2.4 Motivation & demotivation
1/154
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
155 Terms
Motivation
The desire, effort, passion to achieve something
Willingness to complete a task / job w intent + purpose
Why do managers want to motivate their workforce?
To maximise
Job satisfaction
Staff morale
Labor productivity
Pros of increased worker motivation
Higher staff morale + job satisfaction → higher productivity
Better industrial relations (less chance of conflict)
Lower absenteeism
Low staff turnover → reduces recruitment costs
Improvers corporate rep (easier to attract employees)
Higher profitability
Signs of poor motivation
High absenteeism
High labour turnover → increases costs
High wastage level (defective / substandard output)
High no. customer complaints (due to poor quality)
Low quality output (make more mstakes, care less abt quality)
Poor puncuality (time, deadlines)
More disciplinary problems
Absenteeism
% of workforce that misses work w/o valid reason
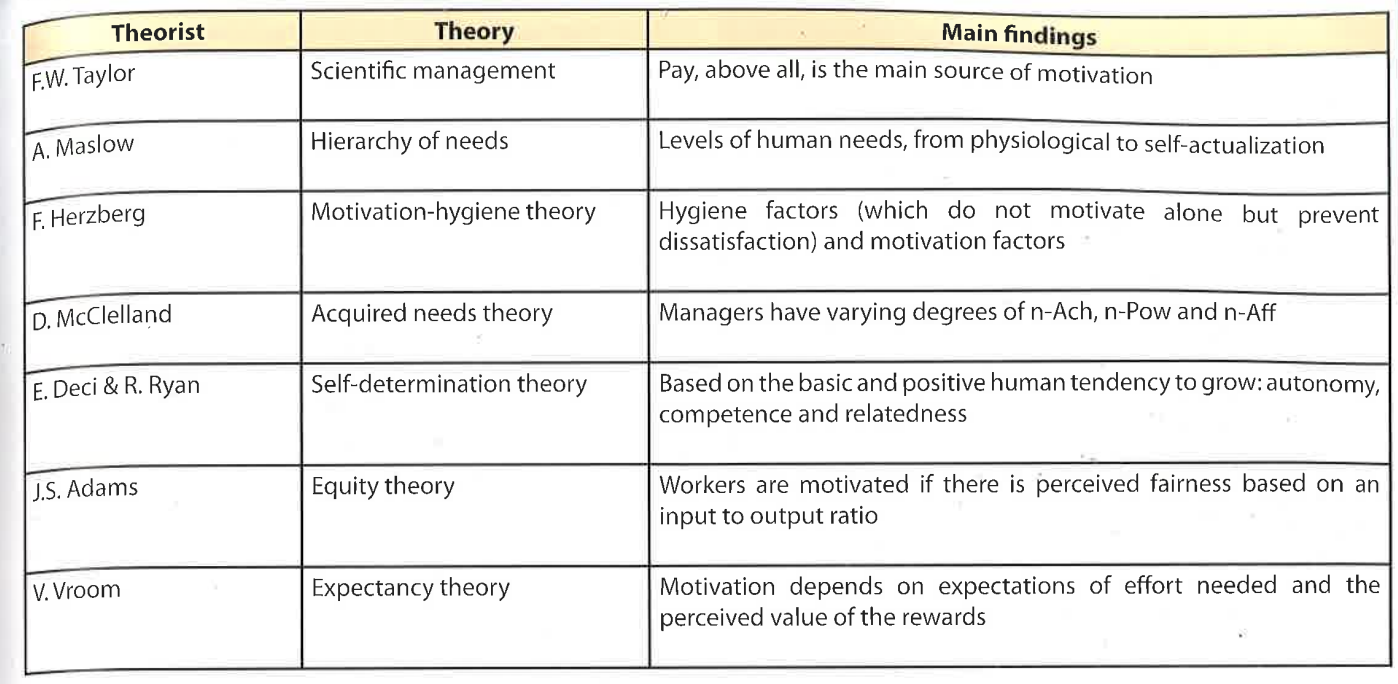
Motivation theories
Taylor
Maslow
Herzberg (motivation-hygiene theory)
McClelland's acquired needs theory
Deci + Ryan's self-determination theory
Equity + expectancy theory
Taylor motivation theory
Employees primarily motivated by money
Scientific management theory
Scientific management
Developed by Taylor
Use specialisation + div of labour help increase productivity level
Esp if pay is linked to piece rate system
How did Taylor suggest to improve productivity?
Set output + efficiency targets related to pay
Use piece rate
Division of labour
Process of breaking down diff aspects of a job
Assign diff ppl to each part of the work
Aim: improve efficiency + output
Differentiated piecework
Incentive scheme that rewards more productive workers who exceed a pre-determined benchmark
Workers paid standard level of output + higher pay if they exceed it
Role of managers vs workers in Taylors theory
MANAGERS:
Plan work using div of labour, differentiated piecework to increase productivity
Train employees
Plan, control supervise tasks / employe
WORKERS:
Perform work in standardized fashion
Receive wages based on differentiated piecework
No input in how things are done
Cons of Taylors theory
Ignores non-physical contributions of workers
Service industry (teaching, healthcare)
Scientific management = ineffective more jobs that focus on mental vs physical output
Ignores non-financial factors that motivate
Ignores that workers can be innovative + independent thinkers
Esp in highly educated societies (dont like being told what to do)
Repetitive + monotonous tasks → dissatisfaction
Maslow’s hierarchy of needs
5 levels of needs
From satisfying physiological needs → seld-actualisation
Lower needs must be met before people progress up the hierarchy
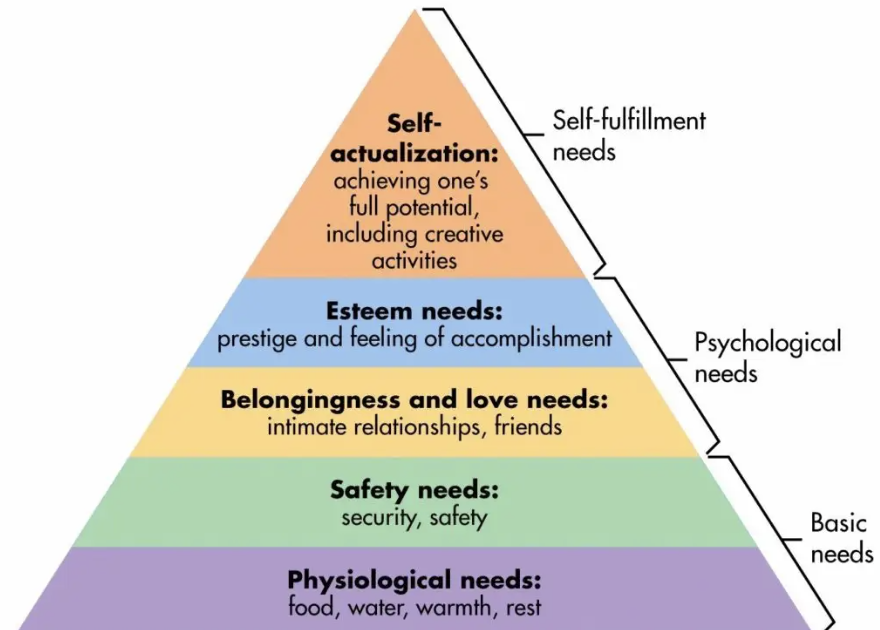
Hierarchy of needs
Maslow’s motivation theory
Ppl motivated by diff levels of needs: physiological, safety, social, esteem, self-actualisation
Physiological needs (basic needs)
Requirements for human survival
Food, warmth, water, shelter, sleep
Ability to achieve these depends on the amount of money workers earn
Safety needs (security needs)
Requirements that make people feel safe
Job security, sick pay, pensions
Predictability (routine), order (protect from harm)
Love + belonging needs (social needs)
Requirement to be accepted by others (friendship, family)
Satisfy by improved communication, gatherings, opportunities for teamwork, compliance w anti-discriminaton laws
Esteem needs
Desire of ppl to feel respected, having value, self-respect
Job titles, praise, training, employee of month, internal promotion (not external recruitment)
Internal vs external esteem needs
I = ppl need to feel good abt themselves (achievement)
E = desire to be recognised by others (status)
Self-actualisation
Highest level of needs
Forces that drive ppl to be the very best they can be + fulfill their potential
Achieve by firm provide opportunities for professional development + promotion
IRL why is it not feasible for firms to motivate all workers to the top of the hierarchy of needs?
Realistic to only satisfy physiological + security of low-skilled workers
Focus on meeting higher level of neesd of core staff (senior manager)
Cons of Maslow’s hierarchy of needs
Difficult to identify / measure workers needs
Not everyone has the same 5 needs (other factors involved)
Self-actualisation needs rarely permanently achieved.
Doesn’t explain what motivates them once they achieve htis
Herzberg motivation-hygiene theory
Looks at the factors that must be met in order to prevent dissatisfaction
+ the factors that actually motivate employees
Hygiene factors (maintenance factors)
Parts of a job that don’t increase job satisfaction but prevent dissatisfaction
Don’t motivate employees to work harder
Motivators
Factors that increase job satisfaction + motivation levels
Lead to psychological growth
Examples of hygiene factors
Cause dissatisfaction
Job security
Organization rules
Pay- salary, wages
Status
Relationship with peers, subordinates supervisors
Physical working conditions
Supervision
Physical security
Examples of motivators
Cause satisfaction
Achievement
Promotion opportunities
Interesting tasks
Personal growth
Recognition
Responsibility
The work itself
Job enrich/enlarge/empower ment
3 ways to improve employee motivation by training employees to perform tasks they weren’t originally capable of doing
Job enlargement
Job enrichment
Job empowerment
Job enlargement
Increase no. of tasks an employee performs
→ reduces / eliminates monotony of repetitive tasks
Eg job rotation
Tasks = same level of difficulty
Job rotation
Form of job enlargement
Workers given diff tasks, but at same complexity level
Reduces problems asociated w repetitive tasks
Job enrichment
Give workers more responsibilities + challenging jobs
Gives thems ense of achievement
Job empowerment
Delegate decision-making authority to workers for their job area
Increases morale
Herzberg: motivation vs movement
Movement
When ppl do something bc they need to (feel obliged to)
Eg part of job
Extrinsic incentive
Motivation
Desire, effort passion to do something bc they want to
Intrinsic
Herzberg theory summary
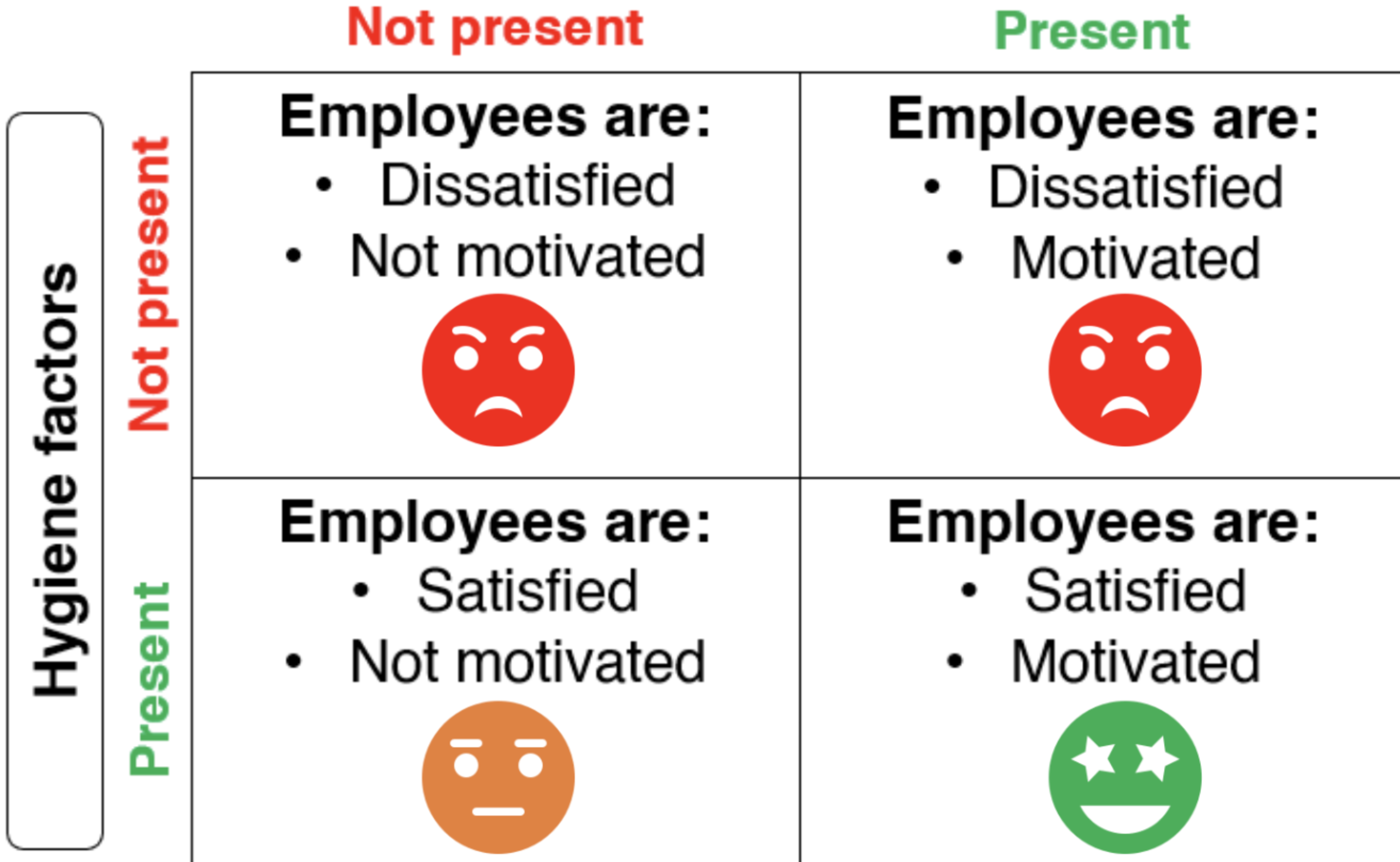
Cons of Herzberg 2 factor theory
Hygiene factors taken for granted
Issues for managers: diff ppl = diff motivators, moods affect motivation level (what motivates someone today won’t motivate them tmr)
Doesn’t apply to many occupations
Eg low-skilled, low-paid jobs
Bc job enrichment, empowermentn ot part of their work
His study only used professional workers, skilled engineers → not representative of other groups
Employees may not want extra responsibility bc more stress
McClelland’s acquired needs theory
3 types of needs must be satisfied to boost motivation (regardless of gender, culture, age):
Need for
Achievement
Power
Affiliation
But relative intensity of each varies from person to person
Need for Achievement (n-Ach)
Achievement motivated people:
Moderate risk takers
Prefer to work on tasks where they hold key responsibilities / work w high achievers
More interested in personal success over extrinsic rewards (recognition)
Prefer not to delegate
Self reflect on performance → find ways to improve
Why do achievement motivated people not like low and high risk tasks?
Low
Too easy
Don’t feel like they have achieved anything
High
Outcome based on luck. Not own efforts
Need for Power (n-Pow)
Power motivated people:
Strong-willed: like to influence others behaviour
Personal or institutional power
Why do ppl seek personal power?
To pass on instructions to others
Makes them feel more imp
But others can view them as bossy
Why do ppl seek institutional power?
Make others work harder to achieve business objectives
Use authority to bring out best in teams
These ppl more likely to be successful
Need for Affiliation (n-Aff)
Affiliation seekers:
Seek good social + working relations w colleagues + senior managers
Makes them happier at work → increase motivation
Conform to group norms to avoid conflict → accepted
Prefer teamwork
What does McClelland’s theory show?
Ppl w diff types of needs motivated in diff ways
Summary: how to motivate employees w diff types of needs (McClelland)?
High:
n-Ach: give challenging but achievable tasks
n-Pow: give opportunities to manage + lead diff teams
n-Aff: give cooperative + collaborative working environments to gain their best performance
Deci + Ryan self determination theory (SDT)
Describes 3 core requirements that facilitate growth + motivation in ppl:
Autonomy
Competence
Relatedness
Autonomy
The need to have control over what a person does
What happens when autonomy is met vs not met?
Met:
Person feels integrity + authenticity w their decisions
Not met:
Person feels frustrated, pressurized
Competence
The need to feel confident in doing a specific task / job role
Sense of effectiveness, value, mastery
How to achieve competence?
Provide opportunities to use + extend ppls skills
What happens if the need for competence isn’t met?
Person feels ineffective, vulnerable, failure
Relatedness
The need to interact, be connected to + experience caring for others
Met when ppl have meaningful RS w others, feel significant to others
What happens if relatedness needs are not met?
Ppl feel social alienation, exclusion, lonely
Reduce motivation, producitvity
Does SDT focus on intrinsic or extrinsic motivation?
Intrinsic
Intangible
Eg sense of recognition, purpose, achievement
These 3 needs r essential for intrinsic motivation bc ppl feel valued
Equity theory
JS Adam’s theory of motivation
Ppl make comparisons of perceived fairness in the workplace based on the ratio of their input (effort) to output (rewards)
Compare effort + rewards to otyers
Inputs in equity theory
Expertise
Effort
Contributions made by the employee
Physical or intellectual
Outputs in equity theory
Remuneration
Recognition (praise)
Rank (status
Responsibilities
Tangible or intangible
Financial or non financial rewards
When does equity exist?
Inputs + outputs = balanced
Workers have greater motivation in their jobs → productive
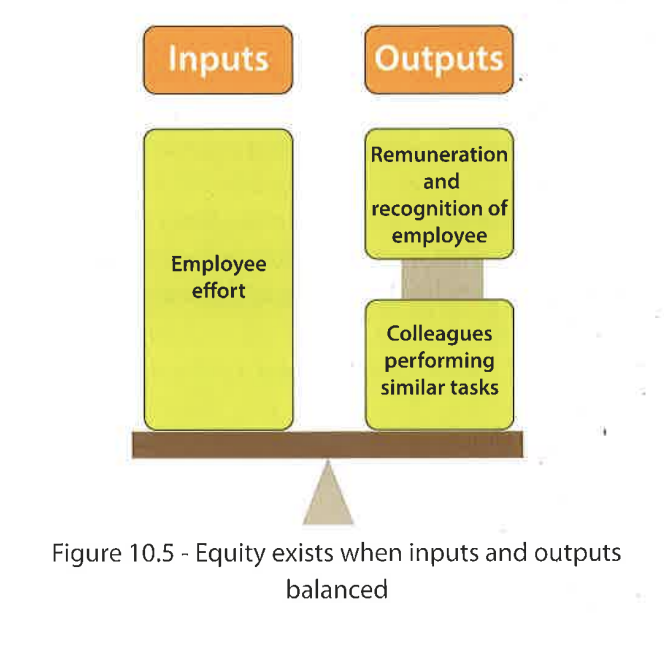
According to equity theory, employees will only be motivated if?
Input to output ratio is deemed fair in relation to others
Degree of equity directly impacts motivation level
3 ways degree of equity impacts the motivation level
Equity norm
Social comparison
Cognitive distortion
3 ways degree of equity impacts the motivation level: equity norm
Workers expect fair remuneration package based on their contributions to the firm
Firms should ensure staff percieve equity throughout organization
3 ways degree of equity impacts the motivation level: social comparison
Workers determine what is fair based on comparison of in+outputs w peers
When does inequity exist?
Workers who put more effort r paid relatively less
Compared to co-workers
3 ways degree of equity impacts the motivation level: cognitive distortion
Workers who feel undercompensation (input>output) → demotivated → withdraw goodwill
Workers aim for a balance → alter inputs (less effort) or outputs (negotiate pay rise)
What happens if inequity isn’t dealt with?
Increase absenteeism
Workers become disruptive (industrial action)
Increase staff turnover
Cons of equity theory
Fairness = subjective
Ignores cultural / demographic factors that affect perception of fairness
Limit to equity → demotivating
Senior managers excessively remunerated / compensated more
Workers don’t always view this as fair
Example of perceived equity in the workplace
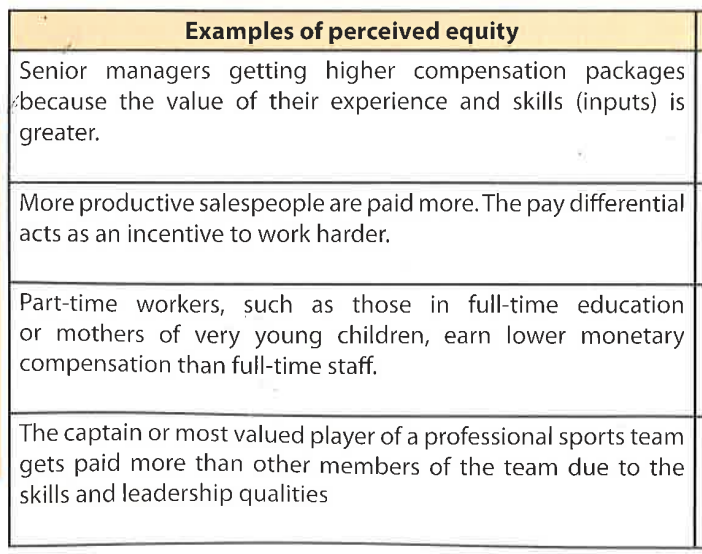
Example of perceived inequity in the workplace
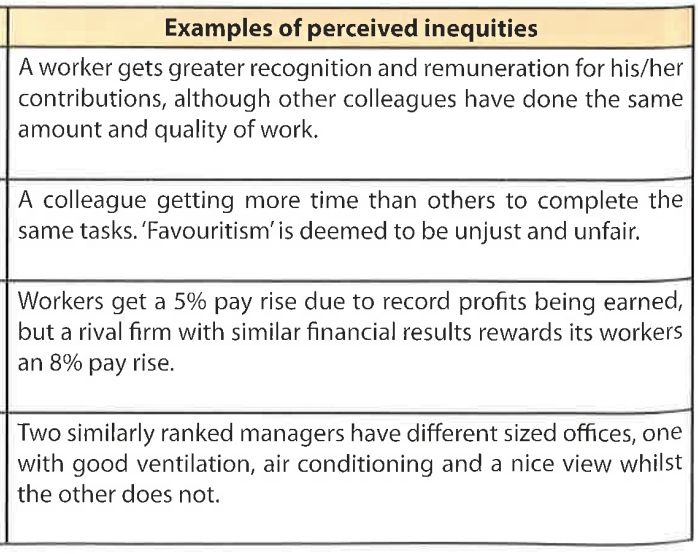
Equity vs equality
Equity = fairness
Equality = same (all paid same despite doing diff work)
Expectancy theory
Vroom’s theory
Assumes ppl behave in a certain way in exchange for rewards based on their conscious expectations
Ppl will only put in effort to do a job if they expect their role will help achieve the required result
According to expectancy theory, what happensif workers feel they lack the ability / skill to achieve a target?
Minimal effort level (lower motivation)
Expectancy theory: level of motivation equation
Expectancy x instrumentality x valence = motivation
Expectancy
The belief that effort will lead to acceptable performance
Ppl have diff expectations abt their ability to do a job + its difficulty level
Instumentality
The performance reward
Ppl have the perception that if they meet performance targets, they will be rewarded accordingly
Managers must keep promises to gain peoples trust, hence loyalty + motivation
Valence
The value of the reward to the individual employee
Managers must find out what staff value
When doing a job, ppl consider if it is worth any extra effort in terms of intrinsic + extrinsic rewards
Values for level of motivation equation
All components betw 0-1
0 = lowest, 1 highest
Higher number = likely employees r highly motivated
Expectancy theory: there is a correlation betw effort ppl put at work +
Expected rewards they achieve from that effort
Expectancy theory: employees will be motivated if…
They believe their strong effort will lead to good performance that will lead to their desired results
Cons of expectancy theory
Doesn’t give specific suggestions on how to motivate workers
Only gives a framework that highlights individual + cognitive differences in motivation
Equity vs expectancy theory
Equity
Ppl gain job satisfaction by comparing input + output ratio w others
Employee is motivated if they feel input:output if fair + in line w others in firm / society
Expectancy
Ppl behave a certain way in exchange for rewards based on their conscious expectations
Employee is motivated if they intrinsically perceive a reward is adequate
Summary of motivation theories
Labour turnover
Measures the % if the workforce that leaves the organization in a given time perod
Usually 1 year
Labour turnover equation
(No. of staff leaving / total. no of staff) x 100
Reasons why people leave their jobs (CLAMPS)
Challenge
Location
Advancement
Money
Pride / prestige
Security (or job)
What does a low labour turnover rate suggest?
Firm recruited right ppl for the job
Existing employees are motivated
What does a high labour turnover rate suggest?
Lack of job satisfaction
Better job opps + remuneration packages offered by other employeers
Cons of high labour turnover rate
Increases costs: train, recruit, less productivity when staff leave
+ new staff need time to adjust
Which businesses are likely to accept high labour turnover rates?
Jobs w:
Lots of part-time staff
Low skilled workers
Low wages
Pros of new employees
New ideas + creativity
New perspectives → improve business performance
Labour retention
The proportion of employees remaining with a business during a specific time period
Appraisal
The formal assessment of an employee’s performance in fulfilling their job based on the tasks + responsibilities set in their job description
Pros of appraisals
Cons of appraisals
4 types of appraisals
Formative
Summative
360-degree feedback
Self-appraisal
Formative appraisal
The planned + ongoing process in which data + evidence are used to inform employees abt how to improve their work practices
Goals of formative appraisal
Monitor learning + performance of employees
Help employees identify strengths + weaknesses (areas need to develop)
Help managers recognise areas where staff r struggling → can adress issues promptly
What type of workers is formative appraisal usually used for?
Workers hired for probation (trial) period
Summative appraisal
A written description of an employee’s performance at work
Summarizes what they have done + achieved during a given time period (1 year)
Goal of summative appraisal
Eval performance / contribution of workers by comparing w a benchmark
→ identify areas of improvement
Do summative appraisals hold staff accountable for their work?
Yes
By testing their knowledge