Business leadership unit 2
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
What is planning?
Planning is the process of setting objectives and determining how to best accomplish them.
Benefits of planning in business
provides an action orientation
improves coordination between departments
improves time management - sets priorities
improves control - identify and measure results
improves focus and flexibility (look at the needs of the customer)
Types of plans
short and long range plans
single-use and standing-use plans
Short and long range plans
Short range plans - one year or less
Intermediate range plans - between one and three years
Long range plans - more than three years into the future
Single-use and standing-use plans
single-use plans - designed for a unique situation and used only once
Ex. budgets, project schedule
standing-use plans - designed to be used over and over again
Ex. policies, rules and procedures
Strategic and operational plans
strategic plan - overall direction for the company, comprehensive (all elements are included), long range, allocate resources, action framework, done by top management
operational plans - implements the strategy with a detail-oriented plan, clearly defines how a department or team contributes to reaching company goals
Planning process
define your objectives (SMART - what do you want to do?, how will you know when you’ve reached it?, is it in your power to accomplish it? can you realistically achieve it?, when exactly do you want to accomplish it?)
determine where you are in relation to your objectives (internal analysis)
anticipate future events (external analysis)
consider alternatives and make the plan (the best alternative becomes the plan
implement your plan and evaluate the results
Simulations
the imitation of the operation of a real-world process or system over time
Inside-out planning
Focuses attention on current production and policies
Doing the best at what is done already
No drastic changes
Results in maximum productivity, satisfied workers
Use when the company wants to improve the “how”
outside-in planning
The company’s external environment is the most important element
Seeks opportunities - finds niche markets and exploits them
Dell Computer built its initial marketplace success with a strong outside-in perspective. Dell built strong relationships with customers earned higher margins from its large "relationship" customers.
Top-down planning
Upper management sets objectives for the company
Lower management creates plans within this framework
Disadvantage - does not allow input from all participants
Bottom-up planning
Plans are developed at the “grass roots”
Passed up the hierarchy
Successful because people “buy-in” to the plan
Disadvantage - many unconnected plans
Time management
Is the process of planning how to divide your time between specific activities.
Good time management enables you to work smarter, not harder. This way you get more done in less time, even when time is tight and pressures are high. Failing to manage your time damages your effectiveness and causes stress.
Causes of poor time management
Not prioritizing tasks
Not delegating responsibility
Not being able to say no
Not writing down objectives in order to meet deadlines
Not using a calendar or notebook to organize commitments
Not shifting priorities to make room for more urgent matters or tasks
Not reducing clutter and/or unnecessary paperwork
Not being able to give up total control
Procrastination
Planning tools
SWOT
PEST-C
Porter’s Five Forces
SWOT
Strengths
Weaknesses
Opportunities
Threats
PEST-C
Political
Economical
Social
Technological
Competition
Political
Laws and Regulations must be understood
Special interest groups (ex. Unions, lobby groups, NGO’s)
Taxes (municipal, provincial, federal)
Tariffs and Duties
Trade Agreements
Crown corporations - businesses owned by the government
Economical
Economic factors affect customers and suppliers
A manager must establish who has the power in purchasing
We will take a more in depth look into Supplier and Buyer power when examining Porter’s 5 Forces (another planning tool)
Social
Demographics
Population growth rate
Change in income
Lifestyle changes
Social values
Changing market tastes
Technological
Available technology
New Knowledge
New Processes
Automation
Artificial Intelligence
Competition
Research major competitors and determine their competitive advantages
PEST-C analysis
A PEST- C analysis will look at external stakeholders, but it also examine any external environment factor that may help or hinder an organization. Overall, the purpose of a PEST-C will help an organization to make informed decisions and avoid pitfalls.
Strategy
A comprehensive plan guiding resource allocation to achieve long-term organizational goals.
Different levels of strategies
corporate strategy
business unit strategy
team/functional strategy
Corporate strategy
Sets the long-term direction for the company
“In what industries and markets should we compete?”
Guides resource allocation for the entire company
Business strategy
Identifies how a division or strategic business unit (SBU) will compete in its product or service domain
“How are we going to compete for customers in this industry and market?”
Choices about product mix, factory locations, new technology
Team/functional strategy
Guides activities within one specific area of operations
“How can we best utilize resources to implement our business strategy?”
Strategic management
The process of formulating and implementing strategies
mission and vision statements
core values
operational objectives
Mission statement
Overall purpose of the company
Organization’s reason for existence
Take into consideration:
Customers
Internal Operations - quality, productivity, cost
Employees
Society
Corporate Culture
Vision statement
A vision statement is a sentence or short paragraph that summarizes the goals of a company. A vision statement is sometimes thought of as a picture of a company in the future. It states what the company is trying to build and serves as a compass for future actions. A vision statement is inspiration, and it will serve as the framework for all strategic planning.
Mission statement vs. Vision statement
Mission Statement
Drives the company
Core of the business
Focuses on the present
What do we do?
Whom do we serve?
How do we serve them?
Vision Statement
Gives the company direction
Focuses on the future
Why do we exist?
What are our hopes and dreams?
What problem are we solving for the greater good?
Who/what are we inspiring to change?
Core values
Broad beliefs about what is important and valued for the company
Helps to build a company identity (culture)
Influences management, decisions and all business functions
Operational objectives
Operational objectives are attainable, action-oriented, short-term goals organizations set as a means of partially achieving larger, long-term objectives.
Strategic and operational plans
STRATEGIC PLANS
Overall direction for the company
Comprehensive
Long range
Allocate resources
Action framework
Done by top management
OPERATIONAL PLANS
Implement the strategy
Ex: production, marketing, HR, sales
Six overall strategies
1. GROWTH STRATEGIES
Increase organizational size through expansion
2. RETRENCHMENT STRATEGIES
Seek to correct weaknesses by making changes to current ways of operating
Reduce operations to gain efficiencies and improve performance
3. STABILITY STRATEGIES
Maintains current operations without substantial changes
4. GLOBAL STRATEGIES
Most businesses have an international component
5. COOPERATIVE STRATEGIES
Organizations join together in partnership to pursue an area of mutual interest
Known as strategic alliances
6. E-BUSINESS STRATEGIES
The strategic use of the internet to gain a competitive advantage
Growth strategies - concentration
Market Development
Adding new customers to existing markets
Launching a website to sell online as well as in store
Finding new markets to sell existing products
Cannabis companies in Canada
Innovation
Creating entirely new products to make the old ones obsolete
Product Development
Research and development focus to create new products in related areas or modify existing ones
Tim Horton’s (all day breakfast, expanded drink menu to match McCafe and Starbucks)
Tide Pods
Growth strategies - diversification
Horizontal Integration ● Expanding operations by purchasing or merging with companies in the same industry ○ TD Canada Trust ○ Best Buy and Future Shop
Vertical Integration
Acquire suppliers (backward vertical integration)
Starbucks buys roasting plant
Subway buys wheat farms
Acquire distributors (forward vertical integration)
Disney purchases ABC
Amazon purchases Whole Foods
Retrenchment strategies
Restructuring - Changing the scale and/or mix of operations
Goal is to decrease costs
Could involve reducing personnel and streamlining operations
Sometimes called rightsizing
Blackberry (RIM)
Divestiture - Selling off part of the business
Loblaws sold PC Financial
Kraft Foods sold snacking side of business to Mondelez
Liquidation - Selling off company assets or declaring bankruptcy
Sears
Target in Canada
Toys R Us in USA
Stability strategies
Companies try to maintain the existing course of action without major changes. Major investments are also avoided.
Often used is the following scenarios:
Company is performing well
Company already operating at capacity
External Environment appears risky
Global strategies
Globalization Strategy
Views the world as one large market
Standardizes products and advertisements for use worldwide
Ex. Red Bull
Multidomestic Strategy
Has some standard operations/brands but customizes products and advertising to fit the local needs of different countries or regions
Distribute authority for major decisions to local managers
Ex. McDonald’s
Transnational Strategy
Seeks efficiencies of global operations with attention to local markets
Operates without a strong national identity and tries to blend with the local economy
Ford - “think globally, act locally.”
Ford draws upon design, manufacturing and distribution export globally to build car platforms
These platforms are then efficiently modified to meet local tastes
International Strategy (Export Strategy)
Company is primarily focused on its domestic operations.
Company does not intend to expand globally but does export some products to take advantage of international opportunities.
No customization of products for international markets.
Global integration
is the degree to which the company is able to use the same products and methods in different countries.
Local responsiveness
is the degree to which the company must customize their products and methods to meet conditions in different countries.
Cooperative strategies (no ownership)
Outsourcing Alliances
Contracting to purchase important services from other companies
Outsourcing Information Technology to IBM
Call centers in foreign countries
Schools outsourcing photocopiers to Xerox
Distribution Alliances
Firms join together to provide products or services, or accomplish sales and distribution ○ Amazon and FedEx (Ended 2019)
Amazon and Affirm - Affirm provides pay-over-time options
Supplier Alliances
Preferred supplier relationships guarantee a smooth and timely flow of quality suppliers ○ Magna and Toyota
Strategic alliance
An arrangement between two companies to undertake a mutually beneficial project while each retains its independence.
E-business strategy
B2B (Business-to-Business) ● Use IT and Web portals to vertically link organizations with members of their supply chain ● Benefits large and small organizations alike ○ Shopify (providing platforms/support for other businesses) ○ Dell (website services for larger corporate customers) ○ EtsY
B2C (Business-to-Consumer) Use IT and Web portals to link organizations to their customers ● E-tailing or Merchant Model - the sale of goods directly to the consumer via the Internet ○ Indigo, Walmart, Gap/Old Navy ● Brokerage - bringing buyers and sellers together to make transactions ○ Etsy, Kijiji, AutoTrader, LetGo ● Advertising - providing information or services while generating revenue from advertising ○ Social media (Instagram, Facebook, Twitter), YouTube
Subscription Model - selling access to a website or product through subscription ○ Netflix, News/Magazine websites, Apple Music, Spotify ● Infomediary Model - collecting information on users and selling it to other businesses ○ Google, Epinions, Survey Monkey
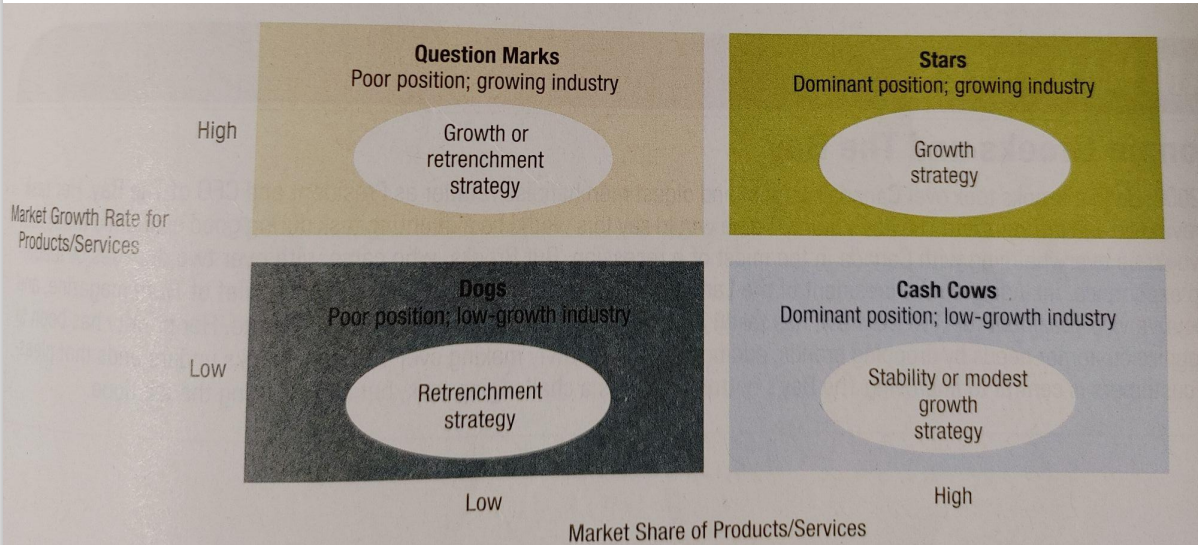
Strategic portfolio planning
When companies operate in multiple industries of various products and services it can be challenging to allocate resources. When developing a corporate strategy, these firms can take advantage of the BCG Matrix. This framework analyzes business opportunities according to market growth rate and market share.