L11 Homeostasis in the Nervous Tissue I (Imported from Quizlet)
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Glia, capillaries, other neurons, extracellular space
What is the neuronal microenvironment composed of?
Extracellular matrix, brain extracellular fluid (BECF)
What is included in the extracellular space?
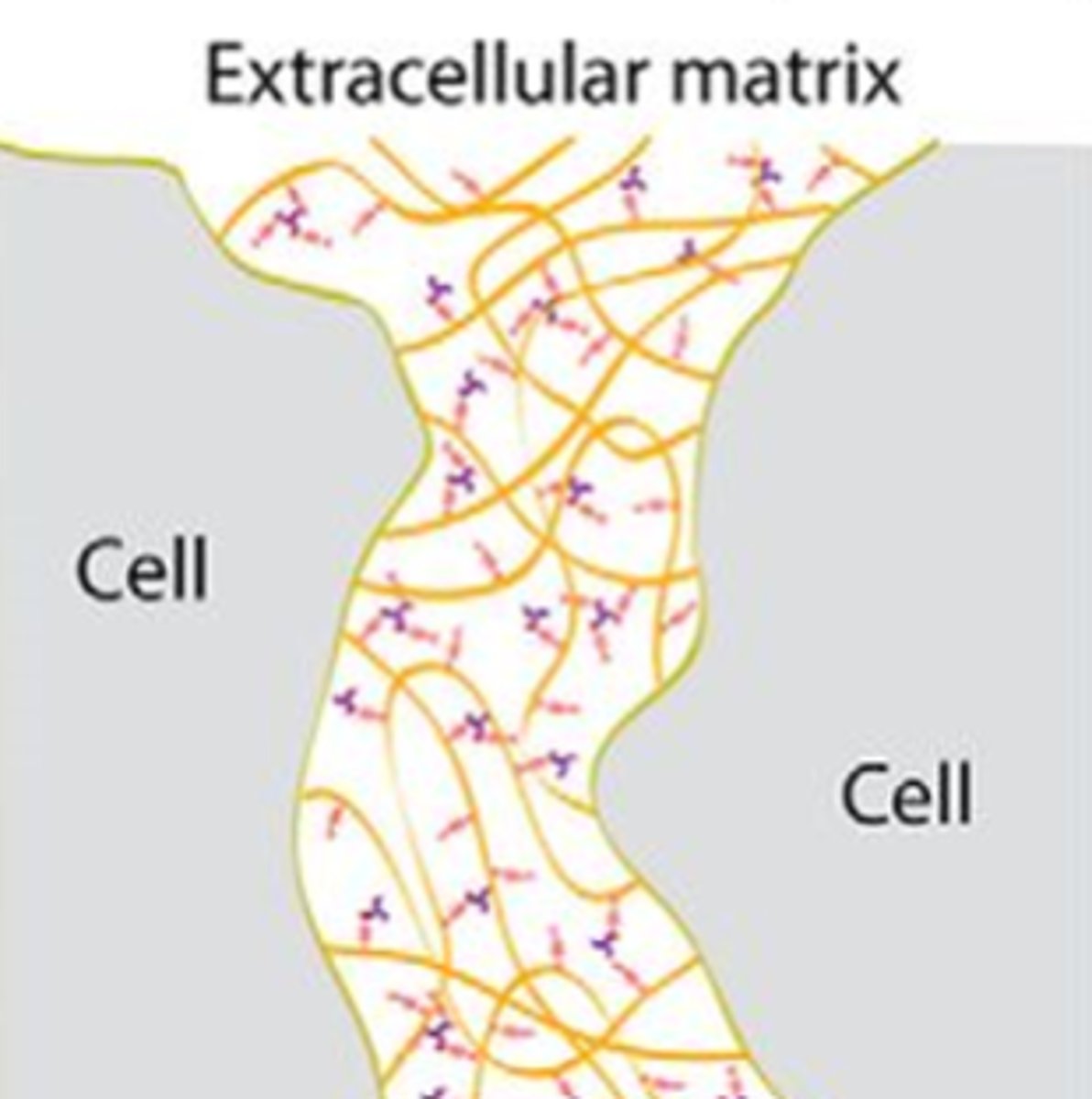
Extracellular space
What is the purple/blue in this image?
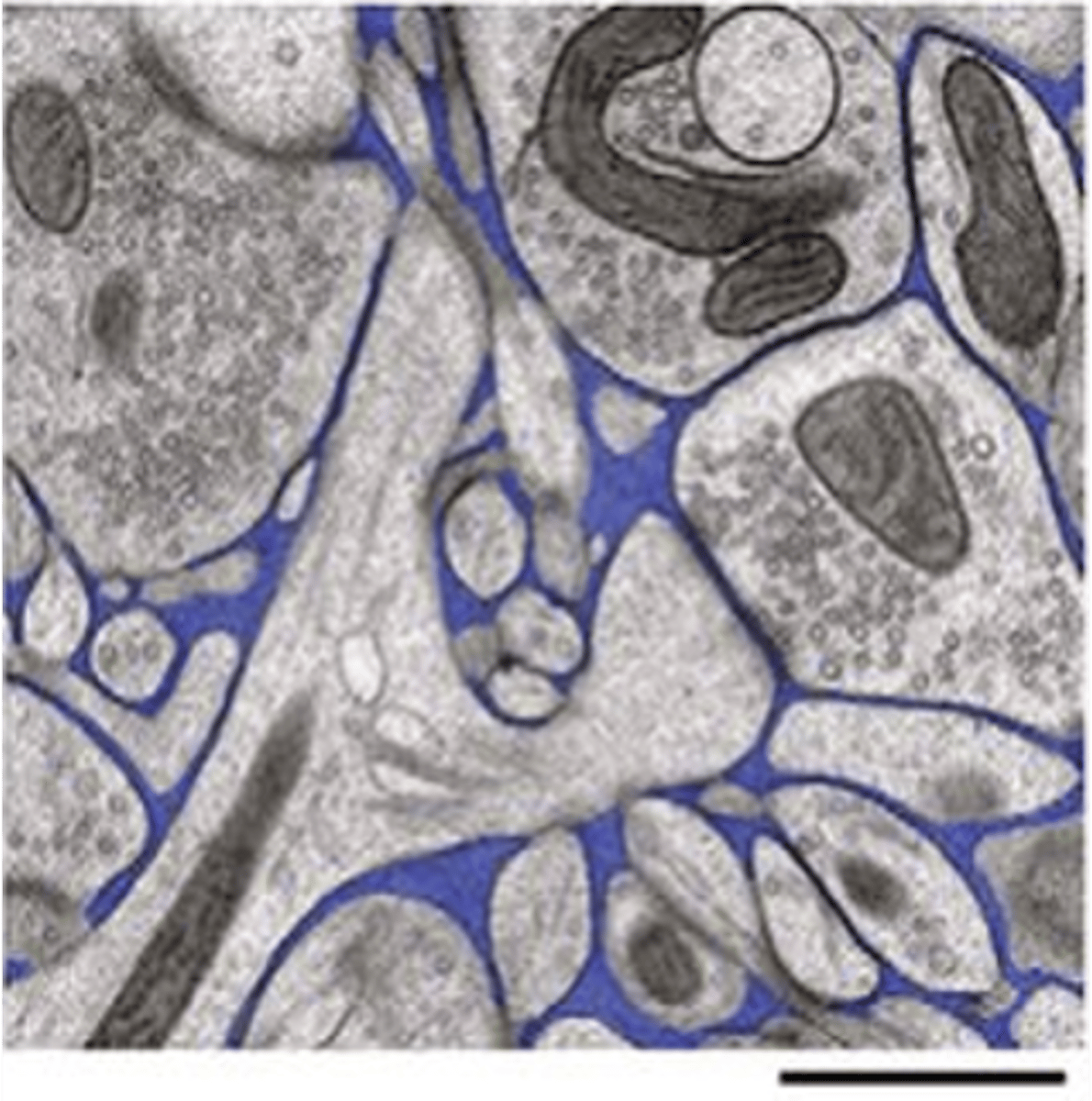
The ECF that is found within parts of the ventricular system
BECF is used to distinguish from what?
Influence neurons and be influenced by neurons
What can BECF do?

Neuronal dysfunction, neuronal death
What does uncontrolled BECF composition lead to?
Tightly regulated
BECF composition must be __________ _______________
Increased K+ concentration
Changes in Ca2+ concentrations
Changes in O2, glucose and CO2 concentrations
Increased H+ thus acidification
Neurotransmitter concentrations change
How could BECF composition be changed by neuronal activity?
Increased K+ concentration in the BECF could elevate resting potential bringing the cell closer to threshold for firing an action potential
Increased neurotransmitter release
Increased neurotransmitter concentrations could lead to an unspecific neuronal activity
How could a change in BECF composition change neuronal activity?
1. Blood brain barrier
2. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in the ventricular system
3. Neurons
4. Glial cells - focus on astrocytes
How do we regulate the neuronal microenvironment, including BECF?
Dyes pass across leaky capillaries
Stain soft tissues
But not in the brain - no staining
How did the intravenous injection of dyes reveal the blood brain barrier?
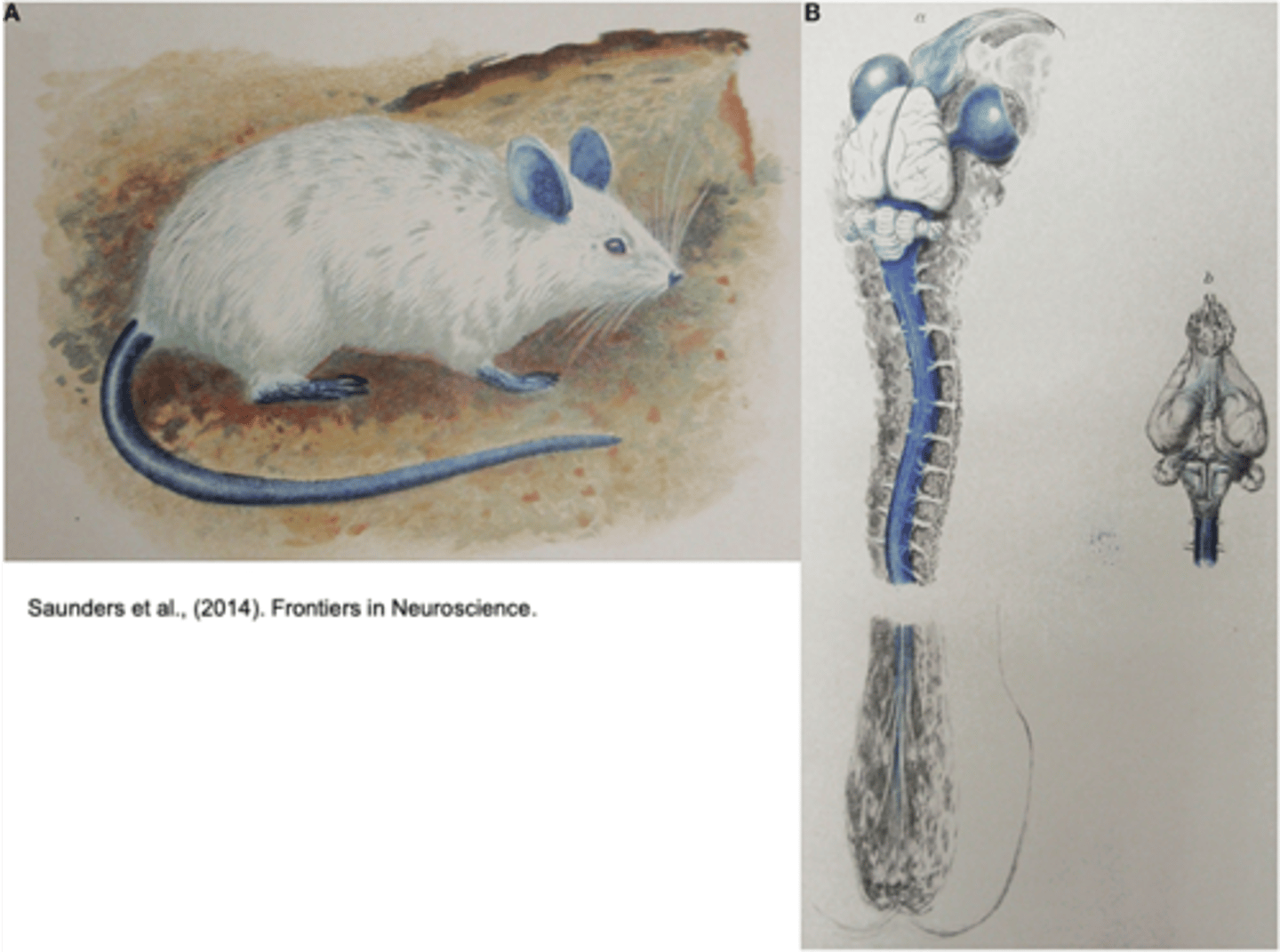
To protect neurons from fluctuations in concentrations of substances in the blood
What is the function of the blood brain barrier?
Increased amino acid concentrations after a meal
Increases in K+ and H+ concentrations after exercise
Circulating hormones
Inflammatory mediators
Toxins
What are the examples of some of the fluctuations in concentrations of substances in the blood?
Non selectively activate receptors, exciting or inhibiting neurons
What could increased amino acids do?
Depolarisation of neurons
What does an increased extracellular K+ cause?
Tight junctions between endothelial cells (transcellular route)
Thick basement membrane
Astrocytic endfeet
How is the blood brain barrier (BBB) maintained?
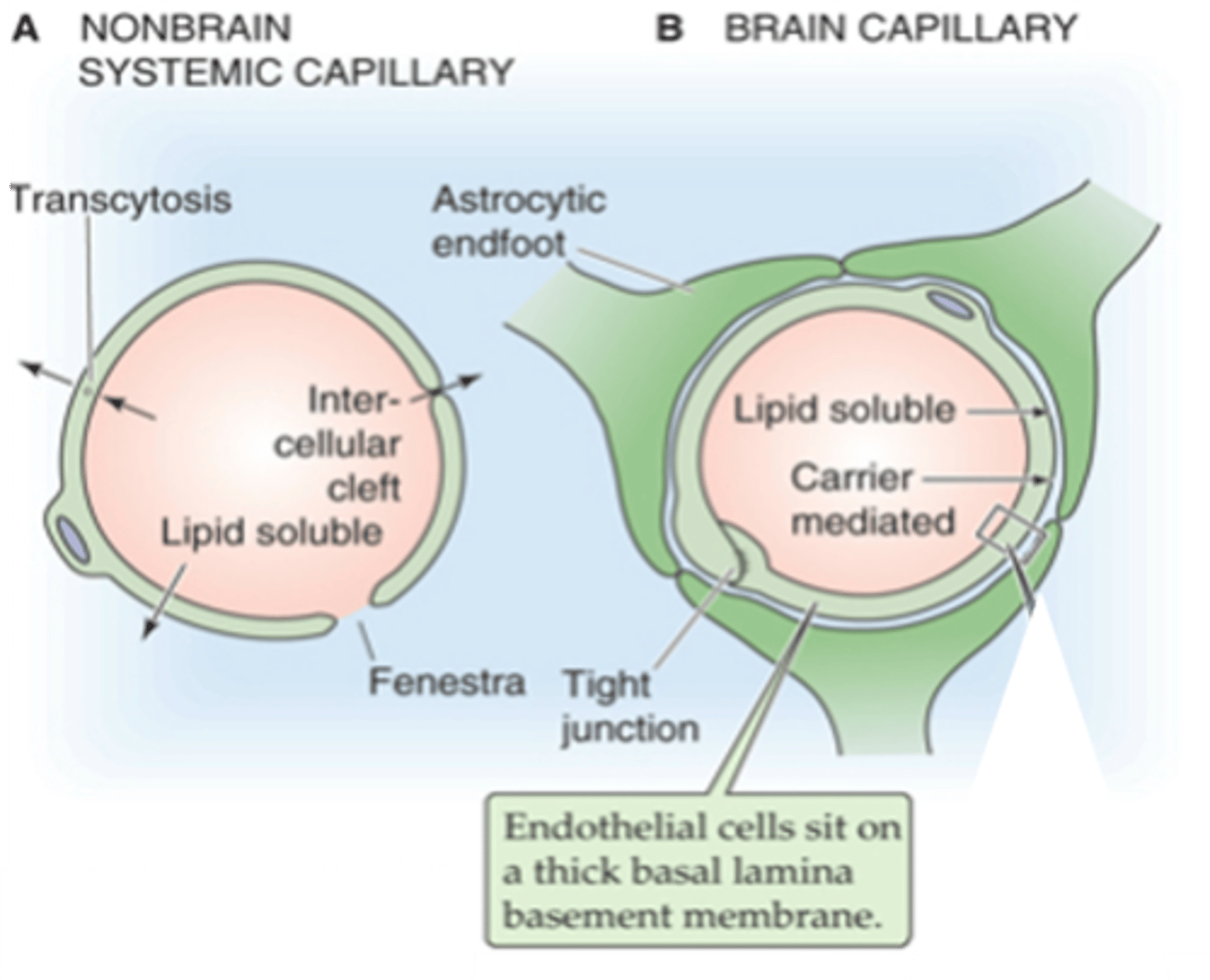
Formation of tight junctions between endothelial cells and may facilitate transport between BECF and blood
What can astrocytes induce?
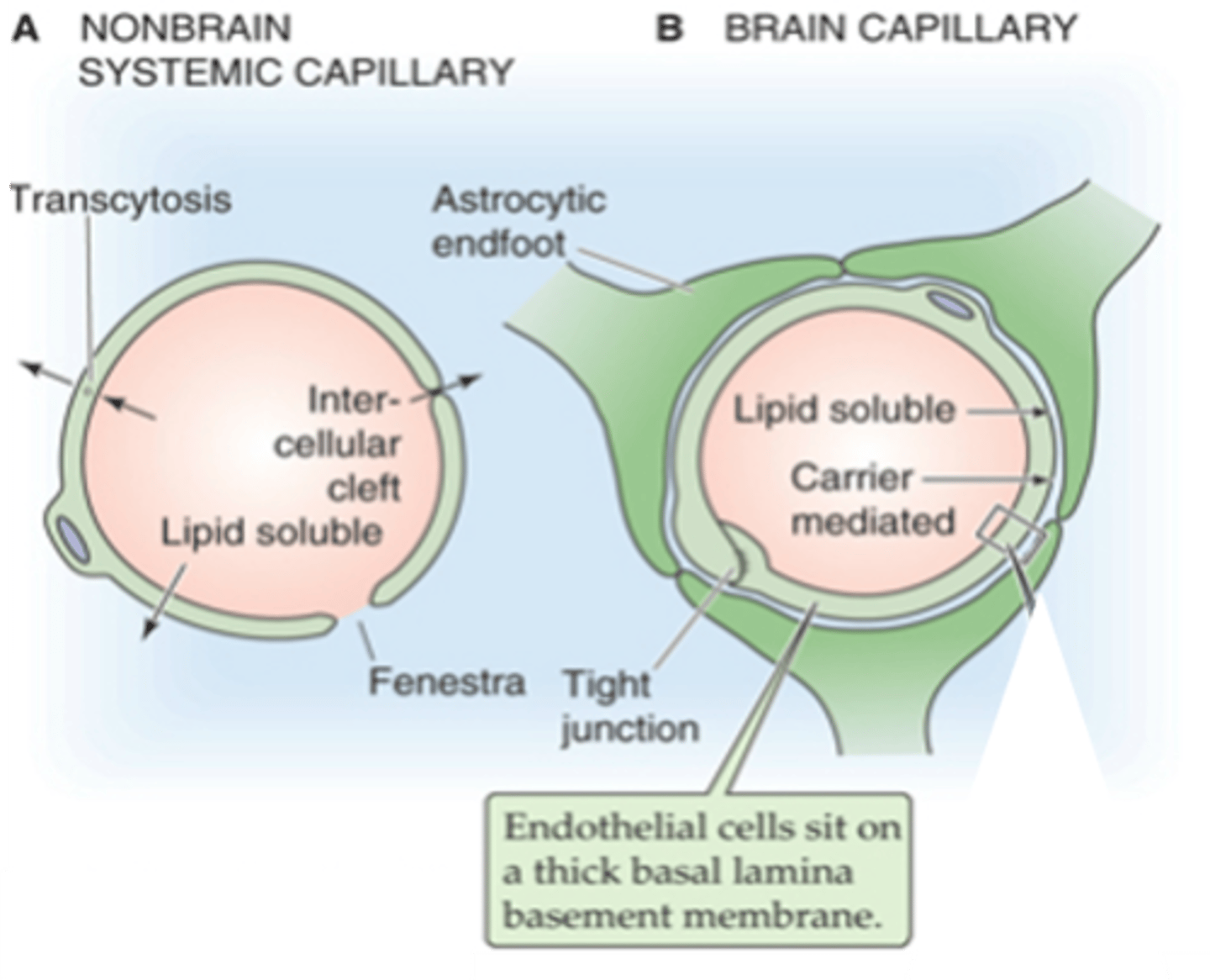
Facilitated transport (e.g. Glut1)
Exchangers (e.g. Na-H exchanger)
Co-transporters (e.g. cation coupled Cl- transporters, NKCC1)
Increased numbers of mitochondria = active transport
Small, uncharged and/or lipid soluble can pass the BBB more easily (e.g. CO2, O2, nicotine, heroin, caffeine)
How do important molecules get through the BBB?
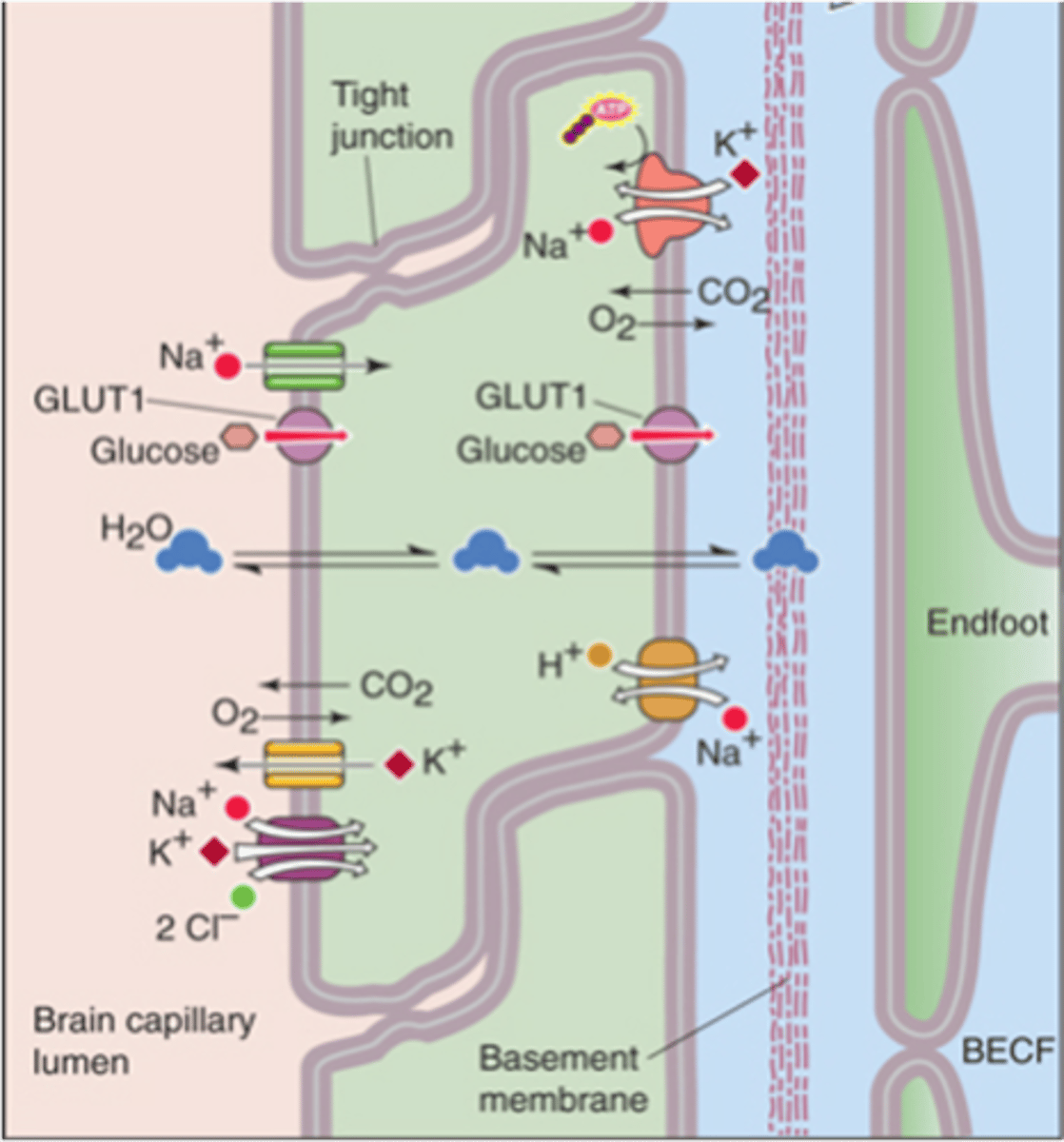
Choroid plexuses (make cerebral spinal fluid) - ventricular system
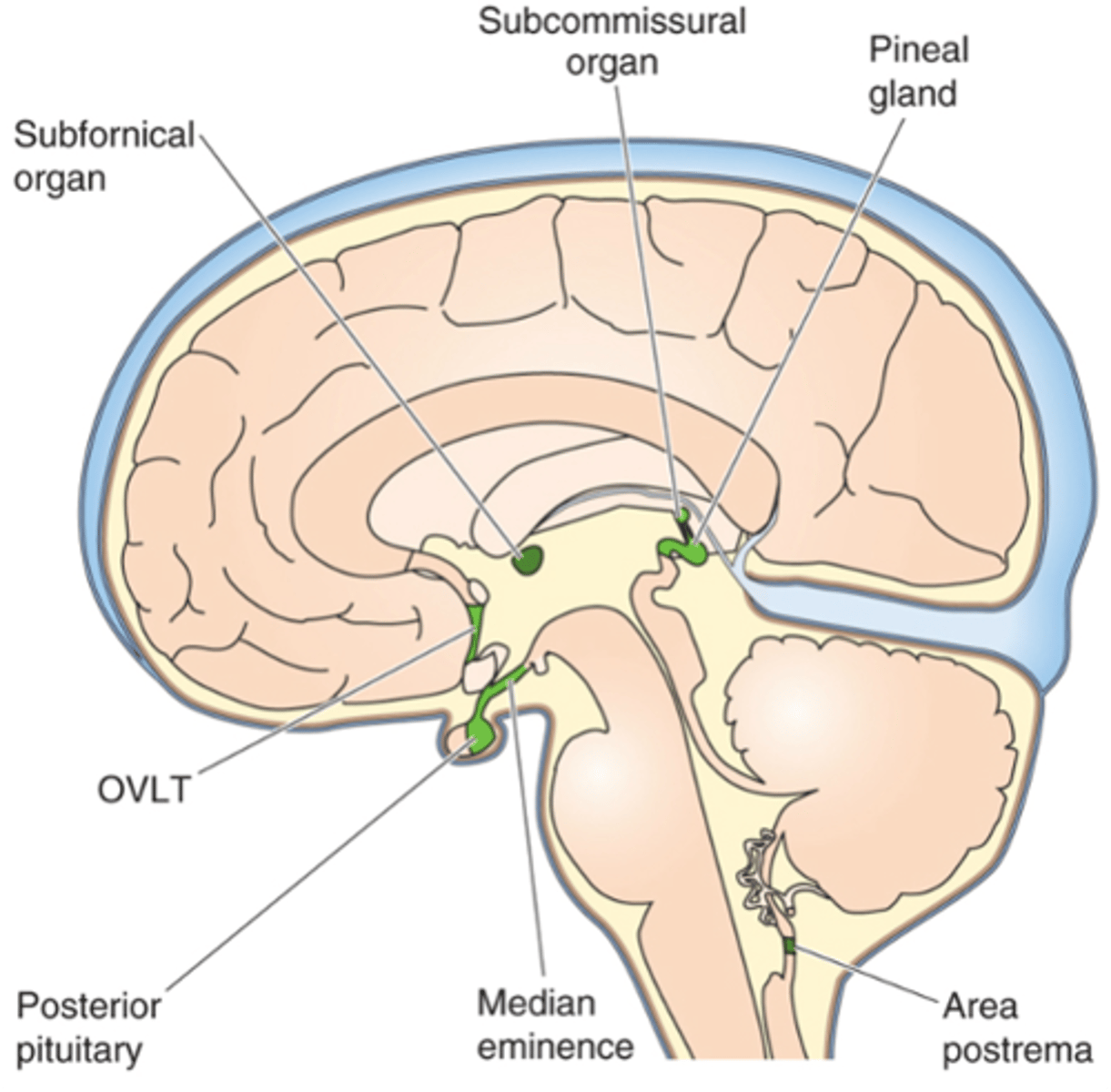
Circumventricular organs (green in the image)
What are the 2 leaky regions in the BBB?
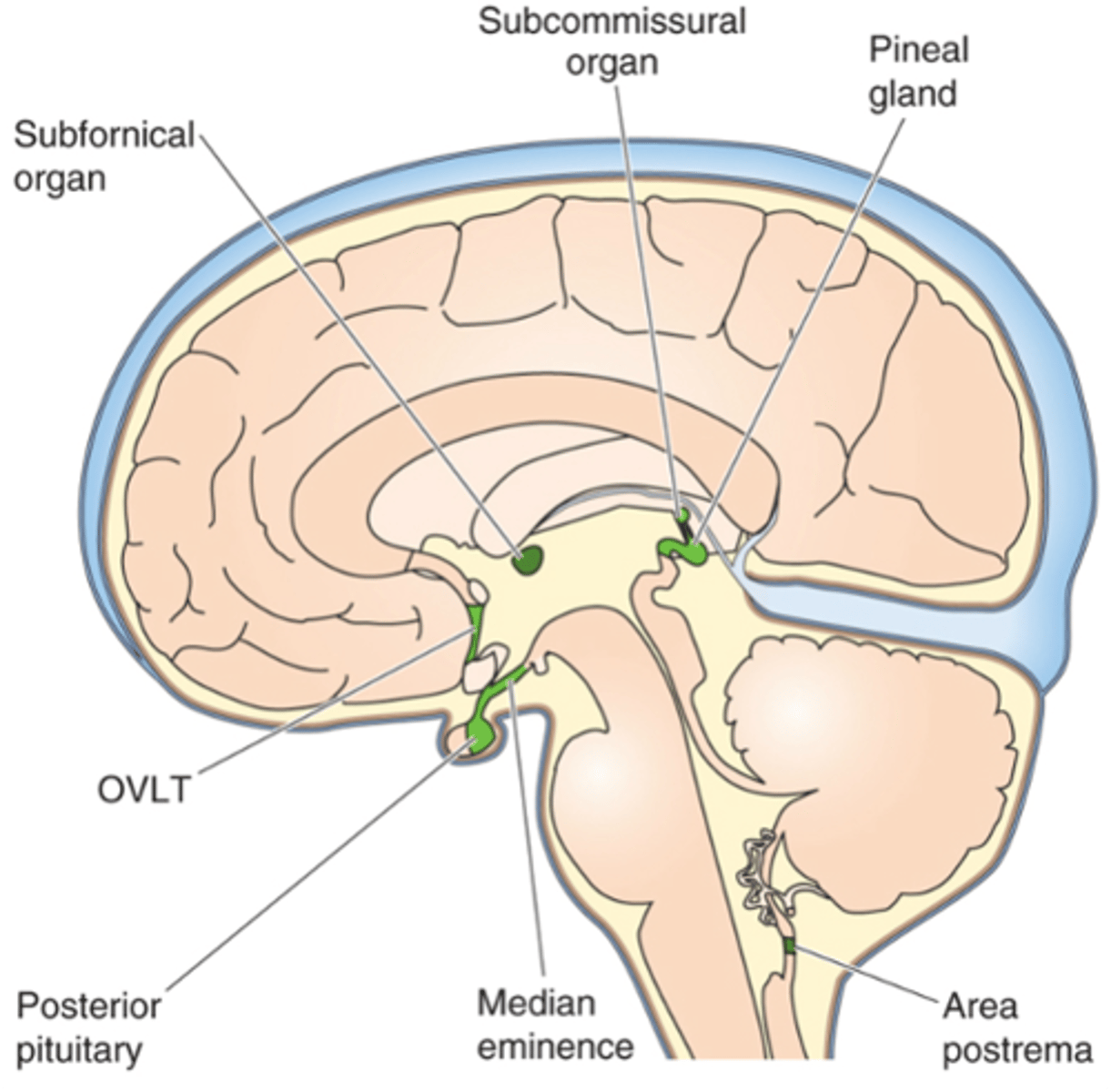
Surrounds the ventricles
What does circumventricular stand for?
Ependymal, tight junctions
In these leaky areas of the BBB, ___________ cells beneath have _____ _____________
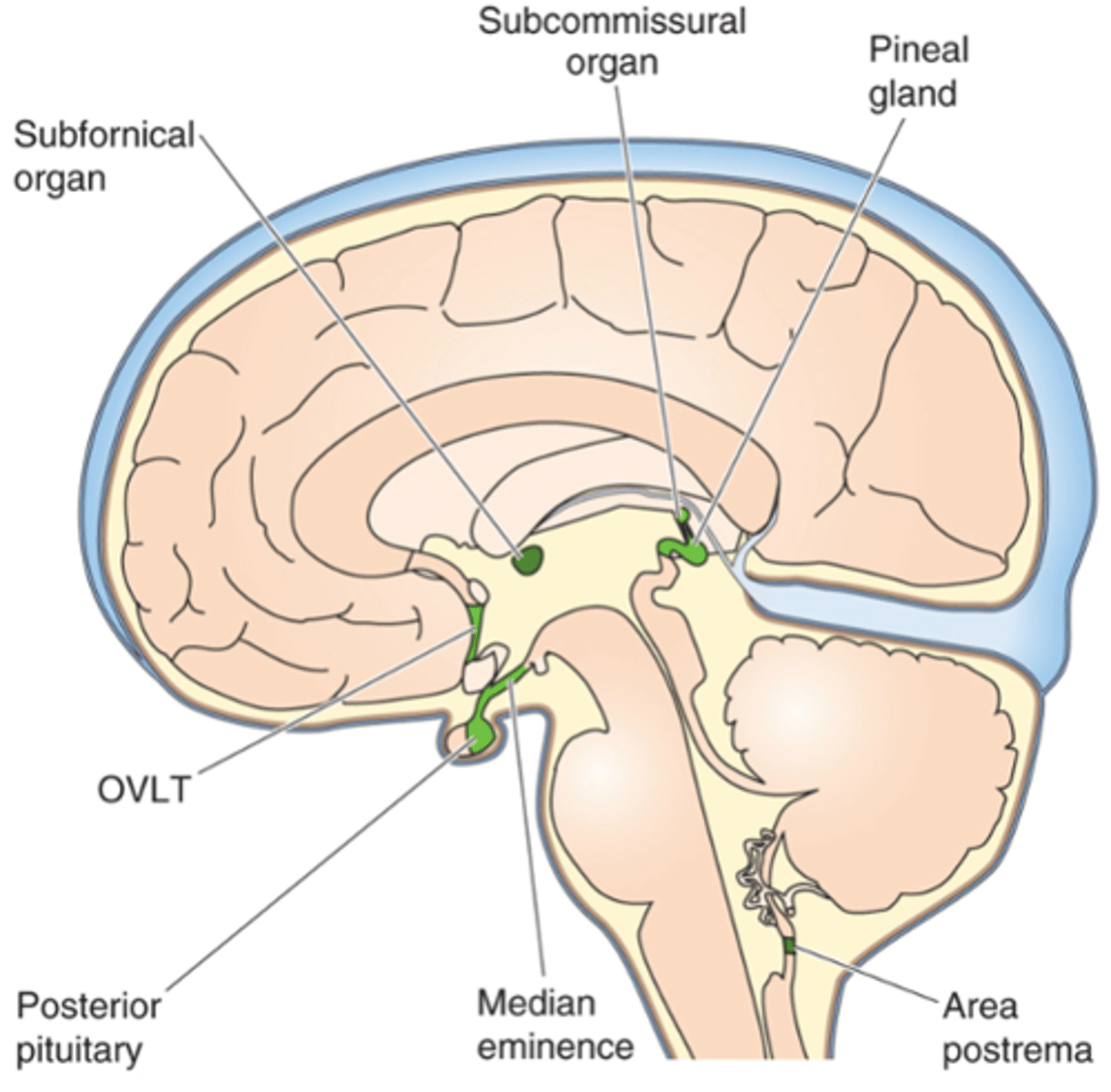
Hormone release (e.g. hypothalamus and pituitary gland)
Osmoreceptors (e.g. OVLT and SFO, hypothalamus)
Temperature control centres and fever - cytokines (e.g. OVLT)
Why have leaky areas of the BBB?
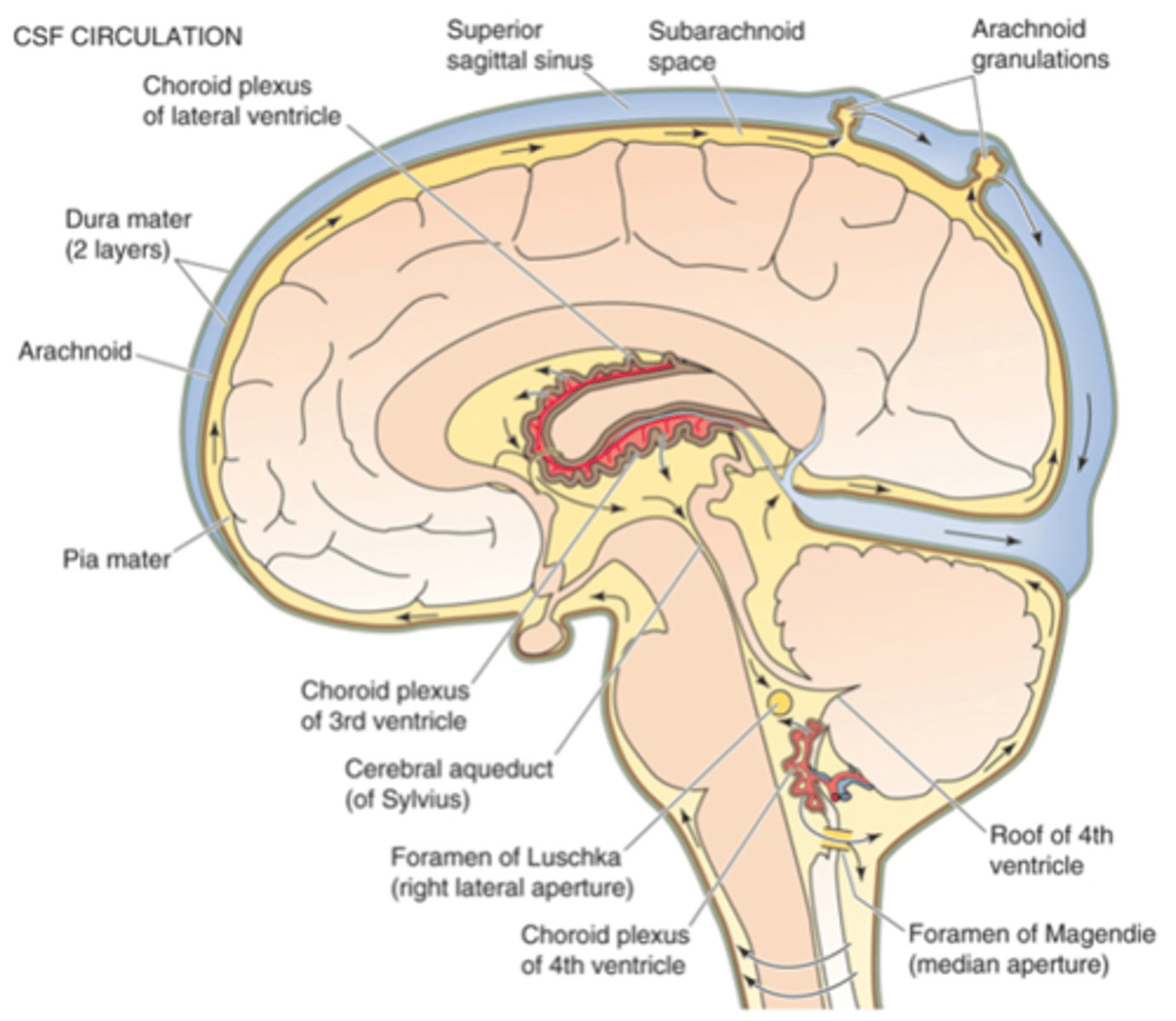
Open cavities (ventricles an central canal) filled with cerebrospinal fluid
What does the ventricular system contain?
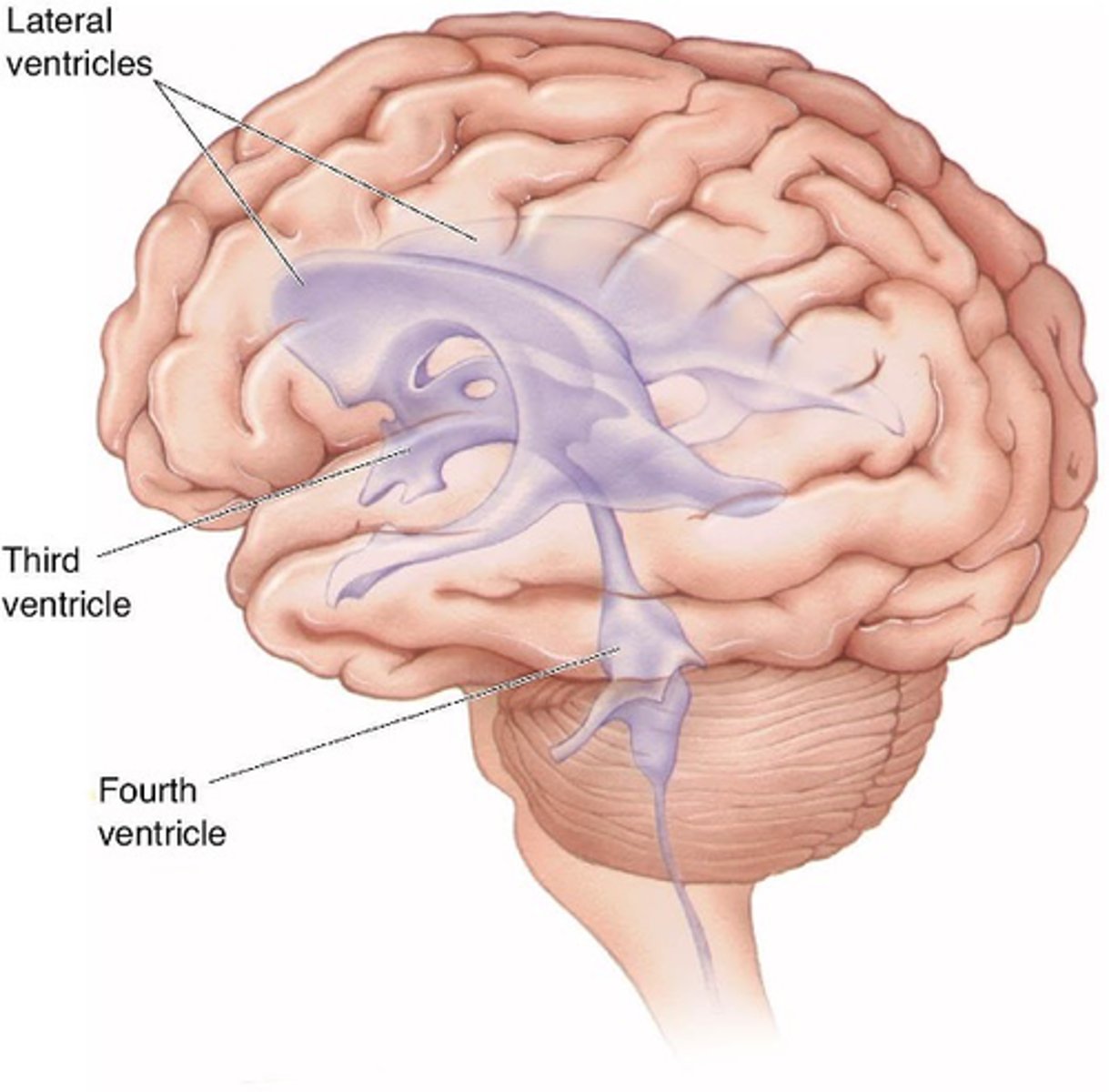
Physical protection - buffer
What does the ventricular system provide?
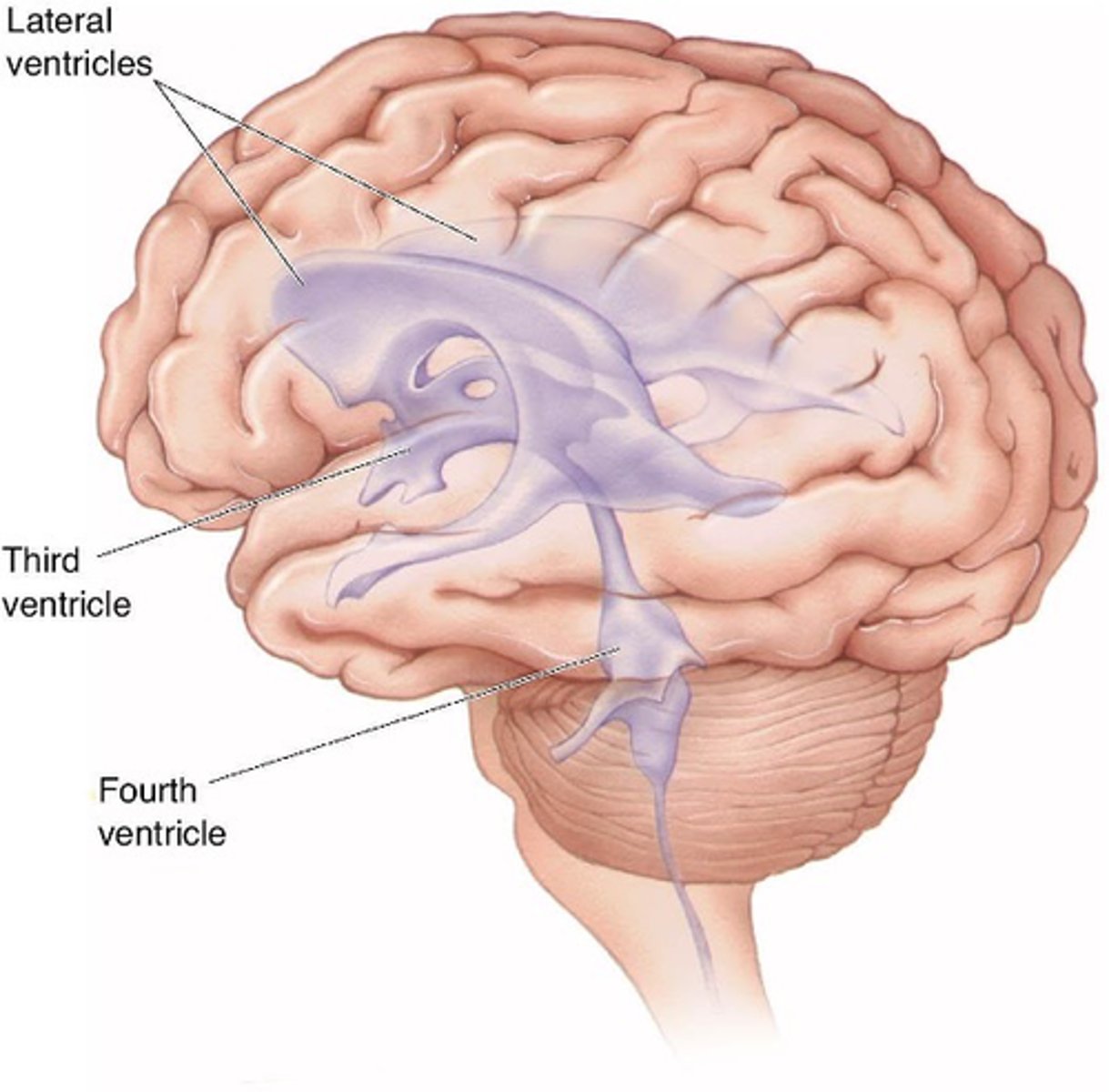
Appropriate levels of ions
What does the ventricular system maintain?
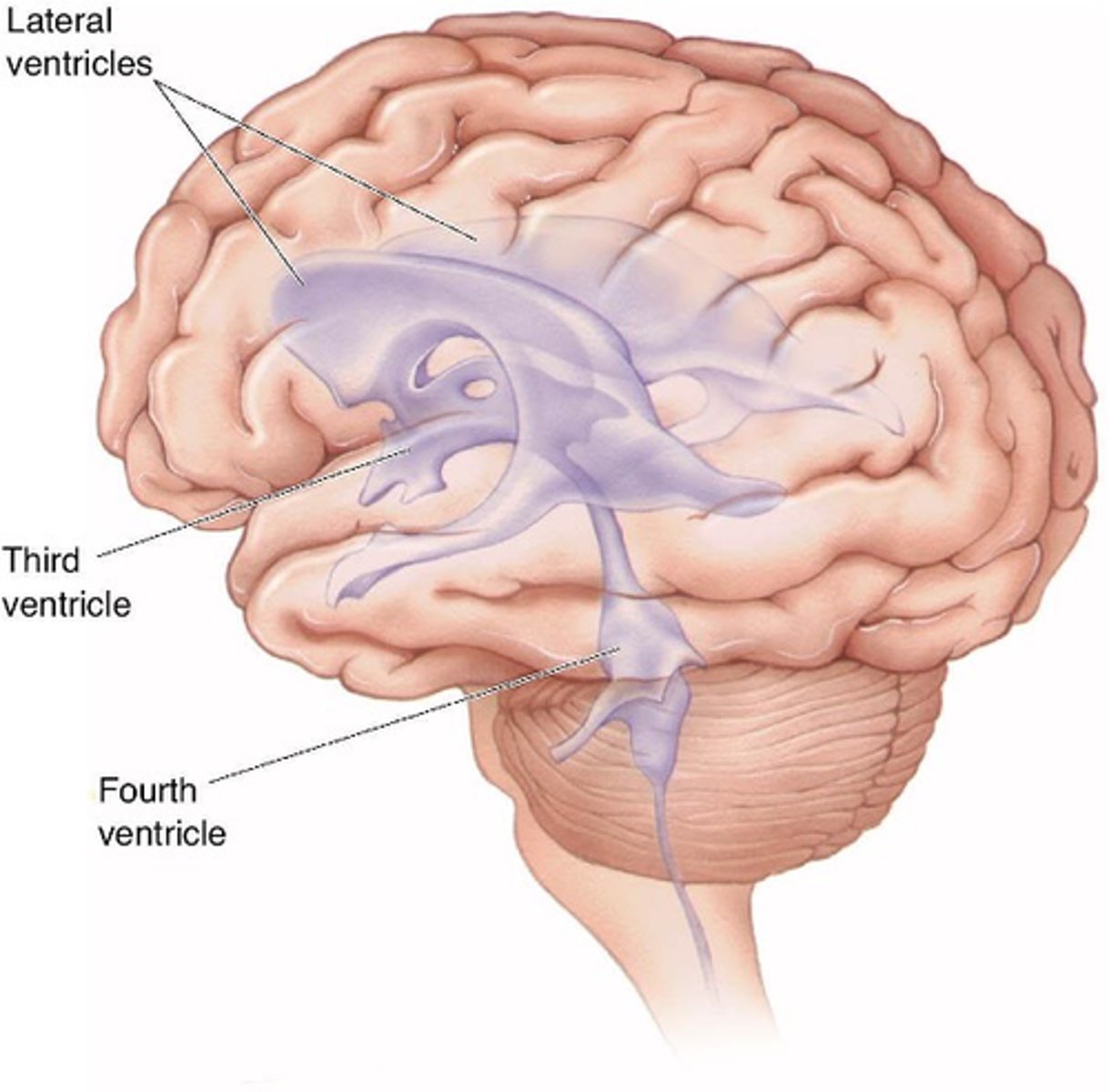
Waste products
What does the ventricular system remove?
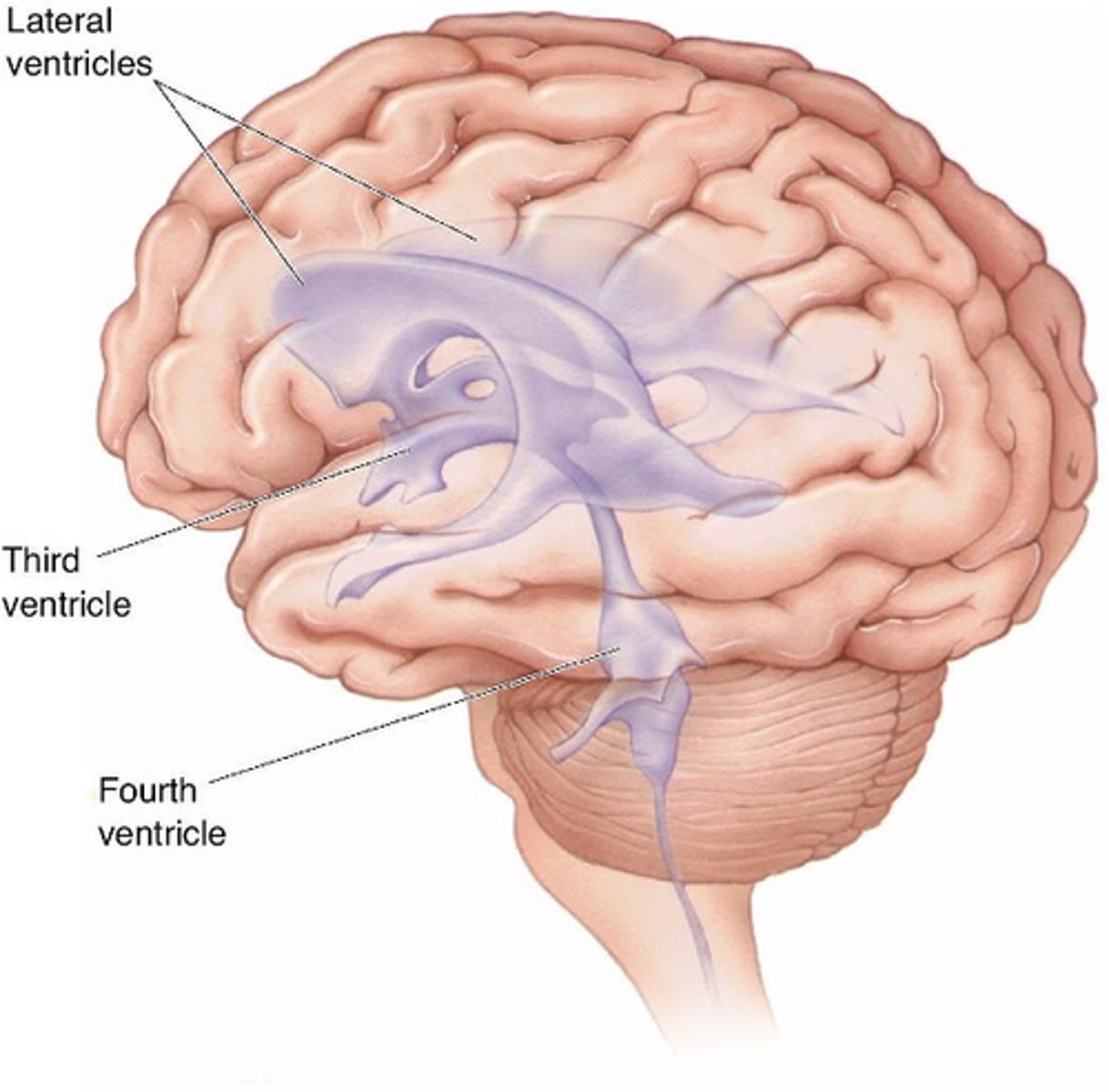
Choroid plexus
Cerebrospinal fluid is secreted by what?

The ventricles and central canal
What does cerebrospinal fluid circulate around?
Subarachnoid space
Cerebrospinal fluid is absorbed from the _____________ _______ to the venous blood system at the superior sagittal sinus
150, 30, 120
~____mls CSF in total, __ in ventricles, ___ in SAS
1400, 50
Cerebrospinal fluid reduces effective weight from _____g to <__g
Accelerating and decelerating injuries
What does cerebrospinal fluid decrease the risk of?
~500mls
How much CSF is produced per day (approx)?
3
How many times a day is CSF replaced?
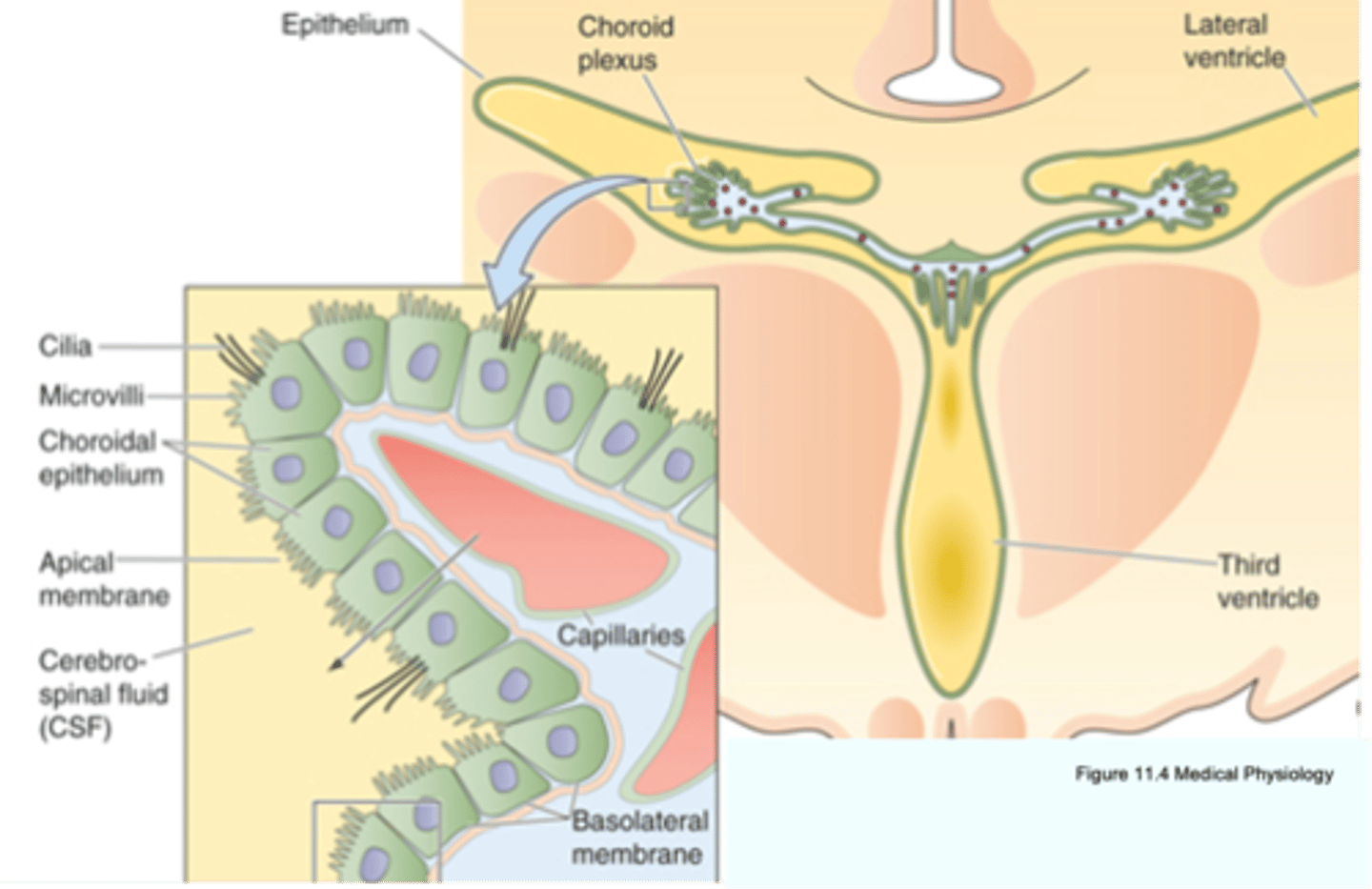
Capillaries
~30% of CSF is made by what?
Specialised glial cells that line ventricles
What are ependymal cells?
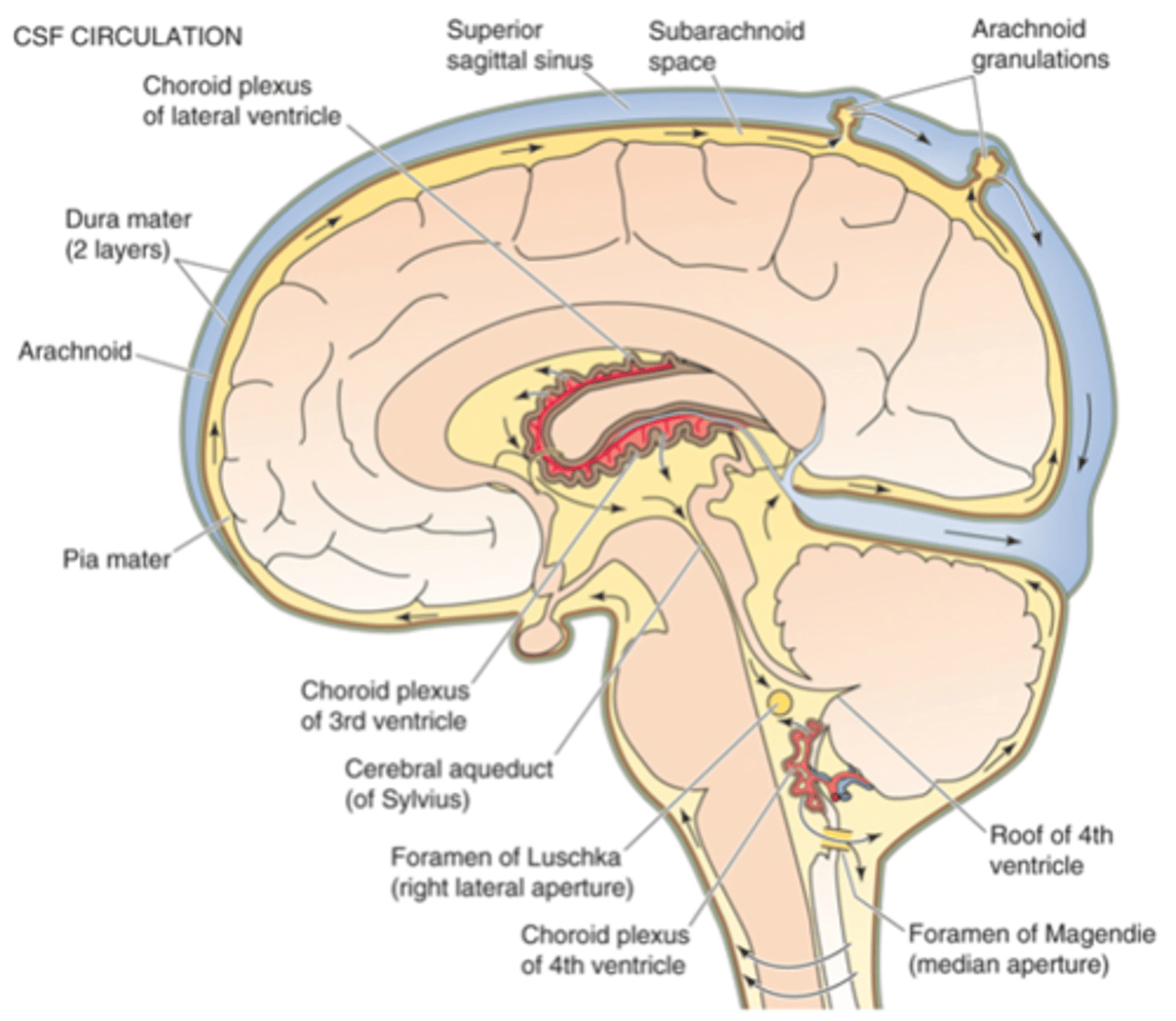
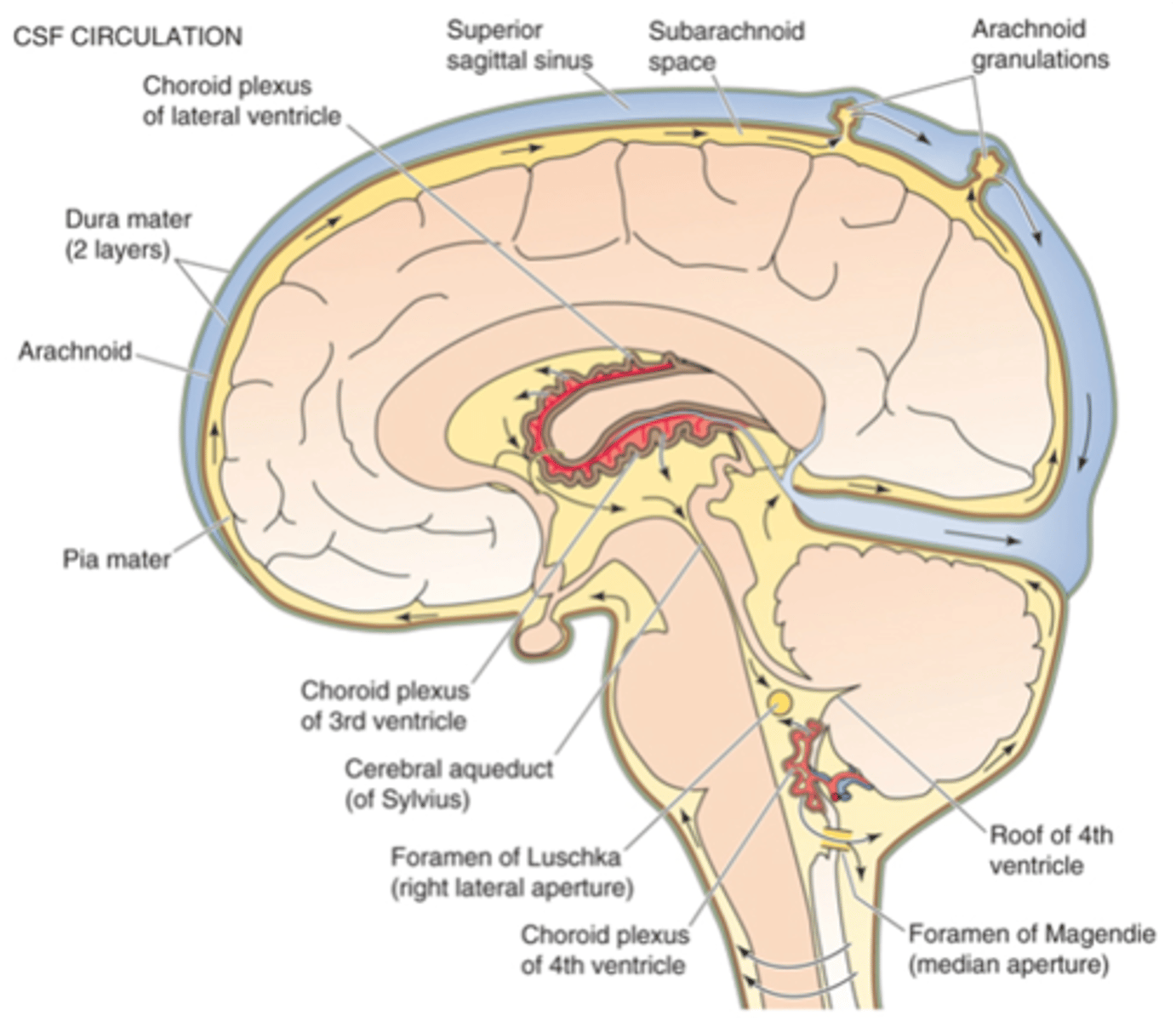
1. Ultrafiltration of plasma into ECF across normal 'leaky' capillaries
2. Selective absorption of substances into CSF across choroidal epithelial cells (have tight junctions)
3. Free movement of substances from CSF to BECF across ependymal cells
Secretion of CSF
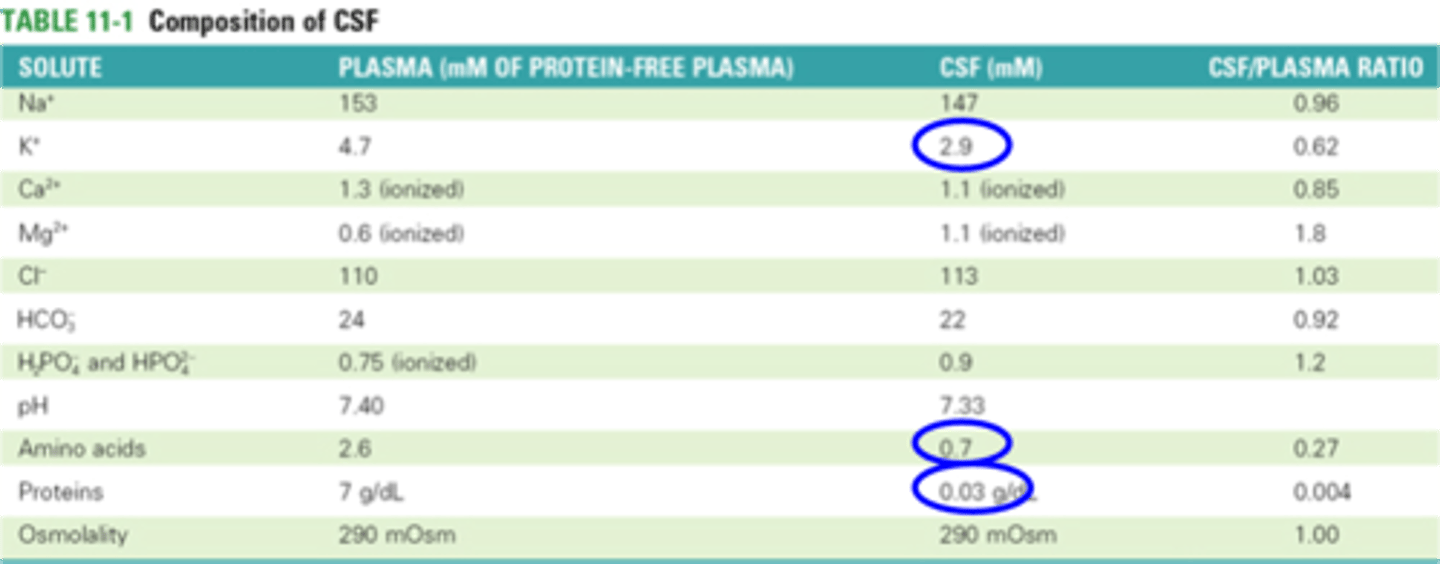
What is in CSF
What does this table show?
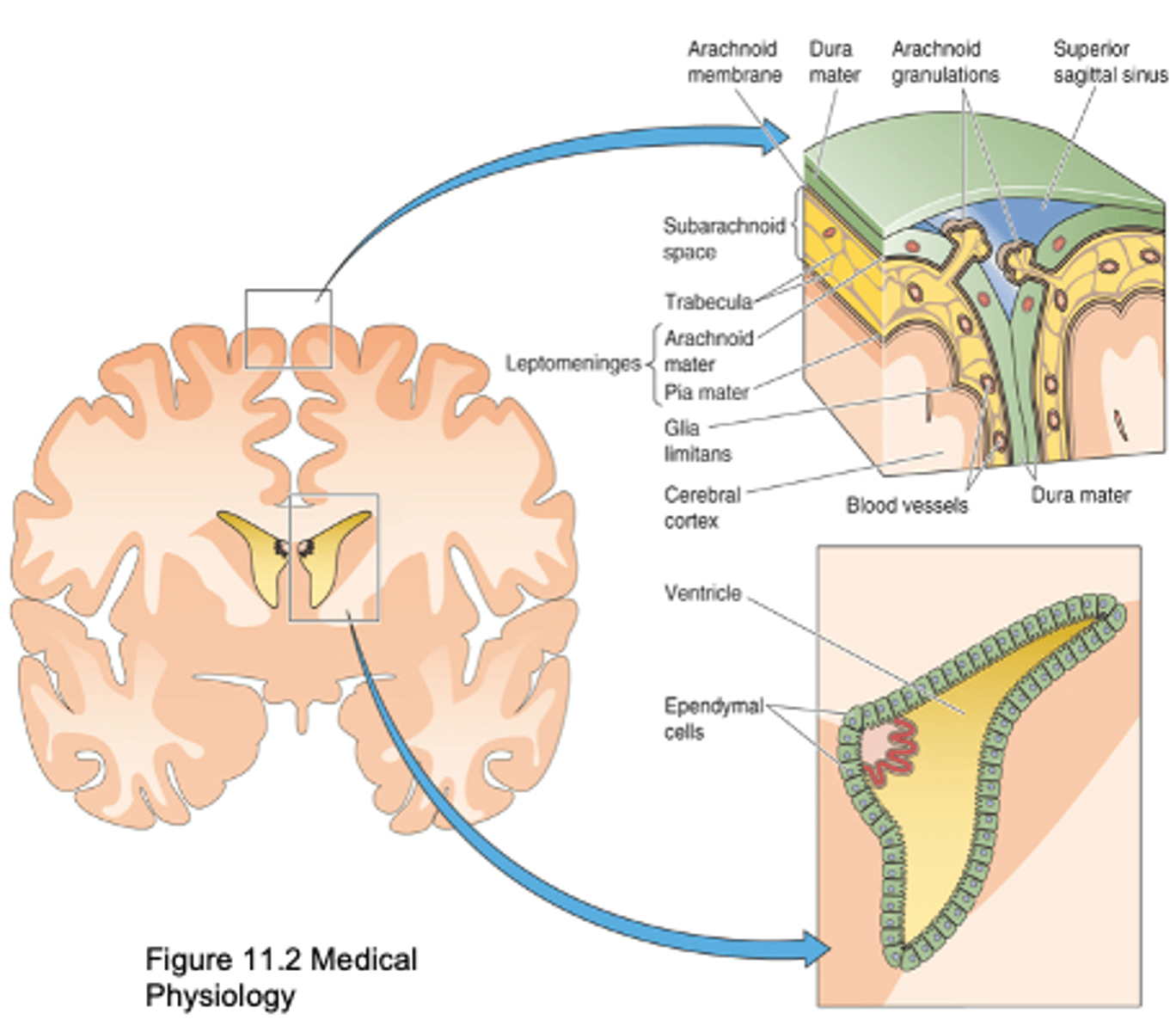
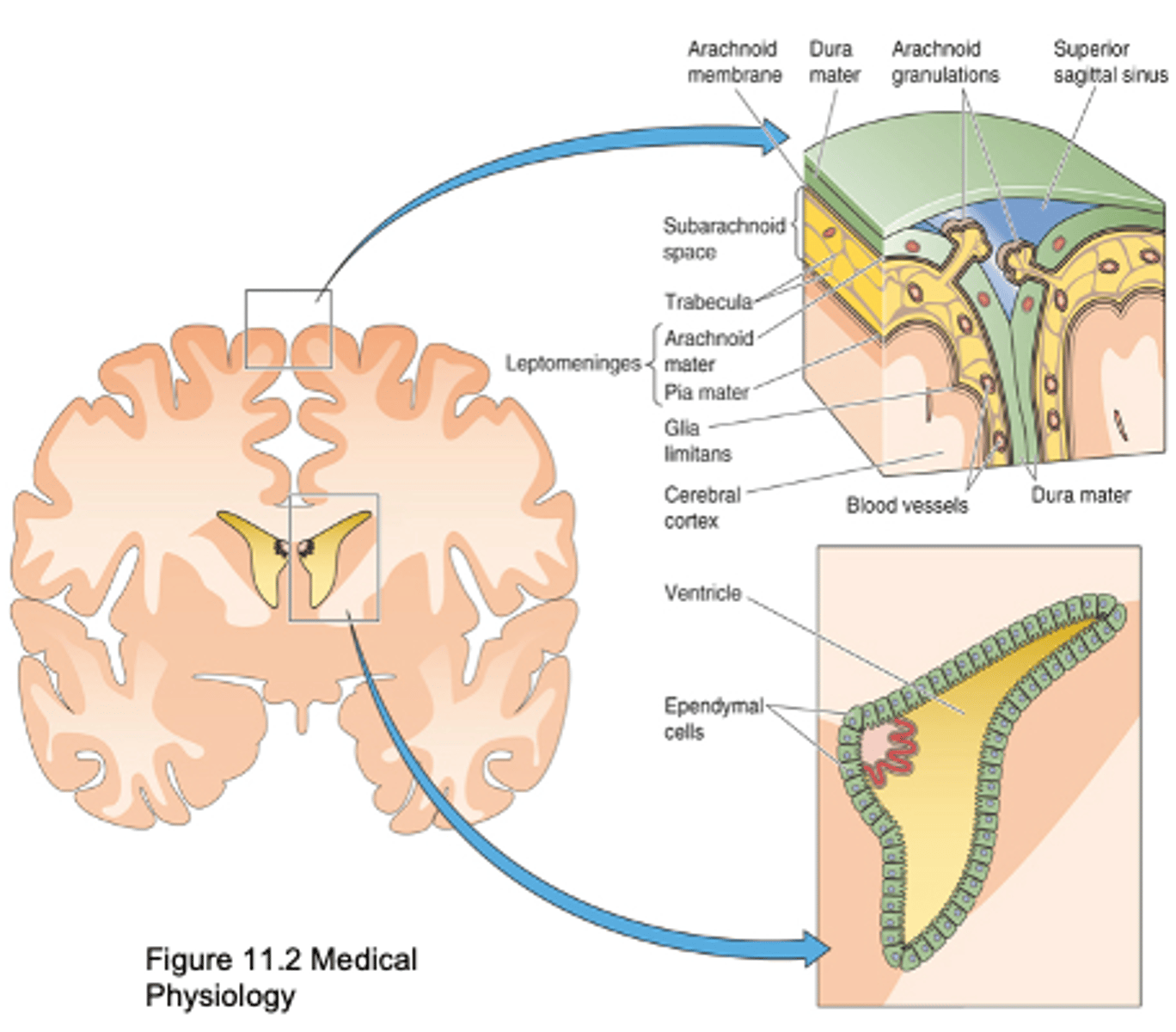
Pia mater, arachnoid mater, dura mater
What are the 3 types of meninges?
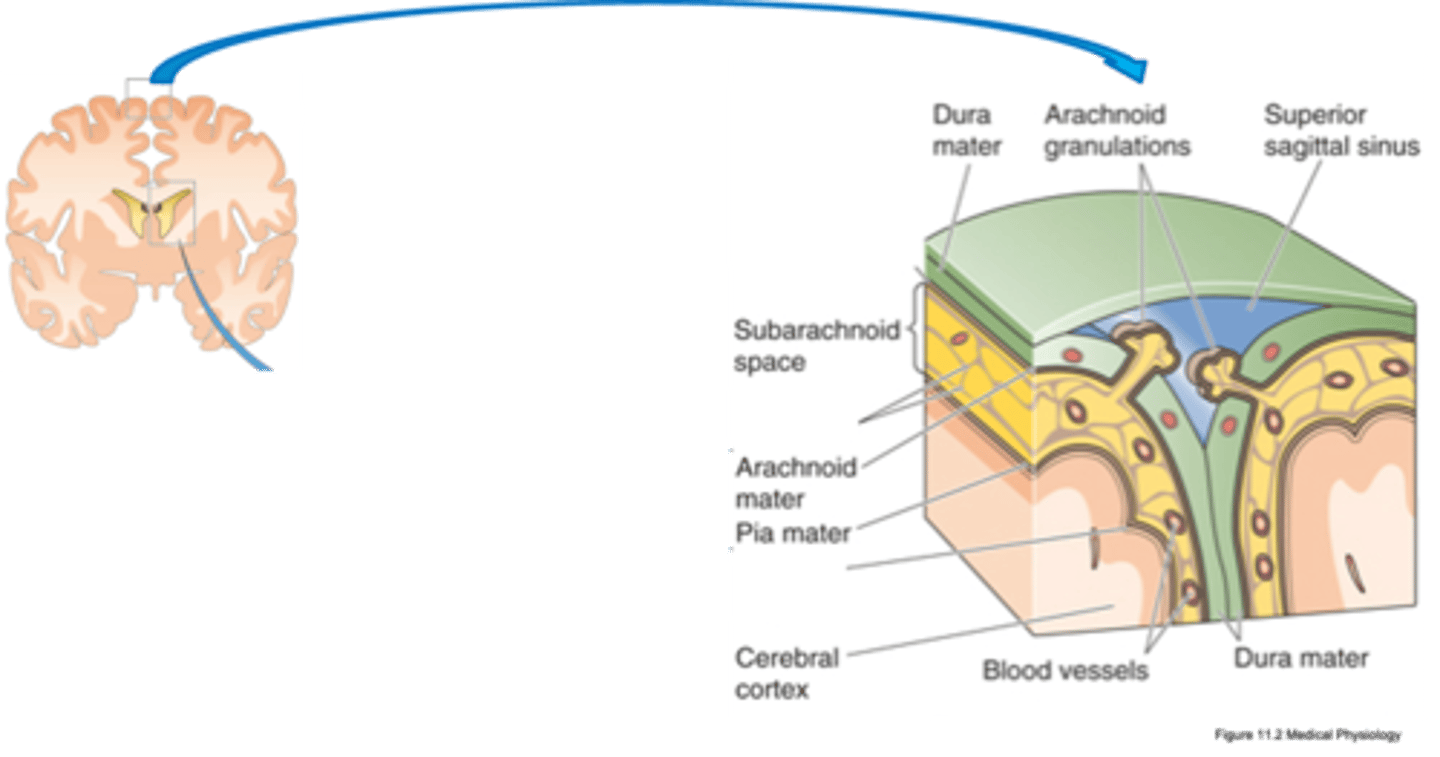
Covers surface of brain and blood vessels and allows diffusion between CSF and BECF
What does the pia mater do?
Cells linked by tight junctions, prevent diffusion between CSF and plasma
What does arachnoid matter have and what does it do?
Thick, inelastic membrane
2 layers - split to form intracranial sinuses
What is the composition of dura mater?
Arachnoid granulations (up to 1cm)
Arachnoid villi
Evaginations of arachnoid membrane
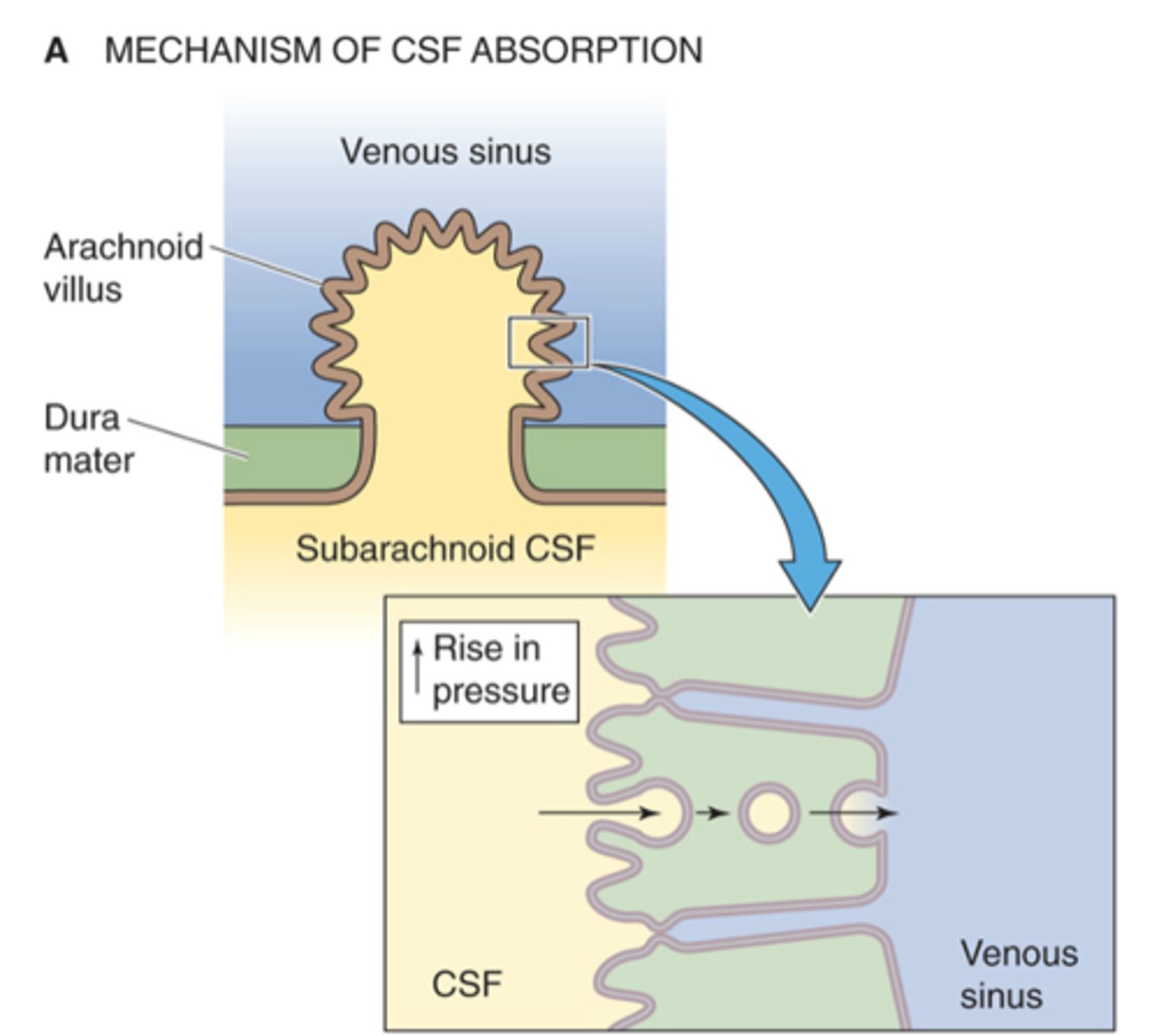
Intracranial pressure
Increased absorption with increased ...?

From ventricles across ependymal cells, from subarachnoid space across the Pia mater
Where does exchange between CSF and BECF occur?
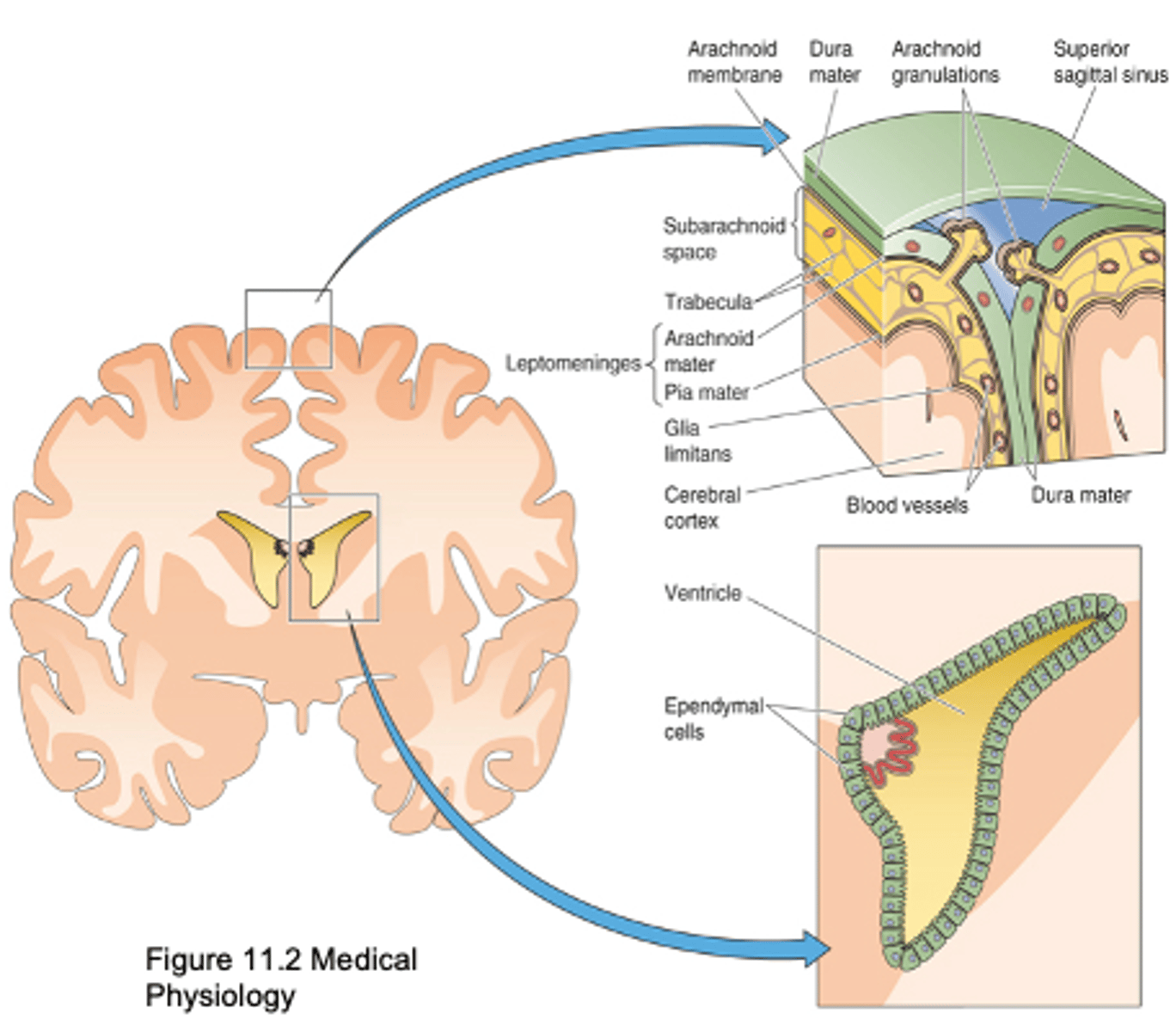
Macronutrients (e.g. Glucose), micronutrients (e.g. vitamins), ions (e.g. HCO3-)
What is exchanged from CSF to BECF?
Metabolic waste products (e.g. CO2), neurotransmitters
What is exchanged from BECF to CSF?
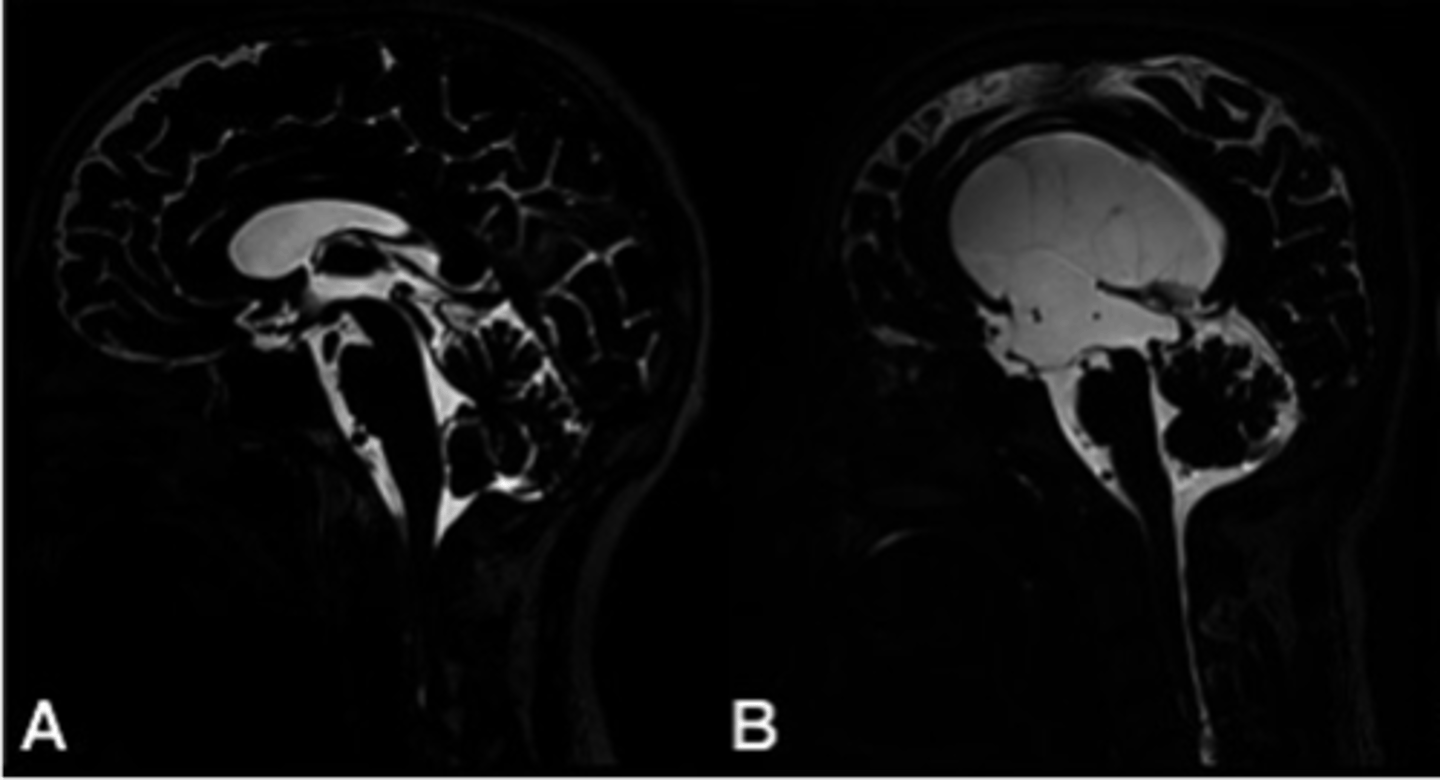
Hydrocephalus
What if CSF cannot circulate properly, what happens?
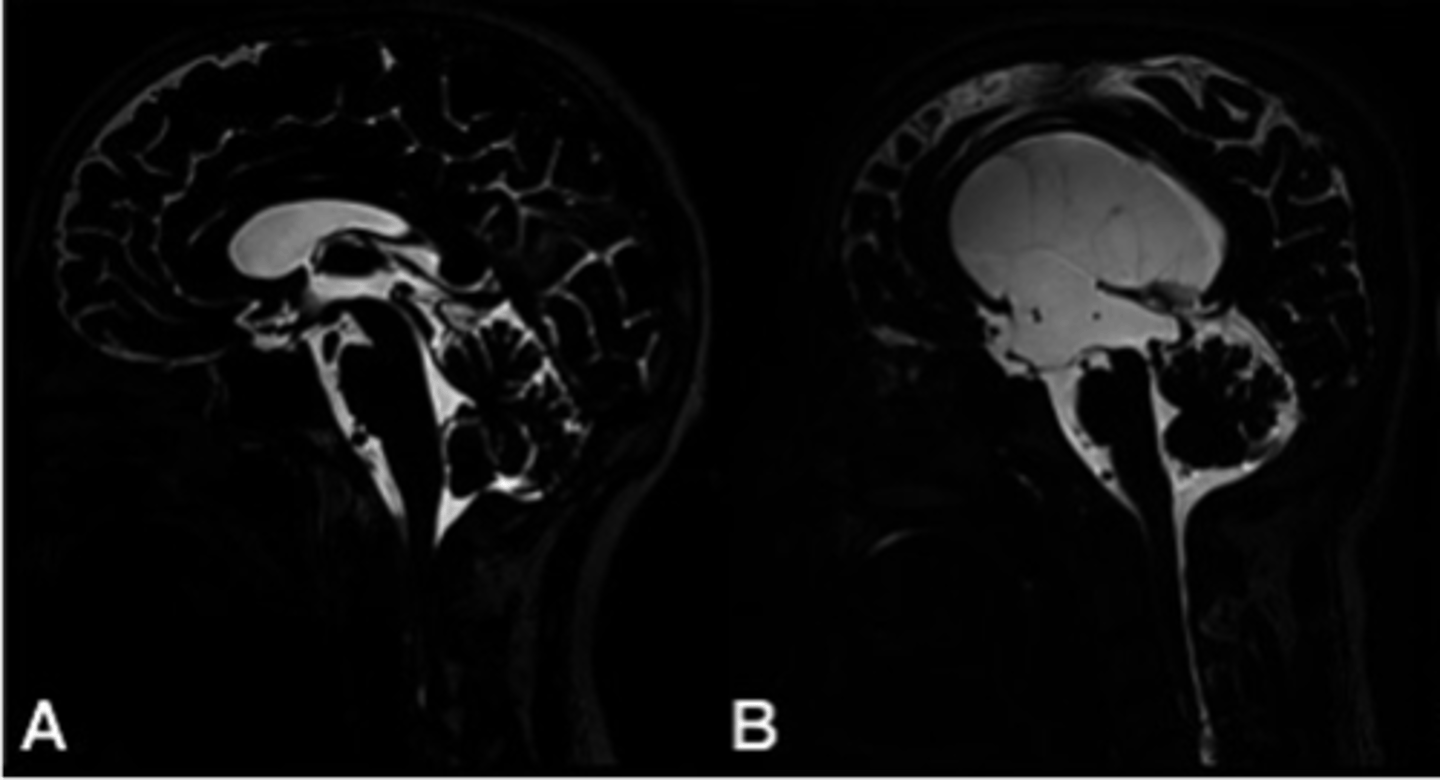
Dilation of ventricular system
Obstruction in ventricular system or interrupted CSF absorption
Increased intracranial pressure
Loss of cells within the brain
Loss of brainstem reflexes
What happens in hydrocephalus?