Ch. 17 - Endocrine System
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
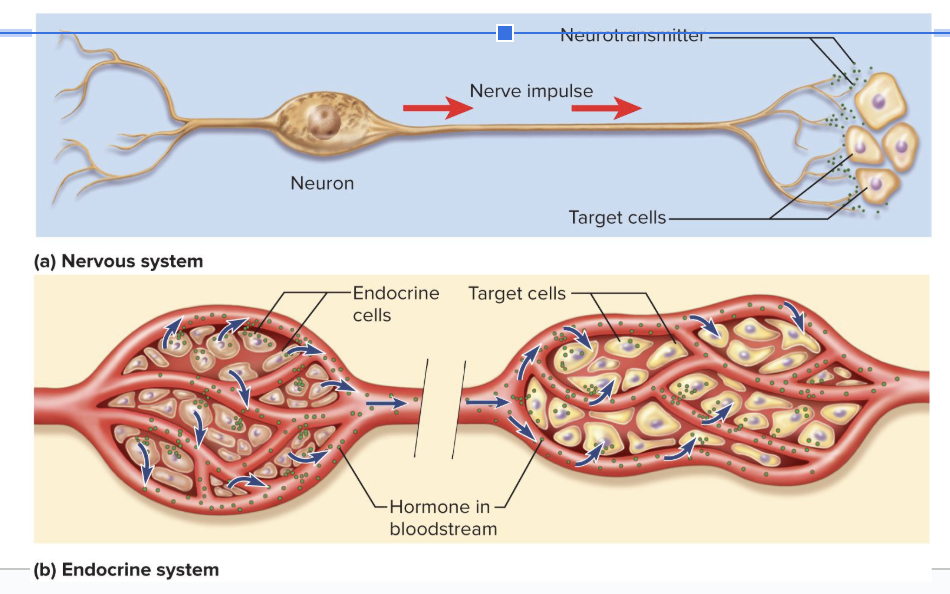
The endocrine system uses ____ while the nervous system uses ____.
hormones
neurotransmitters
4 Principal Mechanisms of Communication between Cells
Gap junctions
Pores in cell membrane allow signaling molecules, nutrients, and electrolytes to move from cell to cell
Neurotransmitters
Released from neurons to travel across synaptic cleft to second cell
Paracrines
Secreted into tissue fluids to affect nearby cells
local
Hormones
Chemical messengers that travel in the bloodstream to other tissues and organs
Endocrine System
glands, tissues, and cells that secrete hormones
slower and more broad than the nervous system
The two systems can regulate each other
Endocrinology
the study of this system and the diagnosis and treatment of its disorders
Endocrine Glands
Organs that are traditional sources of hormones
Hormones
chemical messengers that are transported by the bloodstream and stimulate responses in cells of another tissue or organ
Exocrine Glands
Have ducts
carry secretion to an epithelial surface or the mucosa of the digestive tract: “external secretions”
Extracellular effects
leaves the body
ex) food digestion
Endocrine Glands
No ducts
Have dense capillary networks which allow easy uptake of hormones into bloodstream
Internal secretions
sends into bloodstream
have intracellular effects such as altering target cell metabolism
What type of cell defies the classification of exocrine versus endocrine?
Liver cells
releases hormones, releases bile into ducts, releases albumin and blood-clotting factors into blood (not hormones)
chemicals that function as both hormones and neurotransmitters:
Norepinephrine
Dopamine
Antidiuretic hormone
Norepinephrine and glucagon both cause…
hydrolysis/breakdown of glycogen in the liver
Target Organs/Cells
organs or cells that have receptors for a hormone and can respond to it
Some target cells have enzymes that convert a circulating hormone to its more active form
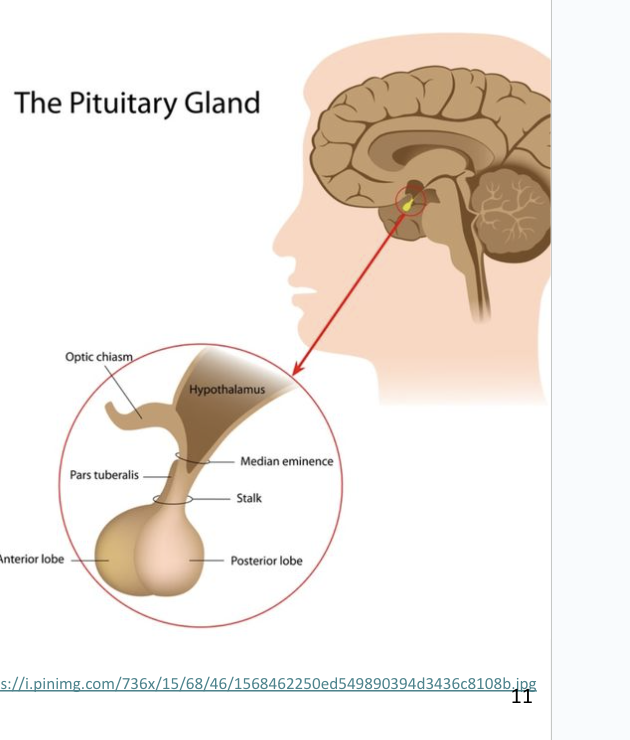
Hypothalamus
Regulates primitive functions from water balance and thermoregulation to sex drive and childbirth
Shaped like a flattened funnel
Forms floor and walls of third ventricle of brain
Many of its functions carried out by pituitary gland
Pituitary Gland
suspended from hypothalamus by the infundibulum
Housed in sella turcica of sphenoid bone
Composed of two structures with separate functions
Adenohypophysis (anterior pituitary)
Neurohypophysis (posterior pituitary)
Adenohypophysis (anterior lobe)
Makes up the anterior 3/4 of the pituitary
larger, has lots of blood vessels
connected to hypothalamus by blood capillaries
Hypothalamus sends hypothalamic-releasing-and-inhibiting hormones to anterior pituitary
causes anterior pituitary to also make and release a hormone
Neurohypophysis (posterior lobe)
Makes up the posterior 1/4 of the pituitary
made of nerve tissue, not a true gland
receives signals from the hypothalamus which sends hormones down the axons to be stored in the posterior pituitary
we do NOT make hormones in posterior pituitary, only store and release them
8 Hormones Produced in the Hypothalamus
6 regulate the anterior pituitary
2 are stored and released into capillaries in the posterior pituitary
Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone (GnRH)
releasing hormone that promotes the secretion of TSH, PRL, ACTH, FSH, LH, and GH in the anterior pituitary
Hormones in the Anterior Pituitary (6):
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
Luteinizing hormone (LH)
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
Prolactin (PRL)
Growth hormone (GH)
What are the 2 gonadotropin hormones that target gonads?
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
Luteinizing hormone (LH)
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
Stimulates secretion of ovarian sex hormones
Stimulates development of ovarian follicles
Stimulates sperm production
Luteinizing hormone (LH)
Stimulates ovulation
Stimulates corpus luteum to secrete progesterone
corpus luteum is a yellow scar tissue mass left over after ovulation
Stimulates testes to secrete testosterone
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
Stimulates secretion of thyroid hormone
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
hormone goes to the adrenal cortex and stimulates it to release glucocorticoids
increases glucose and mineral concentrations
Prolactin (PRL)
After birth, stimulates mammary glands to synthesize milk
Growth hormone (GH)
Stimulates mitosis and cellular differentiation
growth hormone causes fat, muscle, and bone differentiation
during sleep, GH is elevated, allowing us to better heal from daily injuries
GH has widespread effects on the body tissues
Bone growth, thickening, and remodeling are influenced, especially during childhood and adolescence
GH promotes the breakdown of adipose
How Growth Hormone Works
Induces liver to produce growth stimulants.
This causes:
Increase in protein synthesis
boosts transcription and translation, increases amino acid uptake, suppresses breakdown of proteins, helps build and repair tissue
Increase in lipid metabolism
stimulates adipocytes to break down fats (spares proteins)
Increase in carbohydrate metabolism
has a glucose-sparing effect as mobilizing fatty acids reduces dependence of most cells on glucose, freeing more glucose for the brain
stimulates glucose secretion from the liver
Electrolyte balance
Promotes Na+, K+, and Cl- retention in the kidneys
enhances Ca absorption in intestines
makes electrolytes available to growing tissues
Insulin-like Growth Factors (IGF-I) and Somatomedins (IGF-II)
Growth stimulants
Stimulate target cells in diverse tissues
IGF-I prolongs the action of GH
causes a greater effect of growth hormone
Growth Hormone highs and lows:
Secretion high during first 2 hours of sleep
Can peak in response to vigorous exercise
Also activated by ghrelin, which is released by the empty stomach
GH levels decline gradually with age
Lack of protein synthesis contributes to aging of tissues and wrinkling of the skin
Average 6 ng/mL during adolescence, 1.5 ng/mg in old age
fat percentage is higher as we age because growth hormone declines
Hormone Half-Life
the time required for 50% of the hormone to be cleared from the blood
GH half-life: 6 to 20 minutes
IGF-I half-life: about 20 hours
protein based hormones have a very short half-life
lipid based hormones have a long half-life
Hormones in the Posterior Pituitary (2):
Antidiuretic hormone
Oxytocin
ADH (antidiuretic hormone)
Increases water retention, thereby reducing urine volume and preventing dehydration
Also called vasopressin because it can cause vasoconstriction
ADH raises blood pressure by making us absorb more water from our urine and by making our blood vessels vasoconstrict
decreases urine output
Oxytocin (OT)
triggers smooth muscle contraction
Surge of oxytocin is released during sexual arousal and orgasm
Promotes feelings of sexual satisfaction and emotional bonding between partners
Stimulates labor contractions during childbirth
Stimulates flow of milk during lactation
oxytocin releases milk
May promote emotional bonding between lactating mother and infant
Control of Pituitary Secretion
Regulated by hypothalamus, other brain areas, and feedback from target organs
rate of secretion is not constant
Hypothalamic and Cerebral Control of Pituitary Secretion
Brain monitors conditions and influences the anterior pituitary accordingly
In times of stress, hypothalamus triggers release of ACTH
During pregnancy, hypothalamus triggers prolactin secretion
Posterior pituitary is controlled by neuroendocrine reflexs
Hypothalamic osmoreceptors trigger release of ADH when they detect a rise in blood osmolarity
Infant suckling triggers hypothalamic response to release oxytocin
Negative Feedback in Endocrine System
an increase in the target organ’s hormone level inhibits the release of hypothalamic and/or pituitary hormones
ex) the more hormones the thyroid glands makes, the less stimulation they will receive to make hormones
most feedback loops in endocrine system are negative
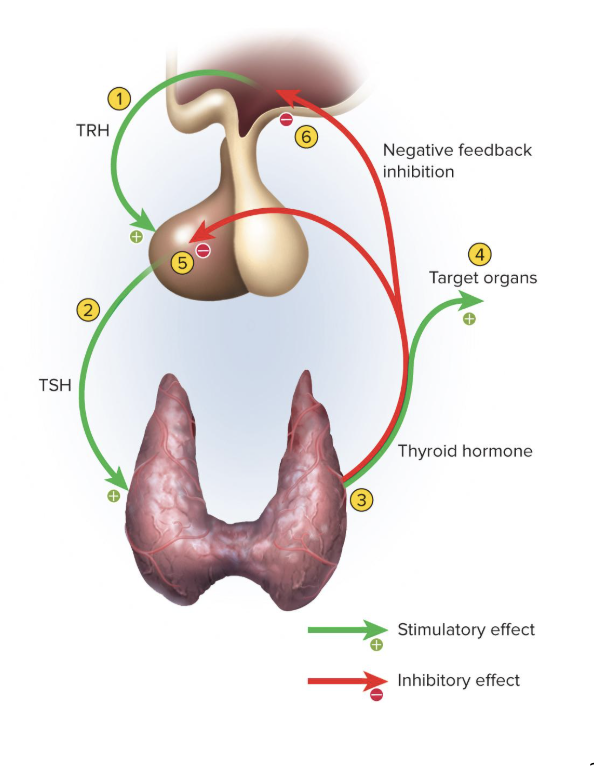
Positive Feedback in Endocrine System
occurs in the endocrine system but not as much as negative feedback
example of positive feedback in endocrine system is oxytocin inducing contractions
Pineal Gland
Attached to the roof of the third ventricle beneath the posterior end of corpus callosum
After age 7, it undergoes involution (shrinkage)
Down 75% by end of puberty
Synchronizes physiological function with the 24-hour circadian rhythms
Makes melatonin from serotonin during the night
Fluctuates seasonally
Pineal gland may influence timing of puberty in humans
Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD)
occurs in winter or northern climates
Symptoms: depression, sleepiness, irritability, and carbohydrate craving
2 to 3 hours of exposure to bright light each day reduces the melatonin levels and the symptoms (phototherapy)
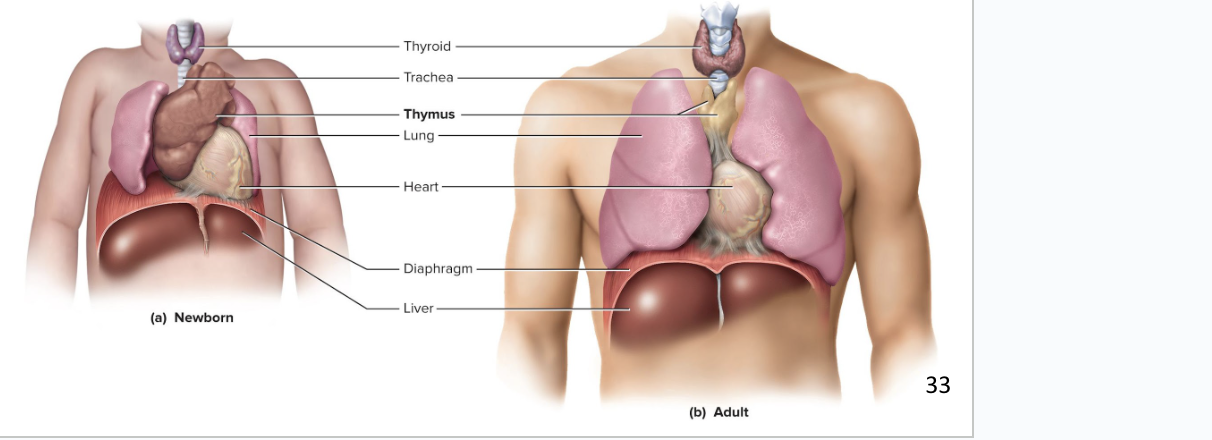
Thymus
Plays a role in three systems: endocrine, lymphatic, and immune system
located on the heart
Goes through involution (shrinkage) after puberty
site where T cells are made, which are important in immune defense
Secretes hormones thymopoietin, thymosin, and thymulin
the 3 hormones are from the thymus and help us make T cells/lymphocytes
Thyroid Gland
Largest gland that is purely endocrine
Made up of 2 lobes and an isthmus below the larynx
Dark reddish brown color bc of rich blood supply
Secretes thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) in response to TSH
increases metabolic rate, O2 consumption, heat production, appetite, growth hormone secretion, alertness, reflex speed
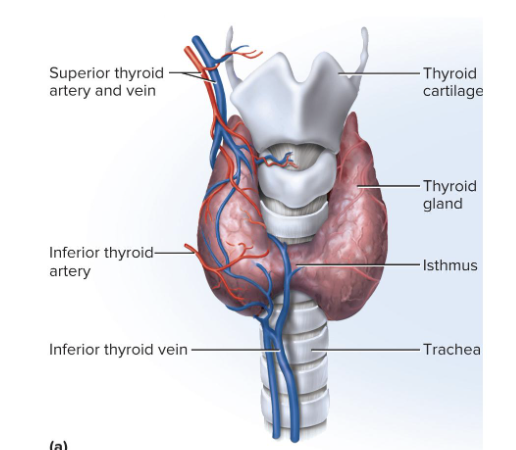
Thyroid Follicles
Sacs that make up most of the thyroid
Contain protein-rich colloid
Follicular Cells
simple cuboidal epithelial cells that line follicles
Parafollicular (C or clear) Cells
cells that secrete calcitonin with rising blood calcium
stimulates osteoblast activity and bone formation in children
Parathyroid Glands
4 glands partially embedded in the back of the thyroid gland
secretes parathyroid hormone (PTH)
cutting out the parathyroid gland would cause us to lose calcium homeostasis
Parathyroid Hormone (PTH)
increases blood Ca2+ levels
promotes synthesis of calcitriol
increases absorption of Ca
decreases urinary excretion
increases bone resorption
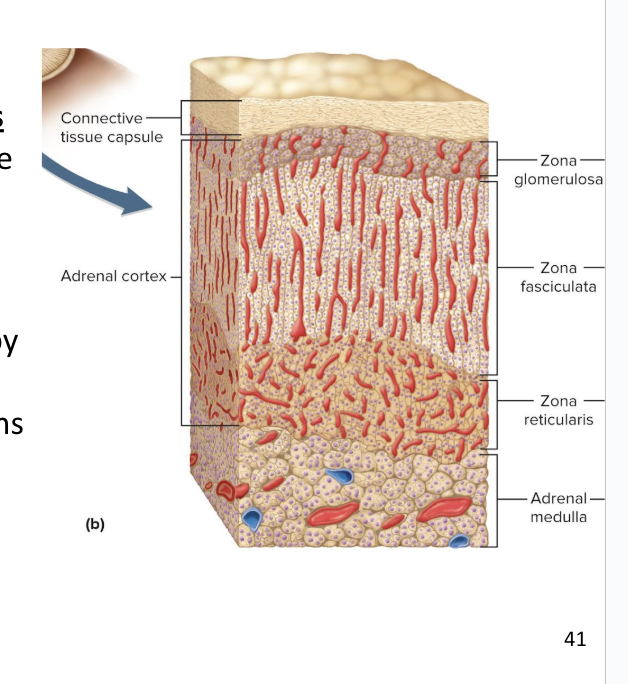
Adrenal Medulla
is the small inner portion of the gland
acts as an endocrine gland and a ganglion of the sympathetic nervous system
made of modified sympathetic postganglionic neurons called chromaffin cells
When stimulated, they release catecholamines (epinephrine and norepinephrine) and some dopamine directly into the bloodstream
Effects of Catecholamines as Hormones
Increase alertness and prepare body for physical activity
Mobilize high-energy fuels, lactate, fatty acids, and glucose
Glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis boost glucose levels
Epinephrine inhibits insulin secretion and so has a glucose-sparing effect
Increases blood pressure, heart rate, blood flow to muscles, pulmonary airflow, and metabolic rate
Decreases digestion and urine production
Adrenal Cortex
Adrenal cortex surrounds the medulla and secretes several corticosteroids (hormones) from 3 layers of glandular tissue
zona glomerulosa
zona fasciculata
zona reticularis
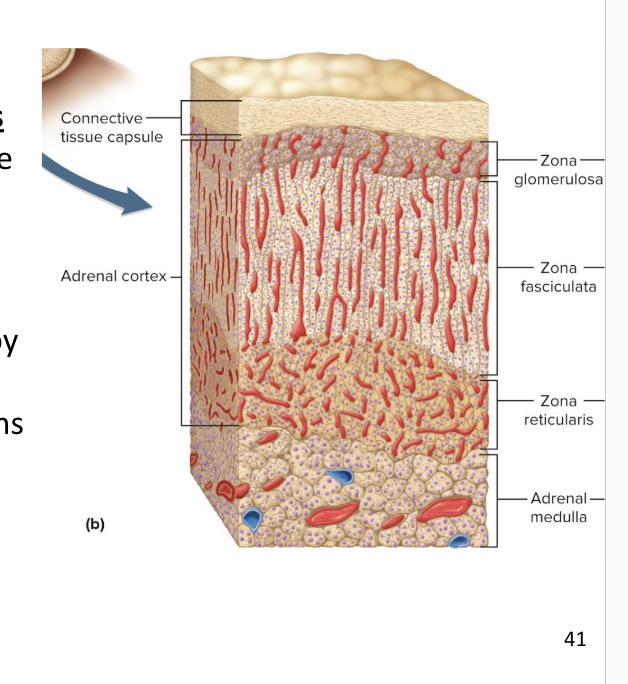
Zona Glomerulosa
thin, outer layer of cortex
Cells are arranged in rounded clusters
Secretes mineralocorticoids
these regulate the body’s electrolyte balance
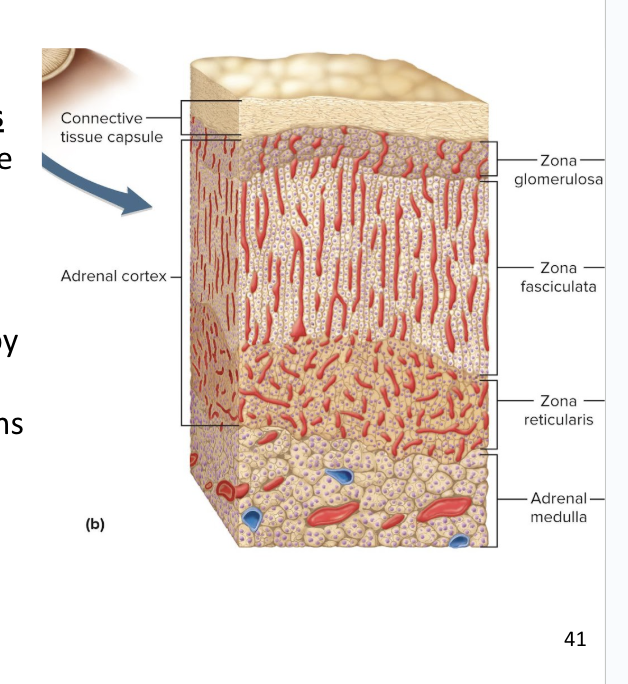
Zona Fasciculata
thick, middle layer of cortex
Cells arranged in fascicles separated by capillaries
Secretes glucocorticoids and androgens (testosterone)
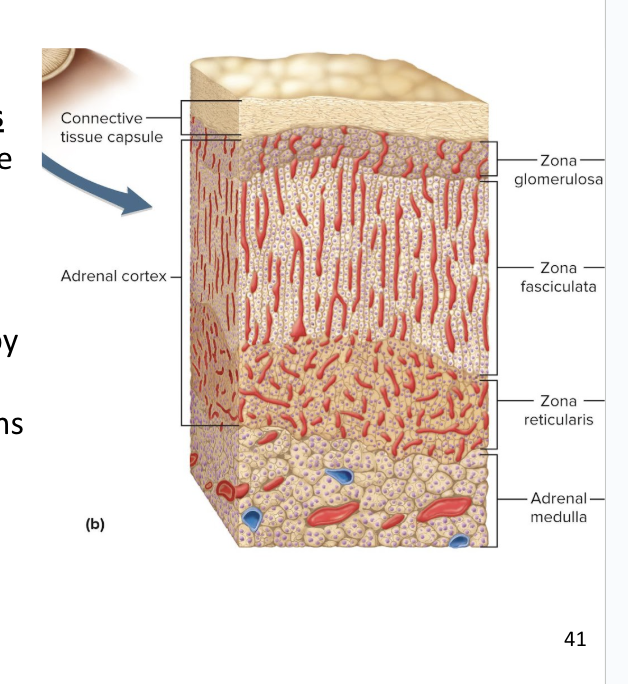
Zona Reticularis
narrow, inner layer of cortex
Cells make a branching network
Secretes glucocorticoids and sex steroids
Mineralocorticoids
Steroid hormones that regulate electrolyte balance
secreted in the zona glomerulosa
aldosterone stimulates Na+ retention and K+ excretion
Na+ pulls more water into the blood
means less urine being produced
plays a role in the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone
regulates blood pressure and fluid balance
Glucocorticoids
Secreted by the zona fasciculata and zona reticularis in response to ACTH
Regulates metabolism of glucose and other fuels
Cortisol and corticosterone stimulate fat and protein breakdown, gluconeogenesis, and release of fatty acids and glucose into the blood
Helps body adapt to stress and repair tissues
Anti-inflammatory effect with short-term use
immune system suppression with long-term use
Sex Steroids
Secreted by the zona fasciculata and zona reticularis
includes androgens and estradiol
Androgens
sets libido (sex drive) throughout life
large role in prenatal male development
includes Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) which other tissues convert to testosterone
Estradiol
produced in the ovaries, but some is released from adrenal glands
this becomes important after menopause for sustaining adult bone mass
a type of estrogen hormone
is most abundant of female hormones
Interdependence of the Adrenal Cortex and the Adrenal Medulla
The medulla and cortex of the adrenal gland depend on each other
Medulla shrinks/breaks down without the stimulation of cortisol
Some chromaffin cells in the medulla extend into the cortex
They stimulate the cortex to secrete corticosteroids when stress activates the sympathetic nervous system
Pancreatic Islets
sections of the pancreas made up of three different kinds of cells:
Beta cells
Alpha cells
Delta cells
Glucagon
secreted by the alpha cells of the pancreas
Released between meals when blood glucose concentration is lower
Raises blood sugar levels
does this in the liver
stimulates gluconeogenesis, glycogenolysis, and the release of glucose into the blood
In adipose tissue, stimulates fat catabolism and release of free fatty acids
Glucagon is also released when amino acid levels in blood are rising to promotes amino acid absorption and provide cells with raw material for gluconeogenesis
Insulin
secreted by beta cells in the pancreas
Secreted during and after meal when glucose and amino acid blood levels are rising
Stimulates cells to absorb these nutrients and store or metabolize them
lowers blood glucose levels
Promotes synthesis of glycogen, fat, and protein
Suppresses use of already-stored fuels
Brain, liver, kidneys, and RBCs absorb glucose without insulin, but other tissues require insulin
Insufficiency or inaction is cause of diabetes
Somatostatin
secreted by D or delta (δ) cells
Partially suppresses secretion of glucagon and insulin
slows down digestive activity so we can pull more nutrients out of food
Hyperglycemic Hormones
raise blood glucose concentration (includes hormones from other glands)
Glucagon, growth hormone, epinephrine, norepinephrine, cortisol, and corticosterone
Hypoglycemic Hormones
lower blood glucose
Insulin
Gonads
Ovaries and testes - sex glands
both endocrine and exocrine
Exocrine product: whole cells
eggs and sperm (cytogenic glands)
Endocrine product: gonadal hormones
mostly steroids
Ovarian Hormones
Estradiol, progesterone, and inhibin
Testicular Hormones
Testosterone, weaker androgens, estrogen, and inhibin
Ovary
synthesizes a lot of female sex hormones which come from the ovarian follicle
Theca cells synthesize a hormone, then that hormone is converted to mainly estradiol by the granulosa cells
After ovulation, the remains of the ovarian follicle becomes the corpus luteum
Secretes progesterone for 12 days following ovulation
Follicle and corpus luteum secrete inhibin
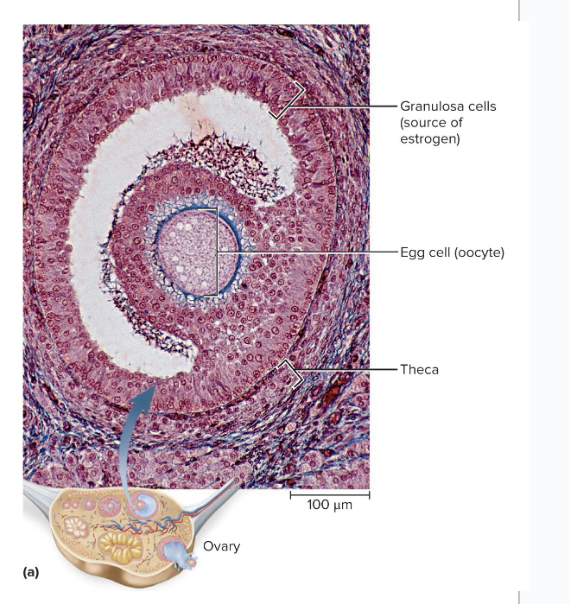
Functions of Estradiol and Progesterone
Develops female reproductive system and physique, including adolescent bone growth
Regulates menstrual cycle, sustains pregnancy
progesterone causes uterine lining to thicken
uterine glands don't get activated until exposed to progesterone
progesterone lowers which causes the uterine lining to shed
Prepares mammary glands for lactation
Inhibin
suppresses FSH secretion from the anterior pituitary
released from Nurse cells
Limits FSH secretion in order to regulate sperm production
Testes
Microscopic seminiferous tubules produce sperm
Tubule walls contain sustentacular (Sertoli) cells
are nerve cells
Leydig cells (interstitial cells) lie in clusters between tubules
testosterone is main hormone in the testes
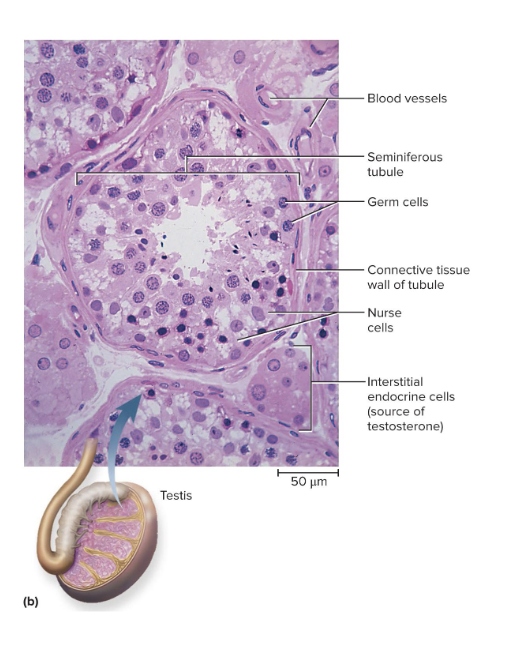
Functions of Testosterone
Testosterone and other steroids from interstitial cells nestled between the tubules
Stimulates development of male reproductive system in fetus and adolescent, and sex drive
Sustains sperm production
Endocrine Functions of Skin
Keratinocytes convert a cholesterol-like steroid into cholecalciferol using UV from sun
vitamin D acts like a hormone
Endocrine Functions of Liver
involved in the production of at least five hormones
Converts cholecalciferol into calcidiol
Secretes angiotensinogen (a prohormone)
Precursor of angiotensin II (a regulator of blood pressure)
Secretes 15% of erythropoietin (stimulates bone marrow)
increases red blood cell production
Source of IGF-I that controls action of growth hormone
Hepcidin
promotes intestinal absorption of iron
Endocrine Functions of Kidneys
plays a role in production of at least 3 hormones
converts calcidiol to calcitriol, the active form of vitamin D
increases calcium absorption by intestine and inhibits loss in the urine
secretes renin that converts angiotensinogen to angiotensin l
angiotensin ll created by converting enzyme in lungs
constricts blood vessels and raises blood pressure
produces 85% of eyrthropoietin
stimulates bone marrow to produce red blood cells
Endocrine Functions of the Heart
the atrial muscle secretes 2 natriuretic peptides in response to an increase in blood pressure
theses decrease blood volume and blood pressure by increasing Na+ and H2O output in the kidneys, and the opposite affect for angiotensin ll
lowers blood pressure
makes us lose fluid through urination more to lower the BP
Endocrine Functions of the Stomach and Small Intestines
secrete at least 10 hormones secreted by enteroendorine cells
coordinates digestive motility and glandular secretion
Endocrine Functions of Adipose
adipose tissue secretes leptin
Slows appetite
Endocrine Functions of Osseous Tissue
Osteocalcin is secreted by osteoblasts
makes us have more beta cells in the pancreas which means more insulin so we can lower our blood sugar
Inhibits weight gain and onset of type 2 diabetes
Endocrine Functions of Placenta
Secretes estrogen, progesterone, and others
Regulates pregnancy, stimulates development of fetus and mammary glands
Type 1 Diabetes
Immune disorder that results in loss of beta cells in the pancreas
results in blood sugar that is too high
body does not produce insulin in the body, so blood sugar cannot absorb into adipose tissue, so adipose will have a hard time making body fat
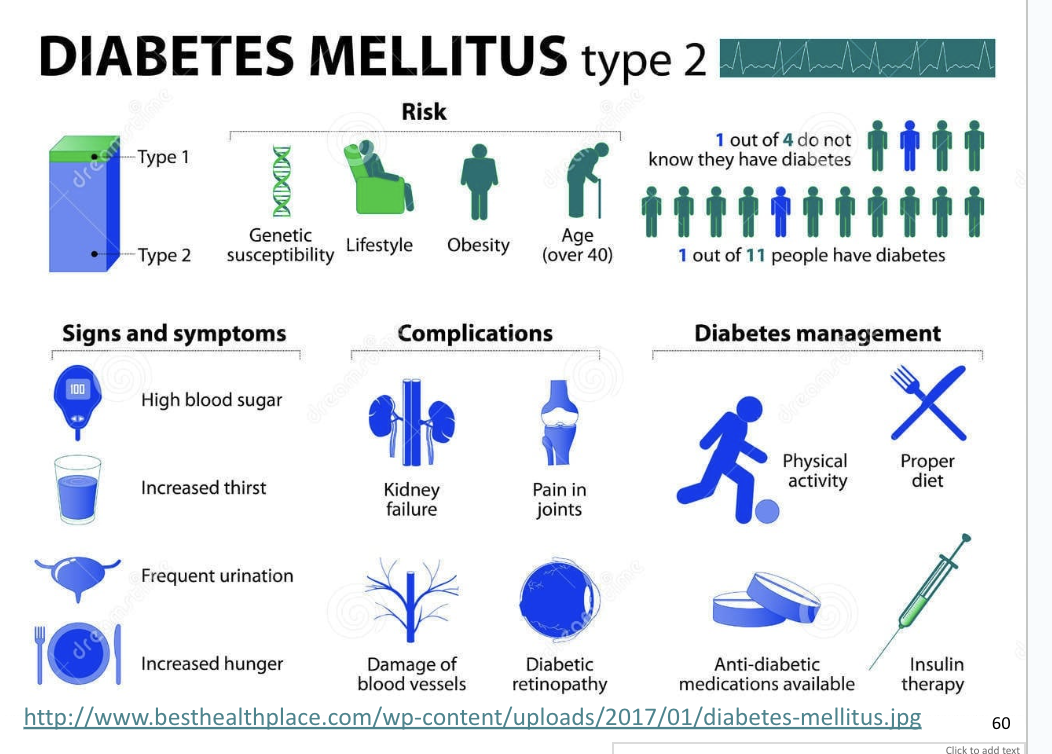
Type 2 Diabetes
Primarily linked to unhealthy lifestyle
Type II diabetes is more common
More body fat decreases insulin sensitivity of other cells
Target cells have fewer insulin receptors
Senescence of Endocrine System
Endocrine system
Degenerates less than any other system
Only reproductive, growth, and thyroid hormones show major declines
Other hormones secreted at fairly stable rate
Target cell sensitivity may decline
Pituitary gland
is less sensitive to negative feedback inhibition by adrenal glucocorticoids
Response to stress is prolonged