Maxillary Anesthesia Part 2 (Dr. Hu)
1/145
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
146 Terms
Which maxillary injection?
- Single tooth or small area
Supraperiosteal Injection
Which maxillary injection?
- Central incisors, laterals, canines
Anterior Superior Alveolar (ASA) Nerve Block
Which maxillary injection?
- First and second premolars
- Mesiobuccal root of maxillary first molar
Middle Superior Alveolar (MSA) Nerve Block
Which maxillary injection?
- Central incisors, laterals, canines. premolars
- Cheek, lower eyelid, alar of nose, upper lip
Infraorbital Nerve Block
Which maxillary injection?
- Three molars (except mesiobuccal root of maxillary first molar)
Posterior Superior Alveolar (PSA) Nerve Block
Which maxillary injection?
- Palatal soft and osseous tissue distal to canine in one quadrant
Greater Palatine Nerve Block
Which maxillary injection?
- Palatal soft and osseous tissue from canine to canine bilaterally
Nasopalatine Nerve Block
Which maxillary injection?
- Buccal, palatal, and pulpal anesthesia in one quadrant
Maxillary (V2) Nerve Block
What can be one of the most painful injections in dentistry?
nasopalatine nerve block
How can you make the nasopalatine nerve block less painful or atraumatically?
- Topical anesthesia
- Use pressure anesthesia at the injection site before and during needle insertion
- Maintain control over needle
- Deposit the anesthetic solution slowly
- Trust that it can be painlessly!
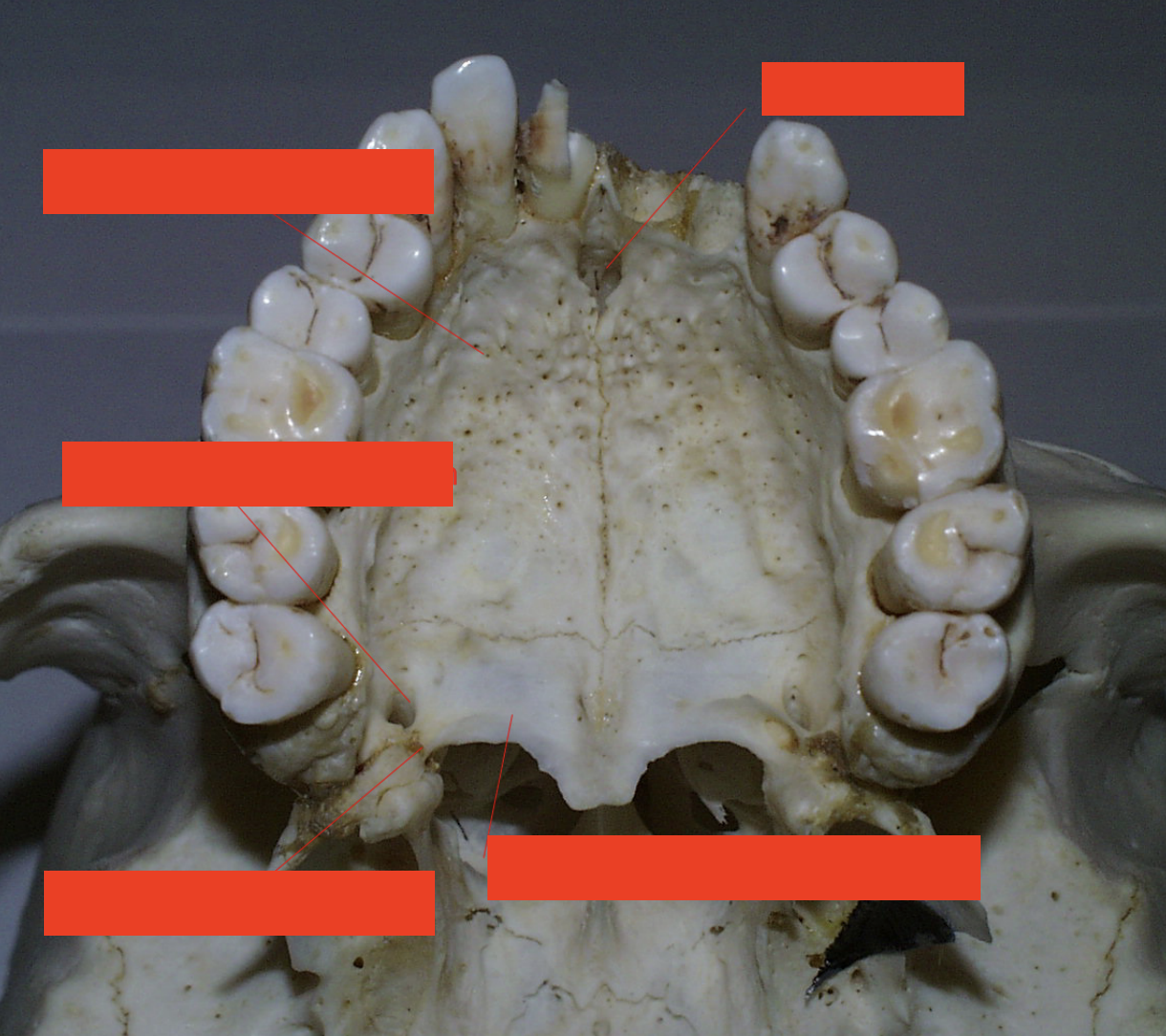
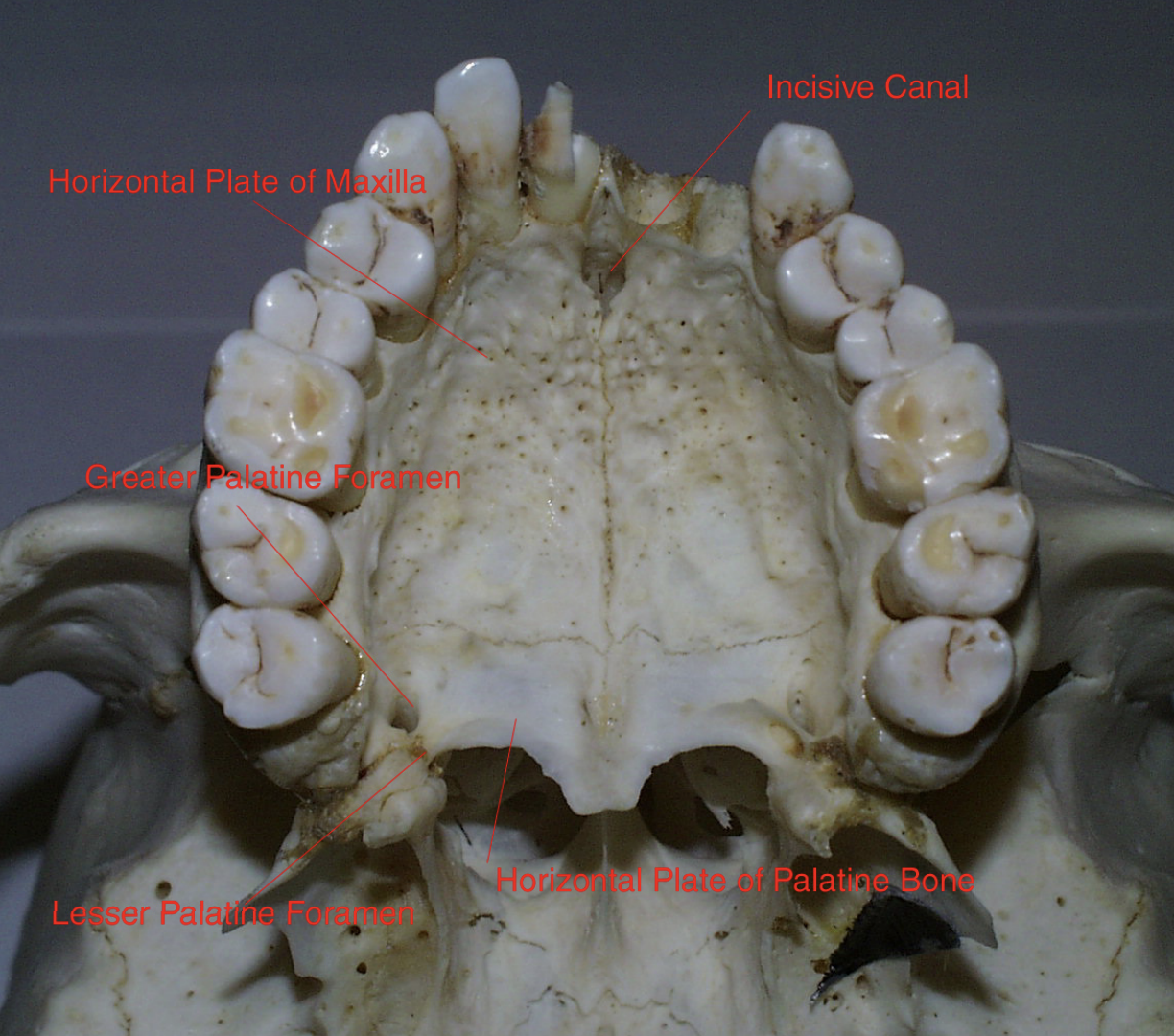
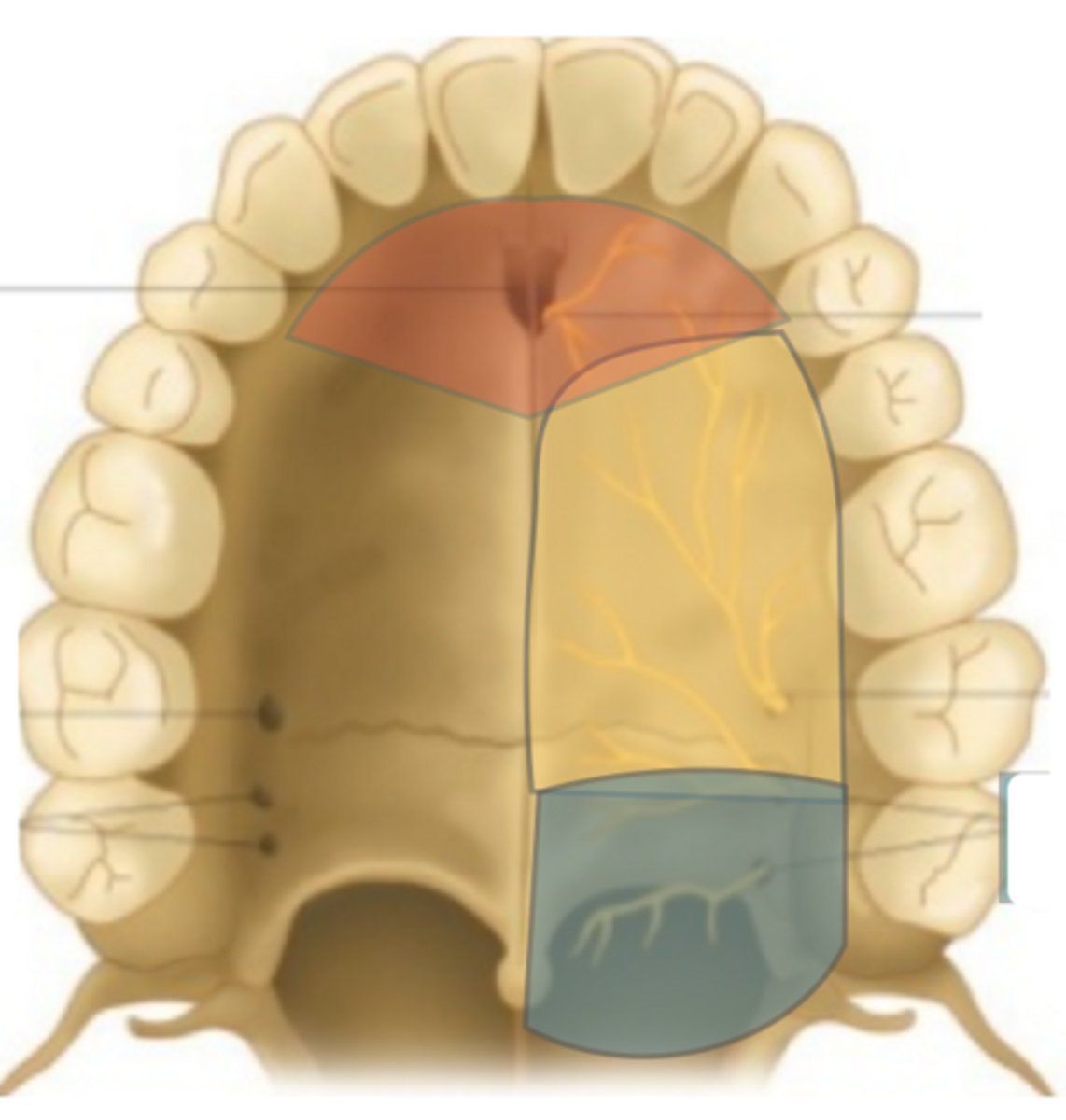
Which nerve provides sensory to the red area?
Nasopalatine n.
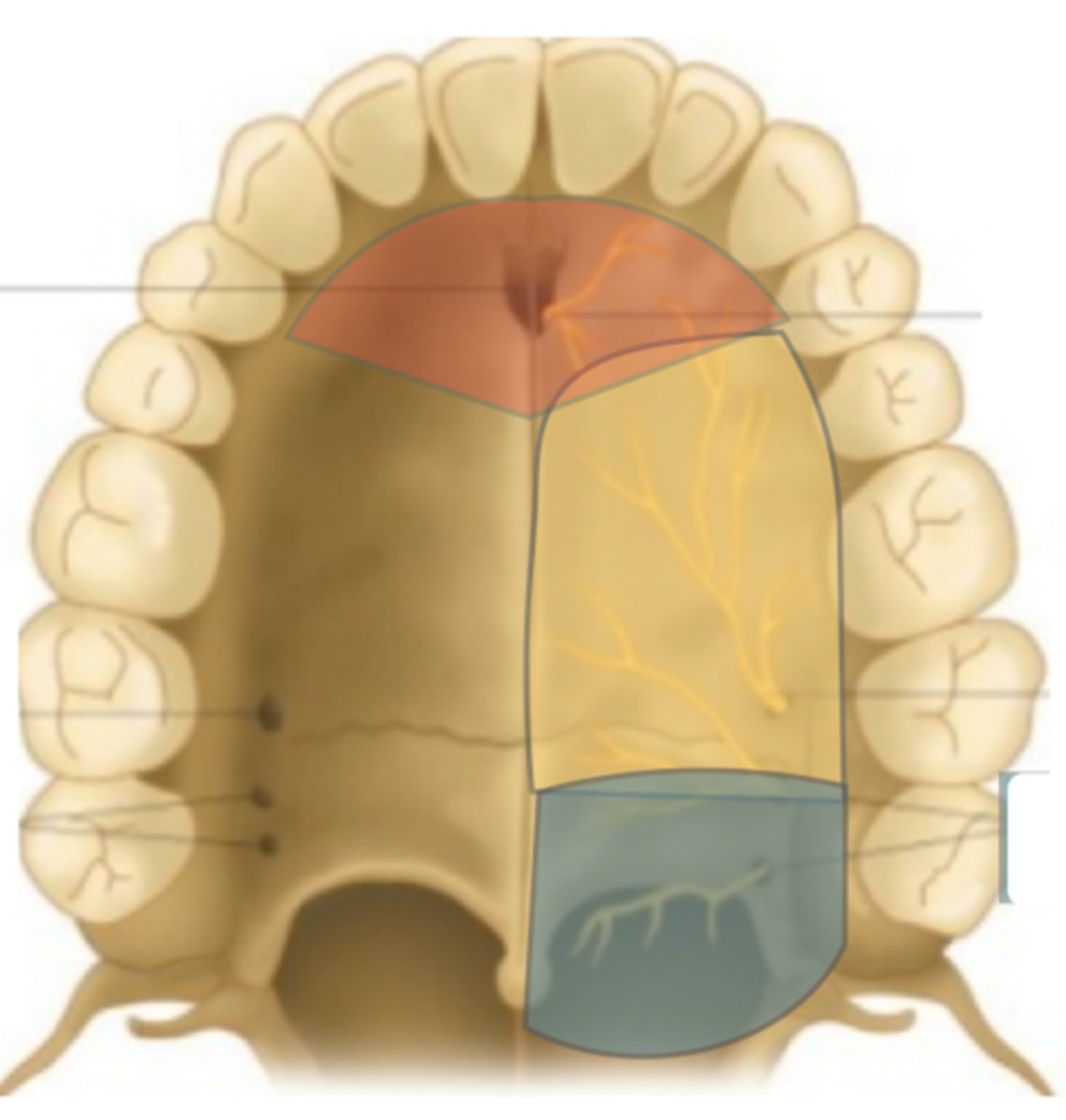
Which nerve provides sensory to the yellow area (on the right)?
Greater palatine n.
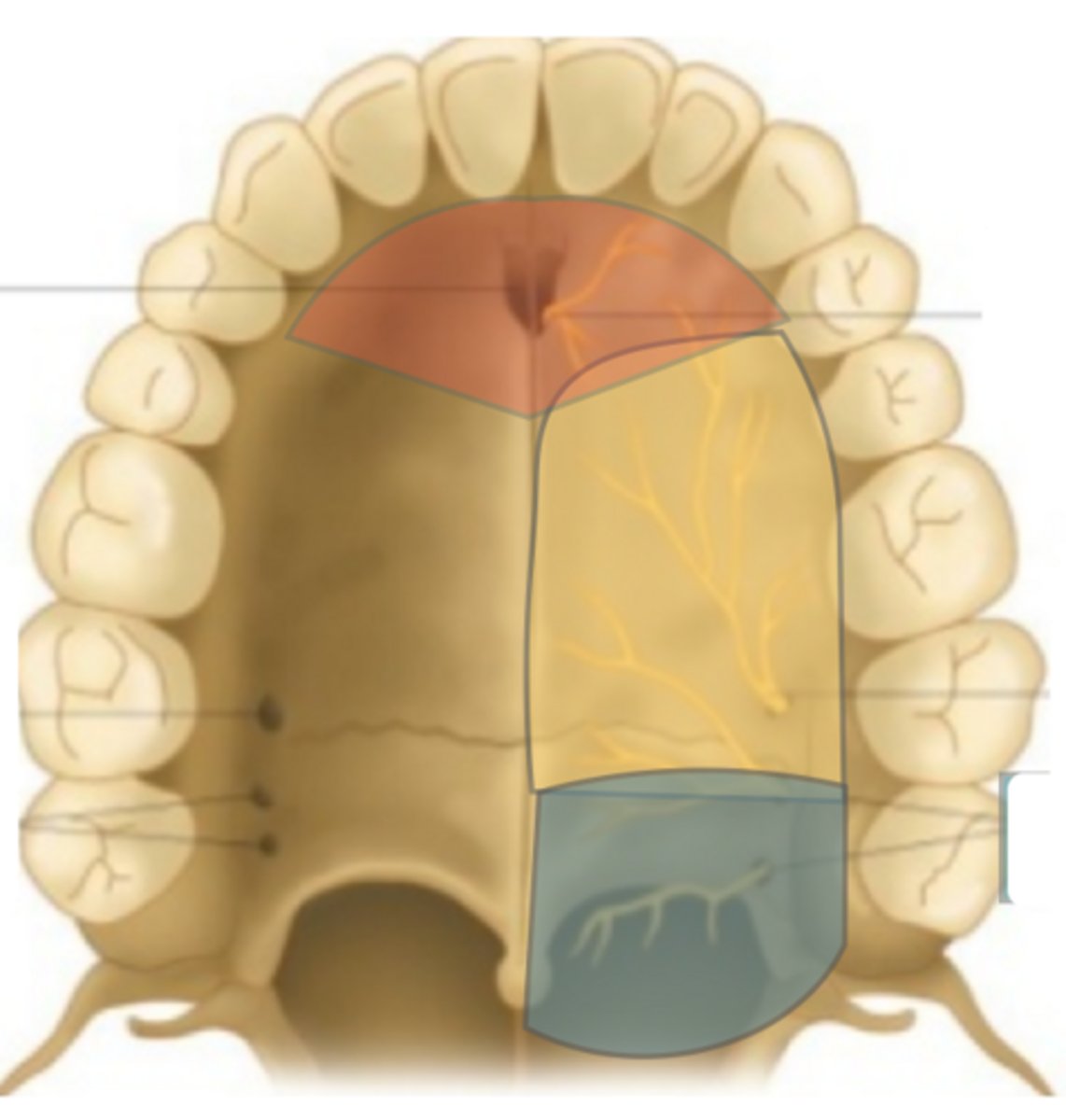
Which nerve provides sensory to the blue area?
Lesser palatine n.
The nasopalatine nerve provides sensory innervation to the palatal mucosa of which teeth?
canine to canine (canines and incisors/pre-maxilla)
*it’s a unique nerve cuz it spread bilaterally
The nasopalatine nerve Ttavels across the roof of the nasal cavity and enters the _________
Incisive canal
The greater palatine nerve provides sensory innervation to the palatal mucosa of which teeth?
premolars, first and second molar
The lesser palatine nerve provides sensory innervation to the palatal mucosa of which teeth?
third molars
Which nerve provides sensory innervation to the posterior hard palate?
greater palatine n.
Which nerve provides sensory innervation to the soft palate, tonsils and uvula?
lesser palatine n.
Which injections techniques are indicated for palatal hard and soft tissue anesthesia for more than two teeth?
- Greater palatine nerve block (posterior teeth and palate)
- Nasopalatine nerve block (anterior teeth and palate)
What are two contraindications for greater palatine/nasopalatine nerve blocks?
- Injection/inflammation at injection site
- Smaller area of therapy (1 or 2 teeth)
What are two advantages of greater palatine nerve blocks and nasopalatine nerve blocks?
Minimize needle penetrations and volume of anesthetics
T/F: Both the greater palatine nerve blocks and nasopalatine nerve blocks can be potentially traumatic/painful
True
T/F: Positive aspiration in the greater palatine/nasopalatine nerve block injection is very rare (<1%)
true
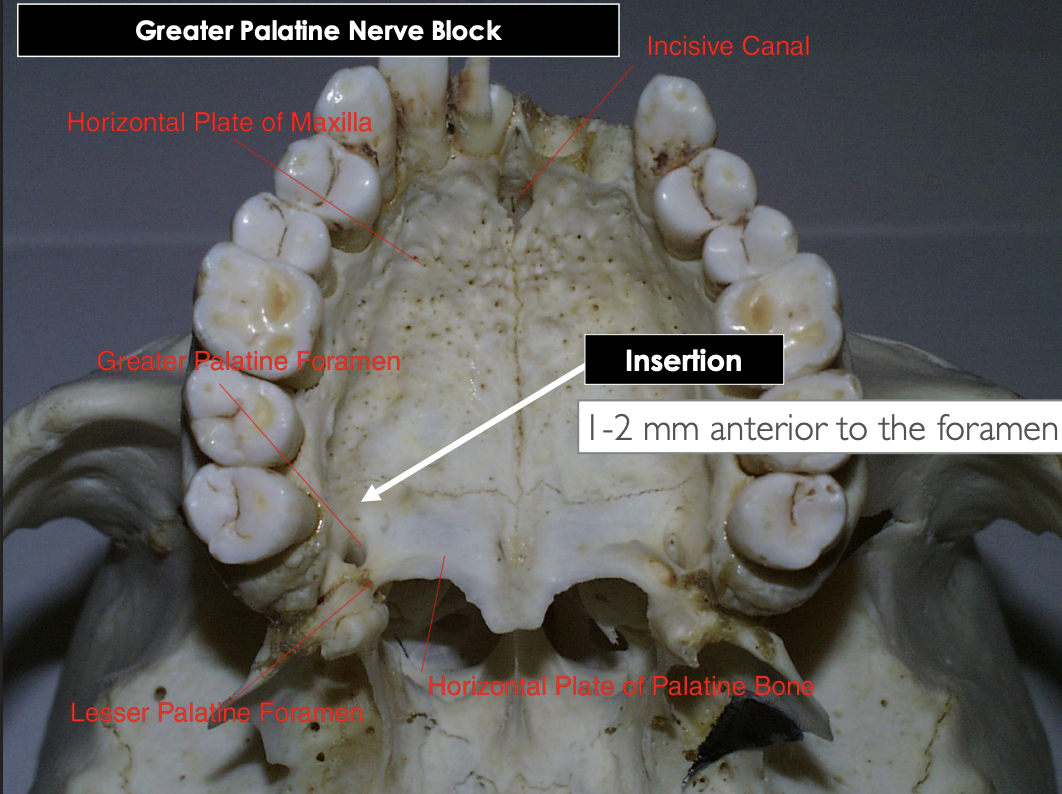
Needle insertion for a greater palatine nerve block is __ to __ mm anterior to the greater palatine foramen
1-2
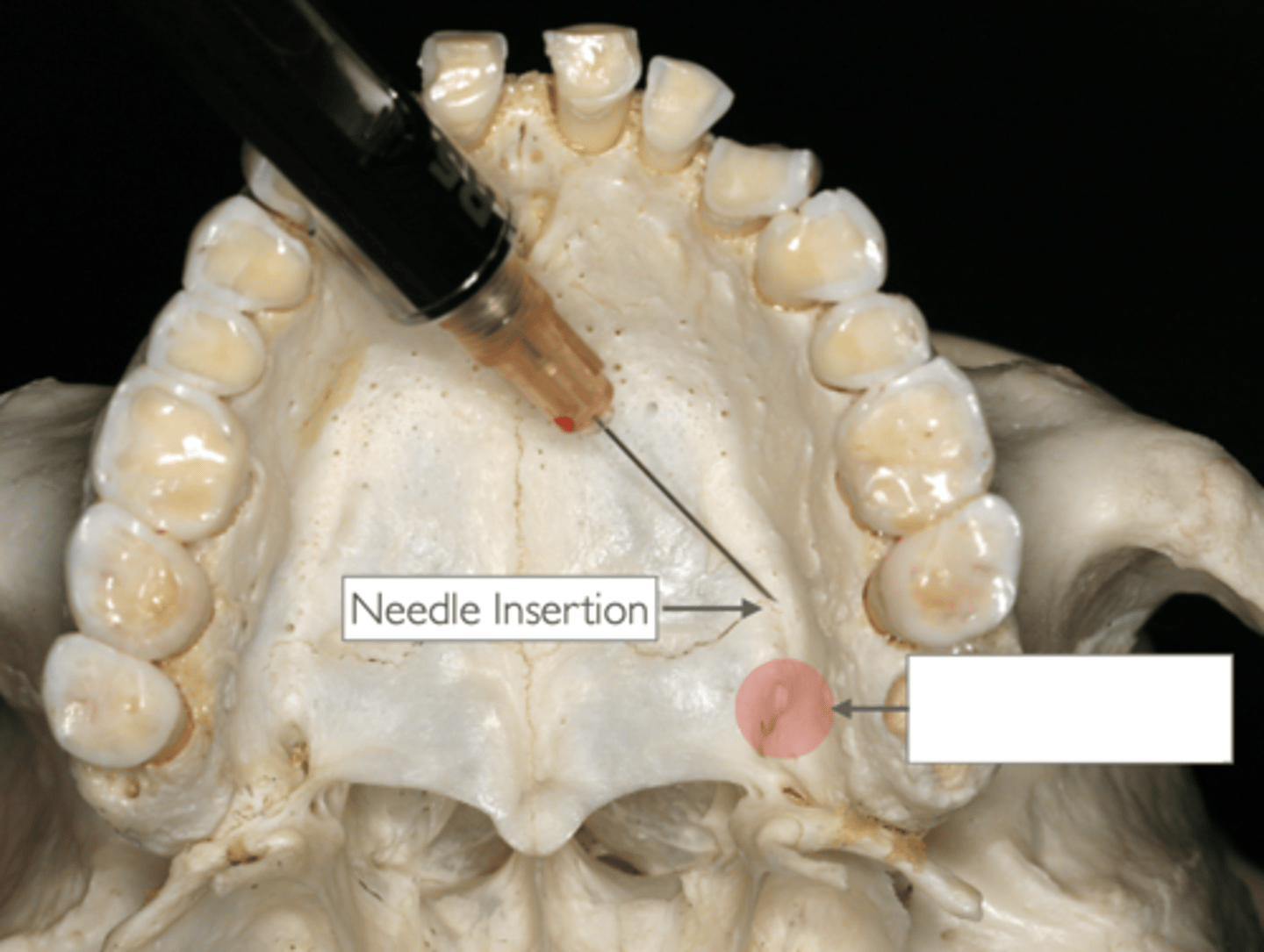
What type of injection and what is the red circle indicating?
- Greater palatine nerve block
- Greater palatine foramen
39.4% of Greater Palatine Foramen are located where?
posterior half of 2nd molar
50.6% of Greater Palatine Foramen are located where?
anterior half of 3rd molar
9.5% of Greater Palatine Foramen are located where?
posterior half of 3rd molar
T/F: In the study of locations of greater palatine foramen, NONE were found in the anterior half of the 2nd molar
true
When locating the greater palatine foramen, where do you start with the cotton swab?
first molar (move distally until depression is felt)
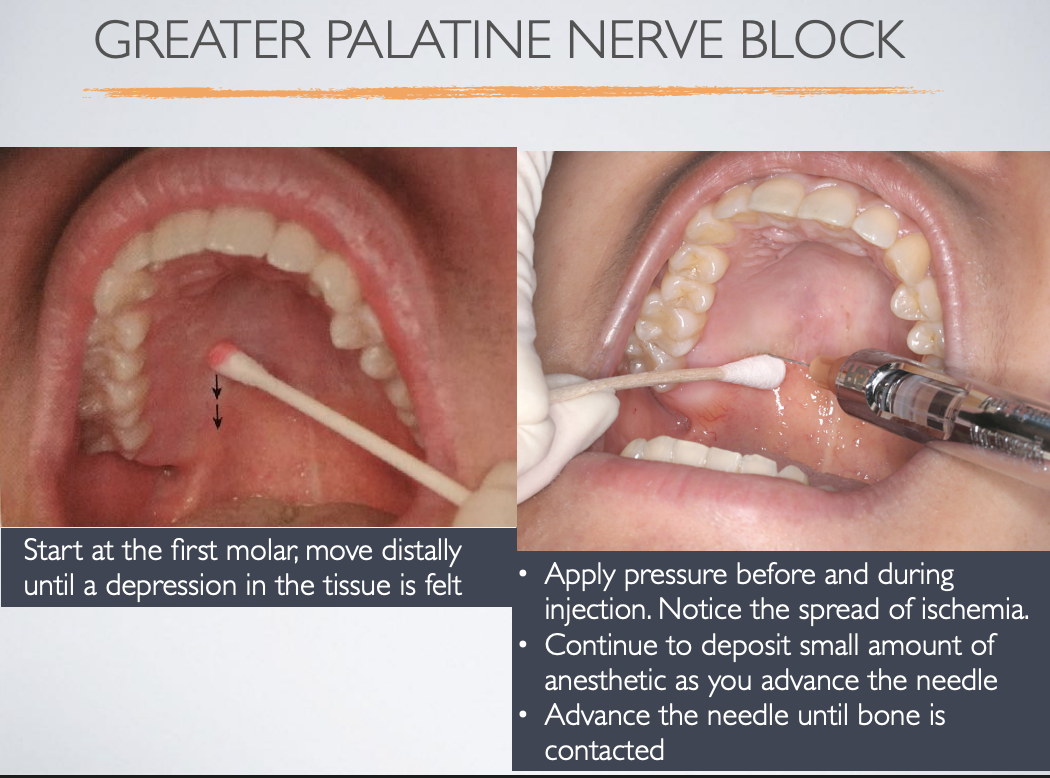
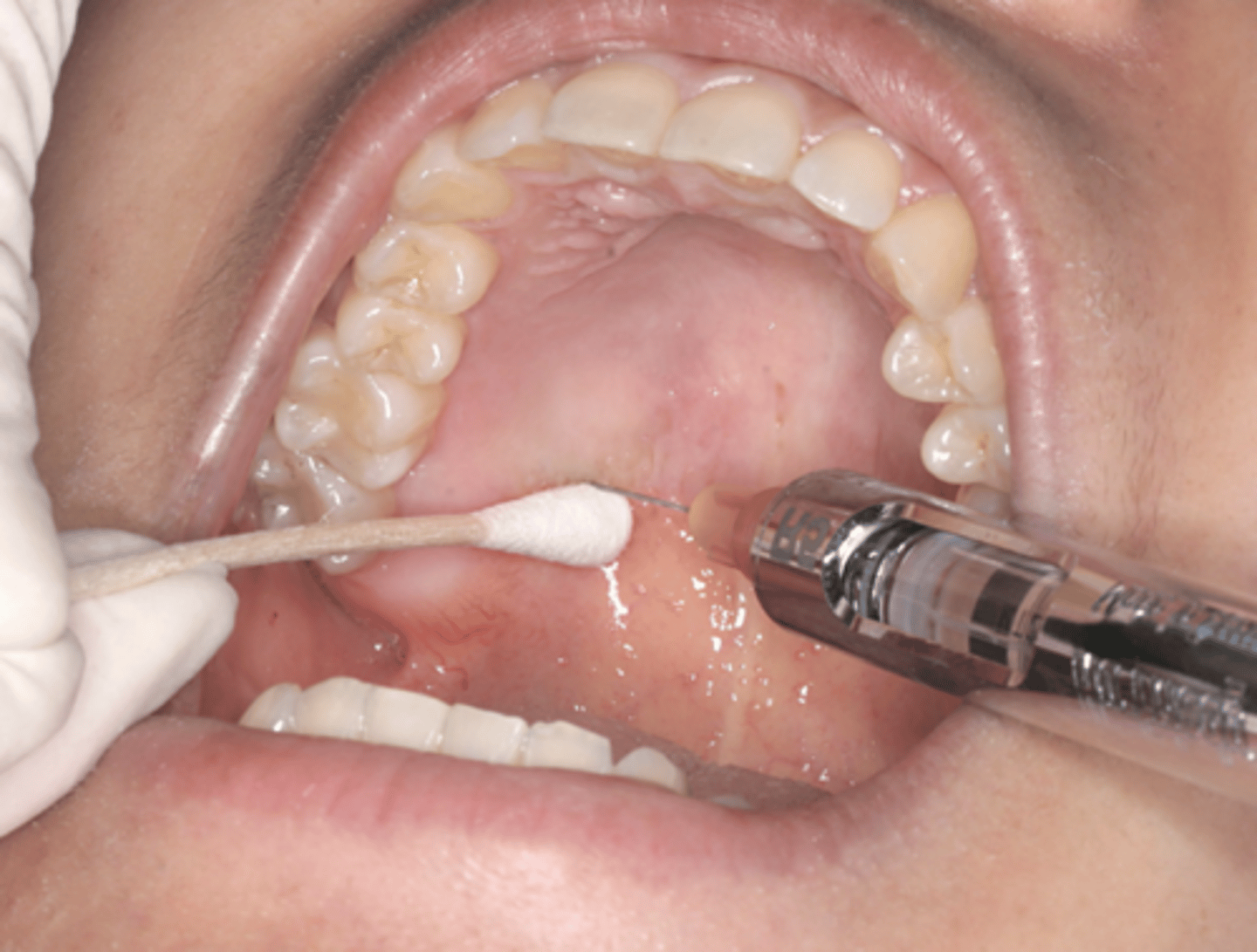
Which injection technique?
- Start at the first molar, move distally until a depression in the tissue is felt
- Apply pressure before and during injection. Notice the spread of ischemia.
- Continue to deposit small amount of anesthetic as you advance the needle
- Advance the needle until bone is contacted
greater palatine nerve block
Which of the following is incorrect regarding the greater palatine nerve block technique?
A) To locate the greater palatine foramen, tart at the first molar, move distally until a depression in the tissue is felt
B) Apply pressure before and during injection.
C) Continue to deposit small amount of anesthetic as you advance the needle
D) You advance the needle until the entire needle is inserted
D (until bone is contacted-not full needle)
What is the operator position for greater palatine nerve block technique?
11 o'clock
What is the needle size used for a greater palatine nerve block technique?
27 short gauge
T/F: The needle target for the greater palatine nerve block is the greater palatine nerve shortly after it emerges onto the hard palate via the greater palatine foramen
true
What is the bevel orientation for a greater palatine nerve block?
Towards palatal soft tissue
The insertion point of a greater palatine nerve block is several mm anterior to the greater palatine foramen at the junction of the __________ and the __________
alveolar process, lateral plate of hard palate
what is the insertion path for the greater palatine nerve block?
Bevel towards bone. Laterally and superiorly through the mucosa until bone is gently contacted
What is the insertion depth for a greater palatine nerve block?
4-6 mm
What is the anesthetic volume of a greater palatine nerve block?
0.25 to 0.5 mL
Which injection technique has this area of anesthesia?
- Palatal gingiva of the molars and premolars
- Mucoperiosteum of the posterior two thirds of the ipsilateral hard palate
Greater palatine nerve block
T/F greater palatine nerve blocks are highly successful injections
true (>95% incidence of success)
What are 2 reasons a greater palatine nerve block may only be partially successful?
- Anesthetic deposited too anterior to foramen
- Anesthesia on palate in area of max. 1st PM (cross innervation from nasopalatine)
If a greater palatine injection is only partially successful, what should be done to correct it?
Supplement area with local infiltration
Nasopalatine nerve blocks are bilateral or unilateral?
bilateral
Greater palatine nerve blocks are bilateral or unilateral?
unilateral
what type of nerve block?
nasopalatine nerve block
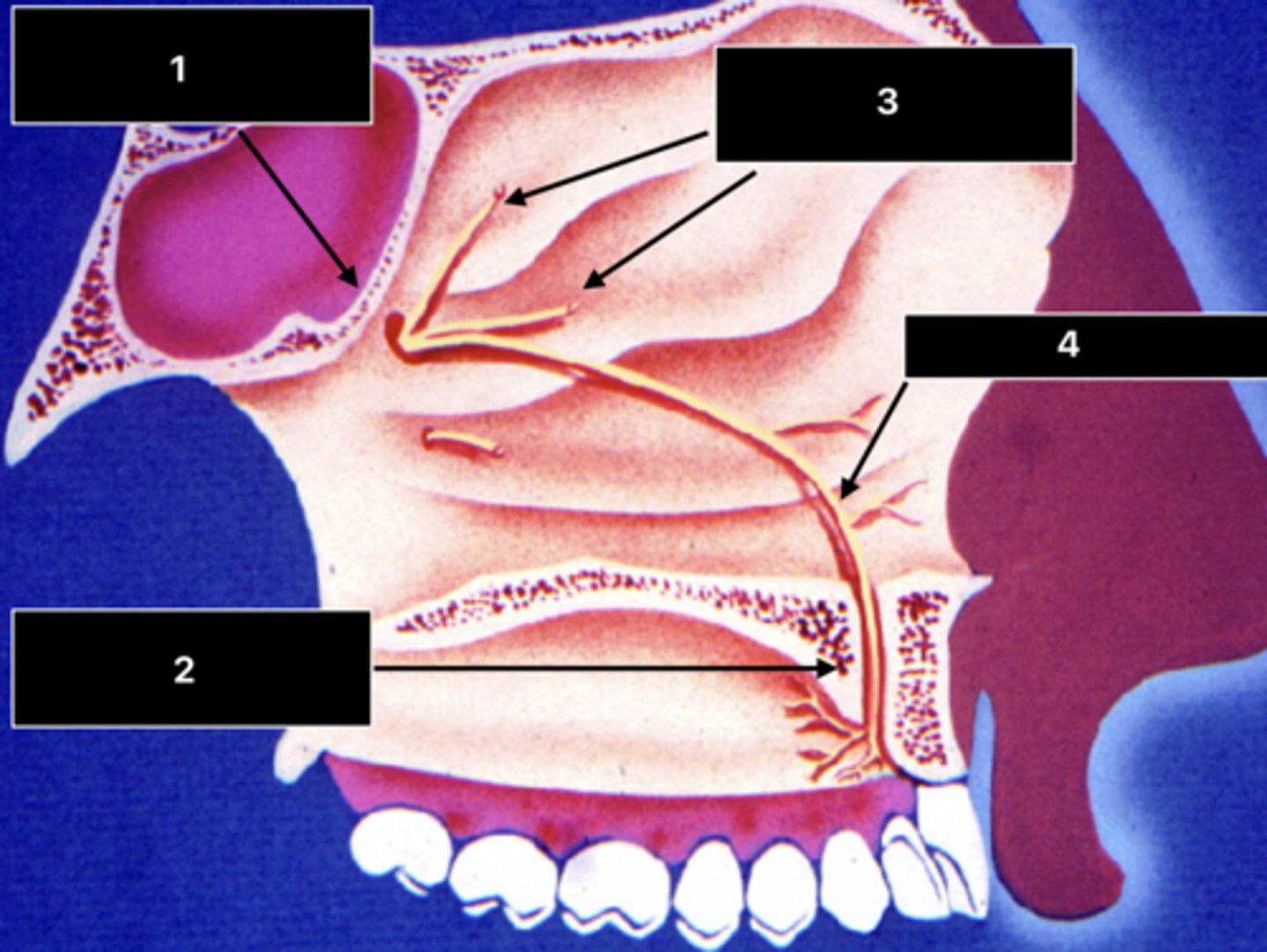
ID the structure at 1:
Sphenopalatine foramen
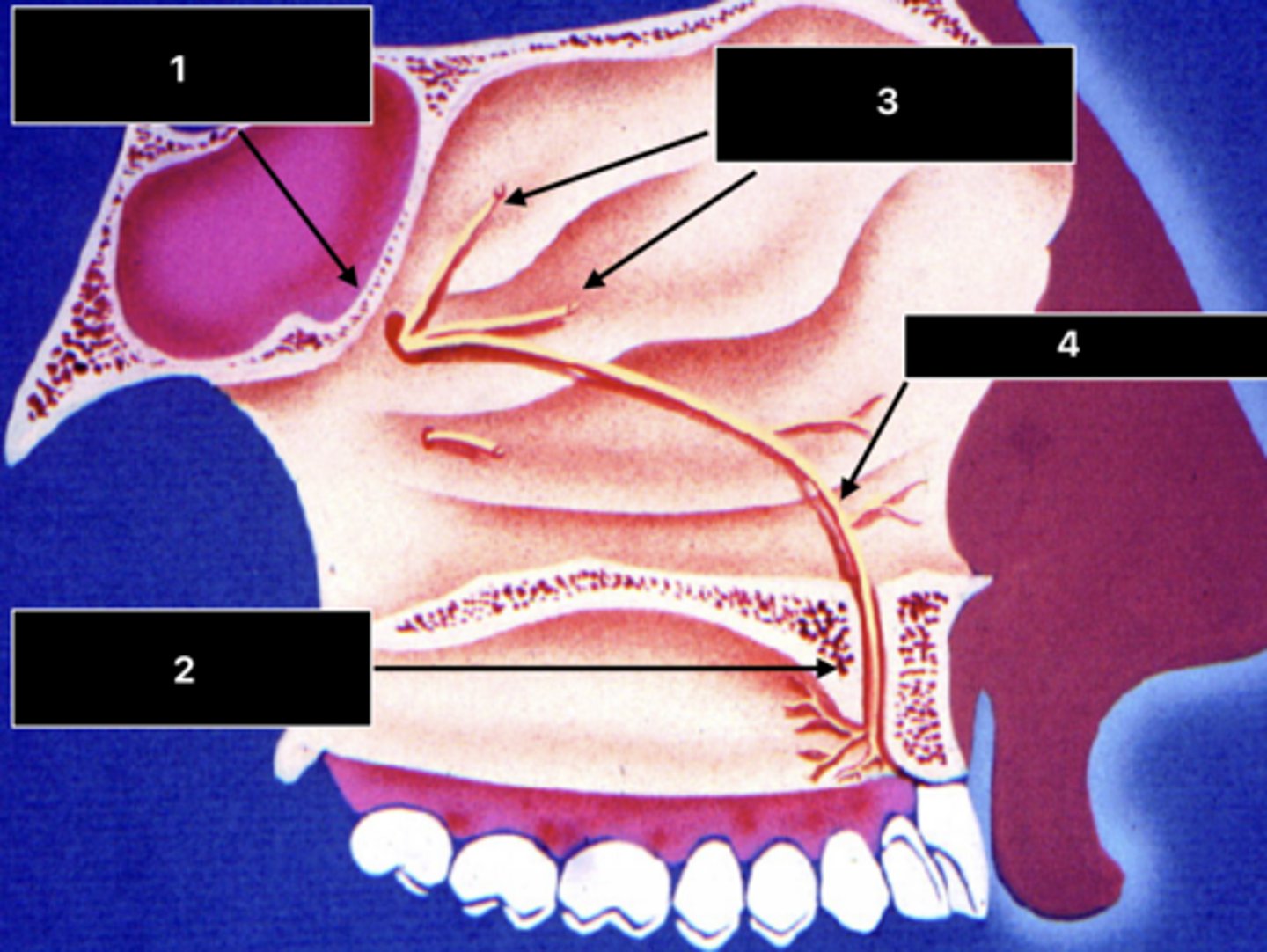
ID the structure at 2:
Incisive foramen and canal
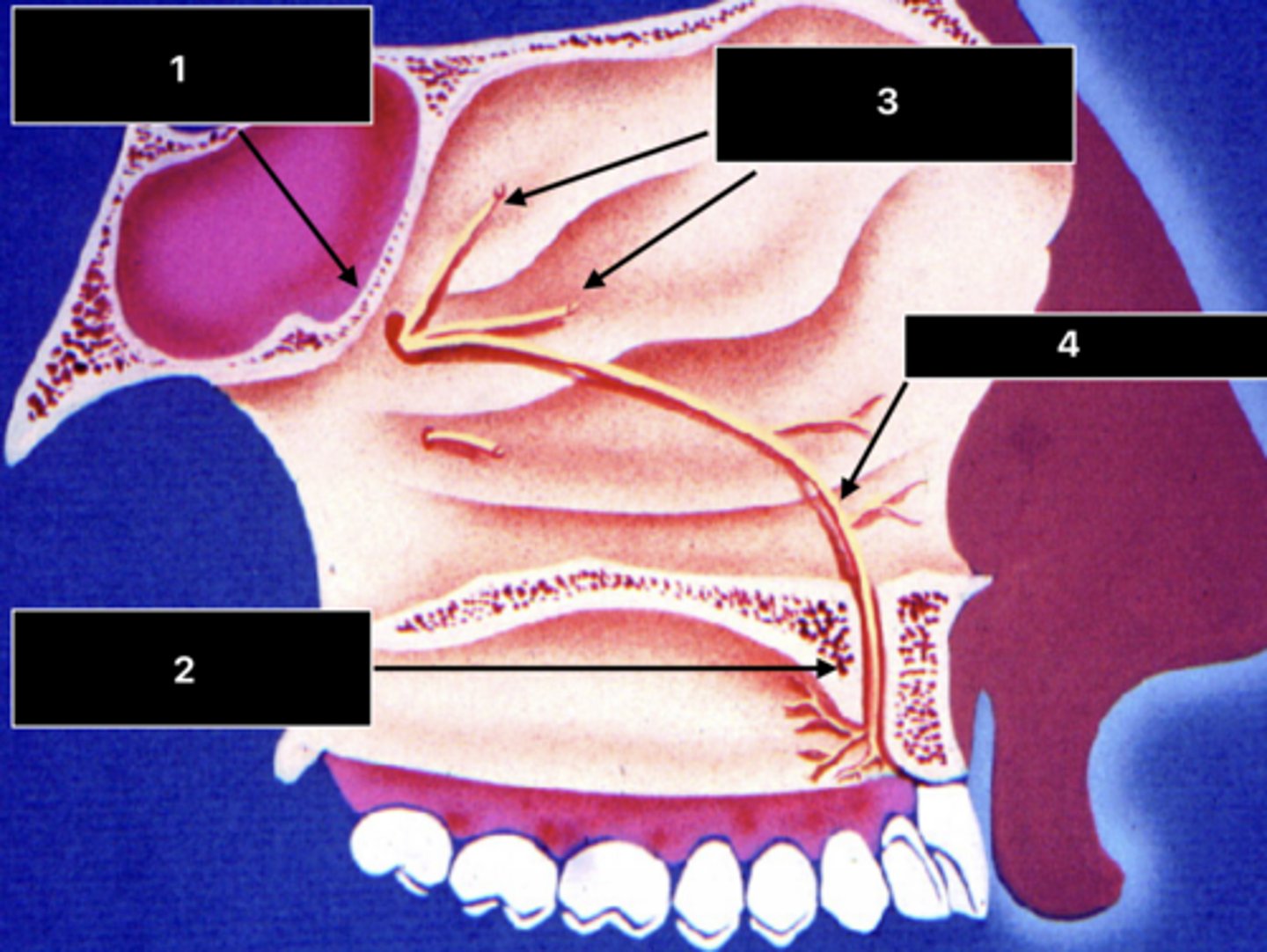
ID the nerve at 3:
Posterior superior nasal nn.
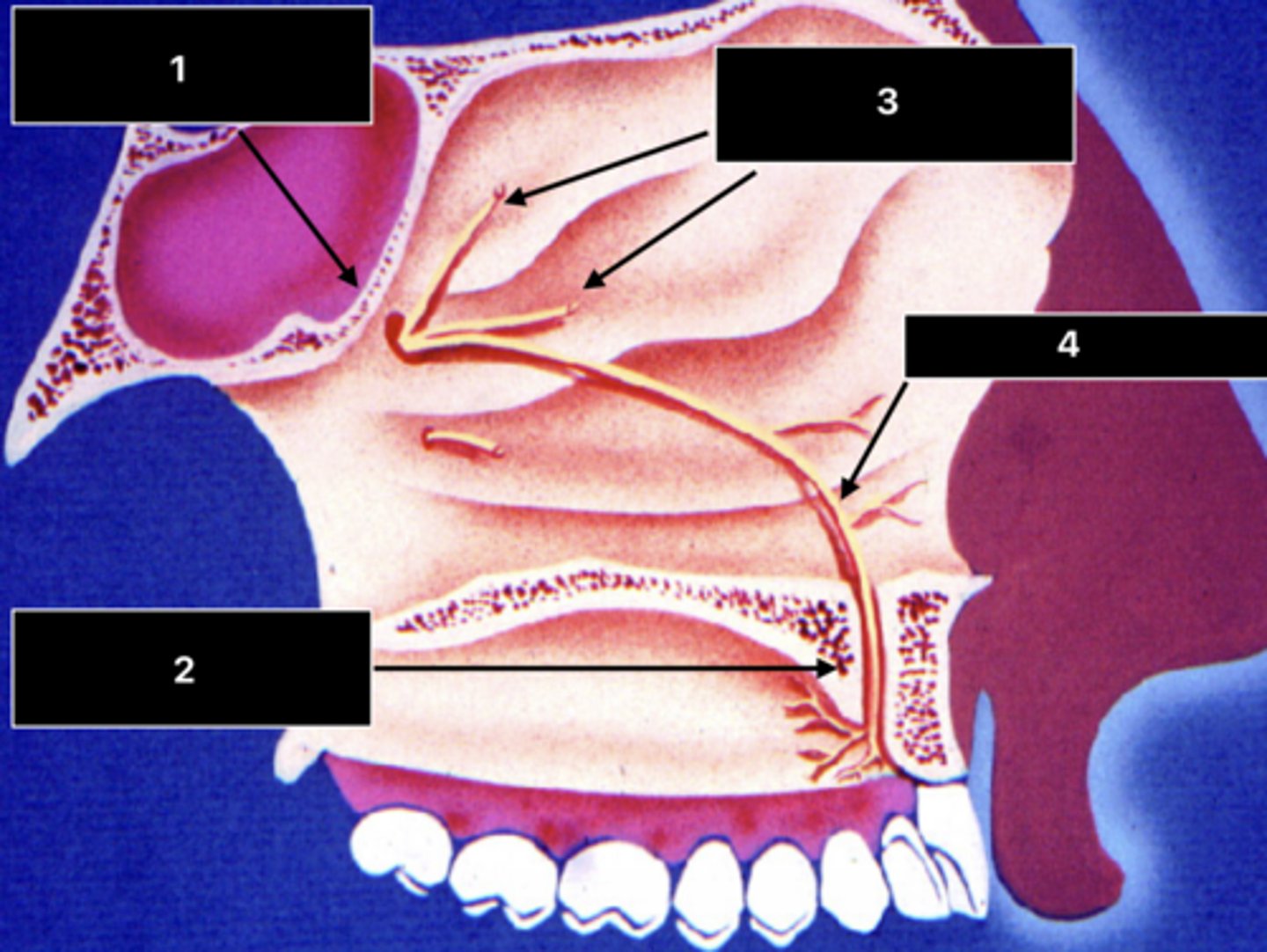
ID the nerve at 4:
Nasopalatine n.
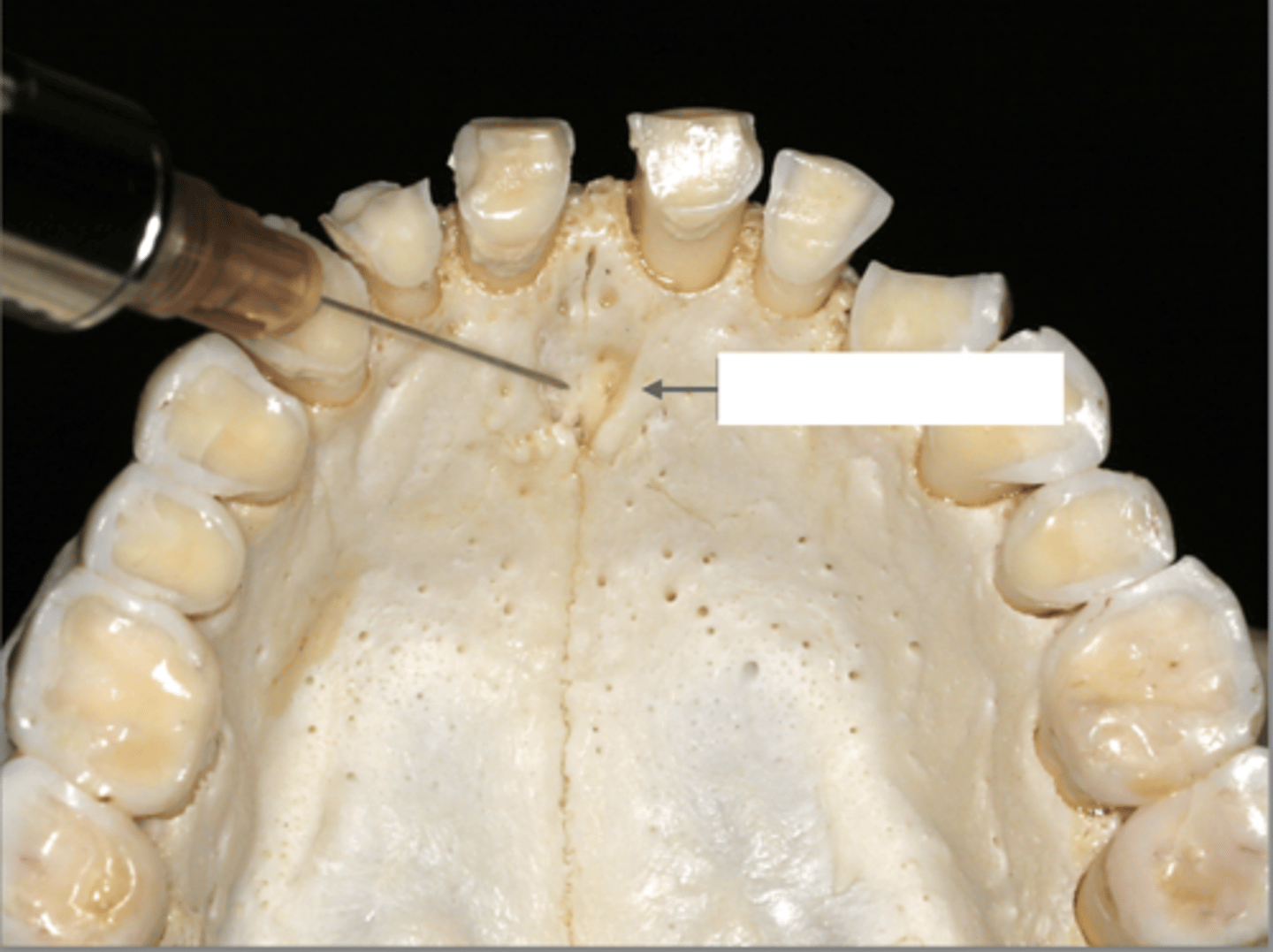
Which type of injection and what is the arrow pointing to as a landmark?
- Nasopalatine nerve block
- Incisive foramen
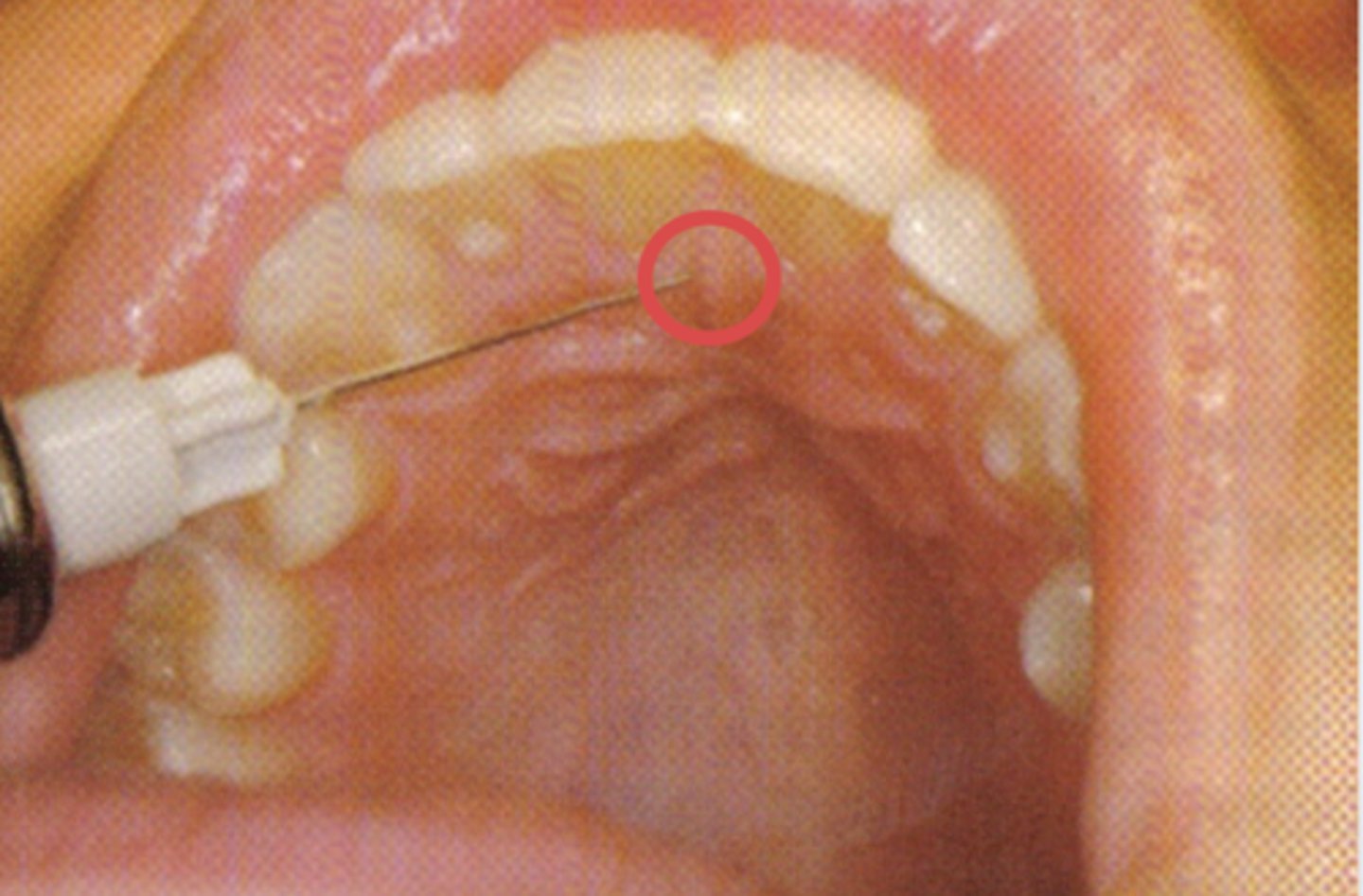
Which injection technique? (be specific)
nasopalatine nerve block - technique 1 (single needle injection) → can be very painful
*inject laterally onto the incisive papilla
why is it important to inject nasopalatine nerve block laterally onto the incisive papilla?
minimize nerve damage/bleeding
How do you decrease pain for a single needle injection technique of a nasopalatine nerve block?
- Apply topical adjacent to incisive papilla
- Apply pressure to incisive papilla
- Maintain pressure, slowly advance needle to bone
- Aspirate
How much anesthetic solution is deposited for a single needle injection nasopalatine nerve block?
0.2-0.4 mL
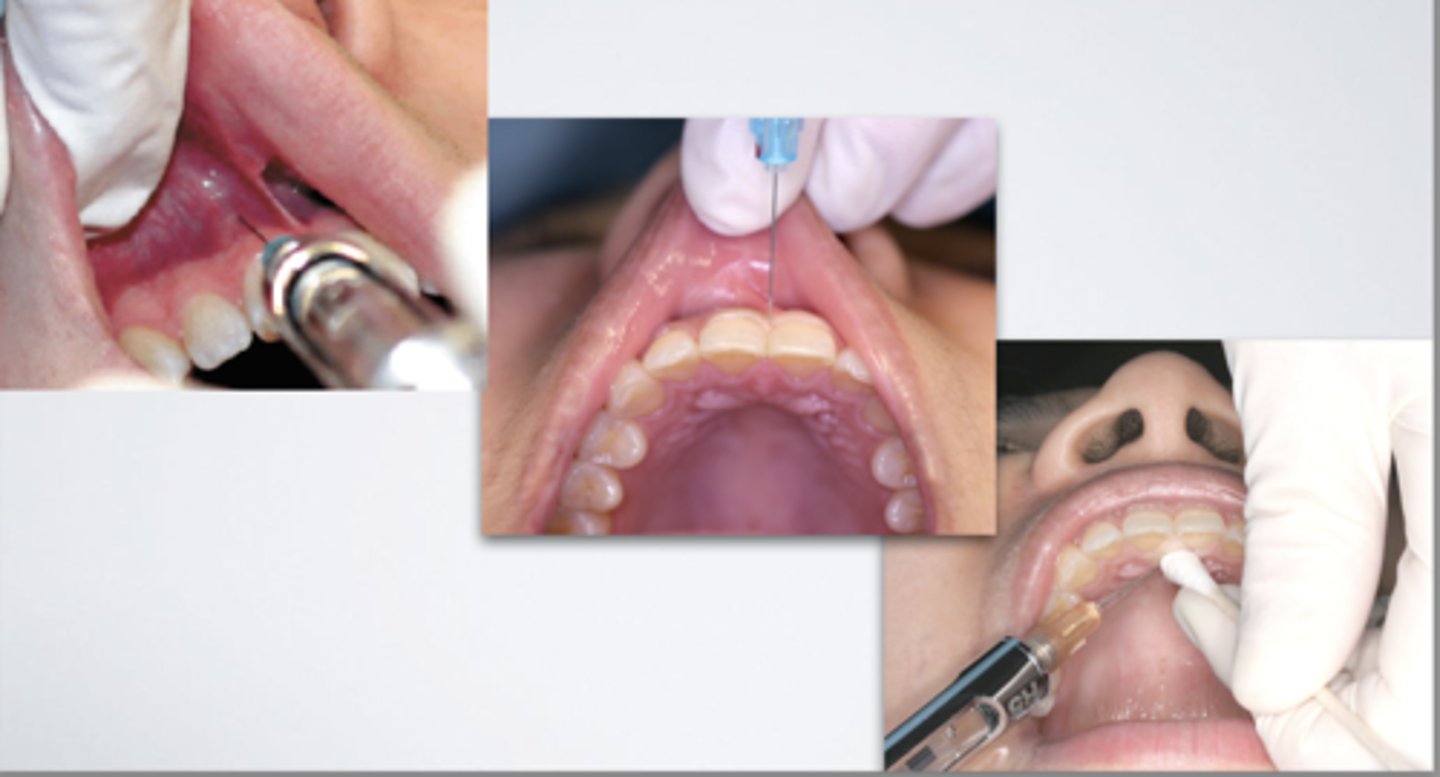
Which injection technique? (be specific)
nasopalatine nerve block - technique 2 (multiple needle technique)
Which nasopalatine nerve block technique is recommended because it is less painful?
multiple injections (technique 2)
Where is topical anesthetic applied for the nasopalatine block multiple needle technique?
labial fold
What is the first injection for the multiple needle nasopalatine injection?
labial frenum
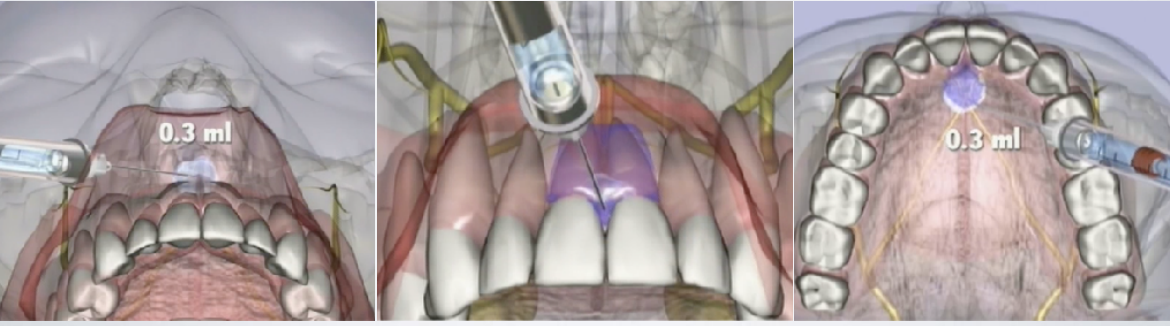
What is the second injection for the multiple needle nasopalatine injection?
interdental papilla between central incisors
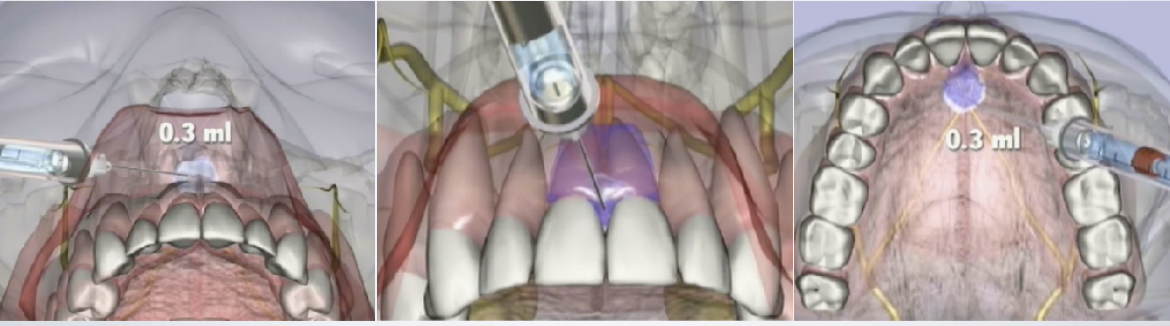
What is the third injection for the multiple needle nasopalatine injection?
incisive papilla (nasopalatine nerve block)
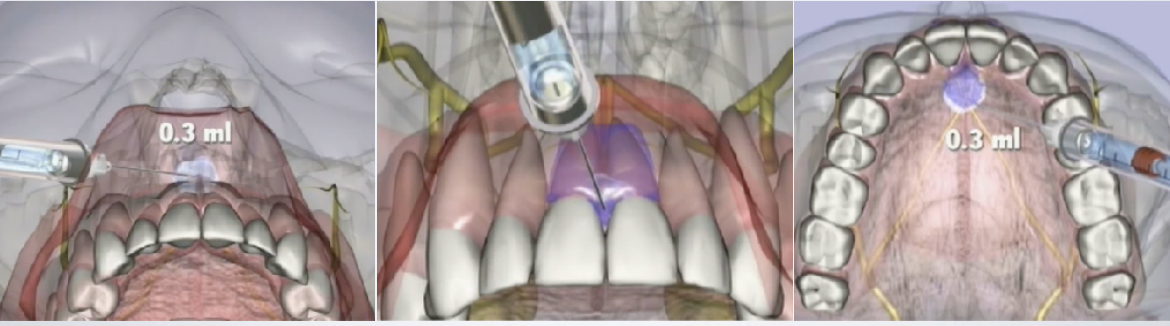
____-____ mL of anesthetic solution is injected at each site for the multiple injection technique nasopalatine nerve block
0.2-0.4 mL
What is the operator position for the nasopalatine nerve block technique?
9 or 10 o'clock
Which needle size is used for nasopalatine nerve block?
27 short gauge
What is the bevel orientation for a greater palatine nerve block?
Towards palatal soft tissue
What is the insertion point of the nasopalatine nerve block technique?
Palatal mucosa to the lateral border of the incisive papilla
For a nasopalatine nerve block, you should approach the injection site at a ____ degree angel toward the incisive papilla (insertion path)
45°
What is the insertion depth for a nasopalatine nerve block?
3-5 mm
What is the anesthetic volume for nasopalatine nerve blocks?
0.2-0.3 mL
Which injection technique has this area of anesthesia?
Palatal gingiva of the six anterior teeth and mucoperiosteum of the anterior third of the hard palate
nasopalatine nerve block
T/F nasopalatine nerve blocks are a highly successful injection (>95%)
true
If a nasopalatine block injection results in unilateral anesthesia (this can happen if it is deposited to one side of the incisive canal), how do you correct this?
Reinsert needle into already anesthetized tissue and re-inject into un-anesthetized area
If a nasopalatine block injection results in inadequate palatal soft tissue in the area of maxillary canines/premolars, how do you correct this?
local infiltration
Which injection technique is indicated for:
- Palatogingival pain control for limited area (1-2 teeth)
- Achieving hemostasis during surgical procedure
palatal local infiltration
Which injection technique has these contraindications?
- Infection/inflammation at injection site
- Larger area of therapy (> 2 teeth)
palatal local infiltration
What are two contraindications for the palatal local infiltration?
- Infection/inflammation at injection site
- Larger area of therapy (> 2 teeth)
Which nerves and areas are anesthetized when doing palatal local infiltrations?
- Terminal branches of nasopalatine or greater palatine
- Area: Soft palatal tissue in the immediate vicinity of the injection
What is the technique for the palatal local infiltration technique?
- Apply topical anesthetic
- Apply pressure on the tissue immediately adjacent to the injection site
- Insertion point: attached gingiva 5-10 mm from the free gingival margin
- Maintain pressure, slowly advance needle to bone
- Maintain control of the needle
- Inject slowly
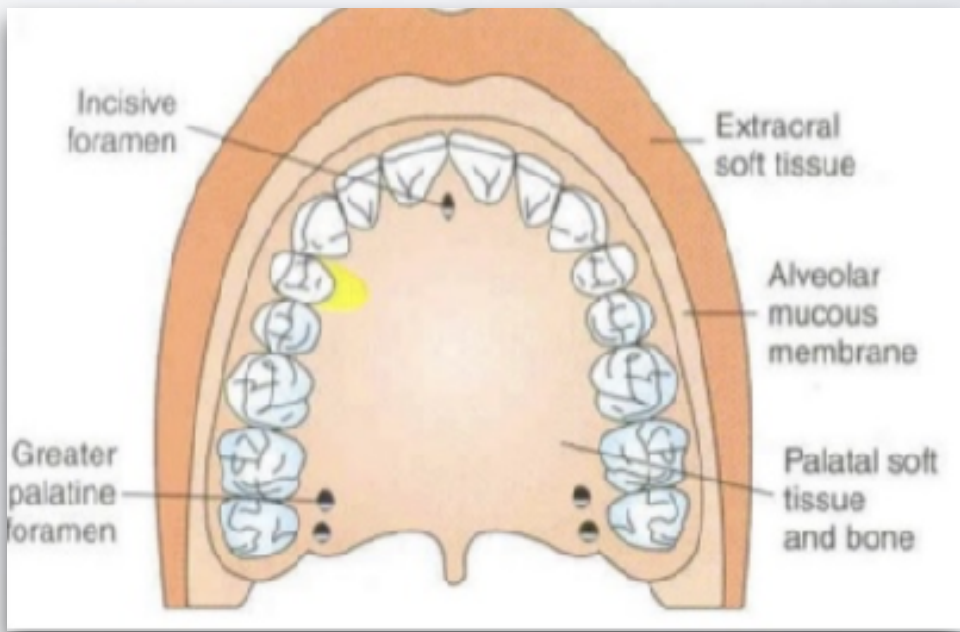
which nerve block?
palatal local infiltration technique
What is the operator position for palatal local infiltration?
10 or 11 o'clock
What needle size is used for palatal local infiltration?
27 short gauge
The insertion point for palatal local infiltration is into the attached gingiva ___ - ___ mm from the free gingival margin
5-10 mm
What is the bevel orientation for a greater palatine nerve block?
Towards palatal soft tissue/bone
When doing a palatal local infiltration, you should approach the injection site at what angulation?
45 degrees
What is the insertion depth for palatal infiltration?
3-5 mm
What is the anesthetic volume for palatal local infiltration?
0.2 to 0.3 mL
describe the proper PALATAL LOCAL INFILTRATION TECHNIQUE
Apply topical anesthetic
Apply pressure on the tissue immediately adjacent to the injection site
Insertion point: attached gingiva 5-10 mm from the free gingival margin
Maintain pressure, slowly advance needle to bone
Maintain control of the needle
Inject slowly
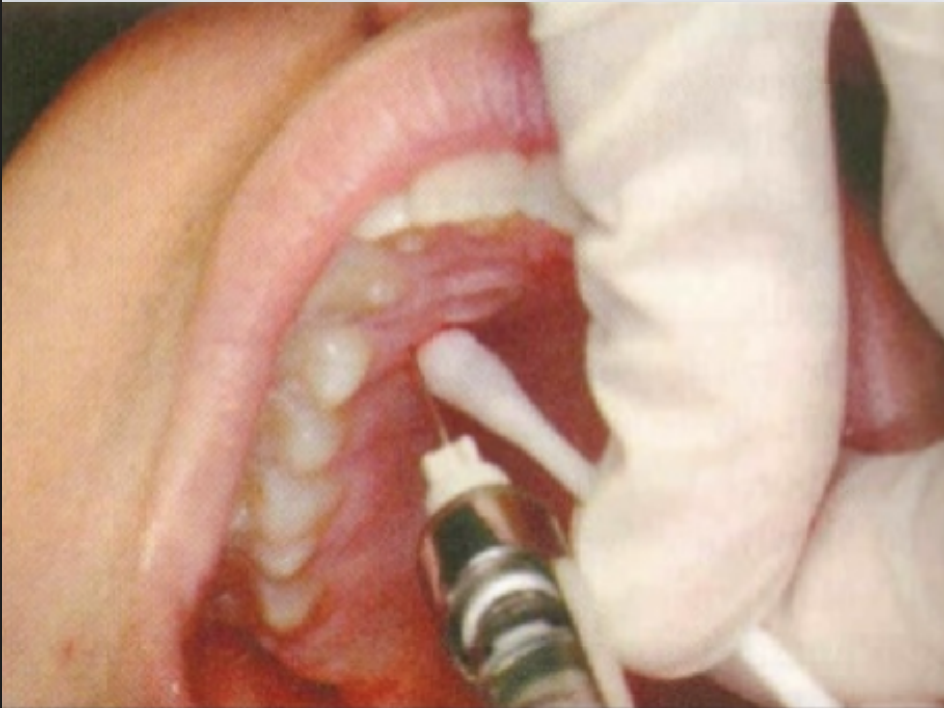
PALATAL LOCAL INFILTRATION TECHNIQUE
With a maxillary nerve block, which cranial nerve is being anesthetized?
V2 (entire maxillary division of trigeminal nerve)
What area is anesthetized with a maxillary nerve block?
Hemi-maxilla
- Pulpal anesthesia of all max. teeth
- Soft tissue-buccal and palatal
- Skin
- Lower eyelid
- Side of nose
- Cheek
- Upper lip
(may be incomplete at midline)
what nerve block technique?
maxillary nerve block
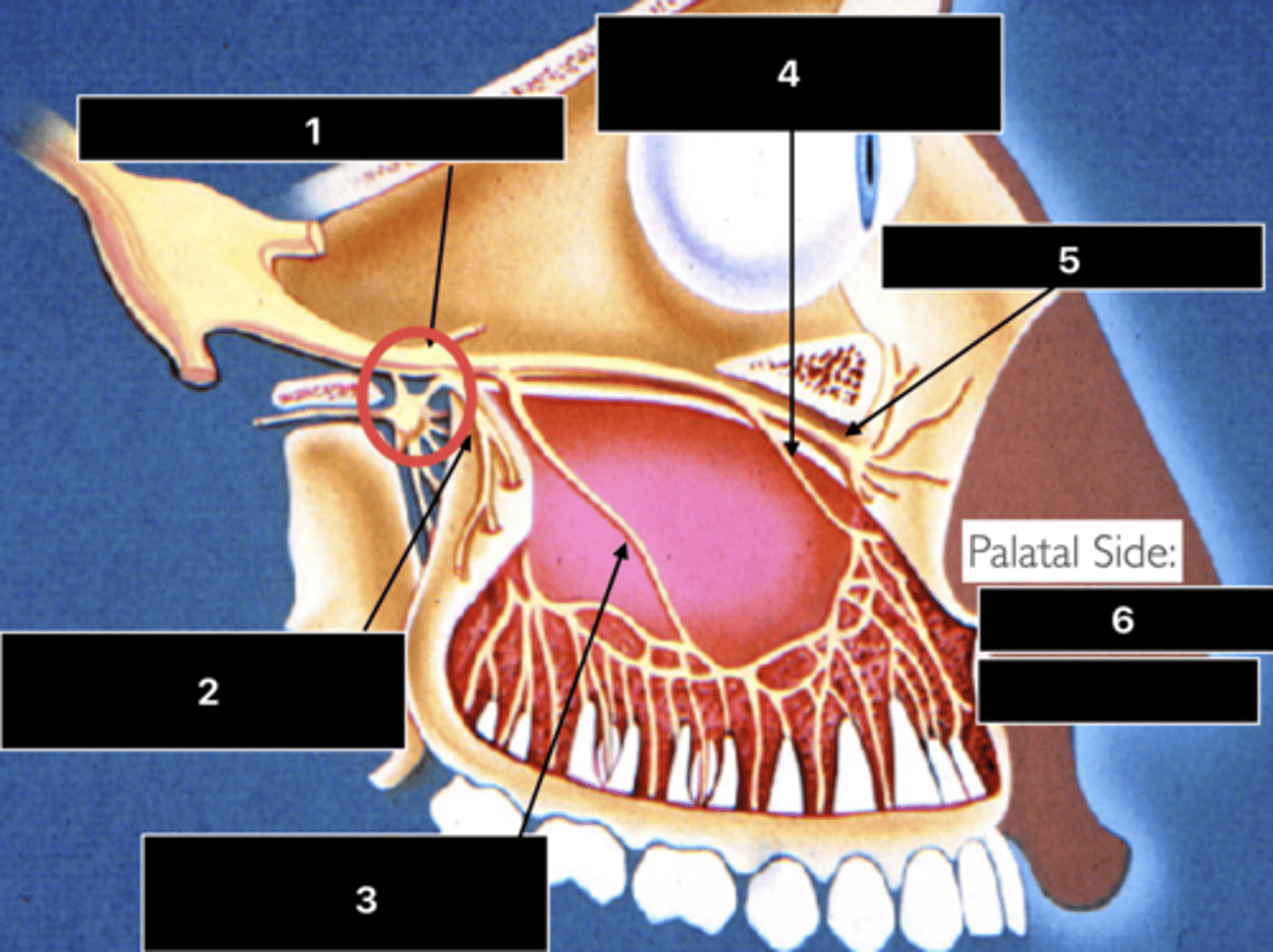
ID the nerve at 1
Maxillary n. (V2)
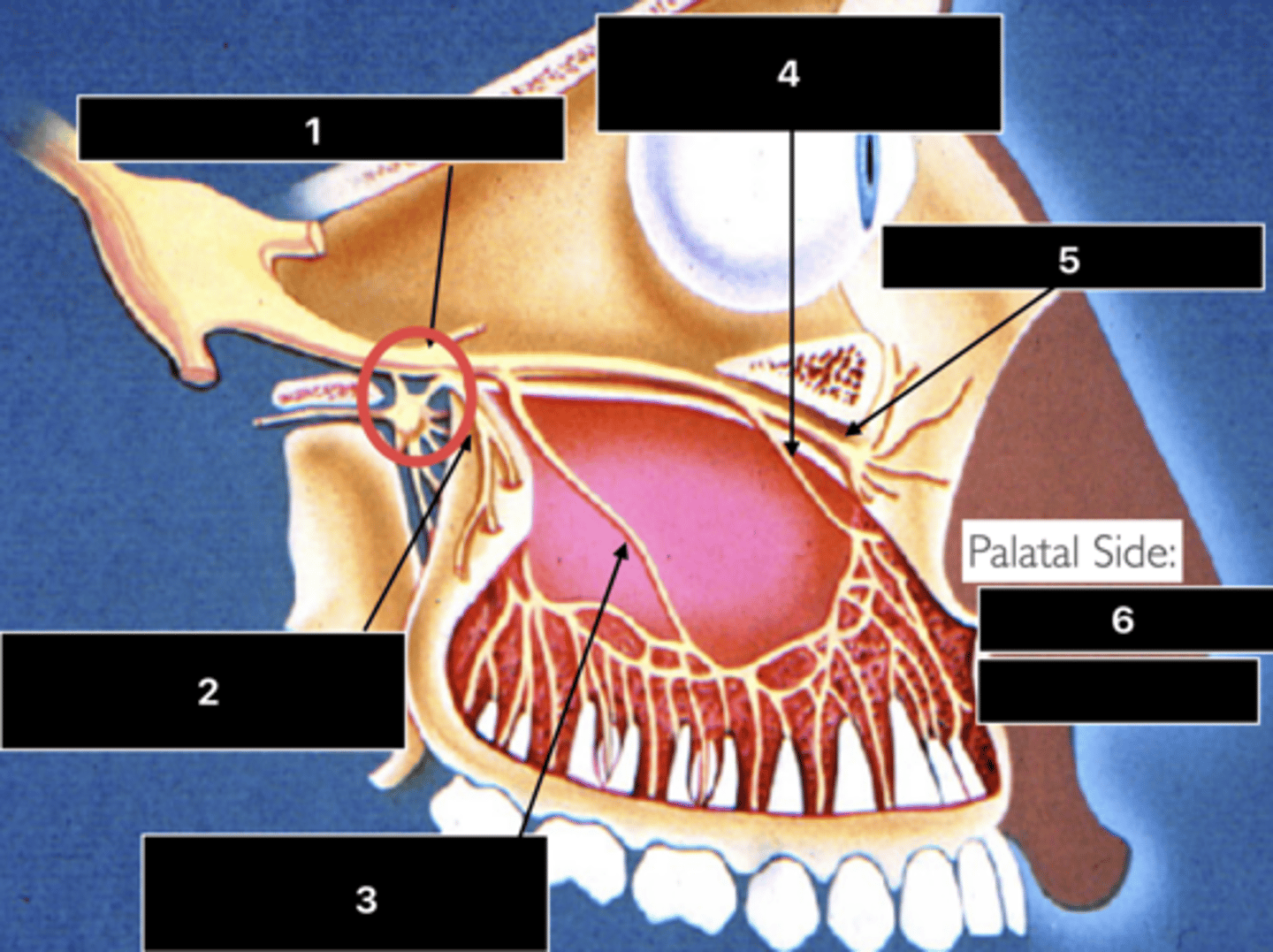
ID the nerve at 2
PSA n.
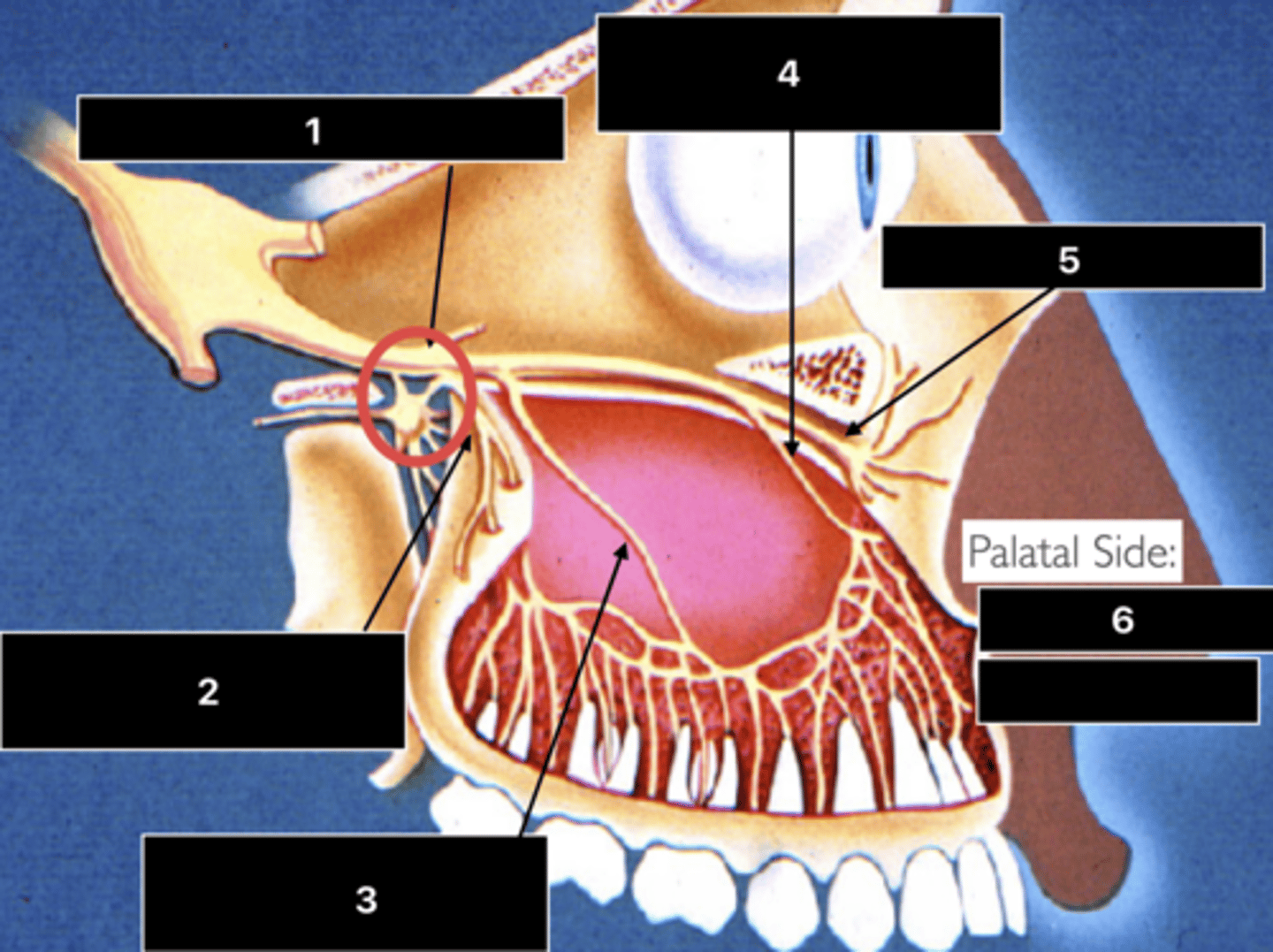
ID the nerve at 3
MSA n.
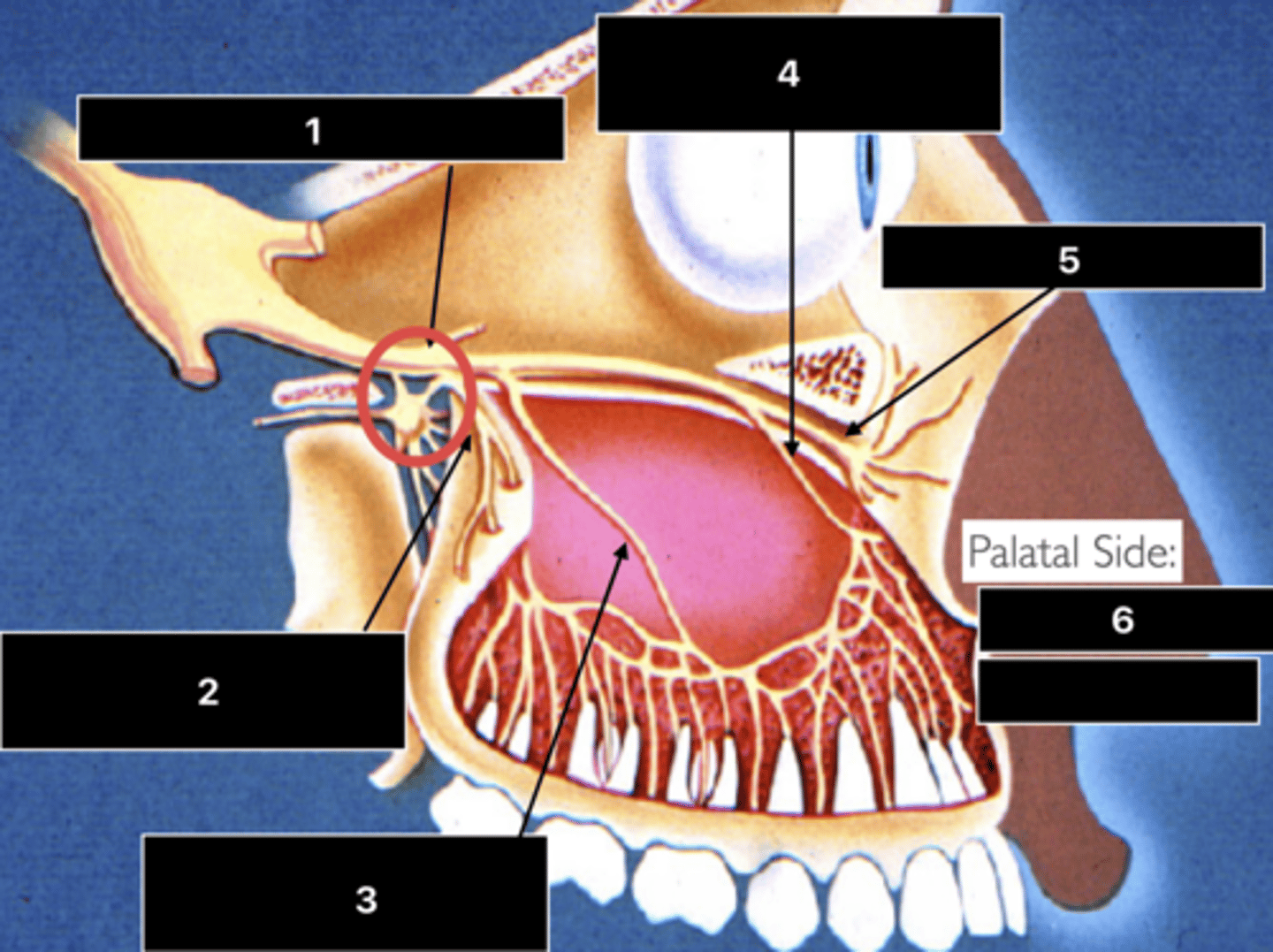
ID the nerve at 4
ASA n.
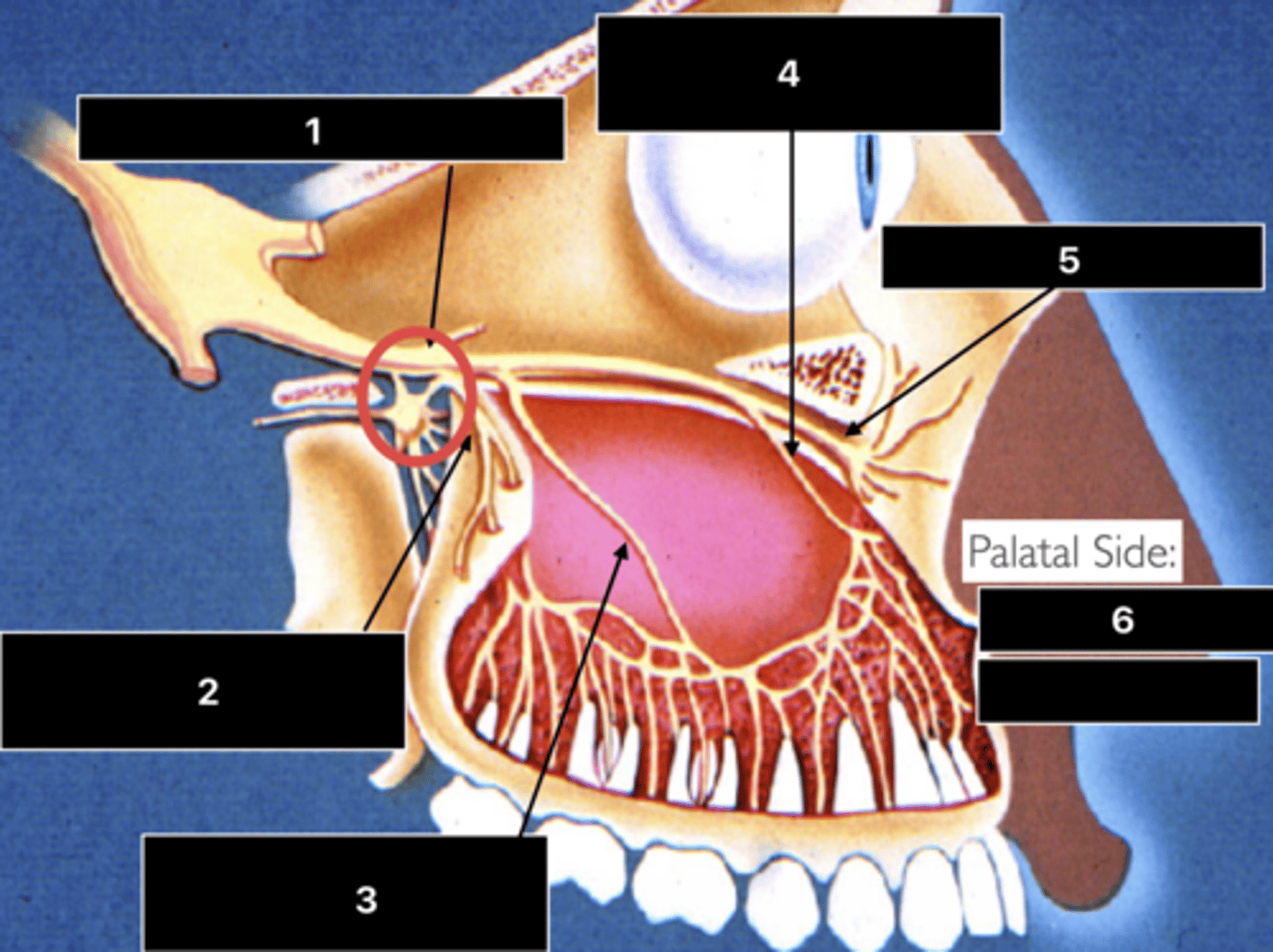
ID the nerve at 5
Infraorbital n.
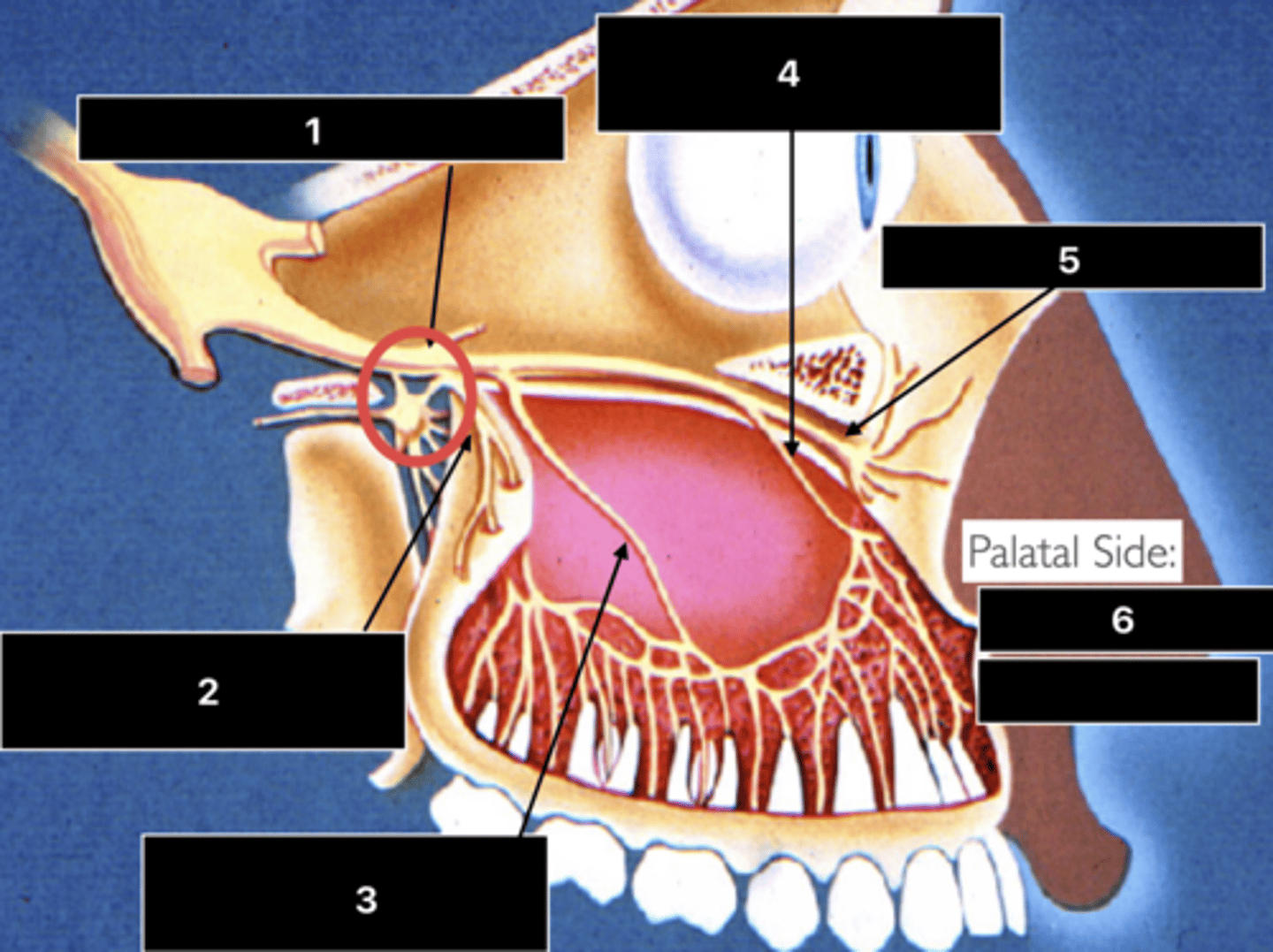
ID the nerve at 6
- Nasopalatine n.
- Greater palatine n.