Lecture 8 - Membrane Transport & Cell Respiration
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
How of thick is the plasma/cell membrane?
5-6nm
What is the plasma membrane?
An amphipathic phospholipid bilayer
What is the plasma membrane composed of?
Hydrophobic and Hydrophillic cores
Which part of the plasma membrane is the non-polar part?
Hydrophobic core
Which part of the plasma membrane is the polar part?
Hydrophillic core
Which part of the phospholipid is water loving (hydrophilic)?
Head group
Which part of the phospholipid is water fearing (hydrophobic)?
Fatty acid tails
True or False: Phospholipids cannot differ in head groups
False
Which part of the phospholipid is the functional group?
The head
True or False: Different lipid composition in different organelles happen for different cellular functions
True
True or False: Phospholipids can't differ in Fatty Acid tails
False
What are the different types of fatty acid tails?
Saturated and Unsaturated
Which fatty acid group has double bonds in the tail?
Unsaturated FA
What does fluidity of lipids depend on?
The length and saturation of hydrocarbon chains
What does butter consists of?
Saturated lipids
What does beeswax consists of?
Saturated lipids with long hydrocarbon tails
What does safflower oil consists of?
Unsaturated lipids
What is cholesterol and important component of?
The plasma membrane
What FA molecule makes up micelle?
Single FA chains
How is micelle packed in water?
In a circle
What FA molecule makes up the lipid bilayer?
Double FA
How is the lipid bilayer packed in water
In a straight line with tails opposite each other
How are liposomes delivered in drug delivery?
They placed into micelle which is then taken in the lipid bilayer
Membranes are:
1. Flexble
2. Repairable
3. Expandable
Membrane flexibility means that ___________________.
cells can change their shape
Membrane repairability means that _______________________.
lipids move to reform a continuous surface
Membrane expandability means that ________________________.
cells increase surface area by adding new membrane lipids
Lipids form micelle and bilayers in _________________.
solution
In micelle and bilayers, the hydrophilic heads of lipids _____________; and the hydrophobic heads of lipids ______________.
face out towards the water; face in away from the water
What is the foundation of cellular membranes?
Lipid bilayers
True or False: The membrane bilayer is not fluid
False
What is the fluidity of the layer caused by?
motions of lipid molecules
What does membrane fluidity affect?
cellular function (endocytosis, exocytosis, membrane signaling, transport etc.)
Is the plasma membrane static?
No
How isn't the plasma membrane static?
Phospholipids are in constant lateral motion, but rarely flip to the other side of the bilayer
What affects membrane fluidity?
1. Membrane composition
2. Temperature
What affects membrane composition?
1. Saturated vs. Unsaturated fatty acids
2. Chain length of the fatty acid tails
3. Cholesterol
Lipid bilayer with short and unsaturated hydrocarbon tails have a ___________________________________.
higher permeability and fluidity
Lipid bilayer with long and saturated hydrocarbon tails have a ___________________________________.
lower permeability and fluidity
What is the higher ratio of unsaturated fatty acids a result of?
Double bonds pushing neighbouring phospholipids aside
Less packed =
more fluid
What is the higher ratio of saturated fatty acids a result of?
Phospholipids packing closely
How does increased temperature affect membrane fluidity?
It causes a sharp transition from a more rigid membrane to a more fluid one
How does decreased temperature affect membrane fluidity?
It causes a sharp transition from a fluid membrane to a more rigid one
What is desaturase?
An enzyme that catalyzes the formation of double bonds to create an unsaturated FA to increase membrane fluidity
When do orgnanisms increase the expression of desaturase?
To add more unsaturated FA to their membrane when more fluid membrane is needed
Higher temp ____________ fluidity of membrane.
increases
Why does higher temp make the membrane more fluid?
To overcome the temperature effect, organisms need lower fluidity by increasing saturated FA (SFA) and lowering desaturase
Lower temp ____________ fluidity of membrane.
decreases
Why does lower temp make the membrane less fluid?
To overcome the temperature effect, organisms need more fluidity by increasing unsaturated FA (UFA) and lowering desaturase
How do organisms maintain optimum fluidity for the function of the membrane?
Organisms adjust FA composition at different temps
Which organisms are high in pre-formed EPA/DHA?
Ocean algae, phytoplankton, fish-eat algae, organisms that consume sunlight and CO2
Where are organisms high in pre-formed EPA/DHA found?
In the cold, in whole cells, oil in flesh
Which organisms are high in omega 6?
Canola plant, sunflower, organisms that consume sunlight and CO2
Where are organisms high in omega 6 found?
In the semi-cold, leaves/seeds
Which organisms are high in saturates?
Farm raised animals, pork & beef, organisms that eat grass and grains
Where are organisms high in saturates found?
In warm blooded breeds, body fat
Which organisms are very high in saturates?
Milk fat and butter
Where are organisms very high in saturates found?
In items hard at cold temp, milk fat
Which organisms survive better in the cold?
Organisms with more YFAs in their membranes
How does cholesterol maintain fluidity at lower temp?
By reducing packing opportunities (relative to non-cholesterol condition)
How does cholesterol maintain fluidity at higher temp?
By reducing phospholipid movement (relative to non-cholesterol condition)
Cholesterol has a ________________ effect on Cholesterol on membrane fluidity
bidirectional
Membrane composition _________, _________________________ and ___________________________________.
varies, is complex and dynamic, is essential to function
What model is the bilayer membrane considered to be?
The fluid mosaic model
Membranes consider a diversity of ____________ and _____________
protein, lipid
What is the purpose of freeze-fracture preparations?
They allow biologist to view membrane proteins
What is the first step in freeze-fracture preparations?
Fracturing the cell
Explain fracturing the cell
Striking frozen cells with a knife to split the lipid bilayer
What is the second step in freeze-fracture preparations?
Separating the parts
Explain the purpose of separating the parts
It must be done to prepare for transmission electron microscopy
What is the third step in freeze-fracture preparations?
Microscopy
What happens in microscopy?
Puts and mounds in the membrane interior are observed
What is the fourth step in freeze-fracture preparations?
Interpretation
Explain the free-fracture preparation interpretation
Image supports fluid-mosaic model of membrane structure
What does the semi-permeable membrane act as a barrier to?
Water soluble (polar) molecules
Charged ions
Charged molecules
Large molecules
What can readily pass through the semi-permeable membrane with the concentration gradient?
Hydrophobic (nonpolar) molecules like O2, CO2, N2
What molecules have the highest permeability?
Small, nonpolar molecules (O2, CO2, N2)
What molecules have the second highest permeability?
Small, uncharged molecules (H20, glycerol)
What molecules have the third highest permeability?
Large, uncharged polar molecules (Glucose, sucrose)
What molecules have the lowest permeability?
Small ions (Cl-, K+, Na+)
What is passive (simple) diffusion?
Movement of substances from high concentration towards low concentration
How does passive diffusion occur?
Spontaneously (ΔG < 0, ΔS > 0)
What does passive diffusion not require?
Transporters or energy
What are the steps involved in the process of diffusion across a lipid bilayer?
1. Separation of solutes
2. Diffusion
3. Equillibrium
What process is an example of passive diffusion?
Osmosis
What is osmosis?
The diffusion of water, based on solute concentration across a selective permeable membrane
What direction does osmosis occur?
From a region of lower solute concentration (higher water concentration) to a region of higher solute concentration (lower water concentration).
A selectively permeable membrane must allow __________ to pass, but not _____________________.
water, solute molecules
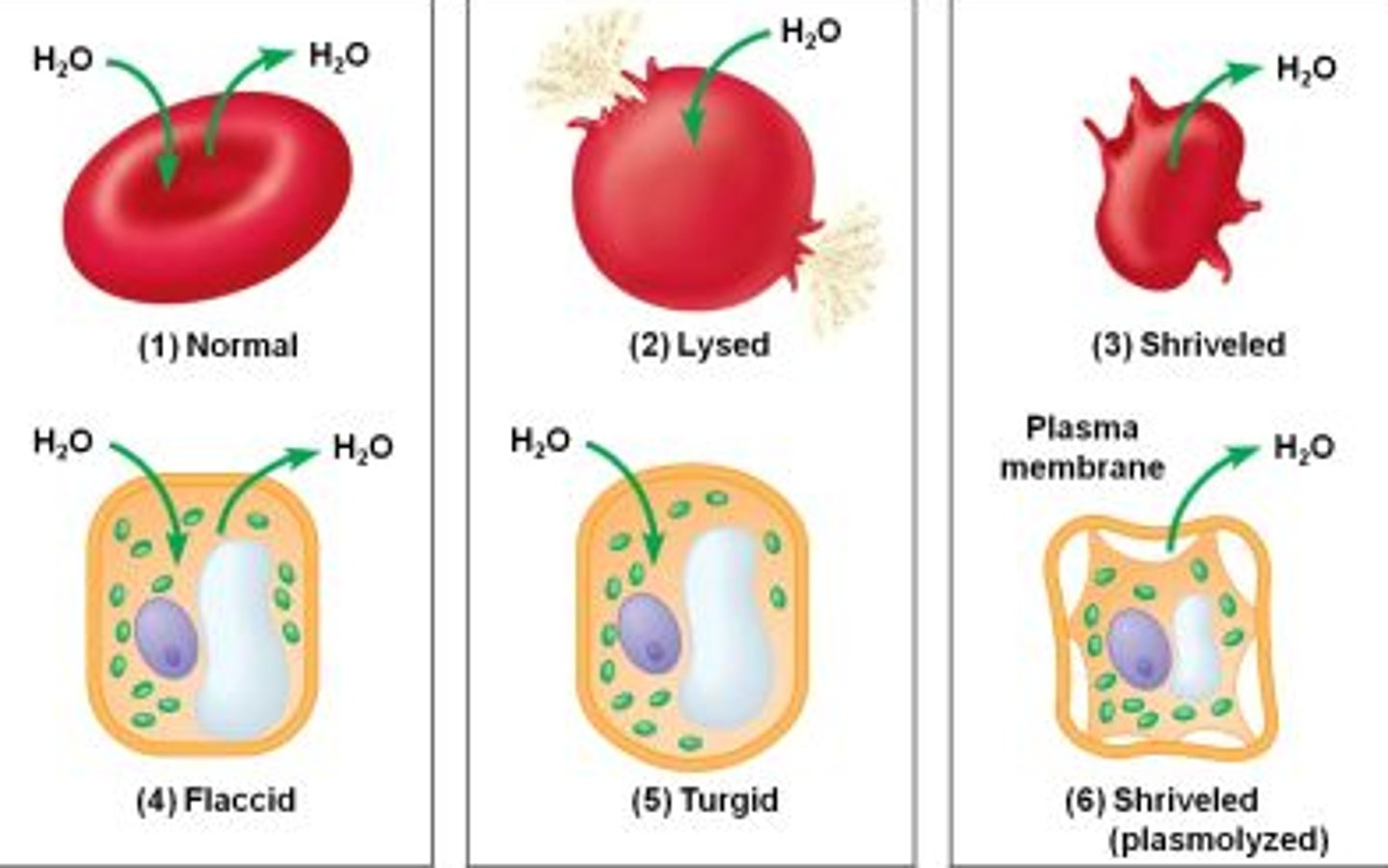
Hypertonic:
Solute concentration is high relative to the comparison solution
Hypotonic:
Solute concentration is lowrelative to the comparison solution
Isotonic:
Comparison solutions have the same solute concentration
What happens when the outside solution is hypertonic to the inside?
Shrinkage (Net flow of H20 OUT of vesicle)
What happens when the inside solution is hypertonic to the outside?
What happens when the outside solution is hypotonic to the inside?
Swelling/bursting (Net flow of H20 INTO vesicle)
What happens when the inside solution is hypotonic to the outside?
What happens when the outside solution is isotonic to the inside?
No change
Tonicity in plant and animal cells:
How do polar, charge molecules and large molecules get across the membrane?
Through facilitated diffusion