Art History Survey Exam #1
1/114
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
115 Terms
Scale
How big/small something is
Medium
What something is made out of
What are the benefits of stone?
Hard
Longlasting
People in ancient Greece experimented with?
Metal
Dye comes from?
Animals
Plants
Lapis lazuli
Certain stones had powers which created a healing/protective barrier
What is the context of a piece you should consider?
Social
Geographical
Cultural
Philosophical
Art History
Study of artistic works made throughout human history
Archaeology
Study of past human life and cultures through material remains (ex: tools, pottery)
Identity
How personal characteristics, cultural heritage, beliefs, and social roles are expressed and explored through artistic creation and expression
Cultural
How the social, political, economic, and historical environment shapes and are reflected in art
Material Culture
Study of physical objects people made, used, or valued, to understand their culture, beliefs, and daily life
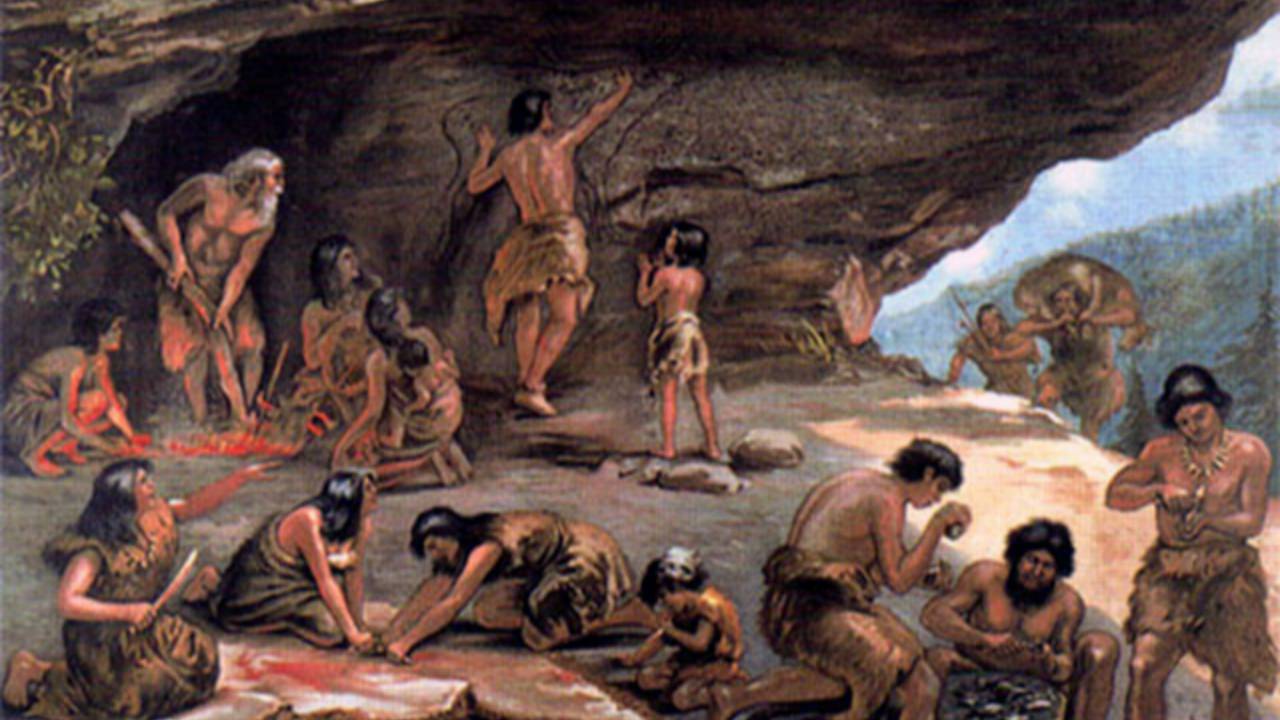

Paleolithic Period
2.5 mil yrs - 10,000 BCE
Stone tools
Hunter-gatherer societies
What does Paleolithic mean?
Paleo = old
Lithos = stone

La Pasiega Cave
c. 65,000 BCE
Puente Viesgo, Cantabria, Spain

Pech-Merle
France
c. 22,000 BCE
Details to note: pigment, torch, handprints, holes in walls = scaffolding

Megaloceros Gallery Cave Paintings
Chauvet Cave, France
30,000 BCE
Bison, mammoth, horse, antelope (most depicted animals at this time)
Sideways —> only way to see the whole animal
Bison, mammoth, horse, antelope → most depicted animals
Females are beginning to be more prominent in pieces
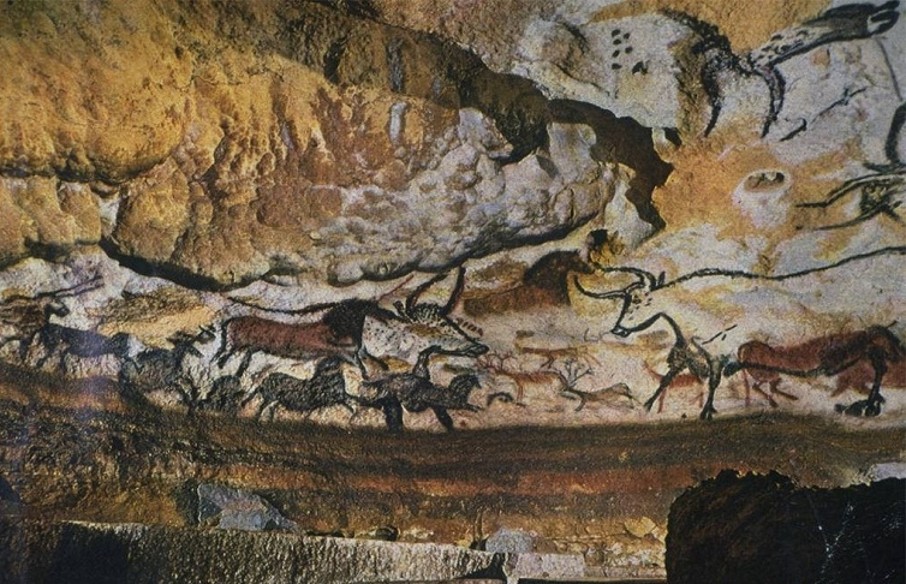

Hall of Bulls
Lascaux Cave, France
Twisted perspective
Ground line

Twisted perspective
Multiple viewpoints of a single subject within one image

Ground line
Ground upon figures are standing

Animal from Apollo 11 Cave
Nambia
Charcoal pigment
Composite image
Composite image
Combines multiple images/elements into one piece
Lion-Human Figure
Germany
Sculpture in the ground was carved all the way around
Estimated to take 400 hrs
1 ft high

Sculpture in the round
Carved all the way around

Woman of Wildendorf
24,000 BCE - 22,000 BCE
Fertility imagery
Woman holding a bison horn
Laussel, France
25,000 BCE - 22,000 BCE
No facial feature
On a test, you could mention: exaggerated features and hunter gatherer societies
Neolithic Period
“New Stone Age”
10,000 BCE - c. 2000 BCE
Fertile Crescent (Mesopotamia)
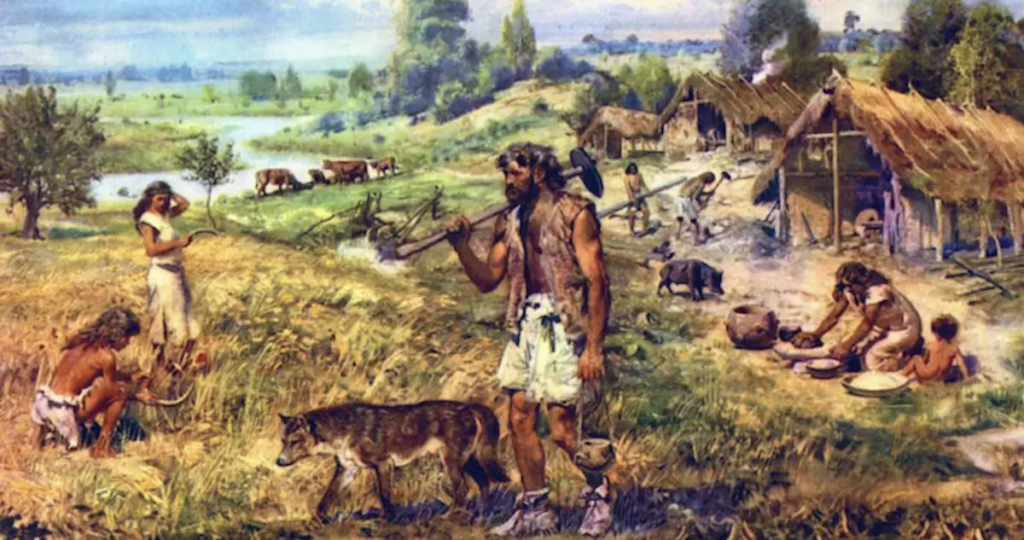

Neolithic Revolution/”Neolithic Package”
This brings about: houses, agriculture, textile production, domestication of animals
Social complexity: people are becoming more organized → permanent settlements
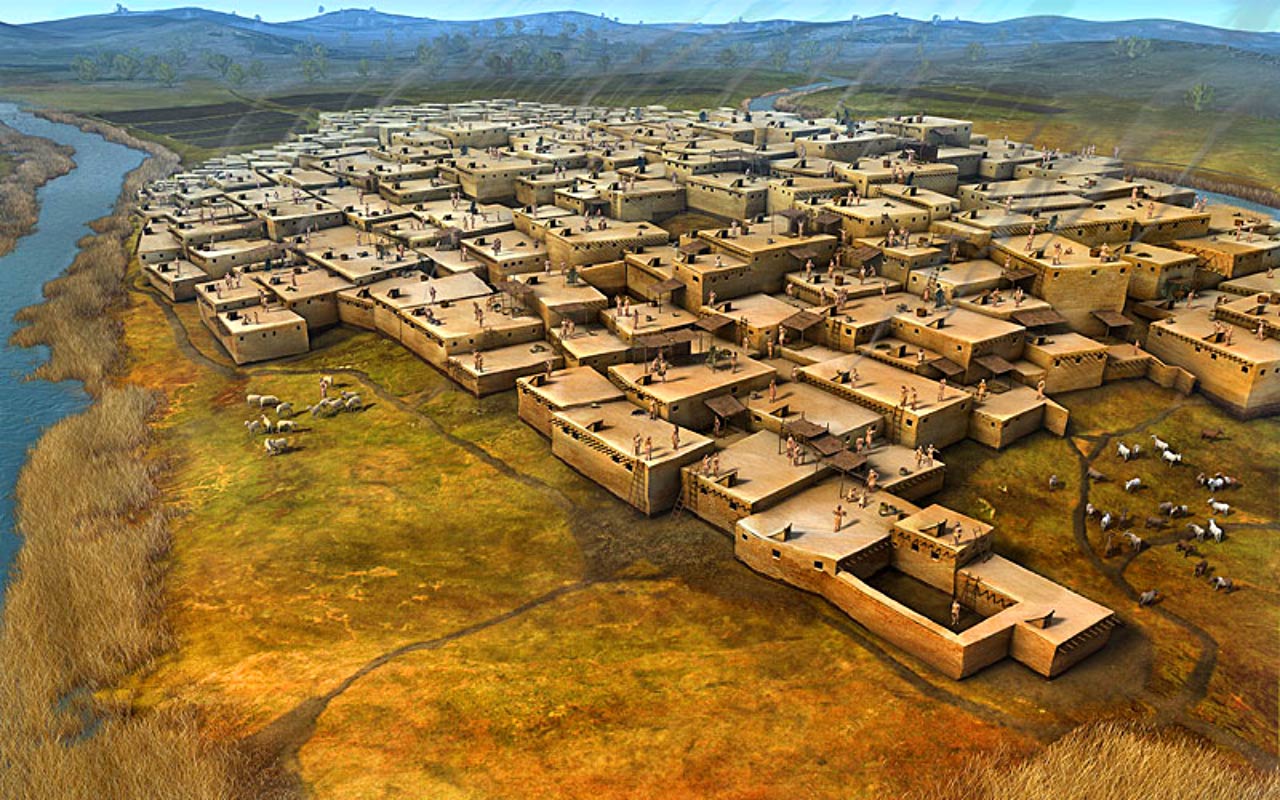
Çatalhöyük settlement
Turkey
No urban planning and grew overtime → doubles as a defense
Very stable with openings in roof which were used as chimneys
Made of mudbrick and timber
Organized around an oven
The floors were made with lime plaster
Bulls heads were a sign of?
Male fertility
**sign of support of this idea in general
Austria v. Çatalhöyük
Facial features
Ideas travelled
Pottery fragments, c. 19,000 BCE
China
Pottery is coarse and functional and undecorated
Baskets
Skeuomorphism
Skeuomorphism
A design that was once functional but is now decorative/symbolic
Mesopotamia (3000-3500 BCE)
Brought about the development of;
The first cities
Long distance trade and exchange
Writing
Urban life
Sedentary life and domestication of plants and animals leads to…
Surplus
Free time → ability to devote time to things outside of
Subsistence = development of knowledge including specialized labor and crafts
Surplus
Extra of something
City states are…?
Small and theocracies
Monumental architecture
Power/identity of these cities
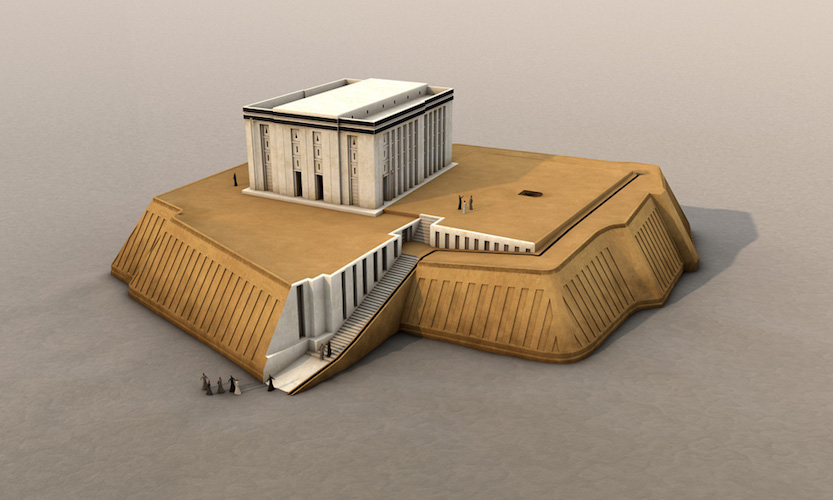
Temple of Anu (White Temple) of Uruk c. 3300 BCE
Sky god (Anu)
Mudbrick and stone bracing
Ziggurat
Insane amount of labor/coarse labor → weren’t reimburse
Changes in architecture = change in society as a whole
Cella
Gypsum was a token to keep track of stuff
Cuneiform
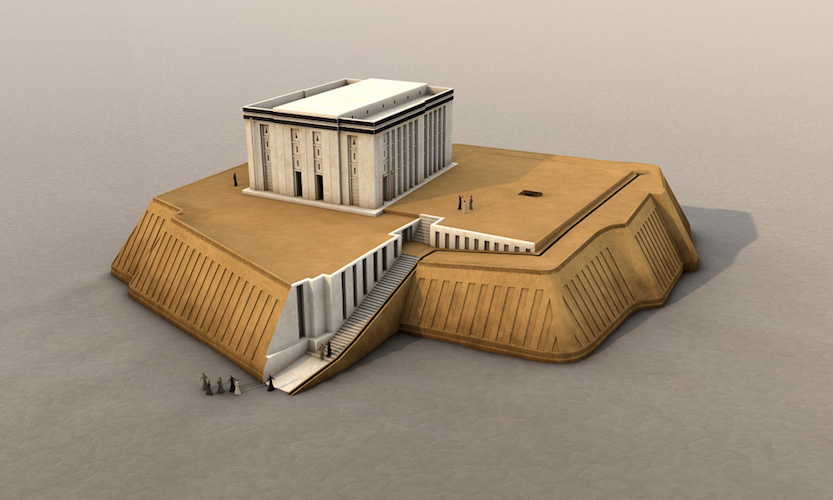
Ziggurat
Made from mud bricks with a shrine at its summit

Cella
Approached from main entrance (best access) → encouraged humility and time to contemplate before we meet with the divine

Cuneiform
Used for legal texts; clay tablets written on with a reed stylus
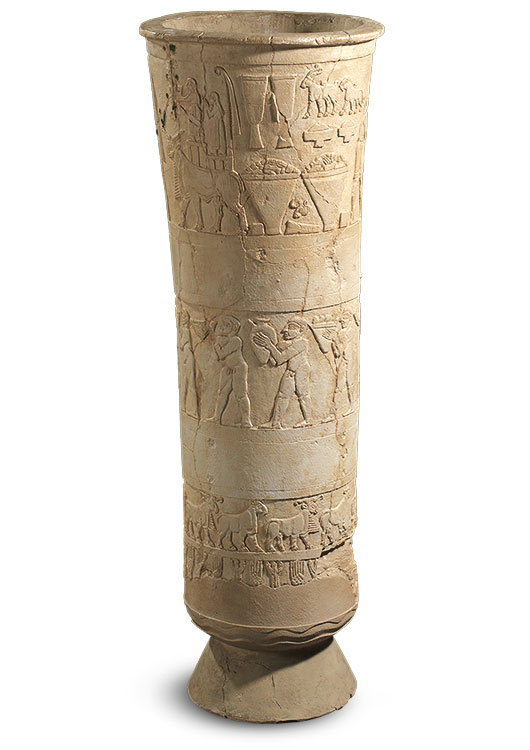

Uruk vase c. 3200 BCE
Alabaster
First great work of narrative relief sculpture
Relief sculpture = sculptured elements poke out from a solid, flat background, remaining attached to it
Registers → groundlines
Composite view
Reflects lived experiences of these people
Upper band - goddess Inanna and there’s surplus being delivered to her
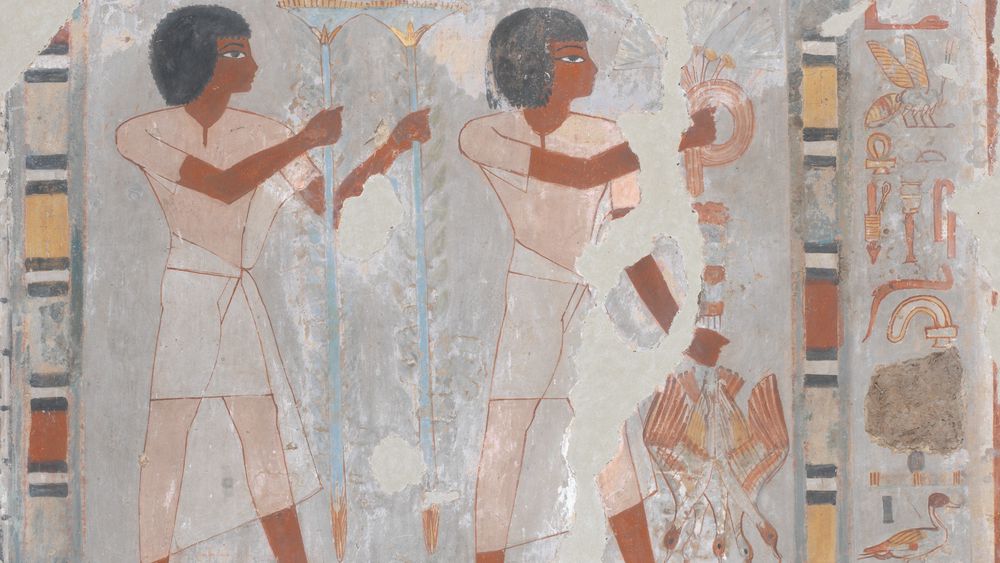

Composite view
Seeing something from the fronts and side
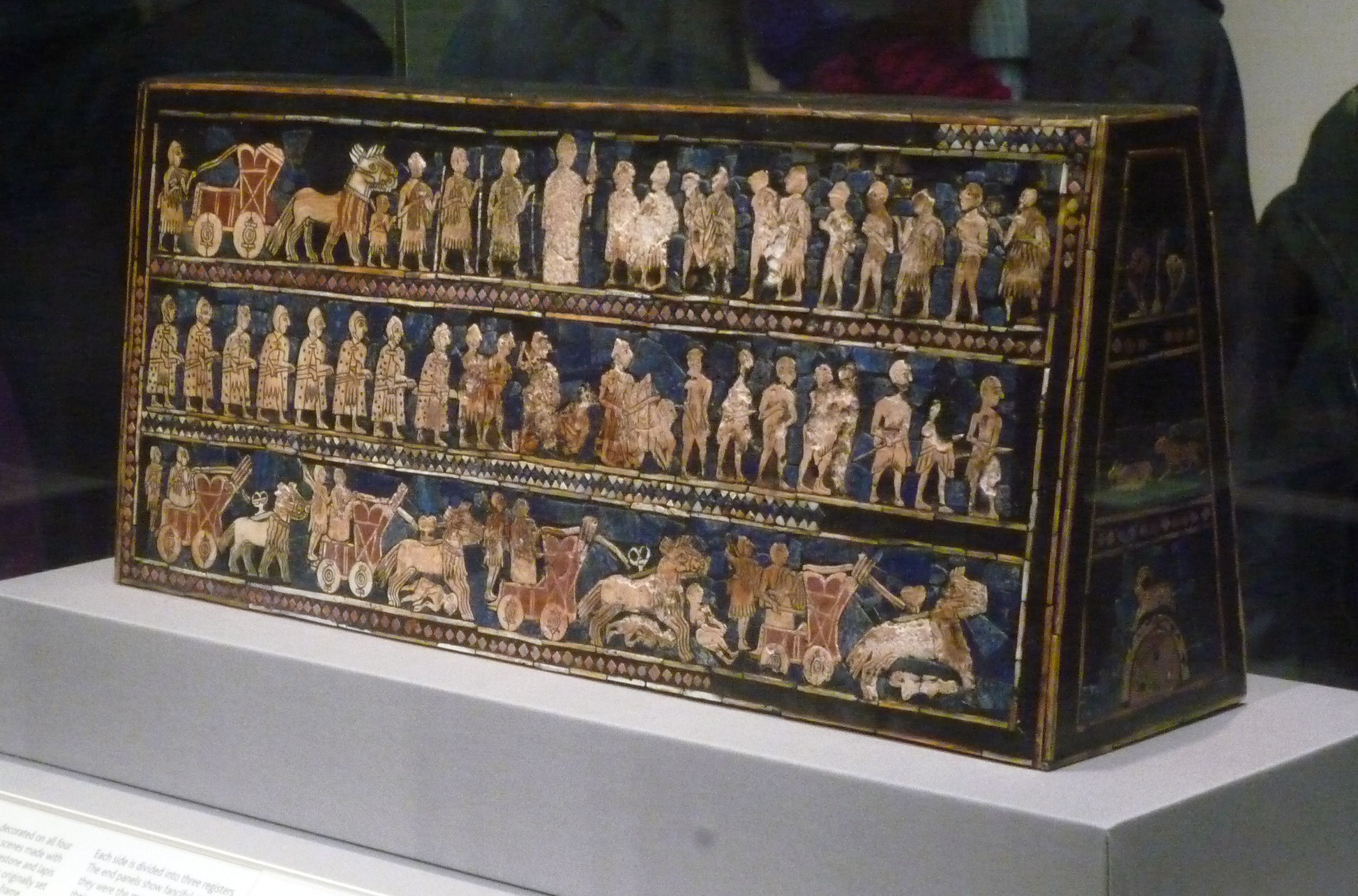

Registers
A distinct horizontal band within a composition that serves to organize and separate narrative or thematic elements
Relief sculpture
Sculpted elements remain attached to a solid background of the same material, projecting outward from a flat surface
Priestking (master of animals)
Iconography
Cylinder seal —> rolled to create an impression in clay, signature would be above doorways
Votive offerings
Wide eyes were a symbol of devotion
Iconography
Culturally interested
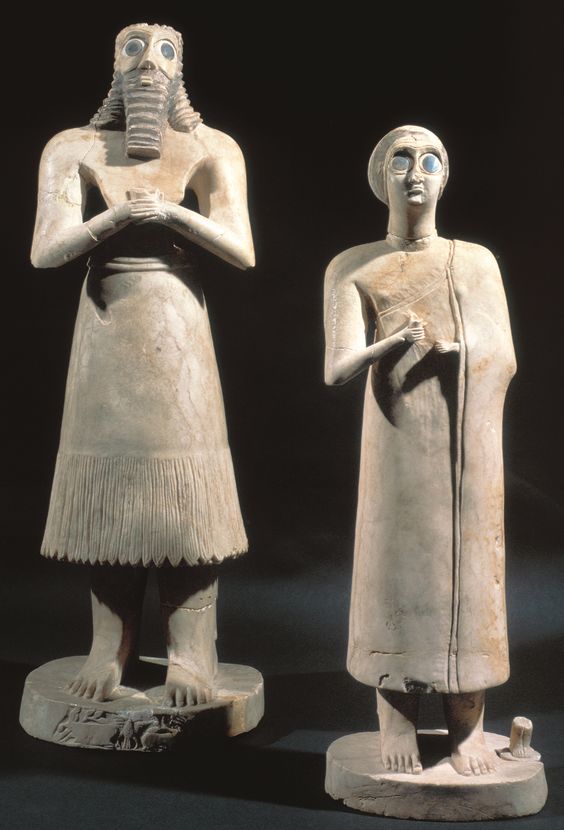

Votive offerings
A material object/action dedicated to a deity/saint as a promise as thanks for a pray being answered/blessing received
Corvée labor
Unpaid labor
Bent access
A building’s layout

Hierarchy of scale
Usage of difference in size (if something is big, it’s typically more important!)

Abstract
Non-realistic art that doesn’t try to create an accurate image

Naturalistic
Goal is to represent something as it looks in the real world
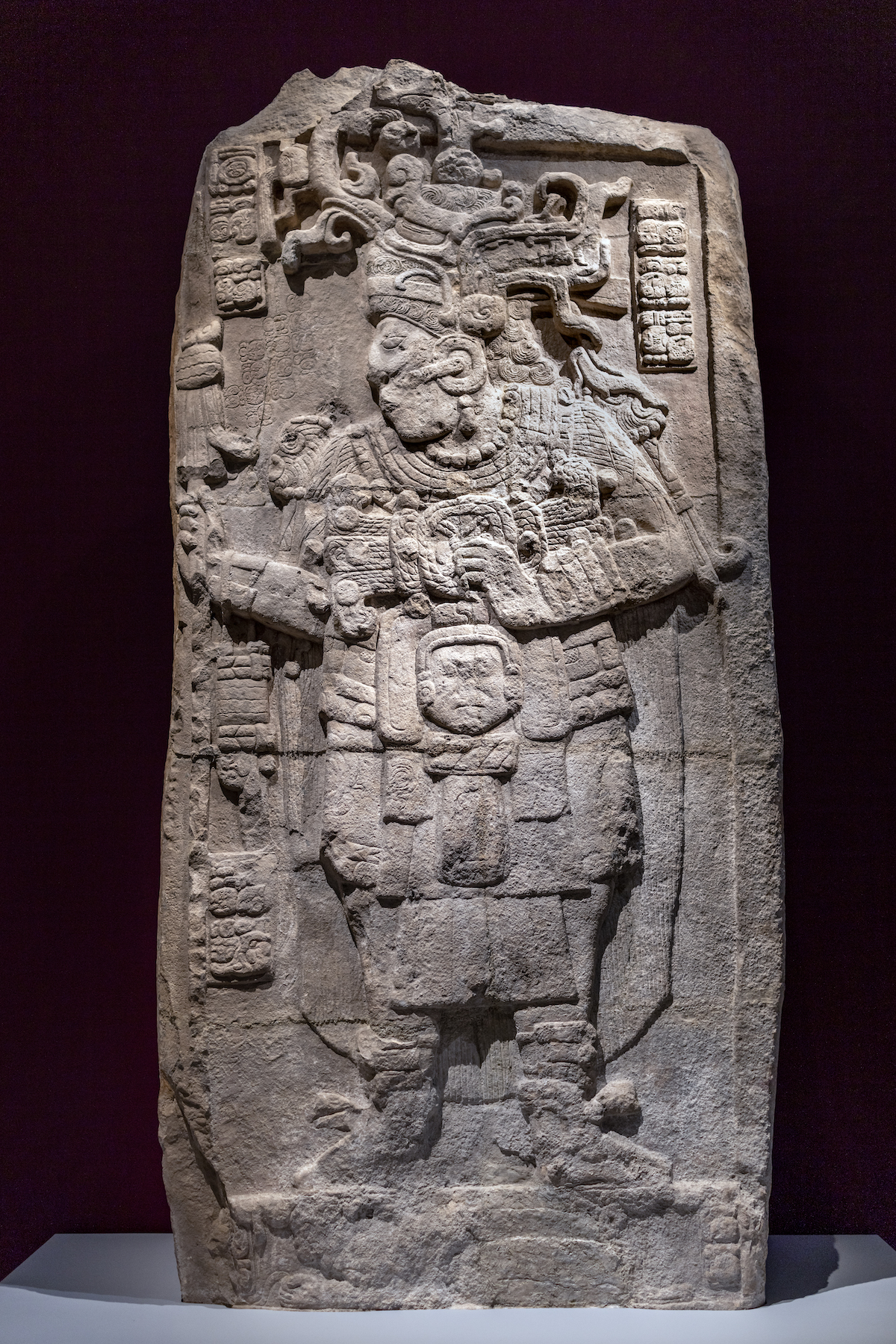

Stele
Upright pillar that functions as a monument
Ancient Nile Valley
Small farming communities but eventually grew, development of kingship
Funerary evidence comes from burials
Burials aren’t disturbed and they put stuff into their tombs
Death and Immortality
Egyptians believed that every person had a Ka or life-force that continued to exist after death
After death the Ka could reinhabit the corpse and live on as long as the body remained intact
The deceased’s body was mummified, and then food, drink, clothing, and furniture were provided in the tomb for their use
Statuettes called ushabties were also placed in the tomb to perform labor for the deceased in the afterlife
Statues of the deceased provided an alternate dwelling place for the Ka in case the mummified body was destroyed
Egyptian tombs, particularly royal tombs, were elaborate, had a lot of stuff in them, and were meant to last for a long, long time… into eternity
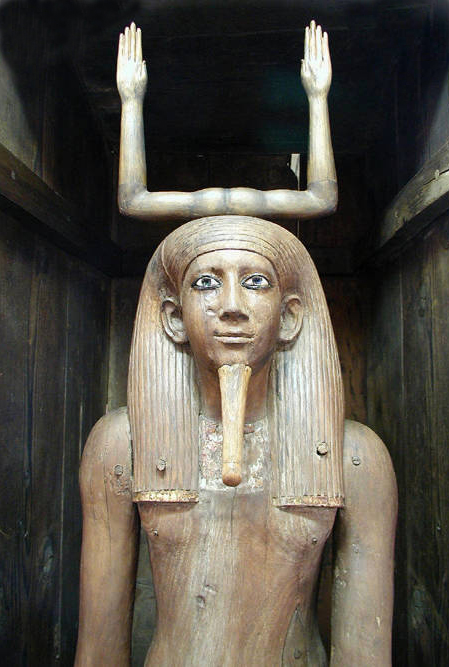

Ka
Spiritual life force or double of a person, thought to reside in the physical body during life and needed a permanent substitute
What do archaeologists and art historians care about?
Archaeologists care what people are doing
Art historians care about cultural
Mastaba
“Bench”
Made from mudbrick
Architectural section building is cut from center but we can see from the side
Main parts:
Funerary chapel
False door (dead could pass through it)
Serdab
Serdab
Small room which held statues of the deceased, often completely closed off, no one was really intended to see it
The Old Kingdom (c. 2686 - 2160 BCE)
Naramsimha considered himself part divine
Labor → created spectacular funerary monuments
Djoser’s Funerary Complex
Pyramid was a series of mastabas

Djoser’s Funerary Complex
Protected his Ka in afterlife
First time there’s a mortuary structure in stone+ first time there’s a mortuary building being combined with ritual buildings
Included very first pyramid
Had processional spaces (festivals took place here)
Real functional buildings and false buildings (meant for King’s Ka to use in afterlife) + completely solid on inside, architect is none
Dual function: advertise (symbol of godlike power of the king) + provide the king a home in the afterlife
Serdab of Djoser
Tilted back rectangular box
Only opening was for Ka statue to look out
Ka Statue of Djoser, 2592-2566 BCE
Oldest known life size statue in Egypt (good to know on an exam!)
Eyes: raw crystal and obsidian
Nemes headdress (symbol of kingship)
Could’ve held in his hands: Flail and crook, or mace
Blockiness is a hallmark of Egyptian statues
Idealized face/Idealism: perfect

Nemes headress
Worn by pharaohs/gods in Egypt
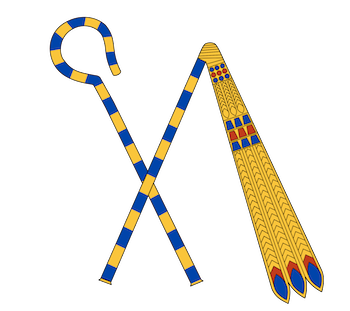
Flail and Crook
Symbol of authority/divine power
King is a shepherd and controller of land’s fertility
Idealism
Representation of perfection
Pyramids on the Giza Plateau
Great Sphinx
Partially carved from bedrock and stonework (colossal statue because of immense size)
Associated with sun god
Uraeus serpent
Uraeus serpent
Represents royalty/protection
Cobra worn on the brow of pharaohs and gods
Thutmose IV’s dream
Stele put there
Dream Stele, describes a dream he had fell asleep between arms of the sphinx → came to him in a dream and promised if he cleared the sand he will make him king (wasn’t first in line at this time)
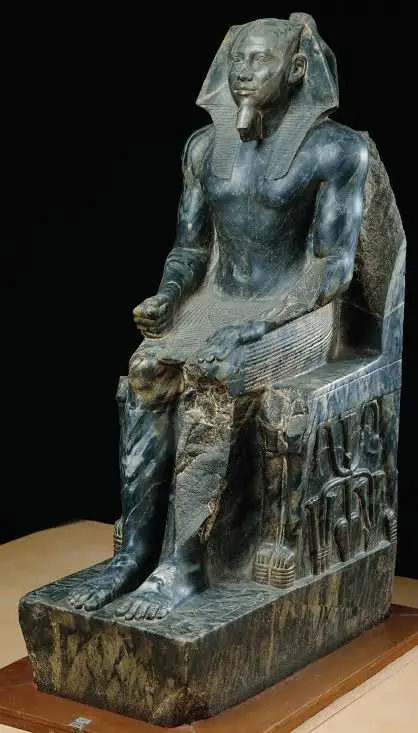

Kahfre Enthroned
Made from gneiss
Imported from 400 miles away
Wearing a shendylit kilt
Horus (protector of the king)
Shendylit kilt
Symbol of unification
Horus
Falcon god
Protector of the king
The Middle Kingdom (2055-1650 BCE)
Will be reunited by Mentuhotep
11-14th dynasties are known as middle kingdom
Rock-cut tombs
Rock-cut tombs
Not royal tombs (ex: tomb of amenemhat); mountainside provides structural support, carved out of rock
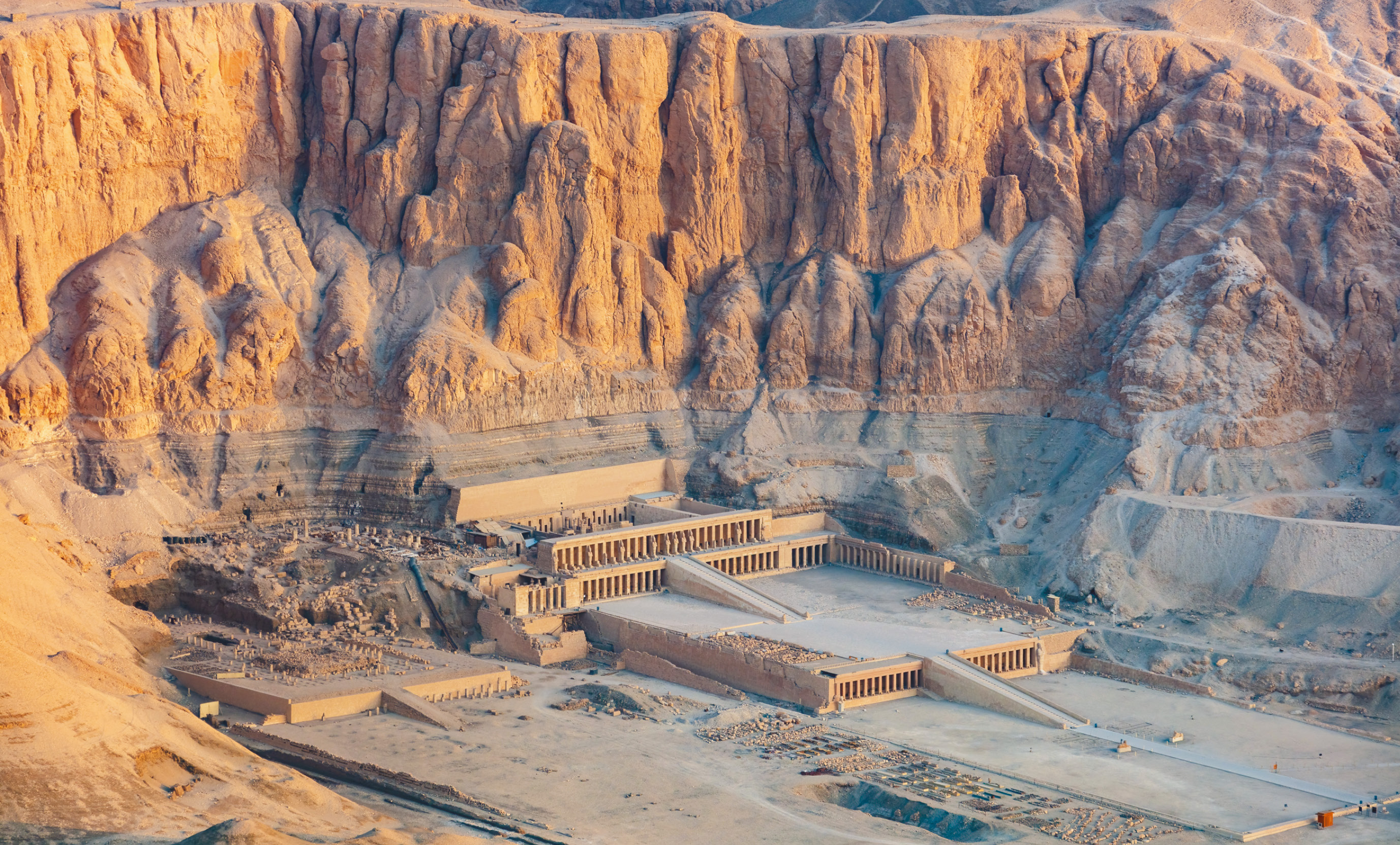

Funerary complex of Mentuhotep
Causeway that leads from Nile → upper terrace of stacked porticoes (columned space)
Ritual offerings were made
Behind courtyard were a hypostyle hall (purpose: visual) and behind it was a statue of the king
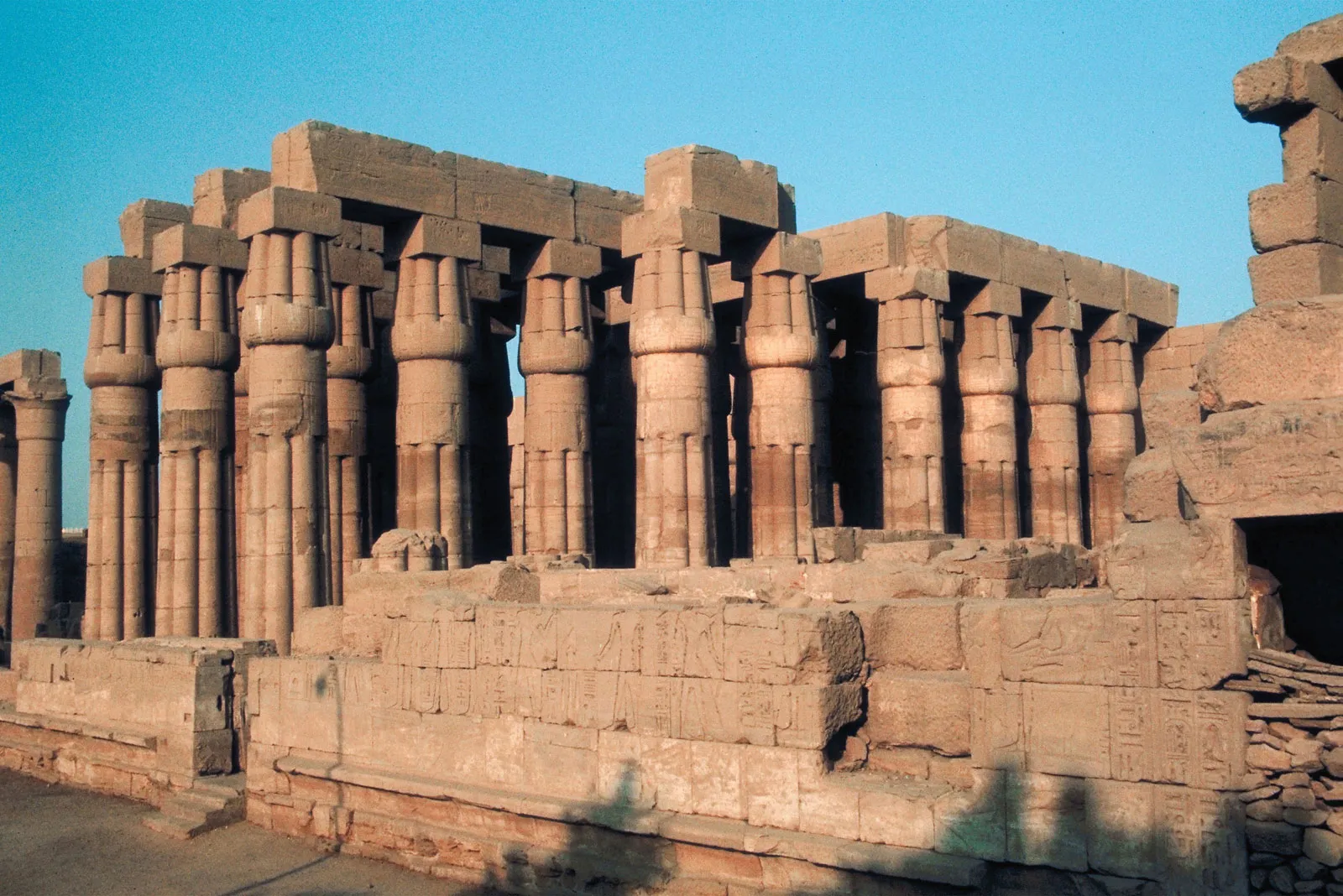

Hypostyle hall
Large interior space whose roof is supported by many rows of columns
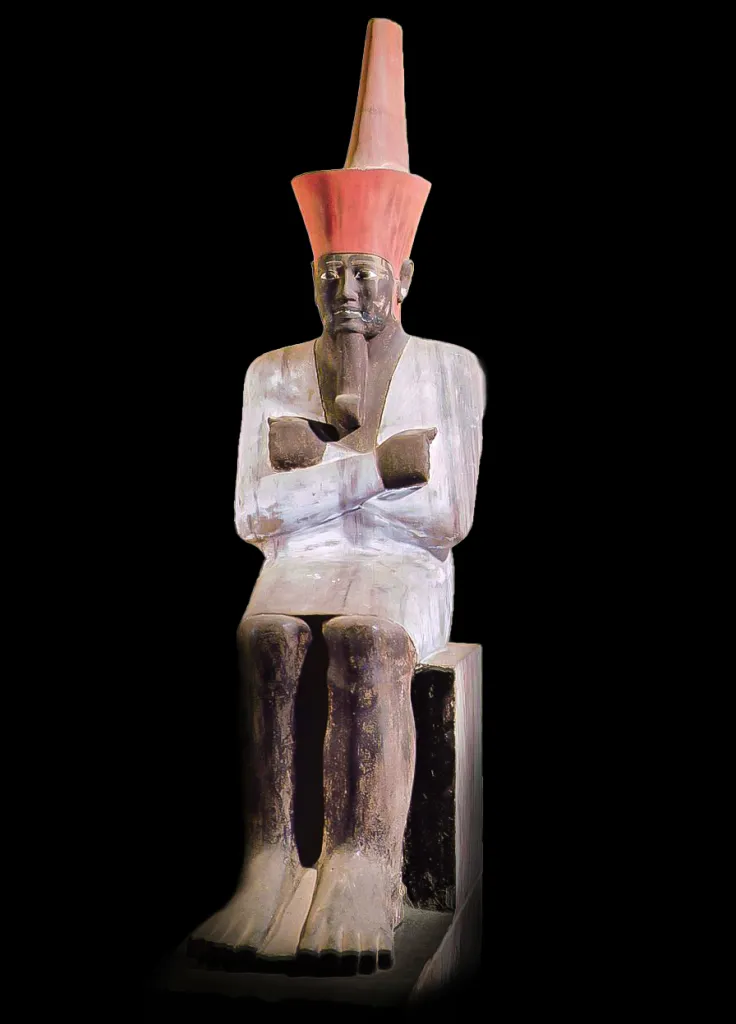

Crowns of ancient Egypt; Statue of Mentuhotep II
Composite crown
Wearing a jubilee robe
Would’ve held crook and flail
Skin was painted black, pharaohs are being associated with Osiris (typically represented with black/green skin)

Head of Senusret II
Example of realism
Sign of age (felt to be important for the king’s face to show the weight of rule)
Realism
Goal: depict everyday life
The New Kingdom; Valley of the Kings
Structured to keep remains of King safe
Tomb of Hatshepsut
Next door to Mentuhotep’s temple
Hatshepsut → She was a woman
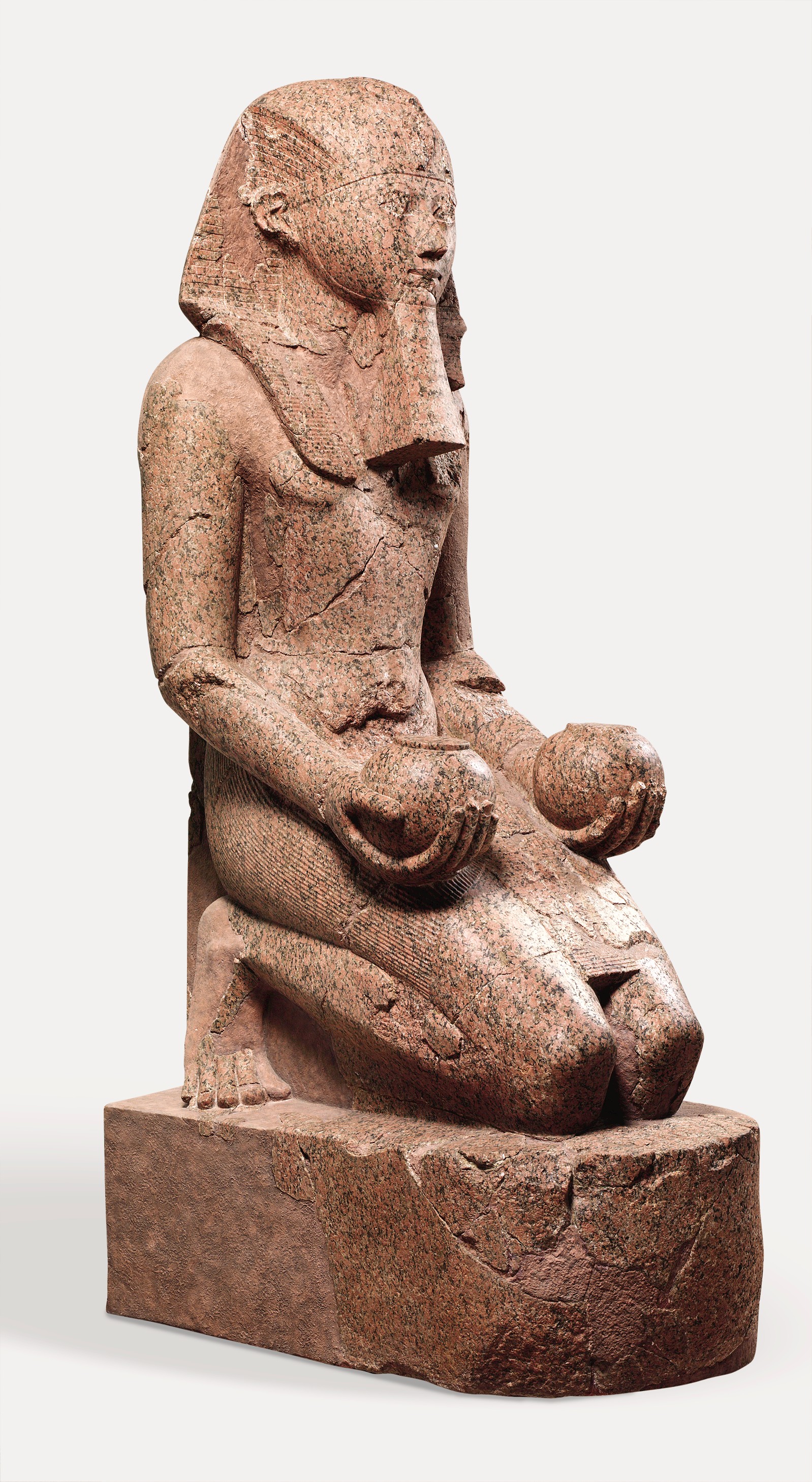

Large kneeling statue of Hatshepsut
Shows tradition
Depicted as a male
Holds offerings in her hands
Idealistic → connects to past
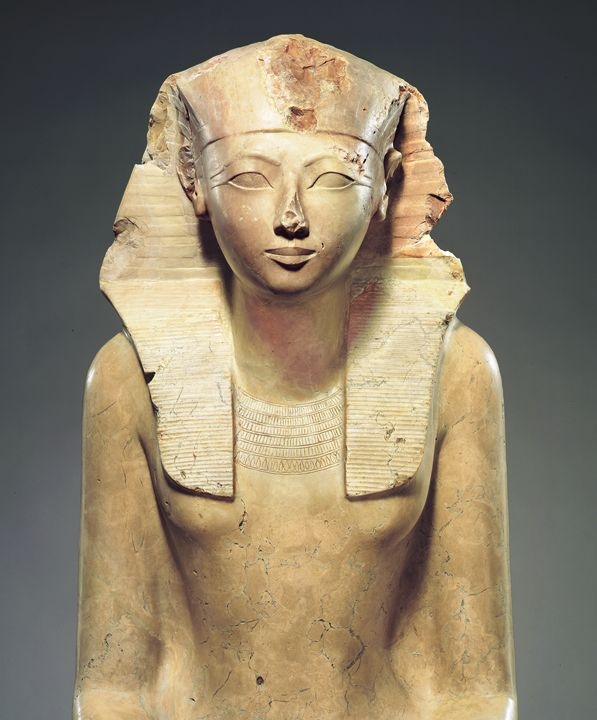

Hatshepsut
Osiris
Composite crown
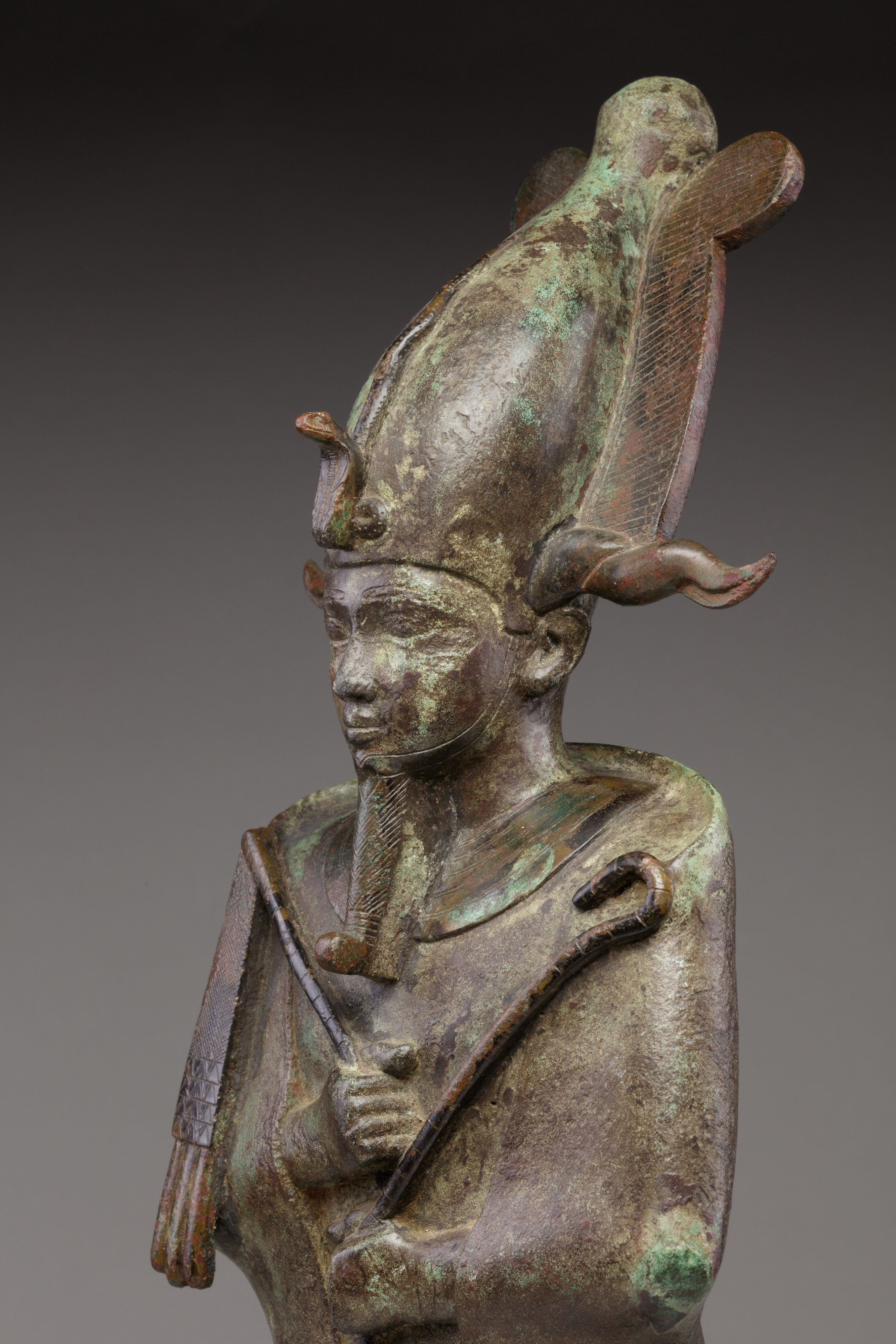

Osiris
Egyptian god associated with afterlife
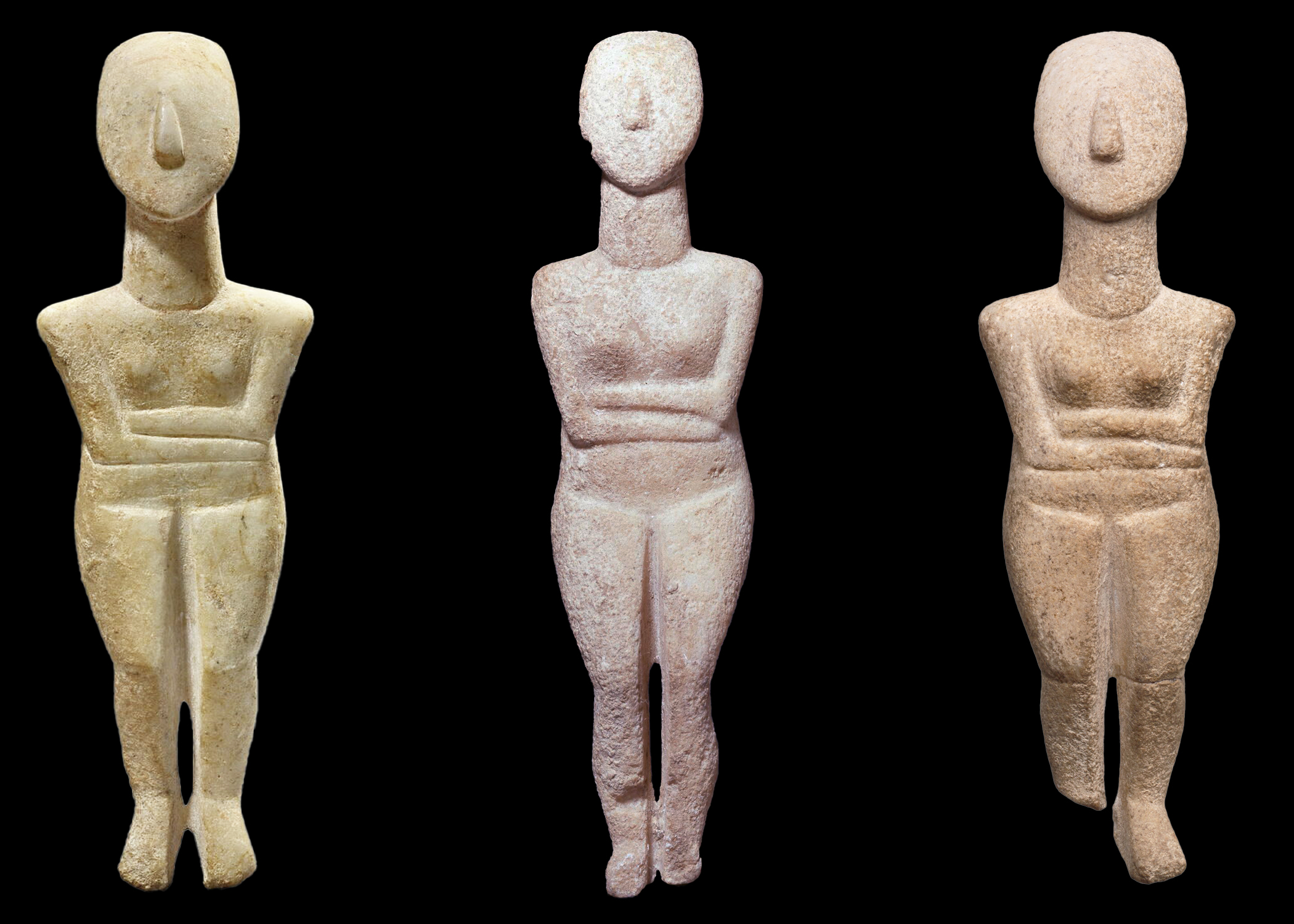

Cycladic figurines
Late Neolithic
Spatial and temporal location has a striking similarity: posture
Folded arm-figurines
Differences: Curvy → abstract figures, oddly shaped head, pronounced nose, painted facial features, jewelry, hair, tattoos, displayed standing up
Found in grave and ritual settings and settlements
Found purposefully broken, destruction could have been important to ritual context

Folded arm-figurines
Arms crossed over the abdomen
Abstract form
Blank face with only a sculpted nose
Difference between female and male marble figures
Female = Late Neolithic, 5300-3200 BCE, Cyclades
Male = Early Neolithic, 6500-5800 BCE, Knossos Crete
Minoan civilization
Centers of political and religious power
Kept track of livestock, agriculture, raw materials (wood), collected through taxes/ownership
Either redistributed or value added goods (taking raw material, using labor often slave, to produce something new out of that material)
Used for export or elite
Cretan hieroglyphics
2000 BCE
Difference between Linear A and Linear B?
Linear A - we can’t read
Linear B - used a Minoan script to write Greek
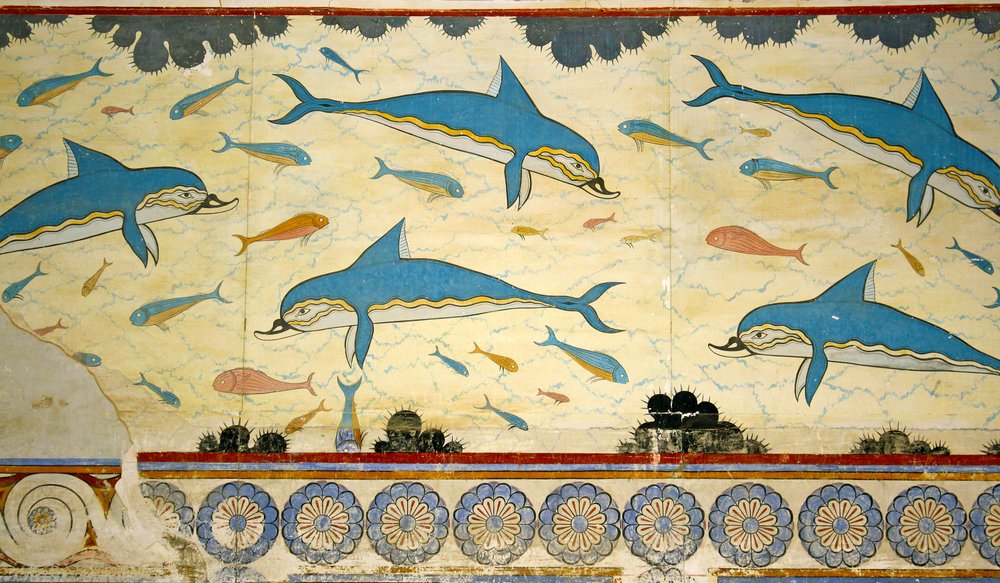

Dolphin Fresco, c. 1700, Knossos
Secco fresco
True fresco
Naturalistic, no registers, composition fills entire space, all Minoan frescos have been fixed (because they’d fall off the walls)
Secco fresco
Pigment painted onto dry plaster
True fresco
Painted onto wet plaster
(Minoans used true fresco)
Problems with true fresco
Much more difficult, has to work quickly, incredibly durable, bright vibrant colors
Minoans were known for…
Animal pictures and natural worlds (depicted in naturalistic styles)
Egypt and Middle East → lots of warfare and emphasis on kingship
Minoans were stereotyped as?
Peaceful and nature lovers
Key things to know about Minoans
Color
How space is used
Naturalistic use of images
Nature is important for them!!
Vasiliki Ware (found in Vasiliki)
Beal Spouted Jug
C. 260–2200 BCE
Minoan
Characterized by distinctive color
Produced by coating vessel in uneven distribution so when it is fired different colors pop out
Kamares Ware
Minoan pottery from Crete
Poly chrome