CCNA
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/328
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
329 Terms
1
New cards
Extended ACL range
100-199
2
New cards
What function is performed by a WLC in a Split MAC Deployment?
Security/QoS management, client authentication, client association
3
New cards
What function is performed by a LAP in a Split MAC Deployment?
“Real-time” operation such as transmitting/receiving, encryption/decryption, and sending beacons/probes
4
New cards
GLBP MAC
**0007**.B400.0102
5
New cards
HSRP
0000\.**0C07**.AC0B
6
New cards
VRRP
0000\.**5E00**.0101
7
New cards
What is the normal OSPF neighbor state for a router that is neither the DR or BDR?
2-Way
8
New cards
Default VTP mode on new switches
Server Mode
9
New cards
When is **PSK** used?
WPA2 passphrase in ASCII format
10
New cards
On which interfaces is the OSPF point-to-point network type enabled by default?
PPP and HDLC
11
New cards
What is Weighted Random Early Detection (WRED)?
Congestion avoidance method that drops lower-priority packers if network congestion is detected
12
New cards
What can cause late collisions on an Ethernet LAN?
Duplex mismatch and long cable segments
13
New cards
Standard ACL range
1-99
14
New cards
External EIGRP AD
170
15
New cards
Internal EIGRP AD
90
16
New cards
Static Route AD
1
17
New cards
Directly Connected AD
0
18
New cards
IS-IS AD
115
19
New cards
OSPF AD
110
20
New cards
RIP AD
120
21
New cards
Router-ID OSPF Selection Order
1. Manuel router ID
2. Highest loopback
3. Highest active IP address
22
New cards
Configure a hostname associated with an IP address
ip host __name__ __ip address__ __subnet mask__
23
New cards
OSPF State Order
1. Down
2. Init
3. Two-way
4. Ex-start
5. Exchange
6. Loading
7. Full
24
New cards
Where is a standard ACL placed?
Placed close to the destination
25
New cards
Where is an extended ACL placed?
Placed close to the source
26
New cards
What command shows the current NAT translations?
show ip nat translations
27
New cards
What command shows the active NAT translations?
show ip nat statistics
28
New cards
Types of Enterprised-managed remote access VPNs
1. Clientless SSL VPN
2. Client-based IPsec VPN
29
New cards
The action of adding a value to a packet header so the packer matches a defined policy
Traffic marking
30
New cards
What is Low Latency Queuing (LLQ)
LLQ is a QoS mechanism that allows delay-sensitive data to be sent first before other packets
31
New cards
What is “config-register 0x2102” used for?
To ensure that the device loads the start up config file during start up
32
New cards
How are syslog levels ordered by?
Syslog levels are ordered by severity whereby 0 is the most severe and 7 is the least
33
New cards
What does ASIC do?
Allows multi-layer switches to forward IP packets without calling on the CPI to make routing decisions
34
New cards
What programming language does YAML look like
Python
35
New cards
What is Cisco Express Forwarding (CEF)?
A packet-switching technique is used within Cisco routers to optimize the forwarding of packets and increase packet-switching speed.
36
New cards
What is the CEF made up of?
1. FIB (Forwarding Information Base)
2. Adjacency Table
37
New cards
What is the FIB?
The FIB is a mirror copy of the routing table
38
New cards
What is the Adjacency Table?
The adjacency table maintains Layer 2 next-hop addresses for all FIB entries
39
New cards
All devices in a service set share the same ___
SSID (Service Set Identifier)
40
New cards
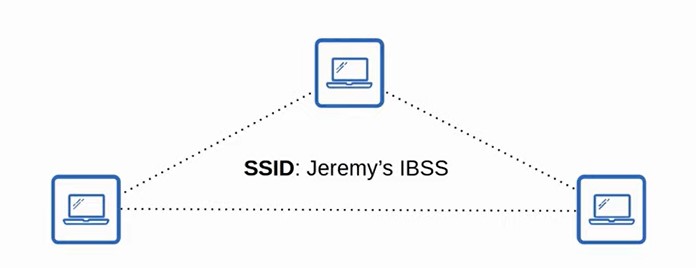
Independent Basic Service Set (IBSS)?
A wireless network in which two or more wireless devices connect directly without using an AP. An example of this is AirDrop so it is not scalable
41
New cards
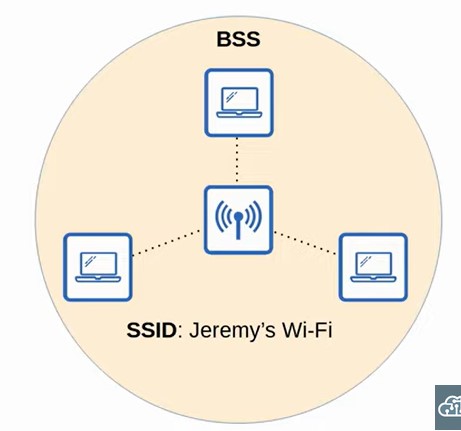
Basic Service Set (BSS)?
A wireless network in which clients connect to each other via an AP but not directly to each other.
42
New cards
What is a BSSID used for?
Identifies an AP in the BSS
43
New cards
Extended Service Set (ESS)?
One or more interconnected basic service sets (BSSs) and their associated LANs
44
New cards
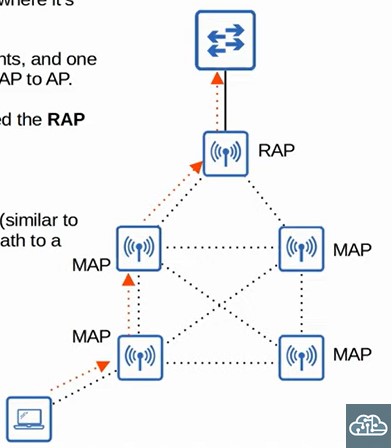
Mesh Basic Service Set (MBSS)?
One access point is connected to the wired network while the rest of the APS are interconnected wirelessly
45
New cards
How many bits are in an IPv4 address?
32 bits
46
New cards
How many bytes are in an IPv4 address?
4 bytes
47
New cards
How many bits are in an IPv6 address?
128 bits
48
New cards
How many bytes are in an IPv6 address?
16 bytes
49
New cards
What is the default reference bandwidth in OSPF?
100,000,000 bps
50
New cards
OSPF Cost Formula
Interface Cost= Reference bandwidth/interface bandwidth
51
New cards
What are MD5 and SHA used for?
Data integrity
52
New cards
What is AES used for?
Confidentiality
53
New cards
What makes up the three-layer hierarchal model?
1. Core
2. Distribution
3. Access
54
New cards
What makes up the two-layer hierarchal model?
1. Collapsed Core/Distribution
2. Access
55
New cards
What is the purpose of the core layer?
1. provide high-speed **backbone** connectivity
2. functions as **aggregators** for all campus blocks
56
New cards
What is the purpose of the distribution layer?
1. established **Layer 3 routing** boundaries
2. implements **network access policy**
57
New cards
What is the purpose of the access layer?
1. represents the **network edge**
2. provides **network access** to the user
58
New cards
Explain the spine-leaf achitecture.
A network topology that consists of 2 switching layers—a spine and a leaf.
* The leaf layer consists of access switches that aggregate traffic from servers and connect directly to the spine or network core
* Spine switches interconnect all leaf switches in a full-mesh topology.
* The leaf layer consists of access switches that aggregate traffic from servers and connect directly to the spine or network core
* Spine switches interconnect all leaf switches in a full-mesh topology.
59
New cards
What command specifies the source for the Cisco IOS Software image to load?
boot system ____
60
New cards
When does refraction occur?
When a wave is bent while entering a medium where the signal travels at a different speed
61
New cards
When does diffraction occur?
Diffraction happens when the wave goes around an object
62
New cards
What causes scattering?
Scattering is caused by dust, smog, uneven surfaces, etc
63
New cards
What is stored in the NVRAM?
NVRAM stores the configuration information on the network server in text form as configuration commands
64
New cards
What is Cisco DNA Center?
Cisco DNA Center is an appliance to configure that provides a GUI and programming interface to design and troubleshoot a network.
65
New cards
What is Cisco DNA Assurance used for?
Used for troubleshooting
66
New cards
What is Cisco DNA Security used for?
Enforce policies and contain threats across the network
67
New cards
What are the 5 main areas of Cisco DNA Center?
1. Design
2. Policy
3. Provision
4. Assurance
5. Platform
68
New cards
What is Cisco DNA Design used for?
Modeling an entire network
69
New cards
What is Cisco DNA Policy used for?
Creating policies to automate and simplify network management
70
New cards
What is Cisco DNA Provision used for?
Providing **new services** to users
71
New cards
What is Cisco DNA Assurance used for?
Proactive **monitoring** and **insights** from the network to **predict** problems and **ensure** policies and configurations achieve the business' intent
72
New cards
What is Cisco DNA Platform used for?
Provides the use of **API**s for end-to-end solutions and add support for multi-vendor devices
73
New cards
Four WLC Deployments
1. Unified WLC
2. Cloud-based WLC
3. Embedded WLC
4. Mobility Express WLC
74
New cards
Unified WLC
The WLC is a hardware appliance in a **central** **location** of the network
75
New cards
Cloud-based WLC
The WLC is a **virtual** **machine** running **on** a **server**, usually in a private cloud in a data center.
76
New cards
Embedded WLC
The WLC is **integrated** within a **switch**
77
New cards
Mobility express WLC
The WLC is **integrated** within an **Access** **Point**
78
New cards
What is the function of a WLC?
WLC manages network access points that allow wireless devices to connect to the network.
79
New cards
What is Light Weight Access Point Protocol (LWAPP)?
An open Cisco proprietary wireless management protocol
80
New cards
What is Control and Provisioning of Wireless Access Points (CAPWAP)?
An open industry-standard protocol for wireless management
81
New cards
Describe Split MAC
Some traffic is performed by the AP and the remainder is handled by the WLC
82
New cards
What is (Link Aggregation) LAG?
Also known as EtherChannel to bundle multiple ports into one.
83
New cards
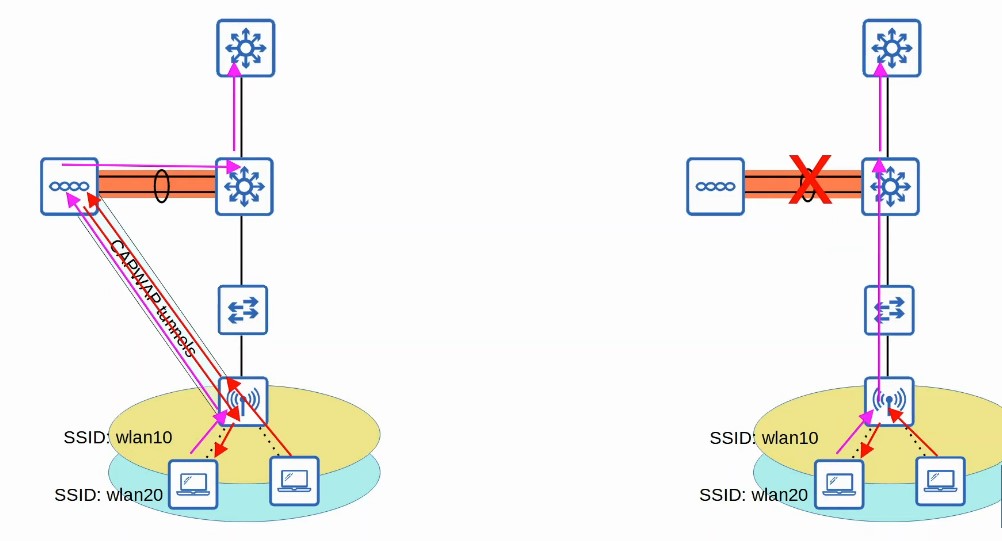
What is FlexConnect mode?
Allows the AP to locally switch traffic between wired and wireless networks if CAPWAP tunnels to the WLC go down.
84
New cards
What is Local mode?
The default mode for an LAP where the AP offers a BSS for clients to associate with
85
New cards
What is Sniffer mode?
The AP does not offer a BSS for clients, but it is dedicated to capture 802.11 frames and sending them to a device running software such as Wireshark
86
New cards
What is Moniter mode?
The AP does not off a BSS for clients, but it is dedicated to capture 802.11 frames to detect rogue devices.
87
New cards
What is Rogue Detector mode?
The AP does not even use its radio, but listens to traffic on the wired network only to receive a list of suspected rogue clients.
88
New cards
Explain SDN?
A network architecture that separates the control plane from the data plane, allowing network behavior to be defined and controlled using software
89
New cards
What is the control plane?
The "brain" of the network, making decisions about how the network should behave (traffic routing and network topology).
90
New cards
What is the data plane?
The "body" of the network, performing the actual work of forwarding network traffic that has been defined
91
New cards
What is the application layer (SDN)?
The interface for network administrators to configure and manage the network. It includes the network management software and the APIs used to interact with the network.
92
New cards
List the SDN layers
1. Application Layer
2. Control Layer
3. Data Plane Layer
93
New cards
Define underlay
The physical network of devices and connections which provide IP connectivity (multi-layer switches and their connections)
94
New cards
Define overlay
The virtual network built on top of the physical overlay network
95
New cards
Define fabric
The combination of the **overlay** and the **underlay** (physical and virtual network as a whole)
96
New cards
Explain TCP
Connection-oriented protocol that provides retransmission of lost data packets
97
New cards
Explain UDP
Connectionless protocol that is much fast that TCP
98
New cards
IPV6 Multicast Address
FF00::/8
99
New cards
What is an Anycast Address?
“one to one of many”
100
New cards
What is Modified EUI 64 (EUI-64)
Method of converting a MAC address into a 64-bit interface identifier