Lab 9: Hematology & Intro to Heart and Circulation
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Plasma
55% of blood; the majority of whole blood
Plasma proteins
proteins within plasma
Albumins
60% of plasma
important for regulating osmotic pressure
Globulins
35% of plasma
immunity & transportation of lipids and hormones
Fibrinogen
4% of plasma
blood clotting precursor in injury
Formed elements
45% of blood
RBC, WBC and cell fragments (platelets)
Erythrocytes
RBC- concave discs that transport O2 in blood
Leukocytes
WBC- immunity defenses
Platelets (cell fragments)
help with blood clotting
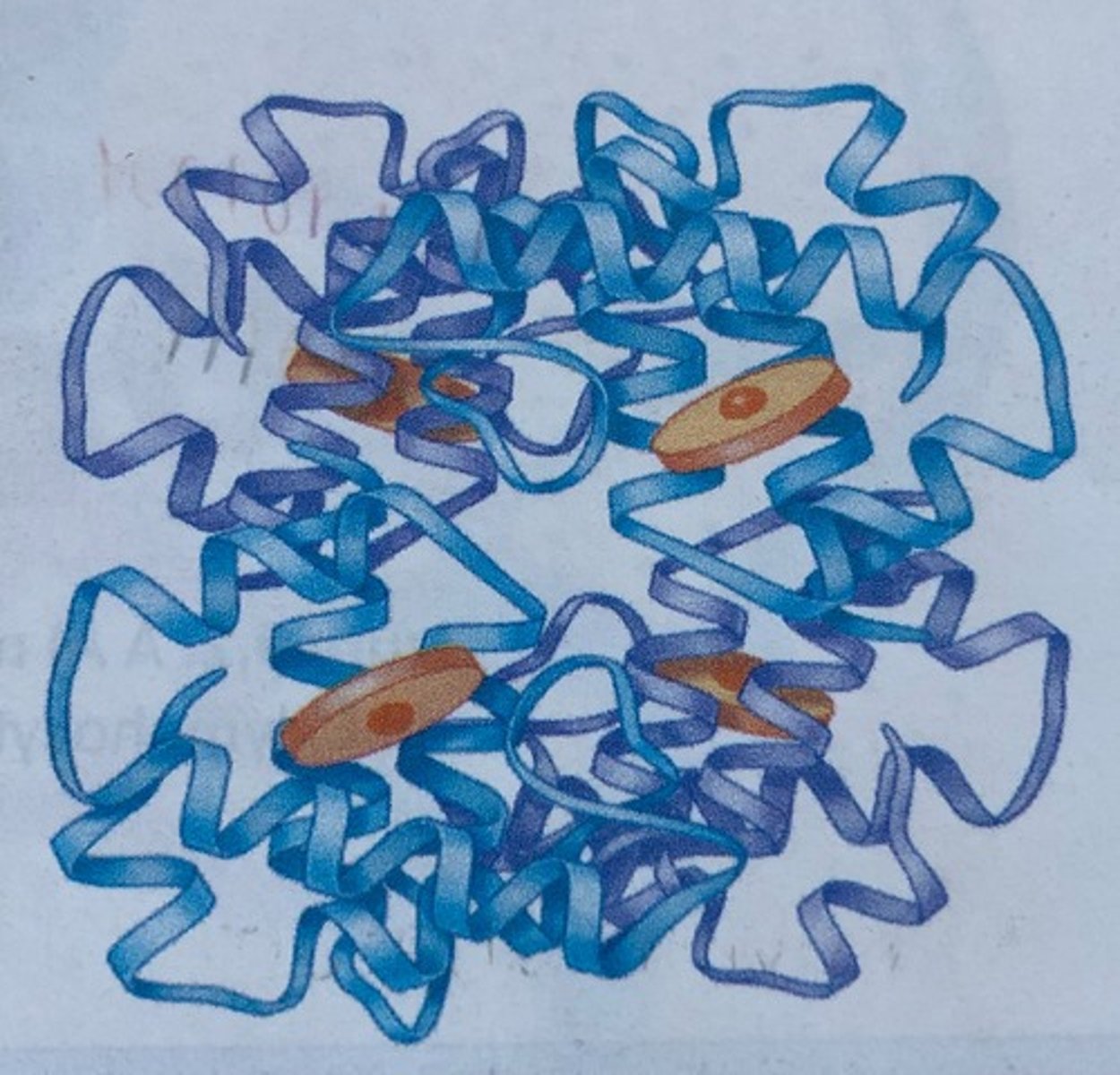
Hemoglobin
Red pigment in blood (purple molecule)
Transports O2 and CO2
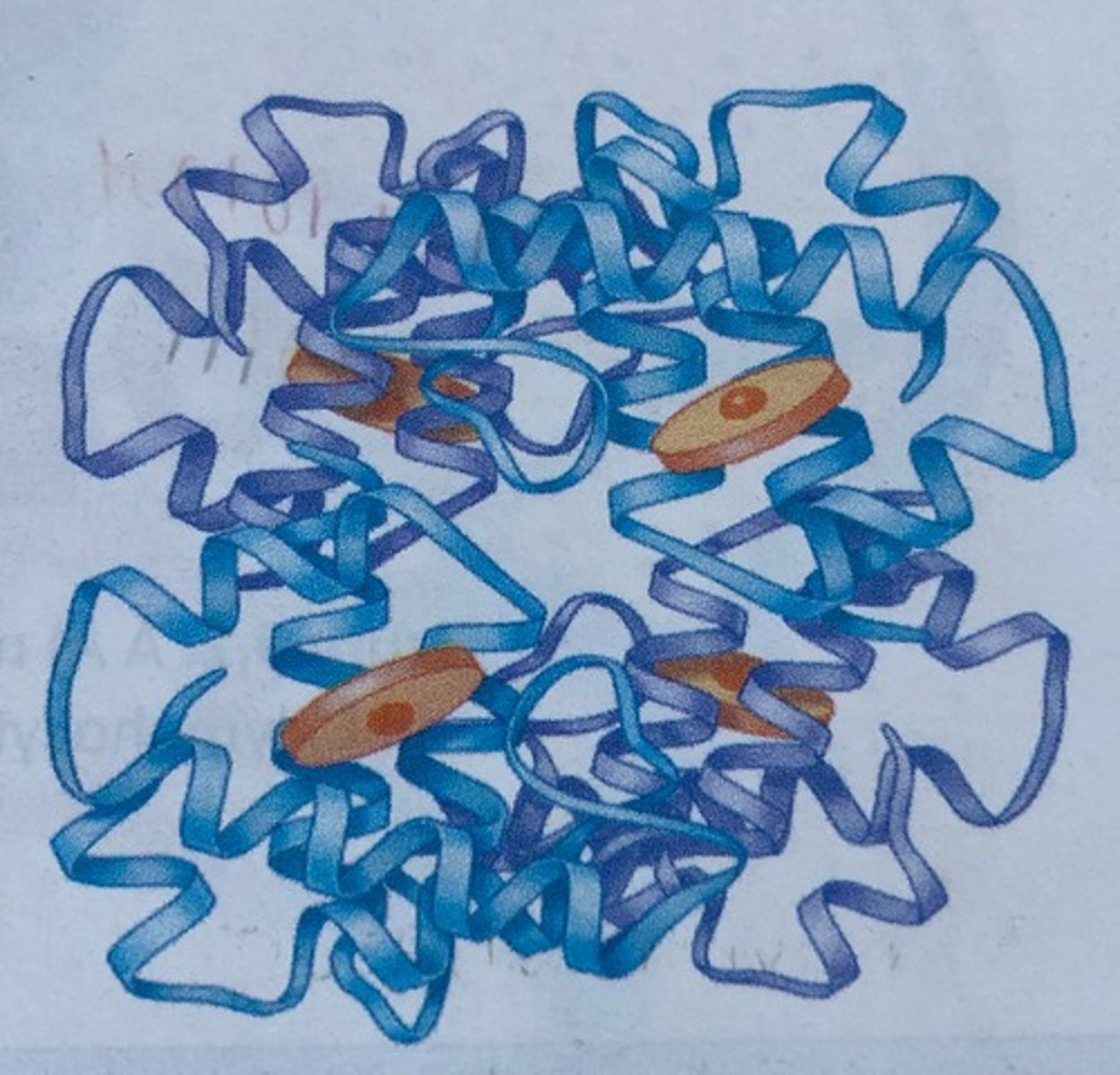
Heme
(orange discs)
Where O2 binds
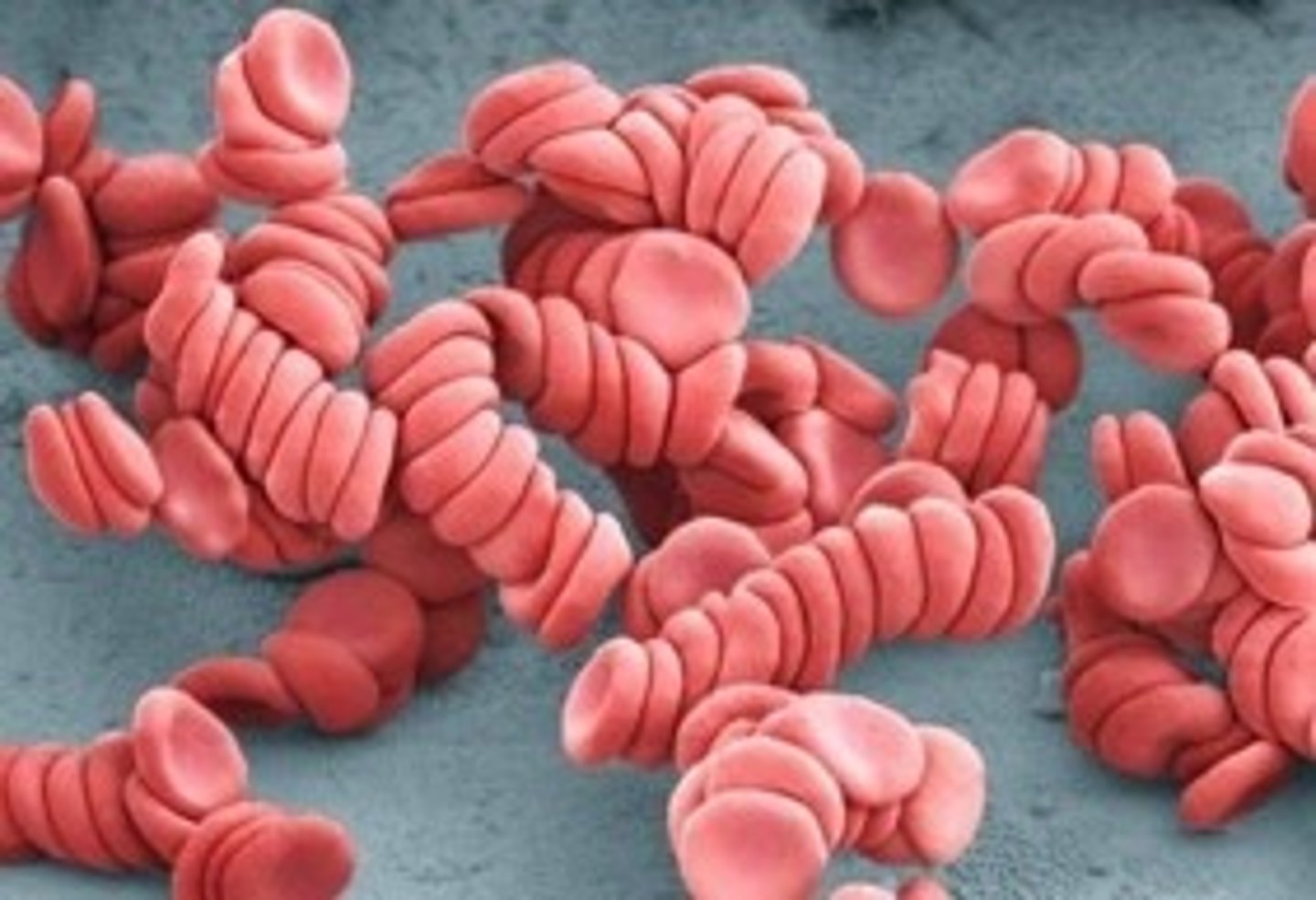
Rouleaux
single file of stacked RBCs
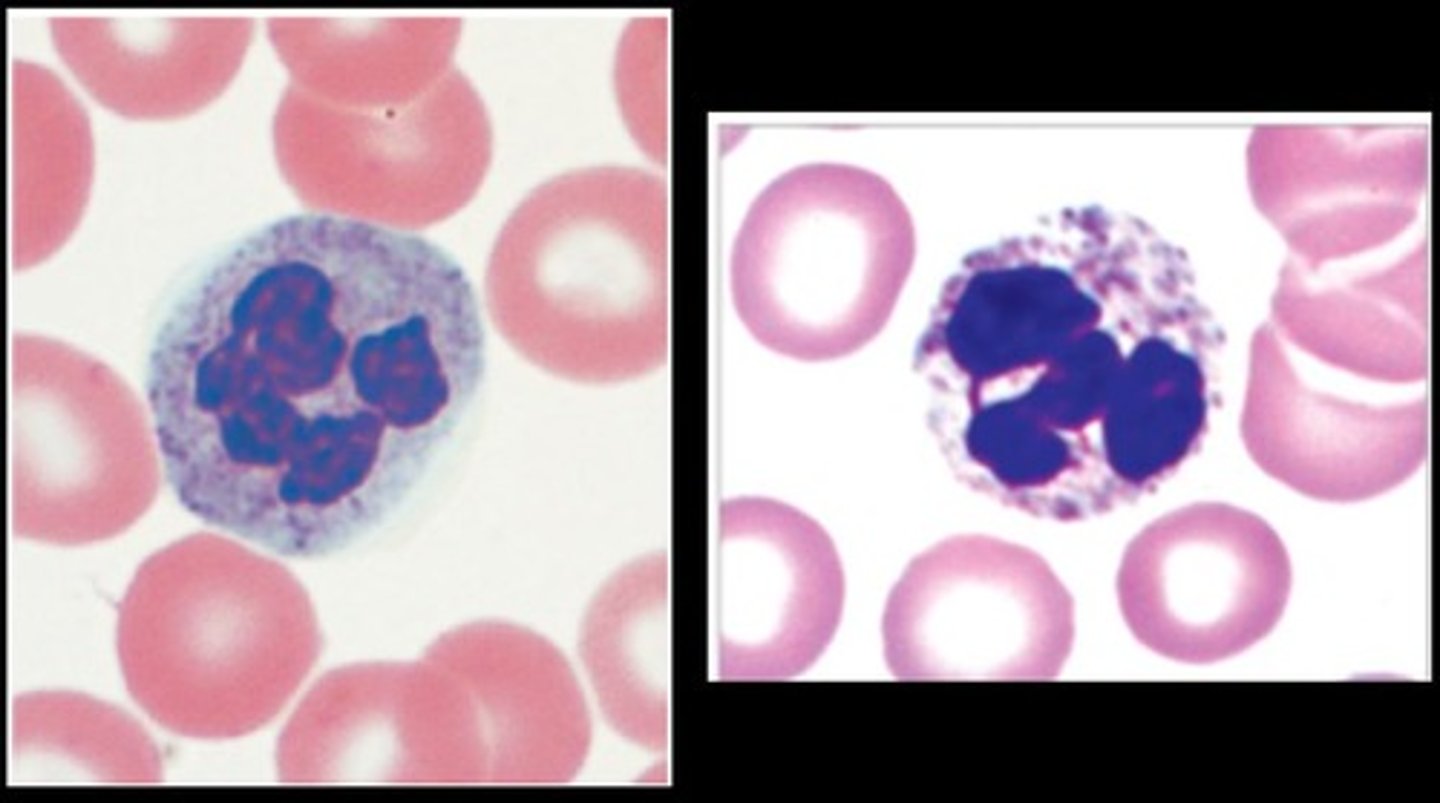
Neutrophils
circulating WBCs
Multilobe nuclei (2-5) nuclei
Most abundant
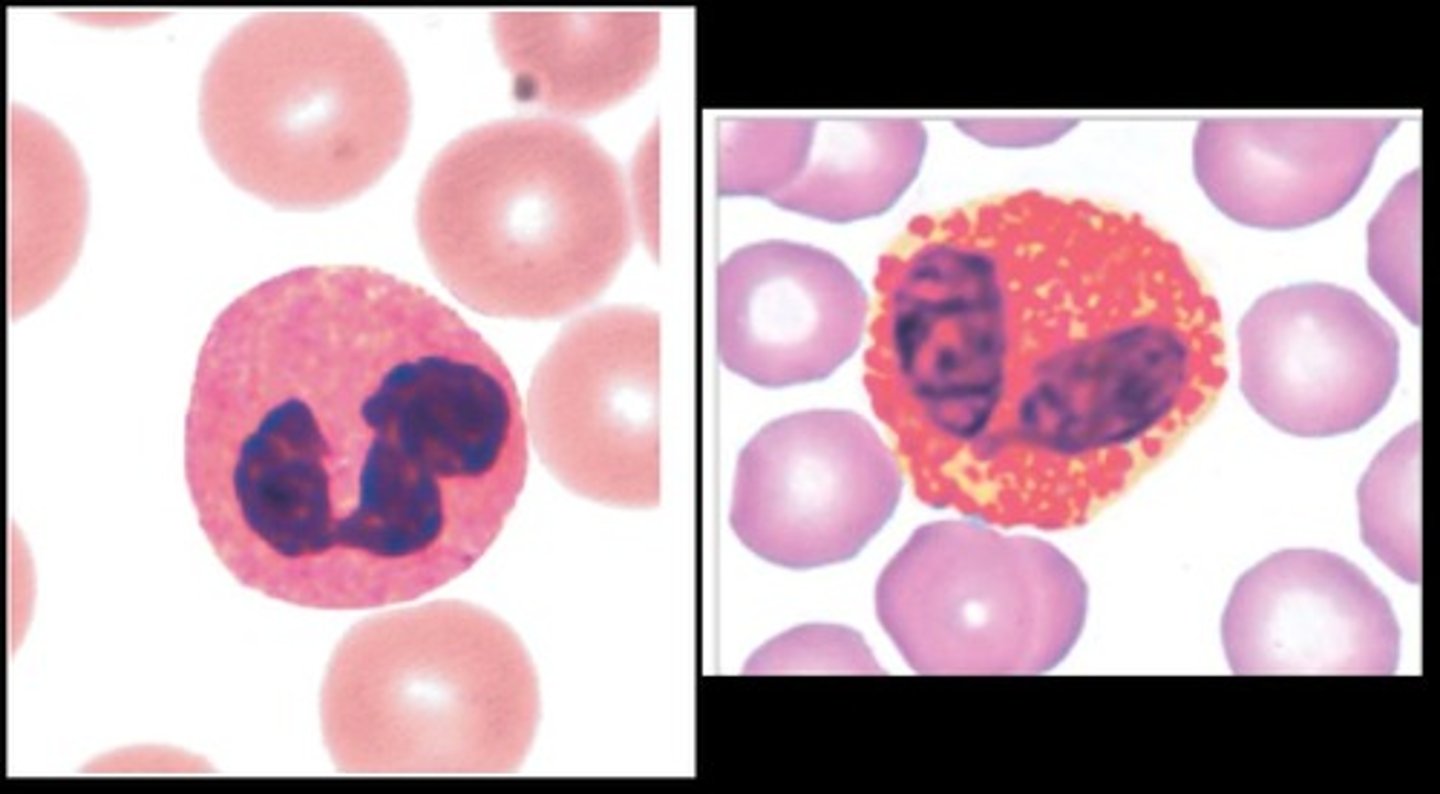
Eosinophils
Red color
Bi-Lobe
fight parasites
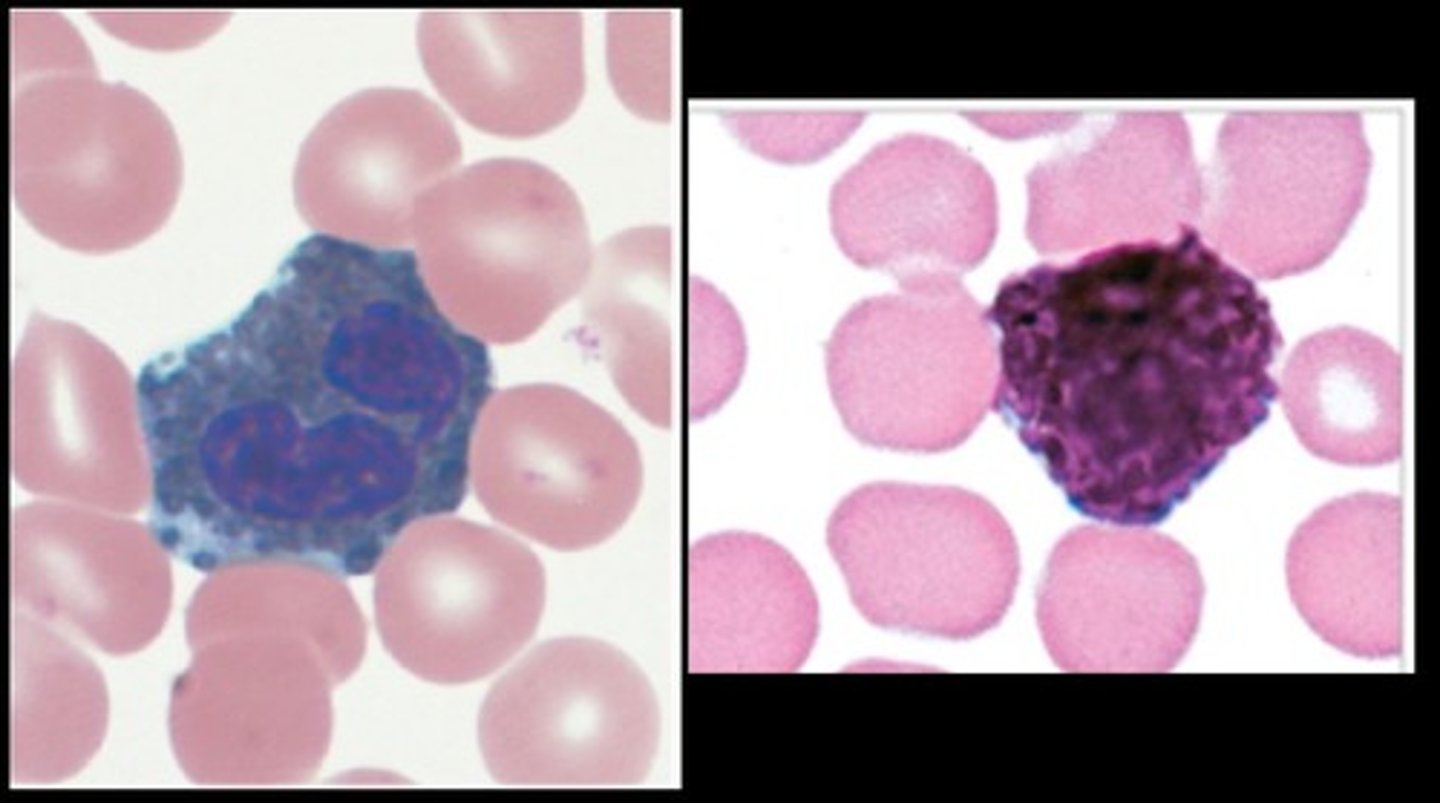
Basophils
Dark granules- cannot see the nucleus
least abundant
allergic reactions
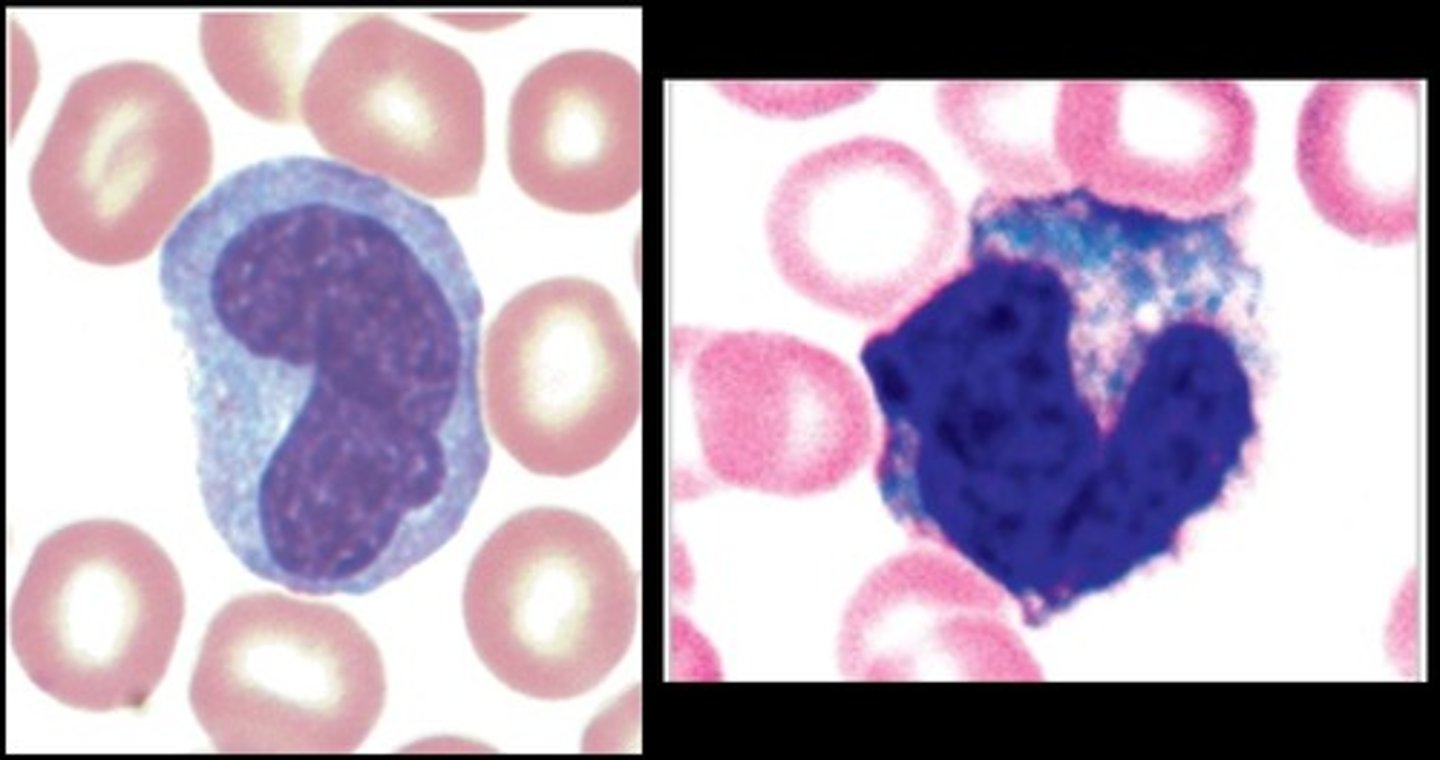
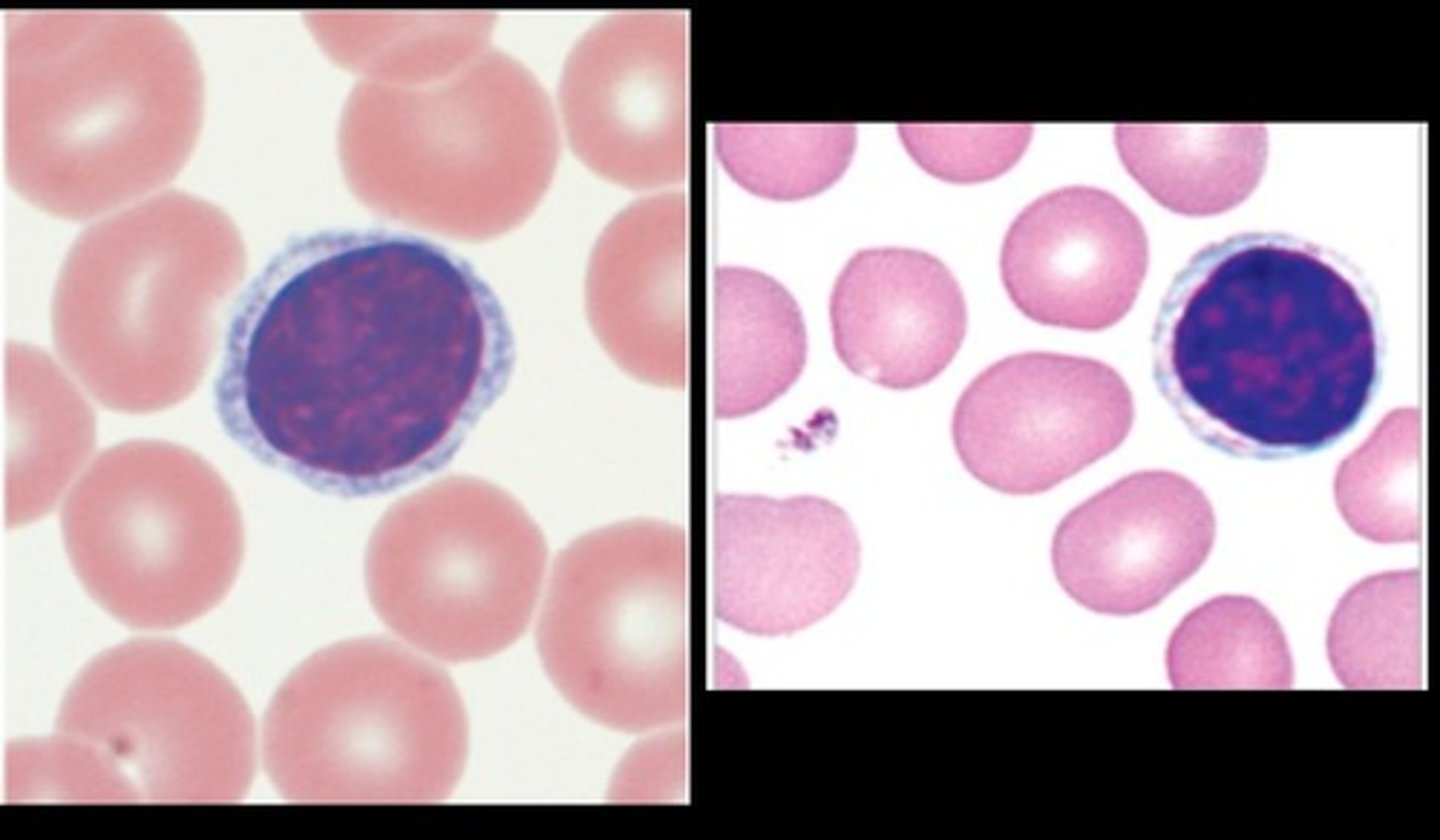
Monocytes
Have an irregular shape and a large nucleus
lymphocytes
T cells, B cells, Natural killer cells
Have a halo effect/ring around the nucleus
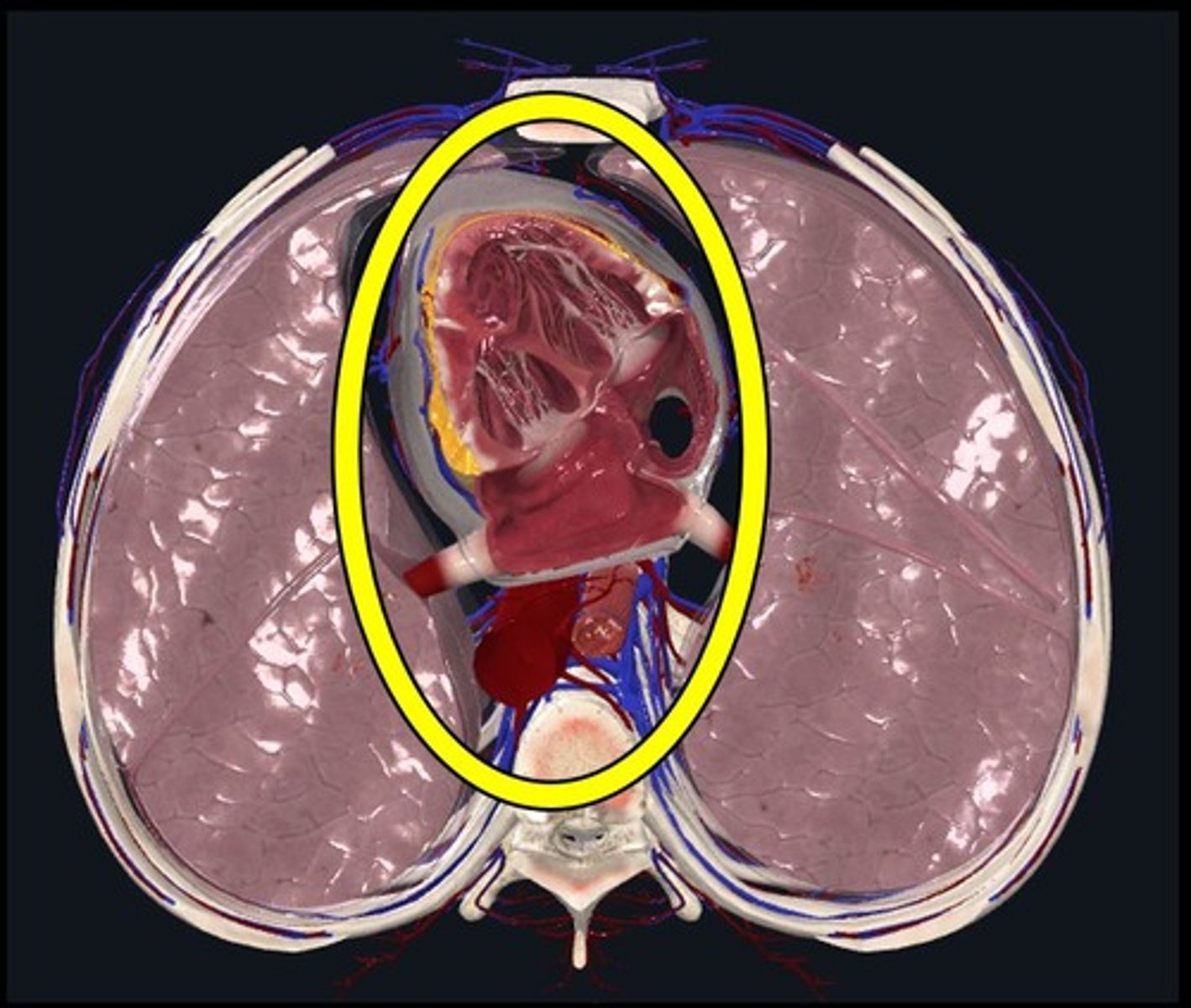
Mediastinum
Chamber between 2 pleural cavities where heart, great vessels, trachea, thymus and esophagus are located
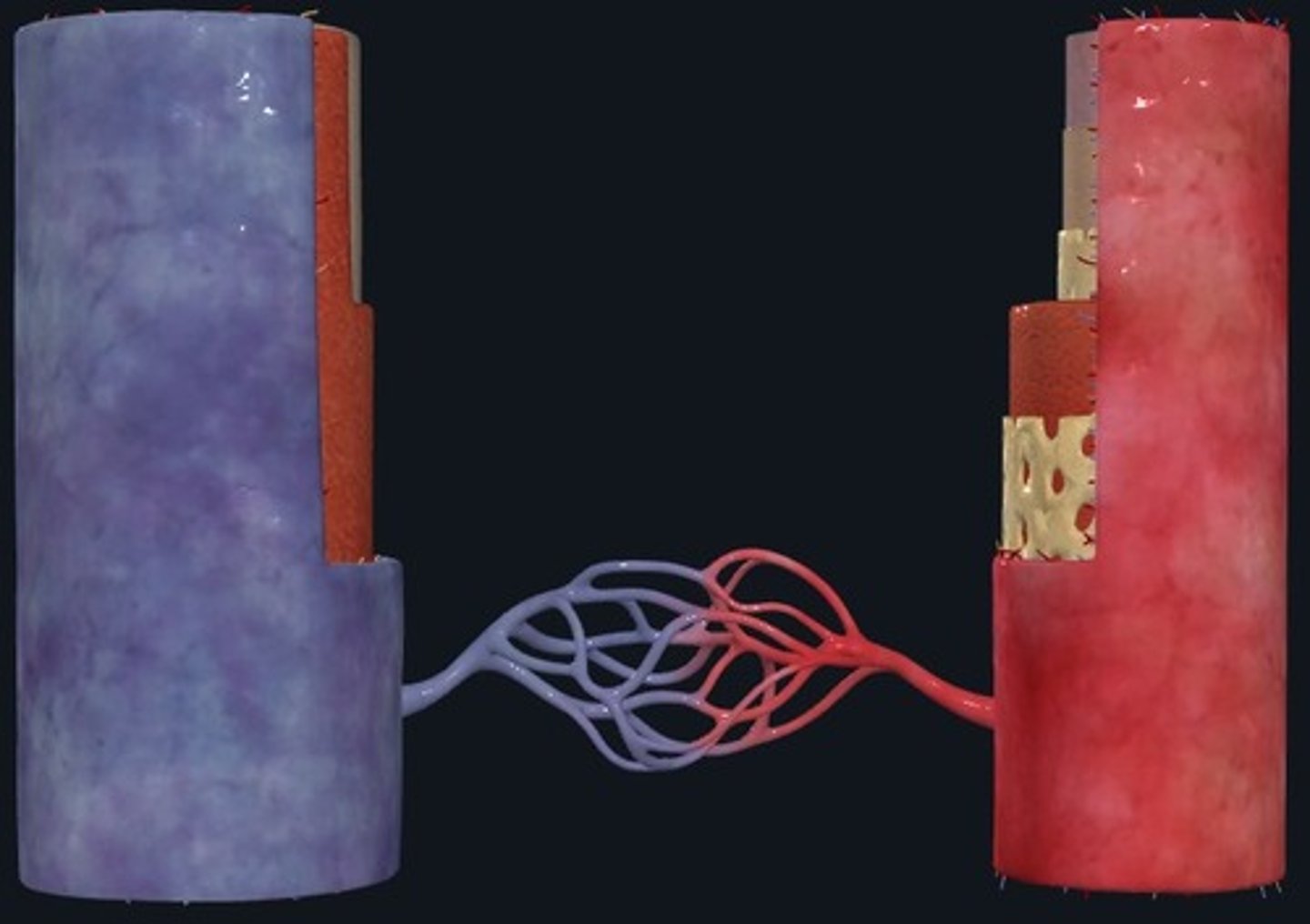
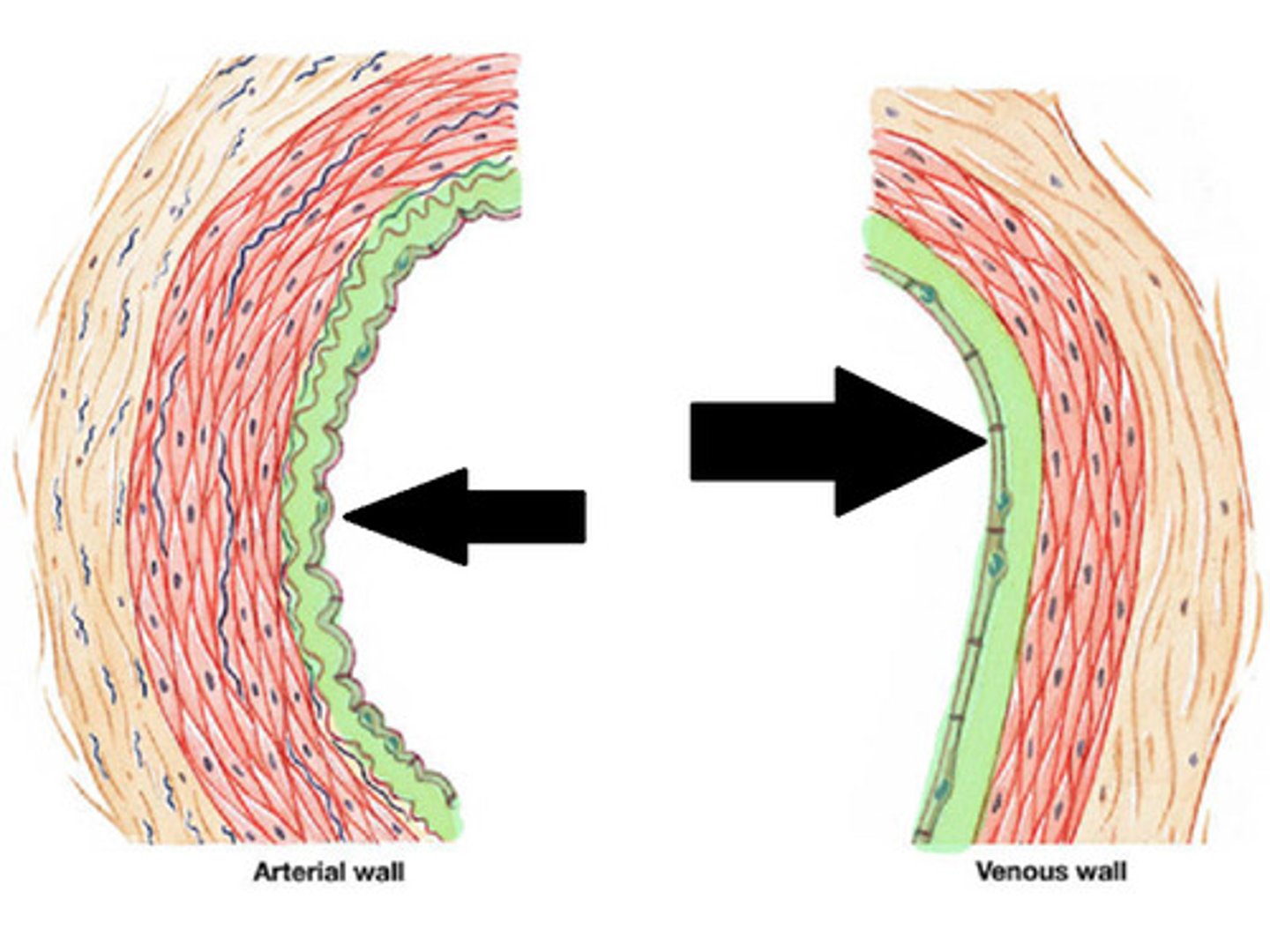
Artery
more muscular
Rebound back to circular shape
carry blood AWAY from the heart
Vein
Thinner and not perfect circles
Carry blood TO the heart
Capillaries
connections between veins
gas and nutrient exchange occur here

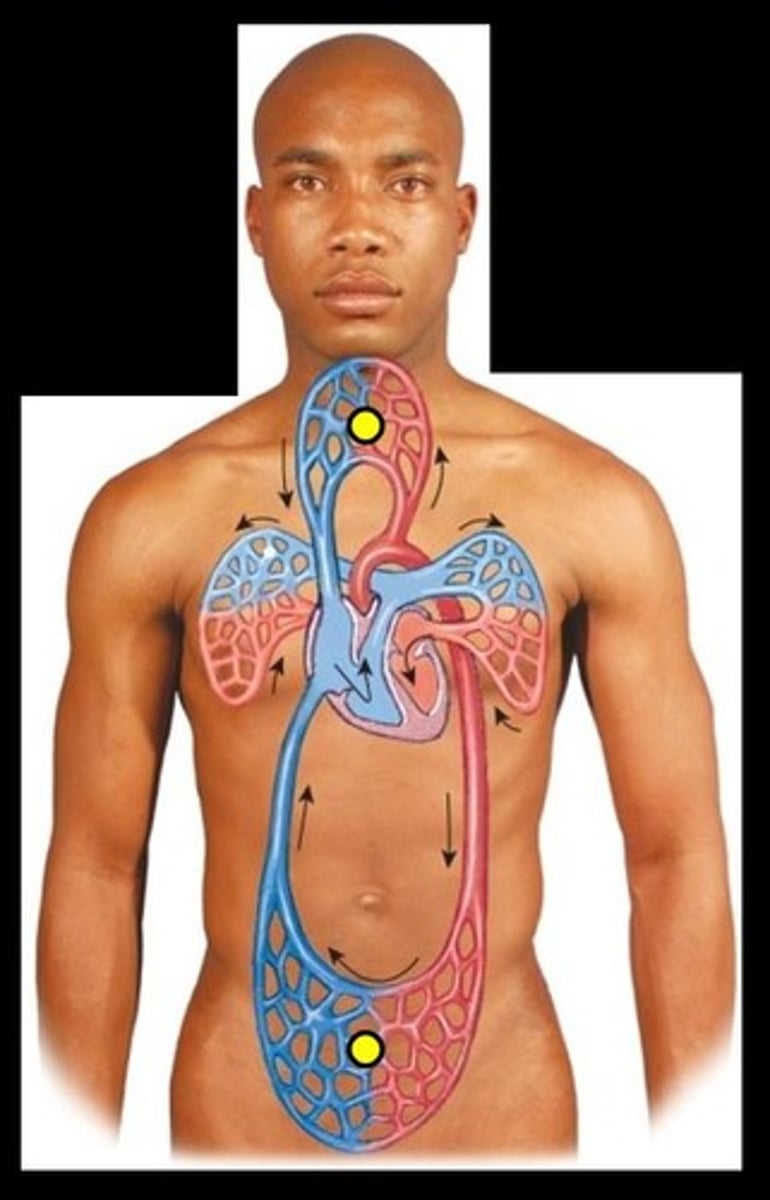
Pulmonary circuit
the arteries and veins in the lungs
Pump blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs
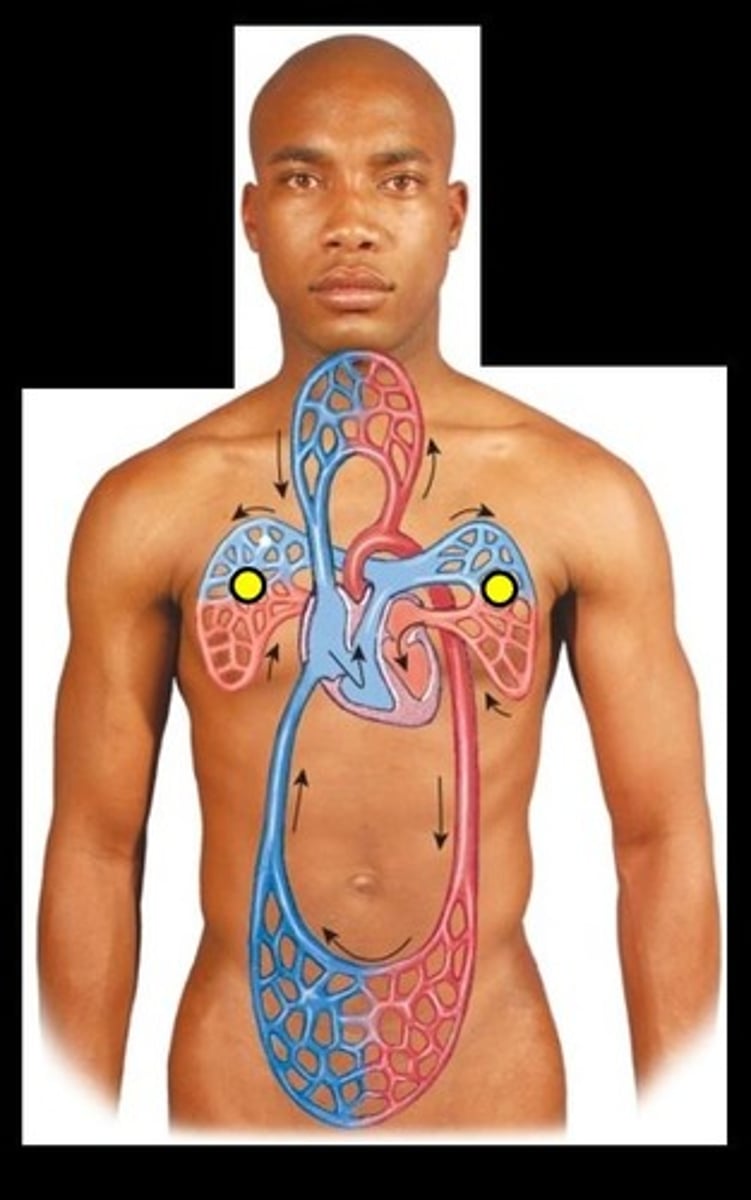
Systemic circuit
carries blood to the rest of the body
Tunica intima
(vessel wall structure)
Innermost layer
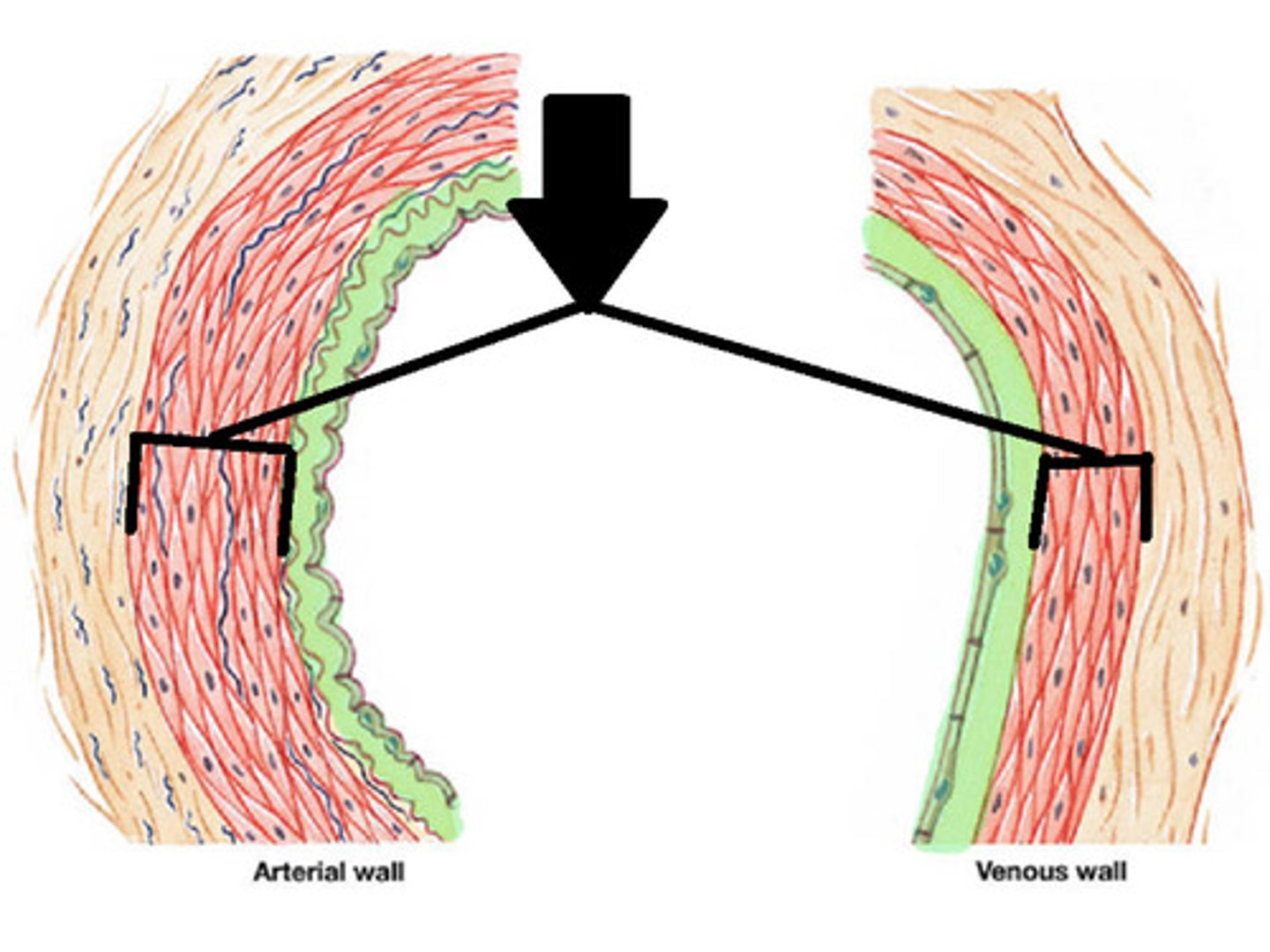
tunica media
middle layer of vessel wall
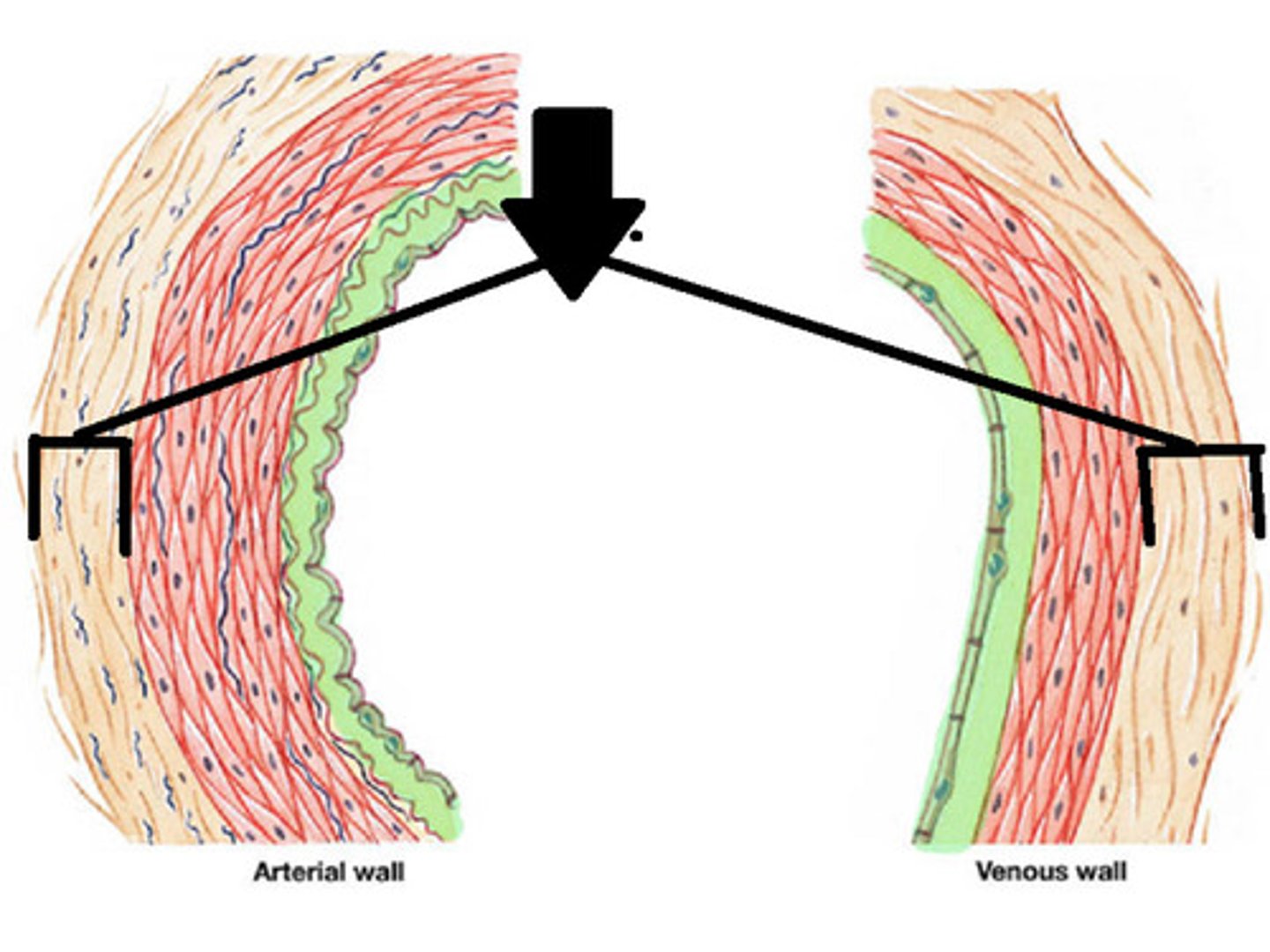
Tunica externa
outermost layer of vessel wall
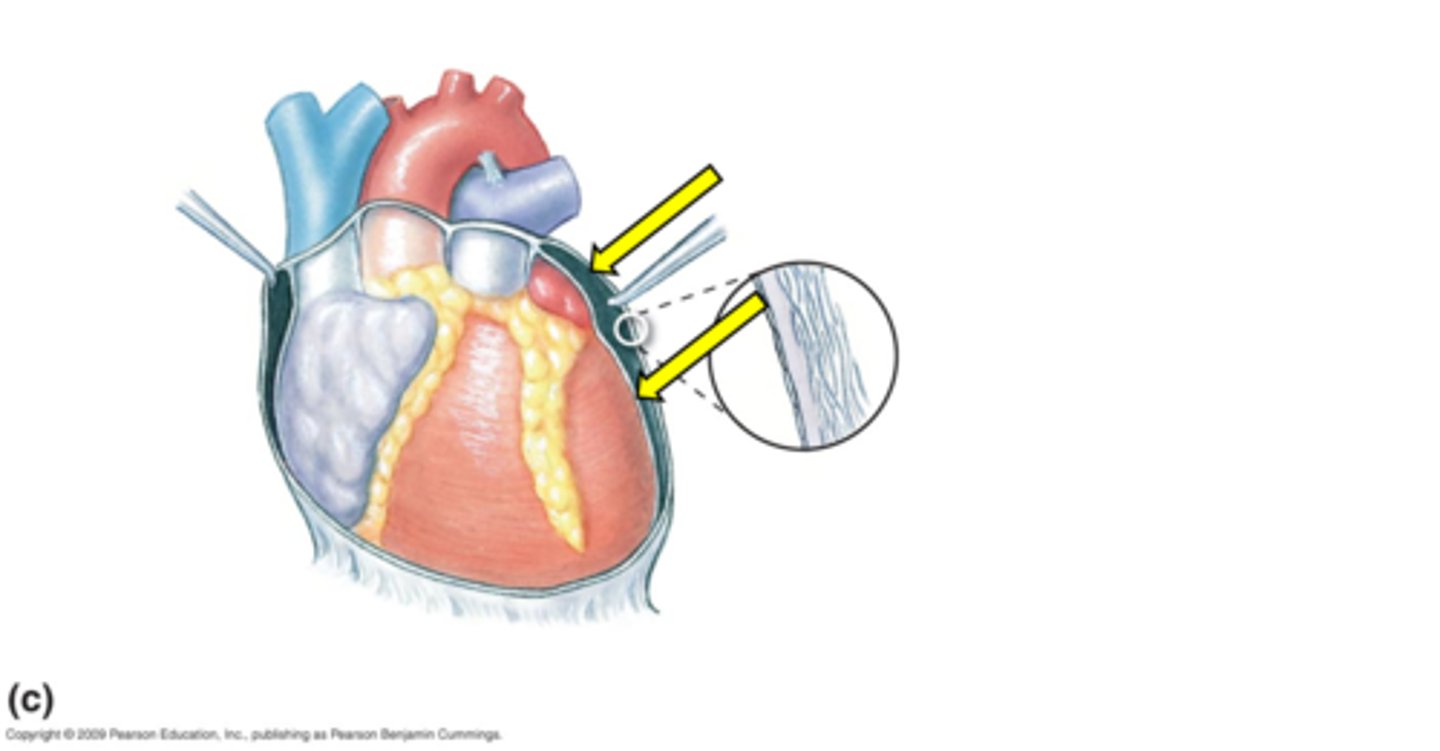
Pericardial cavity
the space where the heart sits
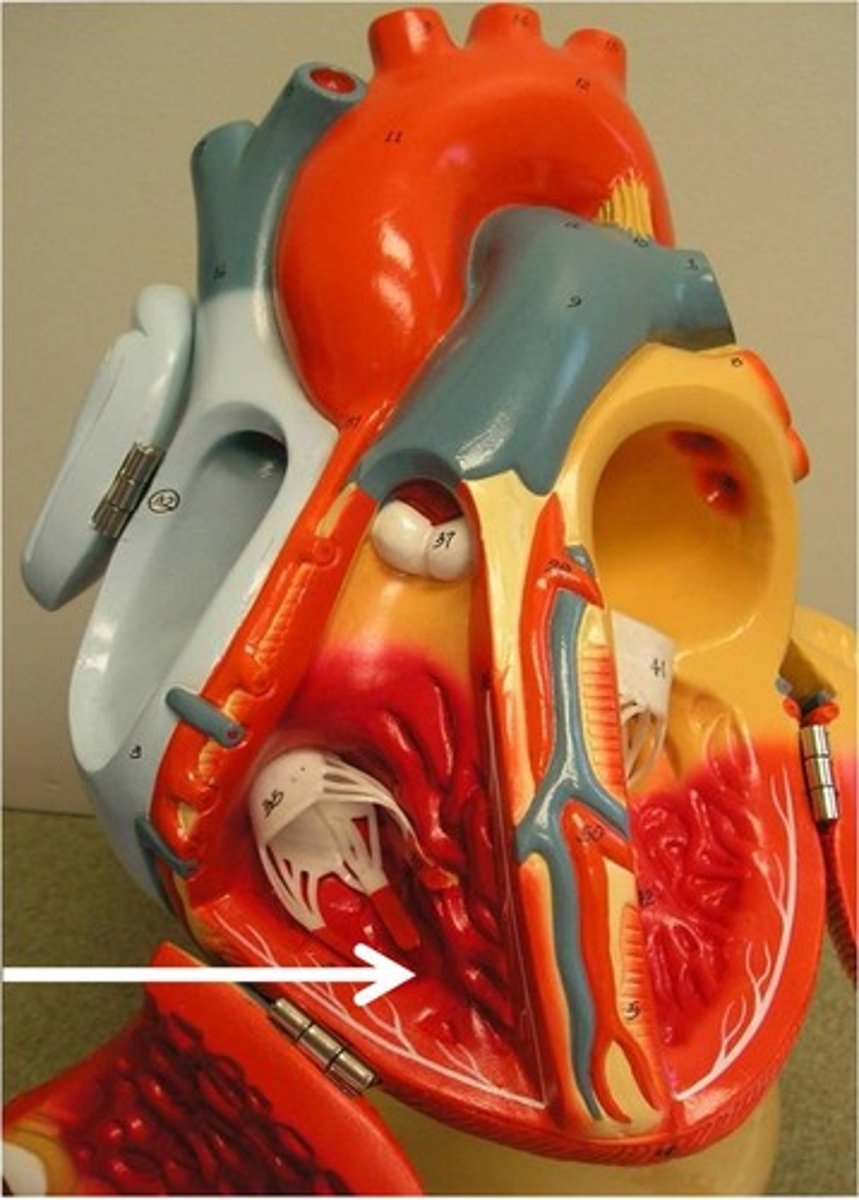
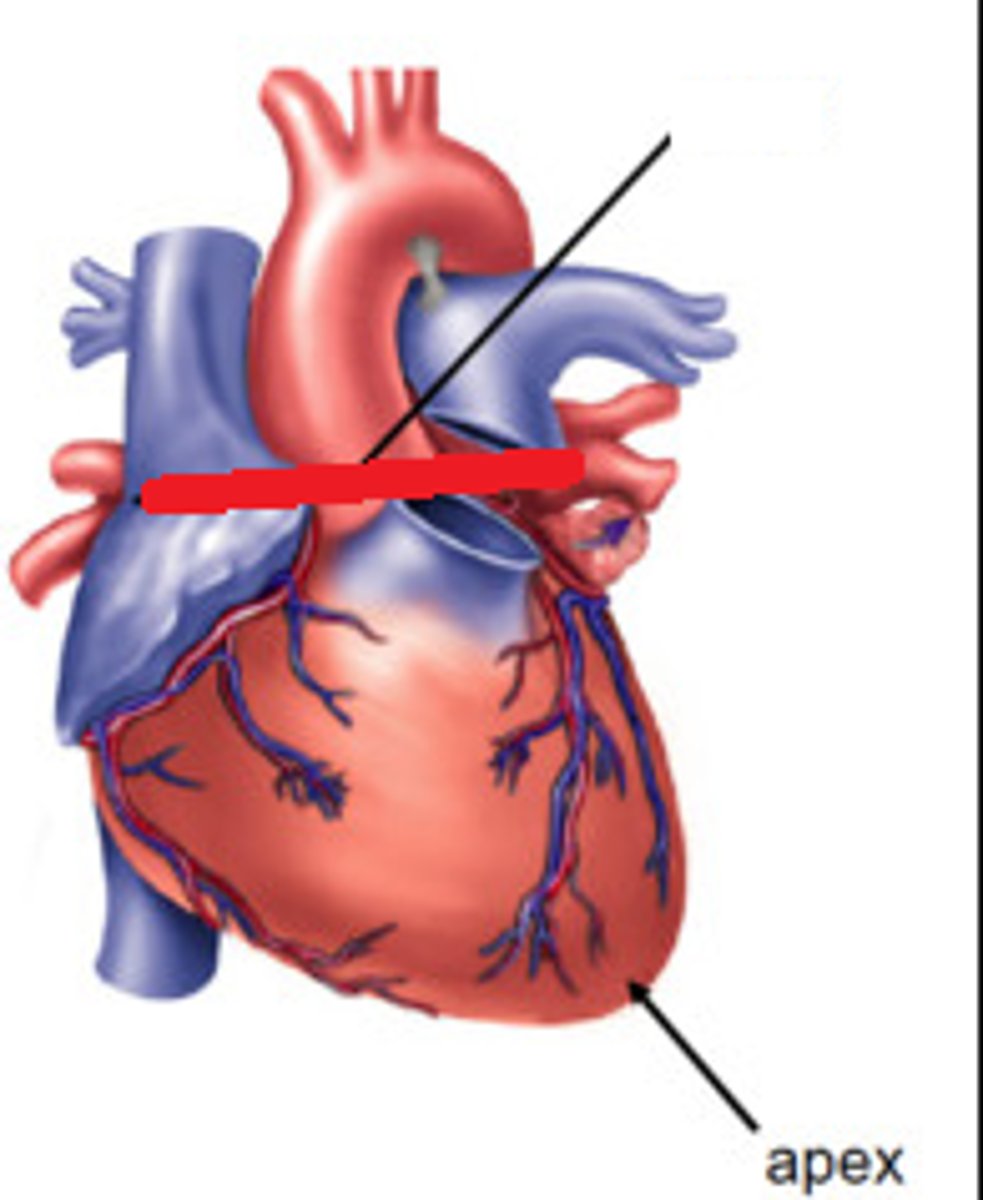
Apex of the heart
point of heart
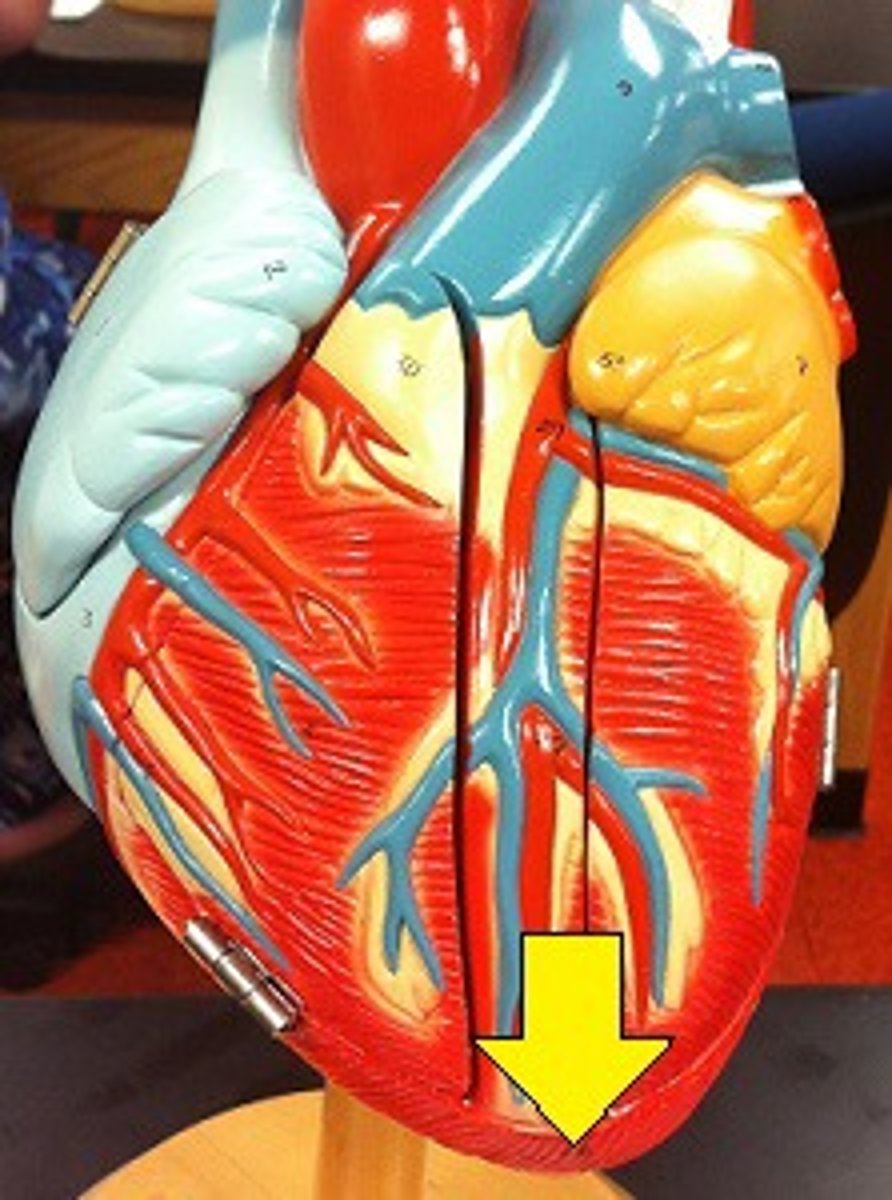
base of the heart
the widest, top, flat part of the heart
Atria
the top two chambers of the heart
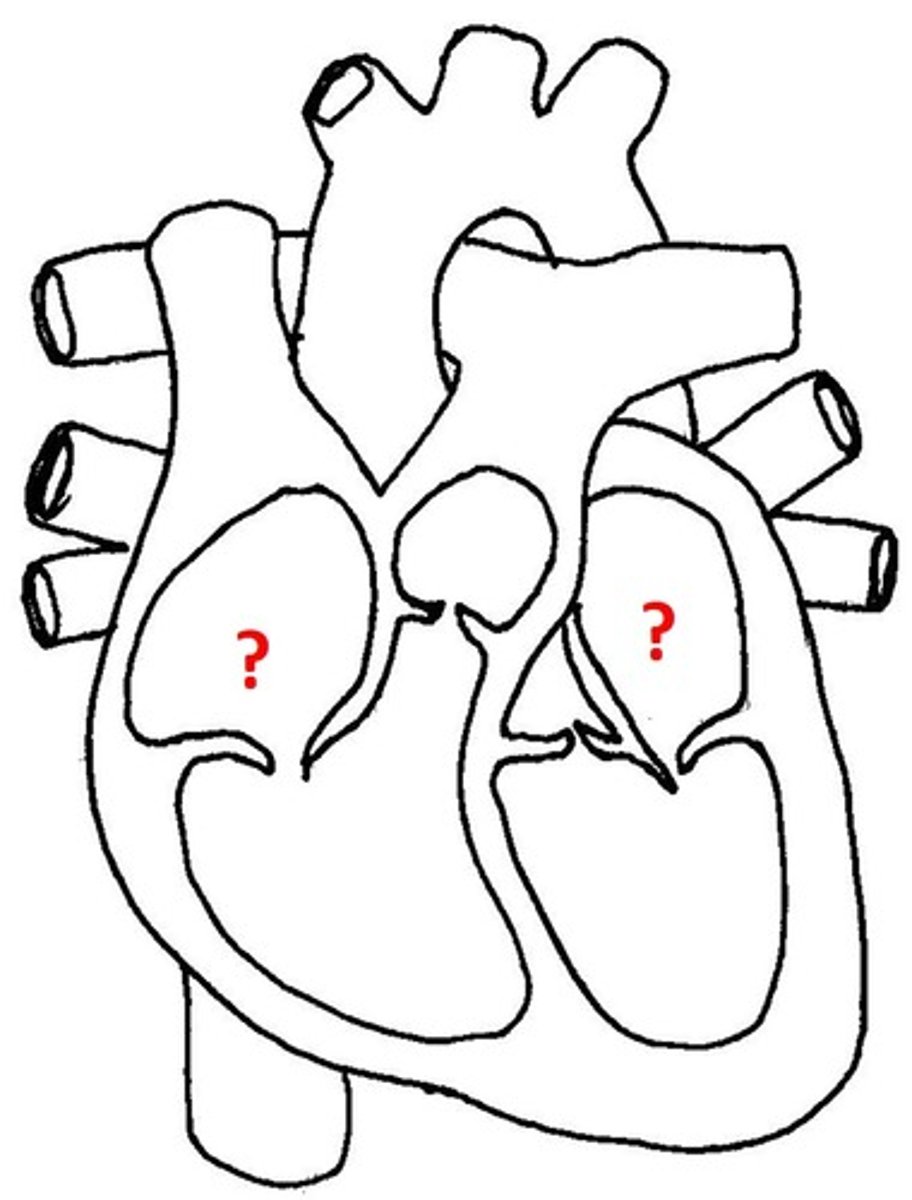
Ventricles
Bottom 2 chambers of the heart