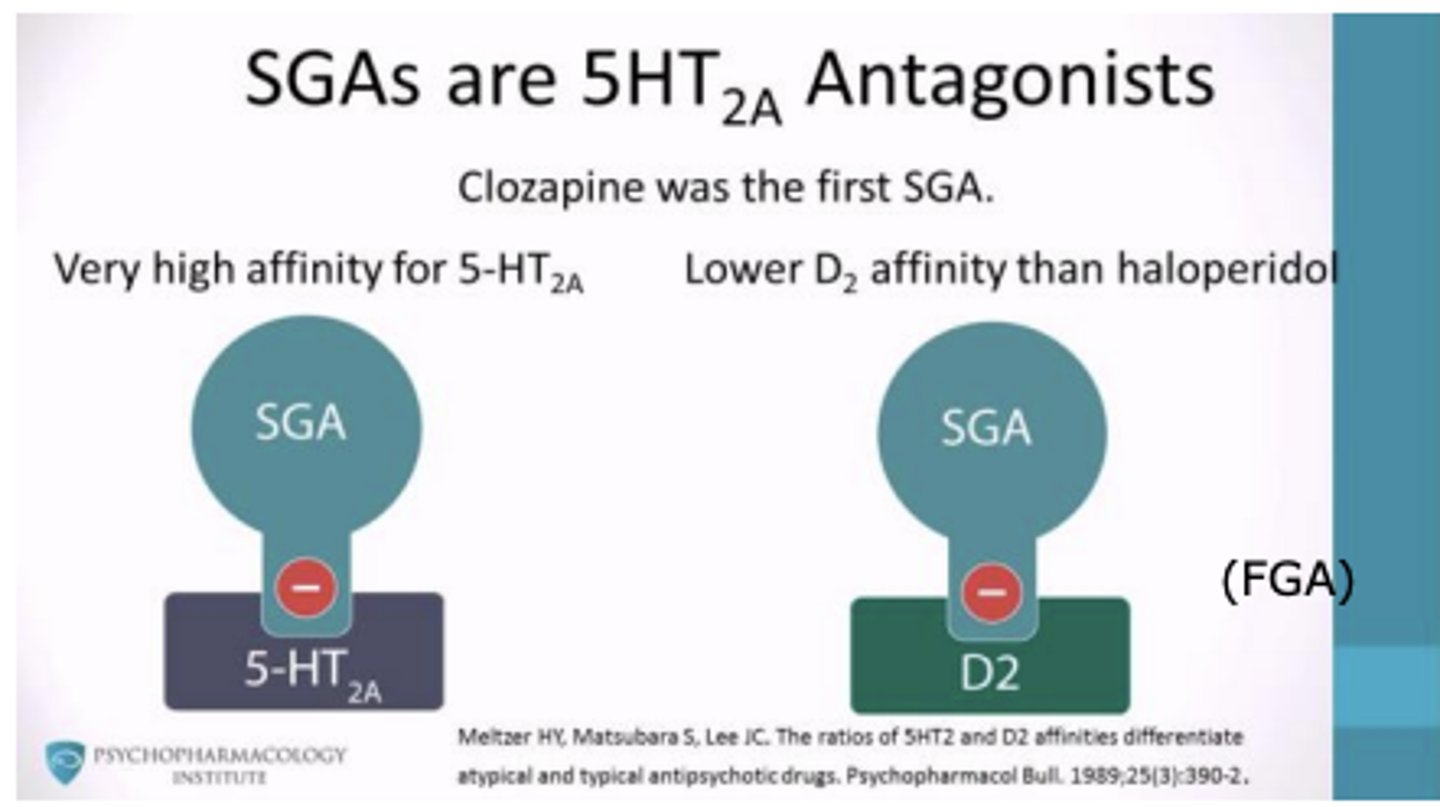
Antipsychotics for the treatment of Schizophrenia: Second Generation Antipsychotics (SGA)
SGAs are 5HT2a antagonists
- Very high affinity for 5-HT2a
- Lower D2 affinity than haloperidol
- clozapine was the first SGA
Adverse effects of atypical antipsychotic treatments
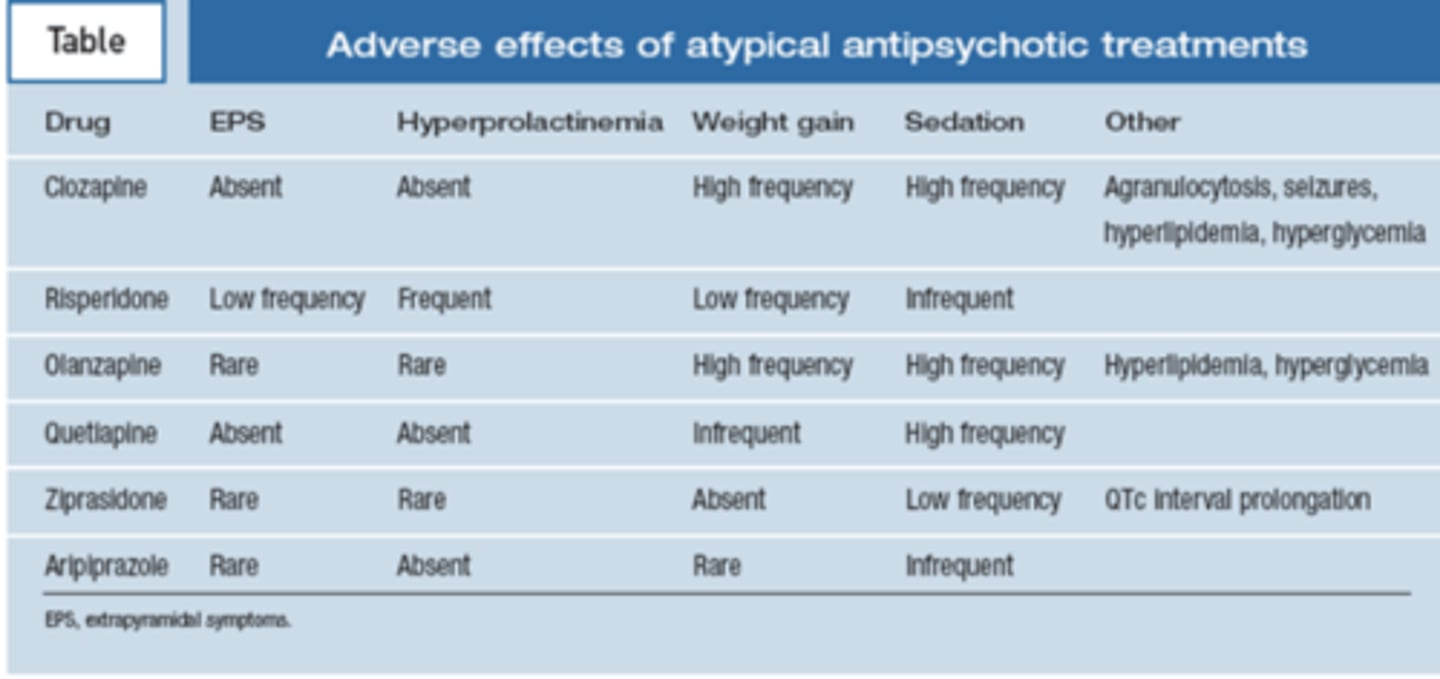
- Extrapyramidal symptoms
- Hyperprolactinemia
- movement symptoms
- increase in prolactin, a protein involved in breast development and lactation
The addiction cycle: From use to abuse
What 3 things do current theories for substance abuse identify as the factors driving addiction?
1. Increases reward sensitivity (dopamine, basal ganglia)
2. Increased negative affect (CRF, amygdala)
3. Impaired executive function (glutamate, cortex)
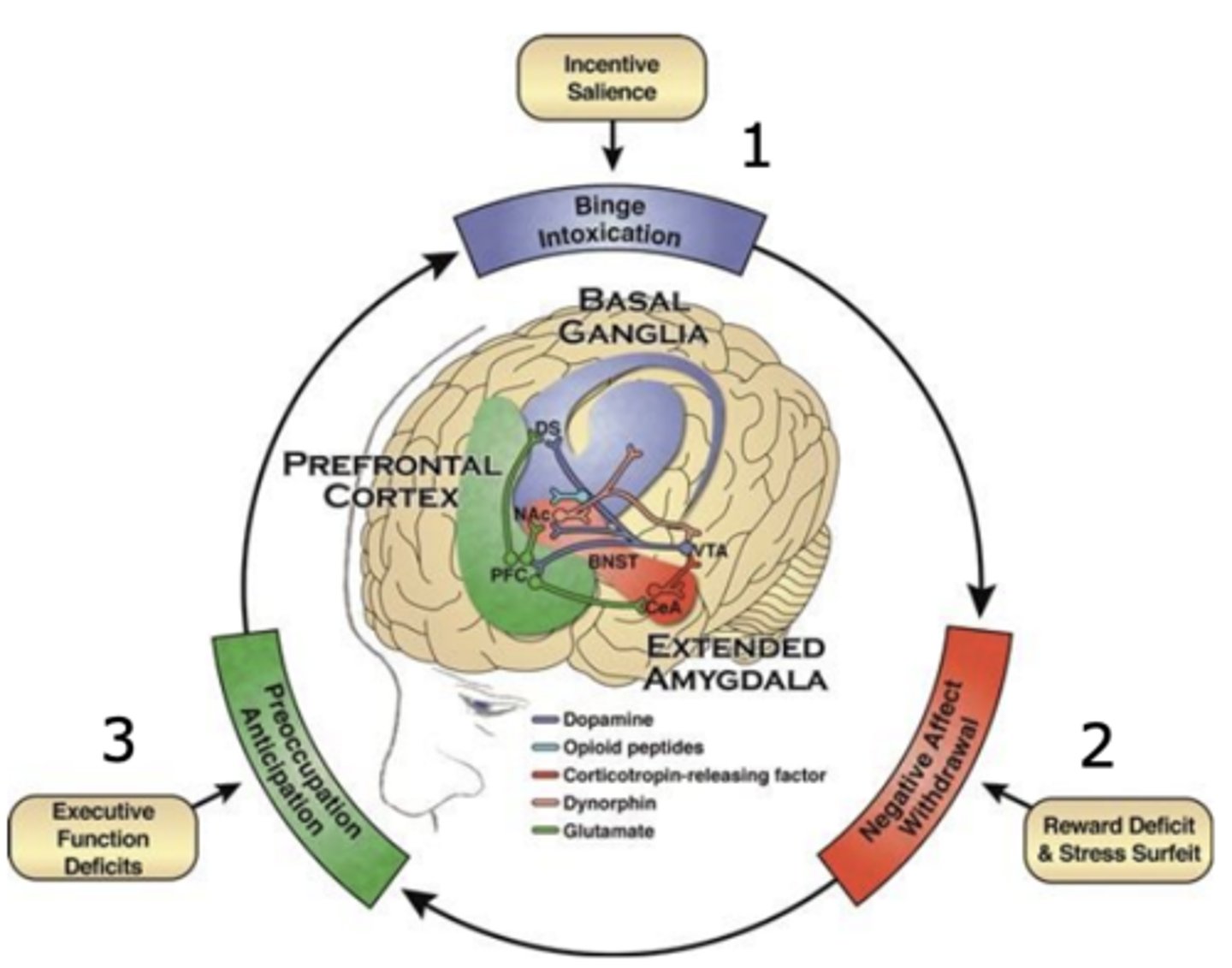
Initial drug use is driven by....
pursuit of positive reinforcement
Later drug use is driven by motivation to....
avoid negative affect (emotion)
Where is dopamine released by addictive drugs of abuse?
released in the nucleus accumbens
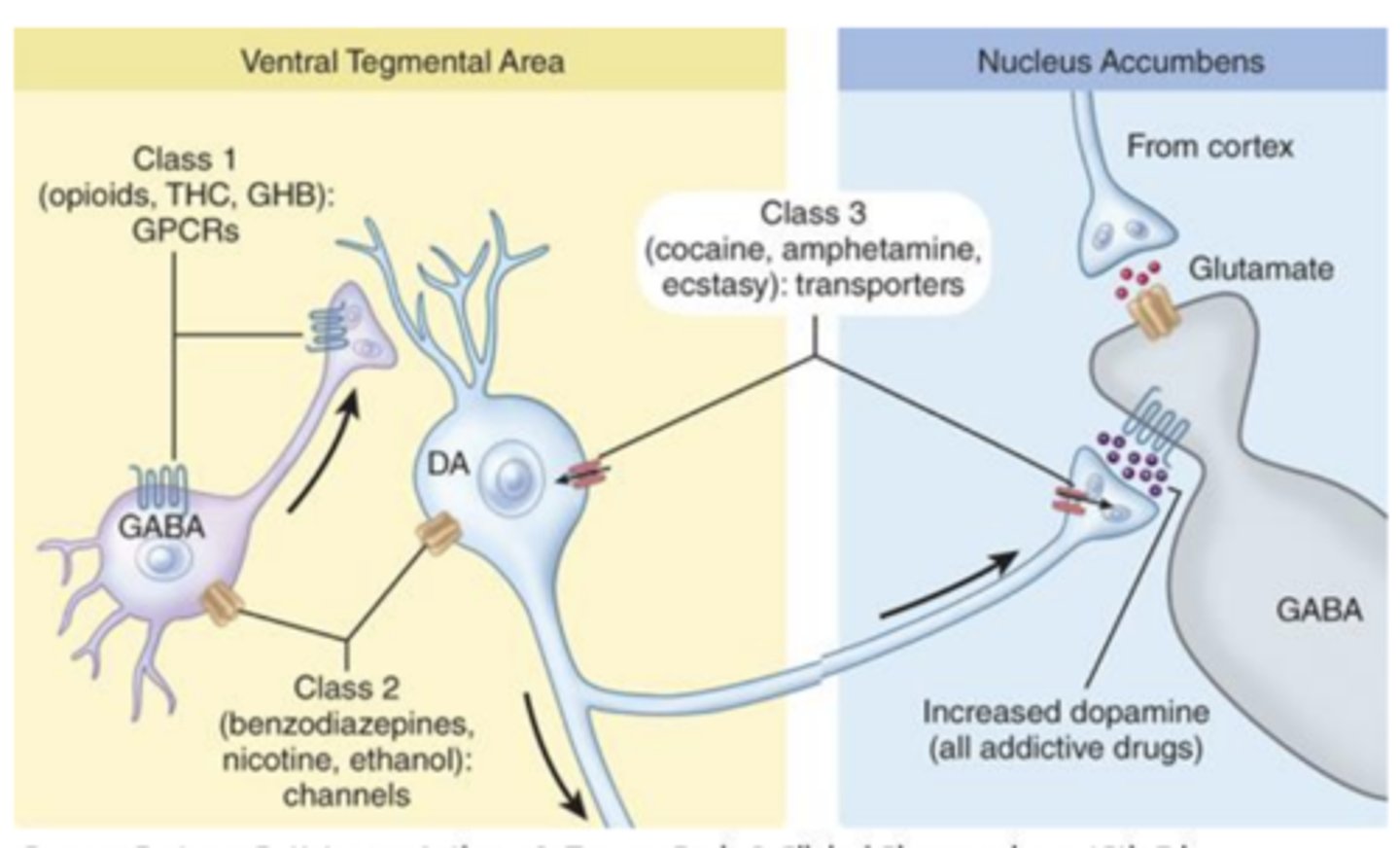
Dopamine release in nucleus accumbens following exposure to addictive drugs is suggested to....
drive reward seeking behavior
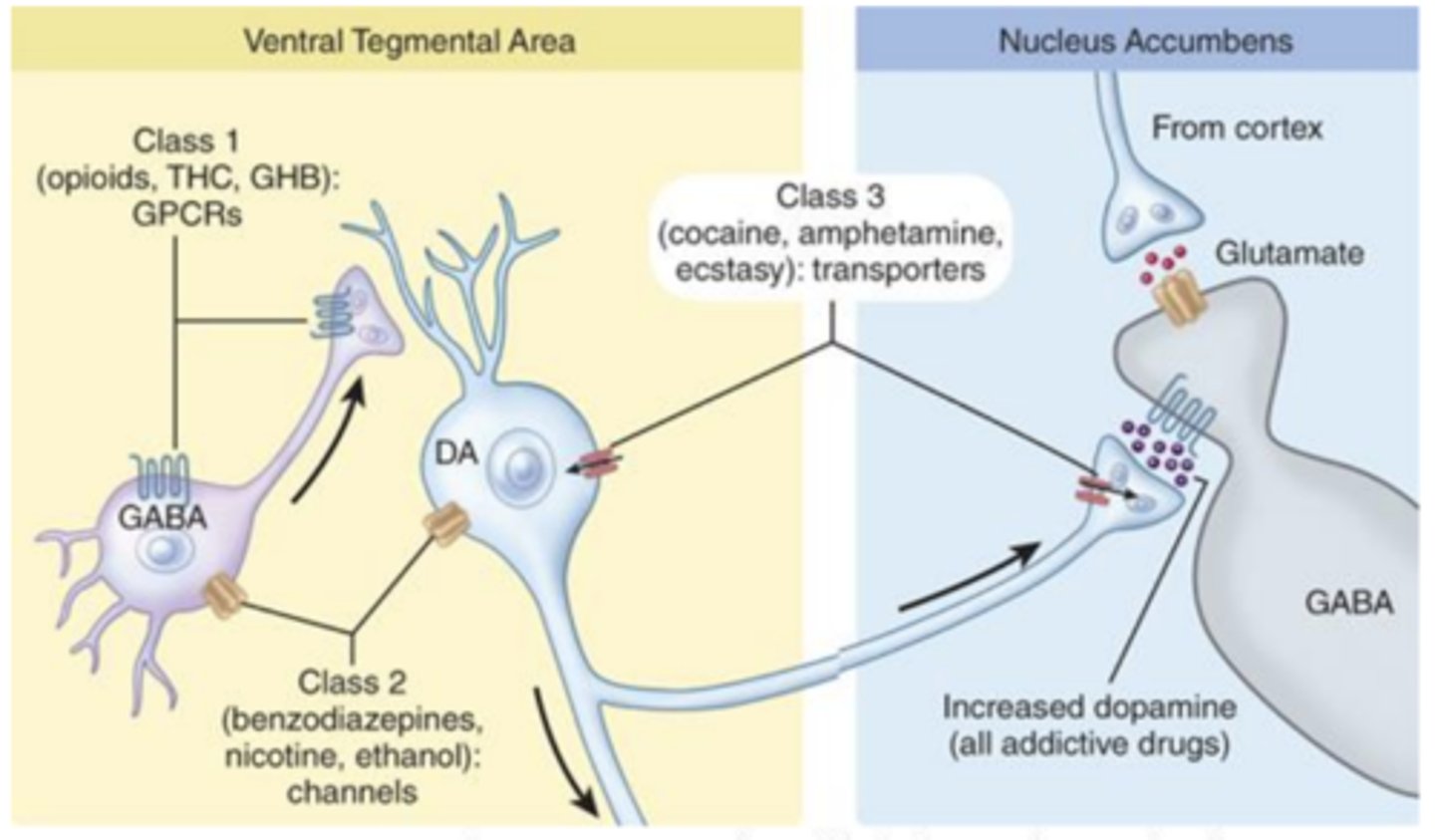
Release of what from which areas can inhibit reward seeking behavior?
glutamate release of cortical areas
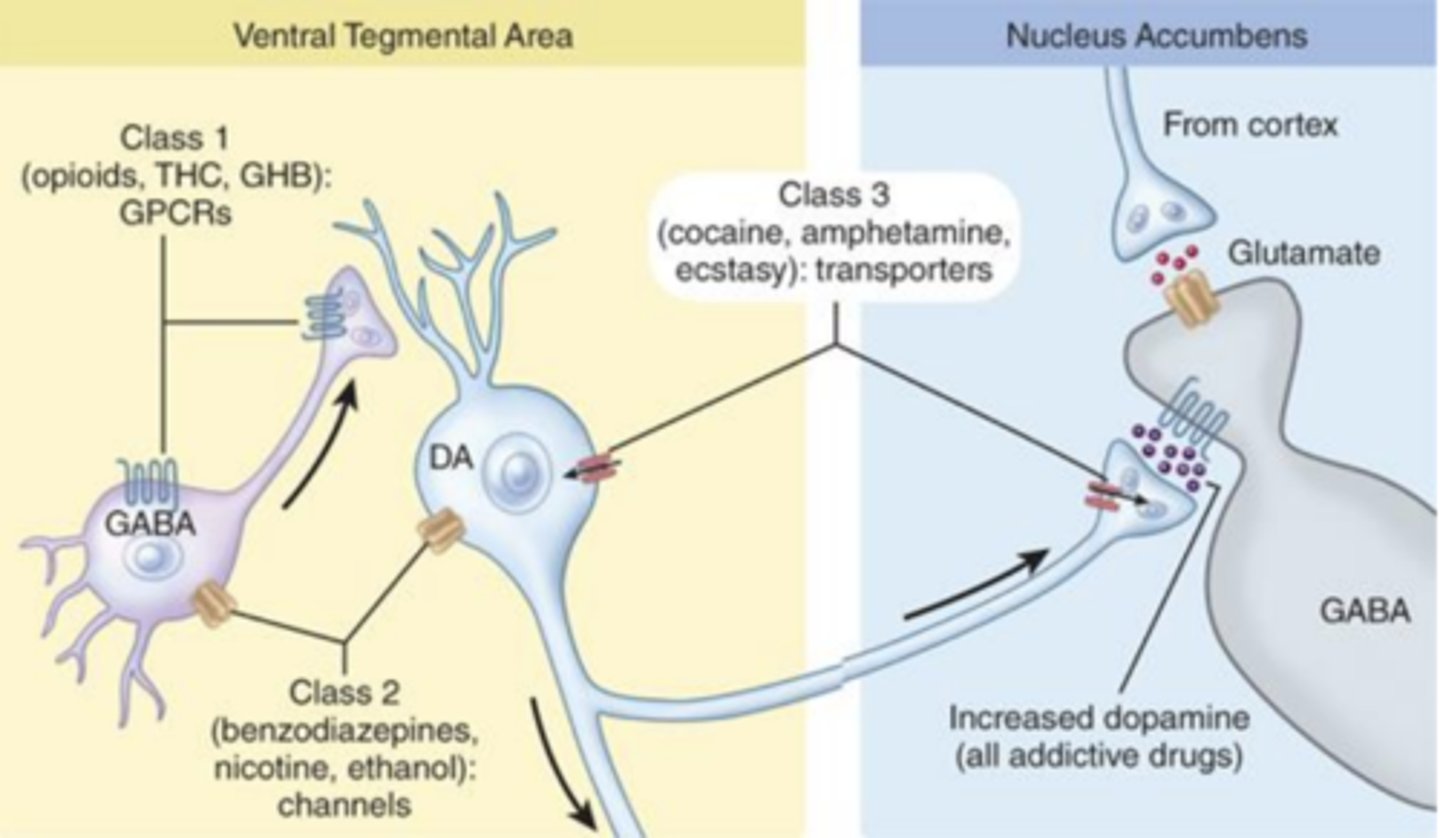
Varenicline (Chantix) for the treatment of nicotine addiction
used primarily for smoking cessation
- best we have at moment
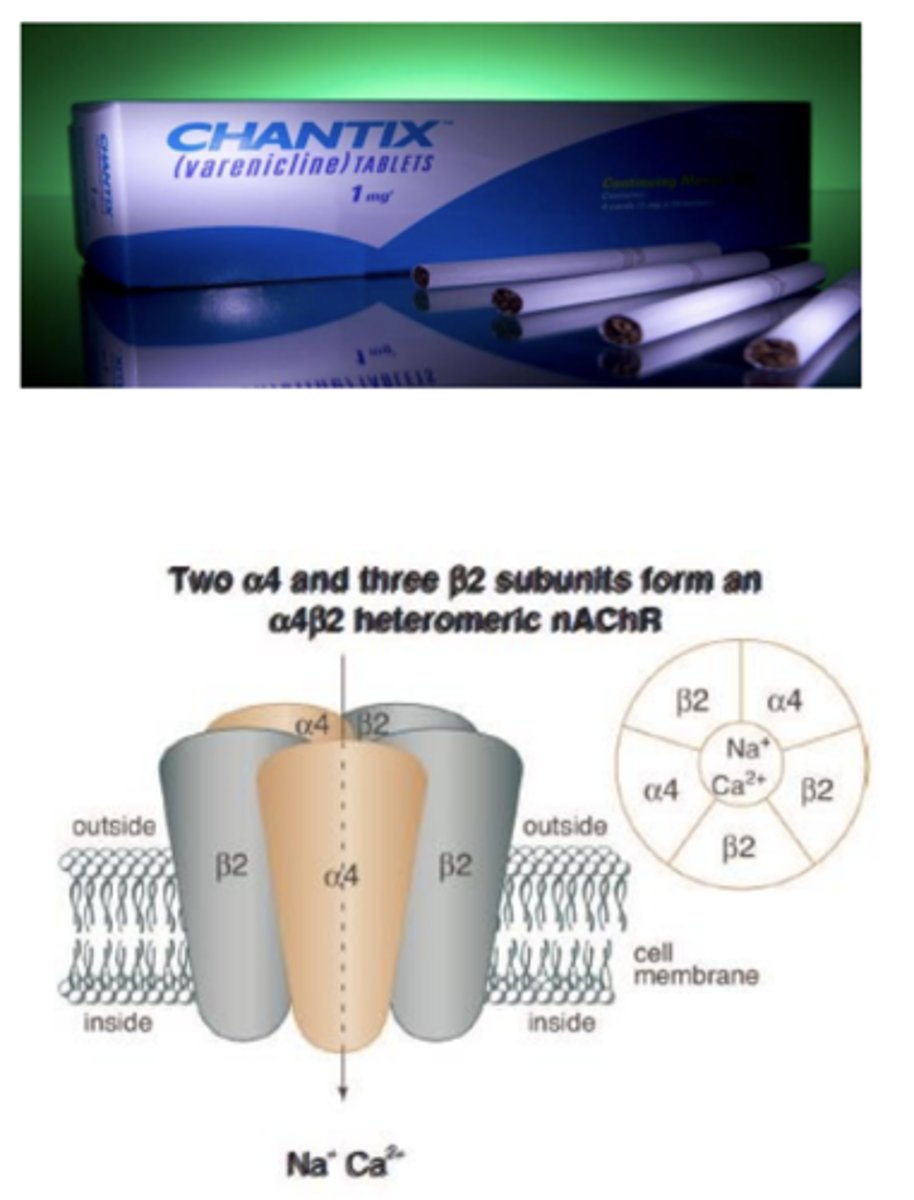
What does varenicline activate? What does it function as? What does it drive?
- activates many receptors; however, functions as a partial agonist for a4β2
- may drive reductions in striatal dopamine release and cravings
What is the half-life of Varenicline?
approximately 25 hrs and excreted renally
Only a ______ success rate after 6 months in people who want to quit, but have failed to do it cold turkey
14%
What do most opioid overdose deaths occur as a result of?
respiratory depression
On April 5th 2018, US surgeon general released a report: "I...am emphasizing the importance of ....health care practitioners... __________________ and keeping it within reach..."
knowing how to use naloxone
Texas enacted Senate Bill 1462, which contains provisions designed to....
make it easier to get naloxone when it is needed